Introduction
Mercedes-Benz is one of the most revered brand names in the global automobile industry. Owned by Germany’s Daimler AG Corporation, Mercedes-Benz manufactures a wide range of classic vehicles ‘ranging from coaches, buses, trucks, and luxury cars’ (Mercedes-Benz 2016, para. 3). The automobile manufacturer has its headquarters in Stuttgart, Germany. The company uses a powerful business model in an attempt to deliver quality products to its global customers. The purpose of this research paper is to give a detailed analysis of the firm’s business strategy. The analysis uses different frameworks to understand Mercedes-Benz’s business environment and strategy.
Analysis of Mercedes-Benz’s Business Strategy
Mercedes Benz leans towards a differentiation leadership strategy. The strategy is implemented in such a way that the firm focuses on its market segment. The differentiation strategy is guided by several practices that can deliver the intended competitive advantages (Mercedes-Benz 2016). The Potters Generic Strategy presented below, therefore, describes the firm’s leadership model.
The Red Ocean Strategy can be used to explain Mercedes Benz’s business model. The concept of differentiation has made it possible for the firm to produce unique and superior products for the target market. The uniqueness, quality, and attractiveness of the products make them appealing to the customers. In an industry that is providing similar products to the targeted customers, Mercedes Benz has gone a step further to produce superior cars that appealing products (Bloomberg market: Daimler AG 2016). To emerge successfully, the company has been using the Red Ocean Strategy. The information gained from the strategy is expanded in an attempt to support the differentiation leadership model.
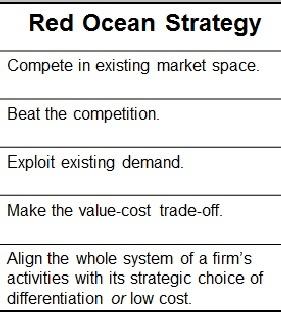
Notably, Mercedes Benz’s Red Ocean Strategy supports its differentiation leadership. This is the case because the company has been existing in its current markets. It exploits the existing demand and focuses on the best measures to tackle competition. The company’s whole system is ‘aligned in such a way that the undertaken activities support the strategic choice of differentiation’ (Vargas-Hernandez 2014, p. 28).
The company has been working hard to monitor the parameters to come up with a generic strategy that has the potential to improve competitiveness. Even if this analysis indicates that Mercedes Benz is currently using a differentiation approach, the agreeable fact is that several generic strategies are evident in the firm (Weihrich 2013). This is the case because the company has been focusing on various attributes such as customer service, brand loyalty, trust, and reliability to support the emerging needs of the customers.
Analysis of Mercedes-Benz’s External Environment
Mercedes-Benz operates in different countries such as the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom. The company has subsidiaries in different continents that undertake various marketing responsibilities. The company’s external environment is used to develop the most suitable business model (Wheeler 2014). The analysis presented below describes how the external environment dictates Mercedes-Benz’s business strategy and model.
Political
The company operates in different countries in an attempt to achieve its business objectives. To begin with, both Germany and the United States are characterized by effective political systems. The political stabilities associated with these countries make it easier for companies such as Mercedes-Benz to focus on their goals. The political climate promotes various laws and protections that support entrepreneurial activities. Michelli (2016) indicates that governments support the performance of different companies because they play a positive role in economic development.
Economic
Mercedes-Benz has been operating in countries with large nominal Gross Domestic Products (GDPs). For instance, Germany’s GDP stands at around 3.8 trillion US dollars (Weihrich 2013). The country has an economic growth rate of around 1.8 percent. This economic situation explains why more companies have decided to do business in Germany. With its headquarters in the country, Mercedes-Benz has managed to achieve its business potentials. The current economic development experienced in these countries makes it easier for more people to earn better incomes. The level of unemployment in such countries has been extremely low. These economic indicators explain why the company has managed to achieve most of its potentials (Vargas-Hernandez 2014).
Social
The success of Mercedes-Benz can be attributed to the social factors experienced in different countries such as Germany and the United Kingdom. For instance, many Germans believe that they should own luxury cars. This is seen as a popular aspect of the people’s culture. Many people in the United States have been ‘working hard to achieve what is popularly known as the American dream’ (Michelli 2016, p. 92). This social attribute encourages more citizens to purchase magnificent cars that deliver the desired class, prestige, and image (Vargas-Hernandez 2014). These social attributes have made it easier for Mercedes-Benz to produce superior cars that address the unique needs of specific members in society.
Science and Technology
The current wave of technological advancement is supporting the goals of many firms in the automobile industry. Germany is the third-largest producer and exporter of automobiles around the globe (Michelli 2016). Research and development (R&D) are taken seriously to produce prototypes that can compete successfully in the global automobile industry. Some of these countries embrace the best scientific studies in an attempt to transform people’s living standards. Research is used undertaken to produce fuel-efficient, secure, and affordable cars (Ahuja 2014).
Environmental
The automobile industry is pressured to produce fuel-efficient cars. This is seen as a critical step towards minimizing the level of pollution. Technological advances are considered to ensure every new automobile is sustainable and capable of safeguarding the integrity of the natural environment (Luikens & Hedberg 2015). Many professionals are focusing on new measures to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels. Pollution has remained a major challenge in the developed world.
Legal
The European Union (EU) is associated with different laws that govern different business activities. Corporations are allowed to market their products across the countries forming the EU. Such laws make it possible for many companies to promote desirable business agendas. The legal stability experienced in the United States and the EU continues to support Mercedes-Benz’s business model. These regions use powerful legal measures to protect patents and trademarks (Luikens & Hedberg 2015). Fair competition is regulated using authoritative legal frameworks.
Mercedes-Benz’s Business Strategy
Porter’s 5 Forces
Supplier Power: Mercedes-Benz uses advanced technologies to produce superior cars for its global clients (Mercedes-Benz 2016). The luxury segment requires exclusive supplies from specific business partners. Quality is a critical issue that must be taken seriously. The number of suppliers capable of delivering most of the required materials is very low. These suppliers, therefore, consider the details, expectations, and standards outlined by the company. This means that the suppliers have diminished bargaining power in the industry.
Buyer Power: The number of customers preferring luxury cars has increased significantly due to the current rate of economic growth. Consequently, buyers are managed to wield much power in the industry. Such potential customers can choose the most preferable cars from the existing competitors (Mercedes-Benz 2016). The availability of substitute products in the market explains why Mercedes-Benz has been forced to focus on the issue of quality. However, individuals who have purchased a car might not consider having another one for a very long time. This fact explains why the bargaining power of the buyers is high.
Competitive Rivalry: Competition rivalry in this market segment is extremely high. There are specific companies that market luxury cars in the global market. These companies have reshaped the nature of competition in the market. The major competitors in the segment include BMW, Audi, Chrysler, and Mercedes-Benz (Parish 2016). Toyota’s Lexus brand has also promised to deliver similar features to the targeted customers. These corporations understand clearly that competition is extremely high. This knowledge explains why Mercedes-Benz has been undertaking new research and development (R&D) initiatives to attract more potential customers (Michelli 2016).
New Entrants: Mercedes-Benz’s market segment is characterized by massive investments, marketing strategies, and R&D initiatives. This situation explains why the luxury car segment has not attracted new entrants. Companies that want to compete in the segment must engage in extensive research and incur numerous expenses to produce superior luxury automobiles (Wheeler 2014).
The threat of Substitute Cars: Mercedes-Benz’s uses a powerful manufacturing model to ensure its consumers get superior cars. However, researchers have indicated clearly that such cars support two unique consumer needs. These needs include ‘social prestige and transportation’ (Wheeler 2014, p. 68). This issue explains why Mercedes-Benz is currently facing an increased threat of substitute goods (Weihrich 2013).
Mercedes-Benz’s Strategy
The above Porter’s Five Model and external forces have always been considered by this company in an attempt to design the most desirable business strategy. For instance, the firm embraces the power of modern technologies to innovate and produce new automobiles that deliver the most desirable promise to the targeted customers (Mercedes-Benz 2016). The use of technology makes it possible for Mercedes-Benz to produce outstanding products that fulfill the diverse needs of the targeted customers (Ahuja 2014).
The increasing level of substitute products in the market encourages Mercedes-Benz to focus on new features that can support the targeted goals. The corporation’s ultimate intent is to have profitable and sustainable growth. This goal can be realized through the use of exemplary business practices.
The strategic areas taken seriously by the company include ‘the desire to strengthen its core business, grow globally, embrace the use of new technologies, and support the needs of different stakeholders’ (Mercedes-Benz 2016, para. 5). Marketing has focused on specific regions that have the potential to support the company’s business goals. New features are introduced in every new product. The strategy is embraced in an attempt to deal with the increasing level of rivalry. Business partners, suppliers, and stakeholders are always involved to ensure every objective is achieved. The company’s stock price on 24th October 2016 was 65.11 Euros (Bloomberg Market: Daimler AG 2016).
Operating Data and Stock Price
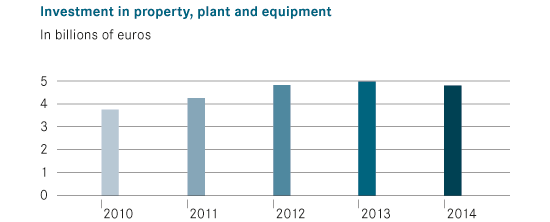
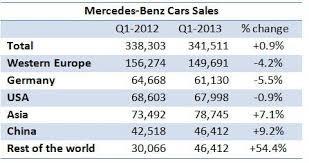
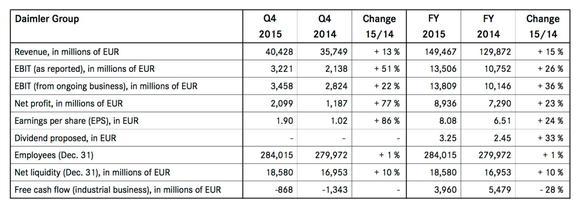
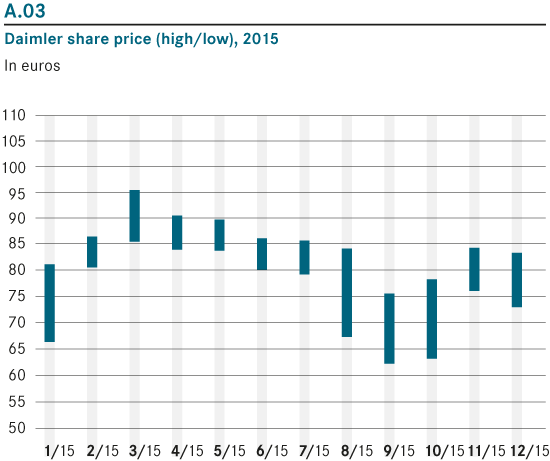
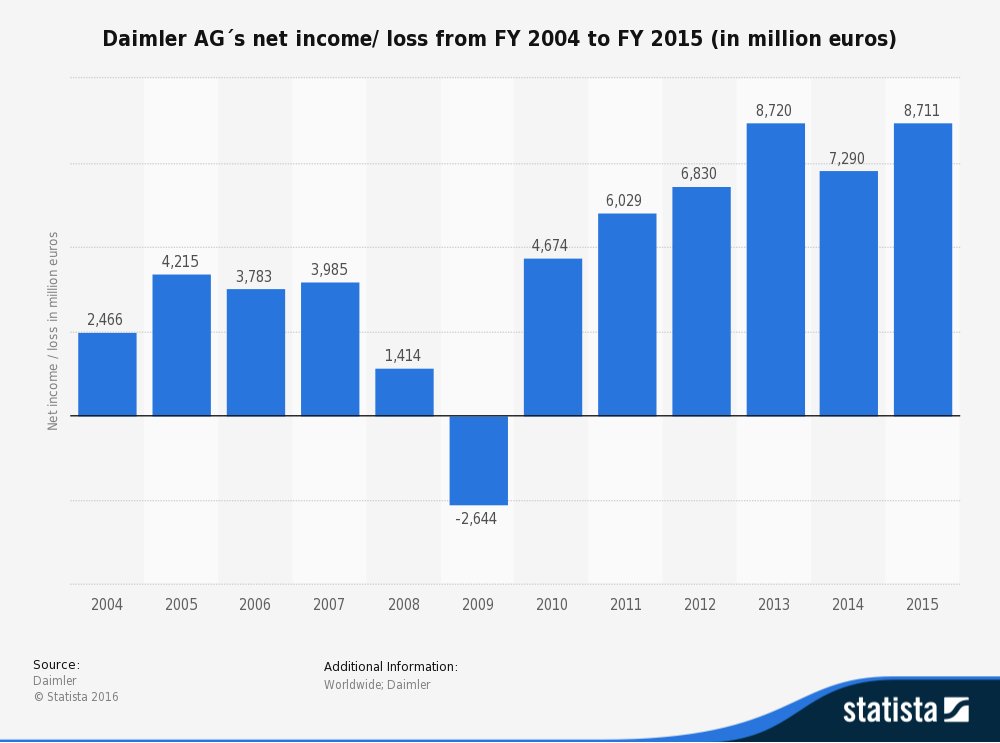
From the company’s operating data and stock price, it is agreeable that Mercedes Benz and the parent company, Daimler Group, have been making adequate profits. In 2015, the share price for the group averaged 65-90 Euros (Mercedes-Benz 2016). This is a clear indication that the future might be brighter for the company. With a new business strategy, the company will find it easier to attract more customers, implement powerful models, and eventually become profitable.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Porter’s Five Forces and PESTEL frameworks have been used by the company to identify the major issues affecting its performance. The existing forces in the industry are used to design the most appropriate business strategy that can deliver positive results.
Despite such initiatives, the presence of substitutes in the market is something that affects the effectiveness of Mercedes-Benz’s business model. The leaders at the company should, therefore, focus on new measures that have the potential to transform its performance (Michelli 2016). The company should, therefore, design a new business model that supports the needs of more customers in the developing world. Fuel efficiency should be considered to produce admirable and sustainable cars. Such measures will eventually make Mercedes-Benz a leading competitor in the industry.
References
Ahuja, P 2014, ‘Luxury cars: a new definition of necessity in India’, International Journal of Commerce, Business and Management, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 260-268.
Bloomberg market: Daimler AG. 2016. Web.
Luikens, J & Hedberg, M 2015, Standard catalog of Mercedes Benz, Krause Publications, London.
Mercedes-Benz. 2016. Web.
Michelli, J 2016, Driven to delight: delivering world-class customer experience the Mercedes-Benz way, Wiley, New York.
Parish, J 2016, Mercedes-Benz W124: all models 1984-1997, Veloce Publishing, New York.
Vargas-Hernandez, J 2014, ‘Automotive industry in Mexico: segment analysis of luxury cars’, International Journal of Engineering & Technology Innovations, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 26-31.
Weihrich, H 2013, ‘Daimler-Benz’s move towards the next century: with the TOWS Matrix’, European Business Review, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1-9.
Wheeler, J 2014, Mercedes-Benz, ABDO Press, New York.