Abstract
This research focuses on the use of training and development to control stress. Employees are an important resource to an organization that whenever anything happens to them, the performance of an organization is affected. Employees are affected by various factors emanating both from the work environment and their home environment. They are therefore prone to stress. An organization can improve its performance by reducing work-related stress that affects employees in many ways. However, this study focuses on training and development as a means of reducing employee stress hence improving organizational performance. The study would focus on the various sources of stress for employees and the ways that they can be avoided. The study would utilize a quantitative research methodology with a deductive approach. Structured questionnaires and interviews would be used to collect data from sampled employees from various firms. The findings of the study confirm that training and development helps employees reduce stress at work hence improving their performance and the performance of the organization.
Introduction
Background of the organization
Saudi Railway Organization founded in 1976, is an independent public entity by the board of directors in support of the government. The organization earlier was Saudi Arabia Railway Corporation. As a new organization, there were many expectations from them. The market hoped for better transportation of passengers, goods and shipment services within the urban centers and across the neighboring countries (Pratelli, 2010, p.160; International Business Publications, 2005, p. 87). This means of transport aims at improving the economy, social networking, agriculture, industry development, and commercial activities in the North and South of Saudi Arabia (Shoult, 2006, p. 100; Europa Publications Limited, 2003, p. 982).
Two custodians of the holy city lead the organization. They are King Abdullah Bin Abdullaziz and H.R.H Trustworthy Crown Prince Sultan Bin Abdullasiz. The King Abdullah Bin Abdullaziz gave the public investment fund mandate to form the Saudi Railways Organization to carry out the project of constructing railway North to South of Saudi Arabia. The H.R.H Trustworthy Crown Prince Sultan Bin Abdullaziz in charge of the public investment fund (PIF) agreed to work on the established project upon concern by the council of ministries decision no. 56 dated 04/03/1424H, which discovered the need for exploitation of minerals (International Business Publications 2005, p.65; Muassasat al-Naqd al-Arabī al-Saūdī 2009, p. 210).
The trains have three classes. The first class is Al-rihab, which has the most luxurious facilities for the rich people. It has soft and cozy seats, larger spaces, and provides newspapers and TV entertainment for their customers. The second class is Al-taleaa for the middle class people with relatively less luxury compared to the first class. The third class is Al Qafela for the ordinary class and is always crowded with very many passengers in a small space (International Business Publications 2005, p.97). They are fast trains for long distance and around the urban centers with quality urban systems services such as the latest signaling and communication systems (Mobile Reference 2006, p.1).
The board of directors requested for research to determine the progress of the organization in terms of training and development. The organization wants to complete its projects on the scheduled period for the contracts and its services satisfy the needs and wants of their customers to maximize their profits. It has to ensure that their employees train and develop necessary skills to reduce stress that affects their plan. The research will be due on July 8, 2011.
Statement of the Problem
The organization reported accidents, delays, and complaints from the employees. There arose different views from the management that makes decisions on the responsibility of their employees to reduce these challenges. They discovered that their employees are under stress due to the problems they face in their workplace and in their personal affairs. The organization aims to ensure customer satisfaction through their employees’ interaction and create a good image in the country by empowering their employees. This will help the organization to achieve their objectives of profit maximization through employee practices and operations, and fulfill the anticipations of its stakeholders (Williams, 2009, p. 39).
In 1976, Saudi Railway Organization established a training centre and in 2003, it was under the directorate general of human resource. This was an effort of the organization to dedicate its employees to training and career development. Currently, there are more than 1400 employees of the organization undertaking training programs that include train operation and supervision and English language programs. The organization engages in various cooperative training programs arranged by local universities, colleges, and institutes. The organization wanted to know whether their efforts were of great help to their employees in improving their working conditions (Price2007, p.581; Saudi Railways Organization, 2010, par. 1).
Research Objectives
The purpose of this study is to examine training and development in controlling stress in the workplace. The researcher aims to fulfill the following objectives:
- To investigate the sources of stress that affect employees in their workplace.
- To determine the importance of training and development in solving the problems that face employees in the organization.
- To find out the challenges the organization and the employees face in solving the problems of workplace stress.
- To examine the other sources of stress that affects an employee in the workplace.
Research Questions
- Does training and development help employees to control stress caused by the organization?
- Is there any challenges faced by the management and the employee in controlling stress in the work place?
- Does the organization try to control employee strain in the organization?
- Are there external stressors affecting employees in the organization?
The Scope of the Study
The study began in June 2010 and ended in June 2011. It was limited to primary and secondary sources. The research involved discussion with experts, previous research studies, and the media. It was a success due to the accessibility of the area of study, books, journals, records of the employees, and respondents (Anna 2004, p.66).The research was on a field setting where the data gathered was from an organization. It included analysis of theory and opinion of the respondents. The research was an open discussion and filling of questionnaires (Laird 2003, p.20).
The Significance of the Study
The research will help create a better relationship between the organization management and its employees. Both will become aware of their expectations and the ways to improve the performance of their duties. The study will come up with strategies that will determine whether training and development is effective enough to control strain that leads to stress at the workplace, and other actions to take as an organization to ensure they minimize stress in the organization (Ornelas 2003, P.64).This research is important to both the organization and the employees. The experts and professionals of the organization support the research by giving out their views on their experiences (Hughes 2009, p.520).
Assumptions and Limitations of the Study
The researcher assumes that the information collected is free from error and bias, accurate, and is reliable by the organization. The management and employees of the organization provided the information gathered. The employees are honest in the hope of a solution for the problems they undergo in the organization (Price 2007, p.585).
Literature Review
Introduction
Training and development controls workplace stress. Training is concerned with the immediate improvement of the employees by providing ways that make the employees more effective in their current roles. Training focuses on short-term learning needs. Development on the other hand aims at broadening individual skills for future responsibilities. The process makes the employees efficient enough to handle critical situations. It focuses on developing long-term strategic capabilities (Hughes 2009, p.526).Therefore, training and development controls stress at workplace through orientation of employees, globalization, customer sophistication, social and legal changes, technological advancements, organizational changes, improvement of performance, avoiding managerial obsolescence, and promotion and succession plans (Gennard 2005, p.369).
Stress in workplace is by the external and internal influences on the employee. The organization has only control on what happens within the organization. Stress is by strain in the activities of the organization therefore training and development play a key role in improving the skills and performance of employees. Organizations rotate their activities and decision-making to control the problems of their employees. The management communicates with the employees to ensure order in coordinating the duties and responsibilities of each one of them in the organization (Croome, 2006, p. 92).
Causes of Workplace Stress
Work family stress bundles (McDermid 2007, p.527).
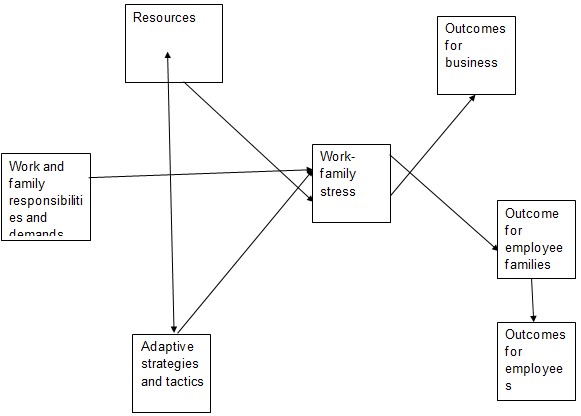
The diagram explains the challenges that employees undergo that end up causing stress. They receive pressure from their family and the workplace. Both expect the best from the employee but sometimes the employee is not able to fulfill their expectations. The demands from either side affect the employee psychologically (Anna 2004, p.63).Time Constraints: when a worker is unable to manage the job and the work systems, he or she suffers unmanageable demands and pressure that consequently lead to stress (Christopher 2004, p.1). Lack of Control: when jobs do not match employee knowledge and abilities, he or she has trouble in handling the job leading to frustration. For instance, potential investor issues threats of withdrawal from the company causing pressure on the employees (Ornelas 2003, P.69).
Workload: giving too much work or multiple reporting lines on unrealistic deadlines causes pressure to an employee (Cooper 2005, p.233). Lack of good communication leads to a poor structure of communication and leadership that result into employee conflicts, a blame culture, and harassments. Some organizations however, do not have trade or professional unions to fight for their rights and opinions in the workplace leading to strikes and employee dissatisfaction (Haraway, 2005, p. 11).
Poor Interpersonal Relationship at the Workplace: Some acts such as bullying destroy strong relationship in organization. This leads to a feeling of isolation since when faced with difficulties there is no chance of consultation and this ends up causing stress to the concerned individual(Haraway, 2005, p.12).
Adopting Changes: unqualified promotion or hiring of employee causes difficulties and challenges, therefore, discouraging employees from the job. An organization coping with changes in the business environment causes a lot of tension at the workplace especially when it comes to job insecurity (Ornelas, 2003, p. 66).This reduces the morale of employees and leads to frustration (Pretrus, 2003, p. 72).
Signs of Workplace Stress
They include mood disturbances, lack of sleep, increased family and friends’ conflicts, employee strikes, psychological distress, stomach upset, absenteeism, and headaches. Stress over a long period leads to chronic health diseases such as cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal and psychological disorders. There is shrinking in output, bodily, and emotional wellbeing (Egan 2009, p.70).
Prevention Measures
Training and development programs
Performance Appraisal
It is the process of reviewing an employee’s past performance. The organization becomes aware of the worth of the employee in its activities. It takes place annually or semi-annually depending on the individual organizations requirements (Chambers 2002, p.82). Performance appraisal gives employees feedback on performance, identifies training needs, documents criteria used to allocate organization rewards, guides and manages career development, and forms a basis for personnel. It gives employees the opportunity to discuss performance standards regularly with their top management to provide basis for salary recommendations and validation of human resource policies to meet requirements and an opportunity for organizational diagnosis and development. It also provides documentation for human resource actions that result into legal actions and improves performance through counseling, coaching, and development (Kizza, 2010, p. 156).
Employee Remuneration
Every organization aims at reaping maximum profit through reduction of the costs incurred during production. Employee remuneration is part of the costs that a firm incurs during production and they form part of the operating costs that must be maintained low for the profitability and operation of an organization. According to Ornelas, (2003, P. 64), the policies that a firm pursues regarding the salaries paid out to its employees must always be consistent with the objectives set by the firm. Remuneration of employees can either encourage or discourage employees from working in the organization. It is therefore advisable for the management to base the compensation to employees on various factors such as employee skills, the structure and policies of the firm and legal requirements among other factors. The salaries should aim at motivating employees to increase their efforts and productivity while at the same time promoting employee retention and reduce employee turnover.
Firms that compensate their employees well have been reported to maintain their skilled employees hence maintaining their competitiveness in their respective industries. They also reinforce the organizations key values and desired organization culture, ensure remuneration is maintained at the desired competitive level, control remuneration to costs, and ensure optimum value for each remuneration expenditure and compliance with the legal requirements (Treven, 2005, p. 640). Well-compensated employees are able to meet their obligations with ease. They face little issues both at work and at home, hence reduced work related stress and increased productivity for the firm (Fairbrother, 2003, p.8).
Job Evaluation
It determines the walk of a job in the organization in relation to other jobs. It is concerned with how big or small a job is. It aims to ensure that jobs of different sizes attract the appropriate pay differentiation. Job evaluation base on job ranking, job grading, point system, and factor comparison system. Pay surveys conducted relate organizations salaries to those of other organizations in terms of similar jobs in context and size. They include pay structures, pay range, pay rates, base pay, contribution based pay, employee benefits, and incentive remuneration (Cannon, 2010, p. 3).
Employee Health and Safety
The employers are responsible for ensuring health and safety in the workplace. Nevertheless, employees should take care of their health and safety. This right is not an obligation but a law. Employees have a right to take leave incase their health needs more attention. Due to complications of illness and risks today, most organizations have their employees cover their health expenses through savings. The organization cut their employees salary to cater for their health that is outside the organization. Then the organization caters for the expenses of its employee’s health caused inside the organization (Cooper, 2005, p. 231).
Theoretical framework
Training and development system
Organizations approach training and development through a complex system that involves a number of distinct interrelated phases. It considers the efforts before and after the trainer and trainees are together.
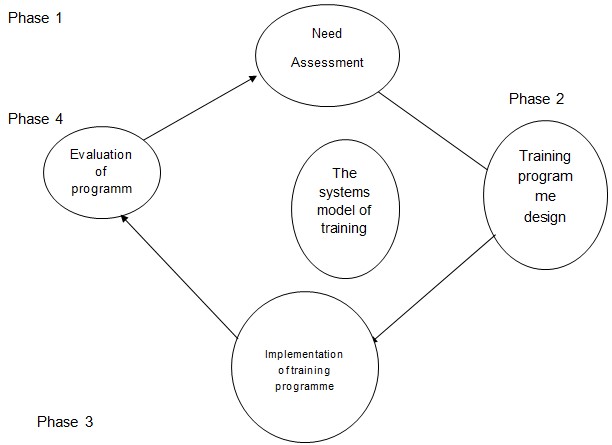
Phase 1
It comprises of the organizational analysis, task and operations analysis, and the person analysis. Organizational analysis entails the problems, achievements, and goals of the organization. The operations analysis involves the knowledge, ability, and skills of the employees while the person analysis necessitates performance, skills, and ethics test and assessment sentence (Anna 2004, p.61).
Phase 2
This is where the employee decides on the training programme to undertake which includes the methods, workbooks, exercises, and activities available in the organization. A well-designed programme focuses on co-related issues, instructions, objectives, trainee readiness, and motivation principles of learning and characteristics of the instructors (Panari, 2010, p.166).
Phase 3
It involves implementation of the concepts of the training. The importance of training lies in this phase. The whole concept behind training is lost when implementation handling is poor. Success derives the right and best choices of training methods (Panari, 2010, p.168).
Phase 4
The managers access the programs successes and failures to determine whether the trainees actually learned new skills, attitudes, and knowledge because of the programme (Jackson, 2007, p.474)
Conceptual Framework
The evaluation strategy of the training and development programme forms Kirkpatrick’s four level model of training evaluation (Kirkpatrick 2006, p.1; Documents and Resources for Small Businesses and Professionals, 2011, par.1).
- Level 1 → evaluation reaction
- Level 2 → evaluation learning
- Level 3 → evaluation behavior
- Level 4 → evaluation results
- Level one. It is the evaluation reaction of how well the trainees enjoy the session or the course.
- Level two. Evaluates learning on the principles, facts and techniques learnt.
- Level three. This stage evaluates all the behavior changes in the job resulting from the training especially through appraisal.
- Level four. This stage evaluates the tangible results of the training in terms of improved job performance.
Methodology
The methodology of research will cover the processes and procedures of data collection and analysis. It will elaborate on the sampling techniques to be followed, the target technique, sampling technique, data analysis and data presentation. The research will use both primary and secondary data sources. The primary data will entail observation and face-to-face interviews, which will use a combination of semi structured and unstructured forms of questions in the form an interview guide that will contain the pertinent issues on training and management. Secondary data will entail library searches, internet searches, books and journals. The research will therefore be quantitative so that the study can generate numerical data for statistical and deductive analysis. This methodology is also the most ideal to test or verify the theory (Dubrin, 2008, p.602).
Study Design
This research will take a deductive approach that will involve the researcher working from assumption. Therefore, the study takes a top down approach as compared to the inductive approach that takes an up down strategy. Questionnaires use quantitative tools of collection and analyses to realize the use deductive approach. Quantitative tools are preferred as compared to qualitative tools because they enable the researcher to come up with facts. This is unlike qualitative tools that first come up with an abstract idea followed by creation of theories and concepts about the idea. The data in quantitative research is hard and reliable as compared with qualitative research where data that is rich and profound (Dubrin, 2008, p. 604).
Data collection methods and instruments
This will entail mainly face-to-face interviews through a combination of semi structured and unstructured forms of questions with the use of an interview guide and the organization selected on a stratified random sampling. This will also ensure that the interviews are not restrictive. The study will use a detailed administered questionnaire in which research instrument constructed use open and closed ended questions. Semi- structured questions are open and elicit an individual’s response while unstructured questions provide the researcher with an opportunity to ask broad questions. Questionnaire formulated will check on the employee’s willingness to engage in training and development and their opinions on the idea. This provides a high degree of objectivity, probing and clarification.
Unstructured interviews will also enhance the study because the interview direct on the relevant questions in the guide. The questionnaire piloted before implementation re-examine the research instruments from the additional feedback about the questionnaire instrument (Sheppard, 1995). A letter of identification will be prepared to serve as an introductory document when conducting the research. As a researcher, I will continuously monitor the progress made in answering the questions and giving clarification when required.
Face to Face Interviews
The research conducted will be through open interviews with use of interview guides on relevant issues concerning the research problem. The interviews will therefore, focused and combine semi structured and unstructured forms of questions. This will be important, as it will help the researcher interact closely with the respondents and get as much information as needed to enhance the research. The down side is that a lot of time will be required in this exercise but the researcher will overcome this through proper planning.
Observation
Observation is a research tool to collect supplementary data. This will be through the technique of participant observation since the researcher will participate with the subjects. This will be through hearing, seeing, testing and personal intuition. This will avoid bias; will give the researcher the opportunity of observing natural behavior at anytime. Observations recorded will be on notebooks and will supplement the findings of the descriptive statistics.
Secondary Data
This data will be through analysis and review of books, journals, papers, magazines and previous lectures on knowledge management in Organization implementation. We shall also rely on the past surveys and observation within the scope of the study.
Questionnaire Design
The questions used are mainly from surveys and questionnaires and are usually open ended, closed-ended questions and likert scales. Open ended questions do not always give answers that a respondent can choose from but allow participants to answer freely. On the other hand, closed ended questions provide answers for the respondent to choose. Likert scale questions requests respondents to respond to the question along a given continuum from the given responses.
The questionnaire test validity of the research hypotheses and model. It will be inclusive of variables like technological advancement, organization processes and communication, social and legal changes, new employee orientation, organization changes, and globalization. In some instances, dependent and independent variables will be assessed using likert scale that would array from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”. The questionnaire in this study will contain evaluation strategies on employee need for training and development. The development of the questionnaire will consider questions that will give rise to information that is relevant to the importance of training and development in controlling stress.
Limitations of the Study
The quality and reliable data was limited to time, budget, and a small geographical area (Cooper, 2005, p. 228).
Findings
The organization trains their employees as part of their strategic plan in all the fields, especially on the operations, maintenance, and other relevant technical fields. They develop their employees’ profession and personal skills to make it easy for them to fulfill the economic and service objectives at ease and be able to overcome the challenges of the changes in the environment (Panari, 2010, p. 176).
The top management for instance, the directorate general of human resource supports the training. The organization encourages the individual to be responsible of their professional development as much as the organization puts efforts to make them success. The organization views their workers as the most important asset in the organization (Channuwong, 2009, p. 334). The diagram below shows the stress training flow chart: (Source: Laird, 2003, p. 5).
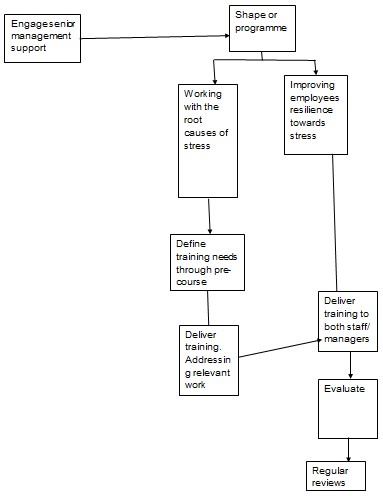
The chart above shows that efforts of controlling stress begins in the top management. When delivered through training and development the process created involves continuous analyses and evaluation of the programs (Contrada, 2009, p. 144). An accident occurred in Jeddah, 25 kilometers east of Riyadh and killed five employees and left one injured. The employees were from Archirodon Construction Company, four killed were Nepalese, and the fifth was an Indian. The person reported injured was from Nepalese. This led to distraction of the transport processes between Riyadh and al Hofuf. The president of the organization gave his apologies and requested for further investigations in the cause of incident. The lives of employees are threatened and this causes a lot of tension in the workplace (Saudi Railways Organization, 2010, par.1)
The employees are responsible for ensuring that the passengers get other means of transport and that tickets are refundable. During this process, the employees face conflicts from their fellow employees and their customers. In this incidence, the director of public relations and media, Muhammad Abu Zaid ensured order of customers in the cancelled trips. He requested the buses to help transport their passengers in need of emergency transport (Saudi Railways Organization, 2010, par.1)
The drivers and employees in the trains are at risk of losing their lives and maybe injuries at one point. For instance, end last year; two freight trains collided out of human error. By good luck, none of the passengers reported injured but the driver and one of the employees sustained injuries and were rushed to the hospital (Saudi Railways Organization, 2010, par.1)
The employees’ challenges come in when they are responsible for these mistakes and some are imprisoned. The employees are under pressure for any occurrences or incidences along their job activities and these amounts to stress in the long run (Contrada, 2009, p. 146).
The climate is not conducive for the employees in Saudi Arabia. All the seasons the year round are not conducive for the construction activities. The employees spend most of their working hours under the hot sun during summer. The temperatures rise even to 50 degrees. When the temperatures are lower, there is a lot of humid and workers become very uncomfortable. Their winter is during December and the temperatures at night drop even to below 0 degrees forming snow at the construction sites and this distract the construction of the rails. There is a lot of rain during spring and due to the open environment of the work place, the workers have to stop their activities to allow the rain to pass. This leads to low productivity as the workers cannot exploit their full potential yet the company still expects result in the end (International Business Publications, 2005, p. 72).
These changes in climate also threaten the health and safety of the workers and incidences of sickness lead to employee tension. Workers become unsatisfied the whole year round and there are no hopes for better changes since climate is uncontrollable. The organization has an advisor to communicate on the needs of their employees in terms of health and safety since their activities are very risky. The employees consequently gain confidence if the leadership is well done and their needs are satisfied. The employees in turn work very hard and efficiently due to the comfortable environment (Contrada, 2009, p. 138).
Some of the religious practices such as Ramadan prohibit the workers from eating and drinking. The organization activities require a lot of energy hence the workers may not be able to perform efficiently. The employers expect the same work turn over as the religion discourage less involvement in the daily activities hence the workers work under pressure to meet their target despite their feelings and perception. The workers then suffer with no option (Saudi Railways Organization, 2010, para.1)
The foreign employees face challenges due to the poor interpersonal relationship with the other workers from Saudi Arabia due to the difference in language, cultures and beliefs. This makes some of the employees feel isolated. For instance, holding hands shows friendship in the country in which the foreigners forbid hence, difficult for them to show their friendship. The organization has introduced English classes and counseling their employees to cater for the diversity (Kaila, 2005, p. 495).
There is a commission that ensures the employees comply with the required standards and activities of the organization. They monitor the efficiency of their employees and ensure their health and safety. The organization has a training centre to enable the employees to be responsible of them (Pretrus, 2003, p. 64).When the Damman project is complete most of the employees will remain unemployed. The country also wants to make their projects owned by foreign private companies (Saudi Railways Organization 2010, par.1).The employees are in fear of job insecurity. The employees work under tension and sometimes fail to work for the best since they know they will lose their jobs soon and they may fail to promote before the job is over. The organization has tried to intervene to the government to create new job opportunities for their employees. The government has in return authorized the foreign companies that 70% to 90% employees in their company should be from the country (Harzing, 2004, p. 148).
Some of the projects delay making the employees remain idle. For instance, the railway that is to connect the phosphate mine. The employees become impatient and even after starting their jobs they remain dissatisfied therefore, the organization has to make their employees understand the progress of their job activities. Good communication between the employer and the employee is very important to ensure the activities are of high standards (Laird, 2003, p. 5). Saudi Arabian government has great investment programmes to ensure that the railway projects complete successfully. These efforts of the government stimulate the employees to utilize their full potential so that the government can support them in their needs and wants especially when the contracts are over. The organization hires experts in the job fields to ensure the employees are well conversant with the activities they carry out so that they can work at their full potential (Bhargava, 2003, p. 75).
Discussion
Personal Environment Fit
This involves family and organization individual experience and perspective. Families in South Arabia are peaceful due to the strict religious practices. Employees in the organization relate well as they hold hands as a sign of friendship. This closeness gives opportunities for exchanging ideas reducing the chances of stress. However, this can also cause stress, in case of isolation (Cordesman, 2009, p. 323).
Workload
Employees have to meet strict deadlines since the jobs are under a contract. The employers have to design a strict working schedule to ensure their work is complete before the contract period is over. When there are problems that disrupt their processes, they have to work extra time to ensure that their schedule is accomplished. The employees live under pressure. The organization has to train their workers to work efficiently even when they face challenges. For instance, they can use machines to make their work easier and faster (Kaila, 2005, p. 505).
Hours of Work
Saudi Arabia has poor climatic conditions that make it difficult to work for long hours under an open environment. The organization encourages employees from the country to take their jobs since they are well conversant with the climate of the country hence can work for longer hours. The foreigners however face so many problems when adopting the climate. They undergo training to become aware of what they should expect and what to do under such circumstances. The country is peaceful hence, the employees face less challenges when it comes to working time. They can even extend they work until late at night (International Business Publications, 2005, p. 74).
Environmental Design
Due to changes in the society, management has adopted issues such as globalization, women in the workforce, and academic and organization standards. These issues help to reduce stress in terms of performance and communication in the organization (Kohut, 2008, p. 135). The cities where the railway lines passes are very distant from each other and some of the railway lines pass through some deserts making it difficult for the employees to work efficiently (Saudi Railways Organization 2010, par.1).The employees have to work very hard to complete their projects. They take long to travel from one city to another. This makes the employees to get fatigued slowing down their activities. They are also prone to accidents due to the long distance covered. They have to train to ensure that they function out of experience. The organization motivates them to increase their morale for the jobs (Price, 2007, p. 586).
Ergonomic Factors
The organization develops fast trains with comfortable seats to ensure the passengers and transported goods reach their destinations on time and comfortably. There trains travel over long distances hence they have to be fast to cater for the needs, preferences, and wants of their customers (International Business Publications, 2005, p.72). The employees receive a feeling of pride and sense of belonging when they see their customers satisfied. The organization aims at ensuring urban systems services such as signaling and communication systems to ensure the employees communicate efficiently to their reporting stations. This helps to reduce accidents and misunderstanding as they carry out their jobs. The employees train to use those equipments to be efficient in their jobs (Laird, 2003, p. 16).
Autonomy and Control
The organization has maintained employment stability with the support of the government consequently protecting the interest of their employees. The railway line moves across the cities to balance regional development and maximize the use of resources and the market opportunities. This enables the organization to ensure its employees are comfortable at their jobs and their morale improves to cause development in the country (Saudi Railways Organization, 2010, par.1).
Work Pacing
The government supports the organization by offering funds for investment of the railway line. This speeds up the activities of the organization. However, there are a few projects delayed but soon they begin operating (International Business Publications 2005, p.92). This encourages the employees to invest their profession on this job. The organization hires experts to prepare the work schedule to ensure the work completes at a favorable pace. This reduces the pressure caused by deadlines (Shoult, 2006, p. 102).
Electronic Work Monitoring
The activities of the organization follow a strict schedule that the employees must follow. Failure of the employee leads to inconveniences in the organization. This leads to blames from the top management. The employee then looses interest and confidence in their job. The employees train to communicate and to understand their work demands (Neider, 2003, p. 10).
Role Clarity and Overload
The organization has departments for each job sections to ensure they carry out all the responsibilities in case of circumstances that need urgency. This helps employees be at ease in case of problems arising from the job. The jobs divide to reduce unfair treatment of employees (Jackson, 2007, p. 477).
Interpersonal Factors
The organization has training institutions to train their employees in English language so that they can communicate with foreigners and any customer not conversant with their language (Saudi Railways Organization, 2010, par.1). Due to the differences in the language used, the employees often use non-verbal communication. This reduces the chances of interaction and creation of relationships. This leads to isolation of some employees in the organization and the capabilities minimized due to the inability to share ideas effectively. Lack of good communication leads to poor interpretation and consequently causes conflicts in the work place (Kohut, 2008, p. 136).
Total Quality Management of the Organization
Experts and professionals manage the employees. They are aware of the changes in the modern society and make use of the best international practices (International Business Publications, 2005, p. 72). This makes the employees motivated to get experience and work to their full potential to make the organization successful. Due to the complexity of the decisions making processes and strict follow up of the religious practices, the organization has to engage in continuous analysis and evaluation of the changes in the market and reforms in the organization to ensure transparency, accountability, integrity, efficiency, and flexibility of the employees as they carry out their duties (Champoux, 2010, p. 410)
Manager Styles
The managers know how to communicate with their customers and employees to ensure they have a good experience, satisfaction, and remain loyal to the organization. The managers undergo training and counseling to improve their social networking. The managers have a good relationship with the other companies for example, the bus transport company and the government safeguarding their disputes, operations, and investments. Through training, development, and involvement in effective programs, employees get to understand their roles in the organization helping them to control stress especially in the case of workload pressure (DuBrin, 2008, p. 600).
Organization Structure
The structure of the organization is well organized and each management department is aware of its responsibilities. It divides according to the needs of the organization and the organization survives in the market due to the coordination of the activities in the organization. This reduces confusion improving the performance of the organization (Neider, 2003, p. 8).
Climate and Culture
Training on the acceptance of different cultural diversity helps to characterize good relationship between the employees. They are able to respect and understand one another (International Business Publications, 2005, p. 89).
Performance Measures and Compensation
The workers follow a schedule that enables them fulfill their duties. The organization pays their employers for their services and offers free training to increase their knowledge and experience on their job (Stranks, 2005, p. 220).
Staffing Issues
The organization provides 1400 employees with training programs. The organization has an advisor on the welfare of employees in terms of health and safety since the organization engages in highly risk activities. The board of directors makes decisions for the organization and ensures they create a good relationship with the government (Gennard, 2005, p. 374).The organization attracts employees with the potential of creating a good image for its products and services for instance, the influential people in the society. It provides further training and development to improve their employee performance, competitiveness of the company products and services in the market, and the use of advanced technology (Croome, 2006, p. 93).
Conclusion
Workplace stress is inevitable but can be managed well and kept as low as possible. The organization and its employees monitor their working conditions to ensure that the strains reduce to maintain and improve their performance. The trainee goes through their records to measure the effects of the strain on the employee to advise the management on the adjustments required. Nevertheless, stress control is a test and error method involving continuous analysis and evaluation of the working conditions. Training and development gives the employee strength and knowledge to overcome the stressors in the job. However, stress effects and reactions vary from one individual to another. The experience derived from the challenges of the workplace help to reduce stress sin the future. The employee is able to improve his or her performance and creativity through quality planning and management (Malloch, 2010).
Organizations control their workplace stress by valuing the welfare of their employees in a flexible and understanding manner and ensuring good communication between each other. Trainees and specialists in stress control programs are becoming an important asset of an organization since the well-being of their employees reflect in the productivity and potential of the organization. Today organizations have adapted recruitment, selection, trade unions, change of environment especially transfer and leaves, health and safety programs to try to reduce stress in the workplace. They have open discussions in meetings, seminars, gyms, and suggestion boxes to guide on tackling the problems associated with stress.
Training improves the employee ability to handle the stressors that affect the performance of his daily routine. Training accompanies counseling especially if the problem affects the employee psychologically. The counseling involves physical and spiritual therapy. The employee is able to balance his or her family affairs, personal characteristics, and the demands of the organization when trained. He or she gets a broader attitude, understanding and perception of the surrounding and gets experience on what to do when a certain problem comes up.
The relationship between the employer and the employee is very important more than the training received. The employee is able to communicate the problems in the workplace and his personal life. Most of the employees face problems from pressure, isolation, financial difficulties, family and organization conflicts, blames from the top management, and lack of health and safety in the organization. Most of the organization’s reward their employees for their efforts to control strain while carrying out their activities. It is upon the organization to take these considerations very seriously and improve their methods of training and development programs to reach out to the needs and wants of their employees. Although stress is unavoidable, there are possibilities of minimizing it to a point of not affecting the organizations performance.
Lists of References
Anna, S 2004, managing workplace stress: how training can help, Industrial and Commercial Training Journal, vol.36, no.2, pp.61-65.
Bhargava, P 2003, The saga of Indian science since independence: in a nutshell, University Press, New York.
Cannon, W 2010, The reality of stress and the need for management, Managed Care Outlook Journal, vol.23, no.16, pp. 3-7.
Chambers, R 2002, Beating stress in the NHS, Radcliffe Publishing, New York.
Champoux, J 2010, Organizational behavior: Integrating individuals, groups, and organizations, Taylor and Francis, New York.
Channuwong, S 2009, Strategies for reducing stress among managers: an integrated physical and spiritual approach, International Journal of Management, vol.26. no.2, pp.334-340.
Christopher, R 2004, Recognizing the perceived causes of stress-training and development perspective, university of Sanford, Manchester.
Contrada, R 2009, The handbook of stress science: Biology, psychology, and health, Springer Publishing Company, New York.
Cooper, C 2005, Research companion to organizational health psychology, Edward Elgar Publishing, Northampton.
Cordesman, A 2009, Saudi Arabia: national security in a troubled region, ABC-CLIO, New York.
Croome, D 2006, Creating the productive workplace, Taylor and Francis, New York.
Documents and Resources for Small Businesses and Professionals 2011, Kirkpatrick’s four level model of training evaluation, Documents and Resources for Small Businesses and Professionals. Web.
DuBrin, A 2008, Essentials of management, Cengage Learning, Boston.
Egan, M 2009, Evidence-based interventions for social work in health care, Taylor and Francis, New York.
Europa Publications Limited 2003, The Middle East and North Africa, Routledge, Routledge.
Fairbrother, K 2003, workplace dimensions: stress and job satisfaction, Journal of Managerial Psychology, vol.18, no. 1, pp. 8.
Gennard, J 2005, Employee relations, CIPD Publishing, Oklahoma.
Haraway, D 2005, Analysis of the effect of conflict –management and resolution training on employee stress at a healthcare organization, Hospital Topics Journal , vol.83, no.4, pp.11-16.
Harzing, A 2004, International human resource management, SAGE, Bullhead.
Hughes, P 2009, Introduction to health and safety at work, Butterworth-Heinemann, Woburn.
International Business Publications 2005, Saudi Arabia King Fahd Bin Abdul Aziz Al-Saud handbook, Intl Business Publications, Vatican.
Jackson, J 2007, Human resource management, Cengage Learning, Boston.
Kaila, H 2005, Human resource management, vol.2, Gyan Publishing House, New York.
Kirkpatrick, D 2006, Evaluating training programs:Tthe four levels, Berrett- Koehler Publishers, San Francisco.
Kizza, J 2010, Ethical and social issues in the information age, Springer, Springer.
Kohut, M 2008, The complete guide to understanding, controlling, and stopping bullies & bullying at work: A guide for managers, supervisors, and employees, Atlantic Publishing Company, Atlantic City.
Laird, D 2003, Approaches to training and development, Basic Books, Atlantic.
Malloch, M 2010, The sage handbook of workplace learning, SAGE Publications Limited, Oliver’s Yard.
McDermid, S 2007, HRD responses to work family stress, advances in developing human resources, Journal of Management, vol.9, no.4, pp. 527-543.
Mobile Reference 2006, Travel Mecca and Saudi Arabia for Smart phones and mobile devices-illustrated guide, phrasebook, and maps, Incl Mecca, Medina, Riyadh, Jeddah and more. FREE general info, basic phrasebook, and a map in the trial version, Mobile Reference Publisher, New York.
Muassasat al-Naqd al-Arabī al-Saūdī, 2009, Annual report, Pennsylvania State University, Panama.
Neider, L 2003, New directions in human resource management, IAP, Kansas.
Ornelas, S 2003, New developments in managing job related stress, Equal Opportunity International Journal, vol.22, no. 5, pp. 64-69.
Panari, C 2010, Can an opportunity to learn at work reduce stress, Journal of Workplace Learning, vol.22, no.3, pp.166-176.
Pratelli, A 2010, Urban transport xvi: urban transport and the environment in the 21st century, WIT Press, Vatican.
Pretrus, T 2003, New development concerning workplace safety training: managing stress arising from work, Management Research News, vol.26, no. 6, pp. 68-75.
Price, A 2007, Human resource management in a business context, Cengage Learning EMEA, New York.
Saudi Railways Organization 2010, Organizational chart, Saudi Railways Organization. Web.
Shoult, A 2006, Doing business with Saudi Arabia, GMB Publishing Limited, Berlin Adlershof.
Stranks, J 2005, Stress at work: Management and prevention, Butterworth-Heinemann, Woburn.
Treven, S 2005, Training programmes for stress management in small businesses, Education and Training Journal, vol.47, no. 8-9, pp.640-651.
Williams, N 2009, Employers set out to reduce workplace stress, World Health Organization, Los Angeles.