The educational services sector establishes institutions and organizations that provide various kinds of training from elementary schools for children to educational centers for adults. This sector plays an essential role in our daily life since every citizen is obliged to receive an education. Besides, many adults have to take refresher courses and learn new skills to become employed or for personal development. In addition, educational services adapt to the requirements of people with special needs. Anyway, the significance of educational services for ordinary people is undeniable. Apart from that, the government also pays a lot of attention to it since the domestic education of high quality not only raises the country’s prestige but also gives competent experts who become employed in other sectors of the economy. Besides, education is one of the tools of soft power that is used to affect other countries by non-violent means. Therefore, the current economic brief analyzes the sector of educational services.
Industry Goods and Services
As it has already been mentioned in the introductory section, the described sector provides numerous services related to learning and training. More precisely, the educational services sector includes the establishment of elementary, secondary, professional, and business schools, colleges, universities, and management development training (1). Apart from this, the sector deals with cosmetology and barber schools, flight training, language and automobile driving schools, exam preparation courses, and educational support services (1). These services’ target audience includes children, youth, adults with and without higher education, people with disabilities, and aged people. In some cases, the consumers use services for free, for example, if they attend a public school. In other cases, the services are provided in exchange for payment, as in the case of specialized courses or higher education.
Market Structure and Characteristics
The education industry could be characterized as monopolistic competition in which the producers provide goods and services of different quality and price. To illustrate this, one could use the example of universities. Some of them are more prominent and take higher rankings, while others are less well-known and more affordable. At the same time, it should be noted that this sector demonstrates a low market share concentration that signifies greater competition among businesses (2). The top-three out of 1,378,915 companies with the highest annual revenue include the State University of New York, the University of Pennsylvania, and North Wildwood School District (1).
Besides, the industry of education acts at regional, national, and worldwide scales simultaneously. Businesses that deliver such services as refresher courses or language schools operate at the regional level since they aimed at US citizens from a particular city or town. On the contrary, universities, and colleges target not only local citizens but also students from other countries. American universities proved to be the best in the world, and, therefore, they attract individuals from nations with the weaker educational system.
Finally, the industry is characterized by a great extent of variability. This means that demand and supply change depending on socio-economic, political, technical, and cultural factors. For instance, the current strained relations with China will lead to a decrease of Chinese citizens that would try to enroll at American universities. Additionally, the rate of unemployment caused by pandemic could be regarded as a factor that contributed to the growth of the popularity of training courses among adults.
Trends
Digitalization is viewed as inevitable and the most influential trend in the industry of education. The pandemic of COVID-19 and the forced self-isolation made the vast majority of schools, colleges, universities, and training courses shift from traditional teaching to online one. However, even before the pandemic, there was a noticeable and stable rise in the percentage of students who preferred online courses to offline once (3). Although the statistics indicate that less than 50 percent of students choose online courses, it is still evident that academic institutions should heed to this tendency.
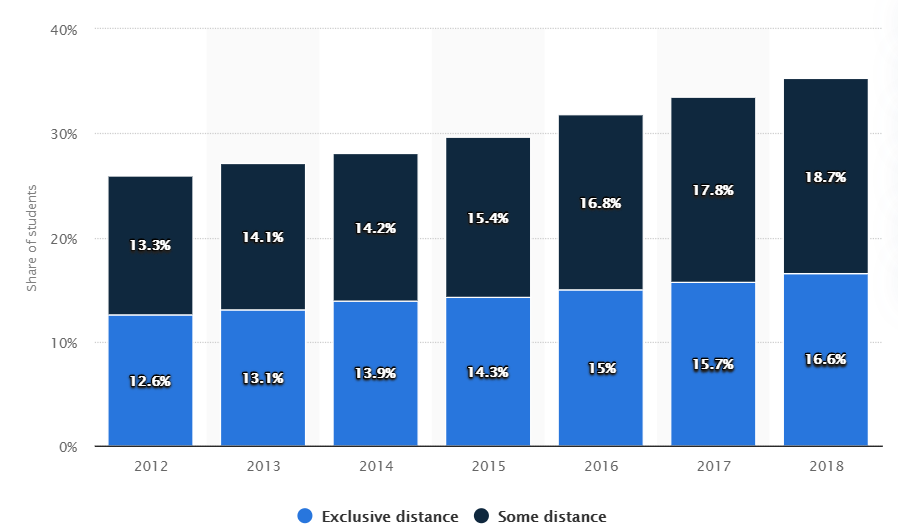
Most importantly, digitalization signifies additional costs for the businesses that act in the sector of educational services. Academic institutions have to install new specialized equipment and pay for the training of teachers. In other words, businesses should reorganize themselves to follow the trend and remain competitive in the market. Undoubtedly, there are debates on the pros and cons of the digitalization of education. Still, the trend towards digitalization touches almost every single industry in the US economy. Therefore, companies in the discussed sector are recommended to put more effort into the inclusion of digital technologies and online platforms in the usual teaching practice.
How Government Intervention May Impact the Industry
The education industry is not totally free from government intervention because of the existence of academic institutions subsidized from the states budget. Tutoring and training services are more discretionary and, this way set prices depending on other players at the market. It could be suggested that government intervention would lead to a decrease in average market prices and minimize the number of actors in the market structure, moving it towards oligopoly. The prices would fall as the result of additional financial support of the industries and, in turn, would create higher demand. Simultaneously, for the government, it is unprofitable to spend budgetary money on many weak companies. If it invests in more promising enterprises, those of lower quality will not sustain the competition. As a result, such companies will be forced to leave the market.
Sources
NAICS Association (n.d.). 61 – Educational services. Web.
IBIS World (2020). Educational Services Industry in the US – Market Research Report. Web.
Statista (2020). Percentage of students in the United States taking distance learning courses from 2012 to 2018. Web.