Human beings work in groups to achieve their goals much faster. Members of a particular team should promote the best communication skills. Such skills will improve the performance of the targeted group. Members of the group will share their competencies and ideas. The approach will produce the best outcomes. Mealiea and Baltazar (2005) support ‘the importance of effective communication in a team’ (p. 142). Team leaders should establish the best practices that can produce quality outcomes. Positive group communication produces new ideas thus improving the level of performance. Effective communication also establishes a supportive working environment among the targeted members (Robbins et al. 2014). The performance of our team explains why communication is a powerful factor in getting quality outcomes. One of our teammates was non-cooperative. He always postponed his duties thus affecting the success of the team. Our leader did not empower most of the members. This malpractice affected the success of our group.
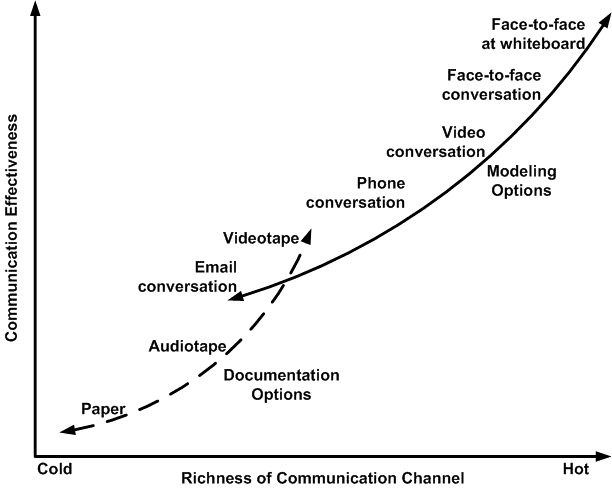
Many studies support the importance of positive group communication. Members of a group can use both nonverbal and verbal communication to interact with one another. The important thing is ensuring that such individuals have a common understanding. Such members should design the best structural functions. Groups should also have competent leaders. These aspects will ‘promote the best practices such as problem-solving, decision-making, collaboration, and teamwork’ (Argenti, Howell & Beck 2005, p. 89). The targeted members should also communicate naturally. The practice will improve the level of understanding. That being the case, modern studies do not oppose the importance of effective group communication. This graph supports the use of face-to-face communication in a group setting. A powerful leadership approach will make every group.
Theories of group communication support the importance of positive interactional practices. According to Argenti et al. (2005), Organisation Theory (OT) focuses on the best interactions between two or more persons. The theory supports the best practices that can produce the targeted goals. Organizational Behavior (OB) theory promotes efficient strategies that can produce the best goals in a group. The theory encourages teammates to work together to achieve their potentials. The theory supports the objectives of many groups. Some scholars have highlighted new theories that can support the performance of different groups. The ‘functional theory focuses on the best group behaviors and practices’ (Mealiea & Baltazar 2005, p. 142). The theory encourages group members to communicate effectively. The practice will make it easier for them to solve their problems. They will also be ready to make accurate decisions. Groups should combine these theories in order to achieve the most desirable outcomes.
Effective communication makes it easier for different individuals to address their differences. The practice also encourages members of a group to promote the best behaviors. The members will also make accurate decisions. Effective communication promotes new practices such as critical thinking. The individuals will also be ready to make rational judgments. Positive communication ‘is a powerful tool that makes it easier for groups to achieve their objectives’ (Mealiea & Baltazar 2005, p. 147). Group members must work together to get the best outcomes. This practice will improve the level of productivity. The partners will also become more responsible. Teams should, therefore, embrace the power of effective communication.
List of References
Argenti, P, Howell, R & Beck, K 2005, ‘The Strategic Communication Imperative’, MIT Sloan Management Review, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 83-89.
Mealiea, L & Baltazar, R 2005, ‘A Strategic Guide for Building Effective Teams’, Public Personnel Management, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 141-160.
Robbins, S, Judge, T, Millett, B & Boyle, M 2014, Organisational Behavior, Pearson Australia, Frenchs Forest.