Introduction
Background
In the last few decades, most organizations in the world have attempted to globalize their business by diversifying their marketing strategies in order to tap the opportunities provided by the large world population. In particular, most American corporations have extended their marketing strategies to include Asia, Europe, and other areas as their target markets because these foreign markets have been experiencing positive economic growth over the last few decadesi.
Harley-Davis Corporation is one of the American companies that have seen the need for diversification and globalization. Over the last few decades, the company has embarked on selling its motorcycle products to Asia and Europe in addition to its American markets. However, the company has been using different strategies to enter and remain in the target foreign markets. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a comprehensive understanding of the company’s strategies and the differences that exist between the strategies used in the US and those used in foreign marketsii.
Purpose
The purpose of this paper is to examine how Harley-Davis Corporation succeeds in developing different marketing strategies for the local and international motorcycle markets. In particular, the paper examines the company’s strategies based on Porter’s five forces, generic strategies, as well as the corporate financial ratios and stock trends.
Key questions
To develop a good understanding of the topic, this paper addresses some key questions that arise from the case study. These questions are;
- Are the US and Global motorcycle industry profitable and attractive?
- What are the key elements of Harley-Davidson’s US competitive strategy?
- What are the key elements of Harley-Davidson’s international strategy?
- How would the HD strategy be classified in generic terms?
- Should shareholders be encouraged to invest in the company?
Identification of key issues in regards to the company’s US and Foreign marketing strategies
Nature of the US and global motorcycle industries in terms of profitability and performance
The US motorcycle industry is relatively lucrative, a phenomenon evidenced by a good performance of the companies involved in manufacturing and selling motorcycle products. According to economic analysts, the industry has been growing by a significant margin since the 1950s. For instance, more than 650,000 new motorcycle products were sold in the US in 2000 alone, which represented a growth of more than 20%1. In addition, statistics indicate that the industry’s market was expanding significantly, with customers spending more than $5 billion in the same year. Between 2000 and 2007, the industry was experiencing a positive growth of more than 16% per annum on average. However, the economic recession of 2007-2010 had a negative impact on the US industry due to reduced sales, which declined by more than 30%. Nevertheless, the industry recovered quickly after 2010iii. For instance, the company’s in the industry experienced a sharp rise in profitability between 2010 and 2013. The profitability increase rate of more than 23% was recorded in 2011 and 2012. In addition, there is a consistent increase in the number of sales throughout the year, which makes the US motorcycle industry relatively profitable.
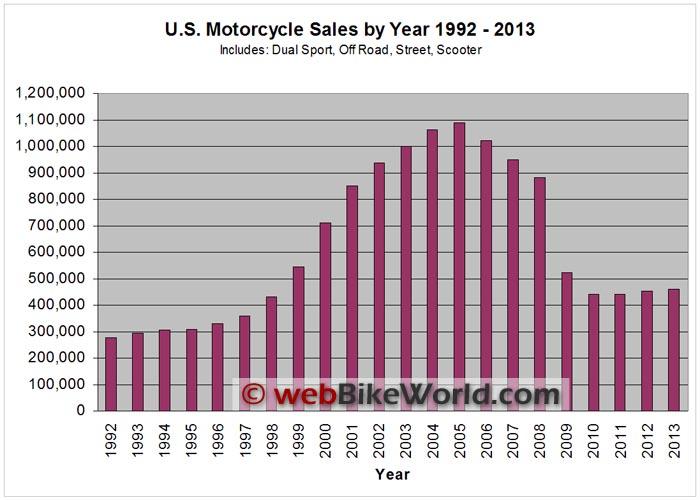
On the other hand, the world motorcycle industry has a larger profitability levels than the US market. For example, statistics indicate that Asian and European motorcycle markets have some f the best performance, with some countries like India and China recording average annual growth rates of more than 26%. In India, a number of foreign manufacturers have either set up new production plants or multiple outlets. For instance, Harley-Davis Corporation, Ducati Motor, Yamaha, Triumph Motorcycles, and a number of other multinationals have a huge presence in the country.
Thus, it is evident that both the US and global motorcycle industries are relatively profitable.
Figure 2: Global trend of production of motorcycles in 2013
The key elements of Harley-Davidson’s US competitive Strategy
Over the years, Harley-Davis has been producing and marketing multiple motorcycle brands to meet the market demands, which are characterized by the differences in consumer behavior patterns. For instance, the company has been producing different brands to satisfy customer needs according to age, profession, purchasing power, and other aspects. The young people have a tendency to prefer sporting motorcycles and seek for the products with a high capacity for speed. On the other hand, older people and professionals seek products that provide them with the comfort and convenience of traveling.
Moreover, corporations are looking for quality products with the capacity to meet the demands of ferrying mails and other items with ease and at a reduced cost. Thus, the company has been using this knowledge to develop different products to meet diverse consumer needs.
Secondly, the company focuses on the automation of production processes to increase or reduce the rate of production in response to the market needs and reduce costs at the same time. As such, the company seeks to increase efficiency at its American production units. This strategy has allowed it to cut on the cost of production because the need for human workers has declined Ibid significantlyiv.
The key elements of Harley-Davidson’s Global competitive Strategy
The company’s presence in India is a good example of a case in which it focuses on the nature of the local market as well as the consumer characteristics to develop effective marketing strategiesv. For example, the company has a direct marketing strategy that allows it to obtain licenses to establish multiple outlets for the wholesale and retail sale of motorcycles. In addition, it has allowed retailers to stock their products in their stores throughout the country.
Moreover, the Indian motorcycle market is characterized by the differences between the rich and the poor, the young and the old consumers as well as poor and good road networksvi. Therefore, price is an important aspect that consumers consider when purchasing products in India. As such, the company has been developing products specifically for the Indian market. Cheap products are developed to meet the needs of young and poor people, while strong motorcycles are developed to meet the demands of individuals using bad roads.
This strategy seems to be working because the company has been selling thousands of products in India every year. In addition, it is a generic strategy because it is based on an in-depth examination of the market characteristics and consumer behavior.
Options and alternatives
To enhance sales in foreign markets, it is recommended that the company’s strategy in India be expanded to other regions in Asia. For instance, there is a high demand for motorcycles in the Middle East, where the economies of such countries as Qatar, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia are developing fast. In addition, this strategy should be taken to China
Recommendation
It is recommended that the company retain its foreign strategies but expand its market to cover more countries. For instance, competitors are focusing on the African market because it is the fastest-growing in the world. It is recommended that the company focus on the African market in addition to its previous markets in Asia as the major foreign markets.
Works Cited
Choudhury, Santanu. “High-end motorcycles rev sales in India”. The Wall Street Journal 3.1 (2014): 1-3. Print.
Hagerty, James. “Harley Goes Lean to Build Hogs”. The wall street journal (2013): 1-3. Print
Teerlink, Rich and Lee Ozley. More Than a Motorcycle: The Leadership Journey at Harley-Davidson. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 2010. Print
Footnotes
- Hagerty, James. “Harley Goes Lean to Build Hogs.” The wall street journal (2013): 1-3. Print
- Teerlink, Rich, and Lee Ozley. More Than a Motorcycle: The Leadership Journey at Harley-Davidson. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 2010. Print
- Ibid.
- Ibid.
- Choudhury, Santanu. “High-end motorcycles rev sales in India.” The Wall Street Journal 3.1 (2014): 3. Print.
- Choudhury, 3