Introduction
The city of Riyadh has attracted many local and foreign investors who come to tap on the lucrative economy that has been consistently expanding over the decades. With an open market economy, this city has witnessed a massive increase in the number of firms over the years. According to Al-Mulhim (2009), the government of Saudi Arabia has adopted a hands-off approach in the market where foreign firms are not subjected to unnecessary bottlenecks when they are trying to invest in the country. There has been a need to stimulate the economic growth of the country and one of the best ways of achieving this is to encourage local and foreign investment into the local economy (Lippman, 2004). This means that the level of competition has become so high that only those firms with proper management strategies can become successful. As Long (1997) notes, the current business environment requires management practices that are conscious of the dynamism in the in-market, and other changing external environmental factors.
According to Madawi (2006), the economic performance of firms is always dictated by the management practices that are adopted in their normal running. Baamir (2010) notes that the management is expected to offer leadership that would steer a firm into economic success. The strategic policies adopted by a firm would always determine how successful a firm can be in the market. These policies would always dictate the moves taken by the firm in handling various issues such as emerging technologies, changing market trends, dynamism in human resource management, and other environmental factors. The way these environmental factors are handled will always shape the economic performance of a firm (Lippman, 2012). This research paper will investigate the impacts of management practices on the economic performance of firms located in the Riyadh region, Saudi Arabia.
Literature Review
According to Belanger (2011), human resource is the most important asset within any organization. Senior employees at the top management unit will always determine how successful a firm will be in the market. Roberson (2005) notes that success within an organization is achieved through employees and the management practices that are employed. Firms within the City of Riyadh have been forced to come up with strategies that would enable them to become competitive to survive the stiff competition that has been witnessed in the recent past with the increase of the number of firms in various sectors. One of the sectors that have seen a sharp rise in the level of competition in this city is the financial sector (Mai, 2005). Firms in these sectors have found themselves in the stiff competition following the influx of firms into the industry. Some of the major players in this industry within the city of Riyadh include Samba Financial Group (SAMBA) and Saudi British Bank (SABB). These two firms are a true demonstration that the economic performance of firms within this city is greatly affected by the management practices that are employed by the management (Rubin, 2005). To make this clear, it would be important to discuss the two firms independently based on their management practices, and how this has affected their economic performance.
Samba Financial Group, initially Saudi American Bank, is one of the leading financial institutions in the City of Riyadh. This firm was once a subsidiary of the giant City Bank of the United States, but its shares were bought locally, and currently, it is a Saudi bank owned by Saudi Arabians (Henry & Springborg, 2010). This firm has been very successful since it became fully owned by Saudi Arabians. Within the City of Riyadh, this firm has experienced massive success over the years because of the management practices that it has employed. According to Husk (2011), it is always important for a firm to ensure that it understands the prevailing environmental factors that have a direct impact on its normal operations. An outward-in approach of defining management practices is highly advisable if a firm is to achieve economic success (Kline, 2010). This approach means that the management would need to understand the prevailing environmental factors and formulate policies that are in line with these factors. The management of Samba Financial Group has been focused on this approach when setting its management practices (Biswas, 2011).
Methodology
Every research project applies a given research method to arrive at a specific conclusion. In this study, the researcher used a quantitative data analysis approach. Quantitative analysis was considered more desirable because of the need to use mathematical tools. The researcher used a simple statistical data analysis approach to analyze data. The results obtained from the research were presented in tables, graphs, and charts to enhance clarity. The research used a small sample population which was determined using the following formula.
n=N/ {1+N (e2)}
Where:
n = sample size
N= Target population
e= Degree of freedom (Aarts & Nonneman, 2006)
The research used questionnaires that were sent to the sample population electronically. The sample population then sent back the filled questionnaires with the data needed for analysis. The research will use ANOVA analysis in concluding. SPSS spreadsheet version 20 will be used in this statistical analysis.
Analysis and Findings
The following are some of the management practices that have been employed by this firm over the years as a way of promoting its economic performance.
Creation of female banking
Samba Financial Group did not have different banking halls for male and female customers. Both male and female customers had the liberty of choosing any of its branches in Riyadh for any financial transactions (Weiss, 2011). However, upon careful market research, the management realized that although this firm was successful, this strategy was hindering it from experiencing further success. According to Cordesman (2003), the strict Islamic culture prohibits any bodily contact between adults of opposite genders who are not close family members. When people are queued waiting to be served in a banking hall, it may be difficult to avoid bodily contact (Krivenko, 2009). As Champion (2003) observes, it is important to understand that this is not a discriminatory act by members of society. When men avoid banking halls that are frequented by women, they are avoiding circumstances that would make it possible for the two genders to have bodily contact, not because they look down upon these women.
Similarly, when women avoid male banking halls, they are only trying to keep the Islamic law by staying away from environments that would facilitate breaking the law, even if it is by accident (Manaschi, 1998). The management of Samba Financial Group realized that it had to act as soon as possible to avoid losing customers. It developed female banking to serve exclusively female customers (Grossman, 2011). This would mean that men had a banking hall that was exclusive from that of women. This management practice had a massive economic benefit to this firm. As Falah (2005) notes, the best approach to delivering high value to the customers is by understanding their needs and meeting this need in the best way possible. When the firm realized that there is a need to have different banking halls for male and female customers, it had to fine-tune its management practices to reflect this (Vincent, 2008). It was a demonstration that this firm respects the culture of the society, and is willing to go to great lengths in protecting it (Minja, 2009). The number of male and female customers increased drastically when this management practice was finally implemented. The research used the following hypothesis
H1a. The introduction of female banking at Samba Financial Group has improved its performance.
To determine the impact of this practice on the performance of the firm, the researcher used chi-square for equal proportions to determine the calculations. The data collected from the field was fed into SPSS and the table below shows the results that were obtained.
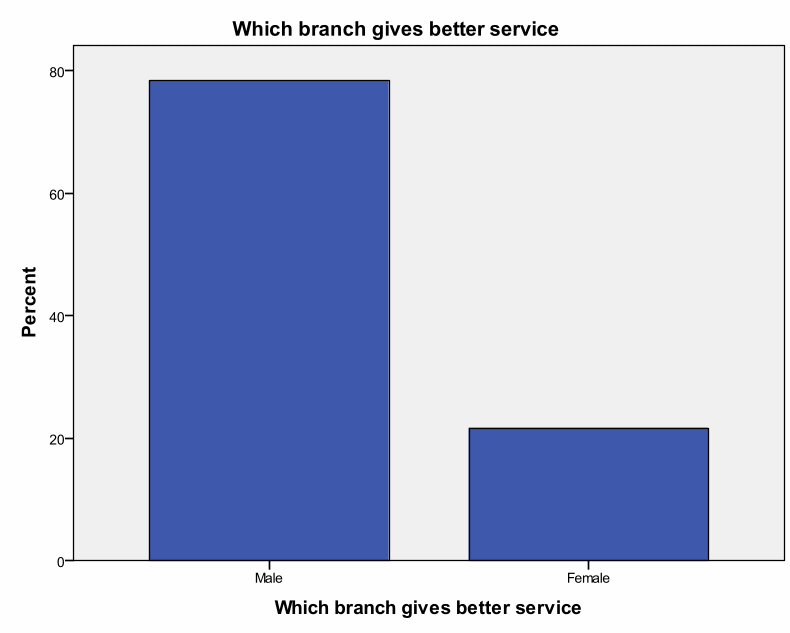
To test whether there is a significant difference in the performance of male and female employees of Samba Financial Group located in the Riyadh region, chi-square for equal proportions was applied using SPSS, and Table 1 below shows the findings.
Table 1: Which branch gives better service?
Source: Analysis of survey data
Table 2: Test Statistics
Source (Analysis of Survey Data)
It is clear from Table 2 above that the value of the chi-square statistic is 31.186 and its corresponding p-value is 0.000<0.05. Since this p-value is less than 0.05, it can be concluded that there is a significant impact of this new strategy on the general performance of the firm. The new strategy has improved the performance of the firm in the market.
The management practices of Saudi British Bank (SABB) and its impact on the firm’s economic performance
The Saudi British Bank, also known as SABB, is an Islamic Financial Solution that is part of the British HSBC Bank. It was started in 1950 in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The bank has employed various management practices that have helped it become very successful in the market. This success can be attributed to the management practices that it has employed to help it manage the market competition (Ramady, 2010). The management of this firm realized that it had to change its management practices to be in line with the changing environmental factors. The following are some of the management practices that this firm employed as a way of boosting its economic practices (Lombo, 2012).
Giving promotions based on performance
According to Lacey (1982), most firms around the world always promote their employees based on their experience and academic background. However, the Saudi British Bank has always taken a completely different approach when handling the issue of promotion (Tollitz, 2005). The firm has been promoting its employees based on their performance level in their respective areas of assignment. This has seen employees work hard to be promoted irrespective of their academic backgrounds (Panagariya, 2008). The table below shows the incentives used by this firm. The hypothesis below was developed to determine the appropriateness of the incentives.
H1o. The incentives given by Saudi British Bank have not helped improve its performance in the market.
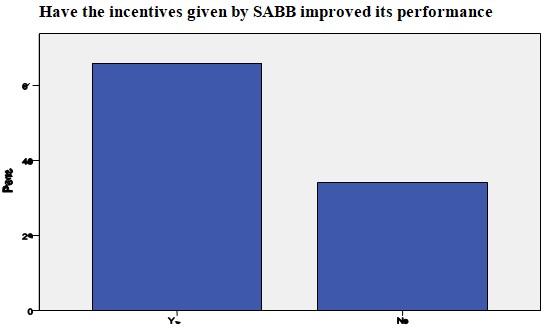
Chi-square for equal proportions was applied using SPSS to obtain the desired response.
Source: Analysis of survey data
Source: Analysis of survey data
The value of the chi-square statistic is 28.189 and its corresponding p-value is 0.000<0.05. Since the p-value is less than 0.05, the null hypothesis can be rejected and it can be concluded that the incentives given by the bank have improved its performance.
Conclusion
It is clear from the above discussion that management practices employed by a firm would have a direct impact on its economic performance. Samba Financial Group has introduced several management strategies focused on promoting the interests of its customers. It has introduced female banking as a way of meeting market needs. This has helped them increase the number of customers in their banking halls. On the other hand, Saudi British Bank has been keen on motivating its employees. This has helped the firm develop a pool of dedicated and highly skilled employees capable of driving this firm to higher heights of performance. In both cases, it is confirmed that these practices improve the economic performance of the firms in Riyadh City.
References
Aarts, P., & Nonneman, G. 2006. Saudi Arabia in the Balance: Political Economy, Society, Foreign Affairs. New York, NY: New York University Press.
Al-Mulheim, N. 2009. Islamic Funding of Small Business in Saudi Arabia. Mumbai: McMillan Publishers.
Baamir, A. Y. 2010. Shari’ a Law in Commercial and Banking Arbitration: Law and Practice in Saudi. Burlington: Ashgate Publishing.
Belanger, C. 2011. Our World: Saudi Arabia. Riyadh: Cangage.
Biswas, S. 2011. Commitment, involvement, and satisfaction as predictors of employee performance. South Asian Journal of Management, 18(2), 92-107.
Cordesman, A. 2003. Saudi Arabia Enters The 21st Century. New York, NY: Greenwood Publishing Group.
Champion, D. 2003.The Paradoxical Kingdom: Saudi Arabia and the Momentum of Reform. London: Hurst & Co. Publishers.
Falah, G. 2005. Geographies of Muslim Women: Gender, Religion, and Space. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Grossman, R. J. 2011. The care and feeding of high-potential employees. Hrmagazine, 56(8), 34.
Henry, C & Springborg, R. 2010. Globalization and the Politics of Development in the Middle East. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Husk, C. 2011. U.S Department of State, Diplomacy in Action. Washington, DC: Potomac Books, Inc.
Kline, J. 2010. Ethics for International Business: Decision-Making in a Global Political Economy. New York, NY: Routledge.
Krivenko, E. 2009. Women, Islam and international law: within the context of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women. Danvers: Koninklijke Brill.
Lacey, R. 1982. The Kingdom: Arabia & the House of Sa’ud. Harcourt Brace: Jovanovich.
Lippman, T. 2004. Inside The Mirage: America’s Fragile Partnership with Saudi Arabia. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Lippman, T. 2012. Saudi Arabia on the Edge: The Uncertain Future of an American Ally. Washington, DC: Potomac Books, Inc.
Lombo, G. 2012. Banking Industry in Saudi Arabia. New York, NY: Nova Publishers.
Long, D. 1997. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Gainesville: University Press of Florida.
Madawi, A. 2006. Contesting the Saudi State. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Manaschi, A. 1998. Comparative Advantage in International Trade: A Historical Perspective. Cheltenham, UK: Edwards Elgar Publishing.
Minja, D. 2009. Ethical Practices for effective leadership: Fact or Fallacy- A case of Kenya. KCA Journal of Business Management, 2(1): 1-14. doi.org/10.4314/kjbm.v2i1.44407.
Panagariya, A. 2008. India: The Emerging Giant. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ramady, M. 2010. The Saudi Arabian Economy: Policies, Achievements, and Challenges. New York: Springer.
Roberson, B. 2005. Shaping the Current Islamic Reformation. London: Frank Class Publishers.
Rubin, B. 2005. Crises in the Contemporary Persian Gulf. New York, NY: Routledge.
Tollitz, N. 2005. Saudi Arabia: Terrorism, U.S. Relations, and Oil. New York, NY: Nova Publishers.
Vincent, P. 2008. Saudi Arabia: an Environmental Overview. London: Routledge.
Weiss, W. H. 2011. Building morale, motivating, and empowering employees. Supervision, 72(9), 23.