Abstract
Ever since the Global Financial Stability Report issued in October 2008, perils to worldwide monetary steadiness are greater now than ever before, indicating a narrow-minded turnaround in development made over the precedent three years. The swiftness of the trade and industry recuperation has been a sluggish, halted growth in balance sheets repair technologically and otherwise developed nations’ economies too. Self-governing pressure in the euro region has now finally dribbled over to the banking schemes, pushing up loan and market possibilities. Stumpy interest charges could show the way to unrestrained behaviour. Up to date marketplace disorder puts forward that shareholders are losing staying power with the want for impetus on monetary revamp and reorganization. Strategy makers require increasing speed performance to address long-lasting monetary weak points to make certain constancy. In such circumstances, Islamic banking is giving a picture of little hope to the economists to successfully work out the financial crisis. This research will explore the possibility of implementing Islamic banking and its pros and cons.
Introduction
This section elucidates the research background and statement of the problem. The problem statement will be describing the situation/state of the study. This chapter will also be recognizing the research questions and the significance or the purpose of the study.
Background
The worldwide financial scheme (GFS) is the financial arrangement consisting of organizations and controllers that take action on the international stage, as measured up to individuals that do something on a countrywide or district level. The major participants are the global entities, such as IMF, State bank/ Central bank, state divisions and state agencies and ministries such as finance, Internationally working privately owned entities, e.g., fudge funds, and other entities such as regional institutions, e.g., the European belts zone.
Banking
A method of trading in money which involved protection of deposits and making finances available for borrowers, banking started in the Middle Ages in reaction to the mounting need for credit in trade. The lending chores of banks were undertaken in UK by money- lenders. Until their eviction in 1921 by Edward I, the most vital money-lenders were Jews. They were substituted by Italian traders who had papal dispensations to lend currency at interest. In the 13th century credit was vital to finance trade and important projects. The most vital was the wool trade but other illustrations included huge buildings such as Edwards castles in North Wales. When Italians had their actions in England restricted in the early 14th century, they were taken over by English traders and goldsmiths, whose interest rates were adequately low to evade the usury laws.
Monarchs had lent from traders and landowners for centuries. By the late 17th century, the increase of parliamentary power over administration spending needed more regulation. The Bank of England, was founded in 1694, provided the government and other end users of credit way into English funds. Comparable progress occurred in Scotland and Ireland. These banks stayed without stiff competition until the late 18th century, when increasing commercial activities gave possibility to traders, brewers, and land lords to create banks based on their own funds. Faults of decisions sometimes took place and runs on the bank happened when depositors, unsure for the security of their funds, demanded its return.
Variations in the worth of currency because of the return to a gold-based currency after the conclusion of the Napoleonic wars (1815) a series of crises took place. To steady the currency the government eventually initiated the 1844 Bank Charter Act, which gave the Bank of England the functions of administering the note issue and of overseeing the activities of the banking system. Regulatory powers were implemented in 1845 to control banking in Scotland and Ireland.
In the 19th century, cross country trade and the growing British empire reinforced the city of London as a core of merchant banking. The expertises of these specialist bankers created an attention for business from overseas firms and governments looking for loans. These efforts made possible the speedy creation of railways, heavy engineering, mines, and huge industrial developments. A lot of the merchant banks endured, including Rothschilds, Lazard Brothers, Kleinwort Benson, and Schroders. Interior trade was funded mainly by a greater number of local banks which, after the middle of the 19th century, became merged into a much smaller number of banks. Numbers continued to reduce so that by 1980 banking was swayed by four companies: Barclays, Lloyds, Midland, and National Westminster.
Banking has been distinguished, mainly because of technology modernization, by progressively more systematic provision of banking services and an extension of consumer credit. The business of protection and lending money is often organized through machine-interpretable cards and continuous access by telephone (Banking History 2011).
Islamic banking
Islamic investing is banking or investing goings-on that are stable with the regulation of Islamic commandment and its pragmatic function in the course of the development of Islamic money matters. Sharia prohibits the flat or afloat imbursement or reception of precise interest or charge recognized as Riba for credit of currency. Putting in business that makes available possessions or services supposed contrasting to Islamic policy is in addition Haraam (not allowed). While these codes were utilized as the foundation for a progressing economy in past , it is in the latter half of the 20th century that a good quantity of Islamic banks were established to implement these codes for Muslim communities in private or semi-private commercial institutions.
History of Islamic Banking
Introduction
In early 8th-12th century the economy and an early mercantilism were grounded, which many suggested to as Islamic capitalism. The financial economy of the time was based on the broadly dispersed currency the dinar, and it joined together areas that were earlier economically independent. Loads of financially viable thoughts and means were put into practice in premature Islamic banking, which incorporated demands for payment of switch over, joint venture such as controlled affiliation, and kinds of cheques, assets, capital adding up, assignments, loaning, ledgers, promissory notes, and trusts transactional accounts. From the 13th century onwards independent organization/entities from the country also existed in the Islamic world, while the agency institutes were also established at that time. Many of these initial capitalist thoughts were implemented and further progressed in medieval Europe.
Islamic financial process expressions
Bai al inah (transaction and exchange accord)
Bai al inah is an economics examination which indicates purchase and retail subjects among the issuer and the customer. The associate acquires an asset from the customer on spot foundation. The worth agreed by the issuer makes up the imbursement beneath the provision. Consequently the asset is sold to the client on a deferred-payment basis and the price can be paid in episodes. The second sale provides to establish the compulsion on the part of the client under the service/facility. There are variations of view amongst the intellectuals on the permissibility of Bai al inah, however this is observed in Malaysia and the like jurisdiction.
Bai bithaman ajil (delayed imbursement deal)
This idea refers to the auction of commodities on a delayed imbursement foundation at a cost, which includes a yield margin established in cooperation by involved individuals. Interest payment can be ignored as the client is giving the market price which is not the same as interest charged on a loan. The difficulty here is that this includes association of two transactions in one which is prohibited in Islam. The all-purpose view is that this is simply undemanding and clear-cut implication of interest camouflaged as an auction.
Bai muajjal (credit auction)
Factually bai muajjal indicates a credit auction. Murabahah Muajjal is a funding practice utilized by the Islamic banking system. It is an agreement in which the bank takes home a yield on margin for an acquired cost and permits the procurer to disburse the value of the good at a prospect stage in an absolute imbursement or in partly payments. It has to specifically state cost of the product and the margin of yield is commonly agreed. The value set for the good in this kind of a contract can be the comparable as the spot cost or better or inferior than the spot cost. Bai muajjal is also recognized as delayed-imbursement auction. Though, one of the vital explanations of Riba is a groundless defer in payment or either escalating or lessening the price if the payment is instant or delayed.
Musharakah
Revenues made are shared among the associates according to the invested amount. Combined undertaking in other words, Musharakah, is an agreement amid two or more acquaintances, whereby every individual related offers money to be made use of in a course of action. For fear that of failure, no connect gives up finances in the equivalent quantity. If the Bank offers funds, the same clauses apply. It is this monetary risk, according to the Shariah, that validates the banks claim to portion of the yield. Each associate may or may not contribute in carrying out the dealing. A working partner gets a bigger portion of the profit as against to a sleeping partner. The distinction among Musharakah and Madharaba is that, in Musharakah, each associate gives some fund, whereas in Madharaba, one partner, e.g. A bank, gives the entire fund and the other partner, the individual, provides no funding.
Madharaba
Madharaba is an unusual kind of partnership where one person gives fund to another person for investing it in a commercially activity. The speculation approaches as of the first individual who is recognized as rabb-ul-mal; at the same time as the vocation is an elite responsibility of the former, who is referred to as mudarib.
The Madharaba which means profit Sharing is a contract, with one party pays 100 % of the funds and the other party gives its know-how to invest the funds and handle the project. Proceeds completed are distributed among the in cooperation associates according to an in advance decided relative amount. Compared to Musharakah, in a Mudarib only the issuer of the fund has to take losses. In this concept no more than rabb-ul mal undergo from losses, mudarib do not undergo with loss. On the other hand, earnings are disseminated amid both rabb-ul-mal and mudarib.
Murabahah
This thought refers to the auction of goods at a value, which encompasses an earnings decided to by in cooperation parties. The acquiring and selling price, other overheads, and the yield margin must be clearly signifies at the instance of the sale contract. The bank is remunerated for the time value of its funds in the shape of the profit margin. Fixed-profits credit is then what it used for the acquiring of a real asset (for example a means of transport), with an unwavering charge of earnings by means of the revenue margin. The bank is not paid for the time value of funds outside of the agreement term; however, the asset kept as a mortgage with the bank until the non-payment is settled.
Musawamah
Musawamah is something like barter in price that parties do in terms of any reference by the seller to the value. At the same time, one who is selling may not be confident enough in terms of his knowledge grip over the price of the product that is under discussion to be traded; such parties are not influenced to reveal the value as piece of the trade of bargain. This demarcation in accountability by the vendor is the chief feature among Murabahah and Musawamah by means of all additional rules as portrayed in Murabahah lingering the similar. Musawamah is for the most part normal kind of buy and sell arbitration observing in Islamic business.
Bai Salam
An obligation in which advance imbursement is agreed for commodities to be prearranged afterwards is known as Bai salam. The retailer obtains to a few detailed substances for bringing in to the purchaser at a potential stage in swap over of an advance worth completely inward bound at the instance of binding. No indistinctness leading to some trouble is to be kept away from for that it is essential that the excellence of the product planned to be paid for is completely particular. The substance on the other hand cannot be bullion, silvery, or currency based on these alloys. Apart from for this, Bai Salam wraps each article that is competent of being emphatically made clear as to amount, superiority, and workmanship.
Essential description and circumstances of Salam
- The business is looked upon as Salam if the customer has agreed to acquire worth to the retailer entirely when paying for. It is compulsory so that the procurer can show signs of that they are not to go into money owing with one more or second party. With the intention of eliminating the money owing with the first party, a work prohibited under Sharia. The notion of Salam is dissimilar from the others as in dimension or in superiority or mass their precise explanation is not probable.
- Salam cannot be practiced on a precise article of trade or on an article of an exacting meadow or ranch. For example, if the seller takes up to provide the rice of a specific field, or the vegetables of a particular tree, the salam will thus will be un-valid, because there is a chance that the item of that specific field or the vegetables of that tree is damaged before delivery, and, given such likelihood, the delivery remains doubtful. The similar regulation is connected to each article the delivery of which is not convinced.
- It is required that the quality of the product is fully particular leaving no uncertainty which may lead to a disagreement. Everyone the probable particulars in this admiration must be unambiguously talked about.
- It is also essential that the amount of the commodity is decided upon in clear terms. In case the item for consumption is enumerated in mass as per to the utilization of its dealers, its heaviness ought to be considered / calculated, and if it is considered through method, its accurate estimate must be recognized.
- The precise day and situate of delivery ought to be stated in the agreement.
- Salam cannot be affected in spite of things which must be transported at spot. For instance, if bullion is purchased in swap over of gold bars it is essential, according to Shariah, so as to the swap over of both be concurrent. Here, Salam does not imply. In the same way, if wheat is bought and sold on behalf of rice, the liberation of both is essential at the similar point in time for the soundness of auction. Consequently the agreement of Salam is cancelled in this case.
- This is the most favoured financing mode and carries greater Shariah compliance.
Ijarah
Ijarah signifies rent, lease or salary. More often than not, Ijarah signifies business the benefit of utilizes or examination for a pre-determined cost or earnings. Under this, the Bank makes accessible to the clients the service of assets / equipments such as factory, office automation, car for a predicated period and price.
Ijarah thumma al bai (hire purchase)
Associates are bequeathed concord that comes into result in sequence, to shape an entire rent/ cash in contract. The primary agreement is an Ijarah that brings about the conditions for rental or leasing over a permanent period, and the subsequent agreement is a Bai which makes active an auction or purchase just the once the phase of the Ijarah is complete. For example, in a bike financing, a client enters into the first contract and leases the bike from the issuer/owner, at an agreed sum over a certain period. As soon as the charter period concludes, the moment agreement comes into functioning, which constructs the purchaser to acquire the vehicle at a settled to cost.
The bank takes out earnings by knowing in advance the price of the article, its outstanding worth at the conclusion of the phase and the occasion worth or yield margin for the finances being built in obtaining the article to be leased for the looked-for period. The combining of these three becomes the base for the agreement between the Bank and the customer for the primary lease contract.
For this kind of business dealings, they can be compared to a set of contracts, which is an officially permitted process commonly used by the European bankers and vendors during the Middle Ages to avoid the limits on interest bearing credit levied from the Churches.
In an agreement, two associates would go into three concurrent and consistent officially authorized agreements, the entirety consequence being the paying of a charge for the utilization of finance for the period of the credit. Using simultaneous interconnected agreements is forbidden under Shariah Law as well.
Musharakah (combined course of action)
An organization flanked by two sides or additional, of who pitches in money to commerce, and divides the disposable return loss pro rata is recognized as Musharakah. In the case of property, the bank reviews an assigned rent and will allocate it as decided in advance. All contributors of funds are entitled to take part in management, but not essentially required to do so. The return is disbursed among the parties in pre-defined ratios, while the loss is taken by each associate strictly in proportion to respective funding. This exercise is like chalk and cheese as of fixed-profits spends (i.e. issuance of credits).
Sukuk (Islamic bonds)
Fixed-profits & interest-comportment bonds are not authorized in Islam. For this reason, Sukuk are securities that accomplish in relevance to the Islamic commandment and its speculation regulations, which prohibit the induction or imbursement of interest. Financial possessions that convene the conditions with the Islamic main beliefs can be classified in agreement with their exchangeability and non-exchangeability in the less important marketplace.
Takaful (Islamic indemnity)
Takaful is a replacement structure of cover up that a Muslim can advantage himself as be in opposition to the jeopardy of failure due to misfortune. Takaful is of the thought that what is indistinguishable with regard to anyone might come to an end to be indistinct concerning an extremely large figure of comparable persons. Cover or Indemnity by integrating the jeopardy of a lot of individuals facilitates every single one to take pleasure in the reimbursement made available by the standard of better information.
Islamic equity finances
Islamic speculation equity finances marketplace is one of the fastest mounting subdivisions surrounded by the Islamic monetary structure. At the moment, there are around more or less hundred Islamic equity finances internationally. With the nonstop interest in the Islamic financial system, there are encouraging signals that more sums will be initiated. Some Western key players have recently joined the battle or are thinking of creating similar Islamic equity offerings.
Regardless of these achievements, this marketplace has observed an evidence of awful advertising as significance is on substance and not on dealing with the requirements and wants of shareholder. Over the previous decade, great statistics of amounts have taken out. For the most part of the money fit in to targeted elevated net worth shareholders and commercial institutes, with smallest amount reserves comprising as of US$50,000 to as full-size as US$1 million. Aim marketplaces for Islamic financial support differ; a few make available for their confined marketplace, for instance, Malaysia. Others objective the Middle East and Gulf areas paying no attention to limited marketplaces and have been liable of failing to provide the Muslim centre of population.
As per an article, “in the fact since the commencement of Islamic even-handedness money in the 1990s, there has been the formation of criterion equity standard by Dow Jones Islamic marketplace index and the FTSE international Islamic Index Series” (Islamic Banking n.d).
IMF cautions of worldwide monetary catastrophe
A brittle global trade and industry revival could tail off unless Europe prevents supreme ruler defaults, the United States gets its financial house in array and up-and-coming financial system avoids overheating.
In its usual evaluation of global trade and industry projection on the rampage on Friday, the Washington-based global lender cautioned the US and in arrears European states that they are playing with fire except if they take instantaneous steps to lessen their budget deficits. It said larger intimidation to expansion had materialized in view of the fact that it’s preceding report in April, quoting the euro zone debt catastrophe and symbols of overheating in up-and-coming market economies. IMF foretells that US gross domestic product would produce an indifferent 2.5 per cent this year and 2.7 per cent in 2012. In its predicted two months back, it had probable 2.8 per cent and 2.9 percent growth, in that order.
With look upon to the global economy on the whole, the IMF smack a deliberate tone, saying the hold back of current months be supposed to be provisional. It trimmed it’s predict for worldwide expansion this year only to some extent, to 4.3% from 4.4%, and sustained its estimation for vigorous Chinese expansion of 9.6% regardless of current signs of a hold back there.
Yet that comparatively gentle global viewpoint could speedily fall away from each other if politicians in the United States and Europe do not establish viewing more management in addressing their countries liability tribulations. No one can have enough money to have a world country where these imperative decisions are deferred because it’s really playing with fire, said Jose Vinals, director of the IMF’s monetary and capital markets subdivision.
We have now come into very unmistakably into a new segment of the (global) catastrophe, which is the opinionated period of the calamity. (Jose Vinals interview in Sao Paulo, where the updates to the IMFs World Economic Outlook and Global Financial Stability Report were published) In the United States, the supporting troubles include a battle over raising the authorized maximum amount on the nation’s liability. A first-ever US failure to pay would stir up markets, and Fitch Ratings said still a technical non-payment would put at risk the countries AAA rating. The IMF said the viewpoint for the US financial plan shortfall this year has better to some extent due to higher-than-expected proceeds. In a disconnect account, it estimate a shortfall of 9.9 per cent of GDP, improved than the shortfall of 10.8 per cent of GDP it foresee in April, but still in close proximity to significant highs.
Markets more and more on perimeter
The finance, which has endured its own political catastrophe due to the acknowledgment of its chief, Dominique Strauss-Kahn, on sexual physical attack accuse, said the global financial system has expand soil in spite of a hold back it deemed not comforting. It accredited the weak point to momentary commotions such as the Japan earthquake. Global development is supposed to reaccelerate for the period of the second half of the year, the report said. The finances predict for worldwide development next year lingered unaffected at 4.5 per cent. The IMF hoisted its expansion outlook for the euro region in 2011 to 2.0 per cent from 1.6 per cent. For 2012, the IMF saw development at 1.7 per cent, little altered from its previous 1.8 per cent.
Up till now Europe also pretences a few of the major jeopardy to the global financial system. If a list of the countries in the globe that have the principal grounding in re-establishing their community finances to a rational state of affairs in conditions of money owing levels is made, you come across four countries: Greece, Ireland, Japan and the United States. Greece has bordered more rapidly to default as euro zone bureaucrats differ on an intended second aid package for the obliged kingdom. With smacks and objections in the region of the country, following commotion has further to ambiguity, stoking doubts that the administration will not be capable to tauten its belt an adequate amount to lessen crippling shortfall. Doubts of infection in the euro zone have ambitious global stock markets inferior in current conference.
Forecasts for outsized up-and-coming marketplace hanged about constant or tripped. At the same time as Chinas GDP vision remained untouched, the IMF lessened its Brazil viewpoint to 4.1 per cent from 4.5 per cent. Those countries, along with Russia, India and South Africa, make up the rapidly-mounting BRICS, a grouping of up-and-coming financial system whose vigorous spreading out has outperformed that of industrial marketplaces in recent times.
Forceful trade and industry intensification and going up price increases have rooted up-and-coming financial system to constrict financial policy with elevated interest charge and to put to one side the necessities, still as a lot of developed countries maintain policy ultra-loose to attempt to enhance insipid expansion. The IMF notified that loads of up-and-coming marketplaces still need more contraction. In China, for instance, the far above the ground inflation charge means downbeat real interest rates. A number of up-and-coming marketplaces have been unenthusiastic to stiffen too far, apprehensive of earth-shaking development or magnetizing approximate speculation flows that could move forward their exchange rates even elevated (IMF 2011).
2011 Global Economic Outlook: The Euro Catastrophe, Exchange Pressure, and Resurgence
While the international financial system is without a doubt on the put back together and current statistics is hopeful, apprehensions predicament stay put over the likely worsening of the European liability catastrophe, the possible effects of U.S. counter-recurring actions (more than ever QE2), long-lasting money stress, and the weakness of the banking division in a number of highly developed states. At the same time as the Great Recession is falling down, in branch thanks to the instantaneous crisis-combating procedures, strategy creators are weakening to lecture to the structural modification and authoritarian transform essential to make sure that a replicate of the predicament is circumvent, and worldwide guiding principle harmonization is proving not enough to the chore. Carnegie formed or brought a renowned group of professionals to speak about these issues, these professionals included names such as Hans Timmer, Jörg Decressin, Philip Suttle, Desmond Lachman and Uri Dadush from World Bank, IMF, Institute of international finance, AEI (Finance American Enterprise Institute) and CE (Carnegie Endowment) respectively.
Crisis in Europe
Despite the fact that more than a few panellists decided that a number of type of liability reformation is to be expected in quite a lot of the side-line states, the panellists opposed on the subject of the collision on European banks and the euro.
- Money Owing Reformation: devoid of the capability to way out to deflation, it will be easier said than done to reignite augmentation at the same time as involving in huge degree economic consolidation. Debit lumber will go on to get higher, and in quite a lot of euro zone countries an arrears write-off is very probable, Lachman said. Dadush settled that some appearance of reformation is practically unavoidable for Greece and conceivably Ireland as well.
- European Banks: Banks from countries like France, UK and Germany embraces mainly the fringe of nation money owing, and Lachman forecasted a catastrophe waiting to happen at the later part of the year 2011 for the Euro banks set in motion by sovereign funds owing which they will be not able to payback. Dadush recommended a soft reformation—with long-standing deferment, minor interest tax, and potentially a biased assurance by a long-drawn-out European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF)—could keep away from this conclusion.
- Euros Termination? Lachman understood the euro is expected to be disentangled, at the same time as Dadush argued that Europeans can—and must—restrain the predicament by elevating the EFSFs size and mounting liquidity inoculations, consenting to instant for states in the outside edge to take on financial and structural modification. Suttle and Timmer decided the euro zone can live to tell the tale, but simply if countries take crucial act, such as growing fiscal incorporation and recuperating competitiveness.
- Germany: Dadush argued that Germans are very of two minds on the subject of the stepladder required to hold back the crisis, and felt the crisis may perhaps call for to get shoddier sooner than policy makers arrive at an agreement that extra across-the-board stepladder is required. Decressin pressed that, despite the fact that the state of affairs will linger undecided as interest spreads broaden in a fresh regular, marketplace undervalue Germany’s obligation to the European development.
E-bonds: Dadush portrayed the freshly anticipated e-bonds— euro zone bonds—as one nuclear alternative that states possibly will track if the catastrophe becomes deeper, other than noted that initiating them at this time would take the weight off transformation in the outside edge states. Some shape of autonomous money owing streamlining apparatus is required to enclose the expenses of the salvage and alleviate ethical vulnerability. Timmer added that prevailing over German antagonism to such bonds would be not easy, barely since they would have need of Germany to increase its prop up to European disturbed countries, but in addition for the reason that they would augment German borrowing expenses.
United States
Speakers presented changeable measurement of the current quantitative easing (QE2) and projected tax slash expansion in the United States, but they by and large approved that Washington requires taking steps to encourage demand.
- U.S. viewpoint: Lachman made available the majority unenthusiastic examination of the U.S. economy, symptomatic of the flimsy recuperation has little likelihood of becoming stronger due to a scrawny housing segment and elevated idleness. Decressin, in contrast, recommended that upgrading in current months will possibly show the way the United States to go one better than the IMFs mainly up to date augmentation guess.
- Tariff slash extension: Decressin, Suttle, Lachman, and Dadush decided that agreeing to the tariff slash to terminate would have damaged development, other than that Timmer said the slash is not embattled an adequate amount of to be competent. Suttle noted that such temporary incentive be required to be go with by obvious indication of medium-term financial transformation, such as that projected by the presidents assignment on tumbling the financial plan shortage.
- QE2: Prop up for the Feds QE2 expansion by Suttle, identified to the at hand market jostle offered as testimony of the directing standards achievement. Lachman and Dadush, then again, enquired its efficiency, noting that long-standing the U.S. interest charges have in point of fact risen. Further than that the strategies impact on the United States, Timmer and Dadush concerned that the liquidity inoculation could harm up-and-coming marketplace, which at the moment face positive reception heaviness and potentially unpredictable funds inflow.
Exchange Tensions
Decressin quarrelled that exchange positive reception in up-and-coming marketplace is dependable with their well-built, flexible augmentation and the more slow-moving development in highly developed countries, but noted significant disparities.
- Area Admiration:Decressin recommended that additional admiration should be taking place in Asia and not as much of in Latin America.
- Renminbi Admiration:It was pointed out by Lachman that China perils a do business conflict by not being pleased on the subject of at an occasion of far above the ground U.S. and European joblessness. Positive reception would be in Chinas favour, Dadush said, other than that it would probably injure countries that have huge job disproportion with China, such as the United States, for the reason that of elevated trade in worth.
- Conjugal Demand:At the same time as Suttle approved that China should consent to its exchange to value; he felt that Chinas household demand augmentation had by now made better the universal recuperation a lot. Timmer and Dadush approved that the worldwide meeting point should be a lesser amount of on exchange and more on sustaining elevated expansion in China.
Fiscal and Banking Reforms
Lets now discuss fiscal and banking restructuring in highly developed countries and their impacts on up-and-coming marketplace
- Transformation in highly developed Countries:On the economic frontage, strategy creators must arouse the financial system now at the same time as setting up transformation that will subordinate expenditure in the outlook, such as moving up the sequestration age. In banking, they have to endorse long-standing improvements, such as elevating resources ratios and changing from across-the-board to retail backing, at the same time as satisfying in short-range openings in resources. On the other hand such modification would noticeably weigh down the banking recuperation. Even as they would have been ready to lend a hand proceeding to the emergency they will simply make stronger the approaching alterations at the present, even if the guideline is not put into practice for quite a lot of years.
- Up-and-coming marketplace:Banks in highly developed countries are before now altering to reflect the lessons of the catastrophe. Banks are on familiar terms with the dangers connected with prime of life alteration—turning short-range money owing into long-standing mortgages—which can be standardized as the chief matter leading to the monetary calamity. However reformers are paying no attention to the threats in up-and-coming marketplace organizations, which are at the moment providing loans uncontrollably and in a hostile way. As a consequence, it can be foreseen that the subsequent monetary predicament possibly will well approach from up-and-coming markets, while highly developed countries holding-up deed produces unsteadiness for just beginning nations (Timmer et al. 2010).
Statement of the problem
Worldwide monetary predicament unfastened quite a lot of chances for Islamic Finance, and the Islamic finance Model, it has been argued, was the only solution to the continuing economic turmoil as it was unaffected by the sub-prime crisis in the mortgage industry (Sesric Reports 2008).
A lot of non-Muslims found their hide out with Islamic banking, for the reason that customers who were predisposed by the Western or conformist banking structure understood that Islamic banks were safe and sound, as it was flexible to international catastrophe as a consequence of inhabitant commerce principles in the Islamic banking (Kaplan 2008).
Given this situation of the affairs, this dissertation intends to investigate whether or not the Islamic Mortgage System is the only solution to the current credit crisis compared to Conventional Mortgage systems which triggered the recent credit crunch.
Research Questions
- Q1. What is the difference between an Islamic Mortgage system and Conventional Mortgage system?
- Q2. What are the most important structural reasons and costs of the recent credit crisis?
- Q3. What opportunities did the Islamic Mortgage system encounter over and above the conventional mortgage system from the credit crisis?
- Q4. What part does Islamic finance play in securing the mortgager against credit crisis?
Significance of the study
This study intends to compare the Islamic Mortgage system and the Conventional mortgage system and determine the best among them that is most effective in insulating against the credit crunch. Therefore, the study will help to throw light to the financial institutions and banks on how structural differences in their systems may lead to varying performance of the mortgages. Thus they will be able to choose the best system to use. It will also benefit the mortgager in giving them the relevant information on the best type of mortgage system they can borrow money from.
Literature Review
Economic overview
The world’s economies were faced by the global credit crisis which speeded up the international economic recession; this financial crisis brought confusion and fear in 2007 within the international financial markets resulting in mortgage market of United States to go burst (Hassan, 2010). The crisis took over $3,000 million of liquidity and bailout amount from some developed nations, to cave in a certain degree of the crisis intensity; however, the credit may have exposed the international economies to a long-term financial hold up (Wilson, 2009). Therefore, the need for a new financial structural design was necessary to reduce the rate and sternness of such an occurrence in future (Perry n.d).
Global financial crisis: five key stages 2007-2011
From leading to demote, the five phases of the most grave catastrophe to hit the international economy ever since the great depression can be found in above mentioned dates.
Phase 1 i.e. 9th August, 2007 began with the stoppage in the banking arrangement started when BNP Paribas, announced that it was seizing its activities in three hedge funds that focused in mortgage debt. This was the instance it became apparent that there were trillions of dollars value of dodgy imitative were rounds which were a lot less valued than the bankers had earlier thought.
No one knew how large the losses were or how big the revelation of each bank actually was, so trust vanished overnight and banks closed conduction business with each other.
It took about a year for the l crisis to come to a halt, but it did so on 15th September, 2008 when the investment bank was permitted to go bankrupt. Up till that point, it had been implicated that governments would step in always to bail out any bank that was facing serious problems; the US did so by finding a purchaser for the bank while the UK had to nationalize another bank.
When Lehman Brothers bankrupted, the idea that all banks were too tall to fall no longer remained there, with the conclusion that every bank was thought to be risky. Within a space of a month, the problem of a domino effect was surfacing through the financial system, forcing western governments to insert vast amounts of funds into their banks to stop them from collapsing. The banks were saved just at the right time, but it was a bit too late to rescue the global economy from entering into slide.
Credit line for the private sector was strangled off at the same time as did the confidence of consumers and businesses. All this happened just after a short period of high oil prices had made central banks agree on knowing that the priorities to keep the interest rates high as a barricade against inflation rather than to slash them in expectation of the financial crisis thinning out to the real economy.
2008-09 saw combined actions by the recently formed G20 group of major nations in an effort to stop recession shaping into a slump. Interest rates were brought down, fiscal packages of different sizes were announced, and electronic money was created. At G20 summit on 2nd April, 2009, world leaders resolved a $5tn (£3tn) fiscal expansion, an additional $1.1tn of resources to assist the IMF and other international institutions to increase jobs and growth, and for bank reformations. From that point on, the global economy took a turn, international assistance started to fall apart as individual countries carried out and stacked to their own agendas.
On 9th May, 2010 was the point at which the attention shifted from the private sector to the public sector By the moment the EU and IMF announced that they would assist and provide financial help to Greece, the problem did not remained of solvency of banks only but stretched out to the point of solvency of governments. Budget deficits had peaked, mainly because of lower tax receipts and non-discretionary spending, but also because of the fiscal packages announced 2008-09. Greece had problems as it recovered the dire state of its finances and had problems in collection of taxes, but other countries also became nervous about the extent of their finances. Austerity was the word, impacting policies and decisions worldwide. Private debt chaos turned into a country debt crisis when the rating agency, S&P, announced that America’s debt is not classed as a top-notch triple A. This could barely have come at a bad time, and not just because we witnessed the biggest sell-off at stock markets. Policymakers are faced with an ever slowing international economy and a chronic crisis in one of its integral parts, Europe.
In the current circumstances, it is difficult to be positive about how things will end out. Markets are bound to stay jittery, although it looks highly unlikely that American bond yields will go up as a result S&P announcement. Japan also lost its triple a ranking long ago and has debt well above 200% of its GDP and its bond yields remains very low. The cause for that is easy to understand that Japans prospects for growth remains poor. Same is the case with America, which is the reason why its bond yields will remain low despite being the largest economy in the world. The current scenario gives the Washington clear signals that Beijing subsequently, the S&P announcement was, however, significant. Growth rates of approximate of 10% would make them feel that they can tell the west how to execute plan to run economies. 5th August, 2011 will be always in eyes of the world (Elliott 2011).
Causes of the Crisis
The Housing Bubble
Housing bubble occurs when the value of real estate property increases rapidly and finally reaches an uncontrollable level. After the prices of housing have risen too high, there starts a process in which the prices start to decrease, a huge difference is created between the financial value of housing and its real GDP value and then the mortgage debt is higher than the actual value of property.
The meltdown began as the US housing bubble began in 2001. The bubble arrived at its peak in 2005. Such bubbles are usually discovered after a market correction. In the USA a market correction occurred in 2006. Alan Greenspan, then Federal Reserve Board Chairman, admitted in 2007 that the USA was facing a housing bubble and it was identified by 2006 (Bianco 2008).
Low Interest Rates
Low interest rates were one of the major causes of the housing bubble in USA. The interest rate was reduced to 1% by the Federal Reserve Board. The chairman of the Federal Reserve, Alan Greenspan acknowledged in 2007 that the housing bubble was caused by the extremely low interest rates.
Mortgage rates are determined in relation to Treasury bond returns for the next 10 years. These mortgage rates are influenced by the federal funds rates as well. There is a relationship acknowledged by the Federal Reserve between low interest rates and increasing values of housing. The high value of housing is, in one way, is beneficial for the economy but for a short period of time (Fed, International Finance Discussion Papers No. 841 House prices and Monetary policy, A cross country study, 2005).
The Housing Bubble burst
From 2004 to 2006, the Federal Reserve gradually increased the interest rate from 1% to 5.25%. This process of increasing the interest rates was slow and gradual because the Fed feared a downfall in the housing market which may have adversely affected the economy as a whole.
Some economists like Nouriel Roubini of New York University, issued warnings of a recession to hit the US by 2007 as by fall 2006 the sales and prices of the housing market were falling rapidly and an economic meltdown could be likely (Bianco 2008).
The Correction in the Housing Market
Many economists predicted a correction in the housing market as the values had reached the highest peaks so rapidly during the housing bubble. Some economists even predicted two-digit depreciation by the end of 2009 (Economy.com). Contrary to the belief that the housing prices never fall, economists like Robert Shiller argued, in his 2007 report presented to the Federal Reserve that a decline on housing prices was likely and that housing prices would fall as much as 50 %. This notion came to be true soon (Bianco 2008).
Subprime Lending
Subprime borrowing was majorly responsible for the increasing home ownership rates in the US. From 1994 to 2004, a ten year period, the home ownership percentage increased from 64% to 69.2% or almost 70% which marked the highest level of home ownership rate. The demand for housing has been increasing in the US. The increasing demand led to increasing housing prices and also consumption spending. In a decade, from 1996 to 2006, housing prices had increased by 124%. This increase in the values of houses encouraged many homeowners to refinance their houses at lower interest charges. They also took out previous mortgages for spending on consumption. This move led to the US household debt to 130% of the income.
As the housing bubble burst, the default rates on many mortgages especially subprime and other loans with high risks, increased rapidly. The default rates increased for Alt-A mortgages as well. These mortgages are categorized as between prime (low risk) and subprime (high risk) mortgages.
Mortgaged amount was around 600 bn dollars. This was in 2006 around 20% of the home loan market in the US. This was not entirely a game of borrowers. Lenders were equally involved in setting up the stage for a crisis in future. Lenders became confident to lend as they believed housing prices were to increase and everything will remain normal. Therefore, the lenders started to take more and more risk by easing the availability of credit to subprime borrowers. Wall Street helped the lenders in such ventures by transforming all the subprime and other mortgage loans into securities. These securities were sold by the lenders to big investment companies seeking high profits in future.
Difference between prime and subprime mortgage rates shrunk
As per a Federal Reserve study in the year 2007, the difference between prime and subprime mortgage rates had shrunk considerably from 2.8 percentage points in 2001 to 1.3 percentage points in 2007. The implication; risk premium for subprime loans reduced. However, under these circumstances, the outcome should have been completely the opposite considering the fall in loan characteristics between 2001 and 2006. This unusual decline led to a consequence where high risk borrowers started being preferred by lenders.
The New-Found Lender
It would be fair to blame the materialization of a novel kind of mortgage lender for igniting the mortgage crisis. Unlike the traditional banks, these lenders were given leverage from regulation. This is evident from the fall in the traditional banks hold over the mortgage market which dropped from approximately 60 percent to a mere 10 percent.
Incorporation of Negligent Mortgage Products and Lending Standards
The New Found Lender brought with him a new and rather confusing generation of subprime loans. Adjustable rate mortgages and stated income loans are just few of the offspring of this era. No Doc loans, Liar Loans are a few names given to the vastly famous Stated Income loan. This subprime loan incentivized the borrower by not having to provide documents to validate the stated income on the application for financing home purchases.
This era saw the rise of such loans in almost all areas of the country. As previously stated, these new loans went from unrecognized to customary. The San Diego County was a rich example of the dominance of these loans with eighty percent of all mortgages being adjustable rate. Moreover, with the increasing popularity of these high risk loan options, borrowers were offered various incentives. One of these incentives was the teaser rate. The teaser rate offered a minimal introductory rate to magnetize a large number of buyers. However, this rate would only be temporary and would increase in the following period to the extent of doubling the monthly payment.
Down-payment assistance programs were also born during this time. These programs, which were seller-funded, would allow the seller to give money to non profit organizations which then passes it on to the buyers. The Government Accountability Office (GAO) determined that “the default and foreclosure rates for these mortgages are much higher than what they are for the traditional ones”. Many sellers also magnified the prices of houses to recover their money. However, in 2006, the Internal Revenue Service put a hold to this practice by stating that DPA plans are not appropriate for non profit status.
A Moral Catastrophe
As many economists state and as the facts show, the carelessness of the mortgage standards was clearly due to a moral malfunction in the society. Every person in the chain was under a belief that he/she is passing down risk while accumulating profits.
Another Weak Link
Since they do not offer their personal money, Mortgage Brokers have no direct relation with the status of the loan. They receive monetary benefits in the shape of commissions for selling mortgage loans. As per a certain study, mortgage brokers were the foundation for sixty four percent of residential loans in the country. The bulk of the volume being Alt-A and subprime loans. They have been said to profit from this escalation but were lazy to ascertain if buyers would be able to repay the loans. This led to the disastrous outcome where banks and lenders were left as defaulters.
Mortgage underwriters are people responsible for determining the risk of lending to borrowers under certain considerations. The risks considered fall under 3 categories; Credit, Capacity and Collateral. As you might have heard that automation comes with its consequences, it applied to the underwriting process as well. The computerization of decision making in this process led to much faster decisions and much lesser documents. This new technique was considered as a more viable option than the manual underwriting process which would often take weeks before determining if the loan was to be granted. Unlike the old times, forty percent of subprime loans were granted by automated underwriting in the year 2007.
It is truly believed that due to the careless standards and the improvised shortcuts was the reason for approvals. Clearly, the case would have been much different under manual or less-automated processes.
Securitization
Securitization can be referred to as a structured finance process in which assets, receivables or financial instruments are acquired and offered as collateral for third-party investment as defined by Black’s Law Dictionary. It is because of this phenomenon that the investor’s inclination towards MBS and the propensity of rating agencies towards investment-grade ratings increases. Due to this, loans with high tendency to fall in the default category are granted.
The Ratings
For offering investment-grade ratings to securitization transactions holding subprime mortgages, credit rating agencies are now under strict inspection. The agencies claimed that the higher ratings were to denote the numerous independent mortgages held in the mortgage backed security. On the contrary, experts claim that this was due to a serious conflict of interests. The Government Accountability Office (GAO) determined that the default and foreclosure rates for these mortgages are much higher than what they are for the traditional ones.
A speech made my Mr. Greenspan states the problem was that people took that as a triple-A because ratings agencies said so. Yet when they tried to sell the products they ran into difficulties, which shook confidence. What we saw was a 180 degree swing from euphoria to fear and what has been learnt over the generations is that fear is a very formidable challenge.
According to statistics, during this period credit rating agencies were responsible for downgrading over $50 billion in debt obligations. However, a more staggering figure is also possible. Agencies such as Standard and Poors Corp, Moodys Investors Service Inc and Fitch Ratings are being targeted for the slow decline of ratings on securities based on loans to buyers with inadequate credit rating.
Are The Borrowers Wrong?
The conditions of that era convinced many subprime borrowers to resort to ARMS. However, even with easy credit, it was not affordable to many after the incentive period has passed. Once the bubble had burst, and housing market correction took place, the housing prices saw a sharp decline. Therefore, refinancing became virtually impossible. This is when the borrowers started becoming defaulters of their own loans while the interest rates soared above the sky. A few decided to walk out and call for a foreclosure of their residence.
The interesting part is where about 70 percent of all original loan applications were found to be containing fraudulent data about the borrowers. According to a study carried out by the company Base Point Analytics, fraudulent applications had five times the chances of going into default. The study also mentioned some methods of fraud carried out by the borrowers. Under automated underwriting, borrowers simply had to lie about their income or forge their documents to have the loan approved.
The Blame Game
The blame game started in March 2007 when at a Senate Banking Committee hearing the members of the committee threw the blame on the regulatory authorities. The members made a point never sought after before the hearing. As per the Chairman of the committee, it was the carelessness of the regulatory authorities that caused the extensive foreclosures. He termed it as the chronology to regulatory neglect. Our nation’s financial regulators were supposed to be the cops on the beat protecting hardworking Americans from unscrupulous financial actors. Yet they were spectators for far too long. On the contrary, the argument presented by the authorities denoted an immense lack of authority over the crisis itself. They claimed they had little power to do anything because many mortgage lenders did not come under the supervision of the Fed. The legislators thought otherwise and claimed that Fed had every right to stop those lenders and improvise the regulations.
Is Fed To Blame?
The New York Times added to the controversy by publishing an article written by a Fed Governor, Edmund L. Andrews. Edmund emphasized that he had been warning the Fed of the subprime crisis since the year 2000. He also stated that Fed remained silent while the crisis and the new-found lenders grew when they had the power to stop them. He wrote that his expression of fear to the then Fed Chairman, Alan Greenspan was rejected without thought.
The controversy took a severe turn when in 2004, a group of people from California, met Greenspan and conveyed their fear of unscrupulous lending by two lenders of the Greenlining Institute. The lenders were namely John C. Gamboa and Robert L. Gnaizda. Even after severe pressure from leaders of a housing advocacy in California, Greenspan was unable to deal with the situation as expected.
When asked, Greenspan defended himself by stating that the Fed was not adequately equipped to deal with deceiving lenders. He added that Fed was not to be blamed for the creation of the housing bubble (Andrews 2007).
The Government Is Also Responsible
Economists, over the years, have also claimed that the housing bubble was a result of government policies such as the Community Reinvestment act. They state that these policies have forced banks to lend to borrowers with poor credit ratings.
Economists argue that alterations to the reserve requirements of banks and sweep accounts led to greater liquidity for the banks which in return allowed them to offer more credit. The reduction in the Federal Reserve Funds Rate led to a radical decline in ARM rates. This caused the demand to shoot and hence creating the infamous housing bubble.
Crisis 2011
2011 is backside to the actuality. The international monetary catastrophe and depression left in the rear un-payable personal and community arrears and an unreconstructed political arrangement. It was bound to hit back in 2011. Not only has that but in addition the Greenspan credit gurgled with Chinese description, the out of order global financial structure, a restricted worldwide lubricate supply that damages underneath the demands forced on it by politicians selling and importing it on credit based transactions of money supply and that can only be controlled by the communal ability of the oligarchs economists to discover new-fangled point of view to give good reason for it more speedily than proceedings pull them down. The broken, repellent age first rounds in 2006 give the thought of being like this:
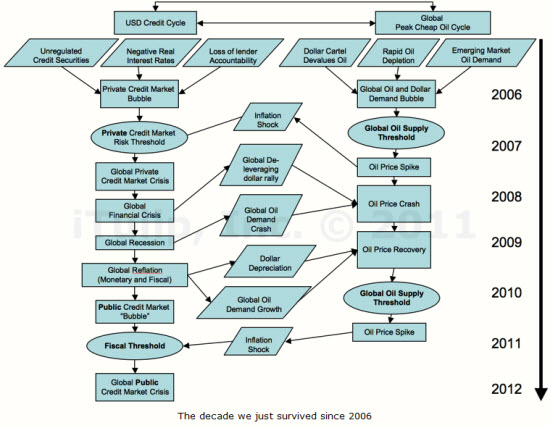
Accommodations costs are plummeting once more, even subsequent to billions in administration financial support were exhausted to support them. Fifteen months following the authorized end of the depression, the midpoint period of being without a job a gauge of how extended the middle-of-the-road of the unemployed have been out of employment remains at just about twice the point it was at 15 months subsequent to the 1983 depression.
GDP escalation below a 3% twelve-monthly rate, at the same time as well again than zero, is merely too sluggish to seal the production crack fashioned by the Housing Bust Recession earlier than a new depression reaches our destination to broaden it once more. The US has undergone a credit sequence depression each 10 years on regular from the time when World War II ended. The commencement of the Pinnacle of Not Expensive Oil Cycle in the order of 2005 will make depressions more recurrent, and it is considered another is due previous to the end of 2012.
What is required is more development, but no one gives the impression as to be acquainted with that how the financial system can develop any more rapidly devoid of a new boil to make better development the way the housing bubble and war-spending liberated the financial system in the near the beginning of 2000s. With interest tariff at zero, the financial system is short of a tailwind of declining interest tariffs as it had in the early on 1980s. A play again of the 1960s tax slash bang is highly unlikely, given the nations assets, as are additional New Deal-style considerations, or a high-quality sell overseas and housing boom like the one that drag the financial system out of a whirlpool after World War II.
In actual fact, each deception that produced the 4% in addition twelve-monthly GDP escalation that the US requires to arrive at to abridge productivity hole and run away speed is not feasible, put aside the unthinkable: an inflationary bang as in 1975 until 1980 that produced an run of the mill 5.6% twelve-monthly real escalation (Janszen 2011).
The Mortgage industry
Mortgage lenders provide finance or loans to people to buy a house or a property. When people obtain loans to buy a house or a property they pledge their property to the financial institution or lender. This means that if the borrower defaults on repaying, the lender will have the right to seize the property and put it up for sale to some other buyer. In other words the lender will have a claim on the house. The mortgage industry has grown rapidly over a few decades. In the US the mortgage industry consists of thousands of mortgage companies and millions of borrowers. The entirety possessions handled throughout these quantities at present exceeds US$5 billion and is continuing and on the increase by 12–15% per annum (Mortgage n.d).
The US mortgage industry consists of around 16000 companies. The total annual revenue of this industry crosses the $60 billion mark. The biggest mortgage companies are JP Morgan, Citigroup, Bank of America and Wells Fargo. The biggest 50 companies in the industry generate around 70% of the total revenues of the industry (Mortgage Banking n.d).
The demand in the mortgage industry is determined by the income of the consumers and the demographics of different regions within the country. The mortgage companies develop and offer competitive products for different kinds of borrowers to enhance their profitability.
The effect of crisis on the Mortgage industry
A credit crisis influences the mortgage borrowers significantly. When the profit margins of the lending institutions tense up and uncertainty arises in the market on a big scale the loans offered by the lenders to mortgage borrowers reduce and so does the variety of products created and offered by the lenders. Lenders fear that borrowers will not repay the loans and so they offer their financial services to much selected borrowers, those with high credit scores.
The credit crisis also influences the businesses directly. High rate of inflation and is one of the most prominent characteristics of a credit crisis and most businesses make their day-to-day transactions on credit. For the smallest as well as the biggest businesses, credit has become the life blood which makes it possible for commercial activity to take place and aids in running the economy smoothly. During a credit crisis, banks and other financial institutions are reluctant to give loans and thus tighten up their lending policies and charge much higher interest rates. Inflation rates, then start to rise as businesses pass on the increased costs to customers. Layoffs and job losses are other major results of a credit crisis. Soaring inflation rates increase the expenditures of the consumers in the economy and layoffs reduce the income as well as the confidence of the consumers. Mortgage borrowers are consumers in the economy who usually obtain mortgage loans for financing their dwellings. The credit crisis affects the borrowers of mortgage loans in many ways in addition to those mentioned above. When lenders tighten up their lending policies and offer money to selected borrowers only the variety of mortgage products previously available becomes small. Borrowers with smaller amounts to deposit become the losers in the market as if becomes impossible for them to obtain a loan on easy terms.
As mentioned earlier, subprime lending increased substantially in the market which was probably the most major cause of the crisis. It becomes impossible for the mortgage borrowers in the subprime market due to either poor credit history or low or irregular income. Yet an added motive for the drop in the real estate values was the growing number of houses obtainable for transaction. As borrowers start to default, many are forced to leave their dwellings as the lenders take back the properties and put them up for resale. As supply of houses gradually increases as compared to the demand, the housing prices fall significantly.
Following the fall in the prices, many borrowers find themselves paying loan repayment amounts more than the actual value of their property. These borrowers add to the list of those who have already stopped repaying to their lenders. The lenders played an active part in creating this turmoil in the housing market. The irresponsibility with which the lenders carried out their lending activities became quite apparent when the bubble burst and crisis set in (Credit Crunch 2009). The lending institutions, banks and other financial institutions faced the threat of bankruptcy which showed signs for government intervention in the form of bailout plans. This threat of bankruptcy further helped lenders tighten up their lending policies and so credit became even scarcer (Larkin n.d).
Not only the mortgage financing but other forms of financing such as car financing also declined to lack of consumer confidence and strict lending policies (Credit Crunch n.d).
Closed vs. Open Mortgages
Open and closed mortgages are the two types of mortgages which offer different benefits and different costs to the borrowers. The major disparity amid the two kinds is the liberty of buying-off the mortgage credit or the fines for prior disbursement.
Open mortgages can be paid back anytime. The borrowed amount can be repaid without any penalties. This kind of mortgage is ideal for people who prefer flexibility in the payment schedule and receive income from commissions which are irregular. The interest rates charged on open mortgages can either be fixed or variable. The interest rates charged on open mortgages are higher than those charged on closed mortgages as the payments are inconsistent in the open mortgages. These mortgages can be easily refinanced before maturity by the borrower (Mortgages n.d).
Closed mortgages have a pre determined and fixed term for the repayment of the loan by the borrower. The borrowers cannot make the payment before the due time. In case of prepayments the lender charges the borrower a penalty fee. People with a regular salary opt for such mortgages usually and those with a settled and stable families (Open / Closed Mortgages 2009). The interest rates charged on closed mortgages are lower than those charged on open mortgages. These mortgages cannot be refinanced before maturity (Help Globe 2008).
Islamic Finance
Islamic finance is based on the laws or principles laid out by Islam which is also known as Shariah. The foundations of Shariah are the Holy Quran and the Sunnah (Sayings and traditions of Prophet Muhammad PBUH).
Islam prohibits interest (or Riba). Transactions based on interest are totally void and prohibited. Contrary to the modern or conventional banking the prohibition of interest, as commanded by Islam, has led many Muslim scholars and economists to develop methods of interest free financing.
Islamic financial institutions, as compared to the conventional banks, are young and in the process of growth. Islamic financing started in the 1960s in the Middle East. Today, many Islamic financial institutions have been set up all around the globe including the UK, USA and China. Countries like Pakistan, Saudi Arabia and Malaysia have also enthusiastically set up platforms and regulations to promote Islamic financing. The recent credit crunch has led many people, Muslims and non-Muslims, trust and show confidence in Islamic financing as it offers lesser complications, easy conditions and above all, freedom from interest and all the other problems which come along with it.
The main principles of Islamic financing are:
- Prohibition of Interest. Interest cannot be charged or paid in any transaction.
- The capital or finance must only be provided to the businesses or individuals who are taking the money for ethical and socially beneficial purpose. For example, Islamic banks cannot provide finance to businesses which manufacture or sell prohibited items such as alcohol or illegal drugs or pornography and the like. The effect on the entire society is more valued than money making. Ethics in financing derive from the sacred scripture The Quran and the Sunna (traditions of Prophet Muhammad PBUH).
- Speculation is prohibited by Islam. Gambling and other games of chance are prohibited as well. Any transaction involving speculation of any kind is also illegal and unethical. Finance cannot be provided for any speculative commercial activity which may lead to devastating results for the society and the economy as a whole.
- Gharar is also prohibited. The term Gharar stands for the uncertainty about the subject-matter and the terms and conditions of the contracts. According to the principle laid out by Islam, people cannot sell anything they do not own. (Abdul Ghafoor, Islamic Banking and Finance, another Approach)
Islamic financial institutions generate their income through sharing of profits from investments and the fee charged to the customers for the provision of services. If the lending institution demands a lawful profit under the Shariah, it should participate in sharing the risk as well, along with the borrower. If the lender is not sharing the risk with the borrower, then the lender does not retain the right to any profit or gain in return over the amount loaned to the borrower. In such a case, the amount received over the amount loaned will be categorized as interest and declared illegal (Islamic Economics 2006).
Islamic financial institutions offer two kinds of services. One set of services include safe deposits, fund transfers, trade finance, and sale of property, purchase and management of investments (IBB n.d). These services charged a fixed fee (Islamic Banks 2008). The second set of services includes transactions which involve the sharing of profit and loss, and partnerships in which the lender and the borrower become partners of the assets bought (Islamic financial practices 2011).
Islamic Banking: Steady in Shaky Times
As large Western monetary institutions have gone down or slumped one by one in the recent financial crisis, another financial sector is achieving fresh confidence i.e. Islamic banking. Advocates of the prehistoric practice, which looks to Islamic law for direction and forbids interest and trading in a state of debt, have been encouraging Islamic funding as a remedy for the International financial breakdown. A lot of voices are being heard from different countries that the worldwide crisis will encourage more countries to use Islamic banking in operating their economies. Trends in U.S. are also moulding as experts have been involved in learning the model of Islamic banking.
However, Islamic banking industry still have to counter challenges such as the fall in real estate and stock prices, experts says that the system has incorporated protection from the kind of escapee fall down that has affected so many institutions. Derivatives which are an agreement between any two concerned associates that specify certain conditions in specific the resulting values of the underlying variables and dates are considered to be one of the major reasons for the downfall or loss of banking and speculation institutes. Hence derivatives are banned, as well as unwarranted risk-taking. The beauty of the system and the rationale it can be used as a substitute for the present market is that you only pledge what you have and is your own. Islamic banks are not sheltered if the economy goes downwards but it can endure because of its built-in systems. The idea of Islamic banking is scripture that equates that gathering of interest is a kind of usury, which is barred in Islam. In today’s world, that interprets into an approach toward money that is diverse from that institute in the West.
Another unique point of Islamic banking is in the world, bankers crafting investment instruments have to please only state regulators. In Islamic banking, there is a further group to satisfy — religious regulators. Finance lawyers toil personally with Islamic finance scholars, who revise and re-evaluate a product before giving any ruling, on its observance with Sharia law.
An Islamic banker explains customers who are funding as similar to partners – their capital is invested, and they divide the profits or, tentatively, even the losses that takes place. In interviews, not a single depositors case could be remembered who lost his deposit or sum. This demonstrates that banks put such finances only in low-risk investments. Instead of lending money to a property purchaser and getting interest on it, an Islamic bank purchases the property and then leases it to the customer for the term of the loan. The customer gives a set amount every month, and then at the conclusion gets the rights for full ownership. The payments are organized in a manner which includes the cost of the asset, but a predetermined profit for the bank.
It can be a little harder to get a loan as compared to a conventional bank.
Islamic banking has developed/grown by about 15 % annually since its modern commencement in the 1970s, injected by the Middle East oil boom of the 70s. Islamic finance now stands for about 1 percent of the international market. It is thought be at 12 % of the international market by the year 2025, but now facing this financial turmoil, It is thought to be there faster.
Progress in Islamic banking started up even prior the present financial crisis, mainly because of good net worth client demand for reliable, religiously suitable investments and a recent bang in new and creative financial instruments. Islamic banks have now started contributing credit card services in which the absolute outstanding quantity ought to be remunerated at a particular month’s conclusion. They have formulated a type of commercial instrument known as sukuk, which makes a determined return that is called a profit, not interest. It is attached to a particular asset and expresses ownership of it. A sukuk might be released by a government or an organization that is constructing a building or a flyover, for example. Work conducted in Islamic banking by the King & amp; Spalding law firm has grown-up around 40-fold in the passing four years, according to Jawad Ali, a Dubai-based partner at the company. The company has around 35 advocates “who are working constantly in structuring Sharia-obedient investment and financing,” he said. Islamic finance first developed attraction in the United States in the late half of the 1990s.
The Dow Jones Islamic Directory was completed in 1999, and the Dow Jones Islamic Finance, which places finances in Sharia-compliant corporations, the succeeding year. But attraction waved off after some Islamic banks were blamed of financing terrorism in a lawsuit filed by one of the victim’s family of the 9/11, and a lot of Persian Gulf money went away from the United States to Europe. In 2004, Saxony-Anhalt in Germany issued a 100 million-euro independent Islamic bond. That particular year, the first of Islamic bank was founded in Britain, which encompasses six financial institutions. At the same time as the most important Islamic banks are in the Gulf — Dubai Islamic Bank, Saudi Arabia’s al-Rajhi Bank and Kuwait Finance House — Malaysia and London is fitting as full-size focal point of Islamic banking as well. Islamic institutions are not untouchable to problems dealt by other banks, such as dishonesty charges and ghastly investments. Disparity of explanation between Sharia scholars about what is permitted and what isn’t also generates disorder. The sukuk market, which multiplied every year since 2004, increased to a sum of about $90 billion in bonds issued, decreased to 50 percent this year after a Bahrain-based group of Islamic. Scholars pronounced that largely the bonds were not in line with the Sharia law (Hamdan 2007).
Islamic Banking Vs Conventional Banking
The main dissimilarity amid Islamic and conventional banking is so as to Islamic education says that cash itself has no inherent worth, and forbids populace from earnings by giving somebody the loan of it, devoid of compliant a level of risk – in other words, interest (also called Riba) cannot be charged. To make cash from money is forbidden–affluence can only be made in the course of lawful deal and asset. Any increase connecting to this dealing is communal amid the person providing the assets and the individual providing the know-how. At Islamic Bank of Britain, all profits are made in the course of Sharia obedient trade and speculation actions. We then contribute to the proceeds with our clientele at an already agreed upon rate. In order to contribute to proceeds one has to grasp one of our investments or speculation financial records. There are two main differences amid Islamic Banking and Conventional Banking:
- Conventional banking put into practice is troubled with abolition of threat while Islamic banks put up with the possibility when engage in any business.
- When Conventional banks engage in business with customer they do not take the legal responsibility only obtain the advantage from customer in shape of attention while Islamic banks stand all the legal responsibility when occupy in business with customer. In receipt of out any advantage with no manner its legal responsibility is affirmed Haraam in Islam.
While the fundamentals of what the commerce is are the similar, the word refers to working the commerce surrounded by Islamic law. The major thing that a belonging this commerce beneath that rule is that Islam forbids the charging of interest. Positively a difficulty in modern banking!
On the other hand, what is well thought-out to be interest has dissimilar descriptions by different Islamic academic. A number of them articulate it can only be considered on gold and silver, except amortization of the same heaviness as you took on loan (the similar heaviness of paper money for instance), is not interest. Like in all spiritual things, there would appear to be several disagreements and dissimilarities among followers that might appear bizarre to foreigners. So on the whole, contemporary Islamic banking might take many outward appearances, every one of which struggled to stick on to its understanding of Islamic law.
Research Methodology
Introduction
The chapter focuses on how research will be designed and structured. It outlines the approach of the research design and also gives details on how the data will be collected, analysed and presented.
What is Research?
Research can be distinct as the look for for information, or as any methodical examination, to set up narrative evidence, get to the bottom of new or existing problems, establish innovative information, or build up new hypothesis, more often than not using a systematic process. The most important reason for essential exploration (as opposite to practical) is finding out, understanding, and the expansion of methods and schemes for the progression of human beings awareness on a wide array of technical subjects of our world and the creation.
The Research Methodology
Stepladder of the technical means is fashioned like an hourglass – preliminary from wide-ranging enquiry, lessening down to focal point on one detailed feature, and scheming investigation anywhere we can scrutinize and analyze this characteristic. In the end, a conclusion can be made and comprehensive to the real world.
Devising an Investigative Problem
Researchers put in order their investigation by putting together and defining an exploratory trouble (Methodology 2008). This lends a hand to them to spotlight the research procedure so that they can illustrate wrapping up reflecting the actual world in the most excellent probable way (Research 2011).
Positivism
Positivism is a truth-seeking scheme first developed by Auguste Comte (1798-1857). This scheme upholds that information is on the subject of explanation more willingly than inquiring. Positivists are familiar with no more than positive particulars and visible proceedings – those effects that can be witnessed, calculated and be counted as particulars (BIS 2011).
Phenomenology
Started on by Edmund Husserl (1859 – 1938), phenomenology is a very dissimilar way of presenting the world in contrast to positivism (Farber 1940). Phenomenologist is anxious with what things signify, more willingly than with recognizing and gauging phenomenon. They are for the most part paying attention in the thought that human knowledge is a precious starting place of information, as contrasting to the thought that true investigation or detection lies in merely gauging the existence of corporeal phenomenon (phenomenological worldviews 2007).
Deductive vs. Inductive Reasoning
Inductive and deductive reasoning are two techniques of reason used to reach at a winding up supported on information understood to be factual. Both are used in investigative study to set up hypothesis.
Deductive way of thinking arrives at a precise ending supported by sweeping statements. Inductive way of thinking on the other hand, takes proceedings and makes sweeping statements.
Deductive reasoning is a way of thinking that engages a pecking order of declarations or facts. Opening with a restricted numeral of straightforward declarations or suppositions, more multifaceted statements can be developed from the more crucial ones. For case in point, one would have almost certainly considered deductive geometry in mathematics; in it the beginning is with a few main beliefs and attestation of a variety of proposals by means of those main beliefs. To establish more convoluted proposition, one might use propositions that have by now established in addition to the novel main beliefs. In additional prescribed reason terms deductive reasoning is a way of thinking from affirmed location to conclusions officially or unavoidably disguised by such premises.
Inductive reasoning is fundamentally the conflicting of deductive reasoning. It engages demanding to generate all-purpose main beliefs by preliminary with many exact instances. For illustration, in inductive geometry you may calculate the interior angles of a collection of aimlessly drained triangles. As soon as one comes across the sum of all the angles is 180°, it becomes easier to come up with a comprehensive assertion of a triangle. Putting frontward all these take part particulars make available proof in arrange to help hold up your all-purpose declaration about the interior angles.
This is the type of way of thinking used if you have slowly but surely put together an understanding of how things work. Instead of beginning with rules and main beliefs and making inferences, most people bring together applicable knowledge and attempt to put up main beliefs from it.
Once more the difference among the two kinds of reasoning is not for all time prominent. In mathematics it is significant to be acquainted with which type of official scheme you are using and to fasten to it. Inductive evidence is not allowable in a deductive system.
Research method
The study will use descriptive design, analytical method and comparative (normative) approach; these are preferred because researcher will be able to analyse a wide range of content on the Islamic mortgage system and differentiate it with conventional mortgage system (Aalto 2010).
Data description and collection methods
The data for this study will primarily be collected through a survey in form of reading the existing material concerning Islamic Mortgage System and Conventional Mortgage System during and after the current credit crisis.
Data Assessment
The study will analyse the data collected using normative comparison. This is because the aim of this research is to identify, explain and improve on the current situation of affairs or to develop the same items in future and also to show the best amongst the options available.
Presentation of Findings
Autonomous Susceptibilities and Corruption Dangers
Autonomous balance sheets stay on to be brittle in various numbers of highly developed financial systems in spite of the steps taken with respect to monetary consolidation. The need of adequate prop up from the political side for the medium-time economic modification and growth-ornamental improvement deteriorates financial support stress for monarchism between softer expansion viewpoints.
These strains add to the danger that the money owing dynamics of susceptible monarchs will slither addicted to a twisting of worsening in the nonattendance of a rational strategy structure and sufficient backstops to put off the increase of contamination. The spread out of autonomous perils to the depository division has put financial support damages on a lot of banks in force in the euro region and dejected their marketplace capitalization. Examination enumerates the considerable blow that the spread outs from high- extended euro region monarchs have had on the European banking arrangements and that help give explanation of the in progress stage of marketplace pressure.
Nearly after a four year period of monetary disaster, community balance sheets have now been lumbered with arduous money owing loads and brusquely elevated financial support requirements. Inferior tax proceeds, sluggish augmentation forecast, and across-the-board prop up for confined to bed monetary organizations have focused on communal funds into unstable region. In a lot of cases, these tests have been additional to an inheritance of economic thoughtlessness, as a number of governments survived further than their resources for the duration of more benevolent periods. Strategy makers in numerous highly developed financial systems have commenced to lecture to these challenges by reducing the monetary posture and putting down multi-year tactics for debit lessening. Without a doubt, as portrayed in the IMF’s September 2011 Monetary Check, development has been considerable in only some instances, particularly in fractions of the European Union.
In this scenario, Islamic banks remain unaltered by the subordinately most important credit crisis; to a certain extent a lot of non-Muslims are moving towards Islamic banking as clientele haunted by commotion in the Western banking scheme sensing Islamic banks as a safe and sound retreat for the reason that these are resistant alongside such crisis due to intrinsic business principles inside Islamic banking.
Discussion
Worldwide Monetary Disaster 2008 Versus 2011: Is the past about to Replicate?
It was fewer than three years in the past when the worldwide monetary arrangement underwent a just about deadly stroke, and the global financial system has been deceitful in the ICU from that time. In spite of the affirmations by experts and policymakers that the unparalleled stages of communal money owing sustained from the time has saved the worldwide financial system, there are plentiful symbols that the warning signs of 2008 are recurring with a retribution.
Accommodation cost in the U.S., is the most important factor at the border of the breakdown of the CDO and monetized disillusioned mortgages that unbalanced the whole thing in 2008, are once more sliding. In spite of administration programs meant at shifting of personal debt to the communal division and altering long-standing book-keeping principles so that valueless scrap can be discreet as valuable possessions on bank balance sheets, credit marketplaces linger on being feeble. Even though the past does not accurately repeat itself, if often beats around the past and what is happening nowadays has a sore so far recurring quality to it.
Now, here are two major dissimilarities from 2008. Joblessness tariffs in all the most important highly developed financial systems are far superior than was the casing in 2008. Additionally, the height of community money owing has been long-drawn-out by jumps and limits. Altogether, this means that the worldwide financial system has a great deal less autonomy obtainable for gripping prospect trade and industry and worldwide jolts such as a most important point in oil value, systemic have an account fall down or, as is more and more probable, autonomous debt failure to pay. If, for instance, Greece were having a failure to pay on its debts in the close by prospect, that would impulse an alarm inside the worldwide financial system that not yet the craftiest central banker with the major printing press could put off from steamrolling over what is absent of worldwide financial constancy (Filger 2008).
Islamic Economics: A Probable Explanation to a Fragmenting Financial System
Islamic banks observe stricter rules and need that their borrowers provide more guarantees and have greater income. The payments are organized in a manner which includes the cost of the asset, but a predetermined profit for the bank. The financial crisis began has now reached a very severe phase. It is expected that this can be controlled to a minutely little number of organizations that very soon completed mistaken commerce conclusion and are not there to any further extent. While it began with a dilemma which was subprime mortgages, the whole banking industry is facing the problem now and this has been the most terrible crisis ever since the Great Depression. The difficulty has been pointed towards by the FED that is of the unmanageable credit situation. Throughout the credit boom, financial establishments along with normal masses in America acquired a lot of debt. Amid 2002 and 2006 respectively, the domestic debt nurtured at a rate elevated more than the financial augmentation itself. Credit taken by financial institutions also went up immensely. The difficulty is that now many of those are unable to pay back the money they took as loans, a trouble that is gone further into a slump by the fall down in housing prices.
The shock of liability determined finances is not new-fangled; it has had its split of olden times preliminary from the Great Depression to the Asian credit/monetary catastrophe during the 1990s. No one at present neither the economists, nor the policymakers have any trouble-free answers. Even the decrease in interest rates and writing incentive checks to people can assist; it does not answer the question. During such point, states usually test with answers or solutions with a degree of success. Subsequent to the collision of 1929 the President Roosevelt did liberate the novel contract program as a possible response to the trouble at that exacting phase.
This problem is made difficult by new financial instruments that are created by Wall Street and disbursed. They do not make the life easier for the states and their executives to know the upcoming risks is just upon arrival and become part of spreading impact of the crisis. Very little percentages of sorting out of any financial crises are known in modern times that are met and put an end to without any government interventions. The conclusion by the experts suggests that everyone will be required which is complex to achieve. The FED has made available credit facilities to pugnacious organizations but only on short-range. It has and in past lower the interest rates, which in turn lowers the borrowing cost through the economy and encourages investments. But the risk lingers that the difficulty will broaden from Wall Street to every town in the US, as credit stiffens for end users and business. Already, automakers in United States have been made to stiffen the conditionings on their leasing. As stated by an economics professor Tyler Cowen, “there has been plenty of talk about predatory lending, but predatory borrowing may have been the bigger problem” (Filger 2008).
As vast financial institutions are falling and wrapping up, another financial sector is gathering new wave of believe and confidence, that is Islamic banking. It is somewhat surprising when the crisis in the States persists; an alternative in shape of Islamic banking comes across, with many opportunities rising for this kind of model from the US market. The present credit tightening provides the Islamic finance industry an apt opportunity for expansion and gain even markets of non-Muslim investors.
Originally it drew interest and attraction in the US during the 1990s. In 1999 Islamic index known as Dow Jones Islamic Index was created and in the year 2000 the index commenced. Though it has still a lot to prove and there are many who were still a little sceptical about it.
Still, the Islamic Finance industry has entered the West just at the right time when the US mortgage was going down and the holdings of billions were tied to home loans and a net of unorganized structure. Commercial banks suffered a lot of losses throughout the globe but in contrast the Islamic model remained untouched. They have a lot of attraction for the individuals and groups. This whole financial crisis has given Islamic banking a wonderful opportunity to play its role in over-passing the vacuum created by the money owing.
Investors who had been troubled by the credit crisis are now can now relax due to strict rules and policies based on Islamic law, which strictly bans some of the methodologies that were really the reason for the mortgage crisis. Islamic finance methods are fiscally stricter with direct input by investors in a path that does not have assets placed in vehicle of balance sheets.
This model of banking is based on Shariah which are Islamic Laws. For the products, they have to be strictly in accordance to the Islamic law; they should be free of gearing and speculation. Islamic banking has specified certain rules where it prohibits any banker or investor to be involved in any sort of interest earning practices, speculations in gambling and or pornography in anyway and it also demands that any proceeds should only be earned from religiously and ethically accepted speculations.
The augmentation of the Islamic possessions is rough and ready to be around 10 to 15 percent every twelve months. Companies from outside Middle East, such as Middle and East Asia are showing its interest in Islamic Banking and its popularity seems to continue growing. The main reason for its popularity is that it is less volatile for example Islamic bonds. Islamic law disbars interest and necessitates transactions to be connected to assets, thus deterring the complexities present in conventional banking.
The Islamic finance is seen to be a remedy, as its strict laws confer to the laws laid in Shariah. Although Islamic banking is an exercise that began in very ancient times, financial experts believe that the strict governing rules and strategy of Islamic finance make it less unstable as compared to conventional banking systems and will convince many banking systems to implement these rules in the future.
What constitutes Islamic banking as steady than the conventional banking system is that is has protection that is built-in from flaws that led to the collapse of so many financial institutions worldwide. For example, the use of banking instruments such as derivatives, which are thought to be behind the collapse of banking of big names of financial industry, is not allowed, along with big risk taking.
One of the major reasons for the present crisis of financial industry is for the reason that of collateral debt commitments. If governance cuts and distributes the mortgage, it makes the money owing multiple times by making a lot more investors a part of it. This creates an even bigger problem, since if the client defaults, there will be more risk associated with credit in contrast if there were limited investors involved.
Like many of the good features of Islamic banking discussed earlier, another one is that the alternative for the current monetary market is that only pledges what is owed which means there is no other option available. In Islamic banking, money cannot be traded and cannot be treated as product. It is just a medium of exchange each item that is to be financed must be based as asset. Letting somebody borrow the capital should not have the motive of making money at the rear. Any kind of funds need to move ahead and capitalize, for this purpose the need to be speculated. But before any financial product and or service is made available to the public for investment purposes it has to be approved the Shariah board of experts. Nowadays monetary legal representatives labour in ligament with Islamic economics researcher, who reconsiders the item for consumption and services monetary legal representatives work intimately with Islamic economics researchers, analyzing and re-examining the merchandise earlier than questioning a fatwa.
Conclusion & Recommendations
Challenges to Islamic Finance
Growth of Islamic finance has managed to attract millions of people from around the globe. The fiscal world has not merely documented Islamic investment means other than is also enthusiastic to investigate and build up the business. A lot of persons and commerce are at the moment bearing in mind Islamic economics as feasible alternative to accomplish their monetary requirements. With far above the ground augmentation speed and speedy development in a small episode of time, the Islamic economics business faces definite confronts.
A confront encountered by the business is the trouble-free ease of use of information to the possible clientele. Lack of consciousness can be accountable for disintegrating down a complete commerce framework. The information and estimation of the community is for the most part significant for any trade. In the same way, the Islamic monetary organizations could do with to build up plans and programs to lift up responsiveness in the middle of the individuals.
An additional most important confront is the differentiation sandwiched between the estimations of researchers. As talked about prior, Islamic monetary organizations have to make sure that the economics made available have got to be for principled and communally advantageous rationales. This concept incites the natural world of dissimilar dealings and deals. Researchers have been at variance over a number of dealings. If a set of scholars agree to a business to be officially permitted, an additional set of scholars may diverge with the previous (Khalaf, 2007).
Director and researchers are diminutive in supply when it comes to the Islamic monetary organizations. As managers are not compliant in the discipline of Islamic financing, there takes place convinced trouble connected to set of laws and process (Karbhari and Shahin, 2004). This difficulty accounts for the little set of connections of Islamic monetary institutions as well.
Scarcity of accomplished managers and practitioners of Islamic economics is one of the mainly most important challenges faced by the business (Bokhari, 2007). The expansion speed and development cannot be continued in anticipation but for a platform is established for schooling in Islamic economics for youthful alumni and consciousness raised amongst the communal to augment the command for the industries contributions.
Approximately above 250 Islamic monetary organizations are functioning all over the globe. From the east to the west, Islamic financial institutions have managed quite successfully to establish themselves in many countries including the USA and China which are two of the biggest economies in the world today.
There remains the element of uncertainty in the accounting standards used by the Islamic financial institutions. To name a few examples, the bases used for accounting, valuation and profit realization are some of the issues which need to be discussed and developed by the authorities (Hesse, Jobst & Sole 2008).
Islamic banks are still to have similar standards of credit analysis (Problems of Islamic Banking 2001). All the Islamic banks must have a similar standard for credit analysis to help in the operations of the Islamic banks such as monitoring of investments and valuation of projects (Khaleej Times 2005).
Short term credit or investments is another major issue for the Islamic financial institutions (HSBC 2001). As credit ratings of the Islamic banks, comparatively, is lower than that of the conventional banks it is a problem to create short term investment instruments (Tahir 2004).
Functioning Disputes and Forecast
Both the hypothesis of Islamic banking and the fast growth of Islamic banks fresh years have established the feasibility and probability of non-interest process. This has got to be astonishing to those who supposed that banks and monetary scheme could not function in a contemporary financial system devoid of dependence on an interest fee method. Without a doubt, knowledge has shown that Islamic banks are influential income of assembling possessions. Operationally, on the other hand, both the Islamic monetary schemes in the three states that have implemented it as well as person Islamic banks face confront that needs to be taken in hand.
The mainly significant in the middle of these confronts is the piece of information that, at the same time as it has been comparatively simple to make a scheme in which deposits do not reimburse interest, the asset collection of Islamic banks do not enclose adequately sturdy mechanism that are based on profit-contribution. The major rationale for this are:
- Lack of a lawful and institutional structure to make possible suitable pacts as well as methods to put into effect them; and/or
- Lack of suitable menus contains a broad variety and a diversity of adulthood arrangement of monetary tool. As a result, a comparatively sturdy threat insight has become connected with profit-contribution means in particular and Islamic banking in common.
This, consecutively, has led to focus of the asset collections of the Islamic banks in temporary and trade-related possessions with unfavourable effects on speculation and financial growth. The difficulty is made worse by the piece of information that Muslim countries, as is the instance of a great deal of the just beginning world, undergo from a lack of bottomless and well-organized assets and money markets that can make available the essential liquidity and security for existing possessions. The deficiency of appropriate long-standing gadgets to hold up assets configuration is reflected in the want for of very temporary monetary gadget to make available liquidity.
The dispute in front of individual Islamic banks
Daunting as the development proof of individual Islamic banks perhaps, the piece of evidence is that at up to date, those banks enclose for the most part supplied as intermediaries in the middle of the financial belongings of Muslims and main industrial banks in the West. In this backdrop, this has been a solitary association, until now.
It also comes into view that individual Islamic banks countenance problems in finance assignment for the reason that they have had a chief preconceived notion in the direction of short-range, tenable, low-return other than liquid savings. The challenge for these organizations stalks from motivational and technological issues.
Inspirationally, their essential plan emerges out to have been that of represent ting the feasibility of Islamic banking devoid of taking a lot of risks. Admittedly, this is a dignified and an extremely significant objective, on the other hand, even though they have achieved something in this attempt and have administered to make a market position for Islamic banking, they do not appear to have attained the market deepness that could make sure long-standing productivity and continued existence. This stalks from the piece of evidence that they become visible to be far at the rear in industrial modernization and monetary market expansion that in current years have transfigured economics and assets markets. There is no proof that these banks have completed any huge speculation in investigative study and merchandise expansion, neither is there any proof that novel monetary goods developed in current duration, for the most part in equity derivatives, which have been made use of to any noteworthy quantity by the key Islamic banks. This is unlucky for the reason that the market openings that these banks have been capable to build up, to permit money from Islamic centre of population to be positioned in Islamic-ally allowable collections, can and will be browbeaten by more well-organized and ground-breaking Western monetary organizations that by now have or will find out this marketplace position. At the same time as that there is substantial space for opposition and development in this meadow, the long-standing survivability of person Islamic banks will depend on how rapidly, forcefully, and efficiently they can expand methods and gadgets that would permit them to take on a cooperative intermediation occupation.
The challenge of adopting an Islamic financial system
The most vital obstacle for Islamic banking is in its overall and systematic execution. Currently, many Islamic states experience from fiscal disequilibria that disturbs the efforts at wholesale acceptance of Islamic banking. Financial unevenness in the financial and external division of these economies cannot give green ground for capable functioning of Islamic banking. Key structural tunings specifically in economic and monetary sectors are required to give Islamic banking with a plane field. In addition, embracing of a legal structure of land ownership and Contracts that would evidently spell out the area of private and public property rights as well as prerequisite of lawfully enforceable rights of sides to agreement that completely put in light the prerequisites of the Shariah, are essential to permit an functioning structure conducive to capable functioning of Islamic banking.
Inspirational issues for Islamic Banking
Motivation and improved significance in Islamic finance industry stands from its good economic, financial and social thoughts, supported by its distinctive attributes. Most important is its attraction to add to financial variety and creativity being skewed towards:
- Asset supported and equity based dealings, which encourages entrepreneur responsiveness and thoughtfulness of project possibility;
- Impartial allocation of risks and incentives among the stakeholders;
- Inculcating market regulation and higher ethical benchmarks given its weight on non-mistreatment and social welfare.
In the response of high Asian local savings rates and put up of the regions foreign exchange reserves as well as oil superfluous of Middle East in the past few years, Islamic finance is now also rising as a way to capital management, both of wealthier nations and high earning individuals.
References
Aalto, B. 2010. The UK housing market: Study of why and to what extent was the UK housing market over-valued and was there a Bubble present in the beginning of the 21st century. Web.
Andrews, El. 2007. Fed shrugged as subprime crisis spread, Web.
Bianco, K. M. 2008. The subprime lending crisis: Causes and effects of the mortgage meltdown, Web.
Business Intelligence System (BIS), 2011. Web.
Credit Crunch and Mortgage Borrowers n.d., Web.
Elliott, L. 2011. Global financial crisis: Five key stages 2007-2011. Web.
Farber, M. 1940. Philosophy and phenomenological research, International Phenomenological Society, vol 1(71).
Filger, S. 2008. Global financial crisis 2008 versus 2011: Is history about to repeat itself? Web.
Global Financial System, n.d. Web.
Hamdan, H. 2007. Islamic banking: Steady in shaky times. Web.
Help Globe, 2008. What is the difference between open and closed mortgage? Web.
Hesse, H. Jobst, A & Sole, J. 2008. Trends and challenges in Islamic finance, Web.
How credit crunch had affected mortgage rates in 2007-2009, 2009. Web.
HSBC, 2001. Global development in Islamic finance-challenges & opportunities. Web.
IBB, n.d. Sharia finance. Web.
IMF Warns of Global Economic Crisis, 2011. Web.
Islamic Banking, n.d. Web.
Islamic Banks are Surviving the Financial Crisis Better Than Western Banks, 2008. Web.
Janszen, E. 2011. Crisis 2011. Web.
Kaplan, S. 2008. The bailout: A primer. Web.
Khaleej Times, 2005. Challenges facing Islamic financial institutions. Web.
Larkin, S. n.d. The current credit crunch and how it affects the mortgage industry. Web.
Lecture Three: Problems and Prospects of Islamic Banking and Finance, 2001. Web.
Mansour, A. 2009. Islamic finance and the global economic crisis. Web.
Mortgage Banking, n.d. Web.
Mortgage, n.d. Web.
Open Mortgage vs. Closed Mortgage, 2009. Web.
Open Mortgages vs Closed Mortgages, n.d. Web.
Oxford Dictionary of British History:Banking, 2011, Web.
Perry, B. n.d. Credit crisis: Conclusion, Web.
Rafiq, M. 2008. Islamic finance, Web.
Research, 2011. Web.
Sesric Reports on the Global Financial Crisis of 2008-2009, 2008, Web.
Tahir, S. 2004. Challenges facing Islamic finance: Research areas, Web.
The Economic System of Islam (part 1 of 2): The Sources of Islamic Economics, 2006. Web.
The Positivist and Phenomenological Worldviews, 2007. Web.
The Research Methodology, 2008. Web.
Timmer, H. Decressin, J. Suttle, P. Lachman, D. Dadush., U & Naím, M. 2010. 2011 Global economic outlook: The Euro crisis, currency tensions, and recovery. Web.
What if the World Had Been Following Islamic Financial Practices? 2011. Web.