Abstract
Kuwait Airlines Company was launched in the year 1953 as a privately owned firm. Managers must retain existing customers to attract new customers. This is possible through implementing strategies for customer satisfaction. Kuwait Airlines is in the service industry, and the quality of services and value of money of customers creates customer satisfaction. The services vary from in-flight entertainment, convenient booking services, handling of baggage, flight schedules, and communication to customers on delays, diversions, and canceling of flights. The company aims to be the best flight service provider globally and maintain a wide network of customers. The company aims to be financially stable and profitable in the long term through investing in quality and standard customer services to attract and maintain a large market share. The failure of Kuwait Airlines to improve customer satisfaction provides the competitors with the opportunity of causing competition for the airline services.
The first part of the study will be on the background of the study problem, objectives statement, research questions, and purpose of the study. The second section will be a literature review and conceptual framework. The third section will be methodology. The fourth section will be on data analysis and presentation. The last section will be budget allocation and the schedule of the research. The research will begin in August 2012 to the end of December. The research report presentation will be at the beginning of January 2013 to the management of Kuwait Airlines.
Introduction
Background of the Study
Two businesspersons in Kuwait formed Kuwait Airlines in 1953. In 1954, the financial crisis hit the company severely leading to the selling of 50% of the shares to the Kuwait government. The government bought 100% of the shares of the airline later became the sole owner of the company and as a result, became a state-owned corporation. The main base of the airline is Kuwait international airport in Kuwait City (Anderson, Baggett, & Widener 2009, p.56). Kuwait Airline Company operates in North America, the Far East, the Middle East, and Europe. Today, Kuwait Airlines operates in more than 38 destinations globally. The airline has more than 17 aircraft comprising of B777-605ERs, A320-200s, A300-605Rs, A310-300s, and A340-300s (Porter 2008, p. 87). Kuwait airline is a member of the Arab Air Carriers Organization. The airline entered into a joint venture with Sabre Airline Solutions acquiring the privileged of full access to the crew and planning an optimizing portfolio (Melly 2008, p. 37).
The mission of the airlines is to provide standard and the highest quality customer services and to become the best airline to work for, invest in, and admire to purchase services. The airline has a vision of ensuring the progress of efforts to satisfy customers for the future success of the company. Among the efforts of satisfying customers, Kuwait airlines introduced new features of fax and telephone check-in services to improve the convenience of passengers in booking services (Monthly Review 2008, p. 13). Kuwait Airlines Company launched a deluxe personal lounge with epicure refreshments and worldwide communications amenities to clientele. It has in-flight services, such as food and beverages, and in-flight entertainment, such as personal video screens and audio channels (Oxford Business Group, 125). There is the BALSAM project for encouraging passengers to donate to help the poor and needy in society, especially children. This project helps the company gain support from the community in which it operates as it creates a good image and reputation (Boetsch, Bieger, & Wittmer 2011, p. 251).
Problem Statement
Kuwait Airline’s plan on customer service covers issues on notifying customers of the lowest fares, notifying customers of flight delays, cancellations, and diversions, allowing reservation or cancellation for a specific period, providing a refund of tickets to customers, and accommodating customer needs. Customers complain of difficult moments at the airline because some of the employees are incompetent and unfriendly. Kuwait Airlines has the highest market share in Kuwait. It has to ensure that it maintains customer satisfaction to prevent them from switching to competitors that include Wataniya and Jazeera Airlines (Kogan Page 2003, p. 78).
Objectives of the Study
This study aims to carry out research to determine the impact of customer service on customer satisfaction in Kuwait airlines. Second, the study will help in understanding the customer services provided at the airline and how the customers perceive the services. Finally, the study will help in determining the segments, which require improvements so that the airline business can improve and the needs of the customers met. Kuwait Airlines needs to create and maintain a competitive advantage of remaining financially stable and profitable (Lapré 2011, p. 506).
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this qualitative study is to examine the positive correlation between the impacts of customer service on the satisfaction of customers. The research will seek to establish the segments of its customers, travel patterns, expectations, demands, and their experiences in the service. The research will also measure their expenses and expectations. The company needs to understand the opinions of the consumers to make good decisions and strategies in the business. This is a sensitive market and failure of immediate action may lead to the collapse of the company in the future. Their marketing strategies should increase the market share of the sector, as it is one of the highest revenue-generating businesses in Kuwait. The service sector comes with many risks that could affect both the customers and the company. The airline business relies on the reputation of the public to make sales. This makes it difficult for Kuwait Airlines to carry out the business without research on its customers’ satisfaction (Shu-Fang & Tzai-Zang 2011, p. 838).
Literature Review
According to Shu-Fang, and Tzai-Zang (2011, p. 742), customer satisfaction can be either a disappointment or pleasure created as a personal feeling about expectations. Service providers major in customer satisfaction as a way of retaining customers. Customer satisfaction leads to marketing activities, such as promotion of word of mouth promotion to families and friends, customer loyalty, and product loyalty. Customer satisfaction is in two forms that include cumulative and transaction-specific satisfaction. Cumulative satisfaction is the overall customer evaluation of experiences during the period purchasing the service or product.. Transaction-specific is the experience derived from the first purchase of a service or product (Grewal, Chandrashekaran, & Citrin 2010, p. 612).
Service quality is a major determinant of customer satisfaction. Quality of service is the rational difference created between the competence and expectations of the important dimensions of quality.
Customer service to have the quality they require tangibles, reliability, communication, responsiveness, courtesy, security, credibility, competence, and understanding of the service accessibility and the customers (Anderson, Baggett, & Widener 2009, p.69). A generic instrument can measure the impact of customer service on the satisfaction of the customer. This instrument is the SERVQUAL model. This model measures the correlation existing between customer satisfaction and customer service in judging the performance management in an organization (Au & Cheng 2012, p. 335).
The SERVQUAL model consists of five dimensions that include tangibility, empathy, assurance, reliability, and responsiveness. Reliability helps companies meet the promises they make to customers on time (Ireland 2006, p. 78). Responsiveness is the degree to which service providers are ready to commit to assisting customers promptly. Assurance ensures that customers have total trust in the customer providers or the services they provide. Empathy is the way the service providers treat and understand the preferences and needs of their customers. Tangibility is the good that the customer can own and can have evidence from communication materials, personnel, or facilities. The services that a company provides must have the five dimensions to satisfy customers (Neil 2011, p. 65).
Conceptual Framework
This study will test the independent variables using the five dimensions to determine the impact they have in providing the satisfaction of customers represented by the dependent variables.
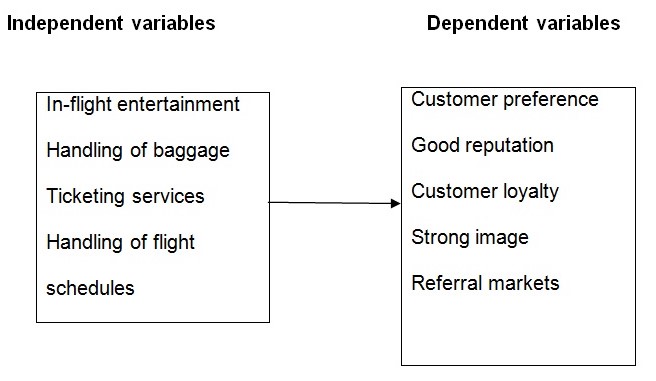
Research Questions
The analysis of the variables under study leads to the formation of research questions.
- What is the impact of In-flight entertainment on customer satisfaction?
- How does the handling of baggage create an impact on customer satisfaction?
- Which ticketing services create an impact on customer satisfaction?
- How does the handling of flight schedules create impact customer satisfaction?
Hypothesis
- Reliability creates an impact on customer satisfaction
- Responsiveness creates an impact on customer satisfaction
- Empathy creates an impact on customer satisfaction
- Tangibility creates an impact on customer satisfaction
- Assurance creates an impact on customer satisfaction
Methodology
The research process will cover the procedures of data collection, analysis, and presentation to create value for the user. The methodology will elaborate on the sampling techniques to ensure the collected data is free from bias, and the user can depend on it. A semi-structured interview will be the best method of data collection. The interview methodology will contain the pertinent issues on customer services that satisfy customers in Kuwait Airlines (Oyewole & Choudhury 2006, p. 19).
Research Design
Research design is the process of transforming the research question into a testing project. In this study, the best research design or type of research recommended is descriptive research under the qualitative research design (Oyewole & Choudhury 2006, p. 30).
Data Collection
According to Myers (2003, p. 126), data collection is a concept used to exemplify a procedure of organizing and gathering information in research work, either as a fraction of process development or comparable assignment. The main intention for data collection is to acquire information to keep on proof, to make choices concerning vital issues, and to provide information. In this research, data will be collected in primary and secondary sources to meet the main objectives of the study that including developing a better understanding of the needs, wants, and satisfaction levels associated with customers who purchase services at Kuwait Airlines. In addition, the data will also help in discovering the various services promoted at the airline. Through the collected information, it will be easier to implement some promotional strategies that could help improve customer satisfaction in customer services at Kuwait airlines. This is because the research will realize various customer expectations and needs at Kuwait Airlines (Lapré 2011, p. 491).
Sampling
The researcher visits the field under study to estimate the number of potential respondents. In the research, the area under study is Kuwait Airlines. The research will major on Kuwait International Airport (Steven, Dong, & Dresner 2012, p. 743). In this research, the target population includes customers, managers, and employees in Kuwait Airlines. This is because they form the potential respondent with first-hand information on the variables under study (Ireland 2006, p. 89).
According to Burns and Bush (2010, p. 28), sampling deals with the selection of a subset of individuals from within a population. The research process will use the probability-sampling method. This study will use random sampling methods. A random and systematic sampling method will be the most efficient for such a large population. The random sampling technique will give an equal chance to all the customers to participate in the research process. These sampling methods will allow homogeneity, low costs, fast data collection, and enhancement of the quality of the study.
The population will comprise 20,000 potential respondents. The research will need 100 participants in the research. The researcher considered the allocated budget and time for the research in choosing the sample size (Myers 2003, p. 149).
Data Analysis and Presentation Techniques
The researcher will use the SPSS software in analyzing and presenting the collected data into tables and graphs. The techniques suitable for this study are descriptive analysis, reliability testing, and influential analysis. Reliability testing will compute the reliability, accuracy, and dependability of the research. The descriptive analysis will quantify the frequency of items on the geographical and biographical data. It will also compute the descriptive statistics on each item in the independent variables using the sum, mean, and standard deviation. The influential analysis will calculate the weight of the dependent variables to fulfill the objectives and answer questions of the research (Jennifer & Thea 2011, p. 87).
Budget and Time Schedule
The research will take five months. This will be from August to December in 2012. The researcher will identify and analyze the research problem within December. In January, the researcher will organize and plan the research process. The researcher will estimate the expected expenditure and decide on the appropriate research methods to use in the research. The researcher will prepare the research proposal to direct the research process. This includes the typing, preparation, and printing of the questionnaires. In February, the researcher will conduct the study by administering the questionnaires to the respondents. In March, the researcher will analyze the collected data. In April, the researcher will organize the report and present it to the user. The research will use approximately $13000. Some of the expenses include transport costs, living expenses, printing, e-mail costs, and telephone costs (Creswell 2009, p. 143).
Conclusion
Customer satisfaction has become a necessity within this important service sector. The analysis mainly constitutes of the reserve situation, communal surroundings, and administration settings. These controls are supplementarily mediated by the research assessment of individual customers according to their socioeconomic actions, intellectual characteristics, knowledge, customs, feelings, and predilection. Kuwait Airlines targets travelers for leisure and business.
The demand for aviation services in the Middle East is growing considering the region is the central hub of oil production, high-income earners, a high young generation, and few means of transportation. The good business opportunities in the airline business attract and maintain new and existing businesses in the region. The emerging airlines include Jazeera, Flydubai, Air Arabia, and Wataniya to meet the high demand for travel in the Middle East. The high competition for market share in the region has led to the need for better customer services to satisfy customers and prevent them from shifting to competitors. The airline industry makes use of quality customer services to survive in the market. Kuwait Airlines has to take advantage of this opportunity to maximize profits.
The airline industry in the Middle East has few airlines because of the increase in economies of scale and difficult access to the distribution channels of the industry. This makes air transport the main and most reliable and convenient means of transport to other regions. The airline industry has easy access to raw materials like oil making it easy for the business to remain profitable. The Middle East region has few airlines and large numbers of travelers making it a potential market for investors.
The airline industry has low intensity of rivalry as the industry has small competitors. Kuwait Airlines has enough profits and financial capability of ensuring customer satisfaction at all levels of customer services.
References
Anderson, S, Baggett, L & Widener, S 2009, ‘The impact of service operations failures on customer satisfaction: evidence on how failures and their source affect what matters to customers’, Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, vol.11, no.1, pp. 52-69.
Au, N & Cheng, T 2012, ‘The formation of employee satisfaction with airline information systems’, Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, vol.29, no.4, pp. 335-351.
Boetsch, T, Bieger, T & Wittmer, A 2011, ‘A customer-value framework for analyzing airline services’, Transportation Journal, vol.50, no.3, pp. 251-270.
Burns, A & Bush, R 2010, Marketing research, Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River.
Creswell, J 2009, Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches, Sage Publications, New York.
Grewal, R, Chandrashekaran, M & Citrin, A 2010, ‘Customer satisfaction heterogeneity and shareholder value’, Journal of Marketing Research (JMR), vol.47, no.4, pp. 612-626.
Ireland, D 2006, Entrepreneurship: successfully launching new ventures, Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Jennifer, B & Thea, C 2011, The travel and tourism competiveness report 2011: Beyond the downturn, World Economic Forum, Davos.
Kogan Page, 2003, Middle East Review, Kogan Page Publishers, New York.
Lapré, MA 2011, ‘Reducing customer dissatisfaction: how important is learning to reduce service failure?’, Production & Operations Management, vol.20, no.4, pp. 491-507.
Melly, P 2008, ‘Kuwait Airways, meed’, Middle East Economic Digest, vol.52, no.42, pp. 36-37.
Monthly Review 2008, ‘Economic performance 2008’, Country Report: Kuwait, pp. 12-13.
Myers, J, 2003, Research design and statistical analysis, Volume 1, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New York.
Neil, R 2011, Kuwait airlines won’t forget the war, Times, The (United Kingdom), p. 65.
Oxford Business Group 2012, The report: Kuwait 2012, London: Oxford Business Group. p.132.
Oxford Business Group, 2008, Report: Kuwait 2008, New York: Oxford Business Group.
Oyewole, P & Choudhury, P 2006, ‘Purchase situations and the level of importance that consumers attach to services in the airline industry’, Services Marketing Quarterly, vol.28, no.1, pp. 19-34.
Porter, M 2008, ‘The five competitive forces that shape strategy’, Harvard Business Review, vol.86, no.1, pp. 78-93.
Shu-Fang, l & Tzai-Zang, L 2011, ‘The influence of trust and usefulness on customer perceptions of e-service quality: Social Behavior & Personality’, An International Journal, vol.39, no.6, pp. 825-838
Steven, A, Dong, Y & Dresner, M 2012, ‘Linkages between customer service, customer satisfaction and performance in the airline industry: Investigation of non-linearities and moderating effects’, Transportation Research: Part E, vol.48, no.4, pp. 743-754.