Introduction
Smart urban development is one of the issues that have gained much popularity in the world as members of the society seek to find ways of achieving sustainable development. According to Lussier and Achua, over half of the world’s population is currently living in urban settings. The percentage is expected to rise to over 75 percent in 2050. However, recent reports indicate that most of the urban centres are unable to sustain their current population. It is worrying how the condition will be in most of the cities around the world as the population continues to increase. Duany and Lydon say that the solution to this issue lies in smart cities that will help achieve sustainable development. It is necessary for responsible stakeholders to embrace the concept of smart urban development as they make an effort to settle the large number of people flowing into these cities. According to Bhatta, leadership is at the centre stage in the development of sustainable cities in the world. The scholar says that some of the current successfully planned cities were as a result of a visionary leadership from those entrusted with different positions. One of the unique aspects of smart urban development is that it seeks to make information flow freely to members of the society as a way of motivating development. It would be important to understand the relevance of leadership in knowledge creation, exploitation, and its spread in the context of smart urban development. This is an important part of research that is largely ignored, and for this reason, there is a knowledge gap. This research seeks to improve the understanding of the role that leadership plays in knowledge creation, exploitation, and spread in smart urban development.
Justification of the research
According to Khoshnaw, it is evident that the complex 21st century urban space needs a rethought of leadership approaches that can improve the exploitation of opportunities in the urban economy. There is a pressure to sustain the current needs of the increasing urban population without jeopardizing the needs of the future population. One of the best ways of achieving this is to not only to emphasize on spatial urban planning, but also to ensure that there is free flow of information to members of the society that will improve creativity and innovativeness in our society. The only way through which we can achieve sustainable urban development is by embracing creativity and innovativeness when addressing various issues.
This can only be possible if there is a free flow of information that can help shape our thoughts on various issues. It also makes it easy for members of the society to come up with new knowledge, spread it to others so that it can be fully exploited. Khoshnaw says that this can be possible with proper leadership in the society. The scholar claims that leaders hold the key to the creation of a smart urban setting. It also means that these leaders have a major role in knowledge creation, exploitation, and its spread within the society. However, it is worrying that little research has been done in this field, making the knowledge we have in this field under-theorized, and its practice untested. This creates a gap in the bodies of knowledge in this field. It clearly demonstrates that there is a need for the current researchers to develop and explain a set of theoretical concepts that would help in identifying the role of leadership in smart urban development. This is what this research seeks to achieve. Not only does it seek to offer more insight into the role of leadership in smart urban development, but also to develop theoretical and practical knowledge of how leaders play a pivotal role in knowledge development and flow in such settings.
Research questions
According to Ichijo and Nonaka, a researcher should always be careful when taking a less trodden path of study because there will be limited pointers to guide the study. This is one such piece of research that has not yet received massive attention of the researchers, and this means that it is necessary to be cautious enough not to deviate from the focus. In order to achieve this, a research question plays a very significant role. It helps the researcher define the research boundaries that will help identify relevant data in the field. In this research, it was important to develop research questions relevant to the research topic. The questions will be based on smart urban development and leadership in smart urban development.
- What is the basic nature of the smart urban development?
- What are the conditions under which smart urban development is taking place?
- In what ways do leadership influence knowledge creation, its use and spread?
- Are there hard facts that confirm that smart urban development is the solution to some of the problems faced in the current urban settings?
- What is the interpretation of leadership and its experience in different environmental contexts?
- When can leadership be a hindrance do the creation and spread of information in a smart urban setting?
- What are some of the indicators that the current world leaders are already working on programs that would promote development of smart cities?
These questions would guide the process of gathering data from both primary and secondary sources that would guide the conclusion made in the research.
Smart urban development
It is necessary to understand the concept of smart urban development at this early stage of the research in order to understand what the entire research will be based on. Smart urban development idea was taken from the concept of sustainable development. Sustainable development refers to the process of achieving the current developmental needs for the present generation, without jeopardizing the ability of the future generation to achieve their own developmental needs. This means that smart urban development refers to the process of meeting the developmental needs of the current generation by coming up with the smart cities, without jeopardizing developmental needs of the future generation. Hawamdeh defines smart cities as “Those that provide for the needs of the residents today without reducing the options for future generations.”
Understanding the nature of smart urban development may make it easy to appreciate its relevance in the modern society where our cities are under pressure to sustain the increasing number of people. Smart urban development can be analyzed from two perspectives.
According to Kodama, the first perspective would be from the spatial urban planning approach. Land is increasingly becoming scarce in the urban settings, and this is affecting the ability to expand these cities. Urban planners are finding themselves in a very delicate situation where they have to find alternative approaches of expansion because they are faced with the problem of limited space. This is where spatial urban planning strategies come in to help address the issue. It involves maximizing on the little used vertical space in order to help address the limitation of the horizontal space. Spatial urban planning also involves trying to ensure that urban centres have adequate facilities to meet the demands for all, such as infrastructure in healthcare, schools, and transport. Recreational facilities for children and adults should also be conveniently located.
The second approach of understanding the nature of smart urban development would be from the perspective of information flow. According to Von, “The promise of ‘smart cities’ is the ability to collect, analyze, and channel data in order to make better decisions at the municipal level through the greater use of technology.” This statement clearly gives a new approach to understanding smart urban development that is not focused on buildings and related faculties. It specifically focuses on the information infrastructure within the cities. Based on this definition, smart cities need to collect data, analyze it, and make it available for different stakeholders within the city. The statement that information is power has become a cliché in our society. However, only a few people have come to appreciate the importance of this statement in the light of information flow. Smart urban development must encompass ways through which information collection, analysis, and distribution will be made convenient and reliable to members of the society.
This way, it becomes easy to identify issues that affect our society, share our views on the best approach to address them and apply the most appropriate means of addressing such problems. This will empower members of the society. It will make them active in the society because they are empowered to share their views and examine the views of others. Innovation will be improved, and this will increase the quality of our employees. The society will be able to address some of the emerging concerns in the fields of health, technology, entertainment among others. It is at this stage that a city would be considered to have achieved the smart urban development goals. The City of London is one of the few cities in the world that is moving closer to achieving this status. It is important to emphasise that London is yet to achieve the status, but with the current efforts made by the leaders in this city, the dream is within reach. It means that leaders have a role to play in smart urban development.
Role of leadership in knowledge creation, exploitation, and spread in smart cities
According to Neck, leadership is one of the most widely researched topics in the world because of its relevance to the society. Leadership dates back to the history of mankind. Leaders are important in our society in order to help in giving focus to the people. As people struggle to achieve economic benefits for themselves and the society, a leader is given the role of taking care of people in the society by identifying issues that may affect them, addressing these issues, and finding the best way through which the society can be successful. A society is as strong as its leader. The Egyptian Empire, the Greek Empire, the Roman Empire, the Han Dynasty, and the British Empire all existed because of the great leadership. The leaders of these empires inspired people to act bravely when addressing various issues, and this led to the great success. Many people still remember how Margret Thatcher, the former prime minister, transformed the economy when we were experiencing economic woes. She put structures and inspired people that the United Kingdom was still a great nation, just as it was once known as the Great Britain. She made people believe in this greatness and convinced them that they had to do it right and the results were impressive.
It is clear that leaders have a central role in the development of smart cities from the perspective of spatial urban planning and development. In order to achieve infrastructural development that comes with spatial urban planning, we need our leaders to be committed towards this front. They are the policy makers. They are trusted with the country’s resources and, therefore, they dictate the path of development. They have the role of stewarding development of various projects in order to achieve sustainable urban development. The role of architects and other city planners is only to offer advice. It is the leaders who make the final decision on how this issue should be taken. For this reason, they hold the key to the sustainable urban development. It is important to determine the role of leadership in knowledge creation, its exploitation and spread in smart cities. It is now clear that cities can only be defined as smart if there is ease of data collection, analysis, and spread of information. At this stage, it is now important to determine how leadership is intertwined with this information management.
According to Coulson, the government of China prohibited circulation of information on some online media claiming that it was radicalizing a section of the society.14 During that period, the Mayor of Washington, DC was trying to find a way of spreading the use of fibre optic cables within the city to help meet the increasing demand for data sharing among institutions and individuals. These are two cases with a clear explanation of what leadership can do to information flow. In China, there was a deliberate attempt by the leadership to thwart free flow of information because of personalized government interests. This government believes that information is power, and it cannot afford to hand over this power to people. On the other hand, in Washington, the leadership is playing a major role by developing structures that make it easy for people to create knowledge, share it freely, and exploit it for their own good, and for the benefit of the society. This is what is taking place in London currently. The leadership is handing over power to its people, by making it easy for information to be generated, shared, and fully exploited without any form of interference. Leadership promotes knowledge creation, exploitation, and spread in smart cities by developing the best infrastructure, supporting brains involved in knowledge creation, and developing legislation that would improve information flow. Actions contrary to this will have a negative impact on information flow within the city.
Theoretical and practical perspectives
It was mentioned before that knowledge of leadership in the smart urban development is under-theorised and its practice remains largely under-researched. Developing relevant theories in the field and defining their practice would be very important in promoting the concept of smart urban development in various parts of the world to people in authority, being capable of bringing the desired changes in our cities as discussed above. Transformational and Transactional Theories have widely been used in the contemporary world to explain the role of leaders in inspiring the followers to achieve a great success. Transformational Leadership Theory is largely practiced in many organizations, and as Palermo and Ponzini15 put it, it is a tested theory whose effectiveness is known. However, there is a need to develop models relevant to leadership in smart urban development. Below is a theoretical model of leadership and knowledge creation and flow in smart cities
Theoretical Model of Leadership’s Doubled-Edged Sword in Knowledge Creation
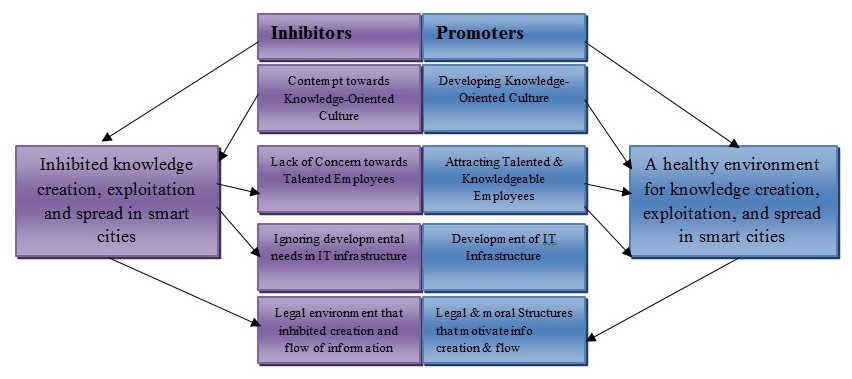
According to the above model, leadership is a like doubled-edged sword in knowledge creation, exploitation, and flow within the urban settings. This model holds that a leader has the power to promote knowledge creation using the promoters or discourage the same using inhibitors whenever they feel necessary. In practice, the statement recently made by the Russian president, Vladimir Putin on online media confirms the truth presented in this model. The president said that online media is a project of CIA to monitor and control the world. Given the admiration he has earned among the Russians, recent reports indicate that there is a massive drop in the use of internet in the country. This simply means that the leader has used his moral inhibitor to discourage knowledge creation and sharing in major cities, in the country. On its part, China used the legal structures to discourage knowledge sharing in the country during the Tibetan uprising.
On the other hand, London has developed IT infrastructure, developed knowledge oriented culture, and scrapped restrictive laws of knowledge creation and sharing in the society. This way, it has become one of the few cities in the world closer to achieving full status of smart urban development. Practically, this theory emphasizes on the needs for leaders to realize that they are centrally located in the quest for smart urban development. They have the power and can, therefore, choose to use it against smart urban development or to promote the same. What they need to appreciate is that the status of smart cities cannot be attained when the creation of knowledge and its free flow is inhibited. The power that is in the knowledge should be handed over to the people, and the government must appreciate that they will have this power through the mandate they are given to lead. This is not a mandate to take the same power away from people.
Conclusion
Leadership plays a major role in knowledge creation, exploitation, and spread in the context of smart urban development. Leaders have the potential to promote knowledge creation or discourage the same using the moral or legal powers that they have at their disposal. They have the capacity to develop or ignore the need for development of information technology infrastructure that is necessary in knowledge management. As demonstrated in Leadership’s Doubled-Edged Sword Model, in knowledge creation, leaders have the power to facilitate or inhibit smart cities where information is easily created and allowed to flow freely among people.
Bibliography
Bhatta,B, Analysis of Urban Growth and Sprawl from Remote Sensing Data, Springer, New York, 2010.
Bontis, N, The Strategic Management of Intellectual Capital and Organizational Knowledge: A Collection of Readings, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2002.
Coulson, C, The Knowledge Entrepreneur: How Your Business Can Create, Manage and Profit from Intellectual Capital, Kogan Page, New York, 2003.
Duany, A, & M Lydon, The Smart Growth Manual, McGraw-Hill, London, 2010.
Hawamdeh, S, Creating Collaborative Advantage Through Knowledge and Innovation, World Scientific, Cape Town, 2007.
Ichijo, K, & N Ikujiro Knowledge Creation and Management: New Challenges for Managers, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2006.
Jaworski, J, Source: The Inner Path of Knowledge Creation, Berrett-Koehler Publishers, New Jesrsey, 2012.
Khoshnaw, F, First International Symposium on Urban Development, Wiley and Sons, New York, 2013.
Kodama, M, New Knowledge Creation Through ICT Dynamic Capability Creating Knowledge Communities Using Broadband, Information Age Publishers, Charlotte 2008.
Larsson, G, Spatial Planning Systems in Western Europe: An Overview, IOS Press, Chicago, 2006.
Lussier, R, & C Achua, Leadership: Theory, Application, Skill Development, (Cengage Learning, New York, 2010.
Neck, C, Self-leadership, Emerald Group Publishers, London, 2006.
Palermo, P, & D Ponzini, Spatial Planning and Urban Development: Critical Perspectives, Springer, Chicago, 2010.
Rouncefield, M, & P Tolmie, Ethnomethodology at Work, Ashgate publishing limited, New Delhi, 2011.
Von, K, Towards Organizational Knowledge: The Pioneering Work of Ikujiro Nonaka, Cengage, New York, 2013.