Abstract
As explained by Taylor (2002), “strategic HR management involves more than just the administration of human resource programs or activities”. Effective human resource management involves applying these strategies to employees’ management. Among these strategies today is reward management. “Reward management involves the analysis and effective control of employee remuneration and covers salary and all benefits” (Serco, 2007). It aims at assessing the nature of rewards available for employees, the expected results and actual results.
This paper seeks to understand reward management and its application in international organizations. The paper uses a survey conducted by the International Civil Service Commission (ICSC) to understand some of the reasons employees join, stay and leave the United Nations system. The most important factors identified in the survey included opportunities for growth, opportunities to practice skills, as well as relationships at the work place.
Google Inc. has been used in the paper to understand reward management. The company enjoys a good reputation as an employer. Some of the strategies identified include job satisfaction, training, health benefits, family benefits, opportunities for growth, freedom to implement ideas, among others. The paper concludes that non-monetary rewards play a significant role in any organization’s employee satisfaction strategies. It recommends that reward strategies implemented in international organizations must support employee satisfaction and freedom.
Reward management in international organizations compared to Google Inc.
Introduction
“Strategic human resource management (SHRM) aligns an organization’s human resources function to its core business objectives” (Fombrun, Noel and Mary, 1999). The task of managing employees is not as daunting as it may sound, as long as an organization fully equips itself with the strategies, skills and knowledge to bring out the best of its employees. Despite the fact that proponents of human resource strategies have outlined their benefits to organizations for a long time now, they are not as widespread as may be expected. The results have been poor management of human resources and increased costs of hiring and training new employees every too often.
Even if this is the case, organizations can draw motivation from those organizations that have perfected the art of getting the best human talent in the market, getting the best out of them and being able to retain them. A good example of such organizations is Google Inc. who has for a considerable amount of time now, been listed among the best employers. A successful implementation of appropriate human resource management strategies have helped many international organizations manage large number of employees, as well as integrating people with different cultural backgrounds to their business and using them to their advantage. It has also helped them save enormous amounts of money that would otherwise, go to recruiting and training new employees regularly.
As explained by Taylor (2002), “strategic HR management involves more than just the administration of human resource programs or activities”. Effective human resource management involves applying these strategies to employees’ management. “Strategic human resource management should help an organization incorporate their plans into the mainstream of organizational strategy and management” (Stewart, 1995). It is also supposed to help organizations think strategically as far as human resources are concerned.
Another significant benefit of SHRM is “designing performance incentives plans with the intention to continuously motivate employees and thus improve customer service in a dynamic environment” (Bratton and Gold, 2003). Furthermore, SHRM is instrumental for businesses which take employee motivation seriously. SHRM programs give room for training and provision of skills in line with an organization’s activities. Those businesses which have been able to implement SHRM successfully are more likely to report improved business capability. Finally, SHRM aims at motivating; engaging employees, as well as helping organizations retain their talented employees.
Reward management
“Reward management involves the analysis and effective control of employee remuneration and covers salary and all benefits” (Serco, 2007). It aims at assessing the nature of rewards available for employees, the expected results and actual results. There are three parts of reward management namely; the purpose, return on investment and the most appropriate places to apply it.
As Heneman, 2002 explains, “it constitutes the financial reward aspect which incorporates processes and procedures for tracking market rates, measuring job values, designing and maintaining pay structures, paying for performance and giving employee benefits”. However, it is important to note that reward management is not just about monetary compensation. It is also about other non-financial rewards which boost an employee’s confidence and provides motivation. Key issues to address in reward management are;
- How to external and internal competitiveness and equity
- How to reward individuals and promote team work as well
- Which performance management processes are appropriate for a business
- How to devolve power and ensure managers can manage their own reward strategies while staying within the corporate policies
- How to motivate those who have reached the highest level of career possible in the organization
- How to ensure increased reward translates to improved performance
- How to structure and design job evaluation schemes
- How to ensure employees are rewarded for both their inputs and outputs
- How to make employees recognize and appreciate non-monitory rewards
In today’s scenario, there are various management trends available for international organizations. As Armstrong, Duncan and Peter (2010) explains “more organizations today choose to develop increased awareness of the need to treat job measurement as a process for managing relatives, which, as necessary, has to adopt to new organizational environments and much greater role flexibility”. Others choose integrated pay structures that cover every employee regardless of their position. Team pay is a common trend today in most organizations as they more importance is being place on teamwork. Other trends include performance awards and more sensitivity to functional markets to enable organizations retains talented employees.
Employee satisfaction
“The success of any business is dependent on a motivated, highly performing and loyal workforce” (Bratton and Gold, 2003). Well satisfied employees are more motivated and as a result, they perform their tasks better and give better results. Loyal employees are more dedicated, will defend the company and stand with it in troubled times, and will always pursue excellence. Employees’ loyalty is taken lightly by many companies, without realizing that lack of it could cost them a lot of money. To be successful, businesses must focus on gaining their employees’ trust and loyalty. Lifetime loyalty, though rare amongst employees, is the biggest asset any business can have.
Employment conditions in many International Organizations have been under constant criticism for a long time now and as a result, employees’ loyalty level is low and so is their satisfaction (Hoffmann, 2006). A multinational organization will have different experiences in different regions. For example, in the Middle East, slave labor conditions have left many people looking for greener pastures in other countries. Those who remain at home do not have stability as they have to keep on changing jobs, hoping for better conditions. “Casual employees are not entitled to leave while absenteeism attracts heavy penalties such as working without pay for a period stipulated by the employing company” (Spark Organization, 2010). Many times, employees have their salaries withheld for months, especially if the business is going through financial difficulties. Even as the era of slave labor slowly comes to an end in the gulf and other regions, multinational organizations investing in these countries have a hard time earning employees’ loyalty. The organizations also tend to be more reluctant to implement employee motivation measures.
In the American and European countries, the situation is completely different and employee satisfaction is a big priority for businesses. Employees fully understand their rights, governments have put in place adequate measures to ensure these rights are respected, and labor markets are more competitive. The rate of employee turnover is high and more businesses struggle to stay profitable. Cost saving measures includes ensuring employee’s retention, which calls for ensuring that their needs are well met and they are well satisfied.
Part of this research will be aimed at establishing and discussing the relationship between employees’ satisfaction and their level of loyalty to a business. To understand loyalty among employees, important points to be discussed will include training and development, respecting employee’s needs, creating working favorable conditions, communication channels, rewards and recognition, and what role these factors play in achieving the same. Promotions and career development, process improvement, corporate cultures, compensations and benefits, and job enrichment will also be discussed and their roles in ensuring customer satisfaction.
Motivation theories
Motivation calls for use of incentives to achieve a higher output and productivity. The biggest factor to consider in motivation is mentorship. The two therefore, go hand in hand in any industry. The argument behind motivation theory is that “a motivated work force will generate much more than a demotivated workforce” (John, 1999). The results are a higher output and more satisfying quality. Employees can be motivated using different types of incentives. The most common forms of incentives today are financial. They include pension, bonuses and pay increment for a certain level of achievement.
Motivation is also deemed a very critical factor for producing high quality work and minimizing wastage. Motivated staff will tend to be more pro-active and have a bigger sense of seeing things happen (Hoffmann, 2006). They will give their best to their organization which helps an organization improve its profitability and as a result, better performances. Motivated employees are also bound to be more open about their problems and concerns and will air them out instead of letting them affect an organization’s performance.
Different philosophers present different motivational theories and give different arguments as to why they support motivation. One of the most significant motivational theories is Frederick Herzberg’s motivational theory. Herzberg argues that “satisfaction and dissatisfaction arise from different factors at work and they are not opposing reactions to the same factor” (Hoffmann, 2006). Those factors motivating people are not the same that dissatisfy them. Satisfaction comes from factors which are involved in accomplishing a task. Dissatisfaction on the other hand comes from factors in the job context.
According to Hezberg, a human being’s needs can be categorized into two sets of needs. One is to grow themselves psychologically and the other is to avoid pain or suffering (Hoffmann, 2006). He also explains the need for safety, food, shelter and even hygiene which he illustrates through a biblical example. According to him, an employee needs status, policy, proper work conditions, security, a good salary, and a relationship with both the supervisor and the subordinate to be motivated.
Another motivation theory is that of Abraham Maslow. His theory explains the human need hierarchy. He arranges the human needs in the form of a hierarchy from the least to the biggest. According to him, the most important human need is the physiological needs, followed by security and safety, social, esteem and self-actualization needs in that order (Hoffmann, 2006). He argued that any time a need is satisfied, the next need on the hierarchy becomes dominant. He also acknowledges that no need can ever be fully satisfied but if an organization wants to motivate their employees, it is important for them to understand their level of need in the hierarchical order.
This theory enjoys a huge recognition from different managers. “This is from the fact that it is easy to understand and it has a logic that is easy to relate with” (Weiner, 2002). However, the theory also attracts criticism for lacking empirical evidence and lacking research support for it. The two theories differ from the fact that Herzberg identifies both motivational factors and maintenance factors. Maslow on the other hand identifies human needs and arranges them in a hierarchical order.
The need for empowerment
As Covey (1999) explains, “empowerment is a leadership tool that has been used in a wide range of circumstances for improving the level of productivity in business enterprises” In any organization, nursing such effective tools need to be implemented to help employees identify a place in it. Employees need to be empowered for various reasons key of them being;
- Empowering employees will increase productivity by enhancing performance. Powerless employees feel helpless to even take initiatives that could improve their performances.
- Job satisfaction is addressed when employees are empowered. Empowerment gives them an opportunity to decide on various issues that affect them at work. Being in a position where they can communicate issues facing them has an effect on their performance.
- Empowerment improves employees’ influence on clients and colleagues.
- Empowered employees tend to have a more energized and positive attitude, which they pass down to their colleagues and clients.
Research background
According to a recent global survey on recruitment and retention by the International Civil Service Commission (ICSC), staff deciding to leave international organizations have quoted lack of opportunity for professional growth and promotion, lack of opportunity to use their skills and competencies, and lack of sufficient training and learning opportunities, as the main reasons for their un-satisfaction. The thesis researches the drivers of employee motivation in connection with reward management as well as examines the success story of Google Inc. with this regard. The review of literature provides information about motivation theories focusing on the issues of employee retention, rewards, training, and career development.
Aim of study
Critically analyze the concept of reward management in international organizations as compared to Google Inc.
Objectives
- Understand current theories in reward management
- Examine how reward management theories are applied in the public sector using the ICSC study to support the arguments
- Discuss motivators used in Google Inc. to motivate and sustain employees
- Research on and explain how international organizations can apply the lessons learnt buy Google Inc. to enhance their performance and retain employees.
Justification of the study
A survey conducted by different organization in the past reveals that employee turnover is a crucial issue in all organizations. The results reveal that organizations likely to expand to global markets are most likely to suffer most. As evident from the statistics, international organizations are more likely to suffer a high rate of employee turnover. According to Naidu (2011), “employee turnover is an issue big enough to make employees lose sleep over the tangible and intangible costs of employee turnover”.
The research conducted by ICSC further reveals that finances are not the biggest consideration for employees. Most employees are more concerned with available opportunities for growth and for exercising their skills. This paper seeks to understand the concept of reward management and the role it plays in improving the situation by encouraging retention. The study will be focused on international organization.
Rationale
This research has specific practical value. Having considered the results, it will be possible to state whether reward management plays a vital role in an international organizations’ human resource management or not. The answers will explain different roles of reward management, motivation, retention and responsibilities of role models, as well as how these processes contribute to the success of international organizations. The influence of reward management in organization’s success is evident in its role in training, coaching and development.
Literature review
According to Heneman (2002), “management of reward systems takes place in a larger context that must be accommodated when designing, implementing, and evaluating strategic reward systems”. The author starts by pointing out that the value of reward and employee motivation cannot be over-emphasized. Human resources are a business’ biggest assets and organizations cannot achieve any competitive advantages if they don’t realize this. Employees must be motivated right from the day they join a company from their job description, resources made available for them to implement their responsibilities, and the kind of people they work with. Apart from the monetary compensation of a job, employees are looking for conductive working environments, opportunities to use their skills and grow their careers, good leadership skills from their seniors, among other things.
Armstrong, Duncan and Peter have in their recent book, explained how businesses can create measurable business impacts from their pay and reward practices. According to the authors “vast amounts of money are being wasted in pay and benefits, but organizations are not getting added value from their expenditure because they are not measuring the effectiveness of their reward practices” (Armstrong, Duncan and Peter, 2010, p.4). To address these issues, the book suggests that businesses must constantly evaluate the contribution of their reward strategies, as well as use feedback from their employees to know what is working or not.
In his book, Mahoney explains leadership skills in the 21st century, and the role leadership plays in managing human resources. To serve as effective leaders, senior managers are expected to establish group and individual identification among their teams by maintaining their effectiveness and using appropriate problem-solving techniques. Mahoney (2001) describes good leaders as being “visionary, equipped with strategies, a plan and a desire to direct their teams and services to a future goal”. Leaders are also expected to be passionate about their work and their teams, have the ability to motivate others, seek to constantly inspire their juniors and find solution to problems.
As the author explains, the expectations on leaders are many and continue to grow, as they get more involved in management tasks and responsibilities. In order for managers to be respected and earn the trust of their teams, they must portray and apply these characteristics. There is also need for someone to offer the much needed support and mentorship. In human resource management, when this is lacking, it may be impossible to develop any proper business practices
Bass, in his book on leadership and performance beyond expectations, explains the role of human resource managers in establishing solid leadership and reward mechanisms in a business. Part of this is using people in senior positions to understand the needs of people in their teams, and offer recommendations on how the human resource management can help solve them. As markets get larger and more competitive, strategic human resource management is a key recipe when formulating effective strategies. According to the author, part of establishing effective strategies is employing rewards and mentorship.
In his book, Benner uses the nursing industry to explain appropriate mechanisms that can be used to help employees develop from novices to experts. The book addresses excellence and power in clinical nursing practice. Among the issues pointed by the author is resolving conflicts and crises. The author explains conflict and crisis management as factors that play a strategic role in ensuring positive results in any sector. According to the author, ensuring open communication channels between senior and junior employees, as well as the managers and the executive management, is the first step towards identifying problems and implementing solutions. Incentives, recognition, rewards and strict discipline measures are key strategies towards ensuring that employees deliver, keep in line with the business’s timeliness, and stay disciplined. When such measures lack, a business’s efforts to have the best talent may not be rewarding.
Covey, a well-known author on leadership and managing human resources, offers significant insights on the characteristics of highly effective people. The book explains how knowledge management can be used as an effective tool in businesses. Being aware of what is happening around a team assigned to them is the easiest way for a leader to help those under his authority. Gaining competitive advantage has become a major challenge for leaders today. Motivating those below them is equally hard but the author explains that using available information to the leader’s advantage, requires advanced knowledge management tools to allow a leader convert available information to useful knowledge.
To review Google Inc. human resource management’s success as a reference for this thesis, Girard’s book explains the revolutionary management strategies that have allowed Google rank as one of the most successful companies. “Google has created genuine enigmas for anyone interested in management strategy” (Girard, 2009, p. 224). The author explains the solutions Google Inc. has adopted to ensure consistency in their success. One of the most significant solutions for Google Inc. is its ability to attract the best employees in the labor markets and retain them longer. Other resources that have helped understand the background of this thesis include Deutschman’s (2005) online article where he argues that “Google Inc. is ever so young, self-satisfied, and happy”. The author attributes this success to proper HRM among other things. An article by CNN money offers a summary of figures that make Google Inc. so great such 0% voluntary staff turnover and more than 1.1 million applicants every year.
Reward management in Google Inc.
Like in many other international organizations, Google Inc.’s human resource management has a structure that fits the imperatives defined by the need for cost cutting and providing operational excellence at the same time. According to Scribd (2009), their structure is designed in such a way to help further develop of the potential of human capital inside the organization. The human resource management team at Google Inc. focuses on enabling the power of the team’s co-operation, optimal processes and communication flow inside the team. Putting such requirements into consideration, the resulting human resource organizational structure is divided into different segments that allow easy management of information regarding human resources.
Google Inc. has remained at the top of the list as the best employer for a long time now. The company receives over 1000 job applications every day. “The company generates a truly unique and attractive working environment for their employees, which is a very visible manifestation of the culture” (Scribd, 2009). The company has mastered the art of non-monetary motivation strategies and currently enjoys a very small rate of staff turn-over. Motivation right form the hiring stage is achieved when strategies put in place ensure “versatile selection processes, proper employment relations, considerate human resource policies and rewards, all these bound together by a commitment for strong employer branding, employee engagement and on-board strategies (Gratton, 1999).
Job designs and diversity
Recruitment forms a very big part of Google Inc. A stated earlier, the company receives more than 1000 job applications every day. “In any organization, recruitment activities need to be responsive to the ever-increasingly competitive market to secure suitably qualified and capable recruits at all the levels” (McNamara, 2009). For the business to achieve an effective recruitment process, its human resource management strategies have to take into consideration the benefits and challenges of sourcing employees from within or outside the company. Motivation during hiring is ensured through sound job designs and robust tasks distribution.
Growth opportunities is a well-developed reward strategy in Google Inc. Internal recruitment is always given priority as it provides the most cost-effective source for recruits and gives employees a chance to diversify and grow (Google Inc., 2011). Further growth is made possible by continuous training, development and other performance-enhancing activities to ensure constant potential of the existing pool of employees. Performance enhancing activities include activities such as performance appraisal, succession planning and development centers. “Such activities help review performance and assess employee development needs and promotional potential” (Girard, 2009).
The Googleplex
“Within the Googleplex there is a gym, pool tables, washing machines, table tennis tables, video games machines and an outside beach volleyball ball court, among other relaxing facilities” (Towes, n.d.). These facilities allow employees to relax, ease off work and personal pressure, and improve on their fitness. It also serves as a very important team building facility. When such facilities are available at work, employees don’t have to leave work early to access them somewhere else. For those who cannot afford these facilities outside work, it is an added advantage.
Dietary needs
These are met through a very reputable cafeteria and snack rooms, which offer a variety of snacks for free. Recently, Google passed a policy which ensures that no employee should be 100m from a mini-kitchen. The mini-kitchens are where employees can serve themselves water, tea of coffee. When employee’s dietary needs are well met, they are not easily distracted by hunger and their health is supported. For those employees who may have medical conditions that require regular snacking, Google becomes a comfortable and safe place for them to work.
Basic physical needs
Google Inc. cares not only for its employee’s financial needs, but also care about their health and fitness. This is illustrated by the company’s efforts to have on site doctors, dentists, nutritionists and other medical experts regularly. Such measures help employees deal with health related issues before they deteriorate and start affecting their performance. The initiative also creates awareness about health and employees are able to take care of themselves.
Stress management
Stress management is a critical factor in employees’ performance. Unmanaged stress is identified as one of the biggest contributors for poor performance. Google Inc. helps its employees manage stress by having massage therapists on site and departmental counselors. The company encourages team activity and employees are entitled to rest and leave days to allow them breaks.
Personal wealth management
Money problems are a major stressor for employees. An employee who is unable to manage money will never be satisfied regardless of the amount of salary offered to them. Employees in Google Inc. are helped to deal with money problems by having financial advisers and managers on site. Employees are free to consult with them at any time and the services are played for by the company. As a result, even employees at the lowest salary scale are able to budget and manage their money well. The company has a percentage of its shares reserved for its employees, a policy that has allowed many of its employees become millionaires through the stock exchange market. Even though this is considered a monetary reward, it creates a sense of belonging for employees by being able to invest in the company.
Office designs
When discussing reward management, the structure of the offices is many times left out. Employees’ ability to access information and reach the human resource managers is an equally important factor. “In many organizations the front office is responsible for being a single point of contact for the rest of the organization” (Taylor, 2002). The front office also needs people who will be able to recognize the real needs of the rest of the employees and be able to translate them into the requests for the responsible offices.
Google Inc. pays a lot of attention to its structural designs. The company has developed office structures that allow the human resource department to smooth out co-operation and communication among its employees. It allows them to have a clearer definition of roles and responsibilities among team members and easily understand definitions of processes. A well-structured human resource department also gives room for potential future development of new initiatives and potential improvement of current human resource processes. Finally it makes it easy for both the internal and external members to understand the structure for the managers in the organization. With well-organized and structured human resource management personnel, it then becomes easier to roll out other human-capital related programs, initiatives and practices.
The interior design is also structured to make employees as comfortable as possible. “Google offices and structures are a geeks dream house” (Hammonds, 2003, p. 74). Employees are allowed to personalize their working spaces, as long as they adhere to the company’s regulations and, as long as the arrangement does not impact the company’s image negatively. The aim of such an initiative is to help employees work in a more relaxed environment and have a place that they look forward to be in.
Family packages
Family is highly valued in Google Inc. The company believes in its employees having time out to rejuvenate their energies and spend time with their loved ones. For parents especially, being close to their children helps them be more relaxed and reassured of their safety and well-being. Google Inc. has built nursery care for kids in their offices and parents are allowed to check on their children regularly. The company hires professionals to watch over the kids as their parents work. Every employee in Google Inc., are also entitled to a 25 days holiday every year. The company also gives free holiday packages to employees based on a well developed criteria.
A united culture
According to Kotter and Heskett (1992) “culture is by no means a superficial concept, but a term used to describe a dynamic part of all organizations”. Cultures differ with organizations, and can be used to measure the level of success for a business. Successful cultures are those that allow employees to create goals that align with those of an organization. In successful cultures, employees are united, and everyone works towards the same goals. Within such a framework, everyone knows what is expected of them and when. Successful cultures recognize the values of all the employees, and decisions are enacted by all the members of the team. “Google Inc. has created an organizational culture which has high levels of sociability which results in informal knowledge and ideas sharing” (Towes, n.d).
Maintaining good labor relations and addressing legal issues
“Understanding legal decisions and legislation is fundamental in any sound management of the human resources especially with the increasingly litigious society” (Griffeth and Peter, 2001). For a company that employs more than 26,000 employees, legal issues are expected to be many and can easily damage the company’s reputation as employer. To avoid such situations, Google Inc. takes and constantly updates itself on regulations and policies that govern human resource management. This includes a constant watch-out for any new regulations, and changes in existing ones from the National Labor Relations Board, the U.S Department of Labor, as well as other regulating bodies in the different countries the business operates in.
Google Inc. as an employer does not discriminate on the basis of race, sex, religion and other differences among people since it is illegal to do so according to the law (Google Inc., 2011). Labor relations in the company are taken serious and this gives employees an opportunity to understand various issues that affect them as employees. Some of these issues include their union’s relationship with the management, whether to remain in a union or not, collective bargains, potential contribution of union representatives and the advantages and disadvantages of a represented work place.
Labor relations in Google Inc. have created a wide range of labor rights to employees including a right to strike, the right to bargain at a union and a right to protest or take action to achieve their desires. According to Tavistock Institute of Human Relations (1999), even though labor relations have at times been a source of conflict between the employees and employers, they have contributed greatly to ensuring that employees’ rights are respected and that employees can easily voice their grievances.
Ensuring job satisfaction
Job satisfaction in an organization measures how content and happy employees are with their jobs (Heneman, 2002). Job satisfaction and motivation are two different factors but they are directly linked. Job satisfaction in Google Inc. is measured through collection of data and holding forums with employees to discuss their level of satisfaction as well as air their complaints. In Google Inc., employee retention is not just the human resource management’s responsibilities but everyone is involved. Individuals are supposed to be supportive of their colleagues and so are managers. The management takes time to understand their employees’ satisfaction levels by ensuring that everyone is heard thorough open communication channels.
Employees value opportunities which is a core value of satisfaction. The management holds meetings with employees to routinely discuss their career paths and provide developing opportunities for those whose interests and skills allow. Google Inc. has perfected the art of working with employees and helping them identify and achieve reasonable career objectives. “In Google Inc., employees are encouraged to innovate through the 20% rule, whereby 20% of employees’ time is spent on whatever project they desire” (Towes, n.d, p. 18). For those projects that become popular, the employee or team is allowed to work on developing it as a main task and responsibility in the company.
Another core element of satisfaction in Google Inc. is recognition which involves praising employees even for the small steps. This includes group and individual recognition. It is not just enough for the HRM department to employ more employees, they also have a responsibility to go a step further, listen to their complaints and compliment them when they have done a good job. This gives employees a feeling of mutual recognition. A conducive working environment is constantly present in the business to raise their employees’ motivation.
Flexible working hours
“Is there is one free reward that rises above the rest, it’s flexible work schedules” (Heneman, 2002). This reward mechanism has the advantage of attracting a lot of gain and very little pain in the business. Flexible working schedules allows employees spend time with their families, run banking errands, attend to personal issues, make it to a doctor’s appointment, and many other errands that affect an employee’s level of productivity. According to Heneman (2002), “as long as the employee is not abusing the privilege, this can go a long way to building trusting and mature relationships with key workers”. Google Inc. has adopted working schedules that allow employees time to attend to personal business. The company has for a long time been considering launching a “work from home” program.
Enjoyable working environment
An employee’s morale is a key determinant of how much he/she can deliver at work. Google has achieved this by creating a conducive and personalized working environment to ensure employees feel relaxed at work, are more friendly to teammates, and are more energetic. One way to boost morale is to create a weekly fun event, have social meeting at work once in a while and, allow people to bring in something personal in their office such as a baby picture or a personal painting. As long as employees can adhere to the company’s moral expectations and stick to the rules, such allowances help employees feel more relaxed to work.
Methodology
Research methodologies applied in this paper included study of books, academic journals, online articles, past projects by different authors, statistics from government and non-governmental organizations on HRM in international organizations. It also included a study of various academic works and research papers on human resource crisis management in international organizations. From books, different academic articles and online articles, it is clear that international organizations are among those suffering the highest level of staff-turn over. To prevent such challenges, many organizations have realized that the most important factors in human resource management today is employee loyalty and retention. These two are best achieved through motivation and appreciation. As a result, a lot of attention is being put on employee satisfaction and reward management.
It is also clear that many organizations are spending a lot of money to ensure satisfaction, safety and motivation of their employees. Communication has proved crucial in many organizations in an effort to have employees air out their dissatisfaction before making a decision to leave. These conclusions and information were collected from reports by research organizations and individual surveys from scholars. Different reports utilized in this paper served very effective and relevant in an attempt to understand the topic’s background. Recent and past books and research papers by different authors were also helpful in understanding different human resource management strategies as far as reward management is concerned. Views from fellow students were also collected to get their thoughts on the subject and how it affects them.
Primary data used in this research project was from a survey conducted by the International Civil Service Commission (ICSC) in 2008. The survey was conducted in cooperation with organizations and staff federations. It was open to all employees in all categories and location. The survey was aimed at informing the various discussions on strategic human resource management, as well as recruitment and retention measures. Involving all employees regardless of their category or location ensured that the ICSC collected comprehensive information representing all employees in the UN Common systems from all borders.
The initial findings of the data focused on three main questions;
- Reasons for joining the UN system
- Reasoning for staying in the UN system
- Potential reasons for employees leaving the system
More than 15,000 staff members participated in the survey. The high number of willing participants demonstrated the level of importance employees attach to the questions listed above.
The survey was divided into three sections. The first section sought to understand reasons that motivated the respondents to join the UN organization at the first place. The second section of the survey was aimed at understanding why the respondents had chosen to stay in the organizations. There were different reasons to choose from varying from financial reasons, career development and relationships at work. The third section of the survey sought to gather information on why the respondents would consider leaving. This part was aimed at helping establish the percentage that had already decided to leave and why.
Another source of information was from an interview with Christine Lloyd, the new director of human resources in UNICEF. Her wide experience in managing human resources made her a suitable candidate for the interview. She has in the past served in big corporations such as Nokia and Shell, and has also served as an executive director of People and Organizational Development at Cancer Research UK. The interview was aimed at understanding how the culture of reward has been appreciated, by studying how the big organizations are able to attract and retain the best employees in the market through various mechanisms.
The interview was used to further establish how this has been taken up in international Organizations such as UNICEF, putting an emphasize on reward management. It further sought the HR Director’s opinion on how through labor unions, organizations are being forced to establish communication channels, a measure that has gone a long way in improving employer-employee relationships. The interview also discussed the role of respecting employees in motivation and how it can be used as a reward mechanism. Creating favorable work conditions is another important tool that was be discussed in the interview, as well as how far international organizations have come in achieving this.
Another significant topic of discussion with the director was employees’ satisfaction and its role in as a reward mechanism. This covered promotions and career development and how they are being addressed in international organizations such as UNICEF. Process improvement was analyzed to understand how by making effort to make a working system better, an organization makes it easier for employees to work. Other important measures in reward management discussed in the interview included the role of a good corporate culture, job enrichment and proper non-monetary compensations and benefits.
Data analysis and discussions will be written from the findings in different academic resources, the survey and the interview. It will review and classify findings from different statistics and the situation in international organizations as far as reward management and employees’ satisfaction are concerned. It will also present statistics and information collected from the outlined sources to get a professional understanding of the topic. The findings will be used to structure an argument and different discussions. International organization’s position and capability to manage reward strategies will also be reviewed, discussed and evidence presented. The results will be interpreted and a more detailed examination given.
Results analysis and discussions
Results analysis
“In June 2008, the ICSC launched the first ever attitude survey of staff serving throughout the UN Common system” (International Civil Service Commission , 2008). Participants in this survey were not limited to any category, location or staff level. The survey will be used as a basis for analysis and discussions in this paper. The survey is divided into three sections; reasons for joining, for staying and leaving. As Scribd (2009) explains, “an organization is as good as its people, and nobody can deny the fact that manpower is the greatest asset of a company”. The author points out that the less human resource turn-over an organization has, the less expenses it incurs in establishing a strong work force.
Recording just how bad the problem is for organizations Scribd (2009) explains that “employee turnover in most organizations is more than 20% a year, enough to make employers lose sleep over the tangible and intangible costs of employee turnover”. The most immediate effect of a high staff turnover level in any organization is inconsistent quality delivery. The customer service-dependent areas of an organization are most affected when employees keep leaving and new ones coming in. Vacancies mean more work-load for remaining employees, a factor that many times harms the quality of the business’ service front. Cunill (2006) further warns that “high attrition rates incur major costs to the company including recruiting expenses, training expenses, unemployment insurance and guest service of a quality less than one has been striving for”. Joining and leaving trends in international organizations can be understood by analyzing the survey conducted by ICSC.
Reasons for joining
Respondents had different reasons as to why the joined the United Nations as an employee. From the survey a majority of the employees chose opportunity to use skills and competencies as the main reason for joining the organization. This was followed by opportunity to serve a good cause, opportunity to work in a multicultural environment, professional growth and a sense of belonging to a global organization, in that order. Interestingly, salary was the number ten reason as to why these employees chose to join the organization. The least of the reasons was interest in working for direct supervisor, followed by work-life balance considerations, and an opportunity to serve in different locations in that order.
Categorizing the results in terms of gender, male employees were more driven by an opportunity to use skills and competencies, while women’s biggest reason was an opportunity to serve a good cause. A bigger percentage of men felt that the opportunity to serve in different locations was a major drive for them, as opposed to women, who would view constant travel as a challenge. Women also considered the location of the job more than men. These results did not differ much when categorized in nationality of the respondents or class of employment. However, it was notable that internationally recruited staff considered the opportunity to serve in different locations as a major motivator. The results can be summarized in the chart below;
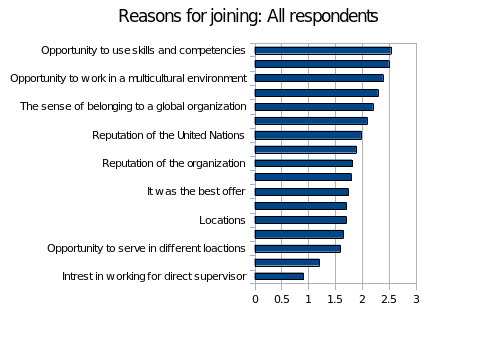
Reasons for staying
Retention in organizations stands as the biggest challenge today. Staff turn-over is not only costly to an organization, it also disrupts operations and affects quality negatively. It is hard to achieve consistency, especially for organizations that offer services and/or deal with clients directly. For any organization to be successful, they need to have a retention program which recognizes the importance of mutual respect between employees and employers, rewards employees appropriately, and motivates employees.
Even though most organizations understand the importance of putting such a program together, they would rather just leave it for another day since it is costly and involving. The results have been an increased cost of employing and training new employees who leave almost immediately, and the cycle continues. Such investments then bare no fruits and instead hurt an organization’s finances and quality.
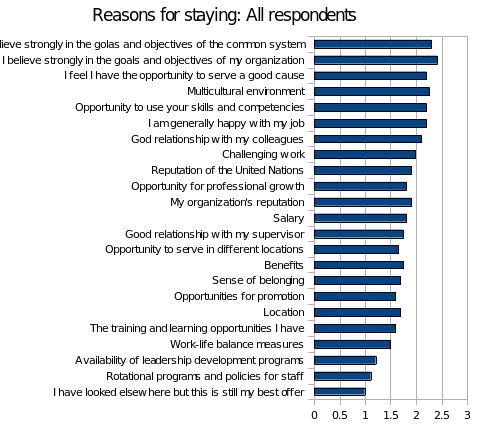
From the ICSC survey, the biggest percentage of the respondents pointed out that they chose to stay because they strongly believe in the goals and objectives of the system. An almost equally big percentage chose to stay because they believe in the goals and objectives of the common system. An overwhelming 70% of the respondents chose to stay because they felt they had an opportunity to serve a good cause, while a percentage close to that mentioned the multicultural environment as a reason to stay. An equally big number pointed out the opportunity to use their skills and competencies as a major reason why they stayed with organization.
As was with reasons for joining, salary was not a big factor and a less number of participants mentioned money as a factor. Only 67% mentioned money as the reason for staying. Other major reasons as to why the respondents chose to stay include the organization’s reputation, a good relationship with their colleagues, they were generally happy with their job, and felt there was an opportunity for professional growth. Rotational programs and policies for staff ranked poorly in this section of the survey, and so did availability of leadership development programs, location and training.
The results did not vary much with gender. However it was notable that men valued the organizations goals and objectives as a reason to stay in a job than women did. Once more location as a reason varied between men and women. Women considered it a bigger reason to stay than men did. Opportunity to serve in different locations was a bigger motivator for men than it was for women. Women on the other hand valued the work-life balance opportunity offered by their job than men did.
International professional at the director level highly valued the organization’s goals and objectives. An approximated 90% of them pointed that as a major reason to stay. International recruited professional hired for specific tasks and duration considered the opportunity to serve in different locations as major reason for keeping their job. They also pointed out that a good relationship with their supervisors was a major factor and consideration on whether to keep their job or not.
The most important reason for respondents to continue working for the United Nations can be summarized as follows.
Reasons for considering to leave
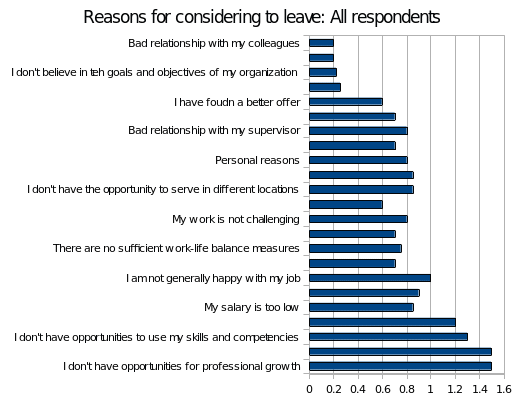
From the survey, only 20% of the participants had seriously considered leaving their organization. 21% were undecided, while 59% had no plans of leaving. 21% of the participants were leaving a headquarter station and 18% just wanted to leave the duty station. Those who wanted to leave had varying reasons for making that decision.
A big percentage of those who considered leaving pointed out lack of opportunities for professional growth as a major concern. Lack of opportunities for promotions was an equally big reason for those who considered leaving. Employees who felt they lacked the opportunity to use their skills and competencies opted to leave and so were those who felt the organization lacked leadership development skills. Unlike in the other sections of the survey, salary was a big concern for those who had decided to leave. A big percentage of the respondents revealed that they would leave if they felt their salary was not enough.
Other possible reasons for leaving include lack of work-life balance measures, lack of new challenges at work, not being able to be with their families, lacking a sense of belonging, a bad relationship with a supervisor, bad relationships with colleagues and personal reasons, among others. From the survey, it is evident that most employees place a lot of value to opportunities for growth, career development and relationships at work.
These results can be summarized as follows:
From the interview, it was established that fostering an environment of growth and learning brings out the best in an organization’s employees and helps them develop confidences. Training and development play an important role in ensuring this happens. In-house training saves an organization a lot of money and makes it easier for employees to open-up, since they are dealing with people they know. Employees are more bound to trust a company that is investing in making them better. The UNICEF HR director agrees with Bratton and Gold (2003) who argue that “such employees are more likely to uphold the business’ best interest and keep an eye on furthering the company’s goals and enhancing its welfare”
The director explained that today, international organizations have adopted a better culture where employees’ are encouraged to develop a work and life balance through more flexible work schedules. Employees retention programs include more holistic packages that include ensuring their welfare is fully considered. More flexible arrangements such as job sharing, part-time jobs and online working are common to ensure that employees have time to cater to their other needs. More organizations are also offering programs that allow employees to do this without much distractions at work.
Many organizations have today realized the need to invest in their employees’ well-being and providing them with good working conditions. Pleasant working conditions encourage a hardworking spirit and motivates innovations. Even though forceful labor practices are no longer in existence in big organizations, they still do happen, especially those set up in rural settings. Working hours in many international organizations still raise questions, as it is not rare to find people working for more than 8 hours a day, many times without extra compensation.
Maintaining open channels of communication is of a big significance when an organization is trying to motivate employees, as well as earn their trust and loyalty. The fastest way an organization can gain its employees’ trust and loyalty is by showing them that it cares and paying attention to their concerns. Organizations today are investing heavily on team building activities, counseling and any other avenue that encourages employees to open up. It is also important for an organization to communicate its vision, mission and plans to its employees, especially plans that affect them directly. It is in the same spirit of communication that an organization will be able to create an environment of inclusion.
“Studies have shown time and again that employees who feel valued, recognized and appreciated are the most loyal” (Girard, 2009). UNICEF’s HR director agrees to this and points out that is has been a point of focus in UNICEF. Performance needs to be recognized and so should good ideas. Employees creativity an inventions should be followed up and implemented where possible. Consulting employees on their ideas also shows appreciation and recognition. Just like Girard (2009) argues “ formal mechanisms for evaluating and rewarding employees need to be in place, and they need to be competitive and in sync with an industry’s norms”. Many organizations today are investing a lot on rewards, and investing more
The director concluded by arguing that organizations with developed programs to promote all titles and levels of employees, have more satisfied employees. Employees are looking for challenges, excitement, growth and fulfillment in a job. If a company does not have the capacity to convince its employees that there is more left for them, they are bound to leave for more challenging opportunities. One way to convenience employees that they are needed is through constant appreciation, recognition and reward.
Issues arising
Issues identified in this study vary from management, work environment, job security, satisfaction to security, just to mention a few. The biggest reason why employees chose to leave or were considering leaving their work place as identified is lack of an opportunity to grow and practice their skills. The same percentage of the respondents also identify the lack of an opportunity to practice skills as a good reason they would leave the organization. The rate of staff turnover is a significant measure of how comfortable or satisfied employees are.
Another important reason why employees leave to leave an organization is lack of sufficient recognition. Surveys conducted in the past reveal that most employees feel like their work is not appreciated. This is common in international organizations due to the large number of employees they employ. The large number of employees make it hard for organizations to recognize each employee individually rather than as a team. pointed out that they felt their work was not being appreciated. Those at the lowest level of the company such as cleaners may feel like the management is treating their work as irrelevant, even though they played the biggest role in ensuring other employees and clients are comfortable. It is therefore important that the management takes the initiative to ensure that every person, regardless of their level of work, is well appreciated and recognized through their managers. It is also important for organizations to realize that regular recognition and appreciation means more than financial rewards to employees.
Reward can be done through ensuring that employees are powerful enough to make decisions and implement their ideas. Lack of influence in an organization is a big problem for employees, especially those at the junior level. Many times, senior managers don’t think this was a big challenge to them. Their positions allow them a chance to participate in most of the organization’s decisions.
Another significant reason why employees feel unappreciated, as evident by the results from the survey, is lack of growth opportunities. Many employees fell that organizations have very few senior opportunities to take care of all of them. They feel that they will not have a chance to grow to levels they desire to, if they continue to stay. As a result, they are always on the look-out for an opportunity outside their own organization. An organization can handle this by having rewards based on performance rather than positions.
Ongoing changes causing instability made it impossible for employees to stay. Changes come in terms of management, reshuffles, change of products and policies. Employees feel that it is hard for them to achieve consistency and perfect their skills in such a changing environment. Poor leadership also plays a significant role in international organization’s high rates of staff turnover. It makes it hard for employees to implement any good ideas they may have, and may force them to implement ideas they don’t agree with.
A considerable number of employee in international organizations feel that security is an important concern for them. This is especially so for those in positions that require constant traveling. Some international organizations such as UNICEF have offices in countries marred by war and political instability. In recent years, terrorists have also tried to target international organizations whose country’s of origin they don’t like, such as the American based organizations.
Labor relations and legal considerations are a crucial consideration for employees when considering a job position. When they are not satisfied with an organization’s regulations, they may easily opt to leave. It is paramount that an organization does not discriminate on the basis of race, sex, religion and other differences among people since it is illegal to do so according to the law. Labor relations in the company must therefore be taken serious and employees must have an opportunity to understand and address various issues that affect them as employees. Some of these issues include their union’s relationship with the management, whether to remain in a union or not, collective bargains, potential contribution of union representatives and the advantages and disadvantages of a represented work place.
Lack of the ability to manage cultural backgrounds may be a big challenge for international organizations. Ensuring good relationships between employees is one way to reward them. When this is lacking, employees are unable to work as a team and they may feel frustrated. “An organization can further encourage good relationships by rewarding team work” (McNamara, 2009). This can also be done through training and team building activities.
One of the questions that international organizations should address to minimize staff turn-over is whether they are doing enough to ensure the comfort of its employees. From past surveys and analysis by different researchers and experts, international organizations have been in the forefront of ensuring their employees are comfortable. Most organizations today prefer to focus on retentaining their employees and developing talents. “The HRM departments in many international organizations act as mentors, coaches, counselors and succession planners to help motivate the organization’s members and build their loyalty” (Heneman, 2002).
However, many of the organizations still face challenges when trying to implement reward management and retention strategies. “Major challenges facing the human resource departments include the ability to manage a diverse body of abilities and use them to bring innovative ideas, views and perspectives to their work without conflict” (Mahoney, 2001). Another significant challenge facing the company’s human resource management is the easy erosion and irrelevance of skills. There are huge amounts of resources being spent on training and skill upgrading in a bid to ensure that its employees remain relevant not only to them but to the human resource market at large. This analysis agrees with (McNamara, 2009) who points out that “retention is one of the biggest challenges facing many human resource departments in most organizations”. Competition for the best skills and talent is on the rise and this creates a constant threat and fear by many organizations for loss of employees. As was established from different articles and literature about international organizations, training and retaining talent is a major focus for most of them.
Employee retention is another significant issue, one that is among the most discussed topics today in organizations. For any organization to be successful, they need to have a retention program which recognizes the importance of mutual respect between employees and employers, rewards employees appropriately, and motivates employees. Many companies understand the importance of putting such a program together but since it takes time and financial resources, many organizations would rather just leave it for another day. As a result they suffer huge costs of employing and training new employees who leave almost immediately, and the cycle continues. Employee retention and increased performance of employees has a huge payoff which is often underestimated by many organizations. It increases productivity, improves employees’ morale, increases turnover as a result of reduced costs of recruitment and training, and trains a business to effectively address employee-related problems.
“In any organization, the human resource management retention strategy is expected to be able to maximize return on investment in the organization’s human capital” (Mehta, 2005). It is also supposed to ensure that the company has reduced financial risks by reducing the cost of new recruitment which can only be achieved by keeping their employees for long. As Sanders (2002) points out, many organizations today are facing major challenges in trying to retain their best employees. The human resource market for both skilled and unskilled workers has become increasingly competitive. For professionals especially, they are constantly looking for better and more rewarding challenges in the now wide market while employees are constantly on the watch for young, developed talent and loyal employees.
With all the money spend on training and upgrading activities, Sanders reinstates that it is imperative for organizations to constantly motivate their work force and keep the work environment as exciting as possible. To retain employees, variable incentives are proving hard and costly to apply and therefore, organizations need a strategy that will last. In international organizations, there is obviously a problem with retention. The fact that their rates are competitive but employees still leave is a clear proof that employees need more than financial rewards and satisfaction to stay.
Applicable reward strategies in international organizations
Flexible hours
“Is there is one free reward that rises above the rest, it’s flexible work schedules” (Heneman, 2002). This rear mechanism has the advantage of attracting a lot of gain and very little pain in the business. Flexible working schedules allows employees spend time with their families, run banking errands, attend to personal issues, make it to a doctor’s appointment, and many other errands that affect an employee’s level of productivity. According to Heneman (2002), “as long as the employee is not abusing the privilege, this can go a long way to building trusting and mature relationships with key workers”.
Making work fun
An employee’s morale is a key determinant of how much he/she can deliver at work. A conducive and personalized working environment is one way to ensure employees feel relaxed at work, are more friendly to teammates, and are more energetic. One way to boost morale is to create a weekly fun event, have social meeting at work once in a while and, allow people to bring in something personal in their office such as a baby picture or a personal painting. As long as employees can adhere to the company’s moral expectations and stick to the rules, such allowances help employees feel more relaxed to work.
Sending tokens of appreciation
Many times, appreciation and recognition are what employees need to find their motivation. For a long time, appreciation has been in the form of money, a promotion or expensive gifts and rewards. Tynan (2011) argues that creativity is equally important when an employer is seeking to keep the employees excited. For senior employees, whose salaries are already big enough, monetary appreciation may not mean much and may even go unnoticed. It is for this reason that an organization should seek personalized ways of thanking and appreciating its employees. For example, an organization can send handwritten notes to its employees, signed by the senior management or partners of the business. The CEO of AdvancedMD consultancy company says that “he has been sending handwritten thank-you notes to employees on a $2 bill and in three years since he started doing so, only one employee has asked if he could spent it” (Tynan, 2011).
Rewarding both effort and success
Even when employees ideas fail, many times they are presented with very good intentions. An organization must ensure that employees don’t stop producing ideas simply because one failed. Some organizations have created awards for best idea that didn’t work. As Tynan (2011) explains, such measures boots an employee’s confidence, stimulate positivity and encourage more innovations. Having trophies or certificates for such accomplishments constantly remind an employee that what they did was good, but they need to keep trying and improve on their innovations.
Publicizing employees’ success
“When employees’ recognition is done publicly, the whole company can share in their accomplishments” (Tynan, 2011). An organization can have employees nominate the best performers, who are then recognized in company events or meetings. This can also be done by having their achievements put in a position where they can be constantly remembered and recognized. A good example of such a measure is having the best achievers nominated for a wall of fame in the company. Their photos can be displayed on a public space inside the company, along with details of what earned them the position. Such measures act as a stimulant for other employees to put in extra effort, improve their creativity and achieve uniqueness.
Training and development
Training offers employees career growth and opportunities. When an organization invests in its employees’ skills, they feel that it is concerned about their development and growth. Another significant HRM reward strategy is coaching and developing leadership in employees. Coaching plays a role in building leaders in a business. In an age when organizations have to deal with overwhelming volumes of information about new strategies, information management is a key strategy for many organizations. Successful organizations have to be able to convert information to valuable knowledge, make wise choices for the organization, and know how to use information in decision-making.
HR managers have the responsibility of training leaders and help them be able to address issues regarding labor. They create leaders through training and coaching. Leaders have to be trained on delegation, authority and responsibility. Recruitment processes play a major role in determining the future leaders of a business. For organizations such as Google Inc., understanding and integrating markets with different cultural and business styles is a hard task left to the HM managers.
Organizational culture
Organizational cultures are determined by the history and ownership of an organization. They may also be developed from the size of an organization and its technology. Goals and objectives are a major determinant of an organization’s culture. The environment which is how things are done and how people relate also determines an organization’s culture. Since organization cultures are made up of leaders’ values and beliefs, a leader may find it hard to accomplish their responsibilities if they are not in agreement with the organization’s culture. Many times, any sector’s leadership will get rid of people who may find it hard to keep up with its cultures.
An organization’s culture substantially affects the ability of employees to execute their responsibilities. It also influences how an organization meets its goals and objectives. A culture of recognition gives employees reason and motivation to work harder. It is also used by organizations as a lagging indicator and allows them give training to people who have had low recognition due to lagging performance. This in turn improves its performance and productivity. A culture of appreciation and mentorship on the other hand ensures that every member of the team is recognized for their good and productive efforts. It also encourages high performance amongst employees.
An organization which has an open communication culture allows employees air their concerns and complains, some of which may be affecting their service delivery. It also allows managers and the executive relate and connect better with every part of the organization including employees at the lowest level. Healthy communication between people on all levels is a good way to source information and allow the executives make more informed decision, considering every person’s needs. A sector which adopts a culture of punishment for poor performance may be able to improve its productivity but will not enjoy the loyalty of its employees since they work from fear. An organization’s culture should therefore provide an environment that allows recognition of performers, as well as the appropriate rewards.
Role of leadership in performance and reward management
There are different types of management styles. The most commonly known are authoritarian, democratic and Laissez-faire management styles. These styles of management determine the area of freedom for the managers and employees. The authoritarian manager does not allow for any forms of negotiation but instead makes decisions and announces them to everybody else. The Laisez-faire type of management is where a manager presents decisions but at the same time the subordinate is free to make decisions and do what they want to. In the democratic style of management, subordinates are allowed to function and make some of the decisions but do so within defined limits.
In this management styles, the difference is level of power. One is more formal and legitimate, one is charismatic while the other is manipulative and exploitative. The level of relationship between the manager and the subordinate varies. Authoritarian management has a one way form of communication where the manager passes orders and decisions to the rest of the team and the decisions cannot be questioned. The laissez-faire allows very little communication between the two levels of management as people do what they want while the democratic form or management allows full consultation and the communication channel is very open.
It is also notable that there are different management perspectives. Classical management is more concerned with scientific management and a pursuit for higher productivity. This form of management is also very focused on how the organization is designed. Behavioral management places much significance on human relations, groups and the social context of an organization. It places priority on organizational behavior and puts more effort on it.
Quantitative management is the mathematical modeling part of management which is more concerned with mathematical modeling and operations management (McNamara, 2009). The main aim of this form of management is to ensure efficiency in the organization. Finally there is the integration perspective of management which deals with systems and the social context of the organization. It is also concerned with how an organization governs its functions.
Different factors influence an organization’s management structure. They include job designs, formalization, arrangement of functional activities, and co-ordination of organizational units (Weiner, 2002). Status, power, role, liking and leadership also play a role in how employees implement their duties and how empowered they are to meet their objectives and targets. When the role of leadership is not recognized is an organization, reward strategies may not be bear much fruit. This is because when employees are not empowered to perform, they are then never going to deliver and be in a position where they deserve or qualify for rewards.
Managing reward strategies
“The best avenues for driving an organization’s performance gains is managing the implementation of its processes” (Weiner, 2002). Identifying the key reward management steps is very fundamental if an organization is expecting to have a successful implementation of its reward strategies. “Reward management is only productive if the results will be aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives” (Weiner, 2002). Key organizational processes are easily identifiable by their level of impact on its success. They are those processes whose success or failure has serious implications on a organization’s goals and revenues. For an organization to succeed in reward management, its implementation and management has to be given priority and has to be right. Its objectives should also be specific to an organization’s unique policies, goals and approach.
Key reward processes should not be too many in an organization. “On average, typical organizations will have ten to fifteen key processes” (Weiner, 2002). Some are external but most of them are internal, meaning the organization has control over how they turn out. The first important step towards reward management is identifying the organization’s baseline in regards to its current environment. The management must know how well the organization plans to execute its key processes before even deciding how they want to go about it. The second step is identifying the most fundamental success factors for the process. These are factors that must be available if the process has to work out and give results. They include things such as employees’ participation, tools for measuring performance and the how the rewards will be aligned.
The other important factor in reward management is the organization and location of the process. Key reward strategies are many times in constant interaction with each other and therefore, they need to be located in a way that makes interaction possible. For example, a reward strategy that targets performance should also be able to identify the employee’s consistency, attendance, and participation in team work. Today, reward models are constantly changing calling for very flexible locations of key processes. “The need for instant process execution in the current fast pace business environments calls for consolidation, standardization and management of cross-functional processes” (Bratton and Gold, 2003). Since organizations may have many similar processes being implemented at the same time, there is need for standardization to ensure high efficiency rate of execution.
A key step in reward management in an organization is automating them where possible and affordable. Automation reduces chances of human error and saves an organization a lot of time. Many organizations avoid automation due to the high costs involved without realizing that the investment will save them much more in future. At an age where consistency is key, automating key processes allows an organization to have consistent quality. For example, an organization should have a system that automatically records what time employees get to work or leave for lunch by having them swipe cards. The system should then be able to award points based on that. A company can also have a system that records deadlines for projects and managers can update it when they are delivered.
Many times key reward processes in an organization may be a new idea that requires high levels of expertise. Training employees is therefore very key in ensuring a successful implementation and management of key processes. Employees need to understand what the organization’s goals are, what role their functions play in realizing them, and how as an individual an employee impacts the success of failure of a key process. Involving employees in key reward processes ensures that every person in the organization feels appreciated and puts their all in ensuring success. It also ensures that nobody feels discriminated against when they are not rewarded, since they understand how the process works.
Every idea, whether small or big, should be respected in an organization. After employees have submitted their suggestions, they should go through vetting and then the company develops them, allowing employees feel part of the process. Such initiatives will also many times save an organization a lot of money on research, as it is amazing how many good ideas employees can come up with when given a chance.
Another important step in reward management is learning to be flexible and embrace change. An organization must be able to identity those processes that are not working and easily redesign them. Inefficient processes can cost an organization a lot of money and even drag the other processes. Once an organization has baselined its reward strategies, it should be able to identify those processes that are either not working or are taking too long and costing the organization much more than it can bear. For smaller organizations, or for reward strategies that require a lot of investments, such as constructing a child-care for employees, key processes can be implemented one at time. This way, on organization is able to bear the costs and management becomes easier with less processes being handled at one time.
Technology is important for effective management of reward strategies. “Technology influences management and workforce in organizations by analyzing production, resource impact, routine to non-routine operations, structure impact, industry impact and work impact as well” (Bratton and Gold, 2003). It allows the managers together with the work force match the resources available with technology through different approaches. The management is able to run operations more easily by changing techniques and processes to better and modern ones. Employees are able to do their work more effectively and meet their goals without much struggle.
Finally, reward management cannot not be complete without putting in place performance measures. These measures should be a continuous process to help an organization establish who and what is working, and what is not at an early stage. They also help an organization identify where to make improvements or put more investment. Performance measurements include scheduling operations and setting targets. It also means measuring an employee’s performance on more than delivery. A good employee must be able to meet their targets, do it on time, be creative, and be supportive of his/her colleagues as they try to achieve their targets.
Overall project plan
This research paper was done in a duration of 1 month
Ethical considerations
There were a number of ethical issues that arose during the research. One of the most fundamental principle that I followed in research is voluntarism participation. The principle requires that no participant should be coerced to participate in a research or give false information. A participant must also give consent before their identity is revealed if there is a need to do so, although for such a project, anonymity would be applied.
During a research project, ethics also demand that the process must not subject the respondents to any danger or harm, a factor I took very seriously. A researcher is supposed to apply the principle of anonymity to protect them from consequences of revealing the information they do. It is also the respondent’s right to be treated with respect and dignity during the study. These ethical issues are expected to be adhered to when the organization is conducting its research.
Limitations faced in the exercise included language barriers since international organizations employee a large number of foreigners. This made it a bit difficult to collect views in preparation for this study. Lack of cooperation from some respondents also stood as a challenge and there were fears that they may not give accurate answers or take too long to respond. Conducting a research project is an expensive activity and finances posed as a challenge. These challenges were addressed by conducting any investigations in English which is a common language, and using translators. There were also comprehensive explanations about the scope of the research to respondents to ensure they understood the objectives and minimize resistance. I also ensured a proper costing and allocation of funds was done before the task commenced.
Conclusion
“Human resources management is the function in an organization charged with the responsibility of implementing policies and strategies related to management of individuals who comprise the work force of an organization” (Bratton and Gold, 2003). In any organization, “the human resource management strategy is expected to maximize returns on investment in the organization’s human capital, and at the same time do so in a way that creates minimal financial risks” (Bratton and Gold, 2003). For an organization’s HRM efforts to pay returns, “the human resource department must align the supply of skilled and qualified individuals and capabilities of the workforce with the organization’s plans to maximize output and secure future success” (McNamara, 2009). Human resource functions have to be performed and implemented effectively and pragmatically.
As McNamara (2009) argues, “successful organizations are becoming more adaptable, resilient, quick to change directions, and customer-centered”. The working environment today is constantly changing and demands strategic planning and organization. Technological innovations such as Human Resource Management Systems have made it easy for organizations to handle HR information.
Human resource management features personnel administration, organizational management, industrial management and manpower management. People in an organization are a key determinant of how successful it is going to be and how long it will last. As the labor markets get more and more competitive and the need for talent becomes more obvious for optimum performance, human resource managers are facing major challenges as the try to get the best in the market, retain them and ensure they have consistent performance.
Gaining competitive advantage has become a major challenge for organizations today. As markets get larger and more competitive, strategic human resource management is a key recipe when formulating effective strategies. Employers must be able to establish what works in their human resource management efforts and what doesn’t, to eliminate those strategies that waste time and cost the business. Another major challenge facing businesses is ensuring talented employees stay motivated and disciplined. A good employer must be courageous enough to let go of employees who affect a business’ results negatively. If such qualities lack, holding on to employees simply because they are talented may be costly for an organization.
Ensuring open communication channels between employers and employees is the first step towards identifying problems and implementing solutions. Incentives, recognition, rewards, and strict discipline measures are key strategies towards ensuring that employees deliver, keep in line with a business’ timeliness, and stay disciplined. When such measures lack, the business’ efforts to have the best talent in the market may not be rewarding.
In SHRM, “reward management involves the analysis and effective control of employee remuneration and covers salary and all benefits” (Serco, 2007). It aims at assessing the nature of rewards available for employees, the expected results and actual results. There are three parts of reward management namely; the purpose, return on investment and the most appropriate places to apply it. Reward management constitutes the financial reward aspect which incorporates processes and procedures for tracking market rates, measuring job values, designing and maintaining pay structures, paying for performance and giving employee benefits” (Heneman, 2002). However, it is important to note that reward management is not just about monetary compensation. It is also about other non-financial rewards which boost an employee’s confidence and provides motivation. Key issues to address in reward management include how to manage external and internal competitiveness and equity, as well as how to reward individuals and promote team work as well.
Reward management addresses the most appropriate performance management processes for a business, how power should be devolved to the managers level, and how they can manage their own reward strategies while staying within the corporate policies to allow every employee is reached. It also addresses how to structure and design job evaluation schemes. These puts into focus performance measures and what they are based on.
The most significant challenge for organizations so far has been how to motivate those who have reached the highest level of career possible in the organization. It is for this reason that motivation should go beyond money and positions. The other challenge that organizations have to address is how to ensure increased reward translates to improved performance. It is also important that an organization ensures employees are rewarded for both their inputs as well as outputs. Making employees recognize and appreciate non-monitory rewards is a key challenge that organizations have to face, especially in a culture where employees are used to the monetary form of of compensation for a long time.
In today’s scenario, there are various management trends available for international organizations. As Armstrong, Duncan and Peter (2010) explains “more organizations today choose to develop increased awareness of the need to treat job measurement as a process for managing relatives, which, as necessary, has to adopt to new organizational environments and much greater role flexibility”. Others choose integrated pay structures that cover every employee regardless of their position. Team pay is a common trend today in most organizations as they more importance is being place on teamwork. Other trends include performance awards and more sensitivity to functional markets to enable organizations retain talented employees.
In any big and busy organization such as Google Inc., there are obviously problems facing employees and that is why they some don’t stay despite the fact their salaries are at a level that is acceptable in the market. The fact that their rates are competitive but a few employees still leave is a clear proof that employees need more than financial rewards and satisfaction to stay. The fact that the organization has been able to retain more employees recently after implementing more non-monetary reward strategies, means that they are more recognizable to employees.
Through the research, there are a number of factors which employees consider as major stressors. Incompetent managers is identified as a major occupational stressor. From the research, many employees pointed out that management is a key challenge for them. The pointed out that their seniors are too demanding and some completely incompetent to manage responsibilities. When employees don’t have faith in the management, it is hard for them to build an open relationship with them where they can easily air out their concerns. It is also hard for them to trust in a system led by someone who does not seem sure of what they are doing.
Big organizations such the United Nations, UNICEF and others, should ensure that hiring is on the basis of qualifications and not on how applicants relate with the managers. Friendship and family must not in any way interact with how human resources are run. In many occasions, there has been cases where employees claim that managers tend to favor those who are friends with them during promotions and other employee related interests. As a result, disgusted and frustrated employees would rather leave than work under supervision of an incompetent person who seems favored by the boss.
Another factor that kills motivation for employees at their work place is managers who lack motivation and a drive. When the junior management is not motivated, it is hard for them to keep the rest of the team motivated. A good number of employees point out that working with managers who lack a drive is too challenging for them. It is the business’ responsibility to ensure only qualified managers are employed, and relevant training is constantly conducted to ensure consistency in leadership skills.
Work overload is identified as a big killer of motivation in international organizations. Overworked employees as a challenge arises from the fact that some organizations are unable to retain their employees. Since there is always a shortage in some departments, some employees have to do more than they should to cover up for the shortage. Overworking employees means they are unable to plan their schedule well and even when they do, it is hard to keep up with it. It also means that employees may not have any time for recreational activities or skill building activities such as training.
Recommendations
“Human resources management is the function in an organization charged with the responsibility of implementing policies and strategies related to management of individuals who comprise the work force of an organization” (Serco, 2007). In any organization, “the human resource management strategy is expected to maximize returns on investment in the organization’s human capital, and at the same time do so in a way that creates minimal financial risks” (Serco, 2007 ). McNamara (2009) further explains that “the supply of a skilled workforce must be aligned with the organization’s ongoing and future business plans to maximize return on investment and to secure future success” (McNamara, 2009). Human resource functions have to be performed and implemented effectively and pragmatically. Measures such as legal procedures and ethics have to be taken into consideration to allow for implementations in a manner that retains the respect and support of the workforce.
One major significant benefit of SHRM is “designing performance incentives plans with the intention to continuously motivate employees and thus improve customer service in a dynamic environment” (Bratton and Gold, 2003). Implementing appropriate SHRM techniques in an organization enables a business build a productive and efficient team, and work with them for a long time to ensure consistency. International organizations should seek the best SHRM techniques after a further review of their need and problems.
Uncomfortable conditions such as being overworked have featured in the research as the biggest reason why employees’ level of motivation is low. The trend is a significant challenge for many organizations. International organizations have not been left out and some still have more than 50% staff turnover annually. As a result of being unable to retain the best employees, many organizations end up with employees who portray several counterproductive behaviors. Lack of motivation also causes high levels of absenteeism. As a result other employees are forced to take up the responsibility of the absentees, making the problem even worse. Asking employees to do more than is their responsibilities regularly is a problem on its own especially when they are not given extra payment for it. Part of reward management is ensuring that no employee suffers for other employees’ mistakes.
The human resource manager needs to act tough to ensure that such habits are not tolerated in the business. This can be done by ensuring the business has clearly formulated rules which every employee has to go through and understand when they join the business. Discipline can also be achieved by encouraging team work so that employees are considerate of each other and the what they put each other through by being absent. Team work is best established through training and team building activities to encourage more open relationships amongst employees.
An organization’s human resources are key in its success. Getting the best in the market is not enough and organizations now need to go a step further to retain them. This saves them a lot of money spent on recruitment and training new employees. It also allows organizations to achieve consistency in their products, as well as maintain a good reputation in the markets they serve. Employee loyalty can only be achieved by putting in professional strategies that allow employees’ continuous satisfaction, strategies which may be costly and involving but which have a huge payoff at the end.
International organizations should also utilize other HRM strategies such as training. Training is aimed at preparing individuals to keep their skills updated and ready to undertake higher levels of work when chance arises. It also provides a possibility of performance change. Training helps the organization retain their pool of human resource and stay up-to-date with current and relevant skills in the market. It also makes employees feel cared for.
Regarding incentives and compensation, the research revealed that Google Inc. uses positive rewards to motivate employees, and negative indicators to discourage under-performance and indiscipline. The company gives multiple targets to each employee to allow a bigger opportunity to the employees for earning at least some part of the performance incentives. This has worked well as a motivator and has also worked successfully as a retention tool. These results support one of the company’s strategies which is “to use incentives and rewards to identify high performers who then become eligible for the succession pipeline for key positions in the organization” (Google Inc., 2011). In the organization, such tools have been broken down into different categories. They have been divided into performance based targets, with each department setting its own specific performance related goals. According to the senior managers in the organization, the category of individual targets is based on individual achievements and constitutes up to 30% and 70% for senior and junior level employees respectively.
Most employees agree that core elements of job satisfaction are not necessarily based on financial factors. Compensation is an important element in their satisfaction and includes other things other than money. However, monetary compensation is equally important and the participants point out that employers must ensure that they pay employees what they are worth, and do the best to stay within the market rates or higher than that. The survey revealed that a big percentage of the participants think that employees should be rewarded for performance and not for seniority. Human resource experts argue that a percentage of their earnings should be based on successful completion of duties.
Reward can also be achieved through developing favourable social setting of an organization. The social factor of an organization is an important factor in any organization. It is the basis for relationships, communication and team work. When they are lacking, any efforts of reward management in an organization may not bear fruits. It is important that employees of an organization feel a sense of belonging in it. An organization which is open to different social factors is bound to develop more loyal employees who feel as part of a family. Social factors in an organization provide a common purpose. Different social factors in an organization include relationships which may be employee to employee relationships, employee to managers relationships or manager executive relationships. These kinds of relationships are more often than not official but when a social element is introduced to them, they become a good source of information among people from the different levels of an organization.
The other socially rewarding activity is team building. This can only be achieved if there are healthy relationships happening between people from the different levels that need team building. Team building can be among employees of the same level or can be between senior and junior employees. Today, organizations are willing to go to great levels and to put in enough investments to enhance team building. Team building is important in improving an organization’s performance in that it encourages communication and it creates friendship and loyalty towards each other. In so doing, everyone does their best at their level to make it possible for someone else at a different level achieve the desired results.
Group trainings can also be considered a social motivator. It allows people know each others strengths and weaknesses. Working with this knowledge makes it easier for employees to identify who needs help and support more. It also makes it possible to establish whose strengths can be utilized most to achieve the desired results in a team. Training together also allows people from different teams know each other, share knowledge and broaden their knowledge about the organization.
Other social factors which occur within organizations is the relationship between people of the same team or department. Healthy relationships between people in a team allow them to watch for each others back in different projects. When one is sick for example, the other people are aware and can help them finish up their duties easily when they resume or have it done by one of them. This translates to very strong teamwork where when one person is missing, work does not have to be so badly affected. The degree of interaction between workers or unit of workers being supervised does matter in an organization’s team work.
In today’s scenario, there are various management trends available for international organizations. As Armstrong, Duncan and Peter (2010) explains “more organizations today choose to develop increased awareness of the need to treat job measurement as a process for managing relatives, which, as necessary, has to adopt to new organizational environments and much greater role flexibility”. Others choose integrated pay structures that cover every employee regardless of their position. Team pay is a common trend today in most organizations as they more importance is being place on teamwork. Other trends include performance awards and more sensitivity to functional markets to enable organizations retain talented employees.
Whichever reward strategies that on organization chooses, it should be able to create external and internal competitiveness and equity in the organization. It should not allow room for some employees to feel discriminated against. It should also address team rewards programs. Most employees may not be able to create uniqueness as individuals but do so everyday through teamwork. Reward strategies and structures must therefore, identify the role of individual employees in creating the best team or departmental results.
Reward strategies in an organization should be able to identify which performance management processes are appropriate for it. An organization must be able to identify its needs and implement strategies that address them. For example, if an organization is faced with many absenteeism or discipline cases, it should set up measures that discourage such trends through positive and negative rewards for such behaviors or the opposite.
Devolving power in organizations is a great way to ensure every employee benefits from the implemented strategies. Devolving powers ensures that managers can manage their own reward strategies while staying within the corporate policies. They are then able to reach employees under them at the departmental level. The human resource management department may not be able to identify, recognize and reward those employees who they have little contact with. Departmental managers can then be used to identify top performers and reward them at their level.
A reward management strategy should address issues such as how to motivate those who have reached the highest level of career possible in the organization. Employees at the senior level can easily feel like there is nothing left for them to achieve in the organization. Set strategies must therefore take this into consideration and be creative enough to reach them. It is also important that an organization reward strategies ensure increased reward translates to improved performance. Most strategies, though non-monitory, will cost an organization finances to implement. As a result, they must have a reasonable level of return.
“How jobs are designed and evaluation schemes structured play a very important role in determining the level of success in an organization’s reward strategies” (Heneman, 2002). Jobs designs should allow employees to accomplish their goals and targets. Undefined job responsibilities make it hard for employees and organizations to measure success. Evaluation schemes must also ensure that employees are tested on all relevant performance levels. They should test target deliveries, punctuality, employee’s relationships with colleagues, and discipline levels among others.
Reward strategies must also that ensure employees are rewarded for both their inputs and outputs. They should also ensure that employees recognize and appreciate non-monitory rewards. This can be achieved through training and developing organizational cultures that support and advertise non-monetary rewards in the organization. This is to ensure that employees appreciate rewards offered to them, and convert them to performance.
Reference list
Armstrong, M., Duncan, P. and Peter, R., 2010. Evidence-based reward management: Creating measurable business impact from your pay and reward practices. Philadelphia PA: Kogan Page Limited.
Bass, B.M., 1985. Leadership and performance beyond expectations. New York, NY: The Free Press.
Benner, P.E., 2001. From novice to expert: Excellence and power in clinical nursing practice. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
Bratton, J. and Gold, J., 2003. Human resource management theory and practice 3rd ed. London: Bath Press.
CNN Money, 2007. 100 best companies to work for 2007.
Covey, S., 1999. The seven habits of highly effective people. London: Simon and Schuster.
Cunill, O.M., 2006. The growth strategies of hotel chains: Best business practices by leading. New York: Wisely & Sons.
Deutschman, A., 2005. Can Google stay Google.
Fombrun, C.J., Noel, M.T. and Mary, A.D., 1999. Strategic human resource management. New York: Wiley.
Girard, B., 2009. The Google way: Revolutionary management strategies behind Google’s success: How one company is revolutionizing management as we know it. San Francisco: No Starch Press, Inc.
Google Inc., 2011. Let’s work together. Web.
Gratton, L., 1999. Strategic human resource management: Corporate rhetoric and human reality. New York: Oxford University Press.
Griffeth, R.W. and Peter, W.H., 2001. Retaining valued employees. Thousand Oaks, Calif.: Sage Publications.
Hammonds, K., 2003. How Google grows…..and grows……and grows, Fast Company Magazine, 69, p. 74.
Heneman, R.L., 2002. Strategic reward management: Design, implementation, and evaluation. Greewich, Conn.: Information Age Publications.
Hoffmann, S., 2006. Classical motivation theories: Similarities and differences between them. Norderstedt: Druck und Bindung publishers.
International Civil Service Commission (ICSC), 2008. Results of the global survey on recruitment and retention. Web.
John, M., 1999. Role of motivation theories. New York: Routledge Publishers.
Kotter, J. and Heskett, J., 1992. Corporate culture and performance. The Free Press.
Mahoney, J., 2001. Leadership skills for the 21st century. Journal of Nursing Management, 9 (5), pp. 269-271.
McNamara, C. (2009). Human resource management. Web.
Naidu, V., 2011. Reducing employee turnover in hospitality [Online].
Scribd, 2009. Strategic HR planning at Google Inc.
Serco, 2007. Reward management. Web.
Spark Organization, 2010. Slave labor conditions in Saudi Arabia.
Stewart, G., 1995. Staff turnover: An analysis of casual factors that contribute to the attrition and retention of experienced nurses and midwives and Auckland Healthcare Services Limited. Auckland: University of Auckland.
Tavistock Institute of Human Relations, 1999. Staff turnover. London:H.M.S.O.
Taylor, S., 2002. The employee retention handbook. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development.
Towes, D., n.d., An investigation into whether organizational culture is directly linked to motivation and performance through looking at Google Inc. Birmngham: The University of Birgmingham.
Tynan, D., 2011. 25 ways to reward employees (without spending a dime). Web.
Weiner, B., 2002. Human motivation: Theories and research. Newbury Park, California: Sage Publishers.