Introduction
Generally speaking, there are four ecological forces, which are the spirited environment, the universal environment, stakeholders’ expectations and the interior environment, have an effect on the supermarket retail industry.
If we analyzed then we come to know that the organization I chose for this task is called J Sainsbury plc. J Sainsbury plc is single of the world’s the majority important retailers, in concert a fraction in the lives of 15 million customers a week. John James and Mary recognized Sainsbury Supermarkets in 1869. Sainsbury’s Supermarkets employs in excess of 138,000 people. Of these 70 per cent are fraction time and 30 per cent are full occasion 58 percent of generation are women. A large Sainsbury’s Supermarket offers in excess of 23,000 products – 40% of these are Sainsbury’s own make. Sainsbury’s serve nearly 10 million customers at 432 stores throughout the UK each week. Of these provisions, 17 are in Scotland, nine in Wales and seven in Northern Ireland. Almost 60 percent of their stores are in town-centre or edge-of-centre position. Sainsbury’s assignment is to be the customer’s first choice for food, delivering foodstuffs of outstanding excellence and great service at a spirited cost through operational faster, simpler and together. The Sainsbury’s group comprises Sainsbury’s Supermarkets Ltd, Sainsbury’s Sava centre, Sainsbury’s Home base, Shaw’s, Star marketplace and Sainsbury’s Bank.
Shaw’s Supermarket has been completely owned by J Sainsbury plc because 1987 and previous to that was part owned from 1983. Shaw’s serves in excess of four million clientele a week at 168 provisions in the six New England states of the USA. Sainsbury’s Bank opened in February 1997, the primary bank to be opened by British supermarket. It is combined business venture owned 55 percent by J Sainsbury plc and 45 percent by Bank of Scotland plc, contribution handset banking 24 hours a day. Home bottom was founded in 1979 and opened its primary store in 1981. In 1995 the Company bought Texas Homecare and the obtain food were rehabilitated to the Home base arrangement. Home base serves over 1.5 million clientele a week at 297 stores all through the UK employing 17,000 populace of which 12,000 are part-time.
Sainsbury’s Business Main Activities. Every business has one or additional business action. The core business movement is the most important movement for the commerce and typically generates the main quantity of income. Sainsbury’s has a core commerce activity of advertising food and unpreserved items. But it also sells flowers, newspapers and magazine, tobacco products, alcohol and a number of better stores, pharmaceutical foodstuffs.
According to the expert analysis it in addition operates as a bank – customers can unlock a savings explanation with Sainsbury’s and pay in or withdraw currency when appointment a store. The aim is to give ‘one stop shopping’ where clientele can get the whole thing they need under one crown. Sainsbury’s Supermarket sells their possess brands as healthy as other brands. In adding to a wide range of excellence food and grocery products, a lot of stores present bread parched on the premises, delicatessen, animal protein and angle counters, coffee shops, restaurants and gasoline stations. Sainsbury’s today becomes the primary UK supermarket to open a mobile phone repair. The service, called Sainsbury’s one is the merely mobile phone service in the state to guarantee customers the most excellent deal by means of a unique scheme which checks calls next to every standard tax from side to side the UK’s four mobile phone networks and charges the lowly price obtainable. Sainsbury’s expanding their commerce on-line, ornamental the ways clientele can supermarket and store by means of them.
Background
According to the expert analysis the overall emphasis on non-price characteristics and the family member importance of the dissimilar characteristics in all countries gives opportunities for retail managers to distinguish their firms away from pure cost competition. These customer responses have been important in determining the advertising strategies of the food retail corporations and have allowed a variety of strategies which variety from a stress on reduction prices, to pure excellence and repair considerations. These planned directions are powerfully held up by promotional programmes which emphasise the characteristics of the food rather than the foodstuffs which are stocked.
In Hughes (1994) in order is obtainable which shows that food retailing firms are ranked figure one, nine and eleven in terms of their publicity expenditure in the middle of all firms, which make obvious the overall significance of promotional activities to these firms. These behavior allow retailers to expand their own ‘brands’ or images which are self-governing of the brands that are sold, and are likely to be the source of control which food retailers are reputed to put forth in excess of manufacturers.
Purpose of the study
In recent years food retail firms have pursued strategies which have provided customers with more and more diversified opportunities for purchasing food. The discussion on top of has shown that these developments have been made possible by the wide range and changing nature of consumer supplies. Firms have recognized the possibilities and have urbanized suitable strategies to struggle in the marketplace put.
The idea of competitive strategies is clearly urbanized by Porter (1980) and has turn out to be an accepted move toward for analysing the method in which firms within a manufacturing struggle to attain marketplace share or enhanced presentation. Porter identified a numeral of general strategies such as a focus approach, a differentiation approach, or a low cost approach which were argue to be the most probable to be successful for a exacting firm. Because this theory is urbanized as a general move toward there is no reason why the general strategies should not be practical to the food retail manufacturing.
One study which attempt to do this is the find out by Alexander and Veliyath (1993) where data is composed from 500 food retailing firm in the USA. It was exposed that firms possess strategic individuality which could be linked with one of these move toward, but that these are not obviously related to straightforward characteristics such as amass dimension or retail arrangement.
Buying Behavior and Sainsbury’s Responding To Customer Needs
Sainsbury is operational hard to revive their make, rising new formats to set of clothes their clientele changing shopping habits. Sainsbury’s recapturing their fervor for food and operational to improve the repair they give to clientele. They also urbanized a variety of amass formats, such as Sainsbury’s Local and Sainsbury’s Central, to meet clientele need in exact site. Sainsbury’s continue to give confidence their colleagues to employ their own person talents in the place of work for the benefits of their clientele.
Aim/Hypothesis
The aim of this project is to examine how Customer perceive the Food Market and how HR influences the Customer. Moreover, during the last years, food ratio in UK has suffered some decreases. This project has also the purpose to find what measures the Sainsbury has taken in relation to the Customer, in order to achieve customer satisfaction and to creation of customer loyalty.
The hypothesis is that some problems exist between Customer and Food Market. There is not all Customer satisfied with the measures that Sainsbury has taken
Objectives
The main objectives are:
- To find out the employee’s perception regarding the Food Market.
- Identify how the relationship between Customer and Sainsbury it’s perceived to be beneficial for both sides.
Dissertation structures
Here is a brief summary of what the following chapters are going to include, which will help the readers to have an idea of what they are going to read in each chapter. The dissertation will be divided into four sections:
The Literature Review
In this chapter existing information from secondary research is going to be given like books, journal articles, reports and electronic databases.
The purpose of this chapter is to give the knowledge for the overview of Sainsbury and how company is working in the food market. This chapter is going to help the author to improve the knowledge from the research subject and to create the appropriate questions in order to give the focus on the research objectives.
The Research Design
After gathering the existing information (Literature Review) the next chapter has the purpose to offer a concise description of the research design and methodology.
The author is being used both qualitative and quantitative research for more complete image of the research situation. The methods that are going to be used for the purpose of this research are questionnaires with close questions for the Customer of the hotels and interviews with open questions to the two HR managers of the hotels.
Analysis
After the research is being completed, with the help of some electronic methods like ‘record’ they will give the analysis of the questionnaires and also the analysis. The data will be presented in this research.
Conclusion
Based on previous analysis and with the combination of the literature review the conclusion will be throwing.
In the final chapter the author is going to compare the research questions he had at the beginning of the research with the final results. Moreover he will give some recommendations from the results and the analysis, which will help the hotels to be improved.
Literature Review
The purpose of this chapter is to provide a summary as well as an interpretation from research findings of the secondary data, by books, journal articles, reports, electronic databases and websites in order to drown the literature. In addition, an in-depth analysis of the roles and purpose of the Food in UK markets in general will be included, how this trade assists in the organization and how food product helps the organization strategy. Moreover, the research is concentrated on the Sainsbury in UK. Finally, some information about the Food retailers in UK will be given.
This chapter is very helpful in increasing the knowledge relative to the studying area since the results and the findings of the primary data will be related with the literature review. Therefore, the knowledge from literature review is going to provide a more professional research that will focus on the purpose of this research. Also, the purpose of this is to offer an overview of significant information published on the topic in order to narrow down the research questions to a specific, suitable form.
Strategy
The policies of Tesco and Sainsbury’s are talk about in three parts: Business-Level Strategy, Corporate-Level and global Strategy, and Strategy Expansion.
Business-Level Strategy
Business-Level strategy is concerning the spirited strategies of an association and its choice. In the container of Tesco, it adopts a cross strategy as its spirited strategy. Tesco seeks simultaneously to attain differentiation and inferior price compare with its competitors. On Tesco’s website or in its amass, it shows which crop are cheaper than other retailers in new pair of days. Tesco also launched a Client Champions repair where 800 Tesco Champions greeting clientele as they enter the stock up and help with any inquiries or concerns.
Corporate-Level and worldwide Strategy
Corporate-Level strategy is a planned decision about the range of an organization. Due to the mature markets and physically powerful opposition in the UK retail industry, Tesco develops the business diversification. Tesco provide not only grocery, but in addition non-food products. At present, Tesco has salaried more attention to the non-food crop. In the third quarter 2005, non-food sales sustained to see double-digit sales enlargement in the epoch. In 1997, Tesco diversify to offer the non-retailing commerce of personal money and retail sales of gasoline. ‘Tesco.com’ was natural and Tesco entered the earth of on-line trading in 1999. The globalization of advertise and rivalry result in the expansion of the global strategy in association. Tesco operates around 2,318 provisions worldwide, around 1,878 provisions all through the UK and others in the relax of Europe and Asia.
Strategy Development
The technique of strategy expansion can be alienated into three types: interior development, attainment and joint expansion.
To construct and develops its possess capabilities, Tesco realized that the completion of new technical advances to the company’s procedure and operations. It established the electronic retailer-supplier communiqué systems and automatic replacement and stock control structure.
Acquisition is also Tesco’s main strategy of organic growth. For instance, Tesco extends its market split in the UK following its gaining of 862 T&S expediency stores, and in Poland following the buy of 13 HIT stores.
Tesco’s joint venture reflects its promise to the customers’ needs, for instance, the joint ventures by means of the Royal Bank of Scotland offers Tesco Personal money, and with Esso and BP provides Petroleum at its Tesco articulate and large arrangement stores.
Sainsbury’s
Comparing with Tesco, Sainsbury’s strategy in the three aspects be able to be catalog as go after:
Business-Level Strategy
Sainsbury’s is the oldest food retailer in the UK. Different from Tesco’s cost aware, Sainsbury’s more concerns itself as a far above the ground quality supplier. In arrange to win the belief of clientele, Sainsbury’s shows the procedure of food manufacture and the technique of choice fabric on its website. In fresh years, due to drastic opposition on retailer, Sainsbury’s also pays more concentration to the price.
Corporate-Level and worldwide Strategy
The same as Tesco, Sainsbury’s also adopts commerce diversification. Subsequent the prototype set by Tesco, Sainsbury’s increases the numeral of non-food appearance it stocks. Around 80 provisions have devoted non-food spaces, and 2,500 new non-food lines are at the there in place. Selected food also stock clothes and children’s products. Furthermore, the company is breach specialist heat shops in key outlets, capitalizing on Sainsbury’s good standing for fresh producing and additional up advertise lines.
Due to the information that Sainsbury’s is be short of market investigate, it has not gained achievement in the global market. Sainsbury’s once recognized its amass in USA and Egypt. However, it is ineffective so that Sainsbury’s had to end in both countries.
Strategy Development
Internal growth. In order to get better the operation organization, a two-day training route has been carried out by Sainsbury’s. There were over 1,000 managers from provisions and middle teams, including the Board attended the route. Furthermore, each store colleague conventional client service preparation to get better service excellence.
Acquisition. Sainsbury’s acquired 14 stores from Morrisons (13 Safeway recognized provisions and one Morrisons store) which were positioned primarily in the Midlands and the north of England. It will be obliging for Sainsbury’s to get bigger its market share.
Joint development. Due to the failure of straight asset in the US market, Sainsbury’s tried to lend a hand with Shaw supermarket to go into the US market.
Closer Relationship with Customers
Sainsbury’s Reward Card goes as of strength to strength, and previous year they issued a new seem card with particular promotions and additional benefits obtainable with third social gathering companies. Their interactive Reward Point terminals characteristic in numerous stores offering clientele discounts connecting specifically to their usual shopping behavior. Sainsbury’s faithfulness clubs and magazines are one more way they present customers in order, recommendation and particular offers on substance they know clientele care concerning. During the year Sainsbury’s additional the Drinks Club to their winning 0-5s Club and Pet Club. Their brilliant new brand and Making Life flavor Better strapline has given a new and reliable look to their entire infrastructure.
Working Environment
Sainsbury’s sustained their programme of alter aimed at releasing the talent of their colleagues, serving them to center on the customer, and restoring their arrogance in operational for Sainsbury’s. It’s obvious to them that new and thrilling working surroundings add to this pride. This will produce as they add to the pace of their programmed of mounting and extending stores. It is in addition why they’re eager to tell everyone about their recognized successes, such as organics and prepared meals, their evidence in protecting the surroundings and behind farmers, and new initiatives, such as their modernisms in e-commerce.
Pastel Analysis
Inside these forces, the major factors are as follows:
- Customers. As for the supermarkets, gathering the customers’ wants be supposed to be leave into the primary place, since the natural world of supermarket industry is market-orientated.
Furthermore, with the development of communal economics, customers have additional choice of shopping methods than previous to. They can decide the lowest price and the majority suitable way to acquire. Meanwhile clientele have become fewer loyal to a exacting make they prefer wider variety of crop in supermarket. - Substitutes. This research focused on this truth that the danger from the substitutes of supermarket industry can not be unnoticed. There are three main substitutes live in the supermarket retail industry. First comes to be the online store. At there, online amass has been developing fast. Many customers favor this shopping way to be fewer time-consuming and more suitable the second one is expediency store (24 hours). Clientele can buy stuffs any occasion they desire. The third one is catalogue shops such as Argos and Index. Compared with supermarket, catalogue shops don’t require big front supermarket and example products, based on this price effectual, they offer smooth lower cost to the clientele.
- Technology. New technology has been worried as a significant factor nowadays. Supermarkets show products and family member services on their possess website, which extremely based on professional knowledge, also it improves operational efficiency and more price effectual.
Additionally, with the growth of Internet, online shopping has turn out to be the fraction of our life. E-commerce commerce provides the well-organized message media flanked by clientele and dealer. - Suppliers. The UK supermarket division has a low competition, market is under enemy manage by a number of main supermarkets, such as Tesco, Sainsbury, ASDA and Morrison, resultant in the authority of supermarkets suppliers is low in the UK. However, as the growth of other store formats, such as expediency store, catalogue supermarket (Argos), the suppliers’ faithfulness is fewer than previous to so supermarkets retailers should disburse more attention to it and expand their worldwide strategy to get more suppliers.
- Government. Government is one more factor influence the supermarket industry, since the tax and health & safety system of government absolutely have an effect on the supermarkets strategy. Furthermore, some overseas governments defend their local supermarket industry, so as intended for the UK international supermarket retailers such as Tesco, the entry fence is comparatively far above the ground.
According to the situation of whole supermarket industry, supermarkets retailers separately decide their competitive strategy, and improve their advertising performance and organizational civilization to be in procession with strategies. The marketing presentation and managerial society of supermarkets are guided by their strategies, on the other give, the strategies are unbreakable by them, in arrange to be more spirited and react quickly to the change of the entire industry.
Marketing
The graph underneath demonstrates the marketplace share of UK supermarkets. From the diagram, we can see that Tesco has the major market share, which is concerning 54%; compared with Tesco, the market split of Sainsbury’s is 29% less than it. Their dissimilar market shares are mostly resulted by their own advertising mix, which will be analyzed as subsequent.
Product
Tesco
- UK Food. Tesco provides a wide variety of products, which can be geared towards far above the ground excellence products, or those with a physically powerful style element, of on the other hand the manufactured goods assortment may be wide, contribution value-for-money to a wide part of the customer marketplace.
- Growing Market for Non-food. The rapid development in Non-food expansion, such as clothes, health and loveliness, with grocers’ share of the non-food market set to get bigger to 12.7 percent this year next to 12.2 per cent in 2004. Tesco sources fashionable goods from ‘grey markets’ exterior the EU and resell them at inferior prices than those optional by manufacturers, which obtain sales to Pounds 14.4b in 2005 alongside Pounds 13.5b previous year.
- Developing Retail Services. With the multidimensional, slot in aspects of services, Tesco launched broad variety of retail recognized such as bank, insurance, monetary services (credit card, loans, mortgages, and savings), phone and petrol station armed forces. The use of product and services help Tesco to gain it spirited benefit in the whole supermarket industries.
- International Expansion. Now, growth occasions in its customary markets are becoming limited, as a result, international growth and diversification out of groceries have turn out to be middle to the Tesco’s strategy. Tesco chooses to get bigger non-food on the internet; it has lately launched its own make of mobile phones, expanding into the Japanese marketplace by trade the Tokyo-based C Two-Network, rising profits by 13% in fiscal 2003.
UK Food
Sainsbury’s and UK Food
- UK Food. Sainsbury’s ‘Taste the Difference’–is the way retailers are looking for to improve their brand individuality and develop sales opportunities to a variety of purchaser objective groups, also give consumers with convenience crop of high quality and greater than before positive reception of dissimilar cuisines.
- Growing Market for Non-food. Around 80 stores have devoted non-food seats and 2,500 new non-food appearances are now in put. Selected stores also stock clothing and for kids products. Furthermore, the corporation is breach specialist heat shops in key outlets, capitalizing on Sainsbury’s high-quality reputation for unmarked create and more unharmed lines.
- Developing Retail Services. Compared with Tesco, Sainsbury’s too provides wide variety of services, such as depository services (involving 12 types insurances), monetary services, but additional worried about with senior standards, especially its online release services. It believes that supermarket goes up by charitable customers excellence crop.
- International Expansion. If we analyzed then we come to know that the online- shopping amenities has enabled Sainsbury’s to transport large electrical appliances, melody and books, farming utensils, etc, straight from warehouses. Consequently, customers from the earth can expediently look for their favorable foodstuffs online, which also abridged company’s price.
Price
Since of the Oligopolistic Opposition, the supermarkets are responsive to every other’s prices. Thus moreover Sainsbury’s or Tesco always considers about its adjacent competitor’s price, and decide its own price to hold up its Price Adjustment Strategy.
Tesco’s cost is relatively inferior to Sainsbury’s, while Sainsbury’s senior cost is based on its higher excellence. However, both of them create discount and particular offers to draw more customers and hold up their own Cost Adjustment policies:
Tesco
- Cash Discount. The cash reduction of Tesco is connected to its Loyalty CardClubcard. Customers can obtain 1.5 pounds vouchers when they gather 150 points of the Clubcard. (The equivalent price is 150 pounds).
- Quantitative Discount. Tesco slowly makes some quantitative discounts, such as pay money for two, obtain a free one’, ‘buy three for two’ and so on. It powerfully attracts clientele who are price-sensitive.
- Promotional Payment. As for Tesco, it frequently uses the ‘buy one obtain one free’ as the major promotional payment. Compared Tesco with Sainsbury’s, the previous one launches this promotional payment more frequently than the concluding one.
- Time Discount. During the Christmas, New Year and additional festivals, all supermarkets slash prices to increase sale, including Tesco. However, in every day living, not every one supermarket frequently has the occasion discount apart from Tesco. For instance, as for the bakeries such as Apple Pie, its cost is cut from 99p to 40p following 6pm. It is helpful to add to sales.
- Local Segmented. Tesco has open many superstores in other country, so it segments the cost in conditions of the local situation. That is, different cost in different state.
Sainsbury’s
- Cash Discount. Sainsbury’s has launch its Reward Card countrywide and clientele can consume in a lot of stores by means of the Nectar Card, such as Vodafone, Debehams, etc. Clientele can get 2.5 pounds cash reduction when they use 250 pounds, say; they gather 500 points in Nectar Card. It is additional supple than the Clubcard of Tesco.
- Quantitative Discount and Promotional Allowance. Sainsbury’s also makes a number of discounts in the supermarket, particularly following Sainsbury’s relocation its place and regulate its price strategy. However, it can not draw as many clientele as Tesco.
Promotion
Both Tesco and Sainsbury’s do promotions from side to side more than a few ways, such as publicity, sales promotion, community relations and backing, E-marketing and New Media, and a number of examples where two company obtainable well will be exposed:
Tesco
Firstly, Tesco is most significant the online shopping supermarkets in UK. It has diversity range of foodstuffs counting non-food products, and all of which be able to be bring to clientele home. The customers have to login the Tesco’s website with faithfulness card which can evidence customer’s details, so Tesco managers be able to use the data to analysis sales consequences and also let somebody know the clientele by the correct products advertisements. This endorsement can help executives to confirm whether the ‘non-food’ strategy is appropriate for companionship.
Another instance is, Tesco created in-store TV network in the big store, which will be used to endorse Tesco itself and third-party foodstuffs, also it can give advice to clientele. This new media helps to teach and inform customers, and supply convenience. Therefore, it very a great deal improves the endorsement of products, particularly for the non-food manufactured goods foreword, such as the sales of Video player or digital camera.
Sainsbury’s
The Sainsbury’s announcement is greatly contributed to its industry presentation, and it is widely recognized by regulars. Sainsbury’s has remarkable go back from announcement of ‘27.25 pounds for each 1 pound’ spend on it anywhere centering on the chef Jamie Oliver’s presentation. This reflects that Sainsbury’s has efficiency communication with clientele from side to side advertisements. Furthermore, the clean food, which Jamie Oliver often brings in the advertisements, pronounces a far above the ground excellence level. This supports the elevated excellence strategy set up by the corporation.
A different move toward is taken in a previous learn by Lewis and Thomas (1990) who used information from UK food retailers to identify planned groups in the division. The hypothesis of planned groups is to recognize collections of firms which follow comparable strategies inside a particular manufacturing. The power of this move toward is that the nature of the strategies is not prescribed and there is the possibility of having different types of strategies in dissimilar industries. Arithmetical analysis of key planned variables that explain the behaviour of each firm is used to recognize the exacting groups.
The weakness in this move toward is that frequently there is little sympathetic about why any particular group or planned approach would be victorious, or whether there be supposed to be any difference between the presentation of the groups. The worth of this exacting learning is that the authors were able to show that characteristic planned groups do exist, and perhaps additional highly, that there were no important differences in key presentation measures such as go back on assets flanked by the collections.
Table 6 shows a number of the results from the find out by Lewis and Thomas and shows how some of chief retail firms that existed in 1986 can be owed to seven planned groups by means of clustering techniques. The groups recognized differ by additional than the numeral of provisions, store size or arrangement which the dissimilar retailers used. The information demonstrates how firms use dissimilar strategic policies such as the figure of food lines stocked, growth of own brands and publicity expenditure, to differentiate their policy from opposing firms. It is unlucky, but perhaps important that these groups are not extremely stable, as numerous firms have compound and perhaps distorted strategy as the information was composed in the 1982-86 period.
This research focused on this truth that the theory of intended groups would suggest that firms expand approach which permit them to struggle by occupying characteristic segments of the advertise, and that these policies are supported by take-over or merging behavior. The fact that there was small significant difference in the productivity of the firms can be a mirror image of the competitiveness of the manufacturing and the fact that no exacting strategies enjoy an complete benefit.
It is unlucky that the measures used in this instance do not completely explain the degree of the strategic growth which has occurred. Although publicity expenditure is old as a variable, the natural world of that advertising is able to have a major impact on the kind of customer and the relative stress on factors such as excellence and price is not reflected in the events used. In the next discussion stress is placed on some of the key move in the direction of which the retailers in the UK marketplace have used to expand these strategies.

Consumer Segments
Even though there is not a considerable quantity of information openly obtainable, it is obvious that exacting stores are additional attractive to dissimilar types of customers. The distinction stuck between the reduction food manacles such as Kwik Save and the elevated repair retailers such as Marks and Spencer are understandable and the continuation of specialised outlets such as Iceland display the amount of specialisation possible. The UK marketplace is arguably the nearly everyone differentiated of the food markets approximately the world, even though examples of the dissimilar strategies exist in approximately all countries. For this cause, the subsequent thorough conversation is listening carefully on this exacting advertise.
Perhaps the majority obvious technique of considering the dissimilar customer segments is to seem at the customer profiles. Recent information in print in super marketing (1993) shows the variety of age and profits distributions of the different customers. The information show that the firms can be separated into four groups of customers depending on their period and profits levels (Social Groups). For instance, it appears that the young, high profits customers are more probable to supermarket at Safeway or Tesco while the older, high profits customers are more probable to supermarket at Sainsbury, William Low, or Waitrose outlets. An still better increase of age differences seems to exist in the middle of the lower income customers (less than 40 per cent of customers in the A, B, C1 profits categories), and an instance is known for the Gateway sequence which has two amass types. At the Food Giant provisions, two-thirds of the income comes from the 16-44 age collection, while at the Gateway provisions only one-third comes as of this collection
If we analyzed then we come to know that these information show the variety of consumers which employ the stores, but there are also theatrical differences in the method in which they utilise them. One more article in Super Marketing (25 June 1993) describes how the average expenditure per client can vary from UK stlg7 to UK stlg30 per client and how the faithfulness of those clientele can vary. Stores such as Sainsbury’s have 60 per cent main shoppers (defined as those who use more there than wherever else) and create up 90 per cent of the income for the chain. Other opening such as Safeway has fewer than 50 per cent main shoppers who explanation for 82 per cent of the sales. Their less important customers, who explanation for 20 per cent of clientele, make up 14 per cent of auction.
This dissimilarity in loyalty and spending apply to outlets which provide to together high and low profits consumers and reflect the difficulty of the relationships which exist for customer loyalty in this advertise. The same piece of writing presents information which shows the altering market shares sandwiched between each sequence for an eight week epoch. The change reproduce the trends which have urbanized over a figure of years, with the self-governing and co-operative outlets behind to both the large multiples and reduction firms, and by means of the discounters mounting the best ever.
According to the expert analysis the reduction stores are viewed as a comparatively new occurrence in the UK market, but they are seen as the most quickly growing type of amass. Some firms such as Kwik Save have been established for a figure of years, but there is rising opposition from abroad firms such as Netto and Aldi which are attempting to get bigger into the advertise. The discount firms have greater than previous to their advertise share from 8.8 per cent in 1992 to 9.8 per cent in 1993 (Eurofood, March 1994) and the cost pressure that has urbanized has resulted in rather lower prices intended for all solids.
Table 7 presents information which illustrates the cost changes that have occurred in new years, and highlights the tapering of price ranges flanked by the reduction firms and the main manifold firms. It can be seen that the family member prices have fallen considerably as the complete prices have dropped with the spirited pressures. The averaging of the information cover the degree of price dissimilarity which can occur. For example, the cheapest of the discounters had prices which were 10 per cent lower than the standard discounter and 16 per cent inferior than the standard of the multiples. The information presented show that whilst all prices contain been prejudiced by the growth of discounters, there is motionless substantial dissimilarity in prices and obviously consumers are ready to pay for factors other than cost. Other firms contain differentiated themselves by contribution option services. For example, Iceland’s promotional material pressures their emphasis on frozen foods, which is an eccentric manufactured goods mix. Of the foodstuffs they offer 60 per cent are ice-covered, compared with 10 per cent in a conservative store and they merely have 23 per cent of their variety as grocery items compared with the usual 51 per cent (Iceland’s Annual Report, 1991).
At one more extreme, firms such as Marks and Spencer have specialised by means of an emphasis on very far above the ground quality foodstuffs sold beneath their own make. These food foodstuffs are usually obtainable in mixed stores which sell a broad range of clothes and additional products. Specialised stores such as discounters and the other instance known, show the niche marketing chances which have been recognized in the UK food advertise.
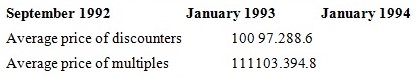
It is possibly the instance set by firms such as Marks and Spencer which has led to the growth of firm’s contribution their own brands of foodstuffs in competition with nationwide brands. The enlargement in this crop has been greatest in the UK market, and is seen as single of the major opportunities for firms to institute a retail picture or overall brand individuality for the firm.
Own Brands
As has been renowned previous in this Report, there has been a stable growth of brands which are possessed by retailers themselves. Food retailers have urbanized foodstuffs, or purchased foodstuffs from manufacturers with the tag of the retailer clearly shows. There are a range of dissimilar strategies which have been used to endorse these products in person markets, but the enlargement has been most in the UK.
Table 8 presents information which shows the degree of the penetration of these confidential brands. There are obviously differences flanked by the markets, but they are continuing to produce at a somewhat slower rate than they had in new years. It is usually conventional that the growth of these brands has been rather slower in the USA marketplace and this is normally credited to the lower heights of retail concentration and the better level of manufacturers. These finishes are arguable, but it is obvious that the enlargement of the foodstuffs is intimately connected to the complexity of the marketing strategy which the retailers follow.
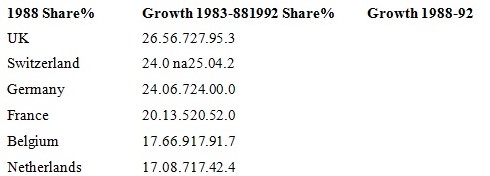
Across the markets where such approaches have been urbanized, a range of option types of own foodstuffs have been urbanized each with different planned objectives. These comprise:
- Generic Products. In a number of markets, such as the USA, these were the original type of own-brand urbanized. The object seems to have been to create a range of products which were usually obtainable in plain letters with little retailer and no producer labelling, that would be obtainable as a reduction manufactured goods. The lack of labelling was most probably future to minimise the disagreement with obtainable brands and to keep away from using the store person’s name on reduction foodstuffs.
- Retailer Brands. Perhaps the widest variety of retailer brands fall into the universal group of foodstuffs which feature usual packaging, but contain the retailer name quite than a product or a manufacturers name on the wrap up. Such products are more often than not pleasingly obtainable and are designed to struggle on excellence terms with national brands, even although they would usually be cheaper. There does appear to be growing anxiety that some of these crop may be take on designs that are an effort to simulate the look of the leading make names, and creator have lobbied administrations to keep away from such behavior (see Eurofood, March 1994).
- Retailer Selection. In a number of cases it is suitable for the retailer to add the retail name to an obtainable manufacturer’s product. This is probable in a situation anywhere there is substantial competition in a marketplace and the retailer is identifying or ‘selecting’ a creation with the meaning of guiding the consumer’s option. Perhaps the most common instance is with wine and a number of the recognized perishable crop such as creature protein or cheese.
- Retailer Labeled Produce. A closely linked group of crop is those that would usually not contain a create at all. These products such as animal protein, vegetables and outgrowth make up a high amount of a retailers income and are not usually branded by dealer. They are also products which contain a far above the ground amount of product unpredictability and can have a clear power on a retailers picture (see Progressive Grocer, January 1994). It has been commonplace for a lot of years for such foodstuffs to be obtainable with retailers price tags, if not wrapping. It is probably this put into practice (which can be seen as a shape of excellence declaration) that forms the basis of a great deal of the present retail branding.
- Retailer Value Lines. These foodstuffs can play a alike role to the ‘fighting brands’ that have conventionally been old by manufacturers to weaken competition or new entrants to a exacting marketplace. The planned objective is to weaken competition without moving the brand image of obtainable manufactured goods ranges. In this case the retailer’s make and packaging would recognize the manufactured goods as a contemptible or value item which might compete with discount crop even although it would have the retailers person’s name displayed.
- Retailer Sub-Brands. Another new development in possess branding is for retailers to expand new make names which are not recognized with the name of the solid and attempt to imprison a share of markets where there are usually strong brands. In a number of cases the ‘brand’ may wrap a solitary creation, such as Sainsbury’s ‘Novon’ detergent or it may wrap a wider range of products such as ‘St Ives’ for ASDA or ‘St Michaels’for Marks & Spencer. The precise planned value of attempting to make these divide brands is not obvious, but they contain been winning for a lot of firms and reproduce the knowledge which some retailers have in make development and advertising.
The examples given on top of show the sophistication of the manufactured goods expansion of retailers and the variety of options which have been explored in the growth of their own foodstuffs. There is often apprehension about the degree to which these foodstuffs are brands in their own right and to what degree they are simply extra products which imprison a share of the marketplace, often through cost competition. This difference is not seen to be significant as long as the foodstuffs play a obvious role in the growth of the approach of the retailer. A recent learn by the market analysis part of the Natwest Securities group give some interesting example of the degree to which these strategies can power market share and price strategy of the firms (Focus UK Food Retailing, 1993). For instance, Table 9 shows the marketplace shares of dissimilar types of foodstuffs in the UK detergent marketplace. It can be seen that even though the own sticker share of the total marketplace is low, it has full-grown considerably. It is also significant to note that the fastest rising own brand creation is the Sub-Brand urbanized by Sainsbury.
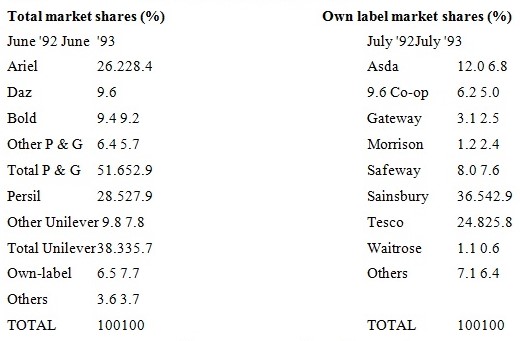
Using information from AGB Superpanel the same learn derived in order concerning the increasing marketplace share of retailer foodstuffs, both for budget appearance and the retailers own-label foodstuffs. These information show the theatrical increase in the sales of a number of retailer based foodstuffs over a two-year epoch.
It can be seen that for the foodstuffs considered, the most important or nationwide brands have all lost split. Of the retail label foodstuffs, ten of the thirteen careful have lost marketplace share in the epoch, however, all of the financial plan brands have increases market contribute to. To some degree these data reproduce the increasing cost opposition which has urbanized in the UK marketplace over this era, but it does show the strategic power that products of this kind can have on a marketplace for exact foodstuffs.
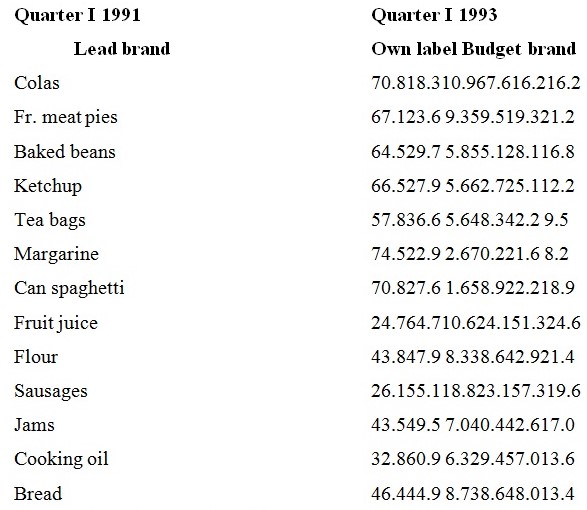
Although the nationwide brands were exposed to have the maximum share of the marketplace for the majority of the products exposed in this study, the total split of the retailer-owned brands is elevated and increasing. One anxiety that the revise raised is that the retailers’ proceeds from the total group could be decreased from the enlargement of the financial diagram brands. Through a sequence of hypothetical examples it was argued that though the income margins on the own-label were senior than for either of the other harvest, the inferior profit margins on the financial plan brands could decrease the entirety profits. The definite income limitations on the individual foodstuffs are not known, other than there are understandable and considerable price differences flanked by the different manufactured goods ranges.
Table 11 shows the family member prices of some person foodstuffs from Tesco and it is obvious that the prices of the financial plan lines are frequently fewer than 50 per cent of the most important make names. As might be expected, the possess label products are more changeable, in cost but are still below the most important brands. This cost difference flanked by manufactured goods lines might vary considerably flanked by firms depending on the plan that is chases.
Although the growth of retailer controlled crop is greatest in the UK marketplace it is obvious that it will expand in the other markets and will show a similar level of variety and difficulty.
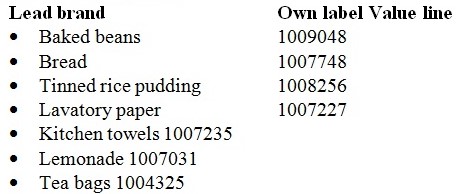
One of the common concerns is to identify the product categories where there is likely to be higher levels of diffusion of confidential labels. It would come into view that the circumstances would depend on the type of possess brand development and the natural world of the there marketplace. For example,budget lines and general products are more likely to happen for staple or Key Value Items (KVI) which are the customary focus of price-based promotions. Retailer assortment are more likely to happen where there are a wide variety of products with small make management, or perhaps where there is small real brand growth at all.
The areas where retailer labels are probable to occur is perhaps additional hard to identify, but present are a diversity of situation which could provide a suitable surroundings. The subsequent reasons are take on from a new appraisal (Eurofood, September 1993):
- Where most important brands charge ‘excessive’ price premiums.
- Where there is complexity in adding value to product items.
- Where high edge products are not identical with the picture of the retailer.
- Where foodstuffs and prices are simple to compare for performance.
- Where there are far above the ground publicity costs for the marketplace leader.
Organizational Relation
A good organizational family member can contribute to the managerial presentation, so both Tesco and Sainsbury’s follow to construct a good association inside and exterior. Here organizational family member is alienated into three fields: Organizational civilization, Recruitment & Assortment and Development & Knowledge.
Organizational Culture
Here are two aspects of civilization: the organizational civilization and the civilization outside the association and particularly when a corporation operates its commerce internationally, it has to become accustomed the restricted civilization.
As the managerial culture, it has been careful within the background of corporate strategy and organization arrangement (Scholz, 1987). So both Tesco and Sainsbury’s have their physically powerful managerial culture along by means of their corporate policies.
The Edgar Schein’s copy culture is the most extensively discussed one. It considers the association culture inside terms of three heights.
First level – Surface manifestations, such as artifacts, words, bodily explain and slogans:
- Artifacts comprise tools, machines and clothing.
- Both Tesco and Sainsbury’s introduce the self-checkout scheme in 2002, in order to put aside staff expenses and brings expediency to clientele.
- Tesco and Sainsbury’s arrogance themselves on their employees uniforms with workers names on.
- Language includes together specialist technical language which is related to the commerce and general identification choices.
- Sainsbury’s does not have workers and has colleagues in its place.
- Tesco and Sainsbury’s do not contain shoppers. in its place, both have clientele.
- Physical layout
- Tesco has a strong idea of group.
- Sainsbury’s does the similar, and every store uses the carroty color as the dye of Sainsbury’s.
- Slogans are old both for client advertising and to inspire employees.
- Tesco – Every small helps.
- Sainsbury’s Before – Making life flavor better. Now – Try amazing new nowadays.
Organization values
These values are said to give a common way for all employees and strategy for their behaviors Tesco’s worth. No one tries harder for clientele:
- Understand customers improved than anyone else is vigorous, ground-breaking.
- Use our mutual strength to transport matchless purchaser care.
Treating populace the way we would similar to be treated:
- Trust and Admiration others, and Support others – praise additional than disapprove of.
- Share knowledge, Enjoy work and study from knowledge.
Sainsbury’s value:
- Get Even Closer to Customers.
- Be Where Customers Want to Shop.
External culture
Internal society is not the only subject that Tesco and Sainsbury’s be supposed to deal with, but also the outside civilization. External culture is in concert a more and additional important position in companies’ oversea growth. International supermarket is supposed to adapt the different local society in the world. Tesco and Sainsbury’s usually expand their abroad market by the method of gaining or joint venture. So they are able to save the work of preparation staffs to become familiar the local society.
Tesco’s continuous growth of overseas processes has been of growing significance, and this is borne elsewhere by the rising number of abroad employees over five years (1999-2003). The number of employees was greater than before by 149% (22,142 of day 1999 to 55,131 of year 2003). Staff levels abroad are set to carry on in line with present growth plans, plus the affirmed aim of by local manpower.
Recruitment
Both Tesco and Sainsbury’s take on the flexible and effectual policies to draw and keep staff to merge their present spirited ability.
Tesco
As the marketplace head in UK, Tesco mostly uses the means of to come publicity, local agency and recommendations from obtainable employees to employ. Meanwhile, Tesco chooses the new employees from side to side online video conferences which good turn the rapidest competence as well. In adding, unlike other common business, the interview in Tesco will be conduct by the line boss in sort to build up the loyalty by means of the recruits plus help to create choices.
Sainsbury’s
Sainsbury’s pays major attention to the fair action of its staff. The most centers are to deal with the candidates by means of its Equality and Diversity strategy at all times. That strategy is framed to employ and select populace without discrimination and injustice as well as aspire to choose workers with the diverse aptitude and character. Especially, disabled candidates might obtain the chiefly advantaged consideration that provides much additional chances for them to work as a widespread populace and show their capability.
Development & learning
Both Tesco and Sainsbury’s attach significance to Human reserve growth to manage with the environment modify, which is not merely the “training cost”, but in addition the “speculation”.
Tesco
Tesco not merely considers much concerning the interaction by means of clientele, but also considers of the communication among employees. The words “Share information Enjoy work and study from knowledge” have been careful as a conviction of Tesco. Tesco believes that the knowledge and information of worker is an important reserve for company, and it be hypothetical to be in use benefit of.
Sainsbury’s
HRD implies knowledge will be considered as a strategy in association. In a knowledge organization, strategy can come out from employees’ events.
As a consequence, Sainsbury’s regards the communication with clientele as a extremely important subject. It has a dedicated side called Customer Insights. Every month the purchaser Insights section talks to over 4,000 people in arrange to understand and obtain earlier to clientele and it interviews clientele in their home about foodstuffs as well. With the communiqué by means of customers, it has probability to learn form the difficulty of its present foodstuffs and services and increase expansion.
Evaluation and Recommendation
From the values communal in Tesco and Sainsbury’s, we are able to see that Tesco definitely emphasizes the association between populace inside the association, and it writes into the system. Sainsbury’s also thinks a great deal of the relations flanked by employees in put into put into practice, but it doesn’t emphasize this summit to the employees.
As for the subject of recruitment, Sainsbury’s strategy for disability populace may perhaps benefit the civilization and endorse the standing of Sainsbury’s. Tesco may believe this issue throughout the recruitment. In adding, the proposal for Sainsbury’s in HRD is that it be supposed to give confidence the interaction in the middle of employee, which can endorse the competence and belongings of knowledge.
Discussion-Overview of Functional Areas
All businesses have a reason, so do the person who works there. Workers have a exact set of duties to take out and they may have a work title that indicates come again? They do, in other words, it states their purpose. In a Sainsbury’s association, populace with the similar type of jobs works jointly in functional areas. These are the regions, which relate to the major functions, which have to be carried out inside the business, and all have a exact purpose. As a industry Sainsbury’s has to take out a range of purpose, which includes:
- Human Resources.
- Finance.
- Administration.
- Production.
- Marketing and Sales.
- Customer Service.
These are not the merely functions that get place in Sainsbury’s industry. They also carry out other functions, such as excellence control and investigate and development. Each useful region in Sainsbury’s operates to hold up the business’s aims and objectives and a variety of behavior goes on in every one. Sainsbury’s business view as a structure or, more specially, as an overall structure that can be viewed as a sequence of subsystems. A structure processes inputs to produce production. The manufacture process in Sainsbury’s takes place inside distinct boundaries. What in fact goes into the manufacture process will be drinkable to make sure only attractive inputs are accepted. For instance, excellence control in Sainsbury’s ensures no wreckage of glass enter the manufacture system. Current capital then combines with rudiments such as equipment and buildings, and flow from one constituent to another element crossways links flanked by the rudiments.
Input filter System boundary Output filter:
- OUTPUT.
- INPUT.
- Waste output.
A production structure in Sainsbury’s: the input/ processes/ output method.
The structure in Sainsbury’s is forbidden by a user, who puts in the main inputs and the secondary inputs. The main inputs are the settings (control parameters) that manage the process of the structure (e.g. the speed of the line, the hotness, the excellence standards and the hours worked etc). The less important inputs are the present capital.
INPUTS Process approved out by useful regions in Sainsbury’s LAND:
- Labor Good or service.
- Capital.
- Enterprise.
- Waste.
Systems and subsystems
In order to take out its operations connecting the use of factors of production to create complete goods or services. Each of the functions in Sainsbury’s organisation works in agreement to procedure resources productively into concluding outputs:
- Finance Production HR Marketing Administration R & D.
- Sainsbury’s organisation prearranged along useful lines Management of the purpose.
The organizations of Sainsbury’s businesses are accountable for location the objectives of the commerce and drafting ready plans, e.g:
- Deciding what products is to be selling in what markets.
- Calculating the quantity of money that will be wanted.
- Deciding what capital (premises, people, and apparatus) will be desirable.
The Human Resource function
Human possessions are concern with the workers who employment for the organization. The human reserve organization or personnel purpose of Sainsbury’s organization covers a variety of behavior. It is responsible for the hiring and dismissal of employees, for staff preparation and growth, and for commerce with matters connecting to manufacturing relatives.
The subsequent are the person resource functions:
- Manpower preparation and incentive.
- Recruitment and selection.
- Training and Development.
- Industrial relations and working relationships.
- Staff records.
- Wages/payroll.
- Staff welfare.
Research and Development function
According to the expert analysis in the Sainsbury’s organisation, investigate and development (R&D) has strictly profitable functions – to additional the company’s industry aims by creating new and improved products, improving ready processes and mounting new ones, and providing expert recommendation to the rest of the corporation and to patrons.
Quality Control
Sainsbury’s organisation working quality controllers to ensure the quality of complete product, either by investigative each finished piece of writing or by random example. In a number of cases excellence is checked by a machine connected to a computer, which determination test that items have been artificial with particular tolerances. Total excellence organization (TQM) is a system second-hand by most organisations. Standards and method are set for each phase of production. Each process or team is responsible for examination the excellence of it does possess labor.
Information Flows within Sainsbury’s Business
Every business needs in order in arrange to plan, run and manage their operations. In order in Sainsbury’s is processed from input data. Most in order in Sainsbury’s necessary data to be taken from a figure of foundations. E.g:
- To decide how a great deal stock has to be prearranged. A supplier will require knowing how many customers they are probable to have for any given manufactured goods. Sainsbury’s therefore gather and contrast data from sales and store records.
- To find out how a great deal money is owed by clientele to the commerce and how extended it is likely to be previous to these bills will be salaried In arrange to do this Sainsbury’s take information as of the sales and financial secretarial structure.
- To find out how a great deal money the corporation owes to its creditor. To do this Sainsbury’s take data from purchase and monetary secretarial systems.
Raw data in Sainsbury’s is contribution into the system for dispensation and this is then returned to the consumer as information. Raw information refers to natural facts, which in themselves have no exacting significance other than the information that they stand for single facts connecting it a specific body. Once they have been processed these facts turn out to be information on which significant business decision bottoms
Recommendation-Marketing mix
Undoubtedly, Tesco has compressed Sainsbury’s productively in a lot of aspects, such as global expansion, non-food foodstuffs and so on. consequently, the Tesco should stay and get better its competitive compensation to maintain its most important place. On the other give, Sainsbury’s should create greater attempt on its marketing combine to be more spirited. For example, inside the aspect of global expansion, Sainsbury’s be supposed to do wider variety of market investigate, in order to appreciate the local culture and costume the taste of restricted clientele.
Report
The aim of this account is to analyse the present Marketing Mix of Sainsbury’s, and to labor out how it would be attuned to satisfy the potential of financial services?development as well as the steps in use when considering the open of the financial armed forces foodstuffs. This report is bottoms on my own investigate by reading Sainsbury’s annual account, its web place and the discussions in the middle of the experts and professor, along with bodily going to Sainsbury’s supermarket and receiving some on paper materials.
The mission of Sainsbury’s Supermarkets is to be the customer’s first option for food, delivering crop of outstanding quality and huge service at a spirited cost through operational faster, simpler and jointly.
Evaluation and Recommendations
Sainsbury’s strategy has been very much changed throughout the previous ten years, and it has obtained some development. For instance, Sainsbury’s has raised its split from 15.6% to 15.9% till June 2005. However, there are deficiency on its plans:
- Strengths Weaknesses.
- Strong brand equity.
- Innovative financial services business.
- Store network Declining profitability.
- Lack of international presence.
- Supply chain disruptions.
- Opportunities Threats.
- Expanding product offerings.
- Store expansions in the UK.
- Favourable trends in the favorite care market Intense cost competition.
- High regulatory oversight.
- Restaurants business picking up in the UK.
Sainsbury’s can appreciate the business environment and planned ability of itself according to the SWOT analysis. Consequently, Sainsbury’s can employ the SWOT medium (Figure 2-1) to expand its strategies.
The SWOT medium for Sainsbury’s (Figure 2-2):
- Internal factors.
- External factors.
- Strengths(S) Weaknesses(W).
- Opportunities(O) SO Strategic options.
- Generate options here that use strengths to take benefit of opportunity WO Strategic options.
- Generate options here that obtain advantage of opportunities by conquers weakness.
- Threats(T) ST Planned options.
- Generate options here that use power to avoid threats WT Planned options.
- Generate options here that reduce weaknesses and keep away from threats.
According to the analysis of Sainsbury’s strategy, a number of recommendations are hoists as follows:
- The brand of Sainsbury’s is documented well by UK customers and it has a strapping store network. Therefore, Sainsbury’s can no-win situation the opportunity to get bigger the number of stores. It is obliging for it to win additional marketplace split.
- Owing to the positive trends in the pet care marketplace, Sainsbury’s can add to its profitability depending on the growth of pet mind market.
- A key subject in Sainsbury’s is the cost. Tesco has replaced Sainsbury’s and turn out to be the main supermarket in UK depending on the low cost. Consequently, currently, Sainsbury’s regards to both excellence and price. Due to the good presentation of process in Sainsbury’s, it can depend on cut the price to reduce the cost.
- Sainsbury’s pays additional attention to its food and it advocates ‘food fan. However, recently, restaurant commerce has developed fast. Most of people prefer leaving out for banquet. Obviously, this occurrence has prejudiced the strategy of Sainsbury’s. Consequently, Sainsbury’s should expand manufactured goods contributions to keep away from this danger.
The Marketing Mix
Since early in 1996, the City was criticizing Sainsbury’s for allow Tesco to obtain so far ahead of the pastime in terms of client service, loyalty and apparent cost competitiveness. Sainsbury’s was also blame of not promote itself sufficiently and while organization many similar client initiatives as Tesco, it has failed to obtain the lead or develop sole crop or services. Further to this, it has show itself to be “unresponsive?in a fast touching marketplace. Therefore, Sainsbury’s adjusted and urbanized its mission. In arrange to attain its new assignment, which is to reconstruct its UK food retailing business. The corporation changed its advertising plan and has productively sold its Homebase DIY sequence in the UK and its commerce in Egypt. This enables the corporation to center the Group on food retailing and connected behavior. Apart from this, the present Marketing Mix? Product, cost, promotion and place is life form better to meet its new assignment. Let me talk concerning them in particulars.
Product
In order to turn out to be the UK consumer’s first option for food, Sainsbury’s Supermarkets proclaim its new business individuality in February 1999, “Making life Taste Better?recognizes that food is at the spirit of people’s lives. “Making life Taste Better?is additional than now a slogan or movement, it is concerning a real educational alter at Sainsbury’s. Sainsbury’s takes exploit to focus on excellence and novelty as well as ornamental the variety of food and rising new foodstuffs. They not only uphold the company’s historic power in fresh foods: exotic fruits, prepared meals, specialty breads and reduced -fat milks, but also Sainsbury launched its new Taste the Difference range In November 2000. It was the biggest food brand name open in the UK history. There are additional than 350 foods in the variety and each one has been full-grown or produced by means of the additional time, care and notice needed to transport out its filled usual flavours. Apart from this, at the start of January 2001, Sainsbury’s Supermarkets first announce the foreword of biodegradable wrapping made from potatoes, Sainsbury’s possess? Label organic outgrowth was selling in the ecological trays at all stores. Now, Sainsbury’s has developed over 600 organic lines with the best sellers in the dairy and create categories and major swelling in grocery, frozen foods, bakery, fresh creature protein and delicatessen. Moreover, Sainsbury’s Supermarkets launch Blue Parrot Caf?in March 2001 ?a diversity of healthier food for brood. The range addresses key dietary concerns and provides complete but clear classification to all parents to create an informed option about the products they purchase for their brood. So far 150 foodstuffs are on shelf and a additional 75 are under expansion. At in attendance, Sainsbury has sustained to expand its own one of the majority well-liked ranges?Be Good to Yourself variety which food is lower in fat targeting persons who want to get steps towards a better diet.
All the on top of ranges, Sainsbury’s is dedicated to the continuous development and growth of its products, as it understands excellence is of supreme importance to clientele. For instance, The Food Centre plays a pivotal function in ensuring fineness and novelty in Sainsbury’s Supermarkets own-label products. A extremely experienced side with extensive information of the food industry provides the corporation with specialist excellence control, original food growth, sensory appraisal and ropes Sainsbury’s Supermarkets range, manufactured goods quality and option programme.
In perform; Sainsbury’s Supermarkets launch new products each year in new years. They exactly reproduce a useful technique? Boston Consulting Group Matrix. Taking Be high-quality to Yourself for instance, when it enter keen on the market in May 1999, it knowledgeable the examination advertising. However, shortly after, it was greeting by vast clientele and turn into most popular range, which is called “cash cow? It is clever to make funds to hold up other foodstuffs, as they are grown-up products with a steady market split. After that, the new main variety Taste the Difference was launched in 2000. So far, Flavor the Difference motionless has its strong life power as it is frequently developed and better, while Be Good to You was re-launched in January 2002, focusing on contemptible cost and less fat in arrange to stop its refuse, which we call it “Dog? What’s additional? It is not deprived of that Sainsbury’s Supermarkets had a poor presentation during the late 1980s and near the beginning 1990s, and it was wedged up by means of Tesco. Therefore, Sainsbury looked forward to the worldwide marketplace to stop the refuse of the marketing split. It resulted Sainsbury announced the gaining of Star Markets in the United States in November 1998, plus took a 25.1% split in Edge SAE, a sequence of food retail outlets based in Cairo, Egypt.
Talking concerning product, we can’t fail to spot creation positioning. This allows commerce to charge not only its own portfolio, but so as to of its rivals as well. In twist, commerce can then position its creation into a suitable section. Let us look at the following creation mapping drawing in Sainsbury’s Supermarkets.
- High Quality.
- Taste the Difference.
- Be good to yourself Blue Parrot Cafe.
- Normal range Organic range.
- Economy range Italian range?
- Low Price High Price.
- Low Quality.
It is obvious that Economy variety targets for cost conscious customers, who strength be semi-skilled and unskilled physical workers or condition pensioners, widows, informal workers and lowest score earners. Blue Parrot Caf?attracts the concentration of relations with brood.
Sainsbury’s Supermarkets forever try to provide high-quality foodstuffs, value of cash. So far, a great Sainsbury’s Supermarkets offers over 23,000 products? 40% of these are Sainsbury’s own brand. In adding to a wide variety of excellence food and grocery products, a lot of provisions offer currency braked on the building, delicatessen, animal protein and angle counters, pharmacies, chocolate shops, restaurants and gasoline position.
Price
Price is a responsive constituent of the advertising mix in Sainsbury’s. Nowadays, Sainsbury’s aims to be the UK customers first option for food shopping by reaffirming its guide in excellence and contribution outstanding worth for currency. In other words, Sainsbury’s objectives to recover its management and to maintain and expand its marketplace split. The key term of pricing policy is “value for money? Also, the assignment mentions a spirited price. In the grocery marketplace it would come into view that you could struggle on price or repair but the two may be equally restricted. If a retailer utilizes low cost to struggle its rivals, the only method to win is by plummeting the overall cost basis, not the profit limitations. In 1996, due to Sainsbury’s deprived profits presentation, it consequently cut down split price, because touching earlier to a low cost platform. The other disadvantage is that customers may turn out to be cynical or even smart. Once a cost has been reduced it is less simple to return prices to their previous stage without alienating clientele. Furthermore, it will give confidence customers to become promiscuous; shopping at whichever amass has the price endorsement. This does not engender faithfulness to the store. Consequently, there is a clear hazard that price-cutting will be old for short-term share gain, still though its long-term effects would come into view to be less positive. Sainsbury’s realized its breakdown in a price war in 1996, so it distorted its assignment and strategies and put onward “value for money? It income Sainsbury wishes to farm a “value for money? Image through attraction and preservation of customers, touching into the excellence of products and services. Moreover, Sainsbury’s strives to spend heavily in its sharing and IT systems to get better the excellence of what it delivers and the efficiency of its action in arrange to reduce the in general cost. The reason of the strategy is to increase the trust of clientele and to reconstruct its leadership. On the other give, according to the manufactured goods positioning, Sainsbury’s set dissimilar price targeting on dissimilar groups.
Promotion
Sainsbury’s always completely takes benefit of above the line and underneath the line promotion to build up its physically powerful brand and to sketch notice to products in arrange to gain additional customers. Sainsbury’s has learnt that it’s possess brand individuality has turn into more significant than the foodstuffs they sell and greater wealth can at the present be shaped by the message of an overall retail brand individuality. In order to attain this aspire, firstly, Sainsbury’s announced its new individuality “Making life Taste Better?indicating its assignment to reinstate Sainsbury’s Supermarkets as the customers?first option. Sainsbury’s uses media such as television, radio and cinema promotion its corporate picture. For instance, at there, Sainsbury’s is promotion on nationwide television -Channel 5 to arrive at a vast audience. At the similar time, it goes to nationwide radio 4 to make a huge impact on audience—-Sainsbury’s, creation life taste improved. Sainsbury’s is one of top ten TV ad remember. This is about on top of the line endorsement that Sainsbury’s has been ultilising. Additionally, underneath the line promotion counting direct mailing, sales promotions, merchandising and wrapping is also necessary for Sainsbury’s. Here, a key bludgeon is that Sainsbury’s launched its Reward Card countrywide in June 1996. With a Sainsbury’s Reward Card, for every? You expend instore you will make 2 Reward Points. When 500 points contain been collected clientele can moreover use them as an routine?50 reduction off their shopping bill or collect a Reward Coupon which can be old for a wide diversity of third social gathering offers which, in a lot of cases, doubles their worth. There are now in excess of 16 million Reward Cards in subject. Reward Cards are as a longer term advertising tool since they facilitate retailers to study more concerning their customers? Situation and shopping habits and act in response for that reason with tailored offers. Moreover, in June 1997 the first birthday of the Sainsbury’s Reward Card, Sainsbury’s launched the Sainsbury’s Pet Club contribution pet mind hints, discounts on foodstuffs and a usual Club periodical. The 0-5 Club was launched in January 1998, and offers discounts to youthful families from side to side their Sainsbury’s Reward Card. It offers economy of over? 00 in the primary year of association and very quickly paying attention over 250,000members. Due to Reward Card, Sainsbury’s can expand its direct letters to introduce some new endorsement, such as 50 buy 1 get 1 gratis offers this week and over 3000 prices chopped and we’re motionless chopping and so on. It is also worth mentioning a intelligence of branding in Sainsbury’s. It engages an emphasis life form placed upon together the corporate and person brand person’s name such as Taste the Dissimilarity and Be Good to You.
Last but not smallest amount, Sainsbury’s in addition aims to fulfill its everyday jobs to the communities and environments in which it function in order to endorsement its picture in public. For instance, over the precedent six years, Sainsbury’s Equipment for Schools programme has known away over? 8 million value of free train gear. This year, the scheme is organization beginning 30 January to 24 April 2002.
Place
Distribution is concerning one of the 4″ps?of the marketing mix ?place. A business must get the product to the correct place, at the correct time. As we previously know, the assignment of Sainsbury’s is to be the clientele first option for food shopping by as long as high-quality foodstuffs, value for money, outstanding service and concentration to detail at a spirited cost from side to side operational faster, simpler and jointly. Sainsbury’s is the main food retailers in the UK. It has 59 largest stores, 273 supermarkets, 119 towns and city centres stores and 8 centrals as well as 23 Sainsbury’s locals. Different formats are mounting to competition store offer to precise customer shopping assignments and sites. In order to get together the needs of vast clientele, forty-five of its stores deal 24 hours a day and other better ones during the night on Fridays. With look upon to amass closures, Sainsbury’s forever takes into thought the impact on customers, its generation and on the centers in which it operates. Sainsbury’s is on target with its major provide chain regeneration programme in which it is aiming to make a world-class grocery distribution system and to work jointly more efficiently. It has already tenable sites for new depots and begun building. Sainsbury is invest heavily in its sharing and IT systems. Because 1998, Sainsbury’s well-known its home shopping delivery repair, called Orderline, which clientele could place order by telephone or on the internet. Its e-commerce urbanized very speedy including a company agreement with LineOne. Its e-commerce repair, Sainsbury’s to you, has made fast progress last year after a late creates into the home release marketplace. Sainsbury’s has now achieved over 50 per cent nationwide coverage with clientele shopping three times for each month on average It will be clever to bring Sanisbury’s with the primary corporation in the world to expand food foodstuffs on the internet.
Conclusion
Sainsbury’s situates for great products at fair costs to serve customers well, they continually get better and develop their creation ranges and services connected. Even additional, to widen the process area, they provide customers an ever civilizing shopping knowledge of non-food products. Moreover, they make sure all colleagues contain opportunities to expand their ability and are well satisfied for their charity.
Sainsbury’s as a most important food retailing sequence should continuously stay its quality policy, which base on its own brand new produce. Meanwhile, with the present global economic growth, worried about its ongoing marketplace share and growth, it is necessary to widen its worldwide market, which largely base on acknowledge the restricted civilization and system, also companying with well taught staffs to offer high normal services. With the continuously managerial knowledge within the supermarket, to recognize outside forces and intelligence important ecological trends and signals, they can put strategy for that reason to cope with environment, as long as us a high the theater association.
In conclusion, Sainsbury’s forever fully uses the marketing mix to attain its assignment. In addition, Sainsbury’s constantly improves its approaches on the advertising mix to convene the wants of its customers. Ultimately, Sainsbury’s never forgets responsibility advertising research that provides a wide diversity of information about the populace who may be paying attention in business its products. Though we all know a supermarket targets vast clientele, Sainsbury’s motionless breaks down a marketplace into sub-groups with comparable individuality, which is be acquainted with as Market Segmentation. Sainsbury’s uses the advertise segmentation to endorse its products to the right populace and to distinguish products towards different groups and to allow it to sell more products overall. Meanwhile, it will enable it to get vast customers?trust and build up client loyalty. For example, as each new variety with Sainsbury’s own tag is launched, Sainsbury’s targets dissimilar segments. Economy variety targets for price aware customers who strength fit in to D and E in IPA. Blue Parrot Caf?attracts the attention of relations with kids. Be good to yourself interestes in persons who have a strong life method and the old populace. Based on Sainsbury’s advertising mix, it also show its outstanding method and client service such as bringing a mixture of products jointly in a convenient site, within a pleasant surroundings, open extended hours as well as bag stuffing, credit/debit card expenses and offering cash rear and so on. In adding to this, Sainsbury’s continually provides opportunities to all workers to develop their abilities and intelligence of client service and well recompense their payment to the success of the commerce.
Marketing expansion
The possibility of finance service
Sainsbury’s has been annoying hard utilizing the full range of advertising mix rudiments to build up a reputation for excellence food and DIY products over a lot of years, urbanized from the near the beginning Sainsbury’s provisions that offered customers uppermost excellence at keenest prices. Sainsbury’s has build on its high height of customer trust to move good worth, without cooperation excellence, into new markets. In other words, having a faithful client base, which trusts the Sainsbury’s make and values the variety of services it offers, Sainsbury’s can aim to serve clientele in new markets and produce its commerce for shareholders? By be relevant skills and competencies learnt in one marketplace it can improve its businesses in others. In exacting, since it launched its faithfulness card recognized as Reward Card, which millions of clientele applied for, it might allow Sainsbury’s to get and analyse its customers? Details such as person needs, shopping behavior and speak to and so on. Separately from this, Sainsbury’s frequently improves its in order technology, online service and increase its shape of formats that it is able to create Sainsbury’s reach its vast clientele. All of them finally resulted in Sainsbury’s initiation its bank. It indicated Sainsbury’s in progress its new market? Finance repair. Sainsbury’s Bank is the first bank to be opened by a British supermarket and has lately introduced a trial of manned in-store Individual Banking centers. Current products comprise instant right of entry investments accounts, permanent stepped-rate savings bonds, direct ISA. Mortgages (flexible options, permanent, variable, discounted and buy to let), three recognition cards, individual loans, Drive, a car acquire scheme, home and contents insurance, journey indemnity and PetCare indemnity. Whatever the form of monetary products is, they have a great deal in common, which they give competitive rates, small risk, and easy move toward as well as extra reimbursement such as Rewards Points additional for customers. as a result, it has paying attention millions populace to connect Sainsbury’s Bank.
The Steps Taken and Deliberation
On 19 February 1997, Sainsbury’s bank was announced with two investments financial records and two credit cards from side to surface direct 24-hour telephone banking.
Sainsbury’s Bank is a combined business enterprise with the Bank of Scotland, which owns a alternative interest of 45%. This bank took benefit of the trust excellence of Sainbury’s, joined with Bank of Scotland’s knowledge and infrastructure. It urbanized new forms of distant organizations and repair release, via call centers, and it operated for a part of the price of conventional monetary services association. In exacting, the new banking jobs are in name centers, and need few of the customary banking skills or experience. Sainsbury’s therefore might offer more good-looking rates to customers to shop approximately. What’s more? Sainsbury’s could create use of the in order about its clientele that Sainsbury’s obtained from Reward Card issued and sent request forms of its money overhaul to its clientele.
By March 1998, Sainsbury’s Bank had 700,000 client accounts with?
1.5 billion On set down, so Sainsbury’s could create the most use of the deposit to make bigger its variety of financial foodstuffs such as Personal loans and an Options Mortgage, which Sainsbury’s objectives the smaller compilation comparing investments accounts.
Since Sainsbury’s launched its general monetary produces similar to its food crop, Sainsbury’s in progress to differentiate its foodstuffs and move toward to dissimilar section. For example, following the open of the Sainsbury’s Pet Club contribution pet care hints, discount on products and a usual Club Magazine in June 1997, Sainsbury’s gained immense opportunities to know the convinced customers?lifestyle which they adore pets and to forecast how a lot of customers?might be paying attention in Petcare indemnity so that Siansbury’s was clever to locate up this new money product. Apart from this, clientele can apply for this indemnity from side to surface the Internet. It improves the procedure efficiently and at the similar occasion it can decrease the cost of process.
Detailed description of monetary products and client portfolio
Sainsbury’s monetary products mainly include savings account, praise card, loan, advance and cover. All compete heavily on cost with cheaper loans and additional attractive investments rate than the payment banks. It utilities new knowledge and a greater readiness in the middle of customers to shop approximately and changes the structure of banking. In exacting, previous to every manufactured goods is announced, Sainsbury’s forever analyses prospective purchaser collection so that it could sensibly evaluate a new monetary product and could be achieve something in each manufactured goods launched. For instance,
Savings account
This is essential financial manufactured goods. In order to expand other foodstuffs and ensure Sainsbury’s Bank to be winning, Sainsbury’s needs to build up funds depending on customer put down. Savings explanation therefore targets clientele as a great deal as it can like Reward Card and it offers tempting advantages to attract vast clientele. Sainsbury’s Bank instantaneous access investments account is just similar to each other aspect its service? Straightforward, suitable and comforting. It’s also competitive, with an attention speed of up to 4.10% gross pa. It can create saving with as small as? And withdraw up to? 50 per day. Furthermore, it has no penalties of withdrawals and provides 24-hour phone banking overhaul.
Mortgage
After initiation savings account and praise card, Sainsbury’s could expand its new monetary products. Mortgage is one of novel products. There are a little different mortgages organization in Sainsbury’s Bank such as discount advance, fixed rate advance and buy-to-let advance and so on. For example, concerning buy-to-let mortgage, it gives populace chance to pay money for up to five properties for leasing and repay over 5 to 25 years and decide between attention only and assets and interest repayments with a changeable rate of 5.5%. Comparing investments account, mortgage targets at exact? Target groups? Based on life-cycle stages. Sainsbury’s is extremely interested in persons who are young wedded couple without child or with youngest kids. Here, it is worth talk about the 0-5 Club that offers discounts to youthful families from side to side their Sainsbury’s Reward Card. It enables Sainsbury’s to plea to this group and gets hold of their loyalty. It evenly helps Sainsbury’s to gain this collection information to open Mortgage.
Insurance
Insurance was launch after Sainsbury’s has had investments account, praise cards, advance and loan, such as journey insurance, pet insurance and home cover. For instance, per insurance is single of only a few insurers who cover the expenses of longer word circumstances such as diabetes, heart disease or arthritis for additional than 12 months and 500 Reward Points of every pet covered. It extremely clearly shows that Sainsbury’s concentrates on the sure groups according to their way of life. After initiation Pet Club, it is easy to create Sainsbury’s objective the members of Sainsbury’s Pet Club to open pet cover.
To sum up, Sainsbury’s as single top of retailers in the UK makes the nearly everyone use of a advertising mix to improve its presentation. Sainsbury’s set new assignment to recover market split back from Tesco because 1995 and to be the primary choice of be the customers first choice for food, delivering products of exceptional quality and immense service at a spirited cost from side to side operational faster, simpler and jointly. At the similar time, Sainsbury’s utilities its make values: excellent excellence range, repair and value, competencies, information and knowledge to influence Sainsbury’s Bank. It ensures the option of development of monetary service that will carry on exploring and expanding growth opportunities. Additionally, Sainsbury’s well design every monetary product with obvious segmentation, advanced psychoanalysis, sensible preparation and lucid steps, especially its exceptional go back and spirited rates as well as small risk. Last but not least, Sainsbury’s continuously strengthen its information skill system and sharing network to create Sainsbury’s products simple to arrive at clientele. All engender the achievement of Sainsbury’s finance repair. Sainsbury’s still endeavors to guide this field in the investigate and release of new products to meet the requirements of its clientele.
Reference
JOHNSON, G., SCHOLES, K. and WHITTINGTON, R. (2005), Exploring Corporate Strategy, Harlow, England: Prentice Hall.
ANDRZEJ HUCZYNSKI and DAVID BUCHANAN. (2001), Orgnaizational Behaviour – an Introductory Text, p627-628.
SCHOLZ, C (1987), Organization Culture and Strategy – the problem of strategy fit, vol.20, no.4, pp.78-87.
JOHN BRATION and JEFFREY GOLD, Human Resource Management Theory and Practice, 3rd Edition. Working at Tesco HSC. 2006. Web.
Sainsbury’s Supermarket, 2006. Web.
J Sainsbury’s PLC News, 2006. Web.
Ansoff, I., Avner, J., Brandenberg, R. C. et al. (1970) ‘Does planning pay?’, LongRange Planning 3(2).
Ansoff, I. and McDonnell, E. (1990) Implanting strategic management, Prentice-Hall.
Anthony, R. and Young, D. (1984) Management control in nonprofit organizations, Irvin.
Argenti, J. (1965) Corporate planning, Allen & Unwin.
Argenti, J. (1997) ‘All things to all men’, Strategy, March: 5-6.
Argyris, C. (1964) Integrating the individual and the organisation, Wiley.
Argyris, C. and Schon, D. A. (1974) Theory in practice: Increasing professional effectiveness, Jossey-Bass.
Argyris, C. and Schon, D. A. (1978) Organisational learning: A theory of action perspective, Addison-Wesley.
Argyris, C. and Schon, D. A. (1996) Organisational learning II: Theory, method andpractice, Addison-Wesley.
Armstrong, J. S. (1991) ‘Strategic planning improves manufacturing performance’, Long Range Planning 24(4).
Barry, B. W. (1986) Strategic planning for non-profit, Amherst Weider Foundation.
Bart, C. K. and Tabone, J. C. (1998) ‘Mission statement rationales and organisational alignment in the not-for-profit health care sector’, Health Care Management Review 23(4): 54-69.
Bartlett, C. A. and Ghoshal, S. (1989) Managing across borders, Harvard Business School Press.
Bartlett, C. A. and Ghoshal, S. (1998) ‘Beyond strategic planning to organisational learning: Lifeblood of the individual corporation’, Strategy and Leadership: 34-9.
Basini, S. and Buckley, F. (1999) The meaning of work in the Irish voluntary sector, AVARI/University of Ulster.
Bass, B. M. (1970) ‘When planning for others’, Journal of Applied Behavioural Science VI(2): 1551-71.
Billis, D. (1984) ‘The missing link: Some challenges for research and practice in voluntary sector management’, in B. Knight (ed.) Management in voluntary organisations, ARVAC occasional paper No. 6.
Boyd, B. K. (1991) ‘Strategic planning and financial performance’, Journal ofManagement Studies 28(4): 353-74.
Bozzo, S. (2000) Evaluation resources for nonprofit organisations: Usefulness and applicability, Canadian Center for Philanthropy.
Bracker, J. S. and Pearson, N. J. (1986) ‘Planning and finanacial performance of small, mature firms’, Strategic Management Journal 7: 503-22.
Burkhart, P. J. and Reuss, S. (1993) Successful strategic planning: A guide for nonprofitagencies and organisations, Sage.
Burns, T. (1961) ‘Micropolitics: Mechanisms of organisational change’, Administrative Science Quarterly 6: 257-81.
Burns, T. and Stalker, G. M. (1961) The management of innovation, Oxford University Press.
Bush, R. (1992) ‘Survival of the nonprofit sector in a for-profit world’, Nonprofit andVoluntary Sector Quarterly 21(4).
Butler, R. J. and Wilson, D. C. (1990) Managing voluntary and non-profitorganisations, Routledge.
Byington, D., Martin, P., Maxwell, M. et al. (1991) ‘Organisational affiliation and effectiveness: The case of rape crisis centers’, Administration in Social Work 15: 83-103.
Cameron, K. (1982) ‘The relationship between faculty unionism and organisation effectiveness’, Academy of Management Journal 25: 6-24.
Carr, C. (1996) Choice. Chance and organisational change, AMACOM.
Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. (1986) Becoming critical, Falmer.
Carroll, D. (1983) ‘A disappointing search for excellence’, Harvard Business Review 61(6).
Champy, J. and Hammer, M. (1993) Re-engineering the corporation, HarperBusiness.
Chanan, G. (1991) Taken for granted, Community Development Foundation.
Chandler, A. D. Jr (1962) Strategy and structure, MIT Press.
Chauhan, Y. (1998) A planned journey into the unknown, Centre for Voluntary Organisations working paper 20, LSE.
Chesterman, M. (1979) Charities, trusts and social welfare, Weidenfeld & Nicolson.
Cialdini, R. B. (1984) Influence: Science and practice, Longman Higher Education.
Clausewitz, K. von (1984) On war, Princeton University Press.
Clutterbuck, D. and Dearlove, D. (1996) The charity as business, Directory of Social Change.
Coghlan, D. (1987) ‘Corporate strategy in Catholic religious orders’, Long RangePlanning 20(1): 44-51.
Cole, G. D. H. (1945) ‘A retrospect of the history of voluntary social service’, in A. F. C. Bourdillon (ed.) Voluntary social services: Their place in the modern state, Methuen.
Collins, J. C. and Porras, J. I. (1994) Built to last: Successful habits of visionary companies, Random House.
Connoly, T., Conlon, E. and Deutsch, S. (1980) ‘Organisational effectiveness: A multiple constituency approach’, Academy of Management Review 5: 211-17.
Cooke, R. A. and Rousseau, D. M. (1988) ‘Behavioural norms and expectations: A quantitative approach to the assessment of organisational culture’, Group andOrganisation Studies 13: 245-73.
Coopey, J. (1995) ‘The learning organisation, power, politics and ideology’, Management Learning 26(2).
Cornforth, C. and Edwards, C. (1998) Good governance: Developing effectiveboard-management relations in public and voluntary organisations, CIMA.
Courtney, R. B. (1992) Making a difference: The story of the Simon Community inNorthern Ireland, Simon Community Northern Ireland.
Davis, R. C. (1928) The principles of factory organisation and management, Harper & Row.
Davis, R. C. (1951) The fundamentals of top management, Harper & Row.
Davis Smith, J. (1992) ‘An uneasy alliance’, in R. Hedley and J. Davis Smith (eds) Volunteering and society: Principles and practice, Bedford Square Press.
Davis Smith, J. (1995) ‘The voluntary tradition: Philanthropy and self-help in Britain 1500-1945’, in J. Davis Smith, C. Rochester and R. Hedley (eds) Anintroduction to the voluntary sector, Routledge.
Davis Smith, J., Rochester, C. and Hedley, R. (eds) (1995) An introduction to thevoluntary sector, Routledge.
Deakin, N. (1995) ‘The perils of partnership: The voluntary sector and the state 1945-1992’, in J. Davis Smith, C. Rochester and R. Hedley (eds) An introductionto the voluntary sector, Routledge.
Deakin, N. (1996) Meeting the challenge of the future: The report of the commission on thefuture of the voluntary sector, NCVO.
De Geus, A. (1988) ‘Planning as learning’, Harvard Business: 70-4.
De Vagal, S. H. (1995) Ethics in O. D., Peiffer.
Dierickx, I. and Cool, K. (1989) ‘Asset stock accumulation and the sustainability of competitive advantage’, Management Science 34(12).
Falk, N. and Lee, J. (1978) Planning the social services, Saxon House.
Fayol, H. (1916) General and industrial management, English trans. by Constance Storrs (1949), Pitman.
Firstenberg, P. B. (1979) ‘Profitminded management in the nonprofit world’, Management Review 68: 8-13.
Flynn, N. and Talbot, C. (1996) ‘Strategy and strategists in UK local government’, Journal of Management Development 15: 24-37.
Follett, M. P. (1941) Dynamic administration (E. Fox and L. Lyndall, eds), Harper & Row.
Forbes, D. P. (1998) ‘Measuring the unmeasurable: Empirical studies of non-profit organisation effectiveness’, Nonprofit and Voluntary Sector Quarterly 27(2): 159-82.
Ford, J. D. and Ford, L. W. (1990) Designing organisations for growth, unpublished working paper, Ohio State University.
Fredrickson, J. W. (1984) ‘The comprehensiveness of strategic decision processes: Extension, observations and future directions’, Academy of Management Journal 27: 445-66.
Fredrickson, J. W. and Iacquinto, A. L. (1989) ‘Intention and creeping rationality in strategic decision processes’, Academy of Management Journal 32: 516-42.
Fredrickson, J. W. and Mitchell, T. (1984) ‘Strategic decision processes: Comprehensiveness and performance in an industry with an unstable environment’, Academy of Management Journal 27: 399-423.
Gable, M. and Topol, M. T. (1987) ‘Planning practices of small-scale retailers’, American Journal of Small Business 12: 19-32.
Galbraith, J. R. (1977) Organisation design, Addison-Wesley.
Gann, N. (1996) Managing change in voluntary organisations: A guide to practice, Open University Press.
Garrick, J. and Rhodes, C. (1998) ‘Deconstructing organisational learning: The possibilities for a post-modern epistemology of practice’, Studies in the Educationof Adults 30(2).
Georgopoulos, B. S. and Tannenbaum, A. S. (1971) ‘A study of organisational effectiveness’, in J. Ghorpade (ed.) Assessment of organisational effectiveness: Issues,analysis and readings, Goodyear.
Gerard, D. (1983) Charities in Britain: Conservatism or change?, Bedford Square Press.
Gherardi, S. (1999) ‘Learning in the face of mystery’, Organisation Studies 20(1).
Ghobadian, A. and Woo, H. S. (1994) ‘Characteristics, benefits and shortcomings of our major quality awards’, International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management 1392: 10-44.
Gilbert, X. and Strebel, P. (1988) ‘Developing competitive advantage’, in J. B. Quinn, H. Monteberg abd R. James (eds) The strategy process, Prentice-Hall.
Glisson, C. and Martin, P. (1980) ‘Productivity and efficiency in human service organisations as related to structure, size and age’, Academy of Management Journal 23: 21-37.
Gluck, F. W., Kaufman, S. P. and Wolleck, A. S. (1980) ‘Strategic management for competitive advantage’, Harvard Business: 154-61.
Gnaerig, B. and MacCormack, C. F. (1999) ‘The challenges of globalization: Save the Children’, Nonprofit and Voluntary Sector Quarterly 28(4) Supplement.
Goldsmith, W. and Clutterbuck, D. (1997) Winning streak – Mark II, Orion Business Books.
Grossman, A. and Rangman, V. K. (2001) ‘Managing multi-site nonprofits’, Nonprofit Management and Leadership 11(3).
Gruber, R. E. and Mohr, M. (1982) ‘Strategic management for multiprogramme nonprofit organisations’, CaliforniaManagement Review 24(3): 15-22.
Harlow, J. (1998) The nature and scope of changes effected by the utilization of strategicmanagement in volunteer-managed nonprofit organisations, Dissertation Abstracts International 59/05A 1775.