List of Figures
- Figure 1: Problem and Prospect of Outsourcing Sales Staff
- Figure 2: Hypothetical View on Islamic Ethical Standard in Business Atmosphere
- Figure 3: Sales Staff’s Critical Role Model
- Figure 4: Influences of Sales Staff’s Job Satisfaction on Job Performance
- Figure 5: Product Quality Factors versus COO Dimensions
- Figure 6: Consumer’s View on Social & Value Perceptions
- Figure 7: Connectivity between Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction
- Figure 8: Typical Consumer Behaviour
- Figure 9: Classification of Published Secondary Sources
- Figure 10: Categorization of Computerized database
- Figure 10: Level of Satisfaction as an Employee of The Bank
List of Tables
- Table 1: Difference between qualitative and quantitative research
- Table 2: – Selected Respondents for interview
- Table 3: Relationship between customer behavior and customer loyalty
- Table 4: Rate services offered by sales agents
- Table 5 How was the experience
- Table 6 Test Statistics
- Table 7 Level of satisfaction as an employee of the bank
- Table 8 Test Statistics
- Table 9: Correlations
- Table 10 Noticeable relationship between customers accepting the credit card and sales staff’s convincing power
- Table 11 Test Statistics
- Table 12: How does the level of education affect sales staff capacity to sell the credit cards?
- Table 13: Reliability Analysis
- Table 14: – Contents of the questionnaire
Executive Summary
The objective of this dissertation is to present the coordination of shifting dynamics of the sales staff behaviour along with the consequential factors affecting customer’s responses. Here, the study ground is the credit card sales staff in Penang, Malaysia, and their associated customers of the location. The organisations concerned with the sales practice of credit card in Penang is most likely to use temporary staff, individual contractors, and outsourced employees. Due to the accelerating number of players in the market, there is a solid base of perfect competition and the sales agency is under pressure to gain a competitive advantage by dropping costs that lead them to use temporary employees or outsourced contracted staff for sales of a credit card. Such appointment of sales staff has generated huge scandal of unethical conduct with the customers and pointed serious ethical dilemma for the credit card industry in Penang.
This study identified that unethical behaviour of the sales staff is not only caused by the limitation of the personal attributes of the sales staff but there is an increasing number of organisational and legislative factors that lead the sales staff to align with unethical behaviour with customers. With the complex nature of customer behaviour, the ethical behaviour of the sales staff has absolutely interlinked with the customer’s responses including their trust in the organisation, customer orientation, and satisfaction maximisation that can generate a strong base of satisfied customers. The sales staff’s customer orientation is a vital area that is unavoidably needed to be addressed for successful business entries in the credit card industry of Penang and it has evidenced that unethical behaviour of the sales staff has harmfully crashed the effectiveness and profitability of an organisation. The paper has concluded with a vital recommendation to standardise the ethical standard with regulatory amendments.
Problem of Statement
Background of the research
Malaysia is a federal state in South East Asia. The king is the head of the state while the prime minister heads the government. The country has three federal territories and thirteen states. The South China Sea separates the country into two regions of similar sizes, Malaysian Borneo and Peninsular Malaysia. It borders Brunei, Thailand, and Indonesia by land, and Vietnam, Singapore and the Philippines by sea. The statistics are given in 2010 showed that the population of the country is approximately 28 million people, with the majority (about 20.5 million people) living on the Peninsula. The capital city of this country is Kuala Lumpur. The country has several ethnic and cultural groups. However, it has enjoyed a relatively stable political environment.
The economy of this country has been very strong since it gained independence on August 31, 1957. The growth of the economy has been estimated to be an average of 6.5 percent per year for the last five decades. Some of the sectors that have constantly propelled the growth of the country’s economy include the tourism sector, commerce, science sector, medical tourism, and its natural resources. Given this attractive economy, the country has attracted a number of financial institutions both locally and from the international forum. These financial institutions play a very important in an economy where there is a huge flow of money, with most of the financial transactions done through the banks. Some of the local banks in this country that are partly or wholly owned by the government include Maybank, CIMB Bank, Agro Bank, and Bank Simpanan Nasional. Chinese businessperson in Malaysia privately owns Hong Leong Bank and Public Bank. There are foreign banks in the country, which include Citibank, Standard Chartered Bank, HSBC Bank, UOB Bank, OCBC Bank, Al-Rahji Bank, Bank of China, and Alliance Bank among others. Some banks, like Al-Rahji Bank, have specialized in Islamic banking, offering products that are specifically targeted at Muslims, while many others, like the Standard Chartered Bank, offer conventional banking to its customers.
Credit card, also popularly known as plastic money, has grown popular in recent years. The emerging technologies have made it easy for individuals to shop without the need to carry cash. It is now possible for credit cardholders to pay bills at the supermarket, petrol stations, hotels, and various other locations using the card. This is an easier and safer way for an individual to carry his or her money. Moreover, some banks offer a discount on their credit cards, making their customers who use the credit card pay averagely less as compared to when the payment is made on a cash basis. Banks have therefore rolled out massive plans on how to increase the sale of their credit cards. Standard Chartered Bank is one such financial institution, which has been aggressively selling its credit cards to its customers. However, some customers have been cautious with credit cards, preferring to use cash instead of credit cards. The case below shows one of the possible geneses of this caution.
Case Study
Ahmad, Basir & Kitchen (2010) presented a customer’s experience with the cheating of a credit card sales staff of the Standard Chartered Bank Credit Card that demonstrates the critical situation of the credit card sales and marketing in Penang and all over Malaysia. The story was like that, while the customer was shopping in the Curve Mall, a sales staff approached her to sign up for a credit card but the customer refused several times. The sales staff constantly followed the customer and continued sales approaches and, though the customer was irritated, the sales staff did not let him free until he forced her to sign up for a credit card. The sales staff said that by using the credit card of Standard Chartered Bank he would get many opportunities to enjoy a great discount in shopping at the Curve, 50% discount at Marche and Japanese restaurants in Penang, Malaysia and so on.
At last, the customer signed up and within ten days, the customer received an SMS from the bank that his application had been approved and soon she received the card. Then the customer went to the Marche for dinner by using the card, and after dinner, when the customer went to make payment with the credit card of Standard Chartered Bank, the cashier did not give any discount. When the customer questioned this, the cashier informed her that the discount was a one-time and one-day promotional program that had expired long before. The customer also got the same shock with the initiative to get a great discount at the Curve Mall. The customer could understand why the sales lied to her, so she decided to cancel the card. While the customer arrived at the Standard Chartered Bank branch, expressed the cheating story of the sales staff, and asked for cancellation, the customer service department informed her that for each signed up application the sales staff are authorised to get a commission. If the customer cancels the card, it does not affect the sales staff, at once, the sales staff will get a commission, and the burden would be imposed on the customer’s account.
The sales agents who sold credit cards to the customers are paid based on the sales made. The more the cards they sell to the customers, the higher they are paid by the bank. As such, these sales agents have been very aggressive in their sales of the cards for them to earn more. This aggression of the sales agents has failed to pass the test of moral salesmanship. Some of these sales agents use dubious means to reach out to the customers in order to make huge sales. Some of these agents literally cheat in order to win the bargain with the customer, only for the customers to realize later that they were cheated. Others collude with other conmen to corn the users of the credit cards in a number of ways. This has caused a great worry among the concerned authorities as credit cards increasingly continue to get negative marketing despite their obvious benefits to the users. This study seeks to investigate the credit cards sales staff (of Standard Chartered Bank at Penang) behavior and how this behavior affects the customer’s responsibility.
Problem Statement
The world is changing in its social, economic, and political structure. Society has experienced radical changes, especially due to emerging technologies. Credit card has become so important in the banking sector. Despite some of the benefits that credit cards have to the holders, it comes with a number of disadvantages. Some of the notable disadvantages of credit cards include the ease with which some cybercriminals can use them to steal from customers. Other credit cards have hidden charges that make them a little more expensive than holding cash. It is also widely believed that credit cards always encourage excessive expenditure because there is the feeling that one is not using money. The behavior of the sales staff is another problem that makes the cards undesirable to many customers. The fact that some sales staff use lies and malice when selling the cards creates huge negative publicity for the cards. More customers feel that the cards are part of a wider scheme for the banks to rob them of their hard-earned cash. Because of this, many customers have been keen to avoid the sales staff, especially when it comes to the sale of credit cards. The bank has also been massively affected given the fact that some of the customers totally withdrew from the bank having felt cheated by the bank. This has not only reduced the asset base of the bank, but also its general profitability.
It is important to understand the profile of the sales staff of this bank in order to be in a position to justify their behavior. This research was conducted at the firm’s branch in Penang and all the employee’s Malaysian nationals. The firm has been keen on ensuring that there is a gender balance in its employment. For this reason, there is an equal proportionality of the genders among the sales staff at Penang. Most of the sales staff are middle college graduates, who are fresh from college. A few of them have bachelor’s degrees in the field of marketing. As such, these individuals were getting their first employment in this firm.
The researcher, therefore, wishes to unearth the relationship between employee behavior and customer response to what they are selling, which in this case is the credit card. The researcher wishes to use existing literature in this research to develop the argument, and the analysis of the primary data to support the entire study, especially due to some gaps that exist in this field in the literature.
Justification of the Research
Many scholars tried to find out the solution to the question of how staff behaviour in a certain company’s marketing practice could influence the customers in the credit card market to ensure the growth of the market share of that company, and how the appropriate marketing drive could increase sales revenue by increasing customers confidence. Some researchers have kept attention to stabilise the credit card market of Malaysia under the recent global financial crisis connecting the previous Asian financial crisis. Most of the remarkable contemporary researchers have concentrated on the marketing standards, customer relationship management, and regulatory reform in the credit card market, but no overarching research agenda has yet been proposed on whether the manipulated and unethical staff behaviour is a conscious drive of the credit card issuers for deliberated cheating or they value for customers respond.
Alboreca (1998) presented a study connecting the ethical and socially accountable marketing where the organisations find out the needs, wants, and interests of the customers and then strive to transmit a greater value chain to the customers through safeguarding and improving the customer’s satisfaction including the development of the society. Though there is enough debate with the marketing operation and social well-being, the corporate culture and both the internal and external environment have a vital influence on the customers and as a whole to the society, thus the marketing system has the opportunity to reshape the society in various contexts. As a result, the modern corporations are considerate to take into account of ethical marketing drive rather than aggressive marketing, while the ethical drives would pursuit to accomplish economic and financial goals of the company focusing on an assortment of micro-level factors of sales and marketing just emphasising on the sales staff behaviour. Most of the marketing literature has long been emphasised on the customer behaviour analysis to fix their marketing strategy but elapsed to integrate customer’s responses linking with sales staff’s behaviour.
Alt & Lieberman (2010) pointed out that both the customers and sales staff have a vital emotional role in marketing and sales while the companies have strong alignment with the sales staff emotions to promote sales, the customers are willing to see that the corporations would value to their emotions cordially. The interaction between customers and sales staff may contain positive or negative emotions, but the ethical treatment without emotional harassment could turn a negative attitudinal customer into a loyal customer, and the sales staff needed to have a well understanding to overcome and handle customers’ emotions. The rationale of this research is to analyse the roles of the sales staff behaviour in Malaysia experience by observing the real scenario of the Malaysian Credit card Market to evaluate to what extent the existing practice of sales staff behaviour is effective to retain customers and increase market share by taking into account of existing guidance introduced by the BNM.
In addition, this research has aimed to escalate the awareness of regulators to take control over the customers’ responses tools while the global financial crisis already socked the credit card Market of Malaysia and the policymakers are anxious to bring back the customer’s confidence. Moreover, this dissertation has aimed to assist the academia, regulators, policymakers, and customers with a better understanding about the lacking of sales staff behavioural practice and related fraudulent practice including its driving force such as non-holy alliance with the marketing managers and sales staff of the outsourcing agents of credit card marketing. Through this investigation and its outcomes, the credit card issuers and marketing companies will get a potential investment environment in the credit card market of Malaysia and get a better level of investor’s confidence, which will endow with the companies a practical advantage over the sales staff and marketing managers who are involved with the present unethical practice.
Research Objectives
The basis of this research is to change the current attitude of the customers, which has deteriorated because of the actions of some unscrupulous sales agents. The researcher therefore seeks to solve the following research problems by the end of this study.
- What is the relationship between the behaviour of sales staff and customers’ loyalty at the Standard Chartered Bank in Penang?
- What are the trends taken by sales staff in their effort to sell the credit cards to customers?
- What is the impact of dubious selling techniques (including cheating) by the sales staff on the customers?
- How may the future effect of this behaviour affect the bank
- What are the mechanisms that would help eliminate this negative practice by sales staff with the aim of restoring customer loyalty.
- What are some of the clear recommendations, both to the sales staff and to the management of the bank on how it can retain customer loyalty
Research Question
In every research, a research question always acts as the guideline to the researcher. In most of the occasions, a researcher will come across a lot of information, most of which may be interesting, but may be irrelevant to the research at hand. Research question therefore would therefore spell out the nature of resources that the researcher should look for the data. The following are some of the research questions that the researcher developed for this research.
- Is there a direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ response to the item on sale?
- What are some of the general conducts of a sales agent that would make a customer buy or fail to buy a credit card?
- How would the management of Standard Chartered Bank at Penang ensure that customers acquire the credit cards in the expected volume?
From the above research questions, the following hypotheses were developed.
- H1a. There is direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ loyalty to the bank.
- H2a. The behavior of the sales staff is closely related to the motivation they receive from the management of the firm.
- H3a. The possibility of the customers accepting the credit cards heavily depends on the ability of the sales staff to convince them that they are beneficial.
- H4a. The ability of the sales agents to sell successfully the credit cards to the customers depends on their level of education.
Importance of the topic
Finance as a topic is very sensitive. All other sectors in a given country depend on it for their normal operations. According to Cadogan, & Lee (2009), all the sectors in a given economy have a direct relationship with the finance department. This sector would facilitate the smooth flow of money from those who have excess and need to save to those who need the same to invest. When managed properly, Cheng (2010) says that it can lead to great development in various sectors of the economy.
Standard Chartered Bank was chosen as the center of study because it is very popular in this region. It is one of the largest foreign financial units in Malaysia and has global coverage. The bank has some of the best ultra-modern facilities in most of its branches. Most local graduates in this country look forward to acquiring employment in this institution as it is considered one of the best employers in this region (Cheng, 2010). The bank is also one of the few in this country that has branches in countries outside Malaysia.
The choice of this bank as a preferred research topic was necessitated by a recent complaint by a customer over the negative experience she had after being lured by a sales staff to sign up for a credit card. The sales staff promised her many discounts on various shopping malls, hotels, and other institutions. This was an interesting phenomenon because, in the current society, every business unit has a responsibility of developing a long-lasting relationship with the customers. According to Hopkins & Laaman (2003), the world has seen drastic changes in the marketing approach. Unlike before when marketing was considered an operational activity focused on instant gains, the current society has seen a new approach where firms embrace social marketing where the aim is to attract and retain customers by offering quality products. Because of this, firms have currently become very truthful to their customers, always ensuring that they avoid any post-purchase dissonance. The current global market views customers as a very important part of the businesses and therefore should be treated as such.
It is therefore intriguing to find an institution as important as a bank basing its operations on lies in order to achieve quick gains. What is raising the urge even further is the fact that the reaction of the bank’s officials does not reflect any remorse towards the actions of their sales staff. The issue therefore was to find the reason for the existence and the resultant effect of such sales staff behavior when on their official duties. The researcher was interested in knowing why such an important bank in Malaysia could tolerate such habits. To achieve this, the researcher launched a study designed to investigate how customers respond to such behavior and measures that can be taken to ensure that customers are retained within the bank.
Scopes of the Study
In every research, there is always the limit beyond which a research may not go. As such, it is important for a researcher to define clearly the scope of the research in order to avoid the possibility of the piece of research being misinterpreted by the concerned authorities. In this study, the researcher conducted the research within the scope stated below.
- This study is relevant to the Malaysian market. The primary data collected was from the respondents at Penang, and most of the secondary resources were focused to the local economy. As such, the application of the research findings beyond this scope may not hold the level of truth it does locally;
- In addition, this paper has the chance to observe internal sales staff behaviour system in Malaysia considering the BNM’s guideline for Best Practice, Business Indicator Report, Financial Standards Report of Malaysia;
- This researcher also scrutinised with Hire-Purchase Act-1967, Moneylenders Act- 1951, Pawnbrokers Act- 1972, Banking and Financial Institutions Act- 1989, along with Islamic Banking Act- 1983,
- This paper concentrates on the principles of customer relationship management, international standards on marketing, objectives and principles of existing listing rules, performance in global best practice indices, taxation policy, and key standards to sound financial systems of Malaysian financial sector;
- However, this study has also scope to give the theoretical framework of staff behaviour, the effectiveness of loyal customers, the impact of the regulations on the credit card market, and the influence to resolve conflicts among in the Malaysian market;
- The entire dissertation will assist to give a fruitful, realistic and applicable suggestions and recommendations to improve the existing credit card marketing regulation to reduce sales staff fraud in Malaysia;
- In addition, the researcher has the opportunity to collect the primary data with the aim to analyse the significant roles and current position of sales staff behaviour in Malaysia credit card Market, and other relevant issues.
Definitions
This research was carried out in a Muslim nation hence there are some words that may not be common in the normal context of English language. The researcher, therefore, set this section for explaining these terms. Some words and phrases considered technical are also explained in this section. This was done to ensure that this dissertation remains relevant in the context from which it was conducted while remaining relevant to those in other parts of the world.
- Affected Class: a group of individuals who have been victims of misdemeanor of the sales staff of this bank.
- Affirmative Action: this refers to a set of procedures or programs that are always aimed at ensuring equity at a workplace, in an organization or in a country.
- Allah: God or the creator.
- CEDAW: Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women: an international body that fights any form of women discrimination across the world.
- Culture: a set of principles that guide the general way of life of a certain group of people.
- Discrimination: prejudice directed towards a certain group of individuals.
- EEOC: Equal Employment Opportunity Commission: a US based organization that ensures there is equality at workplace.
- Formal Complaint: a written complaint made by an individual against another or an institution alleging that stated unlawful acts were done against them.
- ‘Id: a festive day for the Muslims.
- Madrasah: a schooling system among the Muslims
- OFCCP: Office of Federal Contract Compliance Program: a unit within the US department of labor.
- Protected Class: a group of individuals who enjoy some privileges over others within an organization, a region or a state because of their gender, race, religion or any other demographical class considered superior to others.
- Quran: the Islamic holy book
- Reverse Discrimination: unfair or unfavorable practice mated towards the majority members of a given society or group.
- Systemic Discrimination: an employment practice that perpetuates use of different criteria to different employees seeking the same job opportunity, on the basis of gender, race or religion.
- Workforce Diversity: refers to a pool of workers with varied experience and from different backgrounds.
Summary
This chapter shapes the entire research. The background section gives focus to the topic of study. It introduces the topic and makes the reader understand the context under which the dissertation is based upon. It comes out clearly from the chapter that the Standard Chartered Bank is one of the leading banks in this region. It is also clear that due to the emerging technologies, more account holders are keen on ensuring that they use credit cards instead of walking around with cash. Banks across this region are therefore keen to attract as many customers as possible to use their credit cards, Standard Chartered Bank included. However, a new twist is brought up in the statement problem section that negatively affects the popularity of credit cards. It comes out that some sales agents use dubious means to attract bank customers to sign up for the credit cards. Wrong promises were made to the customers, leading to customers’ dissatisfaction. This affects the bank as some customers strongly believe that the bank colludes with the sales agents to dupe them.
The next chapter focuses on the review of relevant literatures in this topic. Credit cards are one of the most recent and very ambitious programs that emerging technologies have brought in the banking sector. As such, various scholars have comprehensively done research on this new technology. Various literatures exits on the use of credit card and its benefits to the customers. Literatures also exist on the strategy that various banks use to market credit cards to the customers. The next chapter therefore would analyze the techniques used by various banks, as well as how effective they are in attracting customers. The chapter also seeks to gather information on how the behaviour of sales staff affects customers.
Literature Review
Conceptual Framework of the Sales Staff Behaviour
Banking Industry in Malaysia
Malaysia is a federal state in South East Asia. This is a multi-ethnic country with the majority, about 51 percent, being Malays. Chinese make 23 percent of the country’s populace, 11 percent are the indigenous, 7 percent are Indians while other races form 8 percent. A report by Keller (2009) is one of the countries in Asia that is being increasingly industrialized, with an economy that has been stable for a very long time. Because of this, many people have found it necessary to open bank accounts with this bank as a way of conducting business easily. The tourism industry, among other industries, have hugely benefited from the banking industry.
The banking industry forms about 11.6 percent of Malaysia’s total gross domestic product. The industry has consistently experienced growth over the past decade, according to this scholar. Due to the attractive economic growth of the country, a number of banks, some locally owned, others being international banks, have thronged into the economy to tap from this rich economy. The country has held an open market policy, where foreign banks are allowed to invest in the country without any restrictions. This has contributed to an influx of financial institutions, making the market very competitive. Some of the local banks in this country include Maybank, CIMB Bank, Agro Bank, Bank Simpanan Nasional, and Alliance Bank, which the government have substantial shares in. other major local banks include the privately-owned Hong Leong Bank, Public Bank. Besides these local banks, the country also hosts a number of major foreign banks. Some of the major foreign banks in this country include Citibank, Standard Chartered Bank, HSBC Bank, UOB Bank, OCBC Bank, Al-Rahji Bank, Bank of China, Alliance Bank, and Scotiabank among others. The country also has a number of non-banking financial institutions. They include MBF, Malaysian building society amongst others. Hosts of other financial institutions also exist in this industry.
The banks in this country offer various products to their customers based on the social background of the customers. The country has various ethnic groups each having different cultural practices. In order to survive in this market, it would require the banks to design custom-made products that would best suited the customers. Given the fact that majority of the country’s nationals are Muslims, a number of banks have come up with Islamic banking to attract customers based on their faith. One of the defining features of Islamic banks that make it distinct from convectional banks is that they have different branches for male and female customers. They also have other unique features. Some of the prominent Islamic Banks include Affin Islamic Bank Berhad, Alliance Islamic Bank Berhad, AmIslamic Bank Berhad, Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad, Hong Leong Islamic Banking Berhad, Maybank Islamic Bank Berhad, and Standard Chartered Saadiq Berhad among others. Some of these Islamic banks are locally owned while others are foreign firms. Other banks offer conventional banking within the country.
The emerging technologies are fast changing and they have affected the normal operations of banks within this country. The market is increasingly competitive, and as the researcher, it forces the banks in this industry to adapt to the emerging technologies in order to remain competitive in the market and avoid a possible face-out. Credit card has increasingly become very popular among various banks in this country. Some of the banks that have been active in issuing credit cards to their customers include AmBank Berhad, CIMB Bank Berhad, Citibank Berhad, United Overseas Bank Malaysia Berhad, Public Bank Berhad, HSBC Bank Berhad, and Standard Chartered Bank Berhad
Standard Chartered Bank is one of the leading international banks in the world According to scholars; this bank has been in this country for long and has mastered the local market. The bank has been keen to ensure that it attracts as many customers as possible through products that are customer responsive. It is one of the international financial institutions in this country that have been keen to implement social marketing, where long-term relationship with the customers is given priority. This bank has managed to attract a large market share, especially among the middle class and the rich.
In its ambitious plans to ensure that it remains competitive in the market, it has embraced the use credit cards by its customers. Kheng (2010) explains that Standard Chartered Bank has been keen to ensure that its customers are issued with credit cards which they can use instead of cash. When this product was launched, the bank would issue the cards to customers within the banking halls. Customers would get the cards from the bank. However, as the card became more common and its relevance became evident, the firm decided to use sales agents to sell the cards. This approach has proven very efficient for this firm because the sales agents would go to the field to look for the customers. These sales agents are paid based on the commission of the sale they make. This approach was favored by the bank because it made the sales staff very aggressive when in the field. However, due to greed of some of the sales agents, Kotler (2003) says that some have developed behavior that is unbecoming, and threatening the good and fruitful relationship that this bank has had with its customers.
Models of Sales Staff Behaviour
Stock and Hoyer (2005) pointed out that the modern literature of marketing has persistent on the market orientation while the organisational behaviour at the individual intensity connects with the interpersonal skills and communication among sales staff and customers along with the capabilities of a sales staff to gratifying the customer wishes correctly. Both from the managerial and an academic viewpoint, most of the scholars have classically persistent on the customer-oriented behaviours of the sales staff like considering the customers’ desires, assisting and influencing them by providing information, motivation and support without any sorts of pressure or misconduct.
Hochschild (1983) identified the dilemma of commercialisation of the human feeling pointing that the sales staff may take action in accordance with the prescribed manner of the organisation but they do not build up any positive attitude or real enthusiasm for the customer-oriented policies and practice though they pretend fake obviousness towards customers. The supervisory employees who manage the sales staff, it is their duty to conduct training to manage and neutralise the anger and frustration pointing to the nature and properties of emotional labour. While in the modern corporate world, the emotional labour is no more a private function but a public conduct purchased by an organisation and sold on the customers, sales staff have enduring emotional job and are no longer treated as individuals but paid, selected and managed to encounter with the customers at their emotional stage to commence sales.
Hochschild (1983) also argued that the feeling rules of the sales staff are no longer just an affair of private prudence practiced in the individual level but positively spelled out freely in public where the marketing and sales managers would guide the sales staff at their training programs and set out standard of discourse. The social exchange of sales staff has kept continuous pressure to broaden the limits of hiding places of individuals allowing less room for personal navigation at emotional stages while the entire structure of emotional exchange in the personal existence has just treated as an ostensible function for the interests and delight of the customers at commercial setting of profit motivation.
Jonesa et al (2003) conducted a rear research on market orientation and its impact on sales staff’s attitude to their jobs and customers under the emergence that the sales staff are the initial point where they get in touch with the company and consider that employee’s values and attitudes as the company’s real picture. In the imperial investigation, they continued investigation with the sales manager’s control over the sales staff’s perceptions and attitudes and presented their model of sales staff behaviour connecting the sales managers, organisation’s market orientation, and sales staff’s customer orientation along with job satisfaction and service quality (Jonesa et al 2003).
The above model of market orientation of the organisation and the sales staff’s customer orientation towards customer retention and service quality has demonstrated the conceptual framework of the influence and control of sales managers upon the sales staff’s awareness of organisation’s market orientation linking with customer orientation, attitudes, and job satisfaction comparing different relationships all together (Engel et al 1995). Meanwhile the model also included the role ambiguity, conflicting situations, service quality, managerial commitments, in the model because previous studies suggest that the job attitudes of salespeople, as service providers, and sales staff’s service delivery in due course while sales manager’s insight of the market orientation of the organisation has certainly related to the sales staff’s perception. Siguaw et al (1993) added that the agreement of orientations in the model has openly condensed and mitigated the role conflict and ambiguity by enhancing the job satisfaction of the sales staff along with organisational commitments (Hochschild, 1983)
Qualification of Salesperson and Customer prospect
Webb (2004) presented the procedure of the road to recovery the principle and practice of quality management for sales and marketing occupation pointing to the expansion of qualification criteria that would assist to winning the customers. The qualification of sales staff would drive them towards best possible practice in context of the organisation and such qualification criteria would facilitate the sales staff to identify solid predictions of the products and services along with a rule of cost-effective solution (Engel, Blackwell & Miniard, 1995). The sales course of action that the sales staff and customers of an organisation would pursue, the qualification of that sales staff would bridge them by occurring successful sales by designing both business value and sales process for the customers of that organisation. The business value mapping would support the sales staff to categorise which value he would convey to the customers in an assortment of marketing and sales purpose while his qualification criteria would make possible for him to recognize which customer needed which value.
Roman and Iacobucci (2010) pointed out that the sales staff would be familiar with qualification prospects such as somewhat he has already in practice by any existing process, some of them he will improve with his learning outcomes that possibly would enable him to get better sales performance ever before. Thus, the organisation could anticipate a reduced amount of confrontation from sales staff for qualification criteria and the organisation could look forward to business value mapping connecting the sales process design. Moreover, the preliminary qualification criteria could be occupied very soon with a small number of training session or panel discussion and could adopt on the sales drive devoid of burdensome escorts of the sales staff. At the same time, qualification criteria correspond to the introductory data for not only to attending sales calls but also to generating marketing strategies connecting the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems as well as just beginning innovative product line addressing the new customers and markets.
Pre-approach Customer and Sales Staff Preparation
Malhotra (2009) pointed out that if staff fails to demonstrate benefit and utility maximisation logic regarding the product or service to the customer then there is no cause to go to customer for approaching those products or services. The prospective customer either would reject the offer otherwise does not allow any further time for approaching while the customer ends up the offerings with frustration and no sales would occur. Thus, it is essential to have sales staff’s preparation before going further to the customer, he would first evaluate to what extent the customer needed to have utility from the product or service prospect and to what extent the customer is capable for spending a particular amount of money, and to do so, it will require to do some preparation. By identifying a prospect of the product or service, the sales staff gets ready for the sale, while the preparatory phase engross with two major function like pre-approach groundwork and generating calls to the customer for face to face interaction or over phone (Bowden, 2009).
Moncrief and Marshall (2004) presented seven steps of selling process while the classical views of marking approached six steps starting from the product prospect, pre-approach level before going to the customer, approaching or offering, demonstration, presenting arguments to incur sales and close the deal but the modern approaches haven’t agreed to end the deal and emphasised on relationship marketing. The pre-approach stage would incorporate with information congregation that generates essential learning outcomes of the applicable facts and findings regarding the prospect of the product or service that necessitates addressing customer’s desired situations. This stage would reveal the customer’s needs and their capabilities to purchase by providing information those would facilitate the sales staff to adapt and modify the appearance of the product prospect. The pre-approach would also represent that information which will prepare the sales staff more than enough serious with strategic errors for the duration of the presentation and ultimately the well designed pre-approach possibly will boost the sales staff’s confidence to encounter with the situation raised during the sales.
Domain of Sales Presentation, Demonstration, and Product Marketing
At this stage, organising affinity with the product and service prospects, the sales staff carry out the proper sales presentation with the intention of demonstrate and give explanation to what extent the offered product or services would congregate the particular requirements of the target consumers. Here the duty of the sales staff is to let customer to know the prospects with reference to the quality, aptitude, and accessibility of the offered product or service, to make sure that the demonstration has successfully educated the customer with better understanding of the prospects, the sales staff would positively make certain through communication. It is essential to organise the presentation with very attractive manner to draw the consideration of the product and service prospects whether it is automated or unstructured but would successful to influence customers decision making process (Kotler, 2003).
Malhotra (2009) added that the demonstration is the central part of the sale procedure where the sales staff in fact point to convey the positive information as well as endeavour to change customer’s mind to the panorama of successful product demonstration to formulate visualisation into a customer’s mind. The most influential factors that are essential to take into account to arrange a product or service demonstration are the cautious practise to diminish the opportunity of all sorts of breakdown while the industrial sales staff has emphasised to take support of the technical personnel.
Customer Approach and Opening Sales Staff dialogue
After having the sufficient pre-approach information and satisfactory prospect of the product and services, the sales staff would drive to the next phase, which is the authentic approach of offering to the customer; this phase would often create or crack the complete arrangement of sales. In real life practice, if the approach fails, the sales staff possibly will not get any scope to offer a demonstration to exhibit to the customers to draw their attention to the product or service prospects that instantaneously inspires the customer’s decision-making criteria. The fundamental criteria of approach or product offering has consisted with several common decisive factor while in the preliminary approach would deliver with the sales staff’s own introduce to the panorama of the organisation that he represent arguing with strapping self image.
At the customer approach, the interaction between the customer and sales person would consist with pointing to the product or service prospects and it would be huge successful while the product or service is enough exceptional along with attributes to draw attention at one glance. The sales staff would switch on the sale with the point where the consumer would enjoy benefits and come closer to the offer through explaining the prospect of the product or service pointing to each advantage that would deliver with sales. In other words, it directs the prospective attention toward the benefits that the firm has to deliver. Moreover, within the customer approach, the indication of referral looms those were successful and generated strong customer base would be more effective in accomplishment of the listeners through prospects that is complicated to witness directly by the customer, for such referral it is essential to take prior permission from the past customer.
Achieving Objections and Problem-Solving Domain of Sales Staff
Bolvako (2011) argued that the achievement of objections and problem-solving domain of sales staff has organised pedestal on the theoretical framework of integrating mutually the consultative selling scheme along with the classical model with the tools of spelled out oppositions that generate from the customers concerns connecting with repeated benefits from the product and services. The functional plan that set up for objections has integrated with this domain while closing and satisfying customers’ needs at the next stage. Thus, this domain is a joint collaboration of customer and sales staff that ultimately indicate relationship-marketing stage.
Hopkins and Laaman (2003) positively argued that the grand sales staff is the great problem solver in the business world and the literature of marketing has exposed that individual sales staff who regularly expand his lexis through reading literatures and participating in different social events, playing games and solving crossword puzzles are more successful to gain problem solving capabilities (Lim, 2010). It has also evidenced that listening to classical music assists to increase mental stamina of the sales staff by stimulating the parts of their brain that boosts healing and motivating capabilities though the thing looks like unrelated to the sales drive but most of the successful sales staff has designed their regular life with such attributes and get tremendous outcomes.
Closing and Satisfying Customer’s Needs
AMA (2003) pointed out that subsequent to having come back with and overcome customers interaction, at this stage the sales staff would ask the customer to place his order from the assortments of offering. If the customer does not place order at once, there is nothing to dishearten or consider the entire efforts has wasted if not the sales staff get hold of customer’s assurance to purchase the offered product or services. The sales staff would keep in mind if the customer has satisfied with interaction and both for quality and the price, he must back, thus this is the stage to closing the deal with that customer and look for another. In practice there are quite a few techniques to closing the deal with customer, the sales staff would select any of them depending on their particular circumstances.
Bolvako (2011) mentioned that there are huge array of closing and satisfying customers’ needs while the direct asking for purchased has emphasised at the top and argued for not to wasting huge time for a single customer who is under uncertainty to make purchase decision. At the same time, contrary to the classic theoreticians, modern scholars have emphasised to keep room with customer for further negotiation with the aim to generate future sales based on the present relationship which would be right use to time and effort and resources.
Follow-Up and Relationship Maintenance with Customers
Bolvako (2011) explained that the function under this domain is to rely upon the major two resources from a lot of factors that involved for promotional activities of sales service along with product support keeping up a correspondence to the techniques of the engagement of customer service practice. Within the area of follow-up and relationship maintenance with customers, the sales staff’s activities would engage with a lot of entertainingly of numerous significant conducts aimed to ensure customer satisfaction, for instance sales staff would send thank notes and communicate with the customers to get feedback and follow-up the satisfaction of the customers who already served. The area of follow-up domain has founded with at least three essential elements like thanks giving, appreciation notes and regular scrutinising the status of customer satisfaction through handling customers complains and objections efficiently with the intend to bring their satisfaction.
The action of performing maintenance would be investigated with the tools that the customers usually adapt by means of the activity installation while such duty has also pointed out in the company’s job descriptions and the supervise integration has tailored to serve by the consultants for providing technical support. Such function of follow-up and relationship maintenance could also be delivered through technical workshops arranged for the customers by the company organised with technical sales staff who are nominated for consultation and providing suggestion. The effectual handling, writing up, and expediting orders by the sales staff are together called follow up while ensuring appropriate payment method, order management, and customer feedback have linked with the process.
Internal Coordination and Personal Development Sales Staff
Serdaroglu (2009) argued that the internal coordination area would perform internal harmonisation duties like information management with operational tasks, order handling, team management, sales staff performance, initiating training program, call recording including sample management where sales force automation is an effectual tool for group performance. To integrate sales force automation, it is essential to have a large database where the regular performance of the sales staff would be exchanged for not to overlap target customer visit and other sales function and it will ensure a high-quality operational system with a state-of-the-art database that supports both the groups and individual performance. At the same time, this process would also utilise for administrative purpose including booking, and management information system to develop further organisational strategies supporting the core value chain of the organisation.
The internal coordination is a system of straddling procedure that is essential to match up the commitment to employ market information to generate supervisory values for customers through order-fulfilment practice along with relevant customers’ service duties where sales force automation would positively enhance internal coordination dimensions. This process would keep extended significance on the personal development of the sales staff by organising training to improve the capabilities of the sales staff with accurate information and organisational values that would generate greatest potentials for personal development of the sales staff.
Determinants of sales Staff Ethical Behaviour
Roma´n and Munuera (2005) explored that the determinants of ethical behaviour of the sales staff and placed the mode of compensation along with control system at the top priority for significant determinants of ethical behaviour where the age of the sales staff is also another imperative factor to deliver ethical behaviour at the first tire. The educational qualification of the sales staff, his job satisfaction, conflict resolution method of the organisation and performance measures are also interlinked with the ethical behaviour of the sales staff at second tire. The significance of the second tire factors are less imperative than the first tire where ethical behaviour of the sales staff leads to inferior stage of conflicting role and superior intensity of job satisfaction without delivering higher stage of performance, their model has presented as follows-
Roma´n and Munuera (2005) argued that the reward and control system of an organisation is the most influential managerial factor that seriously have an effect on the sales staff performance and it has already determined that this factors significantly influence the customer-oriented selling which has strongly based upon ethical behaviour. There are huge researches with the reward and control system, and most of them have identified the relationship connecting the compensation system and ethical standard and acknowledged noteworthy relationship that the reward structure of an organisation appreciably prejudiced the ethical behaviour of the sales staff.
Cadogan and Lee (2009) studied the consequence of control system upon the sales staff’s ethical decision-making and their ethical judgments rather than their behaviour, added that the sales staff testimonies, and pointed out the relationship of control system ethical behaviour. It has been argued that the ethical behaviours would be engaged and motivated to attain sales staff’s individual goals connecting with organisational objectives. They advocated for salary, commission both for the sales staff’s compensation plan and for called attention to adopt an enduring orientation along with devote time and efforts to comprehend the future sales and enhance the ethical climates, and it has proved that the higher present salary of the sales staff produce more ethical behaviour.
Roma´n and Munuera (2005) added that the demographic variables like age and education are the alternatives that together traits and attitudinal features of the sales staff would produce ethical behaviour while the younger sales staff has more opportunity to motivate than older for ethical decision making and more educated sales force produce more ethical attitude.
Ethical Behaviour of the Permanent and Temporary Sales Staff
Defining Unethical and Ethical Behaviour of Sales Staff
Haron et al. (2011) clarified the unethical behaviour of a sales staff, as a most simple form that is the immoral performances relate to ambiguity role with extreme burden of sales target and intention to making prosperity in short cut leads to performing unethical behaviour. To reducing unethical behaviour of sales staff, most influential forces are involved in constant monitoring, support along with motivating and encouraging role to construct transparent performance roles. For more details, there are six key factors that promote unethical task of sales staff namely at the time of advertising, marketing, and conduct sales effort convey disingenuous presentation of the target goods and services. These factors involved with fail to knock with consumer’s desired goods and services and recommend as well lacking of proficiency to performing competently individual’s assigned duties integrating with the matter of inconsistency that minimise individual financial gains (Lo, 2010). The unethical conducts also make parallel to the supplementary personal benefits or individual performance rewards against one’s responsibilities, misrepresentation of individual expertnesses in the area of service delivery management and finally, endorse disparaging remarks about rival’s status as well as their products, services employees or agents.
In responding to these forces, several research reports identified that there are nine ethical issues while the biggest organisational dilemmas obstructing staff’s ethical attitudes and accessibility of employee’s ethical behaviour identified four major catalysts that play behind, for instance, compare to usual compensation and reward. The settlement of claims pays significantly lower, without knowledge of an employer engaged with a part time business, discouraging feedback from prior sales staffs and discouraging practises of regional manager that obviously brought kickbacks from existing and potential rivals. On the contrary, defining ethical behaviour, hypothetically, it has emergent to familiarise with planned behaviour where sales staff’s performances are namely guided through three attributes like behavioural beliefs included behavioural outcomes and evolutions, normative beliefs involved with complying optimistic motivation and sound expectation and lastly, control beliefs attributed through execution of impede performances as well as conduct with perceived power. Alternatively, these three ingredients of ethical behaviour delivered either favourable or unfavourable attitudes, subjective norms to perceiving social pressure and persistence of control behaviour gradually. In experience of ethical ingredients there have several unavoidable control variables where age and experience are considered most significant (Haron et al. 2011).
Ethical Sales Staff Behaviour
Tweedie (2011) added that the ethical sales staff behaviour (ESB) has consisted with eight imperative attributes influenced the buyer and seller relationship and additionally, involved defining circumstances of sects of ethical behaviour. At earlier stage, ESB has influenced valued buyer’s trust and commitment conforming two crucial ingredients those delivered most strong sales leadership potentiality with consistent with the empirical model of constructing positive buyer seller association. Alternatively, buyer trust is a primary condition of resulting effective ESB during constructing significant block of buyer commitment and in gaining buyer trust, expert sales staff should demonstrate reliability as well as high integrity. Consequence of this, buy building foundation of trust buyers’ confidence have increased gradually hence their observable behavioural blocks easily grasp five circumferences since, buyer’s lower incline monitoring on ethical sales staff’s activities proportionately tends towards more valuable buyer seller affiliation thus make them save valuable time and anguish tasks.
Tweedie (2011) also pointed out that during the middle phase, ESB effectively influenced concept of the share of customer that denoted volume of consumer’s devotion for a particular firm as well as their particular product or service. In another word, percentages of share of consumer is equivalent to the economic advantages of reinvestment along with brand loyalty, but there have not any direct affiliation with ESB and share of consumer to build positive buyer relationship commitment proportionately by anticipating higher future returns. Another mid-level phase of ESB influences the buyer’s communication where ESB has passively knock buyer communication to transmitting judicious and on time delivering information from buyer to seller. Under this approach, buyer and seller’s affiliation advance communication conveyed rich benefits both the parties as well as effectively grow strong networks of buyer’s commitment and trust because buyers who trust on ethics of a sales staff more comfortably and frankly communicate and forced by a tendency sharing more information for a continuous relationship development. At last, ESB influenced for positive communication through word of mouth, which is an interpersonal communication mode to elaborating optimistic business reviews by buyers positive sharing with their associated peers; therefore, these interpersonal communications carried rather greater weight that recommended significantly optimal level of trust on the way of buyer trust (Tweedie 2011)
Engagement of Permanent and Temporary Sales Staff
Manpower Inc (2006) stated that in aggregate form, the engagement as well as managing employees has treated under workforce management that included both permanent and temporary sales staff of an organisation. Consequently, motivation and performance mobilisation of aggregate workforce has derived through a dozen of engagement forces where performance evaluation has concentrated on two key dynamics, for instance, clear vision of entire expectation and treated under a meaningful working atmosphere. Meanwhile, sales staff’s chief engagement forces are encompassed sequentially as utmost performance factors effectively patronized by proper treatment of entire staffs with respect that effectively as well as efficiently able to recover frustration and hence convey glowing reviews towards both employer and employees.
In order to supervise contingent employee’s expectancy executing best efforts to do an assignment as well as removal of ambiguous matters fix up an expectation parameter. Establishment of sense of belongingness so that employers would successfully able to pay significant leadership role as well as motivate sales staffs to convey utmost performances; therefore, staffs felt stronger emotional affiliation with their employer. To manage and administer the employees, most of the organisation has significantly suffered from lack of equal treatment practice and treatments, where the policies are either involved to hire the temporary employees through short time contract or outsourced from the different agencies that use freelancers. The usual tendency of the organisations is not permitting temporary workers, attending regular teamwork activities along with the permanent staff and it has delivered an unconvincing workplace attitude that goes out of the employee’s code of conduct.
The engagement of workforce of permanent category have enjoyed superior facilities than temporary employees, consequently, required tools and resources are also delivered following a discriminatory manner that resulted serious frustration of job security, but delivering equal work tools and resources effective to engaging all type of employees as well as boosts their performances. Promoting worker’s performance and engaging them for long both on job training and off job training can play crucial role where authority should be frank, responsible, honest, and appreciate two ways feedbacks for fair judgment along with encouraging critical forces of the organisation fluently. At the end of describing diversified employee engagement, strong team work, fair recognition, abandon opportunities for regular learning, development and progress, under stability to develop success of business effectively and efficiently and lastly, ensure proper security for the entire sales staff would recover all of workforce engagement difficulties (Manpower Inc. 2006).
Effect of Outsourcing Temporary Sales Staff
Erickcek et al (2002) mentioned that the outsourcing temporary sales staff is an essential ingredient of an organisation’s entire workforce to show their selling performances. The significance of prioritising temporary sales staff of an organisation is that there have abandon scope of practicing low skilled labour market working conditions like wages and benefits. In addition, many intensive case studies on diversified industries defined that outsourcing temporary sales staff either adversely affected or highly benefited in consistent with low skill labour market strategy. In brief, adverse effects of temporary sales staff’s compensation package would effective and unambiguous if numerous substitute agencies followed a long-term low skill labour market compensation policy; consequently, outsourcing temporary staffs get high compensation, wage benefits, and assign management functions. For instance, within last decade, number of outsourced temporary employment has increased by 10% and function of these employments had increased dramatically by means of innovative sales and managerial tasks.
Erickcek et al (2002) also illustrated the effects of outsourced temporary sales staff, this part has crafted numerous key issues involved with long–term substitution, low union status, loss of regular wages, potentiality to switch as permanent employee, employer’s motivation to hire temporary staffs. The reduction of employer’s constrains during employment form, screening core competency, ensure and restore quality of well tested systems, control of high employment costs, reduction of layoffs by prioritising enhance staff’s productivity and increase of entire organisational productivity, figure below presented the way by which outsourced staff provide competitive advantage for the organisation (Search Wise 1999).
Theory of Planned Behaviour
Alt and Lieberman (2010) explained that the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) is analytically a hypothesis on human behaviour that connected and concern on human attitudes with action. More specifically, the TPB accessed on the way of individual’s beliefs on a specified –behaviour, beliefs on social norms connected with specified–behaviour and belief on controlling approach regarding to the result of a specified–behaviour. In reference with this argument, the TPB has composed through three ingredients individual behavioural beliefs, normative beliefs and lastly control beliefs. In broader form, intention of the behavioural beliefs involved to assuming direct precursor of an actual action and in addition, empirically, effective for well supported in transmitting diversified behavioural approaches, social domains in relevance with advertising, marketing, communication, and cognitive social psychology. Recent overview on individual behavioural beliefs discipline articulated numerous features, such as, authentic, repeatable along with practicable social simulations. In defining normative beliefs, TPB mostly emphasise on decision-making procedures of public policies significantly including investigations of changes in the beliefs, values and interests whereas control beliefs are a motivation tool that engaged to recover depressing movement of human being with the society whole whether expectation of any action fail to convey positive result (Alt and Lieberman (2010).
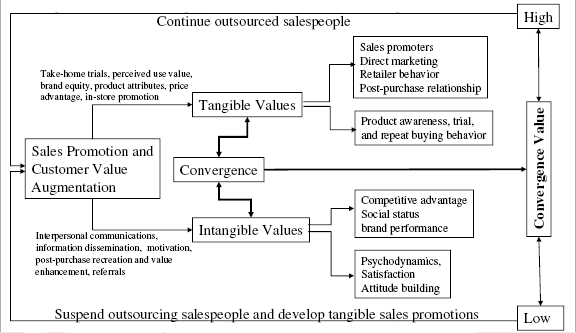
Outsourcing Sales Staff Behaviour Problem and Prospect
Rajagopal (2007) argued that the significant ingredient of entire workforce of an organisation, outsourcing sales staffs is featured with both prospect and problematic issues. To illustrating prospect of an outsourced sales staff, at earlier stage, it needs to notice that they have played a dramatic role on building inter–personal communication bridge along with enhance pre–purchase arousal motivation for organisation’s product or service; therefore, manufacturing and marketing department of an organisation enriched swiftly. Alternatively, prospect of an outsourced sale staff involved to defining and analysing core behavioural motivations of valued consumers that influenced assessing leisure shopping behaviour as well as investigation of empirical consumer values. In this way, outsourced staffs are the significant promoter stimulating consumer interests to buy product or service and additionally, influenced for product attractiveness. Meanwhile, consumer centred business organisations like financial institutions enthusiastic to appoint greater number of outsourced staffs for superior market coverage as well as boost sales volume make strongest competitive position in the industry.
On the other hand, outsourced staffs are typically termed as promoters to performing specialised target activities to expand service network of the organisation as well as disseminate organisation’s brand image to attracting more satisfied consumers and the outsourced staffs can be deployed organisation’s strategic distribution networks or the supply chain management. Another significant issue is direct interaction with the consumer during delivering services and outsourced staffs have wider scope of reducing cost structure and consequently enlarged equity of the organisation. Moreover, employment of outsourced staffs is also a matter of dilemma for several organisation for instance, narrow scope of post-purchase consumer relationship, wrong impression of company image as well as product and service, no clear direction of wages and salary along with fringe benefits and for more details following figure demonstrates problem and prospects of an outsourced staff (Rajagopal, 2007). Figure below illustrates the problem and prospect of outsourced sales staffing –
Standards of Sales Staff Ethical Behaviour
DHFS (2011) illustrated that the diversified attributes in marketing profession experts define the ethical standards addressing numerous performance qualities of technical skills. In sequence of this, sales staffs should to subscribe towards several ethical principles as well as standards to stimulating individual along with team or group decision-making procedures and actions as well. Typically, ethical principles of the sales staff are composed through three components integrity, value, and loyalty. In this way, effects of these three principles establish sales staff’s ethical standards that would encourages extreme devotion for an inflexible ethical behaviour, expansion of awareness as well as acceptance of ethical conducts and finally, emphasise on the key role of ethics during formulating selling decisions. These three motivations are worked for structuring ethical behaviour standards to stimulating entire sales department; in addition, ethical standards of sales staff are not assign to displacing organisation’s policies, but passionate to modelling considerations. However, it has common to all that every sales staff is officially recommended for striving a sound structure of acceptability and adherences in favour of these ethical standards.
Meanwhile, an organisation itself is an encouraging dynamic that significantly develop, publish and make enforceability for an ethics policy in favour of the ethical standards. In addition, ethical policies have to carve up with the entire sales staffs as well as external suppliers of the organisation (ILO, 2007). Alternatively, it should continue that virtually not all of situation does covered through ethical standards and guidelines where sensitivity to cultural diversity, laws, customs and suitable practices have taken places. Considering sales staffs ethical behaviour, there are ten chief ethical behavioural standards involved in perceived such impropriety, conflicts of interest (COI), issues of influence (IOI), convey responsibilities to the employer as well as superior. The other standards are building effective buyer seller relationship, construct sustainability as well as positive social responsibility, reciprocity, assembling applicable commercial and industrial laws, regulations along with trade agreements, building professional competencies with dealing of confidential plus proprietary information with loyalty (ISM, 2008).
Islamic Ethical Standard
In consistent with the case of the present research, this part has involved with Islamic ethical standards in selling financial products or services towards the Malaysian consumer in Penang. In order to engage with the Islamic ethical standards, here significant assessment has executed to draw the religiosity role as well as perceived ethical values to fulfil the demand of marketing and advertisement ethics of an organisation. Regarding this point, idealism, relativism, and religious faith have focused in the light of Malaysian business atmosphere. In this study, it has revealed that both factors idealism and relativism has moderated by means of individual’s religious belief and strength as well. In short, significant under stability of marketing ethics need to discover diversified cultures as well as inter–organisational practices. In reference with globalisation, marketing tasks have transformed and expanded rapidly since repeated change in consumer demand and because of the impact of globalisation, it becomes difficult to maximise profits in highly competitive atmosphere; therefore, companies required to cover greater geographical areas than before in terms of international sales. Attach with this truth, multi–domestic companies obligatorily required to focus on host country’s own religious practices, potential consumers’ perceptions and moderate judicious factors.
Ghani et al (2011) religions have influenced on the people to draw their ethical beliefs by distinguishing right or wrong and for the entire society. In considering this fact, business holders have also in emergent to learn that besides homogeneous societies and countries multi–cultural nations have ethnic groups with diverse religious beliefs as well as practice and hence, diverse moral values are also essential to consider in developing marketing ethics. To highlight the Islamic ethical standards, earlier facts need to account before developing in an Islamic country like Malaysia. For an example, Islamic nations have strictly prohibited alcoholic drinks and other product or service due to their religious directions and in numerous states of India prohibited marketing of beef products.
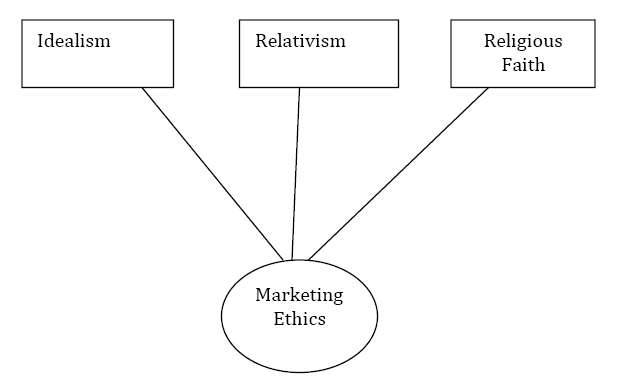
Sales Staff Ethic in Penang
This study has already addressed that Malaysia has three ethnics groups those have strongly influenced through religious beliefs, but in workplace that organised the sales staff’s ethics in Penang, Malaysia has not yet significantly influenced and moderated through religious radicalism. Alternatively, idealism and relativism is strong moderator by religion on composing marketing and advertising ethics. Literally, high marketing ethics possessed thorough high idealism and conversely, idealism is a positive dynamic whereas relativism focused on negative influencers. An assessment on 22–26 years sales staff’s group of Malaysia identified that they are keener to accomplish their job responsibilities and duties rather than practicing religious moderator. Moreover, young sales staffs are more enthusiastic to making money within first third years of their job experiences. At last, major portion of the sales group agreed that religious faith is obviously a significant moderator, but in their workplace and performing job responsibilities, religious belief have influenced at lower volume than their superiors do (Ghani & Rehman, 2011).
Sales Staff’s Satisfaction Connecting to Customers Satisfaction
This chapter has organised with following sections-
Critical Role of Sales Staff’s Service Delivery
Gima and Micheal (1998) illustrated the critical role of a sales staff in time of service delivery it has emergent to know about flow of service delivery management (SDM) as well as essential ingredients of the SDM. Before detail account of critical role of a sales staff, it is indispensable to have a look on essential service delivery elements those compose sales staff’s critical role as following diagram represents
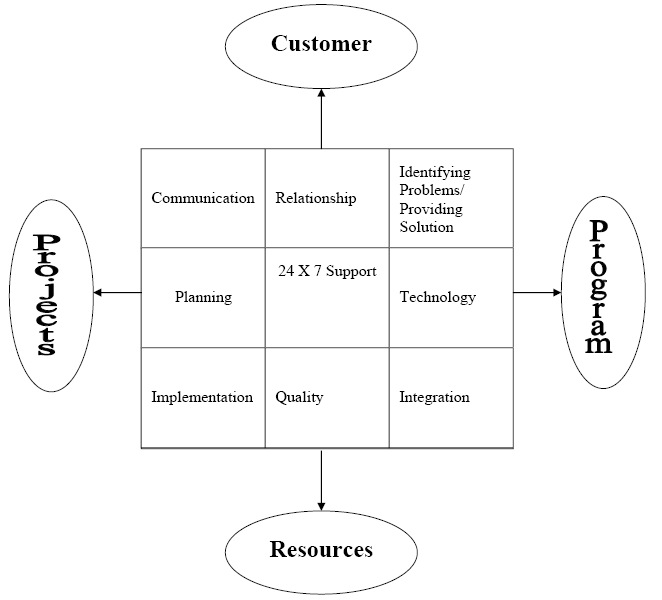
Mehta (2006) explained in consistent with the Figure 3, consumer, resources, projects and program are the four core fundamentals those have treated as heart of SDM and the rest of nine ingredients patronised sales staff’s behavioural role that significantly crafted consumer satisfaction. Initially, to define critical role, crisp, clear and unambiguous communication is the most crucial responsibility of a sales staff with the fundamentals of SDM where consumer should get utmost priority and since valued consumers are considered SDM as primary solution tool. Hence, cordial relationship with consumer is of paramount importance. After effective communication and relationship, knock consumer’s crisis and recommend accordingly make the relationship durable as well as loyal.
Organised planning is effective for conducting project activities as well as scheduling of the sales staff and in addition planning is assign to define and structure execution procedure of scope of the sales project, constraints during selling, forecast assumptions of sales target, discover and pick associates risks of the project, endorsement plans and finally, resource planning. In executing 24 X 7 supports, it has emergent to attach with online business system where sales staffs should to proficient providing a clear guideline of consumer demand. Alternatively, 24 X 7 is appropriate for automation of sales services where CRM practice is much easier through attributing three core dynamics namely; frequently change requests, inquiry on desired services that carried potentiality of change requests and appropriate problem management.
All of this phenomenon should involve in analysing performance issues of SDM as well as potentiality of statistical techniques, scope of RFC deployment, work–log, and UAT. In the area of SDM, technology has covered significantly role by delivering ease B2C functions like ERP, SCM (Supply Chain Management), planning of production, managing contents, business intelligence and EAI (Enterprise Application Integration) and additionally, ensuring high return on investment. After adaptation of technology, growing companies as well as their sales staff should to implement modern technology and continuous upgrading them for a fruitful service management performance. Quality the key performance indicator of SCM along with the sales staff that proficiently reflect client’s expectations and rich benchmarks in consistent with the SLA (Service Line Agreements). Finally, integration of client application considering three forces namely, integration of gathered data and information, integration of application for a specific service and integration of available product and services (Mehta 2006).
Sales Staff’s Motivation and Compensation (Reward) System
Warner (2000) argued that strategically, compensating employees is an effective motivation tools that mobilise an organisation’s selling objectives as well as make flexible accountability to define individual differences along with deliver a fair perceived value, effort and entire procedures towards the available sales staff. On the other hand, sales person motivation via compensation as well as rewards have worked following a hierarchy of worst to best where worst compensation denoted as salary including only bonus whereas best compensation packages involved with a high flexible salary payment where pool, commission and bonus have combined together to motivate existing sales staff.
For more clarification, goals and objective of a well–designed compensation system has enthusiastically included assisting in execution of organisation’s strategic mission, vision and goals, assisting in communicating organisation’s corporate goals, well-defined performance standards or benchmarks, and assessing expectation level, attach a direct compensation package that can motivate current sales performance. For instance, the positions, attracting and grow with good people, generating high motivation towards the current sales staff, continuous involvement to analyse sales staff’s potentiality, account coverage planning, as well as allocation of selling time, be fair to employees and organisation, delivering management control and finally, stimulate superior teamwork as well as cooperative efforts.
Warner (2000) also added that considering sales staff’s duties and responsibilities there are numerous stimulating effects of well design compensation system namely, increase consumer volume, new business development (NBD), keep attach as well as significant growth of existing business, dramatic expansion of consumer loyalty. And in doing so, compensation and reward motivate the sales staff’s to perform on the way of several selling strategies namely, reduction of advertisement dilemmas by increase of selling, highlighted value of advertising hence individual medium of selling, create value for every individual product or service, make sense to be the preferred supplier and be innovative. Above all, there are several difficulties in motivating through compensation packages and two of them are most drastically, hampered positive motivation of compensation system and they are, violation of sales objectives and assisting an organisation to achieve their strategic goals and objectives through communicating corporate goals performance benchmark and match expectation. These two dilemmas are commenced through two ways; at earlier stage make complication in sales management by attaching a direct sales compensation as strategic objective and lack of unambiguous long-term sales tasks, objectives, goals, standards, and expectations.
Sales Staff’s Job Satisfaction and Quality of Performance
Gima and Micheal (1998) explored that in the area of marketing communication process, sales staffs are the most crucial ingredient and under specific circumstances if any organisation wised to introduce a new product or service because of diffusion as well as acceptability among existing and potential buyers. Hence, several studies examined crucial role of a sales staff that consequence respectable sales staff’s effort, their satisfaction areas, and impact on performance by job satisfaction. Meanwhile, significant intra–organisational changes in the area of business and product development have also focused on sales staff’s effectiveness lead towards a successful consumer segment to defining influences of sales staff job satisfaction on their performance’s remarkable effects of a sales staff that concentrated on the earlier significantly. In attached with the hypothetical view of sales staff’s effort followed by arrangement of adjustments significant organisational changes, scope of training, reward and compensation packages in order to enhance sales staff’s psychological acceptability as well as deliver stimulating forces in increasing selling efforts.
On the other hand, success rate of a sales staff in the case of Penang has entirely linked with expansion of their effort, job satisfaction, and superior performances, but this avenue does not follow simple stimulus responses. Because of higher performance, delivery dose not essentially require potential consumer resistance as well as optional market conditions to move towards contingency approach on under stability of sales staff’s efforts to sell a product or service. More specifically, at earlier stage, examination of impacts of sales staff’s effort scheduled on satisfaction along with performance in selling target product or service and investigation of the degree of chosen environmental forces moderating linkages with sales staff. To draw proper linkages between staff’s job satisfaction and job performance (Gima, & Micheal, 1998); however, the following figure shows the obligatory sales forces for a sales staff –
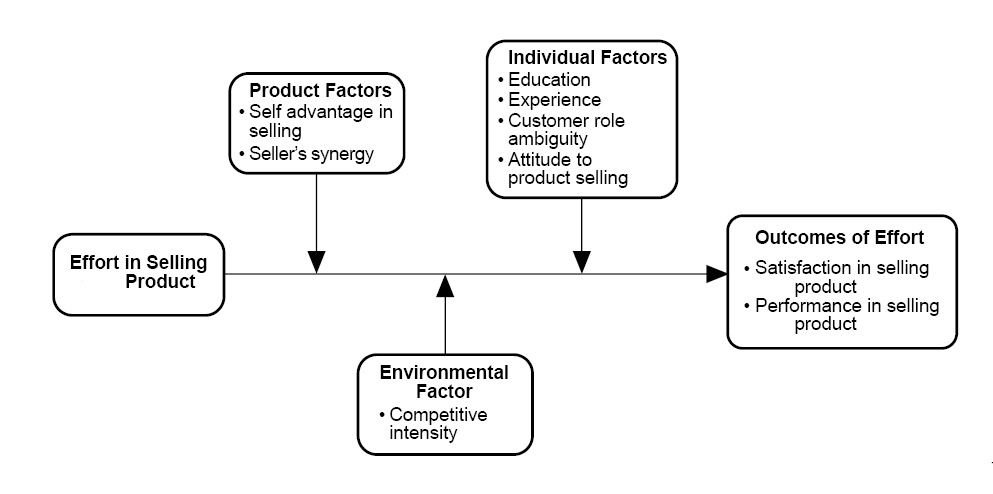
In summarise form, in consistent with the above figure, parameter of sales staff’s efforts those influences of job satisfaction and job performances are mobilised through three obligatory dynamics, such as, product factors, sales staffs, and market competition or rivalry intensity. Among these product forces are conceived through self-advantages by selling, degree of synergy and resources of a sales staff whereas characteristics of a sales staff included education status, experiences, ambiguity in consumer role and attitude to sale new product or service. In this way, examination of linkage between job satisfaction and superior job performance fundamental premises those tends towards forthcoming greater potentialities to draw ambiguities as well as stresses for a sales staff and inversely, in elaborate form efficacy of sales staff’s efforts on satisfaction and performance would have ameliorate by job related stresses.
Customer Orientation of Sales Staff
In drawing the right scenario on sales staff’s consumer-orientation, an analysis by JCM has represented that principally there are two key conditions, for instance, meaningful work experiences of sales staff rationally motivated them to covey enriched consumer-orientation, and on other side, more two effective moderating forces are present employee’s view towards organisational values with assessment of payment received from organisation. Thakor and Joshi (2005) argued that consequent to this, several research reports appraised that pay satisfaction as well as meaningful work experiences optimistically motivated employees to influencing satisfactory consumer orientation. For more clarification, sales staff’s function is also a helping tool for consumers that fostered purchasing decision making as well as ensuring satisfied consumer preferences.
In doing so, sales staff has strategically followed two sales approaches: consumer-oriented selling or sales-oriented selling – it is important to note that these two forms are functionally diverse from each other. In the light of consumer-oriented selling, sales staff’s functions are required to deal with both instant and long-lasting consumer preferences, and usually, instant preferences have felt and articulated clearly; however, the long-lasting preferences are centred with suppressed circumferences. In order to satisfy customer orientation, a sales staff’s functions should to determinant to discover latent preferences of a consumer and at the same time, urgent assurance of prompt sale potentiality. In defining the impact and influence of staff’s function on consumer orientation, key difference between sale orientation and consumer orientation is that sales orientation deal with the opportunistic means where as consumer orientation is processed thorough listening consumer’s preferences. Moreover, to be enthusiastic in executing consumer orientation tasks, sales staff should to be expert in intrinsic activity performances as well as extrinsic tasks consecutively (Thakor & Joshi, 2005).
Customer Convincing Appearance of Sales Staff
In this part of the paper, influences of a sales staff on consumer have discussed where function of a sales staff is five times more essential rather than advertising and promotional actions. To define the coupled interactions and influences between a sales staff and consumer, many researchers have termed as the interaction dyad (Cho, 2001). In the area of selling financial product or service or in another retail atmosphere, sales staff is the most influential dynamic during consumer’s decision-making process due to representing satisfactory loyalty, staff’s efficacy and characteristics. Numerous assessments on staff’s appearances defined that there has strong potentiality for an absolute anticipation of buying a product or service, but a consumer may switch if sales staff did not convey satisfactory performances as well as appearances. In order to featuring sales staff attributes, most of the consumer focused on clothing to denote identity, mood, and attitude; on another hand, a segment of consumer group emphasis on age limit to specify diversified attitudes, values as well as behaviour.
Prioritising key requirement of the part, conceptual model has both hypothetically and from practical evidences, consider most significantly age and clothing type of a sales staff and hence influenced as well as assessed sales staff’s performances and assessment of expectancy on confirmation or disconfirmation between expectation and appraisal. In reference with the statement, the study on sales staff’s appearances principally circled through three dynamics two types of age group either adolescents or elderly, types of clothing either formal or informal and attitudes towards sales staff’s performances and make differences between expectation and appraisal. Consequence of this circumstance, it has affirmatively denoted that there has significantly positive affiliation of consumer attitudes to define sales staff’s performance where higher expectation as well as assessment of a sales staff’s performance closely linked with high satisfaction of a consumer. Alternatively, to draw the relationship status, assessment of expectancy conformation or disconfirmation along with consumer evaluation of consumer satisfaction reflect more satisfied consumer group and meanwhile, if a sales staff’s performance is equivalent or better than consumer expectation consumers are also respond as highly satisfied. (Cho, 2001)
Typically, functions of a sales person and development of trust of their valued consumer required to consider a set of critical elements to delivering as well as nursing effective, durable seller buyer relationship. This segment of the dissertation has developed to illustrate the common functions of sales staffs those proficient to conceive successfully consumer’s trust in the way of Meta-Analysis Model (MAM) where fundamentals of trust along with sales-oriented trust consequences have taken place. Under this circumstances, motto of the sales staff function is obligatorily required to considering judicious as well as beneficial influences in developing consumer trust; on the other hand, sales staff should too modest in influencing trust over valued consumer and themselves as well. It is important to point out that consumer trust on the sales staff is a key determinant assessing quality of seller buyer relationship. In the light of MAM, sales staff is a curial rationale that accountable for building trust in the area of B2B (Business–to–Business) marketing where fundamentals of trust and unavoidable consequences of trust has conducted.
More briefly, ancient nature of sales staff’s function is numerically proportionate with the level of consumer trust; therefore, there have a positive interaction exists among them to magnify sales volume. Meanwhile, sales staff has dramatic influence–ability in intensifying consumer’s level of trust and the post MAM stage resulted that other than common factors modest affiliation is more effective in building positive consumer trust as well as intentions and actions on sales staff. Finally, the MAM reported that the coupled affiliation between consumer and sales staff has also magnitude by competency and benevolence where sales staff’s engagement has faced several limitations of magnitude since of traditional selling techniques attributing negative effects. In the end, hypothetical definitional issues of consumer trust accounted affect, cognition, risk factors to decreasing sales volume, suspicion, examination of sales person attributes including experience, training and gender, sales staff’s behaviour prioritising presenting product or service attributes (Swan et al., 1998).
Interdependency of Sales Staff Satisfaction and Customer Satisfaction
To illustrating linkage among the job satisfaction of the sales staff along with consumer satisfaction, it has still a matter of debate which one is stronger or is sales staff job satisfaction would weaken or strength consumer satisfaction. To identify the connection between these two forces, balance theory of consumer and staff satisfaction have initially analysed with unique attributes of consumer and employee to identify common attributes in order to address influences and impacts of employee satisfaction on consumer behaviour. To locate consumer behaviour attributes, balance theory has enlisted consumer loyalty, preferred pricing strategies, and emergence of required products and services whereas sales employee’s circumstances involved with reliability, empathy, and expertise.
In consistent with the balance theory, these attributes have considered to elaborating the circumstances that either stronger or weaker relationship among salesperson and consumer satisfaction and consequently, contingency factors of a sales staff has reconciled to systematic strengthen or weaken the connectivity with their valued customers. Several researches on this aspect have revealed that currently deals with, however, online business organisations are more favoured towards both staffs as well as consumers, for instance, consumer loyalty and emergence of products and services reflects positive sign towards their preferred suppliers of the company and conversely, awareness of pricing strategies treated as negative moderator. In reference with this example, key relationship of consumer and sales staff tend towards to notify positive influences, but low understanding of a sales staff rationally weaker the connectivity and in addition, ignorance of consumer’s demand of product and services has also influence to weaker this relationship as well. Finally, managerial viewpoint addressed that handsome payment along with satisfactory working atmosphere are greater encouraging forces to ensure consumer satisfaction though still there have several points of ambiguity in the discipline of relationship management (Homburg, & Stock, 2005).
Factors Influencing Unethical Behaviour of Sales Staff in Penang
This chapter of literature has delivered with following sub-chapters-
Supervisory Influence
Ghani, et al (2011) explored the characteristics of religiosity linking with alleged ethical values of the marketers of Penang upon their marketing ethics, and identified that the relativism along with idealism touching the magnitude of ethics restrained by the religion alignment of this region where large segment of the demography inherited from Muslim. It has demonstrated that people of Penang having far above the ground idealism posed with superior ethics while it has also evidenced that sky-scraping relativism has not evidenced any drop off ethics although the idealism linking with relativism had moderated by religion configuration.
Haron, Ismail & Razak (2011) conducted a study to identify the factors manipulate the unethical behaviour of insurance agents in Penang, Malaysia and argued that the external variables like supervisory influence, role ambiguity and the pressure of sale targets are the most dominating factors that drive a sales staff to conduct unethical behaviour.
Haron et al (2011) bring into being that while sales manager has a propensity to favour sales staff for ethical behaviour, but predetermined punishment for unethical behaviour has evidenced to be easy-going by the managerial alignment towards unparallel competition for sales generation. Noor and Muhamad (2005) identified that the supervisor influence has established by keeping full attention and getting opinions from the all individual sales staff while it could carry on an unfavourable psychological along with behavioural injury by distressing job satisfaction, extreme stress and motivational deviation of the individual sales staff. Meanwhile, the sales target relays on the quantity of rewards that the sales staffs receive with consequential impact on the motivational level while there is a momentous association involving supervisory influence to entrust the unethical behaviour.
Role Ambiguity in the Job
Safaria et al (2011) conducted a research with the Malay academia staffs to identify role ambiguity linking with job insecurity, and pointed out that the wave of globalisation has influenced to alter all feature of human heritage together with the nature and how the organisations would operate their human resource. Such changing dynamics of business operation has generated too much nervous tension, stress among the staff of business both manufacturing, and service sector. Consequently, ambiguity and conflicting situation posed on how a task of business operation would be conducted whether they would utilise the traditional staffing or engage outsourced freelance staff. Under this circumstance, employees suffer from invisible pressure of losing job and get in the way to carry out better performance of their jobs while there are reconciling belongings to the job insecurity and stress among the staffs.
This model demonstrates that job insecurity is a negotiator to generate job stress despite the fact that the role of ambiguity along with the role of conflict does not have a straight consequence on job stress. However, it has tremendous roundabout consequence via intervention of job insecurity derived from job stress where the co-worker’s social support could contribute to reduce stress (Ismail, et al 2010)
Moral Obligation & Behavioural Control
Strutton et al (1997) argued that sales staff poses some extends of moral obligation to nourish the panorama of customers, uphold the objectives of the organisation and fulfilling on ambitions. To coordinate these three-dimensional obligations, they continually suffer from dilemma of truth telling (Strutton, Hamilton & Lumpkin, 1997). Such dilemma generates from ignorance and conflicting interest of the stakeholders that usually obstruct the pathway to conduct morally acceptable sales behaviours where implementation of standard ethical codes at organisational level is the most successful preventive measure to keep a stopple toward unethical sales behaviours.
Krishnan et al (2010) conducted a landmark research with job satisfaction as an impending mediator linking motivational job characteristics and employee’s behaviour and identified that the staffs are always aligned with self-interest at the top of priority among the other obligations. Their second priority is the corporate concern while they look to the customer’s needs at the third choice of their obligations along with other obligations like the nature and mode of the transactions. At this level, it is essential for the sales staff to emphasis on the concern of dealing too many mixed motives at a time without any moral hazards complying with ethical standards.
In Penang, Malaysia up to till now, there is no standard of ethical code sales staff has been introduced that could be suitably utilised to conquer the distinctive situations that donate guidance for moral dilemmas that sales staffs repeatedly encounter at their sales drive. For the credit card sales, the concurrent situation demands to have an ethical code, which will provide appropriate guidance towards the ethical paths under an assortment of sales drivers and it would also clarify the rationales of associated spending for moral learning to remove ignorance and conflict. Such ethical code would be valid in context of the globally accepted wisdom of customer expectations along with sales staff’s behavioural reputation to point up the reason why, when, and how the sales staff are ethically essential to speak out the truth keeping attention to the corporate interest, personal interest, and customers’ needs.
Extreme Sales Target
Ahmad, Basir and Kitchen (2010) pointed out that sales target is a dominating force that accelerate the financial performance and profitability of an organisation keeping strong interdependency between the sales staff’s commitments and organisational commitment. The linkage between job performances of sales staff along with their persistence commitment has an inverse relation with sales performance, while extend of commitment increases sales generation decreases with dependable variables like target and commitment fulfilment (Ahmad, Ismail, & Sohail, 2010). Sales target always act as a threat to reduced earning or losing job, thus some researches delivered negative relation correspondence among the measures of organisational commitment and the sales generation of the sales staff.
Salleh and Kamaruddin (2011) added that sales staff who carry out better sales performance, has higher self-efficacy to negotiating and motivating the customers for the reason that they consider that they pose proficiency to gaining the sales targets without any unethical conduct. Thus, the successful sales staff emphasis on their interpersonal skills to reach their sales target while the reluctant newcomer sales staff point to the extreme pressure of sales target. Penglase (2010) added that the sales staffs always look for excuse for not to reaching their sales target and identify uncompetitive price, inferior product or service quality than the competitors, territorial hazards, and weak CRM system but urge that enough sales are in the pipeline.
Lower Profile of Socio- Cultural Orientation
Smith (2004) mentioned that though the modern corporate has been aimed towards global operation, culture and cultural diversity still carry on as a significant factor how corporations would act in global context in spite of the debates between the academia scholars and business practitioners regarding the magnitude of culture among the nations. The multinationals operating globally has been continuing to solicit the consultants and talents of culture to progress their cultural alignment in different countries while culture plays a predominantly applicable role surrounded by the domain of sales staff and their communication and relationships within the customers (Johansson, 2008).
Smith (2004) further added that the culture keeps a significant responsibility to determine how the individuals would behave at the workplace, the way in which staff would interact with each other, what the values they perceive and care for each other keeping an effect on their manner, degree of coordination among their shared vision. Within the sales orientated companies, contacts stuck between managers and sales staff could be more than ever critical than any other type of business orientation in view of the fact that they pose greater closeness along with significance to the sales and profit of the company. Thus, their relationship has usually persistent on the ordinary demographic variables like their age, sexual category, and race by taking into account of the internal features of the sales staff linked with their cultural orientation in the workplace domain.
Smith et al (2002) added that the actual behaviours observed within sales companies has evidenced that the culture may represent both conventional values along with the sales manager’s strong prognostic and prevailing values with linkage to the sales staff behaviour. The culture is the context of overall communication framework of people that replicate the underlying meaning of communicated information and the perceptible structure may interpret in accordance with the both high versus culture along with low dichotomy. The high framework of culture corresponds with extremely imprecise means and usually spells out mutually pointed out set of delicate, indirect, but predetermined messages, while the low paradigm of culture communicates with more open meaning that naturally expressed by simple sign with verbal encounters. Lower level integration of culture among the sales staffs necessarily demand to have training to realise identities, taking motivational spirit along with most wanted outcomes of interactions (Weng and De-Run, 2010).
In context of credit card sales in Penang, the sales staff exhibit differences in culture and their values, though their beliefs and faith oriented from Islamic values with respect to Malaysian local moderate environment while the diversity of culture put into a practice of momentous influence on the sales staff’s behaviour. Among the credit card sales organisations, the existing culture has developed with the values that they put into practice, assumptions that trust, and the way of interpretation at their organisational level with the most common set of the factors influence individual behaviour psychologically along with organisational framework. Among the sales staff in Penang, culture played three-dimensional influence where culture in the credit card companies have supported the fundamental principles of sale revenue maximising trend rather than emphasising on human behavioural factors while culture without any doubt an irrevocable factor of exchange among the sales staff and customer.
Lack of Education
Abdullah et al (2007) explored that the socio-economic progress of Malaysia has the highest degree of influence by human resources performance mutually in the governmental and non-governmental sectors, while the recent national development plan of the country has kept highest emphasise to deliver the growth strategy through knowledge-driven human resource development. Fleming and Søborg (2010) pointed out that the emerging economy of Malaysia urged for skill human resource development especially in professionals and technical categories while 28 % of the existing staffs are under these categories. In the knowledge incentive jobs, females have the greater share, with such a characteristic of the job market there are huge domestic and foreign Universities working to address the needs of skilled human resource in Penang.
OECD (2010) presented the involvement of academia in provisos of teaching and learning with the aim to meet the necessity of skills for the labour market though there is no specific strategy for student defined to recruitment and job market in the state of Penang. The Universities are independent to set up their individual strategy to address the job market needs and to attract students with brilliance of educational programme for both graduate and postgraduate level. There are some Universities in Penang with global reorganisation for their contribution in the knowledge world. Conventionally, the PECC is the state governmental agency to design and develop the system for rational objectives of the educational policy in Penang though it is merely a private sector higher educational institution of the state Penang. The Universiti Sains Malaysia of Penang has dedicated to the postgraduate research aimed to accelerate the socio-economic development of the state by producing competent human resources for the both private and public sector along with the multinationals. There is a remarkable joint effort and alliance among the Malaysian Universities to meet the needs of job market.
Credit card marketers in Penang are under pressure to engage skill and competence sales force, but the shortage of accomplished human resource, they are involving less educated sales staffs, even just coming from high school. Due to lack of education, such sales staffs easily align with unethical conduct with customer, which already generated huge scandal in the market. Thus, it is essential for the credit card companies to introduce immediately huge training and supervision among the sales staff to accelerate their learning outcome in the industry.
Lack of Motivational Drive in the Job
Hong and Waheed (2011) investigate the consequence of motivational drivers on the job satisfaction of sales staff in the Malaysian and argued that sales staff have an explicit and everlasting impact on the customers respond that produce loyalty to the organisation or to the brand. In the concurrent Malaysia, the corporations spend millions of Ringgits to recruit, educate and paying the sales staff as an attempt to encourage the sales force that ultimately accelerates sales revenue in every year with a stable growth of business volume. The sales and marketing companies engage a great deal of sales staff with lower pay rate of freelancer, part-timer, or independent contracting staff that donates very lower morals along with extremely high turnover rate in the company. The ultimate result of this malevolent situation of the staff has generated higher rate of voluntary turnover and lower extend of retention in Penang while job searching has turned into a culture in this region that indicates lack of motivational drive in the job.
For the credit card sales, it is essential to identify the motivational factors of the sales staff and ranking the level of their job satisfaction, with this identification, managers would be benefited to adjust the compensation, and incentive system for enhanced motivation of the sales staff that would generates privileged job satisfaction along with enhanced performance (Hong & Ismail, 2011). However, Hong and Waheed (2011) further added that the most influential motivational driver to generate is the sales staff’s love for money, thus the credit card sales staff would demand for financial benefits for their motivation.
Regulatory Control over the Private Sector Employees
According to the view of ILO (2007), both public and private sector employees in Malaysia has been regulated under the Employment Act-1955 along with Industrial Relations Act-1967 and Employment Regulations-1980 without discrimination of gender, colour and race; however, the common law of the country has a greater influence in the staff regulation. All the legislation of Malaysia relation to the employment has safeguarded by exploring the way of dismissal and termination, which has directed allow at least one month to two-month prior notice with fifteen to twenty days additional payment.
Lo (2010) added that there is a continuous movement among the Malaysian employees union and the government to settle a minimum wage but the business community opposed and convinced the government to do so and argued that the wage should be determined based on the market demand through PLWS. Some of the union leaders supported PLWS arguing that it will bring better pay for the workers. For instance, the sales staff would earn RM 500 in context of minimum wage rate, but by fulfilling his sales target, he would be capable to earn around RM 3000 per month and the organisation would drive to a higher productivity.
Customers Reaction towards Overuse of Marketing Effort
Consumer Ethnocentrism
The term consumer ethnocentrism expresses consumers’ beliefs about foreign brands in replacing domestic products and services; and in broader form, tasks of consumer ethnocentrism refer to amass responsibilities, consumer loyalty, and ethical behaviour during purchasing international branded products and services (Keller, 2009). Alternatively, consumer ethnocentrism concept has also represented effects of COO with either positive or negative impacts on international branded products and services to stimulate consumers’ purchasing decision making process where external environmental factors of an organisation act as significant dynamics that assist to learn about consumer ethnocentric tendencies which can also be termed as concept of foreign products and services. For more details, business analyses have developed “Consumer Ethnocentrism Tendencies Scale (CETSCALE)” for a sound comparative measure of customer behaviour tendencies either in favour or against domestic product and services versus international products or services.
In doing so, product development analysts are required to conduct a set of homogeneous validity tests in order to categorise consumer’s belief and ethics, attitudes, key purpose of purchasing and processing the ultimate purchases and assessment of such tests revealed that diversified culture and country people represent diverse attributes of consumer ethnocentrism. Meanwhile, consumer ethnocentrism has also focused on nationalistic emotions that significantly influence on consumers’ attitudes to define product and service status as well as purchasing intentions. Another involvement of consumer ethnocentrism is that few cases of foreign product and service purchasing treated as an unpatriotic matter; therefore, purchase of international brands might injure domestic industrial growth and it is an assessment module of understanding a comparative view of potential consumers and corporate buyers’ behaviour in order to justify significant cases of biasness as well as error.
Alternatively, highly ethnocentric consumers are enthusiastic to perform more to focus on amazing virtues of international brands as if discount offers rather than horizontally discover the positive virtues of domestic products and services. At the end of this discussion, key observation of the issue expressed that consumer ethnocentrism has conveyed both responsibility and morality during acquiring international branded products and services and in addition, loyalty on domestic products and services. For more details, following is the chart of consumer ethnocentrism in different nations utilising the CETSCALE approach (Lim, Arokiasamy & Moorthy, 2010).
Social and Value Perceptions
From view point of an organisation, concept of the social and value perceptions is assigning to elaborate consumers thought on both domestic and international products and services where several critical rationales have to be justified in favour of conducting innovative marketing strategies that boosts brand sales volume as well as enlighten brand image significantly. Meanwhile, social and value perceptions are also effective approach to define consumers view towards branded products and services that have an intimate attachment with organisation’s marketing strategies. In short, consumer’s social and value perceptions is an assessment module through which an organisation has easily overlook impact of socio–environmental factors on consumer’s buying behaviour, consumption decision-making strategies, needs fulfilment modes and impact of globalisation as well. For instance, from viewpoint of the paper’s demand, Malaysian as an Asian country has experienced a quick change of socio–environmental factors and hence, consumer’s life style has changed promptly though current challenging economic atmosphere of the world would play a significant role during making purchasing decisions.
Conversely, social and value perception is a study approach through which an organisation has promptly appraised quick change of consumer’s needs and demand or in another word, study of under stability of consumer’s frequent changing needs and demand during executing market operations. Escape from significance of social and value perceptions lets have hypothetical look on the core concept on social and value perceptions that refers a complete package of manufactured goods or services, which has a significant influence on consumer’s purchasing behaviour by ensuring satisfactory price and product or service quality. Another hypothetical view addressed that consumer’s perceived values considering quality and price have discussed under the PMS study that eagerly consider and compare aggregate utility of delivered products and services and hence competitive success of a brand established through consumer behaviour that highly influenced by external business factors as well as supply mode of product and services.
Alternatively, modern value perception has dramatically shifted from traditional functional requirements of satisfaction and more interest to enjoy of liberty, pleasure, and entertainment; in addition, modern consumer behaviour parameters are now attached with product attributes, consumer knowledge, consumer functional satisfaction needs and demand and finally, consumer’s cultural and motivation factors. In short, consumer’s social and value perception towards brand possessed through symbolic properties carrying three phases namely, broad cultural motivation, shared social meanings by team or group management and building individual self-concepts focused on prestigious social status. At the end of this segment, positive sign of brand’s product and service significantly reduced research costs of the valued consumer and consequently level of purchasing risks of high-quality products that purveyor several benefits of economic as well as high profile symbolic social value (Lim et al. 2010). From the above discussion, attributes to the four consumer’s social value and perceptions are highlighted.
Green Marketing Ethics and Social Responsibility
Key purpose of illustrating green marketing ethical issues and social responsibility is to justify parameter of safety of the industrial modern technologies and focus advertising ethics in order to criticise several marketing functions conducts through prioritising greed and mismanagement of corporate activities those are cause of permanent ecological injures. More specifically, the term green marketing refers development and distribution of environmentally friendly or ecologically safe products and services, which are attributed through a smaller amount of toxic, better durability, sound reusability and proper utilisation of recyclable raw materials (Kotler & Armstrong, 2006). Alternatively, modern life style as well as advance social standard of human being should require to aware about the significant socio–environmental aspects like finite natural resources preservation and protection, environmental pollution reduction at significant level, protection of endangered species and strict control of excessive land use (Kotler & Keller, 2006).
Meanwhile, green policies have included 3R’s namely, reducing, reusable and recycling; however, in recent time, few more corporate giants have evaluated that modern consumers as well as young generation are enthusiastic to pay more for any green product rather than traditional. Alternatively, the term social responsibility of an organisation expresses awareness of the business people in executing social functions that securing organisation’s existence as well as survival growth as another sole functions; here, it should require to mentioning that earning profit is not the only function of an organisation. For more clarification, social responsibility or the CSR integrating with the competitive advantages and strategies should consider two major things such as business functions should not be treated as charity and any single acts of an organisation should not be harmful for someone.
To illustrate integration of CSR with the competitive strategies, interests’ groups of the organisation have obliged to consider several issues, for instance, public image involved with the goodwill and positive reputation by engaging social welfare programs, government regulations a medium to attach with socio–environmentally friendly values. In this connection, survival and growth are essential factors to supply available resources for well-being of society since society is the chief supporting area of business survival and economic growth where employee’s satisfaction with handsome remuneration package and sound working atmosphere employees are necessary. The expectation of expect several fringe reimbursement to enhance company’s productivity and profitability and finally, consumer responsiveness to secure consumers’ right through supply of quality products at most competitive price among the aggregate market (Pranee, 2010)
Service Quality and Customers Satisfaction
The term service quality has developed globally through explosively and in recent time, it is the most effective approach of outlining an organisation’s corporate marketing strategies as well as financial performances and better parameter of service quality would deliver an extensive outcome to an organisation. Conversely, customer satisfaction denoted that emotional/cognitive responses of a consumer through a holistic assessment to define performance of purchased products and services. Alternatively, post purchase and post consumption responses have shaped customer satisfaction attributes and regarding this view consumer satisfaction can also be termed as the consumption experience that delivers end state results, which might be reflected either positive or negative impression to define scale of consumer satisfaction scale. In reference with the case analysis of the paper, literal overview of connectivity among service quality and customers satisfaction have focused on banking services where proficient banking services are crafted to draw sound consumer need fulfilment model. In another word, in order to earn customer satisfaction, common approach of banking industry is to convey Structural Equation Models (SEMs) and through which justification of correlation among service quality and consumer satisfaction and assessment of perceived service quality through exploring future influence on the relationship (Tsoukatos, 2007).
Alternatively, superior service quality of an organisation acts as an essential success factors of any organisation and modern demand for online or electronic banking services are switched to focus more on high touch/tech dynamics that has already demonstrated a high consumer satisfaction (Mishra et al, 2010). Meanwhile, corporate cultures, pricing strategy, advertising approach in consistent with corporate and social values are the chief dominator of service quality and hence an enrich consumer satisfaction.
Traditional Framework of Customer Behaviour
In defining customers reaction towards overuse of marketing effort, traditional framework of customer behaviour is an effective marketing strategy that worked for screening consumer behaviour during available marketing channels as well as diversified business culture. However, Houghton (2001) argued that development of consumer behaviour has typically known as the buying behaviour that involved in two major segments, namely, consumer activities and consumer responses. Alternatively, traditional structures of the consumer behaviour involved in defining consumer decision-making procedures during buy of any product or services.
In broader form, consumer activities is a component of consumer behaviour that included three ingredients namely, purchasing factors, use or consumption factors and disposal of products and services factors and conversely, consumer responses involved in three phases emotional responses, mental responses and behavioural responses. For more details, three fundamental consumer activities are considered as stimulating factors of consumer that guided them when to buy, how to buy and from where to buy. Alternatively, the purchasing activities is a medium through which a consumer can acquire desired products and services; in addition, assists to evaluate and gather necessary information to make right purchases with modern value added and customised services like home delivery, online consultation and order. The use and consumption activities scrutinise three stimulating sources like where, when and how to make consumption as notice earlier.
At last, disposal of product or service factors involved in post consumption tasks where recycling, reuses and resale had significantly integrated. On the other hand, consumer responses are centralised through emotional responses, which also termed as affective responses, which reflects emotions, feelings, and moods to define excitement and probable uncertainties during to make purchases. The mental responses well-known as consumers cognitive response that weighting pros and cons of any purchase and here, it has to be pointed that mental responses can be neither evaluative or non–evaluative and may fond of particular brand’s product or service. Finally, the behavioural responses that almost similar to the tasks of consumer behaviour activities as earlier described and, in another word, it is a stage of consumer for overt decision-making process during make purchases (Houghton, 2001).
Besides earlier description of consumer behaviour featuring with two major segments, conceptual structure can be modelled through grounded theory with the aid of marketing channels along with diversified cultures and new dimension of the consumer behaviour outline would allow managing diversified consumer segments, selling attributes as well as desired services fulfilment. Key objectives of this modelling are to draw a comparative scenario among typical consumer behaviour and new concept of marketing strategies. Consequence of this, modern consumers are in emergence of proper e–CRM for sound acquiring, great challenge of availability of third generation (3G) and P2P (peer–to–peer) networking as crucial communication modes and significant limitation of wireless Internet services whereas typical consumers enjoy trouble free purchasing medium, less conscious customer service and user-friendly responsiveness. Finally, new concepts of consumer behaviour entered into market to counter traditional thought through bargaining power of buyer and seller, loyalty, security, lack of availability and smart Internet pricing. (Houghton, 2009)
E-Customer Behaviour Model Towards E-Marketing
In defining E–customer behaviour in the season of digital market development or online business building, it has emergent to have a business Website of an organisation to convey vital services required by target consumers. In order to address E–customer behaviour, online companies have faced tough challenges due to rapid change of Internet surfer accessibility attributes during conduct of Internet marketing tasks and meanwhile, exploration of an e–business marketers are obliged to concentrate on two issues regarding consumers view on product awareness and expansion of product purchasing commitment significantly (ISM, 2008). Moreover, this study has also focused on delivering diversified consumer preferences that attributed with traversal patterns and hence, learning of an online business able to discover with the aid of synthesizing greater volume of accessible Web data by means of highly compressed information that instruct to producing optimal access patterns towards the target E–consumers.
During explaining E–consumer behaviour, this part of the dissertation has chosen the OLAM model due to several favourable dimensions, such as, transformation of E–consumers, psychological scenario of E–consumer behaviour, reasons why E–consumers switch towards another and so on. Here, it is essential to notice that E–consumer behaviour has primarily composed marketing strategies prioritising B2C (Business to Consumer) approaches and under these circumstances, E–consumer behaviour model gathered knowledge on both feasibility and advance Web server delivering. In consistent with the OLAM model, analysis of E–consumer behaviour identified that typical core marketing principles have significantly required vast re–examination to restructuring consumer behaviour in times of Internet marketing; in addition, this analysis provide superior knowledge on on–line consumer’s experiences. For instance, initial entry modes, attributes of Web pages to foster decision making processes with huge purchasing options and additionally, it has significant to articulating potential routes of E–consumer’s travelling zones within the Company’s Website in times of constructing online marketing planning. However, OLAM has also enthusiastic to knock individual preferences being a psycho centred model along with group choices and describe hassle free decision-making procedures, potential inferences of experience.
The competence to bring change of decision-making during change of consumer’s choice, smart control of complex operation execution and most importantly arrange of experience sharing proxy models to define generic surfers’ models with aid of E–consumer behaviour diagrams. Consequence of this, several arrangements has demonstrated diverse surfer interactions modes that defines consecutive series of online sites as well as gathered correlated demands within an individual session of marketing. Alternatively, typical requests options with diverse surfers exhibited multiple navigation modes as well as request options to different Web pages featured with multiple-choice options additionally various frequencies.
Conversely, a group of buyers are categorised as frequent buyers; on the other hand, some people are occasional buyers and common attribute of them is that they browse extensively, but commitment to purchasing products and services occurred seldom from online sites of the organisation. Hence, analysis of E–consumer behaviour towards e–marketing has integrated through three phases namely, awareness of the E–consumer, exploration of the E–consumer and commitment of the E–consumer and in short, online or Internet marketing has categorised their surfer requests through three form awareness, exploration, commitment that reflects E–consumer behaviour as well as their potential intentions. Finally, the e–marketing motivation tools inspire the target consumers discover through awareness as well as exploration then settle in the commitment level and cordial relationship among three phases make easier for the valued consumers to identify right track of the critical Web pages with continuous change of online marketing behaviour. (Kwan et al. 2011)
Excessive Marketing and its Impact
From early 90s-decade, marketing researchers have identified several upsetting impact of marketing which are coherently intimated with mainstream marketing practices as well as unavoidable social issues (Sheth, & Sisodia, 2005). In this part of the paper, the central issue is the impact of excessive marketing on consumer behaviour and consequently on the organisational performance or profit margin. Prior to describing diversified marketing impacts, it is essential to acknowledge that marketing is a vital wing of an organisation’s business function with a fundamentally unique role which is highly patronised through consumer’s trust and loyalty and conversely, considerable corporate social responsibility with pleasant sales services.
In defining excessive marketing impact, many marketing researchers have addressed that high ignorance of societal issues during marketing tasks execution would be delivering significant crisis on organisation’s entire performances and in recent time, modern consumers are feared of marketing of any goods and services. For instance, a survey report published that over 60 % respondents hate marketing and conversely 70 % of them favoured marketing as much as possible. Alternatively, 50 % of the respondents pointed out that have depressing impact of excessive marketing on their regular life, which has seriously resisted company’s advertising procedures. Considering this view, it can be argued that marketing is an essential wing of an organisation, but excessive marketing would indulge product and service image even if it does not carry anything harmful (Idrus, 2011). Escaping from these pessimistic experiences, there have also several depressing news of marketing and advertising approach that conveyed surprising data on consumer’s hostile view and this identification revealed that excessive marketing has much cantered to covey managerial agenda rather than representing social norms, values and traditional cultures.
More specifically, current marketing and advertising has primarily considered as temporary corporate interest on boosting profit margin. On another hand, amplification of free market economy system inspires reducing self-control as well as moral connectivity; hence, today’s consumers try keep away from over marketing and advertising. Hypothetically, to recover this dilemma of marketing, an organisation as well as other academies should instruct and train potential marketing executives to speak as the voice of target consumers by conveying moral hazards and to get freedom from excessive negative impact on their daily life (Sheth and Sisodia, 2005).
Solution towards Marketplace
Earlier hypothetical discussion has focused on excessive marketing and advertisement impact on consumer behaviour and following above, existing part has design to discuss on necessary solutions to resolve market crisis. Considering organisational structure or business types, aggregate sales, marketing and advertising procedures, it required vast technical arrangements as well as unavoidable change in consumer’s demand and hence, articulation of right solution would brought greater win rates in the competitive market in terms of high revenue generation along with low cost structure attributes; therefore, ultimate operational efficiency would also develop.
More specifically, it is smarter decision to switch from typical marketing approach to electronic form of advertising and another hand, entire investment outcome is an important determining factor that effectively shaped organisation’s obligatory needs and functional strategies. Meanwhile, the considering factors are listed as pattern of the business firm either service provider or product manufacturer or both, product documentation style and product line specification with pricing sheets as well as legal documents, product development and movements of dynamic forces that forced to transforming marketing and advertising strategies. The workflow of three organisational wings legal, financing and marketing as well as their documentation status, approvals and updating and availability of current technological platform within the organisation. All of these forces are strategically unique to recommend right track for any marketing, sales, and advertising dilemma and subsequently there have several supplementary technical approaches those also enough efficient resolving marketing crisis as early described.
For instance, availability of shared drives separated from organisation’s website for advertising, marketing and sales, effective solution for official document management featuring integration availability with related group technologies, system available to web content management in order to concern marketing and sales requirements of the organisation, system available to collateral management through. It may reduce hostile consumer behaviour towards excessive marketing and their attitude would neutralise by specialised storing method, organising, distribution of goods as well as tracking materials and at last, available hybrid or collaborative solutions to convey Web based marketing collaborative opportunities that would effectively compose bridge among employees and valuable consumers through coordinate, communication and collaboration (RDA Corporation, 2011).
Credit card sales staff and Customers in Penang
This sub-chapter is organized with job resources and job demands in Penang along with cultural diversity values, attitudes, and job satisfaction, perceptions of Malaysian managers, the organisation system HR policies of credit card companies, strategic approach to CRM at credit card companies in Penang.
Job Resources and Job Demands in Penang
Zinnov (2009) pointed out that the electronic and manufacturing sector have treated as a major job resources in the past but in the concurrent era BPO ITES PDH and techno-professional human resources are the top contributor of job sectors in the Penang while there is elevated focus of R&D centres in this area. In the Scrutinising, the Malaysian labour market, it has evidenced that wage rate in Kuala Lumpur is at the top indicator while wage rate in Penang scored at the lowest level, more specifically the wage rate in Penang has assessed fifteen percent lesser in relation to the national average.
Lee (2010) makes it clear that Penang has been moving in the direction of a high-income level economy emphasising on advanced value-added attributes, knowledge predestined economic actions, but failed to encounter the high turnover rates of the staffs while recruiting, and retaining skilled and talented human resources is a greater challenge for the companies. Malaysian staffs always look for better job, switch to the multinationals or any other company without any obligation to their employer while the migrated foreign staffs demonstrate lower productivity, and hamper the usual growth of the business.
Cheng (2010) argued that the development and growth of Penang has deeply concerned upon its rich supply of well-educated and trainable workforce to create a centre of attention of the investors towards the export-oriented electronics manufacturing for last four decades, by this time the skills of workforce has already gained enrichment of human resources. With the changing dynamics of Malaysian’s integration in the AFTA and WTO, today Penang faced serious challenges of both reducing productivity and scarcity of skilled human resources.
The academia of Penang has drawn attention to address the rising need for skilled human resources but failed to respond appropriately, as a result, shortage of skilled personnel, lack of highly qualified HR, deficiency of entrepreneurial expertise have increased in the state while bureaucratic barrier, brain drain, shortage of production force has threaten the growth of the country. Penang, the Silicon Island of Malaysia is under serious challenge to encounter with the changing dynamics of human resources and to respond to this crisis, the local corporations have to look for the foreign migrant workers with lower payment.
Cultural Diversity in Penang
Ahmad (2006) indicated that the culture and heritage of a geographical location are always measured as an elementary factor to understand the foundation of national uniqueness and sovereignty of that realm. The uniqueness of the culture of Penang has exposed as an exciting long-established community are thriving with their culture of broad-mindedness, harmony, multiplicity and stability and modernisation along with societal transformation. For the rich cultural resources and wealthy historical sites, UNESCO has declared Penang as one of the World Heritage while the capital city Georgetown has wonderful universal values illustrating with the architectures of eighteenth to twentieth century the Europeans, Chinese, and Indians along with local rulers.
Mohamed et al (2001) identified that the culture of Penang has organised from the colonial influence Europeans along with the neighbouring Asian counties like China and India while core values has been inherited from the ruling of Sultans of Malaysian Peninsula. The local population of Penang consists of different ethnic groups, large part of Malay, Chinese, and Indian, with different ethical background and generates a multicultural society with moderate ethical standard to fit with the needs of competent human resources for the modern business. The people of Penang are well-mannered and easy going with foreigners without any complexity where the degree of cultural incorporation has wide-ranging for long time and the ethnicity have shaped the key standard for culture.
Values, Attitudes, and Job Satisfaction in Penang
After describing sales staff’s ethics in Penang, this part has involved drawing a scenario on values, attitudes, and job satisfaction in this place. Regarding this view, an intensified research on sales staff in Penang focused that job satisfaction has significantly involved with superior management supportive role, salary structure, and scope of promotion opportunities whereas moderating dynamics influenced through age, gender, job experience, and relationship with the superior management. In another word, three factors salary structure, scope of promotion and work experience has not only shape structure of job satisfaction in Penang but also outlined values and attitudes in several cases. Meanwhile, Malaysian academic atmosphere has also an influential source where a monetary reward is not as exclusive as job satisfaction demand.
Another empirical study addressed that rather than temporary job status permanent guarantee is most dominant in drawing values, attitudes and job satisfaction in Penang emphasising two forces work experience and cordiality of superior management. Regarding this view, it should disclose that values, attitudes and job satisfaction are also govern through leadership quality that intimately linked with organisational phenomena like organisational commitment, employee motivation, employee performance improvement and fairs appraisal of employee performances (Ch’ng, Chong, & Nakesvari, 2010).
Sales Staff‘s perceptions of Malaysian Managers
This part has involved in addressing perceptions of Malaysian mangers during marketing and selling and attached with the demand, in the light of typical leadership style several intensified research reports focused that organisational commitment and the influences of Malaysian managers has strongly reflected transformational attitudes rather than transactional (DHFS, 2011). Moreover, Malaysian managers are expert in building positive connection between two forms of leadership transformational and transactional those deliver satisfactory organisational commitment. In defining Malaysian geography and cultural diversity, Malaysia is an Asian country with Islamic values and perception among the populace, but moderate with global context while the inhabitants are grouped into three ethnics groups. More specifically, it needs to address that highest number of Malaysian natives allied to Malay of Islamic values as well as lifestyle, which are a demonstrating factor of enormous influences on workplace ethics and ideology by Islamic values along with Islamic HRM.
On the other hand, considering hypothetical view, organisational commitment is stated through Malaysian worker’s psychological affection to the company or workplace meant for something pledges, which proficiently draw undersatbility of relationship with leadership style and commitment of the Malaysian sales managers. Regarding to this state, entire outline of leadership style noticed that Malaysian sales staffs and mangers perception is more depends on transformational rather than transactional that shaped their organisational commitments (Marmaya et al, 2011).
The Organisation System HR Policies of Credit card Companies
Financial institutes like credit card Company’s organisational system demands adopting strategic human resource management (SHRM) for an effective practice of HRM policies as well as specify proactive managerial attitude, labour framework, and major industry dynamitic of financial institutes. Meanwhile, HRM policy and practice of a credit card company influenced through domestic industry atmosphere along with competent policies for compensation and performance appraisal. Conversely, illustrative analysis of Company’s industrial relation (IR) following a complete appraisal of personnel policy within domestic entire operations as well as industrial atmosphere. HRM policies and practices has involved with four phase components namely, staffing, appraising, compensating and developing and these items are assigning to perform controlling, reporting and monitoring employee tasks conducting business issues required exercising financial functions of managing credit card.
However, it should aware that like other financial institution and credit card issuers companies are also required to occupy official recruitment and training as well as exercising managerial development, but credit card industry has much ardent to recruiting young people practising top management’s subsidiaries. It would act like team performance, considerable group achievements, autonomy, direction, and individual achievement as well and these subsidiaries are treating as personnel autonomy under HRM policies. Compensation and performance appraisal of credit card companies is typically obligatory to regulate under CAPB due to its compatibility of shaping employee’s payment structure and additionally, has significant leeway of practicing fair performance appraisal approaches. Now, it should to address significantly that compensation and salary policy in the credit card industry featured through flexibility since legal elements are key dominator here. Industrial relationship another HRM policy that assists through analysing domestic market demand, resolving labour or sales staff’s conflicts and simplify complicated industry atmosphere to the staffs at earlier of their job. On another hand, managerial actions have an effective role structuring HRM policies and practices where personnel management is free from top-level management as well as facts of industrial relation.
Finally, the abundant training scopes and commitment has linkage with high turnover in terms of attracting consumers of credit card and conversely, reduces tough competition with rivals. In details, following is the complete structure of HRM policies of a credit card company (Alboreca, 1998).
Strategic Approach to CRM at Credit card Companies in Penang
Strategically, credit card companies in Penang approaches to CRM (customer Relationship Management) in terms of service quality along with value added or customized product or services. Alternatively, electronic forms of customised services like Internet service or online service, ATM facilities and service delivery via phone are modern forms of consumer satisfying approaches in the credit card industry and hence, these forms of strategic service approaches have significant role on effective CRM as well as building consumer loyalty in Penang, Malaysia (Evers, 2011). Several rich researches on credit card companies reported that common tendency of the companies are preferred SERVQUAL model in delivering most modern strategic services to their valued consumer. In defining CRM status in Penang, it has assessed that gradual improvement in service quality enhanced consumer loyalty and dimensions of service quality that get scope playing impressive role through three forms though existing credit card consumers are still now passed through numerous complexities.
Meanwhile, consumer loyalty has also reflected through consumer’s intention on repurchasing and in Malaysian credit card history, they have ten local commercial service providers along with sixteen international commercial institution, but current rush economic status as well as increasing competition forced them to involve with merger and deregulation; therefore, delivering service quality along developing positive CRM has hampered. In order to rescue from this, criticise, financial institution with credit card service providers have recently amended BFIA 1989 and additionally, to convey dedicated service providers form a human intellectual body in terms of ICLIF in 2004 (Kheng, 2010).
Summary on the Research Gap
The above review of the available literature demonstrates that this field has received massive attention from various scholars. These scholars have comprehensively reported on various factors related to credit card issuance by not only Standard Chartered Bank, but also other banks in Malaysia. The research also clearly point out at the general conduct of the sales agents of various banks charged with the responsibility of selling the credit cards to the customers. However, despite this intensive research in this field, there are some obvious gaps that exist in this field in regard to the topic at hand.
Literatures exist about Standard Chartered Bank operations in Penang region, and even the in Malaysia as a country. However, there is scanty information available on how this bank has been selling its credit cards to its customers. Also scanty were the general behaviour of employees of this bank, in specific, as well as how this behaviour affects loyalty of the customers towards the bank. Also scanty are the information regarding direct relationship of sales staff behaviour and the responsiveness of the customers towards the credit cards.
The gaps in the literatures that motivated the researcher to conduct a research that would try to close these gaps and come up with measures that would help this bank, and others in general, give out credit cards to customers in a way that would help retain them to the bank. The researcher therefore developed the following four null hypotheses to help in bridging these gaps.
- H1a. There is direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ loyalty to the bank
- H2a. The behavior of the sales staff is closely related to the motivation they receive from the management of the firm.
- H3a. The possibility of the customers accepting the credit cards heavily depends on the ability of the sales staff to convince them that they are beneficial.
- H4a. The ability of the sales agents to sell successfully the credit cards to the customers depends on their level of education.
The above four hypotheses are to guide the researcher the right direction in the entire dissertation. In chapter four of this dissertation, the researcher would use quantitative analysis to reject or accept the hypotheses in order to develop findings that would help confirm or contradict the theoretical models included in this Chapter 2.
Research Methodology & Design
Introduction
This chapter focuses on various aspects of research development. It includes methods of data collection, its analysis and presentation procedures. Every research project applies a certain research method to achieve its objectives depending on its goals. The methods used to conduct research in this project compared closely with the methods proposed in the project proposal This was so because the project proposal had been proven to be workable. In research, design deals primarily with aims, uses, purposes, intentions, and plans within the practical constraints of time, location, money, and availability of staff.
In this study, respondents were briefed in advance. This was necessary to ensure that respondents were prepared psychologically for the task ahead. This would also help in ensuring that response was given in time to allow timely analysis. The officials of Standard Chartered Bank were given relevant notice by the researcher. The study population was also amicably informed in order to get prepared for the study. Briefing was important because it could enhance reliability of the study. It is also ethical to inform people before researching on them. The findings were also made public to the researched as one way of ensuring morality in the study. Furthermore, the researcher observed researcher-researched ethics by keeping away from criticism. This chapter also focuses on the literature review as one of the methods used in collection of secondary sources of information. It gives the reason why literature review was used as a method to collect data. The chapter gives an overview of the purpose of collecting and analyzing data and the basic questions used to gather the desired responses. Alternative methods of data collection are very important in research for they avail to the researcher a number of ways through which data can be collected.
The chapter brings back the research hypotheses. This is important because it is at this stage that the researcher goes into the field to gather information. It is therefore necessary that the research hypotheses are brought to focus because they would be the guiding light in the process of gathering data. The researcher would be trying to confirm the hypotheses. In order to eliminate criticism, this chapter clearly states the scope of the study. There are limits beyond which this research may not hold because of the method used in data collection and analysis. It is therefore important that limitations are clearly stated to make it clear to readers of this material how far this research reveals what it purports to.
Since the main method of data collection was primary source, the questionnaire was the main instrument used to collect data. This chapter brings out the questionnaire format, reasons for choosing this format, its advantages and disadvantages. Briefly discused in this chapter is the pilot study and its results. In a research process, sampling is very important because certain population can be too big to facilitate a study of the whole population. This chapter discusses sampling theories, importance of research design, methods of sampling-giving their advantages and disadvantages, and the determination of the sample size. Also discussed in this chapter is the data analysis technique. In so doing, the researcher hopes to bring to focus the channell through which data would be collected. This is not only meant to bring clarity to this research but also help young researchers who will be intereseted in futhering research in this field to know the steps necessary to reach the desired results in a given research. The researcher has ensured that the methodology is not only important to the professionals in the financial sector, but also to other related sectors such as insurance, marketing, procurement among other fields
Research Approach
Many researchers including Sekaran (2006), Saunders, Thornhill & Lewis (2006), Miles & Huberman (1994) and Malhotra (2009) pointed out that there are mainly two research methods, for example, qualitative and quantitative approach. However, Malhotra (2009) and Saunders, Thornhill & Lewis (2006) further stated that the former research approach is an unstructured exploratory research methodology based on small samples that gives insights and sympathetic of the problem setting; on the other hand, quantitative approach seeks to quantify the data by applying some form of statistical analysis, such as excel tools. However, Marshall and Rossman, (1999) and Malhotra (2009) stated that the difference between these two methodologies depend on the objective of the research, sample size, data collection method, questionnaire design, data analysis process and outcome of the research. According to the marketing researchers like Malhotra, it should use both qualitative and quantitative research approach to get successful outcomes, where former approach would help to explain the findings obtained from quantitative research. However, the following table would assist the researcher of this dissertation to select research approach for this research.
Table 1: Difference between qualitative and quantitative research. Source: Self-generated from Malhotra (2009).
Considering the above discussion, the researcher of this study has decided to apply both qualitative and quantitative research approaches to deliberate the research. At the same time, the researcher would use both primary and secondary data to formulate the paper and discuss the sales staff behaviour and customers’ respond.
Data required
Purpose of collecting and analyzing data
From the literature review, the researcher gathered considerable amount of information about this field. Many of the reports that exist in this field are very resourceful as individuals of high integrity did them. The manner in which they were done also passes as good enough to be used in various aspects of finance. However, this is a different research. It must be in a position to develop its own arguments based on data collected from primary sources. This does not rule out the importance of secondary sources of data. To ensure originality in any research, there is need to use primary data. The purpose of collecting data was to help facilitate analysis that would lead to giving answers that are desired in this research. The objective of this research was to respond to some of the questions that other scholars had not responded to through the existing literature. To be in a position to respond to these questions, the researcher would need to collect data. After successful collection of data, analysis would be very important. When taken from the field, data is considered raw and therefore cannot be of much help to the target audience. For this reason, it is important to analyze data to produce the desired result that would be useful to various individuals.
Primary Research
Sekaran (2006) and Malhotra (2009) pointed out the purpose of generating primary data by stating that it needs to collect such data to get the proper outcomes from the research particularly focused research problems. The primary research was collected using questionnaire. In this context, the researcher has decided to gather primary data to get accurate results regarding the factors affecting the credit card sales staff, such as, remuneration of the employees, leadership problems, sales target, duration, behaviour of the customers and so on. In order to do so, the researcher would consider two major respondent groups to interview and he would collect data from Penang, Malaysia. However, the following table provides more information about the target respondents –
Table 2: – Selected Respondents for interview. Source: Self-generated.
Interviews
According to the Sekaran (2006) and Zikmund (2006), face-to-face interview is the most effective method of primary data collection though it is time consuming and costly process. Here, it is important to note that the sample groups or target respondents for this research is extremely large; therefore, it is quite difficult to use face-to-face interviewing method for this purpose. As a result, the researcher would use different technological approach to interview credit card sales staff and the customers of credit card in Penang. However, Malhotra (2009) and Saunders, Thornhill & Lewis (2006) mainly classified four methods to collect primary data from the respondents to formulate the research, for instance, telephone interviewing method, personal, mail and electronic interviewing system. To gather instant primary data, the researcher of this paper would consider instantaneous methods rather than face-to-face interviewing or field survey, as it would collect data from more than 344 respondents to analyse the behaviour of the credit card sales person and customers’ responds.
Secondary Data
Cohen, Manion & Morrison (2007) and Malhotra (2009) stated “secondary data collected for some purpose other than the problem at hand” and these data have already published and accepted by the renowned authors, universalities, and publications. Therefore, these data sources are more reliable in accordance with the view of Malhotra (2009) and Yin (2003). However, the rationale to use such data is data sources are available at lower cost or free of costs while data collection process is time consuming and expensive procedure (Saunders, Thornhill & Lewis, 2006). As the researcher of this dissertation would follow both qualitative and quantitative research approach, it is essential to collect significant part of secondary data; therefore, this paper mainly focuses on published data and computerized database to formulate the paper. However, Miles & Huberman (1994) argued that secondary data has numbers of positive factors, for instance, it is easy to collect, and less expensive. In order to formulate the paper, it would use Computerized Database and Published Secondary Data including general business sources; however, the following figures give an idea about the secondary data sources.
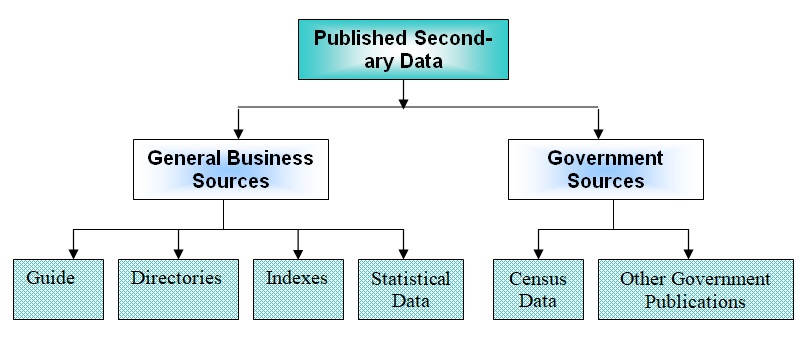
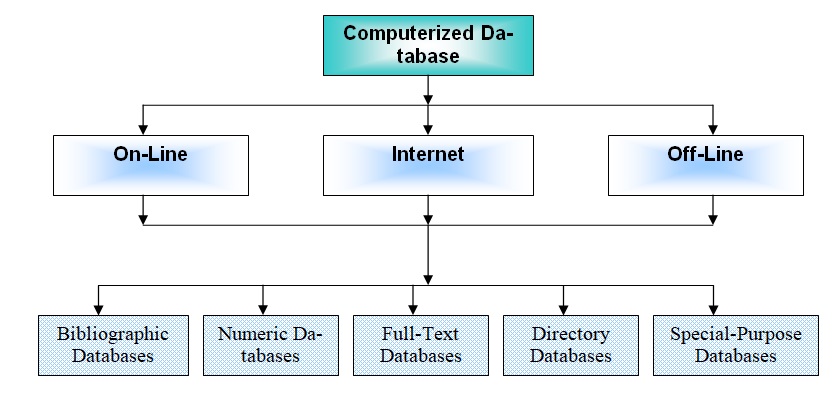
However, the dissertation would mainly focus on the internet databases because this is an easy and less expensive system of data collection. Here, Emerald Journal is an excellent source, which properly analysed the credit card sales staffs behaviour and measured possible responds of the customers though most of the journal address the problems of different areas. At the same time, Journal of Business & Economics Research, International Journal of Business and Social Science, and Asian Academy of Management Journal are good sources for this research.
Sample
It should mention that the researcher prepared questionnaires that were dispatched to the 100 customers of Standard Chartered Bank at Penang and 244 credit card sales staff in this region to collect data. The total population was therefore 344 people. The sample size for this research is defined below.
Determination of the sample size
As stated above, in a study, there is always a need to have a sample population. This population will be a representative of the entire population. The selection of this sample must therefore be designed in a way that would give the expected results. Generally, two constraints that would help in the determination of the sample size: time and financial resources exist. Time is very important in determining the sample size. If a researcher has a lot of time to conduct the research, it would be appropriate to consider using a larger sample size. However, in case the time available for the same is limited, then the researcher would be forced to limit the sample size to be in a position to conduct the entire research process successfully. Another constrain is the available finance for the research. The process of collecting data and its subsequent analysis can be very expensive. For this reason, a researcher would determine the sample size based on the available finance. In the research the sample size was chosen based on the two constrains given above and the five factors stated below. Besides the above general constrains, five other factors should be considered when choosing sample size. The factors are as stated below:
- The variability of the population under study: There are instances where the items under study exhibit differences in characteristics, making it very difficult to choose a representative sample. In cases where the study population does not exhibit serious difference in characteristic, it would be recommended that a researcher use a smaller sample as a representative of the entire population. However, if the study exhibits many differences, then it would be appropriate to use a larger sample as a representative. The researcher would be forced to look for all the varying attributes and include each of them in the sample. In this research, it was noted that there was no big difference in character of the people under the study.
- Confidence level: In every research, there is a given level of confidence desired of any research. This precision will determine the sample size to be used in the study. In most researches, a confidence level 95 per cent is always recommended. Depending on the sensitivity on the issue under investigation, the percentage can be more or less than this standard value. In this research, it was necessary to produce a report that has standard level of precision. The sample population chosen was able to provide this.
- Margin of error: When a sample is taken to be a representative of the population, the result would not always be an exact value. There will always be a variation between the actual value of the population, and the value given by the sample. The aim of every researcher is to ensure that the difference between the actual value of the population and the value given by the sample taken are as close as possible. The larger the sample size, the smaller the gap between the value of the population and that of the sample. By taking into consideration constrains, a researcher would determine the sample size that would give a value close enough to the value of the population. Standard Chartered Bank employees gave closely related answers, depending on their gender. The researcher was therefore convinced that the sample size chosen would produce a value that has minimal difference with the value of the population.
- Population proportion: When a researcher sets to conduct a study in a given field, there are always characteristics that would be considered desirable for the research. According to some scholars, not all items in the population have the desirable characteristics that would enable success in the research. The researcher would hence be tasked with the duty of determining the proportion of the population that has characteristics that are desired in the study. This may not be easy because it may demand interaction between the researcher and the entire population of the study to determine the proportion with the desired attributes. It may be costly in terms of time and other resources. In this research, it was easier to determine the population proportion that would provide the desirable results for the study.
- Population size: The total number of items in the study would always determine the sample size. It is always desirable to have a sample size that would properly represent the population. A large population would demand for a larger sample size, and vice versa. In social science, it is always recommended that the sample size be about five percent of the population. This percentage would be higher if the population is smaller. Conversely, it would be smaller if the population were too large. The population for this study includes all the 100 customers of this bank at Penang and the 244 credit cards sales staff. The researcher used a sampling formula by Ewens (1972) to calculate the sample size of employees for the study.
Sampling formula
n=N/ {1+N (e2)}
Where:
n = sample size
N= Target population
e= Degree of freedom
n=2450/ {1+2450*0.052)}
n=2450/7.125
n=344
With help of this formula, the researcher will collect data from 344 respondents. Customers have also been included in the questionnaire and had to form at least 25% of the sample size and hence 100 customers were included in the sample. As stratified sampling will be used, the two groups will include employees and customers of Standard Chartered Bank.
Data Analysis Process
It can assume that many customers and credit card sales staff would not be completed the questionnaire or survey form in recommended way, thus, feedback would full of error. As a result, it needs to apply several techniques in order to analyse the data without error and get fruitful outcomes. In this context, the researcher of this dissertation would verify all the survey form in order to edit unintentional mistakes, incompatible and fabricated information about the behaviour of credit card sales staff and the customers’ responds in this regard. For the purpose of inspection, the variables would be coded in such way that would not be difficult to analyse the data and it would be easy to the readers, for example, the independent variable in each of the model would be considered by following some special techniques. As the questionnaire has designed with directional options and recommend selecting one option from multiple choice, it would be considered error if any respondent mark on more than one option in a particular question. At the same time, if any respondent forgets to answer any question or give incomplete questionnaire, then it needs to edit to remove such mistakes. After completing the editing, the primary data, it would be analysed and graphically presented by using Microsoft excel.
Scope of Data Collection
Primary data for this research was collected from the customers and the employees of Standard Charted Bank in Penang, Malaysia. This data was collected with the help of a questionnaire. The scope of data collection was limited to the two categories of individuals. This was because of the time that was available for the research. Because most of the employees and customers were Malaysians, they clearly understood the social structure of the Malaysian society and therefore were in a position to respond appropriately to questions regarding the business environment of Malaysian. They also understood how this affected the performance of the Standard Chartered Bank in this region. The level of accuracy needed in this research would be achieved within this scope. Secondary data was gathered from existing literature about the financial sector of Malaysia as a country, and the activities of Standard Chartered Bank as our specific field of study.
Format of the questionnaire
Questionnaire Design
There were two key methods used to gather information in this dissertation. The first one was through a questionaire, which was physically delivered to the staff of Standard Chartered Bank at Penang, and the customers of this bank in this region. This questionnaire is attached to this document at the appendix section (Appendix I). The questionaire sought to capture various attitudes of staff members and customers of Standard Chartered Bank regarding their opinions on the general behavior of sales staff, and how the behavior affects the attitude of the customers. The second source of information used for the research was literature on various aspects of finance in general, and the operational activities that takes place within Standard Chartered Bank in specific. The focus of the literature review was to find information on the application of motivation techniques within the workplace and also to determine the current state of research in relation to the bank. The questionnaire had four parts.
The first part sought to capture the background information of respondents. The second part dealt with the demography and gender of the respondents. This was to ascertain the prevalence of views in varoius categories in order to ensure that if any differences came about, then they would be captured in their demographic space. The third part dealt with academic credentials and work experience of the respondents. The motivation for this section came from the understanding that different sections of population respond differently to issues, based on age and academic credentials. The fourth part delved into the specific issues relating to Standrd Chartered Bank as an institution under our investigation, starting from the understanding of the concept used to sell the credit card to customers, and how the behavior of the sales staff affects the relationship between the bank and its customers.
The questionaire also employed a mix of open and closed ended questions to capture different aspects of issues studied. Open ended questions were used because they give respondents more time to figure out their opinions, which would make them volunteer more information related to feelings, outlooks and comprehension of the subject. This would allow a researcher to understand the position of respondents as regards to feelings. Open ended questions minimize some errors that could have been created in the course of research. Respondents rarely forget answers if given an opportunity to respond freely. Furthermore, respondents cannot ignore some questions because they must go through all of them. Open ended questions generate data that can be used in data analysis by other researchers. In other words, they allow secondary data analysis. On the other hand, closed-ended questions are analyzed easily. That is why they were used in this study. Each response can be coded for statistical interpretation. Nonetheless, closed-ended questions are compatible with computer analysis package. The technique is more specific meaning that its answers are consistent in all conditions. This aspect is impossible with open-ended questions because each respondent is allowed to use his or her own words. Finally, closed-ended questions take less time to administer unlike open-ended questions, which are detailed hence time consuming.
The questionnaire was sent to respondents using drop and pick method. The researcher arrived at this decision after considering time and reseources. The method is time consuming, but very effective. Furthmore, the method allows respondents to reflect on the questions and answer them accurately.
Moreover, the method is not affected by the respondent’s level of literacy. One big advantage of the technique is that there is interaction between the researcher and the researched. This means that respondent’s reactions are easily captured. Reactions are important because they give more information regarding the feelings of respondents.
The literature collected provided information regarding various theories related to banking, which is spread across the last century (Hasnah et al 2011). The body of literature availed a number of theories dealing with sampling and sample designs in the business world and performance issues in the context of human resource develpment in the finance industry. Standard Chartered Bank fits well within this parameter. Finally, the literature provided information on the state of research on the field. Various researchers have conducted studies on various elements of social segregation and its effects on motivation.This gave the study a sound academic backing and a strong basis for drawing comparisons and conclusions.
The use of the questionaire made it possible to capture issues that are unique to Standard Chartered Bank. This is because there was no accessible literature with required degree of relevance to the subject matter of Standard Chartered Bank, in Penang region. The targeted staff responded to the questionaires, which were physically delivered to them. The availability of staff influenced the choice of this method because Standard Chartered Bank operates throughout the day and therefore it is not possible at any one time to find all of them in one place. Physical delivery of the questionnaire increased the accuracy of data collected as there was interactivity. After collection, the data went through analysis, culminating the observations and conslusions discussed in chapter four and five respectively.
Critical Appraisal for Quantitative Research Approach
Ahearne & Schillewaert (2001) researched on the effect of information technology on salesperson performance where they clearly formulated hypothesis in order to find out research gap and the solution of the problems by analysing collected data. In this case, the researchers used quantitative research approach to quantify data, and they interviewed 344 respondents, among them 244 respondents were sales representative and 100 respondents were customers. However, the researchers of above mention study identified that the IT provides huge intermediates and intangible advantages and add extended value towards the performance of sales staff and make it easy to interact between the customer and sales person.
Bass, Tim and Gene (2001) conducted study upon the topic “the moral philosophy of sales managers and its influence on ethical decision-making” and identified that the moral philosophies of the sales managers have major influence on the sound ethical environment within the corporate practice that can similarly influence both sales and marketing staff. Bass, Tim and Gene (2001) identified the major factors that affected the moral values and unethical sales practice of the sales staff in terms of the age, and race. They also addressed the problem area with clearly formulated hypothesis along with quantitative approach because the former researchers discussed the topic considering this research method.
On the other hand, Damnjanovic and Krulj (2006) studied on the important factors for salesperson evaluation using quantitative approach along with simple questionnaires, which were distributed to the respondents. However, present dissertation will use the outcomes of the Damnjanovic and Krulj’s research as they identified that the behaviour-based assessment of sales staff performance is intensely concerned with three most influential factors, for instance, internal, external, and personal factors. These factors related with individual attributes and the model also provide the opportunity to assess the sales staff performance (Murphy, 2002). At the same time, the organisational factors, such as, guiding principle towards the sales staff, concerned manager’s control over them, rising sales volume, their knowledge about the competitors and the buyers, understanding about the objectives and compensation package and eagerness to attain these goals are the attributes to evaluate sales staff performance (Ferrell &Ferrell 2005).
Cadogan et al (2007) in their research “Sales manager and sales team determinants of salesperson ethical behaviour” interviewed 1313 respondents, among them 923 respondents were sales staff and 390 interviewees were sales managers. In findings of the research Cadogan et al (2007) has provided a milestone model with the individual moral philosophy of sales manager that generates enhanced ethical standards of sales staff behaviour concerning to their rewards, job certainty, team spirit and potential results (Mehta 2006). They also mentioned that without any rewarding program, the sales managers do not enough aware regarding the standards of their sales staff behaviour or do not watch over unethical behaviour, but keep effort only on target sales volume and profitability of the company.
However, Homburg and Stock (2005) researched on this area and they have identified that the workers’ job satisfaction has an extensive link with the increased clients’ satisfaction. In their research “Exploring the Conditions under Which Salesperson Work Satisfaction Can Lead to Customer Satisfaction”, they selected 1305 sales employees though only 221 respondents give feedback who regularly communicate with the customers and they recognised that sales staff satisfaction has huge impact upon the customer’s relationship management.
Methods of data analysis
Data analysis refers to the process of transforming raw data into refined useful information that can be of use to people. Before settling on a method of data analysis, it is important to the approach to be taken by the research. The research can take quantitative, qualitative, or categorical approach. This research took a quantitative approach. Depending on the type and accuracy needed, data analysis can take a simple descriptive form, or a more complex statistical inferencing. The technique used in the analysis can be univariate analysis, bivariate analysis or multivariate analysis. In selecting the appropriate method, a researcher should ensure that assumptions relating to the method are satisfied.
In analyzing the collected data, the researcher will use appropriate statistical data analysis tools such as descriptive and inferential statistics in analyzing quantitative data.
In relation to the quantitative analysis, scholars argued that the most commonly used sets of statistics include mean, frequencies, standard deviation, median, and percentages. The researcher will code and enter the quantitative data into Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS version 20). Using SPSS, the researcher will use cross tabulation to sales staff behavior and the level of customer satisfaction of Standard Chartered Bank, Penang branch. The researcher will also use descriptive statistics such as mean, standard deviation, percentage, and frequencies to describe the properties of the target population. Further, the researcher will use tables, figures, and charts to present the findings of the study. Because the research entails comparison of the performance of the two branches of the bank, the researcher will employ correlation analysis to enhance clarity. Therefore, chi-square tests will be used to test the hypotheses. Inferential statistics like chi-square tests help to test whether the observed relationships between the variables are genuine or due to chance. The statistical significance level used in the research is 0.05 indicating whether the observed association occurred by chance in 5 out of 100 results. Chi-square is the most widely used measure of association in social science research, being suitable for use on nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio data.
Reliability and validity of the method
Validity means appropriateness, applicability and truthfulness of a study. It is the ability of research instruments to produce results that are in agreement with theoretical and conceptual values. In this study, internal validity was ensured through checking the representative of the sample. The researcher ensured that the sample used captured all important characters at the Standard Chartered Bank as the target institution, and the Malaysian society, especially the society in and around Penang region, as the immediate environment of our study. During data collection process and in analysis, the researcher steered away from any form of bias. All the respondents were picked randomly, without any preference. Moreover, the response received from the customers and employees of Standard Chartered Bank, and other stakeholders were assigned a similar weight, depending on their category. This ensured that data which was collected was not in any way, influenced by the opinion of the researcher.
External validity was ensured through triangulation that is, the researcher used more than one technique in collecting data. This was necessary to ensure that bias from one end is countered effectively by other techniques. Respondents are human beings with weaknesses when it comes to giving views freely. They would always exegerate or underrate things when they make statements. Working with this in mind, the researcher designed a formula to moderate data gathered from the field to balance off the two extremes. The researcher found literature review to be very important in this part because the opinons they have are already moderated. External validity was also guaranteed by asking respondents to give their views. This would give them freedom of some sort, to provide information based on their own experience and views.
Reliability means that the study is consistent and lacks any ambiquity. It is the ability to trust something to provide an information that addresses the issue at hand. It is related to the accuracy of instruments that is, how accurate the measuring device is in measuring what it claims to measure. In this study, it was achieved through increasing verifiability of the perspective and using statisitical tools to verify reliablity. The researcher adopted the principles of coherence, openness and discourse in order to guarantee reliability.
Limitation of Data Collection Process
To deal with two distinct questionnaires for two distinct groups was one of the most difficult tasks in this research. In addition, data collection procedure was time consuming as the sample groups, such as credit card sales staff, and customers were large for this research. In many cases, the customers were reluctant to co-operate to fill up the questionnaire though sales staff were keen to complete the questionnaire with due time. On the other hand, data collection process was expensive issue and it was more difficult in this case.
Presentation, Analysis, Interpretation of Data
Introduction
Chapter 3 discussed the methodology of this dissertation. In the methodology section, the researcher outlined the steps taken during data collection. It was made clear that data was collected through questionnaires, which were distributed, to customers and employees of Standard Chartered Bank at Penang. In total, the researcher distributed 344 questionnaires, of which 100 were distributed to customers and 244 went to the employees. Although both the customers and the employees’ responses were equally necessary in drawing conclusion, employees were given more weight because they were constantly in touch with the bank, and therefore were in a position to provide more information concerning it.
In the previous chapter, the researcher briefly explained the purpose of data analysis, which this chapter seeks to achieve. The preceding chapter also talked about the role of literature review. This chapter will involve analysis of the primary data. As explained in the preceding chapter, this research used quantitative research methods. Quantitative research involves systematic empirical study of a phenomenon by use of statistical tools. Its main objective is always to employ mathematical theories and models in developing its generalization. As explained above, the researcher took a sample of the total population. This sample was used as a representative of the entire population, and it is the data collected from the sample that the researcher wishes to analyze in this chapter.
Data analysis refers to the process of transforming raw data into refined useful information that can be of use to people. It is through the analysis that the researcher would be in a position to confirm or refute the hypotheses developed in previous chapters. A research’s success would be determined by how well the analysis is conducted. As explained elaborately in the previous chapter, depending on the type and accuracy needed, data analysis can take a simple descriptive form, or a more complex statistical inference. The researcher can also choose to take univariate, bivariate or multivariate approach to data analysis. In so doing, it is very important that the researcher ensure that the assumptions relating to the method are met. In analyzing data, a researcher should choose the best statistical tool that would best lead to the desired answer.
In this study, the researcher has used statistical analysis tools such as descriptive and inferential statistics in analyzing the quantitative data. This would enable tabulation, hence comparison of the behavior of customer behavior and the level of loyalty of customers of the bank towards the credit cards (Poole, 2004). The result would then be presented in tables, figures, and charts. This chapter would thus focus on analyzing the data collected and testing the research hypotheses. It would also answer the research questions that were developed along with the hypotheses. The next chapter would then draw conclusions from the results found in this chapter. It would closely compare the findings of this research to those of existing bodies of literature to determine the variation and the implication of this variation.
Chapter objectives
This chapter is concerned with the analysis of the primary data. The primary data was collected from the employees and customers of Standard Chartered Bank at Penang. The following are the specific objectives of the chapter.
This chapter seeks to ascertain the truth behind the four hypotheses developed in the research proposal. Upon completion of this chapter, the following hypotheses would be confirmed or would be nullified through a comprehensive data analysis.
H1o. There is no direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ loyalty to the bank.
This is the first and the fundamental hypothesis that brought the need to conduct the research. This research seeks to determine the relationship between the behavior of the sales staff and customer loyalty. If confirmed to be true, it would render this research not necessary.
H1a. There is direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ loyalty to the bank
This is the alternative hypothesis to the above hypothesis. This research hopes to confirm it, as it would necessitate further research to determine the extent of this difference and reasons for it.
H2o. The behavior of the sales staff is not closely related to the motivation they receive from the management of the firm.
Employee satisfaction is a sign of better performance. If the above hypothesis were confirmed to be true, then it would be confirming the first null hypothesis above.
H2a. The behavior of the sales staff is closely related to the motivation they receive from the management of the firm.
Confirming this hypothesis would be confirmed the first alternative hypothesis as above. It would call for further research to determine the rationale.
H3o. The possibility of the customers accepting the credit cards does not heavily depends on the ability of the sales staff to convince them that they are beneficial.
Customer satisfaction is directly related to growth and prosperity of a business unit. Confirming the above hypothesis would substantiate the first null hypothesis of this research.
H3a. The possibility of the customers accepting the credit cards heavily depends on the ability of the sales staff to convince them that they are beneficial.
Confirming this hypothesis would be a validation to the first alternative hypothesis of this research. It would necessitate further research.
H4o. The ability of the sales agents to sell successfully the credit cards to the customers does not depend on their level of education.
Through education, employees are always better positioned to serve customers (Gusti, 2011). If the above hypothesis were confirmed, then this would be a justification of the first null hypothesis of this research.
H4a. The ability of the sales agents to successfully sell the credit cards to the customers depends on their level of education.
This hypothesis would be justifying the first alternative hypothesis of this research. Of interest would be to determine the reason behind this and the effect created by it.
This chapter also seeks to answer the three main research questions developed in the research proposal and the first chapter of this research. The questions are as below:
Is there a direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ response to the item on sale?
This question was meant to determine the role of the sales staff in ensuring that there is positive response by customers towards the credit cards. By responding to this question, an avenue for research would be opened to investigate the general behavior of the customers.
What are the general conducts of a sales agent that would make a customer buy or fail to buy a credit card?
This question was meant to bring to focus the experience of the customers of this bank in close relation to general behavior of the sales staff. As the research would be investigating the experience of the customers as posted in the above question, of interest would also be the conduct of employees. This way, it would be possible to compare the two variables and determine the relationship between them.
Assumptions
In any research, there is always the need to hold some assumptions. In pure science research, the researchers would always hold some factors constant. This would enable them conduct the research under different conditions before coming up with a solid report. However, social science comes with one main complication. Social science deals with people. Unlike the specimen used by pure scientists that can be manipulated to suite the need of the research in the laboratory, it is practically impossible to manipulate human beings. For this reason therefore, it would force social scientist to study human being under its normal characteristics. Because research may require some special conditions, which the researcher may not be able to create, it would force the researcher to make some assumptions that would fit the desired conditions.
In this research, there are some assumptions, which were made specifically to suit various conditions that the researcher considered necessary. Some of these assumptions include the following.
-
- The leadership of Malaysia is guided by Islamic principles as taught in the Quran.
The researcher developed this assumption after realizing the strong influence the government has towards the normal operation of business institutions. When conducting a research therefore, it would be wise to develop an assumption that would relate to the leadership of the country. Being an Islamic state, the above aspect about the government was considered appropriate.
-
- The law that is practiced in Saudi Arabia is based on the English common law, but heavily leans towards various aspects of Shariah laws as taught in the Madrasah and other law schools.
One of the most important aspects of the external environment is the legal front. No firm can operate in an environment that is not keenly guided by law. The Malaysian society is guided by various principles of law found in the English common law and Shariah law and it would be appropriate to include this aspect in developing the research findings.
-
- The Standard Chartered Bank introduced credit cards due to the growing relevance of the product in the market.
This assumption was developed due to the strong desire to determine reasons behind the introduction of the credit cards. To avoid speculation in this study, the researcher developed this assumption as a guiding light in finding reasons for the hypothesis that relates to this assumption
-
- The management of Standard Chartered Bank decided to use sales agents to convince customers to sign up for the credit cards because it believed that the approach was more effective.
This study focused on the comparison of sales and staff behavior and the loyalty of the customers towards the product on sales. It was of interest therefore, to determine the role of the management in this. This assumption was meant to justify the fact that if there was misdemeanor on the side of the sales staff, then the management has a hand in it.
After the researcher has set the hypothesis, he or she would proceed to test validity of null hypothesis (H0) against that of alternative hypothesis (Ha) at a specified level of significance. This significance level is always given as a percentage. The significance level adopted would determine the confidence with which an experiment rejects or accepts a null hypothesis. At 5 percent significance level, it means that the research is 95 percent accurate. If the significance level is considerably large (say at 50 percent), the accuracy of the results is reduced. At 50 percent, it would imply that chances that the results of the research are inaccurate are just as much as chances that it is true. Such a result cannot therefore be relied upon.
In this study, the researcher adopted 5 per cent as the level of significance for this study.
-
- Two tailed test.
While testing hypothesis, the researcher can choose the two tailed or one tailed approach. The two-tailed approach would reject the null hypothesis in case the sample statistics is significantly lower or higher than the population parameter that was hypothesized. The researcher adopted the two-tailed test because of the need to reject the null hypothesis.
Analysis of research questions
Conducting a research is like setting on a journey whose destination is not very clear to the traveler. Research is a path whose destination is unknown. However, it is important to note that despite this, there should be a proper plan on how the research would be conducted. A guide should be developed that would help in reaching the desired result in the research process. In a research, research questions and hypotheses are very important guides in developing a desired solution from the field. Hypotheses would always be developed from the research questions. Those hypotheses are always possible response to the research question.
The research questions are the core of any research process. In case it is poorly developed, the entire research process would lose focus and the possible result that may come out of the research may not hold any meaningful truth. The researcher would be seeking answer to these questions.
Having taken the above considerations, the researcher developed questions below. The two main questions were purposely set to meet the above concern raised about the external environment of Standard Chartered Bank. This study seeks to gather and analyze data that would help explain the relationship between customer loyalty and sales staff behavior. It does not seek to find reasons why the society of Malaysia lives the way it does. However, the researcher is conscious of the fact that the society of Malaysia has direct effect on the performance and policies developed by the bank. The questions were thus set to reflect this. The following two questions were formulated. Having confirmed from the literature review that there is a considerable relationship between the behavior of sales staff and customer loyalty, the researcher developed this question to bring to focus, the effect of sales staff behavior on Standard Chartered Bank.
Is there a direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ response to the item on sale?
This question was very critical to this research. It would help explain the relationship between the behavior of the sales staff and customer loyalty. The researcher was keen never to deviate from the research topic. Although the researcher appreciated that the culture and social structure of Malaysia is rich and worth reporting on, this research was limited to the concerns of the bank.
This question was reflected on the questionnaire that was sent to the customers and employees. The result was entered into the SPSS sheet and the data on the table below was found. From the data, it was evident that of the 344 respondents, 301 of them felt that there was a strong relationship between sales staff behavior and customer loyalty. 87.5 percent of the respondents strongly believe that the behavior of the sales staff would have an effect on the loyalty of the customers. In the study, 12.5 percent felt otherwise. The accompanying pie chart demonstrates this.
Table 3: Relationship between customer behavior and customer loyalty.
The next research question was developed to know some of the general conducts of the sales agents when on duty.
What are some of the general conducts of a sales agent that would make a customer buy or fail to buy a credit card?
Based on a scale of 1-5, where one is very poor and 5 is very good, below is how customers rated the general conduct of the customers.
Table 4: Rate services offered by sales agents.
The questionnaire also focused on the experience of the customers based on gender. In order to test whether there is a significant difference in the experience of female customers of Standard Chartered Bank in Penang region by virtue of their gender, a chi-square of equal proportions was applied using SPSS. Table 3 below shows the findings.
Source: Analysis of survey data.
Source: Analysis of survey data.
From Table 4 above, it can be observed that the value of the chi square statistic is 33.040 and its corresponding p value is 0.000<0.05. Since the p value is less than 0.05, it can be concluded that there is a significant difference in the experience of female customers of Standard Chartered Bank, by virtue of their gender.
Testing the research hypotheses
Every research in social science attempts to prove that specific phenomena occurred for specific reasons. Conducting a research is like a walk in the desert without a guiding map to show clear directions that should be taken in order to reach the desired direction. Care should be taken by every researcher when conducting a research to ensure that he or she does not wonder off the focus of the study just by the sheer wonder of the research in question. A path should clearly be set, upon which the research would take on reaching the desired solution.
Research hypotheses always provide solution to this. Hypothesis is a proposition made by the researcher about the research upon which the research would try to determine if it is true or otherwise. It is kind of a proposal or a guess that the findings of a particular research would be in a particular way. A research would always have two hypotheses for every single desired result. There is always the null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis. The null hypothesis would always refute the claim by saying that the proposition does not hold. On the other hand, alternative hypothesis would always try to affirm that the proposition set by the researcher holds. A test would always be conducted on the null hypothesis with an aim of rejecting it. By rejecting a null hypothesis, the research would be accepting the alternative hypothesis. It is always every researcher desire to reject a null hypothesis because when a research accepts a null hypothesis, it would render the whole research unnecessary. It would be rejecting the proposition made by the researcher, a fact that would render the research null and void.
In analyzing the research hypotheses, the researcher would always set the significance level, always expressed as a percentage. This percentage would be the limit within which the researcher would accept a null hypothesis. If the limit were surpassed, it would be said that there is significant difference and therefore a null hypothesis is rejected. Setting the percentage too high would be increasing the chances of confirming a given hypothesis, but it would reduce the accuracy of the research. Setting this percentage too low would increase chances of rejecting the hypothesis and increases chances of accuracy. In most of the social sciences research, 5 percent is always acceptable as the standard significance level. As earlier stated in the assumptions above, this study takes 5 percent as its significance level.
The researcher would test this hypothesis by analyzing the data gathered from both the employees and customers. In total, there were 344 respondents.
Below are the four null hypotheses that the researcher wishes to test and reject in order to accept the alternative hypothesis, which would help in validating this research:
H1o. There is no direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ loyalty to the bank.
This is the main hypothesis of this research whose rejection would validate the need for this research. By accepting this hypothesis, it would be a clear sign that the research confirms that there is no significant relationship in sales staff behavior and customers loyalty. The researcher wishes to reject this hypothesis.
It can be observed from the table and the pie chart below that 91.7% of the customers felt that there was close relationship between their loyalty and the general conduct of the sales staff of the bank. In the study, 91.7% stated that they would be affected by the behavior of the customers, and that this would determine their loyalty towards the bank. Only 8.3% stated that they are not affected by the behavior of the sales agents.
Is there any relationship between sales agents’ behavior and your loyalty towards the bank?
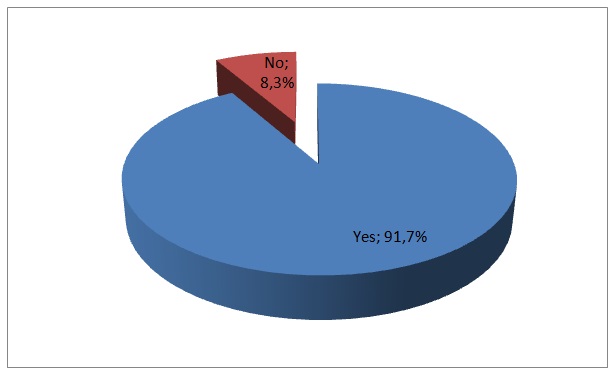
This leaves the researcher with the alternative hypothesis, which states as below.
H1a. There is direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ loyalty to the bank.
Upon rejection of the above null hypothesis, its alternate hypothesis would automatically be accepted. The null hypothesis has been rejected by a wide margin. The researcher has therefore proved, from the data gathered from the population sample that there is direct relationship between sales staff behavior and customers’ loyalty to the bank. Having confirmed this hypothesis by a wide margin, the researcher consequently confirms that there is need to conduct the research that seeks to the effect of sales staff behavior on customers’ loyalty towards the bank. This opens door for the researcher to test other supportive hypotheses, which would further help in confirming this hypothesis.
The next hypothesis was formulated to determine if there was relationship between the behavior of the sales staff and the motivation they receive from the management.
H2o. The behavior of the sales staff is not closely related to the motivation they receive from the management of the firm.
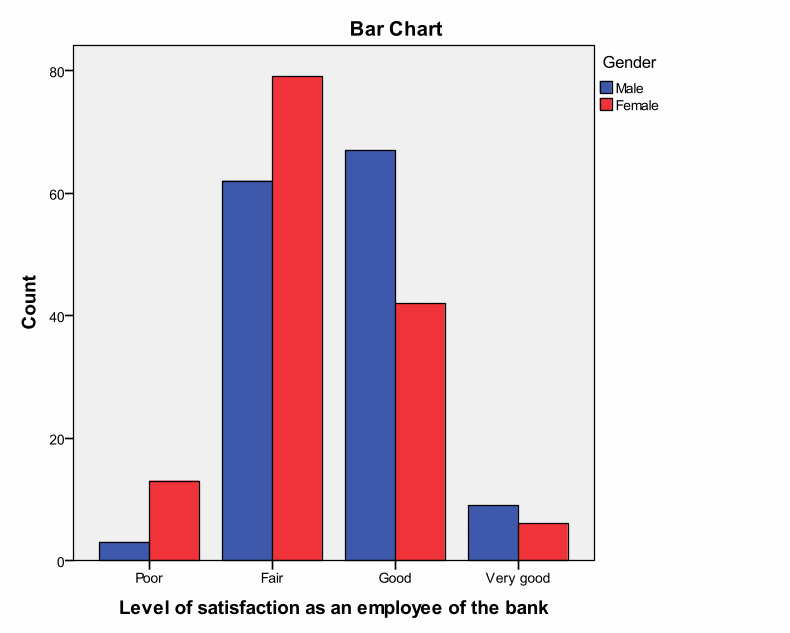
From the graph below, it can be observed that 47.5% of the male employees’ level of satisfaction was good and 56.4% of the female employees had fair level of satisfaction as an employee of the Standard Chartered Bank.
In order to test whether there is a significant relationship between the level of employee satisfaction and their general behavior, chi-square for equal proportions was applied using SPSS and the findings are shown in Table 8 below.
Source: Analysis of survey data.
Source: Analysis of survey data.
From Table 9 above, it can be observed that the value of the chi square statistic is 177.975 and its corresponding p value is 0.000<0.05. Since the p value is less than 0.05, the null hypothesis can be rejected and hence concluded that the behavior of the sales staff is closely related to the motivation they receive from the management of the firm.
H2a. The behavior of the sales staff is closely related to the motivation they receive from the management of the firm.
By rejecting the null hypothesis above, the alternate hypothesis would be accepted. It therefore comes out very strongly that a close relationship between the behavior of customers and the motivations they receive from the management exist. As was previously hinted in the review of literatures in chapter two, it is now clear that the management has a role in the misdemeanor of their sales staff.
The hypothesis below was developed to ascertain the difference in the level of customers in the bank’s two branches.
H3o. The possibility of the customers accepting the credit cards does not heavily depend on the ability of the sales staff to convince them that they are beneficial.
To help in testing the above hypothesis, the researcher used the results from the customers. The research covered 100 customers of this bank at its Penang branches.
The researcher conducted a correlation analysis using the SPSS and the output below was generated.
Using Pearson Correlation analysis, the data above demonstrates that the possibility of the customers to buy the credit cards is dependent on the behavior of the sales staff.
To validate further the above findings, chi-square test for equal proportions was applied using SPSS and the findings are presented in Table below.
Source: Analysis of survey data.
Source: Analysis of survey data.
From Table 11 above, it can be observed that the value of the chi square statistic is 24.253 and its corresponding p value is 0.000<0.05. Since the p value is less than 0.05, the null hypothesis can be rejected and would therefore be concluded that the possibility of the customers accepting the credit cards heavily depends on the ability of the sales staff to convince them that credit card is beneficial.
By rejecting the above null hypothesis, this would help validate the first alternative hypothesis.
The findings would be a confirmation of the alternative hypothesis below.
H3a. The possibility of the customers accepting the credit cards heavily depends on the ability of the sales staff to convince them that they are beneficial.
This hypothesis tries to emphasize the fact that there is need to conduct the research to ascertain the reason behind the behavior of the sales staff and how this behavior would affect the bank’s customers.
Following the analysis of the literature review, one major factor that was coming out clearly as the determinant of the behavior of the sales staff was their level of education. It was coming out clearly that the level of education of the sales staff heavily determined their affectivity on selling the credit cards. The researcher set to test the null hypothesis below.
H4o. The ability of the sales agents to sell successfully the credit cards to the customers does not depend on their level of education.
From the table and pie chart below, majority of the respondents (70.8%) noted that education had positive effect on the ability of the sales staff to perform their duties. Only 20.8 percent felt that that it has negative effect while 8.3 percent stated that it does not matter.
Table 12: How does the level of education affect sales staff capacity to sell the credit cards?
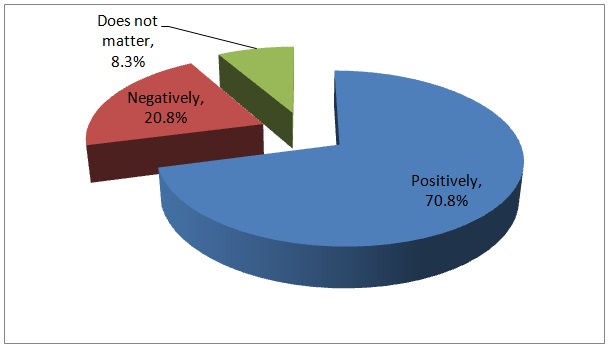
The null hypothesis is rejected and it is concluded that the ability of the sales agents to successfully sell the credit cards to the customers depends on their level of education. This therefore means that the alternative hypothesis below was accepted.
H4a. The ability of the sales agents to sell successfully the credit cards to the customers depends on their level of education.
Confirmation of this hypothesis not only supports the main hypothesis (the first hypothesis) of this research, but also gives more clarification on the manifestation of sales staff behavior. It points out at some of the factors that have facilitated the difference in behavior of sales staff behavior and the effects associated to this.
Sensitivity Analysis
In every research finding, the correctness is always very important because an action may be taken upon the findings and recommendations of a given research. In case the result deviates from the truth by a considerable wide margin, it can result into serious consequences, especially if the action taken is of great impact. However, it is worth appreciating that human being is prone to making errors in a number of occasions. This error can be in the process of input of the data or its analysis. Whichever point it may arise from, the consequences of such errors may be adverse if action were to be taken upon its recommendation. Sensitivity analysis is therefore important in mitigating such errors in a report. It helps in determining how robust a given research is.
In this study, the researcher appreciates the fact that such errors may occur. For this reason, there is a need to develop measures that would help validate this research.
In this research, the main aim was to the relationship between customer loyalty and the behavior of sales staff of Standard Chartered Bank in Penang when selling credit cards. Reliability and Validity studies below help further explain how this research ensured that it maintained correctness of the findings.
Reliability
Reliability means appropriateness, applicability, and truthfulness of a study. It refers to the ability of research instruments to produce results that are in agreement with theoretical and conceptual values. The consistency of the measure, the probability of obtaining the same results again if the measure was to be replicated is referred as reliability. It is the relationship between the true underlying score and the observable score. Internal consistency is also important for the survey since it indicates the extent to which the items in the measurement are related to each other. The most commonly used index of internal consistency is Cronbach’s alpha coefficient.
This index ranges from zero to one, where a reliability of zero means no relationship, and reliability of one indicates a perfect and positive relationship. Since the reliability declines as the length of the question increases, the questions would be designed to be straight to the point. The idea behind internal consistency procedures is that questions measuring the same phenomenon should produce similar results. In internal consistency reliability estimation, single measurement instrument is administered to a group of people on one occasion to estimate reliability. The overall consistency of the customers’ questionnaire in this research was 0.7 and employees’ questionnaire was 0.71 indicating that the questionnaire was reliable. Table 16 below shows the findings of reliability analysis.
Table 13: Reliability Analysis.
It would therefore be true to emphasize that the researcher ensured high level of validity in this research.
Summary
This chapter has focused on comprehensive analysis of the primary data gathered from the customers and employees of this bank. After a successful collection of data, the next stage is always the analysis of the gathered data. Data in its raw form may not be useful unless it is processed into useful information. Following the above comprehensive analysis, it has emerged clearly that Standard Chartered Bank management has a role to play in order to shape the behavior of their customers if they expect to retain their customers. The behavior of their sales staff has direct impact on the loyalty of the customers. As such, the sales staff should be made to appreciate the fact that the customers are long-term partners who should be treated with decorum, and not deceit based on short-term benefits.
Summary of Findings, Conclusions & Recommendations
Summary
Throughout this dissertation with sales staff behaviour in Penang, Malaysia has identified that factors like outsourcing sales staff, unparallel competition among the industry players, lack of organisational ethical code of conduct, unsatisfactory job and regulatory loopholes with governmental policies are most influential factor for unethical behaviour. At the same time, Sales staff’s personal attributes like education, moral values, cultural orientation, and job satisfaction are another source unethical behaviour. The scenario of customers respond to the sales staff’s is very complex in nature, some time they react vigorously and some time they collaborate with the sales staff to get more than one credit card by misrepresenting annual income.
There is no standard coder of ethical be sales staff behaviour policies which is emergence to put into practice which has suggested in the recommendations without any prior measure. The challenging dynamics of quick shifting credit card industry of Penang needed to set up minimum ethical standard for sales staff while the society is arguing to represent optimistic technological needs, social psychology, encouraging incentives, and affirmative sales approach. Due to the vast area to cover in short space and time, some remaining issues are yet to be addressed. This would be explored through further research in this area with the essences of present research with contemporary the sales staff behaviour to enhance the management process improvements.
In the light of the literature review, this chapter would investigate and argue on the customers respond to the sales staff behaviour in context of credit card sales in Penang, which is indispensable to assess by the marketing community to draw the attention of the prospective marketer to increase their sales and accelerate profitability. This part of the dissertation also focuses on the findings that contribute a new learning outcome for the new sales staff and sales agents who are interested in get entry in the credit card market of Penang to formulate their entry strategies to draw impending attention and eager to explore their career and business in Penang with ethical standards.
Changing Nature of Credit Card in Penang
Bahari (2009) mentioned that Malaysia has been establishing insistently the Islamic financial system with the aim to be attractive to turning itself as the focal point for global Islamic financing while the speedy enlargement in the financial industry has encouraged foreign banks to prefer Malaysia as their safe investment destiny to carry out business of Islamic banking. Such trend in the Malaysia economy has generated an indirect competition among the financial institution to align with Islamic banking instruments, these kinds of unhealthy struggle to integrate Islamic financial products or services even as to change the name of some existing products/services into Islamic term keeping full attributes unchanged and comparable with general banking norms in global standard. It is just a cheap strategy to cash the religious sentiment and there is nothing wrong to the financial institution as they are producing accelerated profit by integrating Islamic financial products.
Ferdian et al (2008) added that to respond these rising needs, the Bank Negara Malaysia has established Shariah Advisory Council and in 2003, Bank Islam Malaysia has introduced the first Islamic credit card in this country to attract Muslim by suing European smart card and chip technology. As the Islamic values oppose the concept of interest, the Islamic credit cards are charging their customer profit instead of interest after the 20 days grace period where there is basic difference with the conventional banking (Lian, 2011). The issuers of Islamic credit card enjoy huge opportunity to block customers fund in their Wadiah account and taking the profit money in advance, which generate greater opportunity for the banker to generate more profit than the conventional banking. Moreover, the Islamic credit card is limited for use, restricts to make payment of bars, nightclubs, and for hard drinks that would reduce the rate of transaction and overall people may not go to use them. On the other hand, the spending through credit card illustrates luxury and encourages redundant and unplanned consumption in the economy, which is contrary with the core teaching of Islam, Islam always suggest to avoid debt, thus the Islamic credit card may not keep any new contribution to the economy rather than exploring religious radicalism in Penang.
Conclusion
Ponnu and Tennakoon (2009) argued that the ethical magnitude of the organisational leadership’s ethical behaviour upon the extent of the commitment of staff to the organisation has tremendous missing norms on the practice of Penang and as whole Malaysia where there is no way to avoid the influence of leadership behaviour on the sales staff. In the case of Malaysia, it has evidenced that there is greater association between the ethical behaviour of leadership linking with employee’s behavioural outcomes while there is superior organisational commitment of the sales staff along with trust on their leaders. Thus, the unethical behaviour of the management and co-workers drive the sales staff to breach the ethics code of conduct and the sales staff always try to follow the peers along with the top management and learn to respond to the unethical behaviour with individual conduct. For instance, while the sales staff found that the co-workers are rewarded for better performance through misconduct with customers, what message the overall sales staff receives, obviously they would get the message that the management encourages unethical behaviour by rewarding performance rather than punishment on staff’s misconduct with customers.
Ramayah et al (2002) mentioned that the credit card was first issued by Bank America in 1960 in the USA, which is familiar worldwide as VISA and in Malaysia it was in seventies first introduced credit card. At present, there are nine hundred thousand credit card users in Malaysia, which is growing at a speedy rate of 89.3% per annum, and it reached over several millions due to increased confidence at user level, political constancy, excellence in the economic growth, and social progress. At the beginning of eighties, the process of credit card sales in Penang, Malaysia were totally different from today, customers were willing to get the credit card from banks by paying all costs and they don’t mind to be charged very high annual fee along with joining fees. People, who have credit cards at that time, were well thought-out that they are financially successful along with indication of prestigious status as the banks charged very high cost for annual fee and joining fee. In nineties, credit cards turned into easier accessible to the mass people while foreign banks started and intensified their operation in the Malaysian credit card market. At this stage, consumers still like to apply credit card from foreign banks due to their lots of promotion to attract customers and the local people also started to own foreign bank credit cards with high annual charges and joining fees.
The nature of the practice of credit card sales in Penang has transformed a lot during in 2000; most of the banks waived their annual fee and joining fees to create a centre of attention of the customers. The antagonism among the credit card issuer banks has intense especially the foreign banks and the customers became very choosy and careful; it is not easy to promote any new credit card to customers in Malaysia. As a result, credit card sales in Malaysia have shaped as a curb crucial job and it necessitates to having very good sales people in order to convince customers to apply for credit card.
Ponnu and Tennakoon (2009, p. 17) added that due to the strong competition among the credit issuer banks in Malaysia, incredible number of people enabled to get credit cards without any efforts due to the bank’s careless investigation of the customer’s credit history. At this moment, banks have engaged some screening procedures such as using credit scorecards for their decision making while it is essential for the credit card sales vendor who evaluates new applications in favour of the issuer banks. Thus, it is most important to identify and measure the new applications with very careful manner to protect any misrepresentation about the new credit card issue and to ensure right use of financial resources for the competent individuals rather than any fake or illicit applicant in context of police record.
Consequently, the credit sales in Penang, Malaysia has turned into a very tough and complicated job while omission of annual fee and joining fee seriously reduced the profitability for both the issuer banks and common for the sales vendors. This situation makes the sales vendors bound to look for low paid sales staff as a cost reduction strategy and they drive for hard sales option. Subsequently, the customers’ trend just before the credit card sales staff have distorted and they would like to avoid sales staff at road show, at shopping complexes and any other possible places where sales staff face them. With the mutual aid of such sales staff, most of the customers during this time at least own several credit cards without any hard effort and the credit card issuer banks are under serious pressure to reduce concerned sales cost to sustain in the competitive market of Malaysia. As a result, banks are deeply concerned with credit card sales and started to look for outsourcing service agents from the private sector of Malaysia with very marginal credibility to the customers. Thus, the Outsourcing Companies is needed to have a very good sales strategy and tactic with dynamic sales staff in order to finding new customers and sign up them, which is a very tough job in the competitive market of Penang, Malaysia.
The conceptual framework of credit card sales by bankers in Penang has shifted significantly over the few decades and lost its glorious tradition. Several years back, it was a very sophisticated and socially respected sales job for the preceding generation, but now it turned into a vicious job and the competent jobseekers treat it as a nasty job and never want to do such job. In the preceding era, huge number of dynamic individuals joined in credit card sales career, they already been promoted to the top management position in the issuing banking, some of them are head of the card sales division and overseeing the sales function in South East Asia. Unfortunately, these individuals have forgotten where their roots and where they come from along with long struggle.
During their time, they used to promote credit card in a very professional and ethical manner with the consumers, due to high competition they forgotten their learning outcome and allow to drive the current sales staff to do it completely different way from what they did all through their time. They strongly present the logic of survival to the competition and personal objectives to bring highest personal benefit from the company, they create pressure and made them found to do different unethical things and meeting the difficult sales target. The young jobseekers join in the credit card sales with the dream of career advancement, promotion, bonuses they entitle for achieving, but very a few sales agents in Penang allow sales staff such opportunities, most of them impose prefixed targets in exchange of a nominal commission rather than any fixed salary.
The very first batch of the credit card sales staff in Penang, those who are now at the top management of credit card division of credit card marketer, do not see anymore the needs of consumers to have a good perception headed for credit card sales staff, but they are arrogant to reduce sales cost. With the scope of engaging low-cost sales staff, the number of outsourcing agencies involved with credit card sales in Penang have severely increased and there exists an unparallel competition to offer lower bids to the banks for their credit card sales. To sustain under this unethical market competition, outsourcing agencies engage low grade, less educated and poor paid or unpaid staffs on a nominal commission or target orientated payment basis were deprived youths from the backward communities of the society join in this job. Such of this profiled staff are not familiar with corporate culture and lead to deal different unethical issues and misconduct with the customers, which ultimately effect on the banks’ image and have been discoloured the glorious past as far as credit card sales is alarmed.
The consumers for the most part try to avoid credit card sales staff nowadays for a number of reasons as they generally have a very poor and negative perception headed for credit card sales staff from banks and them outsource companies. In the marketing literature, most of the banks always speaks out regarding how important to safeguard their corporate image, but on the other hand, they allow unethical, inexperience and unprofessional frontline credit card sales staff from all channels to mess up their image every day (Cho, 2001). The banks have all to a great extent derived to increase the number of their credit card sales without caring whatever sales method has engaged to achieve their sales target. Now, one of the mostly applied sales tactics is hard selling and this technique of selling has annoyed and irritated many consumers from all occupation, but the banks take no actions and indirectly supporting it by rewarding for sales performance with unethical conduct and they do it because this method still can contribute significantly to certain target as required.
The legislation for credit card marketing in Malaysia has been considered as the regulatory framework for credit card sales in Penang, there is no different local regulation in this regard. The Bank Negara Malaysia (2011) pointed out that it is compulsory for the credit card issuers in Malaysia to bring into practice of fairness, transparency, and accountability to the credit card customers with their marketing approaches and offerings and they have to ensure that they do not increase the credit limit without any proper credentials or customer’s request.
In Penang, the Credit card issuing banks also urged for not to engage any malpractice of taking any credit advance like “cheque payable” without the request of customers and they requisite to eliminate all hidden fees and publish all fees and payment terms in the advertising of different media. The Central Bank of Malaysia has also made it clear that the credit card issuing banks would exactingly follow the applicant’s minimum income level at RM 24000 per year. They may not allocate more than two cards for the customers’ income level at RM 36000 and below, and would put back the extra cards more than two by the end of 2011. At the same time, the Malaysian legislation made it restricted to increase the credit limit two times more than the monthly income while the guiding principal of the coexisting regulation is to facilitate the customers from all unethical burdens of credit card marketers in this region.
The regulatory authority of Malaysia has seriously investigated with the credit card marketing drives by the issuers and their vendors complicated with nuisance and threats by debt collectors with the customers, imposing high collection charge upon customers, confusing nature of advertisement, antagonistic and cruel marketing mix, unauthorised product line, annoying credit advance and unauthorised limit incensement out of the guidance. The Credit card sales agents in Penang also aligned with missing of accountability, transparency, unclean terms, higher charges, fees and interest rate, hidden fees and violating customer’s privacy without any obligation for customer care. Lian (2011, p. 7) acknowledged that increasing stipulation to protect the credit card and financial products from the challenge of innovative but multifarious risk in Malaysia, evidenced escalating number of non-traditional bodies for marketing, innovative business model simultaneously with delivery channels, irregularities of Information inflow, low profile of financial literacy and borderless and effective operation without border barrier and suspense.
It is also noteworthy that the credit card regulation in Penang involved with many parties, such as, Central Bank of Malaysia, Finance Ministry, Politician, Cabinet, and stakeholders including issuers, salesperson, marketers, and interest groups. In recent times, the politician, Finance Minister, Central Bank of Malaysia have taken quite a few unpopular initiatives to control credit card business in Malaysia, in the name of “To promote prudent spending”, but from the credit card vendors point of view all these are bull shit, ridiculous, and with own agenda to establish central bank’s control over the market. In reaction, the credit card vendors argue that the credit card matter is a very sensitive issue that affected many people while the politician, central bank, and ministers always resembling to make unintelligent announcement, some comment absolutely not make any sense, very stupid and invalid comment to gain publicity at the expense of card vendors and making difficulties for jobseekers. The association of credit card sales companies have talked many things about credit card in the press, interview, and cabinet without proper evident; therefore, it should require further research in this context with prudent spending.
Malhotra (2009) examined with the prudent spending behaviour imposed by the governmental fiscal policy together with political influence institutional features, and legislative directives, identified that such spending has been enabled to pressure, and convince the central government to restructure the financial decisions while the state government of Penang is under serious stress of higher spending and deficits. It has subjective with the situation that the central government of Malaysia possibly will think to restructure the existing legislation in the parliament or may govern the situation through central bank regulation. The significant factors laid behind this scenario are that during 1990 the economics of Malaysia was not doing well while the government of Malaysia took many initiatives to encourage the desired growth of the economy.
Malaysian government has taken enough initiatives in order to stimulate and speed up the local economy and urged that it is necessary to increase the spending of mass people. To do so, the first initiatives was facilitating the mass people through credit card by which they would be encouraged for more spending, the government made it uncomplicated for credit card holders to pay less for what they spend on credit card. The government has altered the monthly minimum payment of credit card from 15% to 5%, it means that while an individual spends $1,000, he only need to pay $50 and the balance of $950 outstanding balance will be charged interest by the issuer banks (Ahmed, Ismail & Sohail, 2010).
Because of this initiative, the credit card sales become very popular and competition intensified in the market, and the credit card business has flourished in anticipation of 2009. In the annual budget of 2009, the government made an unexpected announcement for Government Service Tax and mentioned that GST would be effectual by 2010, with is this option it was confirmed that $50 would be imposed on each credit card own by cardholders. The logic that was presented from the central government of Malaysia is that the imposition of this GST would pick up the pace of ‘Promote Prudent Spending’. Ahmed, Ismail & Sohail (2010) have pointed out that the state government and central government both are allied with the similar ideological ground with the fiscal policy for prudent spending but there were a objection and debate among the people against promoting prudent spending in Malaysia.
Within short period of government assertion, the Prime Minister of Malaysia admitted that the imposition of $50 GST has expected to engender greater income for government, urged for not to make any question as it is a source of income for government, and will contribute further perfection of the country’s economic growth. With the introduction and improvement of GST ruling, the credit sales business has seriously injured in different aspects. through the procedure of the GST, the credit card sales become extremely difficult and customers turned very unenthusiastic to apply for any new credit card while the huge number of existing credit card holders were busy cancelling their credit card to stay away from paying GST.
There was a lot of debates and arguments flourishing regarding the GST ruling, while this author as the Managing Director of CA Merchant Services Sdn Bhd called a press conference to show own disagreement to this new verdict of GST. The Author strongly argued that in order to promote prudent spending, the government should modify the credit card monthly minimum payment from 5% to 20% or 30% and pointed out that by imposing the GST, it will not in actual fact ‘promote prudent spending’ but impose extra burden of liabilities upon the cardholders of the country. On the other hand, the government has not lent their hand in monthly minimum payment issue, no matter what happen, business still need to go on and all the stakeholders of credit card business in Penang working very hard to encounter with these challenging features.
Recommendations
It is always import to give recommendations based on the conclusion of a report. The following are some of the recommendations to this bank.
- To make recommendation on the unethical behaviour of credit card sales staff in Penang and their consequential response of the customers, at first, it is essential to stop rewarding the sales staff for his sales performance, if he aligned with any misconduct or misrepresentation with the customer. The sales managers may not provide any privilege to the sales staff if they engage with any unethical behaviour while it is essential to create evidence for the sales staff for engaging with activities with customers. For any complain against any sales staff, the managers should conduct free, fair, and impartial investigation without looking to the personal relationship or sales performance while the punishment may not be rigid process without any ethical education;
- The organisations concerned with credit card sales in Penang has suggested to create a health culture environment within the organisation that encourages sales staff to come forward to produce highest extent of rational behaviour with customers as well as report the breaches of ethical standards and mitigate with ethical norms. The sales managers would ensure a cooperative workplace environment for the sales staff where sales staffs know that they may not be undermined for co-workers reporting if there is no alignment of unethical conduct.
- The job satisfaction of the sales staff is another dominating factor where all the features of the job including working environment evidence as rewarding by gratifying and pleasing the sales staff and mitigating their frustrations. In the credit card sales organisation, to unsatisfying sales staff in comparison to the non-sales context, would align them to conduct unethical behaviour and it is very much common within the credit card industry of Penang. Thus, it is suggested that the players of the card industry would be more careful to ensure the job satisfaction of the sales staff and the unethical conduct would be reduce while the sales staff would perceive that their company is careful regarding ethical conduct and rewarding for steady performance with ethical conduct. It is general norms for the sales staff that while the organisation would provide higher job satisfaction, the sales staff would demonstrate their highest honesty and sound performance with ethical standards.
- For the customer who would like to report unethical conduct of the sales staff, the credit card sales agents would cooperate them to ledge complain at the office and would be facilitated to place their complain by setting global ethics hotline through online. The organisation would keep prompt action to mitigate the problem and demonstrate to the customers that the organisation is enough caring about the unethical conduct and do not bother to impose any kind of punishment to the sales staff. The organisation would be careful regarding some customers who are always arrogant and at all time look for misusing the organisational commitments by misinterpreting the core essence of ethical behaviour, in some case they misrepresent their annual earning and lead the sales staff to having more credit card that their income level.
- The credit card sales agents in Penang needed to set up ethical training centre to develop the personal morals of the sales staff where they organise the standards of their ethical code of conduct that would enable the sales staff for ethical decision-making. The objectives of the training session would be teaching moral philosophy in the course action of socialisation in the midst of friends and family rather than formal education and would influence societal, business, and corporate cultures by which they would be unable to encounter with any challenging situation to communicate more efficiently with the customers. Moreover, the training would also facilitate the sales staff to create consciousness regarding their rights or duties regardless to the outcome of sales performance.
- The marketing practice and sales of the credit card industry in Penang already been aligned to engage temporary staffing, individual contractors, and outsourced agents and has proven its solid base and resilience by encountering with the domestic economic challenges encompassing with reformation, liberalisation and perfect competition among the industry players. As the credit card issuer and sales agents are under pressure to gain competitive advantage by reducing cost, there is no way to keep a stopple to the use temporary employees and outsourced staff for sales, but it is essential to produce a standard format of contract where the ethical operation of sales would be emphasised. It is also emergence to impose obligatory terms on the outsourcing agents mentioning that if there is any scandal of unethical behaviour of sales staff, they have to take the liability and it needed to have punishment clause in the agreement. Meanwhile the outsourcing agents are eager to bid lower price to win the contract with minimum profit margin, so it would be effective to allow a certain percentage of the contract value as cost of ethical standard maintenance depending upon the total contract value.
- In Penang, the payment card industry all-inclusive debit, credit, electronic card, and online payment have long been associated with hard sales drive, which is required to change with customer’s loyalty program, and the sales agents would shift to the modern approach adopting more emphasis on loyalty and using it as a novel tool for card sales. To attain and sustain strong customer base, the credit card industry needed to align with three-dimensional approach of customer’s loyalty such attitudinal, behavioural, demo-graphical loyalty approach and it is indispensable for the credit card marketers of Penang to concentrate on the behaviour of sales staff to ensure customers satisfaction.
- By introducing prudent financial management, the central bank of Malaysia has taken the opportunity to increase government’s earning from the credit card industry without contributing any terms for market enhancement, while ‘prudent spending’ has generated high risk of reducing customers due to increasing tax. Moreover, the guideline has restricted the use of multiple card use, which directly affects market volume by reducing the numerous credit cards exist in the market. It is statutory obligation for the Bank Negara Malaysia to contribute the credit card industry some scope of accelerating the market by amending the existing regulatory control over the industry.
- Meanwhile, the guideline issued by the BNM regarding the responsible business practices for the credit card industry has mentioned for not to misrepresent regarding offering through advertising or sales approach and urged for transparent product disclosure but there is no single indication what would happen if anyone violates this provision. Thus, it is necessary to amend such regulatory guidance with very specific clause to penalise for violating ethical standards, as the existing legislative framework of Malaysia for credit card sales is not enough to administer the sales staff behaviour.
References
Abdullah, H., Rose, R. C. & Kumar, N. (2007). Human Resource Development Strategies: The Malaysian Scenario. Journal of Social Science, 3(4).
Ahmad, A. G. (2006). Cultural Heritage of Southeast Asia: Preservation for World Recognition. Journal of Malaysian Town Plan, 3(1).
Ahmad, S. Z., Basir, M. S., & Kitchen, P. J. (2010). The Relationship between Sales Skills and Salesperson Performance, and the Impact of Organizational Commitment as a Moderator: An Empirical Study in a Malaysian Telecommunications Company, Int. Journal of Economics and Management, 4(2).
Ahmed, Z. U., Ismail, I., & Sohail, M. S. (2010) Malaysian consumers’ credit card usage behaviour. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 22(4), 2-14.
Alboreca, J. Q. (1998) “The Configuration of Human Resources Management Policies And Practices In Multinational Subsidiaries: The Case Of European Retail Banks In Spain. Web.
Alt, J. K., & Lieberman, S. (2010). Modeling the Theory of Planned Behaviour from Survey Data for Action Choice in Social Simulations. Web.
AMA (2003). The Concept of Modern Marketing. Web.
Bahari, Z. B. (2009). The Changes of Product Structure in Islamic Banking: Case Study of Malaysia. Web.
Bank Negara Malaysia, (2011). New Measures on Credit Cards to Promote Prudent Financial Management and Responsible Business Practices. Web.
Bolvako, N. B. (2011) Exploration of Salespeople Activities and Behaviour in Information Technology Selling. Web.
Bowden, J. L (2009). The Process of Customer Engagement: A Conceptual Framework. Journal of Marketing Theory & Practice, 17(1): 63-74.
Cadogan, J. W., & Lee, N. (2009). Sales Manager and sales team determinants of salesperson ethical behaviour. European Journal of Marketing, 43(7/8).
Ch’ng, H. K., Chong, W., & Nakesvari, K. (2010). The Satisfaction Level of Penang Private Colleges Lecturers. International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, 1(2).
Cheng, I. A. O. (2010). Human Resource: Issues & Challenges, Prospects For Growth. Web.
Cho, S. (2001). Influence of Consumer Age and Clothing Type of Salesperson on Consumer Satisfaction with Salesperson’s Performance. Web.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Research Methods in Education. (6th ed.). New York: Routledge.
DHFS (2011). Standards Of Ethics And Conduct Manual: The University of Texas at Austin. Web.
Engel, J. F., Blackwell R. D., & Kollat D. T. (1995). Consumer Behaviour. 8th ed. New York: The DrydenPress.
Engel, J. F., Blackwell, R. D., & Miniard, P. W. (1995). Consumer behaviour. 8th ed. New York: Dryden Press.
Erickcek, G., Houseman, S., & Kalleberg, A. (2002). The Effects of Temporary Services and Contracting Out on Low-Skilled Workers: Evidence from Auto Suppliers, Hospitals, and Public Schools. Web.
Evers, H. D. (2011). Penang as a Knowledge Hub. Web.
Ferdian, I. R., Dewi, M. K., & Rahman, F. K. (2008). The Practice of Islamic Credit Cards: A Comparative Look between Bank Danamon Indonesia’s Dirham Card and Bank Islam Malaysia’s BI Card. Web.
Fleming, D., & Søborg, H. (2010). Skill formation, employment relations and institutional support. A comparison of emerging knowledge economies in East Asia with the Nordic countries. Web.
Ghani, K., Som, A. P. M., & Rehman, I. U. (2011). Marketers’ Perception about Marketing Ethics: Evidence from Malaysia. Journal of Economics and Behavioral Studies, 2(6). Web.
Gima, K. A., & Micheal, K. (1998). A contingency analysis of the impact of salesperson’s effort on satisfaction and performance in selling new products. European Journal of Marketing, 32( 9), 10-21.
Haron, H. et al. (2011). Factors Influencing Unethical Behaviour of Insurance Agents. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 2 (1). Web.
Haron, H., Ismail, I., & Razak, S. H. A. (2011). Factors Influencing Unethical Behaviour of Insurance Agents. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 2(1). Web.
Hochschild, A.R. (1983). The Managed Heart Commercialization of Human Feeling. Web.
Homburg, C., & Stock, R.M., (2005). Exploring the Conditions Under Which Salesperson Work Satisfaction Can Lead to Customer Satisfaction. Web.
Hong, T.T, & Waheed, A. (2011). Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory And Job Satisfaction In The Malaysian Retail Sector: The Mediating Effect Of Love Of Money. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 16(1). Web.
Hong, T.T., & Ismail, M. I. (2011). Identifying Work-Related Stress among Employees in the Malaysian Financial Sector. Web.
Hopkins, T., & Laaman, L. (2003). The Certifiable Salesperson: The Ultimate Guide to Help Any Salesperson Go Crazy with Unprecedented Sales! Web.
Houghton, T. (2001). An Approach to Predicting Customer Behaviour across Channels and across Cultures. Web.
Idrus, A. S. (2011). Economic Transformation Programme Update. Web.
ILO, (2007). Industrial and Employment Relation Department: Malaysia. Web.
ISM, (2008). Principles and Standards of Ethical Supply Management Conduct with Guidelines. Web.
Ismail, A., Mohamed, H. A., & Sulaiman, A. Z. (2010). Relationship Between Work Stress, Co-worker’s Social Support , Work Stress and Work Interference with Family Conflict: An Empirical Study in Malaysia. International Business Management Journal, 4(2). Web.
Johansson, J. K. (2008) Global Marketing. 4th ed. New Delhi: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company Limited.
Jonesa, E., Buschb, P., & Dacinc, P. (2003). Firm market orientation and salesperson customer orientation: interpersonal and intrapersonal influences on customer service and retention in business-to-business buyer–seller relationships. Web.
Kardes, F,. Cronley, M., & Cline, T. (2010). Consumer Behaviour. London: South-Western College.
Keller, K. L. (2009) Strategic Brand Management- Building, Measuring and Managing Brand Equity. (3rd ed.). New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India.
Keller, K. L., & Lehmann, D. R. (2006). Brands and Branding: Research Findings and Future Priorities. Marketing Science, 25(6): 740-759.
Kheng, L. L. (2010). Creating customer lifetime value through effective CRM in financial services industry. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 2(2). Web.
Kotler, P. & Armstrong, G. (2006). Principles of Marketing. 11th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Kotler, P. (2003). Marketing Insights from A to Z:80 concepts every manager needs to know. (10th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2006). Marketing Management. (11th ed.). London: Prentice Hall.
Krishnan, R. et al (2010). Job Satisfaction as a Potential Mediator between Motivational Job Characteristics and Organizational Citizenship Behaviour: Evidence from Malaysia. Journal of Information Technology and Economic Development, 1(1). Web.
Kundu, S. S. (2010). Sales Management: An Overview. Web.
Kwan, I.Y. et al. (2011). An e-Customer Behaviour Model with Online Analytical Mining for Internet Marketing Planning. Web.
Lee, D. (2010). Labour Shortage Issues Forum. Web.
Lian, K. S. (2011). Bank Negara Malaysia: Consumer Protection & Market Conduct Regulation. Web.
Lim, M., Arokiasamy, L., & Moorthy, K. (2010). Global Brands Conceptualization: A Perspective from the Malaysian Consumers. Web.
Lim, Y. K. (2010) Consumer Credit Regulations in Malaysia: A Country Report. Web.
Lo, A. (2010). The Case: For A Minimum Wage In Malaysia. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. (2009). Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. (5th ed.). Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Manpower Inc. (2006). Engaging The Total Workforce. Web.
Marmaya, N. H., Hitam, M., & Torsiman, M. M. (2011). Employees’ perceptions of Malaysian managers’ leadership styles and organizational commitment. African Journal of Business Management, 5(5). Web.
Marshall, C., & Rossman, G., (1999). Designing qualitative research. (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks – CA: Sage.
Mehta, S. (2006). Service Delivery Management. Web.
Miles, M., & Huberman, M. (1994). Qualitative Data Analysis. (2nd ed.). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Mishra, S. U., Das, J. R., & Pattnaik, S. (2010). Service Quality Attributes Affecting Customer Satisfaction in Banking Sector of India. European Journal of Economics, (24). Web.
Mohamed, B., Ahmad, A. G., & Ismail, I. (2001). Heritage route along ethnic lines: the case of Penang. Web.
Moncrief, W. C., & Marshall, G. W. (2004). The evolution of the seven steps of selling. Web.
Noor, N. A., M. & Muhamad, A. (2005). Individual Factors that Predict Customer-Orientation Behaviour of Malaysian Life Insurance Agents. Journal Pengurusan, 24(125). Web.
OECD (2010). The State of Penang, Malaysia: Self-Evaluation Report. Web.
Penglase, D. (2010). Excuses Salespeople Make For Not Achieving Targets and how to manage a better result. Web.
Ponnu, C. H., & Tennakoon, G. (2009). The Association Between Ethical Leadership and Employee Outcomes – the Malaysian Case. Electronic Journal of Business Ethics and Organization Studies, 14(1). Web.
Pranee, C. (2010). Marketing Ethical Implication & Social Responsibility. The International Journal of Organizational Innovation (IJOI) 2(3). Web.
Rajagopal, L. (2007). Outsourcing Salespeople in Building Arousal towards Retail Buying. Web.
Ramayah, T., Noor, N. Nasurdin, A. M., & Choo, L. H. (2002). Cardholders’ Attitude And Bank Credit Card Usage In Malaysia: An Exploratory Study. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 7(1). Web.
RDA Corporation (2011). The Impact of Marketing Collateral on Sales Success. Web.
Roma´n, S., & Munuera, J. L. (2005). Determinants and consequences of ethical behaviour: an empirical study of salespeople. European Journal of Marketing, 39( 5/6).
Roman, S., & Iacobucci, D. (2010). Antecedents and consequences of adaptive selling confidence and behavior: a dynamic analysis of salesperson and their customer. Web.
Safaria, T., Othman, A. B., & Wahab, M. N. A. (2011). Role Ambiguity, Role Conflict, the Role of Job Insecurity as Mediator toward Job Stress among Malay Academic Staff: A SEM Analysis. Research Journal of Social Sciences, 3(3). Web.
Sail, R. M., & Alavi, K. (2010) Social skills and social values training for future k-workers, Social skills and social values training for future k-workers, Journal of European Industrial Training, 34(3): 2 -27.
Salleh, F. B., & Kamaruddin, A. R. B. (2011). The Effects of Personality Factors on Sales Performance of Takaful (Islamic Insurance) Agents in Malaysia. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 2(5). Web.
Saunders, M., Thornhill, A. & Lewis., P. (2006). Research Methods for Business Students. (4th ed.). London: FT Prentice Hall.
Search Wise (1999). Strategic Staffing. Web.
Sekaran, U. (2006). Research Method for Business. (4th ed.). London: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Serdaroglu, M. (2009). Sales Force Automation Use and Salesperson Performance. Web.
SERI, (2011). Penang Economic Outlook 2011. Web.
Sheth, J. N., & Sisodia, R. S. (2005). A Dangerous Divergence: Marketing and Society. Journal of Public Policy & Marketing, 24 (1). Web.
Siguaw, J. A., Brown, G. & Widing, R. E. (1993). The influence of the market orientation of the firm on sales force behaviour and attitudes. Web.
Smith, B.A. (2004). Relationship Management in the Sales Organization: An Examination of Leadership Style and Cultural Orientation in Sales Manager and Salesperson Dyads. Web.
Smith, P.B., Peterson, M.F., & Schwartz, S. H. (2002). Cultural Values, Sources of Guidance, and Their Relevance to Managerial Behavioral: A 47-Nation Study. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology. Web.
Speece, M., & Pinkaeo, K. (2002). Service Expectations and Consumer Ethnocentrism. Australasian Marketing Journal, 10(3). Web.
Stock, R. M., & Hoyer, W. D. (2005). An Attitude-Behavior Model of Salespeople’s Customer Orientation. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 33(4): 1-18. Web.
Strutton, D., Hamilton,J. B., & Lumpkin, J. R. (1997). An Essay on When to Fully Disclose in Sales Relationships: Applying Two Practical Guidelines for Addressing Truth-Telling Problems. Journal of Business Ethics, 16: 545–560. Web.
Swan, J. E. et al. (1998). Customer Trust in the Salesperson: An Integrative Review and Meta-Analysis of the Empirical Literature. Web.
Thakor, M. V., & Joshi, A. W. (2005). Motivating salesperson customer orientation: insights from the job characteristics model. Journal of Business Research, 58: 584– 592. Web.
The Asian Banker (2011) Bank Negara Malaysia issues new measures on credit cards. Web.
Tsoukatos, E. K. (2007). Customer behaviour, service quality and the effects of culture: A quantitative analysis in Greek insurance. Web.
Tweedie, L. (2011). Insider – Ethical Salesperson Behaviour in Buyer-Seller Relationships. Web.
Warner, C. (2000). Compensating Media Salespeople. Web.
Webb, M. J. (2004). How to Develop Qualification Criteria that Help You Find and Win Customers. Web.
Weng, J. T., & De-Run, E. C. (2010). THE Influence of Personal Values On Sales Promotion Techniques For Convenience Products. SEGi Review, 3(2). Web.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Case Study Research: Design and Methods (3rd ed.). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Zikmund, W. M. (2006). Business Research Methods (7th ed.). Orlando: Harcourt Publishers.
Zinnov, K. (2009). Snippets: Malaysia’s Talent Trend Analysis. Web.