Introduction
The purpose of this paper is to discuss to what extent simulation of strategy could contribute to overcome recession in private and public sector and this dissertation will study the case of British airways.
Background of the problem
According to the report of The Guardian (2009), in the first quarter of 2009, the operating loss of British Airways was £143 million to £221 million though it is one of the world’s major scheduled premium international airlines. In the fiscal year 2008/09, it carried 33 million passengers and earned about £9.0 bn in revenue, which was 2.7% greater than previous year (British Airways, 2009, p.4). According to the annual report 2008/9 of British Airways, it earned about 87.10% from passenger traffic, 7.50% generated from cargo and rest part from other business operations. According to the Mintel (2009), British Airways is presently flying the most turbulent skies where as competitors of this company like Ryanair and Easyjet leads the market by increasing the number of passenger. However, the price of its services is higher than competitors offered price and it provides both short and long haul. To overcome the present financial crisis, British Airways needed to go ahead with a strategy that can contribute the companies. This researcher has selected this simulation of strategy. There are many researches on global financial crisis but this is a unique topic, which intended to address the contribution of simulation of strategy on the company.
Rationale for the research
There are huge professional and academic researches on different type of strategy formulation, design, and implementation, but every strategy need enough time and financial involvement to demonstrate its success or failure. On the other hand, simulation of strategy can identify which strategy would best fit to address any particular problem by using computer based modeling with specific software. Though different management professionals have addressed a lot on different strategies, they are enough reluctant on how simulation strategy can resolve any corporate crisis. Thus, to address these gaps, it is rational for this researcher to conduct the study on” Does simulation of strategy could contribute to overcome global financial crisis in private and public sector: A case study of British Airways.
Research question and objectives
- How does simulation of strategy works under the theoretical framework of evolutionary economic.
- How private and public sector strategies restructure to address global financial crisis?
- How simulation of strategy would work at British Airways
- To what extent current strategies of British Airways are successful to hold top position in short-haul market.
- How is British Airways performing in the global financial crisis and how is BA doing competition with different methods of travel (such as train, bus, ship, etc)?
- As the service price is relatively higher, how does British Airways control the fuel cost to compete with low cost service providers in this industry?
Scope and limitations of the study
The study’s key objective is to investigate whether the simulation of strategy could contribute to overcome recession and here British Airways would be considered to discuss on this issue. Some potential scopes are:
- Enormous resourceful secondary data is available, such as, internet resources, news, journal articles and books provide adequate information;
- This dissertation has use scope to consider recession as global economic downturn adversely affects private and public sector
- It has scope to research on effectiveness of simulation of strategy to overcome from global economic downturn in literature review;
- It will help to develop interpersonal skills with writing ability;
- There are lots of opportunities to apply theoretical aspects in relation with practical condition
The author of this dissertation has suffered many problems to confront this research, such as:
- Author got limited time for survey as the deadline for whole research was very short;
- Obstacles to gather primary data because of management of British Airways is too busy. In this context, it is really difficult for them to manage time to answer all question properly and some of them shows reluctance to give adequate time for interview process;
- It is difficult to co-relate technological issues with vast area of marketing policy of British Airways.
Literature Review
Restructuring Strategy
Mintzberg (2000) argued that the process of strategy development of an organisation has played a major role in founding the design of scrutinised linkage between strategy of that organisation and its structure. Most of the scholars of Harvard Business School have carried out this underpinning thought for most of the process of strategic modeling such as the formulation-implementation model and the analysis-choice-implementation model (Brady 2000). Porter (1998) has added further impulsion on the concepts of industrial economics and formulated the term “competitive advantage”, and argued for distinguished generic strategies as the key source of achieving competitive advantage as well as value chain of the organisation.
Quinn (1998) recommended that the process of strategy formulation and accomplishment may not occurred in isolated way but it come into reality by an incremental ways where the strategy come out by passing of the process of strategy making. Markides (1999) has emphasised to improving operational effectiveness and engagements of total quality management along with the process of business reengineering with central attention on the more speedy alteration in the business arena and the complicatedness that organisations are interacting under the multifarious, self-motivated and fast-changing environment of today’s business.
Simulation Phase
At this stage, the diversity between a model and simulation can identify by stating that the first one is the replica of a real thing when the second one is the reproduction of that model Maria (1997). It is most significant to make it clear that a model is never a real thing but just a replica of the fist one and Its also most advantageous to study and analysis the behaviour of a model rather than handling a real thing because analyzing and examining the real thing need more care and awareness than the model.
Davis & Bingham (2007) pointed out that simulation is the procedure of motivating a model of a particular system by suitable inputs and then scrutinising the corresponding outputs and effect upon reality, thus it stands for technique of theoretical explanation.
Brady (2000) added that it is generally spoken that in the case of real-life business organisations under the modern economy, simulation facilitates the business researcher as a tools of exploratory measures in economic and management to finding means of problem solving through computer aided solution approach.
Simulation as a Strategy Formulating Tool
Maria (1997) argued that it is difficult for the researchers and corporate strategy formulators to experiment with the success rate of any desired strategy due to high risk of loosing corporate resources, lower opportunity to manipulation replication and observation but by applying simulation anyone cam overcome all these difficulties to redesign their strategy. The simulation tools and key techniques has been utilising by the academia and business concerns for strategy generation and practice of management training consultants that turns simulation as an integral part of strategy for modern business concerns.
Brady (2000) added that most of a majority of UK universities as well as business schools are using simulation as a tools of strategy formulation, for instance, London Business School has emphasised on systems thinking and strategic modeling by using simulation software to model strategy for any business dilemmas and practical experience to running a business. He also added that the simulations used by the universities have engaged with theories of strategic thinking based on the economics theories of industrial organisations upon resource-based view of systems as well as complexities where strategic simulations turn to competitive model. At the time of simulation of strategy making, both the internal and external environment would be analysed in primary phase and simulation applied for testing the assorted business scenarios and matching the phase of strategy consideration Brady (2000). Tollin & Castillo (2008) pointed out that the EC 1 has developed Strategy for Sustainable Development- 2001 by integrating the declaration of UN and WCED devoted to the dynamic knowledge based economy that has based on strategic simulation to ensure greater social cohesion for business concerns.
Evolutionary Economics and Simulation of Strategy
Nelson (2007) explained the economic growth and development as an evolutionary process, where the core capability is the technological learning, when the evolutionary economic keeps its keen eyes on how technological learning progresses on economic activity and bring changes, the neoclassic economists argue on theoretical concerns. The significance of evolutionary economics has emphasised due to its well robust to the technological learning progresses and chronological changes and recognised for perfect basis of economic theorising under the modern economic systems that holds a wider mix of business organisations, households, and markets.
Knottenbauer (2004) supported the that explanation of Nelson on the evolutionary economics has facilitated the modern business communities to deals with the dynamic investigation of economic phenomenon those have raised from the increasing varieties of strategy generated by innovations and changes worked within that system.
The motivation for strategic problem solving and new strategy generation needs to have evolutionary structural change and investigation that has come out from the beneficial method along with systemic perspective as well as innovation focus of the evolutionary economics where the amalgamation with most up-to-date results for input-output-analysis would endow with fruitful impending. To work for strategy restructuring under a recessionary economics, the suggested framework integrates a composite hierarchical model where the economy has alienated into micro and macro level environment. Both the level has self-possessed with interconnected subsystems those have influences on each other and the analysis part deliberate upon the system of a particular sectors where the interdependence of all factors impacts of the environment.
Under the mentioned hierarchical model, the structural change of strategies has give explanation with an increasing diversity outstanding to innovations on which the existing strategy could work with grouping mechanisms. The taxonomy of mechanisms to strategy formulation or restructuring is independent to the corresponding sectors such as microeconomics within production, new technology adoption and demand where the macroeconomic development arrangement of sectors suitable to historical events (Knottenbauer 2004).
Thus, the systemic position of a sector would keep crucial role for development of argued strategy where the other sectors work as a part of the whole system and suggests the needs to raise or decline of any attributes corresponding to the advantageous development of strategy. In the modern business arena, simulation tends to exercise with the system dynamics modeling as a motivating mechanism to strongly addressing on the resource-based view of the organisation as an essential theory. Moreover, simulation could support to engender and weigh up strategic options with the other procedures delivered from the management science as well as strategic management with multi-criteria decision-making approach and specific guidelines of strategic choice, in this way simulation of strategy works to overcome any business crisis under the evolutionary economics. Brady (2000) evidenced that Harvard Business School, Dublin City University and London Business School, are adopting huge emphasis on simulation as a tool for strategy making
Public and Private Sector’s respond to the Global Financial Crisis
IMF (2009) reported that the recent global financial crisis and recessionary economics have delivered the challenges at every level of economic policy dialogue where the governments of economically developed countries as well as emerging markets have urged to address urgently to the economically sensitive sectors by bailed out. The core competence of such bailed out is to prevent the usual collapse in economic activity with the aim to protect the vulnerable population due to job cut and unemployment. As a government imitative, it became as a most expensive action that has the reality of fallen revenues of government, decrease of domestic investment as well as foreign financing and both short term and long run consequences budget deficiency as well as debt, but the recessionary packages incorporated with higher public investment and put into practice through PPPs.
Gavieta (2009) pointed out that the world GDP growth has predicted to downward motion at least 5% in 2008, which demonstrated 3% in 2009 due to credit crush in US and European market and Asian economy affected by fall of export while African economy also impacted with recession. To overcome the global financial crisis, the economists addressed more on the public sector infrastructural investment as part of economic recovery plans along with bailouts while the public sectors all over the world have argued to pump up with infrastructure projects.
Gavieta (2009) also mentioned that the infrastructural invest has no longer exceeded 2.0% of GDP for last ten years but to overcome the impact of global financial crisis, it is essential to increase this investment spontaneously. The high investment on infrastructural projects such as power and telecommunication would create job opportunity and national competitiveness for market forces.
The crisis originated from the developed countries and forwarded to the emerging markets due their unsuitable domestic policies but the banks of developing countries have not directly affected badly by the sub-prime crisis. To largely avoid the financial the public sector also came forward with recessionary packages such as US president urged for 2.5 million new job creation while EU droved with Euro 200 billion fiscal incentive plan to encouraging job security and entrepreneurship.
The public sector fiscal policy has been measured for their role in financial crisis their role in the economic cycle and the government has suggested for not to borrow any longer for current expenditure but only for infrastructural investment where the sustainable investment in the public sector would be the remaining debt as a percentage of GDP.
ODI (2009) pointed out that the starting from collapse of Lehman Brothers, global financial crisis tuned into recession seriously injuring the private sectors in falling property market, dilapidated private financial flows, remittances, risk financial products to develop, fall in industrial production and unemployment as well as poverty and hunger. IMF (2009) argued that the potential role of public private partnership and proper utilisation of fiscal policy tools would facilitate to sizeable the crisis condition and support private sector recovery as well as to generate employment. Harris & Pratap (2009) also addressed for reducing the fraction of private infrastructure projects along with public-private partnerships to boost confidence on the government.
Simulation of Strategy at British Airways
Robinson & Stanger (1998) mentioned that The British Airways has a privately owned Operational Research group that works as an isolated wing of the organisation but address any departmental crisis along with hundred research talents. The BAORG has employed the simulation strategy for British Airways and provide paid internal consultancy for the different divisions.
Analysing the simulation strategy of BA Robinson and Stanger (1998) emphasised for further development of the strategy in the course of a process of consultation. Simulation strategy of BA addressed on SWOT analysis to modeling all the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and to properly resolute any dilemmas with commuter by using simulation software with background and context to the strategy.
The initial simulation strategy of British airways has presented with the extent to the strategy, which the company is going to adopt, though a number of components of the strategy may not fit with the company. The simulation team of BA would together to analyse and discuss further recommendations predominantly on the structural issues and necessary changes. There are seven well-organised simulation team working in the organisation insolated from the other divisions and are responsible for their own services. Every team reports to a diverse department that grasps the budget in support of necessary resources such as software etc., consultant’s fees, and other charges, as there is no allotment of central budget for simulation. There are alternative options of simulation strategy team to involve experts of BA by hiring part-time experts with a single full time.
The existing roles simulation strategy has deliberated to fit in along with the centralized simulation team of the operational research group though there is option to take account any other alternative or revised structural options. To delineate any proposal for strategy design, develop and restructure the simulation team convey study by covering the necessary software, customer interface of the specific department, then developing model, and support that department to maintain the model. At present the two segment of BA such as airport and operational research are the highest user of simulation.
To address the impact of global financial crisis British Airways have the opportunity to apply simulation strategy to restructure its corporate strategy rather than existing departmental simulation. In this regards the seven simulation expert team could work together to concentrate on longer-term objects of sustaining as a market leader.
Under the present recessionary economy, it would not be wise to keep maintaining 7 different simulation teams, as there are huge common data necessities among the department for instance, schedule data, fuel price, passenger numbers, competition, and activity timings. Traditionally all the seven teams collect their own data from dissimilar data sources without any acquaintance of the other teams, which rises contradictory issues among them and lead to misuse of resources. BA has simulation practice for more than a decade and gained vast experience and at present, a centrally integrated simulation strategy could show the right way out to overcome the company from global financial crisis and sustain in the market by competing with the low cost airways.
Research Methodology
General notions
The basic objective of this chapter is to design research methodology to formulate this paper and this dissertation will follow exploratory research and descriptive research method.
Justification to use qualitative method
According to Miles & Huberman (1994), quantitative and qualitative researches are two major approach of methodology and quantitative research gives the opportunity to quantify data by implementing some statistical unit, which is more than accurate but complicated process. Marshall & Rossman (1999) argued that qualitative research is a process that includes interpretative paradigm under the measures of theoretical assumptions as well as the entire approach is based on sustainability, which is depended on respondent’s experience in terms of investigation, where telephone and interview would be selected data collection process.
In this context, the author of this dissertation will design the research by qualitative research method, as it would be conducted through interviews and observations as well. Moreover, to organise the paper, it is essential to observe circumstantial and substantial effects of recession on British Airway and to what extent simulation of strategy would be able to recover the company from this crisis.
Reliability and validity
In case of British Airways, interview with customers would be successful enough as they are the reliable source of information because only customer can express that whether they have the capabilities to take the service of BA or not. In addition, they will also express the reason for their dissatisfaction of the services and it will also be easy to compare the company with competitors and offer prospective solution. On the other hand, managements are also fruitful interviewees, as they know the inner problems of British Airways and they always try to help the company by their efficiencies and implementation of strategies.
Data analysis
Creswell (2009) and Zikmund (2006) pointed out that all the irrelevant data sould eliminated from before final assessment of data, which has obtained by several processes. However, it is also important to approve the data by interviewer (here, customers and Management of BA) prior to final analysis as it will give the opportunity to remove all the error that made at early stages. Burney (2008) stated that the qualitative data generation technique is most reliable, so the researcher will apply descriptive research approach and observing methods.
Secondary data sources
This dissertation mainly depends on primary data, as the researcher will interview 50 customers and 50 executives and employees of British Airways and the secondary data will be used to support primary data. The justification of this method is there are huge authentic data available in secondary sources, which are sufficient to identify all difficulties with proper solution. Saunders, Thornhill & Lewis (2003, p 45) argued that secondary data are processed data, which already exist acted as a major source of information for the preparation of this dissertation. They also added that secondary data should used to answer research questions, better definition of the problem and formulation of appropriate research design and various sources of secondary data are newspaper articles, trade magazines, journals, company publications, Internet articles, and books (here books would be used only for theoretical conception). In addition, it has numerous benefits to use secondary data, for example, when a researcher use primary data, he has relied on a particular segment and on the respondent’s self-reports whereas secondary data makeup this gap.
Primary research sources and major focus areas
Cohen Manion & Morrison (2007) stated that the primary research has designed to collect information that are not available or that does not exist any secondary sources and it is the combination of original data. They further addressed that this is the proper way to get information about customer’s attitudes, intention, and preference and this process also assists to find data about products or services of the company. In this dissertation, the author would use interview technique to know the essential information about BA’s strategies, customer satisfactions, and various issues of the recession, customer services, employees etc (Malhotra, 2009).
The author of this dissertation has prepared questionnaire consists of twenty question among them 6 questions for customers and 6 questions for management, which will be enclosed in the Appendix of this paper. These questions will be printed for survey and data will be collected by face-to-face interviews and telephone discussions, and all people between age of 14 and 64 will be eligible for interviews but it is not mandatory to be the customer of British Airways that means customers of competitors are also eligible for interviews.
Limitation of Data Collection
However, customers and management team help to provide adequate information but many times customer cannot asses the actual scenario. For example, most customers (54 to 64 age groups) want better service at lower price but they are not concern about fuel price, so, it would be difficult to take decision from their information. On the other hand, the employees are not interested to disclose the actual strategies and financial position in recession, which may creates information gap between primary data and secondary data sources.
Findings and Results
Compare with alternative services, such as, train
As in global financial crisis the purchasing power of buyer has changed dramatically, they now find out alternative route for travel in recession and the secondary sources demonstrate that railway sector is in good position in recessionary economy, for example, MTR expanded its operation worldwide. Among 50 people who were the customer of British Airways, 16 respondents would like to travel by train for future travel and they will also choose low cost airways for short haul, 20 respondents will take service from British Airways in future, 9 respondents said that they would prefer both services, 5 respondents have no choice.
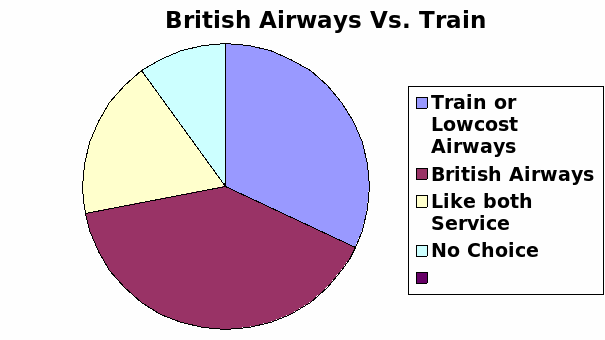
Result: From this data, it is clear that not only BA but other companies of Airlines industry may also affected for recession, as many old customer would like to travel on train for short distance. Therefore, overall customer of train service is increasing, which is really a threat for this industry as well as British airways.
Compare BA with competitors, such as, Easyjet, Ryanair, Virgin Atlantic
It was a descriptive question for the customers, as the researcher should know more information about customer choice. Most of the customer agreed that they would like to take low cost services and some of them have interest on BA, as they believe that most of the companies are aware about customer care. This question has another part for those respondents who select low cost airways and most of them not intended to mention the name of a single company but some of them said about Easyjet and Ryanair.
Proper reason to change their decision
From the answer of this question, the researcher tried to find out the actual reason to change his decision that means why customer will not to take BA services. According to the survey report, 83% old customer said that people of UK are more conscious about his expenditure due to financial crisis, so they will not prefer British Airways services at this moment. In addition, 6% customers have no opinion in this issue and 7% customers want more diversified services.
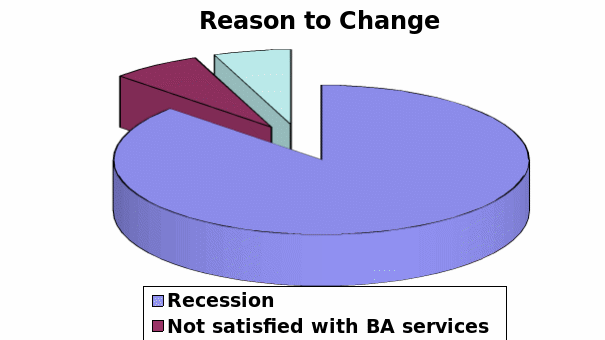
Result: Most of the respondents selected option A, which demonstrates that customers are satisfied with its services but for economic condition, they bound to change their mind.
Whether BA should increase customer services to attract more customers or not
From the feedback of this question, researcher of this dissertation finds that 67% customers believe that existing services of British Airways is good to attract more customer, whereas only 5% customers said it should provide additional services. However, 25% customers have no doubt with the customer services with the company as BA provides additional services than low cost competitors. On the other hand, 3% customers have no idea about recent developments of this industry, so they would not like to response this question.
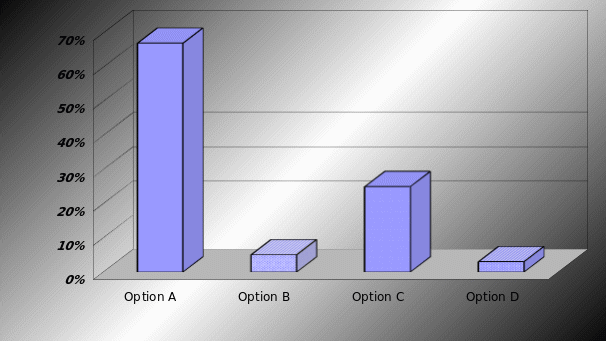
Result: Majority of customer choice option A that indicates British Airways provides adequate services, so it should not invest more money for increasing service level to overcome the company from economic downturn. However, Ryanair (2009, p. 8) reported that British Airways is in third position in customer service issues (flights on time 83%, completions 97%, Miss. bags per 1000 pax – 15.60), whereas Ryanair in first position. As a result, to become a market leader both in short and long haul, it may increase its customer services but it is not an important issue to save the company from recession.
Whether the customers take its services if it reduces price
Among 50 old customers, 44 customers will take its service for future travel if BA reduce it service price and only 3 customers will not prefer it.
Result: Comparatively higher price than competitors is one of the main competitive advantages of low cost airway, so, it should consider customer loyalty to hold these customers and reduce price accordingly. On the other hand, it may create dilemma, as if BA reduce service price then it will not be possible for the company to make profit as BA never use low cost fuel like competitors considering environment.
To the customer point of view, which one is most important
This is really an interesting question and respondents take more time to give answer of this question as it address the dilemma of previous questions. However, price is only considering issue to 17 customers, environment is only important factor to 8 customers, and customer service is only essential to 4 customers. It is interesting that all options (price, environment, and customer service) are essential to 21 customers.
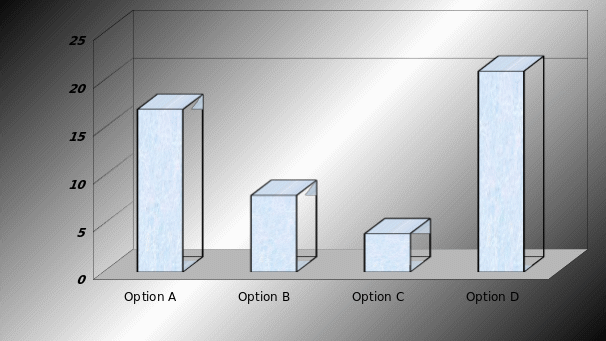
Result: Now the question arise that is it possible for BA to ensure all these issues at a time, as there exists contradictory issues in company perspectives.
Following six questions have answered by the management.
Before analysis the data, it is essential to mention that management can take any decision for the development of the company and they are not bound to disclose justification about their decision. However, they mainly provide descriptive data but questionnaires had prepared in such way that respondents have to select an option to support their view.
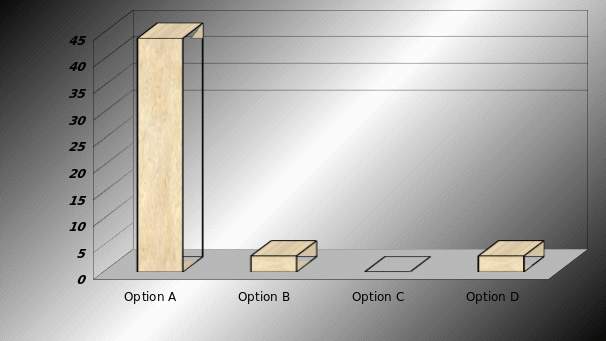
Possibility to overcome from global financial crisis
The purpose to raise this question is to asses the opinion of the employees about its financial capabilities to overcome global financial crisis. The following figure indicates that 29 respondents were agreeing with option A that it is possible for BA to overcome financial crisis within very short period. Only 3 respondents said that BA will not able to overcome recession with short period and 3 respondents stated that it will depend on market whereas 11 respondents selected option C.
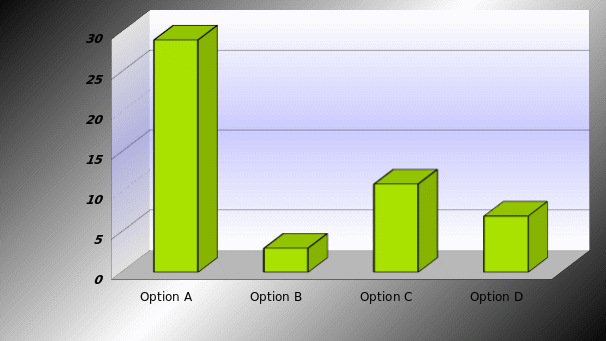
Result: According to the view of Employees and management team, BA is a renowned company and it has enough financial capabilities to minimize risks and sustain in such environment. However, following analysis will help to address major challenges and results will find out to what extent simulation of strategy will help the company to overcome the company from recession.
Most effective way to save the company from recession
Figure 7 demonstrates that 23 of the respondents said that BA should change its strategies and develop customer relationship, 19 respondents only simulation of strategy can save the company and only 7 respondents said about option B.
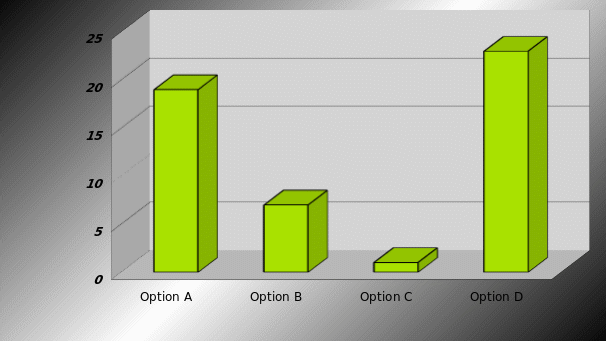
Result: Form the outcomes of this question, it can be said that 42 respondents want to change the strategies as 23 selects option D. Now the question arises, what kinds of reproduction or simulation required for this company. There is no doubt that this response of this question justifies the specified topic of this dissertation.
Strategic options to choice most effective strategy for further development of BA
It is the vital questions for the management as this question directly tried to identify proper solution for the company. The previous table shows that respondents support to change or reproduce the strategies and this question provides specific 5 strategic options for the company. However, respondents provide ambiguous answers, for example, 15 respondents selected option C, 12 respondents selected option D & E and the answers create difficulties to reformulate the strategy.
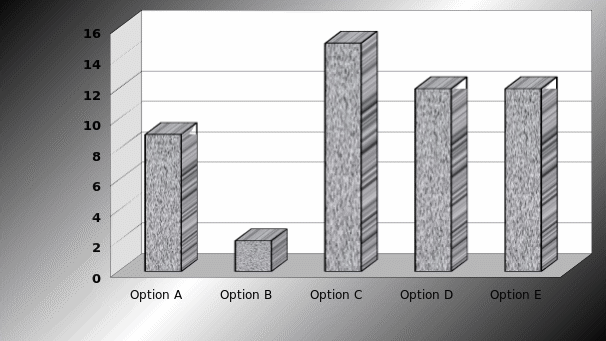
Result: Though the objective of this question is clear but it is not possible for the researcher to find out one or two specific solutions from the answer of this question.
The appropriate way to decrease operating costs of BA
Reducing operation cost is one of the significant factors but the researcher of this dissertation wants to find out the proper way to reduce operating costs of BA. Majority of respondents argued that both job cut and reducing fuel cost would be effective strategy and 14 respondents selected option D. However, 15 respondents argued that it could offer the employees for voluntary service for particular time, such as asked to work for one month without salary or reduce remuneration of the directors.
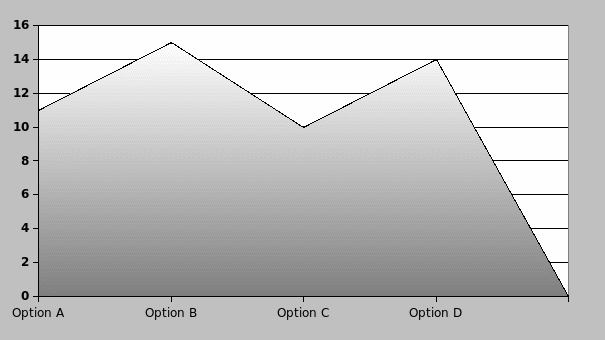
Result: most of the employees said the company should not maintain job cut strategy but reduce the payment of directors and the majority of the directors stated that it should reduce fuel cost and cut job to minimize profit. Therefore, the answer of this question failed provides the suitable solution regarding these aspects.
The reason behind to suffer losses
It was a straightforward question and 40 respondents said that this critical situation arise due to global financial crisis whereas no one has selected second and third option. This result also matched with the secondary data sources
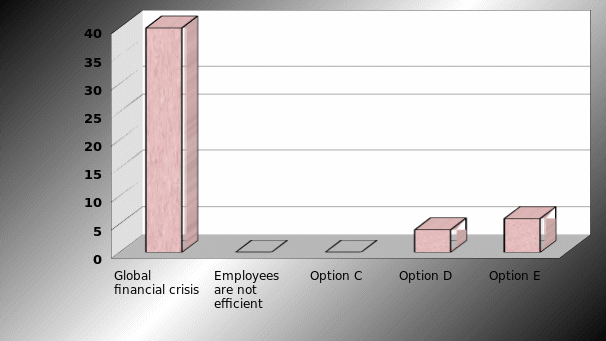
Result: In order to find out the real risks for the company, the researcher design this question and form the table it can be said that annual report 2008 identified few factors for net loss and among these factors global financial crisis is most important factor, which influence other problems.
Why competitors are doing better than BA
The researcher of this dissertation tried to find out the possible reasons, which influence the competitors to make profit in this business environment. The following figure shows that 27 respondents selected option A, 15 respondents picked option E and only 1 respondent selected option C.

Result: it is essential for a company to have a clear idea about competitor’s strategy to select its own strategy. Other competitors such as Ryanair and Easyjet have in positive financial condition though the net profits had reduced than previous years. According to this data, the grounds of their success is using low cost fuel though few other factors like maintaining time frame and don’t seriously bother about global environment involved with this. In this context, management of BA argued that BA always concern about CO2 emissions so it will not use low cost fuel but it will contract with few companies to produce 10% fuel from waste materials.
Discussion
Present Strategies
According to the annual report 2009 of BA, the company is waiting for better economic times and designing its long-term vision to be market leader as it is now in extremely harsh business environment. In addition, it has prepared its 3 years business plan and mentioned that its key goals were to develop Terminal 5’s strengths to improve the client experience, carry on to formulate the business more cost effective, expand its businesses, and make CSR a important component of its business but it wants to revise its plan considering recession (British Airways, 2009). British Airways fixed its strategy considering the expansion of Heathrow Terminal 5 and it will complete BP10 ‘Fit for 5’ programme to set the direction for the next 3 years and BP11 contains a new theme of corporate-responsibility.
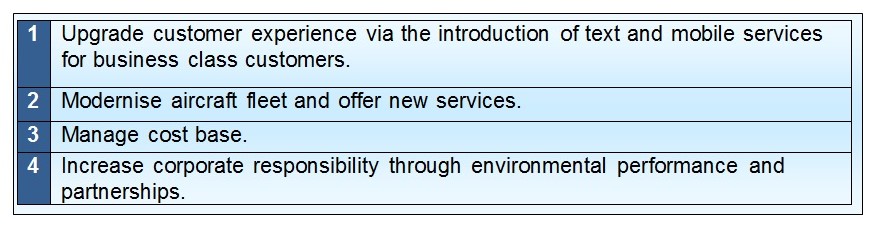
Terminal 5 was created based on the concept of bespoke contract to enhance its operational activities and customer services with intention to upgrade reliability and baggage targets. Its first target is to develop customer service by the attractive product, such as, both Boeing-747 and Boeing-777 aircraft offered some additional facilitates, which are extremely gorgeous and it had also arranged fantastic reception in both terminal 3 and 5 for customer satisfaction. However, its other key strategies are:
- Cost control: Continuous price hike of fuel of the airbus presents actual challenge for British Airways, so the management intensified endeavors to control expenses and Terminal 5 has permitted to cut the expenditure of its Heathrow operations by 14% (British Airways, 2009, p. 25).
- Expansion Plan: In spite of financial crisis it has sustained to meet customer demands and to rise number of customers by launching new routes (London to NY), so it has purchased L’Avion in 2008. British Airways (2009, p. 25) published that BA is going to contract with Boeing to lease 4 “Boeing 777-300ER” aircrafts from this company but from the performance of BA 2009 it can be said that this decision was not effective to overcome recession.
- Corporate responsibility: As its vision is to be global market leader in this industry, it takes many initiatives under the banner ‘One Destination’, which will try to decrease CO2 emissions to save the world from pollution and it will increase charity programme for the development of people and its business.
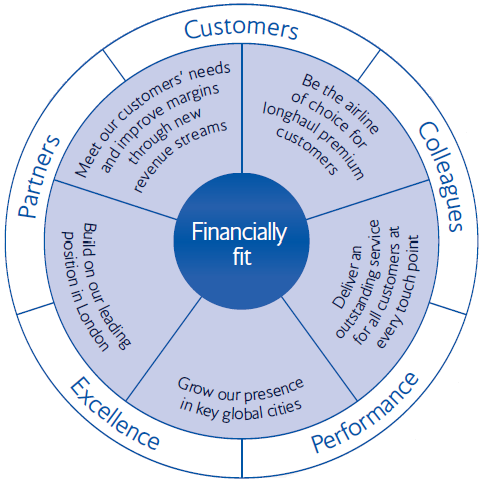
Long-term objectives
To be market leader, it has set few long-term objectives, such as:
- BA targets long-haul premium customers and it will carry on launching enormous products for example it will introduce latest business-class seat and restyled First cabin for the customers of this route;
- It intend to provide outstanding service for clients in all steps through training its employees, so, in 2009 it has introduced new in-flight entertainment method;
- Develop its existence in main cities of the world to offer the best international connectivity for its customers by strengthening with more flights in long routes;
- It would like to build on its leading position in London as its business based on terminal 3 and terminal 5 of Heathrow;
- It will meet its customers’ requirements and develop margins by latest revenue streams by structuring lucrative ancillary services and its goal is to generate more profits from moderator engineering, in-flight deals and new online retail website (ba.com).
Recessionary Impact and Financial Analysis
King (2009, p. 15) argued that increasing operation costs played a significant role to minimizing profit as in second quarter of 2008 the oil price was US$ 135 a barrel. Scribd (2009) pointed out that in the fiscal year 2007/08, British Airways had a fleet of 245 aircrafts, and it has expended £2,055.0 million (in average £8 per day) to purchase fuel and oil. Keith Williams- the CFO of this company provided few data that demonstrates the perfect scenario of BA in recession. For instance, the total costs has increased 15% due to unstable oil price and BA is estimated oil costs about £3,000 million, which is an actual threat for its implementation of cost control strategy.
Harvey & Turnbull (2009) stated that the global financial downturn has created a long distance between management and employees because BA requested employees to work for one month without salary, which reduced the motivation of employees. They further added that the severity of recession on BA has already eclipsed the loss of 9/11.
Wardell (2010) mentioned that more than 13,000 cabin crew of BA had taken an action against the company for breach of its contracts with employees but High Court strongly rejected that argument by stating that BA faced record annual losses (($135 million) due to global financial crisis.
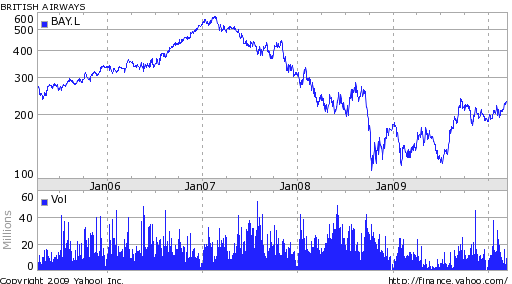
This basic chart of British Airways demonstrates that the share price of this company is in down turns in global financial crisis and in 2007, the market share price was in highest position and now share price is escalating again.
Major Challenges and Risks
- Inflation: Changing in interest rate and inflation affects the debt financing of BA; therefore interest rate and debt financing has positive correlation for example, in 2008, its finance income reduced £18 million from 2007 for higher interest rates, and in 2009, profits fall about 90% (King, 2009);
- Swine flu: British Airways has suffered economic crisis in 2009 and this condition has prolonged due to several external factors, such as, swine flu virus. BBC News (2009) reported that shares in BA fell about 7.70 percent.
- Terrorism: Due to terrorist attack, most of the companies cannot afford to buy new planes after the 9/11 situation, which is another barrier for expansion of its business as BA has to consider security issues of that particular region. According to the annual report 2008/09, repeated changes of rules and regulation to protect terrorism activities is supportive to diminish the external and internal risks but sometimes it demands more consideration on security issues, which is another area of expenses.
SWOT analysis of British Airways
Strengths:
- Brand awareness and strong public image;
- It always gives latest information;
- Regular programme to attract new customer besides regular passengers;
- to enhance service in EU, it has developed euro exchange rate
- Suitable strategy innovation and implementation,
Weaknesses:
- British Airways has paid high remuneration to their employees,
- The competitors had made satisfactory profits.
Opportunities:
- BA will reduce its service price as fuel cost is declining due to producing fuel from waste;
- To raise its revenues, it has free travel and free redemption services option for regular travellers;
- it is enjoying free market for internal flights because of EU single market strategies extend to the EEA6 comprising the EU;
- Heathrow Terminal-5 will help to expand its business by creating new routes.
Threats:
- Drop of its share price and incurs record losses due to economic downturn and H1N1 virus;
- Reducing business profits from Cargo and passenger traffic;
- Lack of operation in non-EU countries comparing competitors,
Key initiatives for sustainable development
Wynn (2010) pointed out that in order to overcome this recessionary impact, BA has signed an agreement with two companies to buy sustainable jet fuel and this fuel will be produced from waste. Here it is essential to mention that BA has already reduced the emission of CO2 up to 28% since 1990 and its present target to reducing the emission of CO2 by a further 25% within 2025 and 50% with 2050 and BA has contracted with IATA to protect the environment from pollution and to save the world from global warming. In this context, this agreement is appreciated by all, as it will help the company to keep its commitment in environmental issues as well as save it from global economic downturn. However, Wynn (2010) also added that this project would reduce cost for fuel purpose because this plant will produce more than 16.0 million gallons green jet fuel by processing and converting 500,000.0 tonnes of waste and BA intended to get 10% of all its jet fuel from this sector by 2050.
Mintel (2009) reported that BA has tried to minimize operating costs from £725.0m to £580m in 2009, and the company is expected that constraints will continue in 2010 and to do so, it will cut 3,700 jobs in fiscal year 2009/10 (it was cut 2500 jobs in the fiscal year 2008/09). This dissertation highly opposes this system to reduce costs and recommends BA to decrease expenditures by reducing salary of directors and employees to motivate them as many large companies have collapsed for high salary of executives.
Besides transferring passengers, BA wants to boost its revenue by extending its business line with sky cargo and in 2008/2009 fiscal year, British Airways has transferred 947000 tonnes of cargo.
Conclusion
Recommendations
- As the competition among airlines industry is too high, British Airways should concentrate on its fundamental service delivery to re-establish its competitive advantage;
- In Annual Report 2003, Ryanair declared itself number one customer service provider and Ryanair (2009, p. 8) stated that its strategy is to provide the best client service performance (for example, better punctuality, less lost bags and smaller amount cancellations) and its success rate is 90% in this issue, whereas BA in 4th position in customer service case.
- In this context, it should consider consumers’ demand first and pay attention in market segmentation that should reflect on both income level and age limit that means It should set up the price of air ticket considering the oil price and global economy;
- This dissertation recommends both people processes strategy and technological advancement strategy would be effective solution for future development of BA;
- Mintel (2009) reported regarding BA “there was a 14.9% drop in premium traffic”, which demand simulation of strategy;
- It should survey the market to asses the customer demands as well as competitors strategies;
- It is important to mention that it has already identified potential risks and started working to minimise this risks;
- BA should reduce operating expanses to overcome the company from the global financial crisis but would not be effective way to cut the job of its employees to minimize costs;
- It should increase the budget for promotion and it should build public awareness about environmental issues by advertising that low cost fuel increase CO2 emmision;
- It should continue to take advantages from technology, such as, recently BA adds a scientific calculator to prove that the price of its service also competitive comparing other low cost airways (Ryanair or easyJet);
- The salary of directors and employees is comparatively higher, so it should follow the Listing rules (Recommendations of several reports), and Companies Act 2006 carefully;
- It must follow the decision of directors and non-executive directors;
- According to the environmental report of BA, its target is to lessen its net CO2 emissions up to 50% by 2050 and to satisfy this requirement it should require additional investment for technological developments (British Airways, 2008, p. 1). Therefore, it is hard for BA to minimise operating costs by using low cost fuel,
- It should also increase advertisement cost to convey the message to its customer that low cost offerings does not mean low quality but low cost service provider use lower quality fuel, which extremely harmful for our environment concerns.
- As British Airways has large contribution on economy; it ought to spend more money for advertising, promotion and R&D;
- It should make the journey safe and comfortable for all customers and passengers;
- Attractive reception is not good enough to satisfy the customer, it will only increase the cost as in recession people demand cost effective services than luxury;
- British Airways has already changed its strategy and determined five goals by considering London Olympic 2012;
- As tourism sector has seriously fall down in recession, pension fund can be effective for risk management of the British Airways;
- It should try to increase the rough though many markets and international route are regulated by the government by the agreement of UK government & foreign states;
- Finally, it must consider their present stock performance with a continuous monitoring.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, it can be said that British Airways has suffered economic crisis due to global recession and its customer services has also fallen down. In this context, the management team of BA took many initiatives to recover the company from global financial crisis and get back its market leading position. This dissertation has analysed the primary data and provided useful recommendation from the survey results. In addition, it has discussed the current strategies, challenges, and other relevant issues to formulate this dissertation. From primary data, this dissertation has identified that simulation of strategy can change the business environment to overcome from economic downturn.
Reference
BBC News. (2009) Swine Flu Fears Hit Travel Shares. Web.
Brady, M. (2000) Simulation as an Aid in Strategy Making, Journal of Operational Research Society. Web.
British Airways (2008) The way we run our business Environment. Web.
British Airways. (2009) Annual Report and Accounts. Web.
British Airways. (2009) Principal risks and uncertainties.Web.
Burney, S. M. A., (2008) Inductive & Deductive Research Approach. Web.
Cohen L., Manion, L. & Morrison, K.. (2007) Research Methods in Education. 6th ed. New York: Routledge.
Creswell, J. W., (2009). Research Design: qualitative, quantities and mixed methods approaches. 3rd ed. Sage Publications.
Davis, J. P. & Bingham, C. B. (2007) Developing Theory through Simulation Methods. Journal Academy of Management Review, Vol. 32, No. 2. Web.
Gavieta, R. (2009) Global Financial Crisis: It’s Effect on Private Sector Investment. Web.
Harris, C. & Pratap, K. V. (2009) What drives private sector exit from infrastructure? Web.
IMF. (2009) The Effects of the Financial Crisis on Public-Private Partnerships. Web.
King, M. (2009) British Airways Plc – Financial and Strategic Analysis Review. Web.
Knottenbauer, K. (2004) An Evolutionary Framework for Structural Change Analysis. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. (2009) Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. 5th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Maria, A. (1997) Introduction to Modeling and Simulation. Web.
Markides, C. C. (1999) Corporate Strategy: A Dynamic View of Strategy. Sloan Management Review. Web.
Marshall, C. & Rossman, G., (1999) Designing qualitative research. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks – CA: Sage.
Miles, M. & Huberman, M., (1994) Qualitative Data Analysis. 2nd ed. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Mintel. Short-haul Airlines – UK – July 2009: Companies and Products. Web.
Mintel. (2009) Short-haul Airlines – UK – July 2009: Market in Brief. Web.
Mintzberg, H. (2000) The Rise and fall of Strategic Planning. 1st ed. London: Financial Times Prentice Hall.
Nelson, R. (2007) Economic Development from the Perspective of Evolutionary Economic Theory. Web.
ODI (2009) The global financial crisis and developing countries: taking stock, taking action. Web.
Porter, M. E. (1998) Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. 1st ed. Free Press
Quinn, J. B. (1998) An Incremental Approach to Strategic Change. The McKinney Quarterly, Web.
Robinson, S. & Stanger, M. (1998) Developing A Simulation Strategy For British Airways. Web.
Ryanair. (2009) Ryanair Reports Record Profits Of €481M up 20%, Fares Fall 1%, Traffic Grows 20% to 51M. Web.
Saunders, M., Thornhill, A. & Lewis., P., (2006) Research Methods for Business Students. 4th ed. London: FT Prentice Hall.
Scribd. (2009) British Airways Strategic Plan. Web.
The Guardian (2009) British Airways climbs as FTSE ends the week on a high note. The Guardian News and Media Limited, Web.
Tollin, N. & Castillo, J. A. (2008) Systems Thinking and System Dynamics in Evaluation of Sustainability. Web.
Wardell, J. (2010) British Airways cabin crew union loses legal battle. Web.
Wynn, G. (2010) British Airways to buy jet fuel from city waste. Web.
Yahoo Finance. (2010) Basic Chart for British Airways (LSE). Web.
Zikmund, W. M., (2006) Business Research Methods. 7th ed. Orlando: Harcourt Publishers.