Introduction
Management is the effective coordination of the resources of an organization towards the achievement of the goals and objectives of the respective organization. There are different kinds of management strategies that can be adopted by any organization in the globe towards the achievement of its goals and objectives. However, the choice of the strategy to use depends on the nature of the respective organization, and its organizational needs, for instance, the project portfolio management system. This management strategy is most applicable to project-based organizations that manage multiple projects. Although the project portfolio management system is an effective management strategy that can be used to increase efficiency, its effectiveness in an organization depends on the appropriateness and effectiveness of the modeling and simulation process. Therefore, the project portfolio management system must be appropriately and effectively modeled and simulated to ensure it increases efficiency in the management of multiple projects in project-based organizations (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000).
There are several organizations around the globe. Generally, organizations are incorporated with an aim of succeeding. Organizations consider themselves successful if they are making profits that were forecasted at the planning stage of incorporation. Management is the effective coordination of the functions and elements of an organization towards the achievement of the goals and objectives of an organization. The success and or failure of an organization are closely connected with the efficiency of the management team of the respective organization (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998). A management team is considered successful if the goals and objectives of an organization are achieved. On the other hand, a management team is considered incompetent in case an organization fails to achieve its goals and objectives. Different kinds of management and elements or businesses factors or functions require management knowledge and experience, for instance, human resources, finance, and projects among others (Bretani 2006).
Project Portfolio Management System
Project Portfolio Management is one of the aspects of management that requires effective and competent skills to monitor. Project Portfolio Management entails the centralization of the processes of management, technologies and processes, which are mainly applied by offices that manage projects or project managers (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). Generally, this centralization process is geared towards the collective management and analysis of numerous projects being handled currently and or those that have been proposed but based on specific characteristics (Denney 2005). Project Portfolio Management is an aspect of strategic management and is decided by the top management team of an organization. Generally, Project Portfolio Management is adopted in case an organization has several projects that it intends to run, and achieve the set objectives within the stipulated time without interfering with the development of other projects. There are several objectives that Project Portfolio Management aims to achieve, for instance, the determination of the optimal mix of resources, which are required for delivery, and scheduling activities of an organization towards the achievement of the financial and operational needs of the respective company (Kaplan & Norton 1996). Furthermore, these are speculating, but considering external business environment factors, strategic objectives and customers. These are considered because they affect the operation and success of an organization in one way or the other (Brunel 2006).
Managers are charged with the responsibility of ensuring that the organizational goals and objectives are achieved. There are several functions in an organization that managers must address, which has affected their ability to manage multiple projects effectively. This has raised the concern and debate whether project portfolio management should be adopted in the management of multiple projects in the project-based organization. It is a fact that managers cannot manage multiple projects on their own without seeking any help. This might compel respective managers to adopt project portfolio management to enhance the efficiency of managing multiple projects (Cooper, Scott, & Elko, 1998). Project-based organizations initiate multiple projects annually and monthly, but they expect high standards of performance in the respective projects that they initiate. Project-based organizations initiate multiple projects because they expect high levels of returns. Furthermore, their levels of returns are determined by the number of projects that they initiate and those that they experience high standards of performance (Kaplan & Norton 1996).
Project portfolio management is a function that is essential in project-based organizations to ensure that multiple projects that are initiated achieve high standard performances. However, there are certain individuals that tend to oppose the introduction of project portfolio management in a project-based organization. The resistance is mainly experienced by established project managers (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). Project portfolio management is viewed as a complement to the duties and functions of project managers, and not assistance used in enhancing performance and efficiency in managing multiple projects by project managers. This has led to poor implementation of the project portfolio management in most project-based organizations, which has also led to the debate whether a project portfolio management can be used to increase the efficiency of multiple project management in project-based organizations (Sanwal 2007).
Project Portfolio Management is a management process that can be used to enhance the possibility of completing projects within an organization in a timely manner. Several research works have been conducted in the past to monitor or test the reliability and efficiency of using it in a project-based organization (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). Different conclusions have been drawn in the past based on the time stipulated for the research and the nature of projects and organizations researched. Management processes are adopted to enhance efficiency in respective areas within an organization (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007). Furthermore, strategies are developed and adopted in an organization to ensure that efficiency in operation is enhanced. Moreover, efficiency in project-based organizations is portrayed if the proposed and current projects are achieved within the stated or stipulated periods. Considering the objectives, functions, and advantages of Project Portfolio Management, I strongly agree that it can be used by individual project-based organizations to achieve or enhance efficiency in operation in the event of managing multiple projects (Brobys 2009).
Several companies or organizations in the globe concentrate so much on their management ability to an extent that individual projects are not well-considered and adequate attention and resources are directed towards the completion of respective projects. This happens due to limited concentration on project portfolio by management of organizations. This situation can only be rectified by effective project portfolio management. Project portfolio management enhances efficiency in several ways (Ibrahim 2011).
Mix of Projects
There are different functions of management and each serves different importance in the running of businesses, but with an aim of achieving the set goals and objectives of an organization or company. The functions of management must be effectively coordinated to enhance efficiency in operation, which is reflected by the level of returns in an organization or company (Sanwal 2007). Project-based organizations require effective and well-coordinated efforts to enhance efficiency. Project-based organizations manage multiple projects, which can easily lead to delay in completion or low or unreliable returns among others. Organizing is a management function that is applied in Project Portfolio Management. Project Portfolio Management involves groups of related projects with an aim of enhancing efficiency (Kevin 2006).
Project mixing is a strategy that is used in project portfolio management implementation. This strategy is important in enhancing the efficiency of managing multiple projects in project-based organizations in several ways. Project-based organizations expect high standard performance in the projects initiated (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). Furthermore, individually initiated projects have deadlines and a timeframe for implementation. Handling multiple projects is not easy, and it might compromise the expected standard performance of individual projects in project-based organizations. However, project portfolio management provides for the opportunity of mixing or group-related projects together. This increases the possibility of achieving the expected performance standards by organizations. Moreover, it simplifies project management, especially multiple projects (Brobys 2009).
Project portfolio management ensures that each portfolio contains the appropriate project mix. This is to ensure the overall returns that are expected are maximized. A project portfolio comprises several projects, which have wide and different values. The variables that are considered in projects are the period and its benefits, for instance, short term or long term; expected returns and investment level. Project portfolio management takes all these factors into consideration when grouping projects. This enables easy planning for projects, which makes the achievement and completion of the respective projects real, and achievable (Harvey & Brown 2001). Furthermore, this ensures that redundancy is reduced in the organization. Moreover, it helps in saving time and costs that can be incurred by an organization in the process of implementing projects individually. This aspect of project portfolio management ensures that there is order in the grouping of related projects. Additionally, this can assist in the maximization of overall returns among related projects. Therefore, it is true that project portfolio management can be used to increase the efficiency of managing multiple projects in project-based organizations (Levin 2010).
Risk Balancing
Different projects have different risks associated with them depending on the nature of individual projects. Project Portfolio Management involves groups of related projects to enhance easy monitoring and supervision geared towards the achievements of the goals and objectives of the respective projects. In case projects are handled individually, they face respective risks, which may affect the achievement of the expected returns within the stipulated period (Mahajan 2009). All organizations are prone to risks, however, the risks and nature differ depending on the nature of respective businesses or organizations and area of operation. In project-based organizations, multiple projects are initiated and organizations expect high returns from the respective projects. However, the levels of returns are affected by the risks associated with the respective project (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007).
Project-based organizations must consider the risks associated with all projects that have been initiated by the company when implementing the respective projects. Although the individual projects are affected by the risks associated with them, they affect the returns of the company in the long run. There are certain projects that share risks but are implemented differently. Project portfolio management enables project-based organizations to assess and evaluate the risks associated with all the projects that they have initiated and group them based on the risks that might affect the overall organizational returns (Fister 2011). Determination of risks that are associated with individual projects in project-based organizations enables respective project-based organizations to effectively spread the risks and address them as an organization. This increases the efficiency of handling risks that are associated with project management and implementation, which is an added advantage in project management for the project-based organization because it can assist in increasing the returns level of the respective organization (Steyn 2001).
Project Portfolio Management enables a project-based organization for group projects with related risks together. This enables the respective organizations to handle the risks associated with the projects as a group, which helps in saving time and resources of the individual organization or company. Risks that are faced in the implementation of projects affect the long-term and short-term returns of an organization or company. Project-based organizations are faced with the task of balancing the risks that face individual projects (Fister 2011). It is the duty of the management of respective project-based organizations to assess the risks that are associated with individual projects and plan on how to address the individual risks associated with individual projects. Generally, project-based organizations have multiple projects in progress, which must be achieved within a specific time or period (Kotter 1996). Assessments of the risks and addressing them consume the time of an organization, which may affect the expected returns in the long run. However, Project Portfolio Management enables organizations to assess risks that affect individual projects and group those with related risks that can be handled together. This assists the organization in balancing the risks and easily addressing them (Hayes 2011). Furthermore, this is beneficial to project-based organizations because it can enable them to enhance their returns and effectively address risks that are associated with their projects. Therefore, considering Project Portfolio Management can enable project-based organizations to balance risks, it is true that Project Portfolio Management increases the efficiency of managing multiple projects in project-based organizations because it gives the management an easier time of dealing with risks (Moore 2009).
Resource Management
Management is the function that determines the level of returns of individual companies or organizations. There are several factors that constitute an organization or company and they require effective management. Without management, companies cannot achieve their goals and objectives. Business enterprises are started with an aim of making profits (Steyn 2001). However, they are faced with competition from other companies because most industries have several companies or organizations in operation. Stiff competition among companies and organizations requires effective management because organizations must make profits despite the intense competition experienced in the business environment (Rad 2006).
All organizations require adequate resources to achieve their goals and objectives. Furthermore, the availability of resources is the core to success in most companies. Business organizations can only succeed if they have access to the required resources (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). There are several organizations in the global economy. However, the available resources are limited, which requires an effective and competent management team in organizations to ensure that the acquired limited resources are adequately utilized towards the achievement of the goals and objectives of the respective organization. Project-based organizations are mainly affected by the management of resources that they have acquired (Bretani 2006). Project-based organizations initiate several projects and expect high standard performance and high returns in the long run. However, the available resources are limited, and several companies or organizations are competing for the same resources. Different project-based organizations may initiate the same project, and requires the same resources in the implementation and successful completion of the respective projects. This can lead to high or intense competition in resource acquisition among project-based organizations (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998).
The limited nature of resources can also affect the returns levels of an organization. Therefore, organizations must manage their resources effectively to attain the expected returns based on the cost used in acquiring the resources. Project portfolio management encourages the centralization of resources in a project-based organization. Project-based organizations that manage multiple projects require effective management of the available resources in order to achieve the expected returns in the long run (Kaplan & Norton 1996). Decentralization of resources does not promote effective utilization of resources, especially in project-based organizations managing multiple projects. Project portfolio enhances the centralization of resources, which enhances the utilization of the respective resources. Generally, project portfolio management enables project-based organizations to centralize the processes, technologies, and methods involved in the management of multiple projects within the organization, which is a way of increasing efficiency in the management of multiple projects within the respective project-based organizations that implement project portfolio management (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998).
Different projects require different resources to be implemented. However, certain resources are universally required by all projects in a portfolio. Furthermore, there are certain resources that can be shared among different projects in a portfolio. Project portfolio management enables project-based organizations to centralize resources within the organization. This can enable the project managers to determine the resources that are required, and when they are required. This is important because it can enable the management team in the appropriate allocation of relevant resources to the implementation of individual projects within a portfolio of an organization. Moreover, this can enable the management team to avoid misuse of the limited available resources (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998).
Individual projects have unique features, which require different resources, and in different amounts. Effective tracking and allocating resources for the implementation of individual projects in project-based organizations managing multiple projects is not an easy task. Tracking relevant and appropriate resources is difficult and can cause an organization’s management time, which may also lead to resource wastage among others (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). However, project portfolio management provides for the analysis of all initiated projects in the project portfolio management office, which is centralized in project-based organizations managing multiple projects (Kaplan & Norton 1996). Furthermore, project portfolio management provides project managers with tools that can enable them to easily track and allocate relevant resources to multiple projects. Moreover, project portfolio management enables project managers to develop frameworks that can be used in managing multiple projects effectively using the available resources within a project-based organization. Additionally, this enables project-based organizations to use their available limited resources to effectively manage and monitor multiple projects within the organization and achieve the expected returns in the long run (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998). Centralization of resources in project-based organizations enables project managers to manage multiple projects to effectively manage collective projects, and achieve the goals and objectives of the organization. Therefore, project portfolio management can be used to increase efficiency in project-based organizations managing multiple projects because it enables project managers and organizations to centralize available limited resources and focus them on the achievement of specific goals and objectives (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007).
Project portfolio management enables an organization, especially project-based to prioritize the projects within the portfolio that need to be implemented and the amount and cost of resources required for the implementation and execution of individual projects. The centralized nature of the project portfolio management system is effective to enable a project-based organization managing multiple projects to assign relevant and adequate resources based on the acquired quantities by the respective organization in order of importance. Projects are prioritized based on their importance and nature. Important projects require adequate resources, and the supply must be timely. The distribution of resources in a project-based organization managing multiple projects may not be equal because projects are rated and grouped based on their priority (Steyn 2001). Determination of projects that should be prioritized in an organization is not easy and may consume time, which leads to misuse and misappropriation of available resources. This is a task that can be easily conducted by project-based organizations managing multiple projects effectively through the implementation of a project portfolio management system. Furthermore, a project portfolio management system must be simulated and modeled effectively for the expected results to be achieved (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007).
Understanding Project Portfolio System
Project portfolio management is a strategy that is used by organizations to determine the kinds of business that they should pursue based on the required start-up cost and the expected returns levels in the long run among others. Furthermore, a project portfolio management system aims at effectively coordinating the available limited resources of a project-based organization towards the achievement of goals and objectives (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998). Generally, project portfolio management blends different management disciplines towards the achievement of goals and objectives. Project portfolio management system is mainly adopted by project-based organizations to enhance efficiency in managing multiple projects within the organization (Brobys 2009).
A project portfolio management system is adopted by an organization to enhance the efficiency in the management of multiple projects within project-based organizations. There are three management focuses that project portfolio management focuses on. The management areas that are addressed by the project portfolio management system are project management, business management, and general management. The management focuses that project portfolio management system address aims at enhancing efficiency in different ways within project-based organizations (Kaplan & Norton 1996). The business management focus is concerned with ensuring the alignment of programs and projects within the strategy of the respective portfolios within project-based organizations. Secondly, a project management focus is concerned with the assessment, review, and management of programs and projects, and ensuring that they exceed or meet planned contribution in the portfolio of the respective project-based organization (Denney 2005).
The project portfolio management system adopts the holistic approach in the coordination and management of projects within project-based organizations. It ensures that the portfolios within project-based organizations contribute collectively to the achievement of the goals and objectives of the respective project-based organizations. Furthermore, a project portfolio management system ensures that multiple project management is easy (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007). It simplifies the management of multiple projects in project-based organizations by ensuring that the projects depend directly or indirectly on the available resources of respective project-based organizations (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000).
Decision-making is a critical part of the management of organizations. Decisions made by the management of an organization should not only focus on individual departments or projects but the entire organization. In organizations, decisions are expected to contribute to the achievement of the overall goals and objectives of the respective organization. Project-based organizations provide for the centralization of the project implementation (Denney 2005). This is important towards the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of an organization. Project-based organizations initiate several projects and intend to achieve high returns levels from respective projects. Individual projects require different decisions and approaches to ensure that they are fully implemented and completed within the stipulated time or period. Responding to the needs and requirements of individual projects is tricky, which has led to the failure of some projects, especially in project-based organizations managing multiple projects (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998).
Decision-making in a project portfolio management system is simplified and universal. The decisions made affect all projects within the portfolio. The decisions made by managers in project-based organizations managing multiple projects using a project portfolio management system must contribute to the overall success of all projects within the portfolio. The decisions made by managers are centralized and made after considering all the projects within respective portfolios (Brunel 2006). Although certain decisions may not favor some projects within the portfolio in project-based organizations managing multiple projects using project portfolio management systems, most of them contribute to the overall success of all projects within the respective portfolio (Kaplan & Norton 1996).
The project-based organization may require the use of project portfolio management in case they manage multiple projects and expect the attainment of the full potential of all projects within the portfolio. A project portfolio management system that is effectively modeled and simulated can assist an organization that is project-based and managing multiple projects in several ways (Fister 2011). This combination increases the efficiency of managing multiple projects by project-based organizations in several ways (Ibrahim 2011). It enables project-based organizations to appropriately select programs and projects, which are relevant to the goals and objectives of an individual organization. The project-based organization faces challenges in the choice of projects to initiate. In the process of designing and initiating projects in project-based organizations, the goals and objectives of the respective organization must be considered (Kaplan & Norton 1996). Generally, project-based organizations managing multiple projects initiate projects that can contribute to the achievement of their goals and objectives. The centralized nature of the project portfolio management system enables the management and project managers to select projects that relate to the goals and objectives of the respective organization (Rad 2006). Furthermore, the selected projects must coincide with the strategies of the respective organization. Strategies of an organization are developed by the top management of an organization. The centralization of project management through the modeling and simulation of an effective project portfolio management system enables an organization to assess, evaluate and consider the strategies of an organization in the selection of projects before initiation and implementation. This enables an organization to develop and initiate realistic projects that can be achieved successfully based on the strategies of the respective organization. The strategies of an organization dictate the projects and programs that can be implemented successfully. The strategies must be considered when selecting projects because they are required to support the implementation of projects within an organization (Kotter 1996).
Organization-based organizations managing multiple projects are affected by the effective management of the individual projects collectively. Project managers in organizations that manage multiple projects tend to address the needs of individual projects without considering the overall contribution of all projects within the portfolio towards the achievement of goals and objectives of the organization. This happens because the implementation and management of projects are decentralized, which is not effective in the management of multiple projects. Multiple projects expect the regular assessment to ensure efficiency in operation (Mahajan 2009). The health of a portfolio is a priority in project-based organizations managing multiple projects because it reflects the achievements of the overall goals and objectives of the respective organization. The decentralized system for managing projects may not enable an organization to regularly, and consistently assess the progress of all projects within a portfolio (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998). However, the centralized nature of the project portfolio management system enables a project-based organization managing multiple projects to regularly and consistently assess the progress of portfolio projects. Furthermore, this enables an organization to assess the contribution of individual projects within the portfolio towards the achievement of goals and objectives of the organization (Sanwal 2007).
Management is a process and not a function. It should be conducted on a day to day running and operation of a business or organization. Management actions are mainly taken into consideration of the goals and objectives of an organization (Brunel 2006). Projects are initiated to contribute to the achievement of the goals and objectives of an organization. Regular assessment of projects within a portfolio may enable an organization to determine the effects of individual projects towards the achievement of the goals and objectives of the respective organization. Management actions can be either to change a project, modify, increase resource supply or reduce resource supply to the respective project among others. Such decisions are mainly carried out by an organization to ensure that individual projects within an organizational portfolio contribute to the achievement of the goals and objectives of an organization (Brobys 2009). Project-based organizations managing multiple projects using project portfolio management can easily achieve their goals and objectives within the stipulated time or period because the management is able to assess individual projects and take management action towards ensuring compliance of all projects within the portfolio with the goals and objectives of the respective organization (Harvey & Brown 2001).
Project-based organizations require an effective project portfolio management system to enhance the possibility of achieving the goals and objectives of the respective organization within the stipulated or stated deadline or period. Furthermore, modeling and simulation of an effective project portfolio and management system enables an organization to use the disciplines of project management effectively at the programs and project determination level in an organization (Hayes 2011). The choice of the right and appropriate projects in an organization enhances efficiency in operation. It also increases the satisfaction of the customer, which later translates into increased efficiency in the management of multiple projects by an organization. This is a way that an organization can also use to minimize the number of risks that are associated with the operation of companies and business organizations. It can also enable an organization to adequately and effectively address problems associated with the operation and running of the functions of project-based organizations (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998). Furthermore, this can enable an organization to increase its chances of succeeding in the business environment. Several people misunderstand the objectives of project portfolio management, especially project managers, and most of them tend to oppose the introduction of a project portfolio management system in an organization with the fear of losing their jobs. However, a project portfolio management system is meant to complement the functions and duties of project managers (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007). Therefore, a project portfolio management system is applied in project-based organizations managing multiple projects to increase efficiency because it can be used to realize the benefits of the portfolio projects, through the application of structured approaches of management (Kevin 2006).
Life Cycle of Project Portfolio Management System
A project portfolio management system is used in business operations. It is commonly used in project-based organizations managing multiple projects. Therefore, a project portfolio management system is considered a process in business operation because it is used in increasing efficiency in operation. Furthermore, the project portfolio management system life cycle requires the effective application of the disciplines and skills of management to ensure success. The life cycle illustrates the stages or phases of the project portfolio management system. The phases must be followed systematically (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). This is illustrated in the model below.
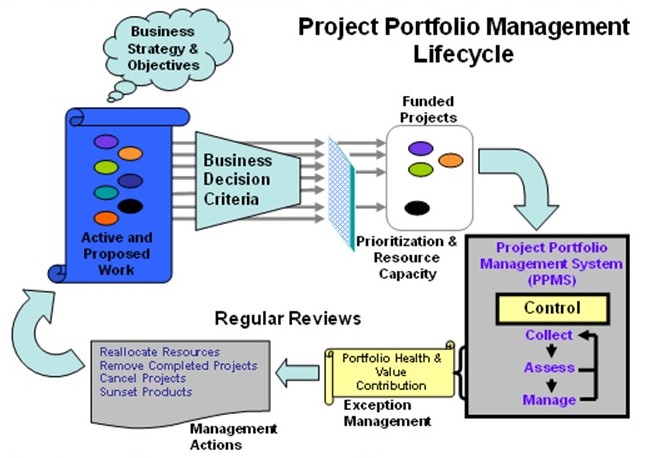
The figure above illustrates the life cycle of a project portfolio management system. The life cycle shows different activities that it contains. There are specific activities that are included in the life cycle of a project portfolio management system. They include the identification, funding, and qualification of programs or projects, which can address the strategies of an organization (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998). Furthermore, identifying corrective actions for projects to comply with the objectives of the portfolio, and establishing an effective communication channel that allows timely reporting and decision making in an organization among others (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007). A project portfolio management system is adopted by organizations to enhance their performance and increase the efficiency of managing multiple projects within project-based organizations. The project portfolio management system that is effectively modeled and simulated must consider specific processes to ensure efficiency in managing multiple projects. The general processes include assessment of the portfolio, selection of a portfolio, monitoring of a portfolio, taking of management action, removal or termination of a project, and re-prioritizing or prioritizing of a project (Kaplan & Norton 1996). A project portfolio management system that is effectively an appropriately modeled and simulated must consider the general processes to ensure that the goals and objectives of the respective portfolio are achieved and contributes to the achievement of the goals and objectives of the respective organization (Moore 2009).
Focus On the Management of Business
Project portfolio management focus on the management of a business is charged with the responsibility of defining the scope and validity of viable portfolios from the perspective of a business. Through the modeling and simulation of an effective and appropriate project portfolio management system, project managers in project-based organizations are empowered to appropriately and select strategies based on priorities (Brunel 2006). Furthermore, it enables project managers to direct their organizations to identify effective indicators of assessing the progress of a portfolio. The criteria of decision making that will be adopted at this stage through project portfolio management system implementation must be associated with the strategies and objectives of an organization (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). This is due to the fact that the implementation of projects in a project-based organization is geared towards the achievement of specific goals and objectives, which contribute to the achievement of the overall goals and objectives of the respective organization (Bretani 2006).
It is recommendable that project-based organizations manage multiple projects to design an effective project portfolio management system. This enables an organization to consider several factors in the process of selecting and prioritizing projects. An effectively modeled and simulated project portfolio management system enables an organization to consider factors such as the expected return on respective investments, revenue growth, the cost of budget, and profit among others. Furthermore, it enables an organization to consider the demand, desire to enter new markets, and mandatory initiatives among others (Denney 2005). Moreover, this system enables an organization to use the decision criteria of a business to cancel or validate projects, which have been forwarded to the implementation stage (Hayes 2011).
Information flow is an important aspect of the management and success of an organization. The flow of information determines the nature of the response to inquiries within an organization. There are several factors in an organization that requires a prompt response, for instance, risks among others. Issues within an organization can be responded to promptly if the channel of the flow of information is simplified, hence relevant information easily reaches relevant parties (Mahajan 2009). Project portfolio management system involves centralization of resources, which includes management too. In the centralized system of management, information flow is effective and easily accessed by relevant parties, which leads to prompt responses to inquiries that require immediate response (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). Centralization of resources also enables the management team to closely communicate and consult on matters without wasting time communicating with relevant persons or authorities. Achievement of the goals and objectives of projects in a portfolio is easy in organizations that manage multiple projects, and have adopted the system because the flow of information within the system is smooth and easy to monitor (Hayes 2011).
The flow of information is crucial in the achievement of the goals and objectives of an organization in several ways, especially when implementing a project portfolio management system. An effective flow of information within an organization is possible in case the project portfolio management system being used is effectively and appropriately modeled and simulated. This can enable an organization to easily manage portfolios (Sanwal, 2007). Effective management of portfolios in organizations involves the choice of the right management action towards a project that is noncompliant with the objectives and strategies of an organization. Moreover, the effective flow of information in an organization can enhance the review and improvement of portfolios within an organization (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000).
Reaping the Benefits
Project-based organizations and other related organizations require effective modeled and simulated project portfolio management. This system can benefit an organization in several ways, which in the long run lead to the achievement of goals and objectives of the respective organization and increased efficiency in operation. A project portfolio management system is an element of strategic management, which must be incorporated with the strategies and objectives of individual organizations to ensure that the goals and objectives of the respective organizations are achieved (Denney 2005). Management of projects within project-based organizations that manage multiple projects is tricky and a challenge to the management of the respective organization. Individual management of projects is decentralized, which does not give the management adequate attention, time, and resources to effectively and appropriately implement individual projects, and achieve the expected goals and objectives within the stipulated time or period (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). However, the use of project portfolio management in project-based organizations that manage multiple projects is effective and beneficial because it allows for the centralization of the resources of an organization, and even and fair distribution towards the achievement of the goals and objectives of an individual project, but with focus on the overall goals and objectives of the respective organization (Sanwal 2007).
The best project management practices are beneficial to an organization because they can contribute to the timely achievement of the goals and objectives of the respective organization in several ways. This is possible if an effective project portfolio management system is modeled and simulated by an organization. An organization can reap several benefits from the application of an effectively modeled and simulated project portfolio management system (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). An effectively and appropriately modeled and simulated project portfolio management system can enable an organization to reduce costs because it allows for consistent management processes. Cost reduction is a challenge that is facing several organizations in the global economy. It is through the reduction of costs, especially expenses that an organization can increase its return levels (Harvey & Brown 2001). The levels of returns of an organization are determined by the costs that an organization incurs in the process of executing or implementing the respective projects. Organizations are able to reduce costs using an effectively and appropriately modeled and simulated project portfolio management system because it allows the management team to consistently review the projects, which is a management element (Fister 2011).
Effectively modeling and simulating a project portfolio management system and its implementation also enables an organization to identify projects that are faced with high risks. Project portfolio management enables an organization to assess the risks associated with individual projects in a portfolio and balance them to enable the achievement of the overall goals and objectives of an organization. Risk management is a challenge that faces several organizations in the global economy and has contributed to the collapse of several projects (Ibrahim 2011). Moreover, ineffective management of risks within an organization has also led to the closure of several organizations. Risks affect the returns and achievement of the goal and objectives of an organization. They must be addressed effectively to ensure smooth and efficient operation, especially in project-based organizations managing multiple projects because failure in an individual project may affect the achievement of the overall goals and objectives of an organization (Kotter 1996).
Implementation of an effective and appropriately modeled and simulated project portfolio management system can enable an organization to enhance the performance of its portfolio. The project portfolio management system enables an organization to closely and regularly monitor its projects in a portfolio in various ways. Moreover, it allows an organization to make improvements or adjustments to its projects within a portfolio (Murray-Webster & Thiry 2000). Regular assessment of the projects enables an organization to take management actions geared towards ensuring that all projects within a portfolio comply with the strategies and objectives of the respective organization. Compliance of projects within a portfolio with the strategies and objectives of organizations enhances the performance of respective projects within a portfolio, which is realized in the timely achievements of the goals and objectives of the respective organization (Rajegopal, Philip, & James 2007).
Finally, the implementation of an effective and appropriately modeled, and simulated project portfolio management system, increases efficiency in the management of project-based organizations that manage multiple projects. There are several factors of business operation that are improved by the use of an effective and appropriately modeled and simulated project portfolio management system, for instance, the effectiveness of the management team. A project portfolio management system involves regular checks on the projects within a portfolio (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998). Furthermore, it regularly involves management in the practice of assessment, evaluation, and review of projects, which increases the practice of management within an organization. Increased management activities by a management team increase the experience and competency of the respective management team. This increases the effectiveness of the management team, which increases efficiency in operation. Furthermore, a project portfolio management system enhances or improves communication within an organization, which enhances the good flow of information within an organization (Ibrahim 2011). The flow of information within an organization is important towards the effective implementation of strategies and achievement of goals and objectives of the respective organization. Information flow ensures that relevant information is relayed in time to avoid delays. Improved communication in an organization is the key to the achievement of the goals and objectives of an organization, and timely response to the needs of an organization (Kaplan & Norton 1996). The establishment of an effective management team and improved communication in an organization increases efficiency in operation in organizations. Therefore, an effective and appropriately modeled and simulated project portfolio management system can lead to the creation of a controlled business environment, and business unit, which can contribute strongly to the realization of the goals, objectives and strategies of a business (Cooper, Scott, & Elko 1998).
Conclusion
Project Portfolio Management is an effective strategy that can benefit organizations. The strategy enables organizations to centralize their operations hence monitor and evaluate the progress of individual projects within a portfolio easily. Moreover, it enables an organization to balance risks, effectively allocate resources and minimize operating costs, which leads to increased efficiency. Therefore, an effectively modeled and simulated project portfolio management system may increase efficiency in project-based organizations managing multiple projects.
References
Bretani, C., 2006, Portfolio Management in practice. London: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Brobys, K., 2009, Portfolio Management. New York: Books on Demand.
Brunel, J., 2006, Intergrated Wealth Management: The new direction of portfolio managers. London: Euromoney Books.
Cooper, R. G., Scott, J. E., & Elko, J. K., 1998, Portfolio Management for New Reading. New York: Addison-Wesley.
Denney, R., 2005, Succeeding with use cases: Working Smart to Deliver Quality. Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Fister, G. S., 2011, Prepare for the unexpected: Investment Planning in Asset-Intensive Industries, Economist Intelligence Unit. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Harvey, D., & Brown, D., 2001, An experimental approach to organizational development. New Jersey: Prentice Hall International, Inc.
Hayes, I. S., 2011, Managing the Project Portfolio. Web.
Ibrahim, N., 2011, Project portfolio management in philanthropic organizations. New York: GRIN Verlag.
Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. P., 1996, The balanced Scorecard. Boston: Harvard University Press.
Kevin, S., 2006, Portfolio management. New York: PHI Learning Pvt Ltd.
Kotter, J., 1996, Leading Change. Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
Levin, G., 2010, Interpersonal Skills for portfolio, program and project managers. London: Management Concepts Incorporated.
Mahajan, A., 2009, Portfolio Management: Theoretical and empirical studies. New Delhi: Global Indian Publications.
Moore, S., 2009, Strategic Project portfolio management: Enabling a productive organization. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Murray-Webster, R., & Thiry, M., 2000, Gower Handbook of Project management. London: Managing Programs of Projects.
Rad, P., 2006, Project portfolio management: Tools and techniques. New York: www.iil.com/Publishing.
Rajegopal, S., Philip, M., & James, W., 2007, Project Portfolio Management: Leading the Corporate Vision. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Sanwal, A., 2007, Optimizing Corporate Portfolio Management: Aligning Investment Proposals with Organizational Strategy. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Steyn, P. G., 2001, Managing Organizations through projects and programs: The modern general management approach. Management Today , vol. 3 no. 12, pp. 1-12.