Introduction
Today Companies placed risk management at top as their agenda because of market globalization and frequent change of customer demand. For a strong position in industry, effective risk management strategy and their practice are necessary. An organisation needs to take action at three level such project level, business strategy and at corporate level for their risk management. There is another significant and fundamental surface of the key topic of this paper is supply-chain risk management. In this case, stakeholders of a firm play beside and have a strong support.
To describe the features of risk management, this paper has presented a theoretical overview of risk management that includes conceptual framework, three basic levels, supply-chain, key factors, importance, methods or techniques, cycle, key concept of Turnbull report and SWOT analysis. Here also selected company is Bradford and Bingley (B & B) as case study.
Background
Under the present recessionary economy the issues of corporate risk management has been emphasised more widely both in UK and rest of the world. The corporate world is in serious threat to keep upheld corporate governance as well as internal control. If the internal control fails, the opportunity to sustain by using bailout should be ruined. Turnbull Report is mainly concerned with internal control and effective for corporate risk management. In September 2008, the UK’s largest mortgage lender Bradford & Bingley collapsed by the hit of credit crush in Europe. The government of UK announced to nationalising B&B and funded £ 18 billion to rescue troubled Bradford & Bingley as an auxiliary part of US bailout.
This paper examines key factors of corporate risk management in context of Bradford & Bingley in the light of Turnbull Report those influence the similar FTSE 100 and other corporate bodies of UK. Here the Bradford & Bingley has been presented as imperial evidence and the object of this investigation is to rationalise rationales the broad-spectrum motivations of corporate risk management including more detailed hypotheses and conceptual framework relating to today’s corporate world.
A short description of the company
In 1851, Bradford & Bingley has started to provide their mortgage product and services at Northern Mill towns of UK. Now they have almost 197 branches those maintain as third-party branch as their agent. These agents are the source of their 140 network. Using these sources they enabled to play an important role on saving business, buy- to-let market and also on the economy of UK.
In order to make available product and services they use three media or distribution channel such as by post, phone and by Internet or online. Not only mortgage products they also offer loans for investing in UK property and to purchase house for personal use or to rent at the rest of the world. Last year (in 2008) their earnings increased by 27% that amounted £8.3 billion. In 2007, B & B’s group investment was about £125 million. At the end of 2007 their profit growth amplified by 5% (£351.6 million).
In administrative level their experienced groups have executed tremendously occupation though they have faced a lot of recessionary constraints at the end of 2007. Sir George Cox gave his ultimate effort throughout his 7 years working at B & B. As a result, this company has achieved a lot of conquest and performs with a communal spiritual attitude. In order to maintain improved credit superiority they reduce their interest rate and also to hold consign in lending market.
Being stronger in the industry now they focused at financial wholesale market. Their prime strategy is to deal with risks. At corporate level their regions of managing risks-attracting competitive markets, prove specialised in mortgage lending, shift funding on a strong base, make an effort to realise and carry out consumers necessity and make variation in mortgage distribution. Ultimate target of mentioned steps is to develop and keep continuing their intense performance level at any circumstance.
Theoretical overview in the context of B & B
Concept of risk management
Main theme of risk management is to avoid and remove risks in order to be rewarded. With the aim of risk minimise and shift, risk management process need to absorb in-identify, analyse, response and allocate. As mentioned in theoretical assumption, B & B also follow risk management procedure at every level of the organisation. Response of risk management could be in three ways-avoid the identified risks, shift or transfer and at last hold on to future performance.
In order to manage risks B & B needs to consider uncertainty, innovative ideas, prearranged responses and realism. The term uncertainty includes world economic recession, inflation rate and socio-political environment. Innovative ideas necessary to understand rapidly change of customers test and try to fulfill their claims.
Third, prearranged responses are for identifying the factors relating to risks. Such as investment or portfolio decision making, take a new agreement or starting a new business, modernising the existing business and expand the project at hand. Finally, realism involves in identifying the product that have optimal demand and choose projects which could be the best solution for this.
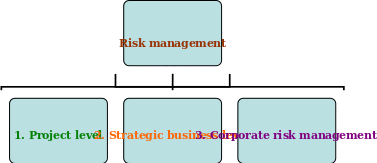
Levels of risk management
Risk management level is alienated into three broader forms. They are respectively as project level, strategic business level and corporate level. A brief description of these levels is presented in bellow-
Project level risk management
The term project is defined as the operation design to bring about several predetermined objectives surrounding a time frame. This time frame might be short or long. On the other hand, project management is a process that plan, organise, direct and control resources (both human and non-human) to assemble a project’s performance, time and costs.
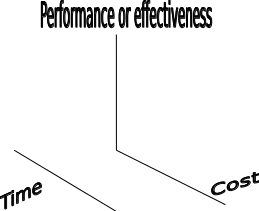
Human resources of a project consist of people and non-human resources are plant, equipment, technology used in the project. To be succeeding in project level risk management B & B apply strategies in three major areas. They are:
- Performance or effectiveness-first area of project strategy is performance or effectiveness evaluation. Though at the begging of world economic recession (fiscal year 2007) B & B faced a serious obstacle of bad credits in their business but now they overcome that by choosing alternative portfolios in mortgage lending. At present their most dominating area of business is mortgage.
- Time frame or lead time is another side in making strategy. Recently it is identified that ratio of house rent is higher than the percentage of taking loan to buy house. Another point is also to be noted that their current offers do not require selling personal home in order to return their loans or investment.
- Costs of the project have a great impact on project management strategy as well as project level risk management. In this case, B & B deducts their cost of capital and as a result their ratio of clients increased.
To entail aforesaid sector of strategies project level risk management pursue a circular flow describe in bellow:
- Plan is a road-map through which objectives and goal of a project is determined and these identified objectives must be risk free. B & B’s goal or objective is for provide loans for personal house, house for rent and housing insurability after retirement. For planning, another important point is considerable percentage of immigration in UK.
- Organising is an arrangement that form the planning into practical structure. B & B’s saving business offer-mortgage lending, loan for housing or rent and loan for investing UK’s property. Their offering is also valid around the world where they direct their business.
- Directing or motivating people inside the organisation (personnel or employees) and consumers both are under this stage. Employees of B & B are hard working, innovative and cooperative. These features attract the clients of B & B and through this they are enabling to meet their necessities. This stage is a way of inspire their employees for better output so that they can reach their ultimate goal.
- Controlling tasks of the confirmation of planned activities, performance or effectiveness estimation, effective application of operating activities. In B & B, estimation of product quality, effective team work, seeking new opportunities, decentralise business activities are the factor for those controlling is needed.
Strategic business level risk management
Strategy is a set of techniques that manage, organise and coordinate people, material and plant in order to achieve an organisation’s goal and enjoys competitive advantages. It is also effective tool for minimise risks. In another word, strategic risk management is engrossed in selecting vision and mission, crafting objectives and evaluate or appraisal performance to attain the desired goals. Steps followed by B & B at their strategic business level for managing risks is described as bellow-
- Attracting competitive markets stand on strong ground B & B always choose competitive markets and offer required rate of return. According to their competitive advantage category loans, products and mortgage arrangement is structured. In the industry, there is an inverse relation between private rental growth and percentage of loans to buy. In addition, private rental growth is higher than ratio of loans to buy.
- Prove specialised in mortgage lending-durable competitive advantage is commitment of B & B for each and every of their markets. All categories consumer can enjoy this advantage and this facility scattered around the whole business. All consumers could use the assets offered by B & B and for this they do not need to sell their home.
- Shift funding on a strong base-in several years B & B’s key component is to branch out funding that include retail saving business. During fiscal year of 2007, this strategy brought a huge benefit for them. On the other hand, in challenging economic period this strategy competent them to diversify funding or investment. Their prime source of funding is their consumers deposit and at present a numerous lenders has involved in their target market. Another important event is that in 2007 they were capable to achieve 11 million ASDA and their existing goal is to increase £2.5 billion within one and half hour (six weeks).
- Make an effort to realise and carry out consumers necessity-in this global market customer claims are hurriedly changing and at present B & B’s current market are patronised by consumers who demand lending products. This specialised products strengths B & B’s business and market value. Since 2007, they continuously involve themselves in investing in their products, systems or coordination and also in their employees and consumers. Not only these they also rapidly revise their model of credit, product design, collected data of consumers. For developing product they deduct cost of capital of the target market.
- Make variation in mortgage distribution-B & B’s mortgage market is distributed under a brand named “Mortgage Express”. Mortgage agents have monitored most of this business. Make variation in mortgage distribution, B & B sign a portfolio agreement with “Kensington Mortgages and GMAC-RFC” in 2007. In fiscal year 2007, this portfolio agreement brought valuable effects and considered as most important alternative at the beginning of world economic recession.
Corporate level risk management
Corporate level risk management faced factors that directly related with capital budgeting decision approaches and investment or portfolio decision making. This is the ultimate level of risk management of an organisation. Aim of investment decision is exchanging current funds in order to get future benefits. Here, long-term assets are chosen to invest. In case of B & B, their current profitable market is mortgage lending business. Corporate level risk management is classified into three ways in decision making. They are as follow-
- Widening the current business-as the criteria of investment decision making B & B has a continuous tendency to expand their current business. At present mortgage lending area is small in scale but it has a bright future. Now mortgage lending has a great demand in market.
- Establish and enlarge new business-according to second criteria B & B try hard and soul in establishing and enlarge new business. To do so they focus on competitiveness and market demand, factors that influence and derive market demand.
- Alternate and restructure to reduce costs and improve operating efficiency-controlling is the prime way to improve operating efficiency, costs deduction, revise and choose alternative portfolios. In 2007, B & B did such an agreement named- “Kensington Mortgages and GMAC-RFC”. When B & B faced a tied economic barrier at the start of world economic recession this agreement brought a fruitful outcome and helps to overcome their crisis.
Aforesaid types of investment decision would be evaluated by following a set of method. Those are presented in a sequence in bellow:
- Net present value (NPV) – NPV is a procedure to evaluate investment proposals. Selection of choosing a project is depending on the value of NPV. Now NPV of B & B is £ 35.6 million.
- Internal rate of return (IRR) – it is a method or technique to measure discounted cash flow. In 2007, B & B’s internal rate of return is increased 5% which amounted £351.6 million.
- Profitability index (PI) – to identify cost benefit ratio profitability index method is used. It is a ratio between present value of cash inflows or funding and initial cash outlay or investment. Amount of B & B’s investment is almost £ 125 million and return on equity is 19.1%.
- Payback period (PP) – time take to return of initial investment is named as payback period. It is a ratio between initial investment and annual cash inflow or funding. Recently B & B took only six weeks or one and half hour to increase their NPV in £2.5 billion.
- Accounting rate of return (ARR)-another term of ARR is return on equity (ROI). It analyses the financial statements and estimate an investment’s profitability. In 2008, B & B’s profitability is about 27%.
- Cash inflows and cash outflows- cash inflows is the amount of money in operating a project and for investment. On other hand, cash out flows are the expenses included both fixed and variable. In 2007, aggregate expenditure of B & B is 5.5% of their earnings.
Supply-chain risk management
Supply-chain is directly connected with manufacturing and production department of an organisation. Controller of this side is client. Turning raw materials into finished goods is the task of this part. According to the B & B’s business category their supply-chain is involved in arranging loan for housing, rent, mortgage lending. To do so their using distributing channels are- third party type agencies, telephone, by post and by Internet or online. As another part of an organisation manufacturing department has also faced risks in processing goods. Here to avoid risks several key factors are considered and those includes-
- Gathered information whether new product or services would need to produce.
- Expand the source of information that could reduce percentage of risks.
- By using a common method of supply-chain in different area of the world and economic system magnify a company’s international market scale and also competition globally. Around the world B & B has 197 branches.
- Make multiplicity to extend product line and thus they could enter into new market. B & B enjoys a competitive advantage in their mortgage lending market though this contains small scale.
- To eliminate numerous barriers there have a strong impact of large scale of production and market.
- Rapidly changes of promotional activities that would helpful for attracting customers.
- Innovative structure of management which would a source of product variation ides.
- Develop advanced technology in communicating between suppliers (retailer, wholesaler, shopkeeper, personal selling etc.) and consumers.
Factors involve in supply-chain risk management
Fostering a successful supply-chain management there have a number of essential factors. Those are describe as bellow-
- Abundant source of supply- there have an inverse relation between number of supply store and percentage of risk. If source of supply would increase then ratio of risks reduced. B & B maintained 140 distribution channels through their agents.
- Secured supply system- to decrease risks system or process of supply should be secured in delivering.
- Pricing method- it is an important factor for supply-chain management for the reason that a sound price level is effective for decreasing risks of supply-chain. B & B always pay attention in pricing level.
- Modern technology- adopting new and latest technology is a factor that involve in reducing risks. In this case, B & B use online or Internet service as a part of modern technology.
- Supreme quality- through ensuring better quality of product risks would controlled of the supply-chain management system.
- Standard of suppliers- with the standard of product quality and technological support suppliers’ standard could control risks.
- Time frame or lead times- another factor that directly involve is time frame or lead time to supply products. Shorter time has an impact on risks of supply-chain.
- Portfolio or investment- appropriate decision of investment or portfolio is considered as most valuable issue of supply-chain risk.
- Reward system- reward system is a way to motivate employee and thus it lessen risk factors. For this reason, B & B pays a sound amount as remuneration and other facilities to motivate employees.
- Individual decision making- individual decision making helps to deny entry of conflict and in that way it controlled risks.
- Product variety- an extensive product line can make supply-chain management risk-free.
- Experiences- statistical data is a source of risk management. On the other hand experience employee could diminish risk.
- Individual achievement- individual achievement is a motivating matter that smooth supply-chain and pass the barriers.
- Inspection- a strict monitoring is helpful in supply-chain risk management.
- Developing both internal and external relationship- another way of risk management is better internal and external relationship.
- Steps to prevent risk- prevention of risk by taking initial steps are better to remove risks and in this case, risk avoidance in the best way.
Significance of risk management
Tasks of risk management are not only identifying area of risks. It is an on going process which includes a sequential step-categorise risks, gather information, analyse them and finally make a decision. These steps follow a circular flow; it does not include a linear form. A company enjoys several benefits through risk management and the importance of this process is explained as bellow-
- Investment decision-It is easy to make decision whether invest or not. Following the steps of risk management there has an availability of information so that analyzing this, investment decision procedure is easier and less time consuming.
- Reduce chance of error-Another importance of this process is that it enlarges confidence level and as a result management can take decision accurately.
- Development of investment planning process- Based on the question “what if” and creative circumstances improve investment or portfolio planning process.
- Proper inspection-For continuous development and amendment there has an inspection team and it is helpful for the firm maintain a standard level of organisational structure.
- Make alternative way-response to a risk factor manager have few alternatives which are fruitful in unforeseen event and also improve consciousness.
- Understand rapidly changes global market-It is a time where market demand is rapidly changes require more variations than ever. Process of risk management assists managers to understand these changes and make variations in product line.
- Change the model of investment structure-Investment structure changes is easier than before because of the accessibility historical data or information.
- Understanding the issues of investment-When investment is needed issues of investment is understood easily by analyzing gathered documents.
- Monitor objective and structure of the investment- Risk management process continued monitoring the objectives and structure of the investment and thus it is trouble-free whether necessitate changing of these factors.
- Reduce time consuming-Risk management facilitates a manager to response swiftly and controlled them in emergency turn up.
Methods or techniques used in risk management
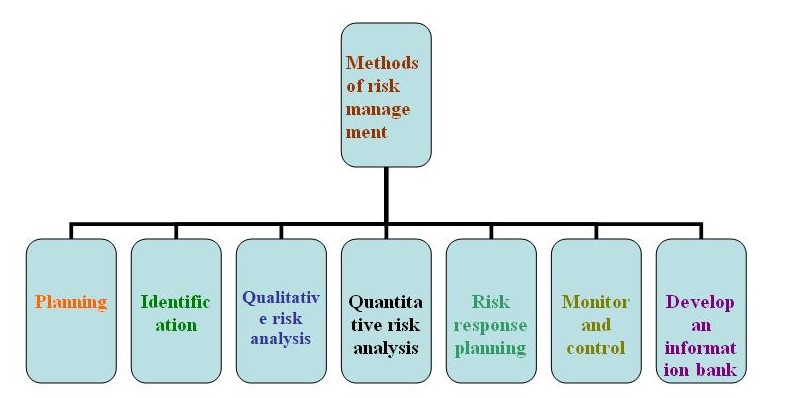
Methods or tools of risk management have maintained sequential steps express as follow. Uses of These steps are cooperative in reducing corporate risks.
- Risk management planning-at first, for a project full adaptation of risk management planning is required. There also should be mentioned the approaches or the way to take risks.
- Risk identification-second; define the risk which could affect organisation’s project. In this stage, criteria of the identified risk also are described.
- Qualitative risk analysis-how project objectives are affected by that risk there should be a predetermined standard level that control performance quality of the project.
- Quantitative risk analysis- task of this step is to determine the way of project objectives implication and possibility of risk identification and the sequence might be occurred.
- Risk response planning-fifth stage develop reducing methods or procedures or techniques of project objectives threats to seek the opportunities.
- Monitor and control risks-in a project life-cycle, accomplish risk controlling arrangement so that existing and new risks could be monitored and controlled effectively at a same time.
- Develop and maintain a risk management information bank-it is the last stage in which list of identified risks, their execution procedures and the achievements after execution is documented. This information bank is circumstanced as bellow:
- Classify environmental factors (both internal and external) that affect the project’s objectives.
- Classify the source of risk and preface hypothesis of the project plan.
- Identify possibility of taking risks and their impacts on the project.
- Key factors of risks and their changes with the change of environment also organised as document.
- Identify the impact of qualitative and quantitative risk analysis on the environment of the project.
- Describe the procedures of actions taken by the management meeting against the identified risks.
- Results occurred after accomplishment of the anti-risk issues.
Aforesaid principles of an information bank is not restricted, those are for ensuring better quality and advanced this collection of information whether required.
Cycle of risk management
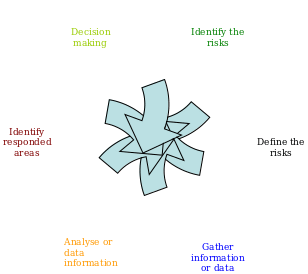
Risk management cycle is a circular flow that includes-identify the risks, define the risks and risks factors, gathered information, analyse the gathered information, identify whether risks are responded and finally make a decision. A short description of this circle is presented as bellow. Throughout a project life-cycle this circular flow acts as a dynamic force.
- Identify the risks: at each level of an organisation-project, strategic business level and corporate level first task of this flow is identify all categories of risks. For corporate level, risks are relevant to make decision whether need to invest. In case of, strategic level at first it is essential to understand project objectives, cost of the project and project plan. Here also be ensured various tools suitable for the project, types of the project and available resources.
- Define or label the risks and risks factors: risks factors are different for each level. Corporate level faced factor related to invest. Strategic and project level involve in performance, costs and time as the risks factor.
- Gathered information: collection of information depend on the level of risk management.
- Analyse the gathered information: analysis of gathered information is categorised into two way-qualitative and quantitative. Quantitative analysis discuss on way of project implication. On the other hand, qualitative analysis measure performance standard of the project. For analyzing risks there also have used Delphi method, Hurdle method, cash flow analysis, and probability analysis.
- Identify areas responded by risks: identified areas responded by risks are-efficient control of events, efficient control of risks, in which area or persons who hold risks, probability of risk occurrence.
- Make a decision: at last risk management cycle reached a decision for all level. They execute strategy for the selected project; make a sequence of the project objectives and choose investment or portfolio criteria.
Risk management presented in Turnbull report
With the aim of risk management in 1999, “Institute of Chartered Accountants” published a report named “Turnbull”. This report is a guide for Directors on the Combined Code. In this report, risk management is clearly identified as justifying risks not to remove risks. Factors focused in “Turnbull” report in the context of risk management is explained as bellow-
- Internal control-as per Turnbull report, risk management can improve internal control system effectively. As a result, conflict among inter-administrative group would reduce competently.
- Internal control system-Risk management develops the internal control system such a way thus a company as well as B & B perform at best and motivate their employees for extraordinary performance.
- Make revise system effective-continuous development of product and adopt new product is a creation effective risk management system. So, risk management is a method to revise manufacturing system.
- Appropriate risk response strategy- adopts strategies in order to identify whether risks would be response or to be taken.
- This report commending that executive uphold & have principal accountability for a method of internal-controls to assess and agreement with both economic as well as non-financial risks between other items, the danger that executives can destroy the corporation’s reputation by their public declarations.
- Efficiently manage risks- cultural environment of an organisation build up the method of managing risks. In Turnbull report, there are a set of steps those would be effective in managing risks.
Reasons of prosecutions
The well known buy-to-let lender Bradford & Bingley has been suffering in the course of a triple impulse of credit crunch associated with write-downs on investments due to elevated wide-ranging borrowing costs as well as growing numbers of borrowers failed to repayments. B&B has been for the most part susceptible to the money markets crisis for the reason that it has formerly raised additional a quarter of its investment from the money market. The process of fund-raising has turned into difficult, more costly to protect and inadequate for the cause of its credit crunch and fall down of the US sub-prime money market as well as recession
The management of B&B had failed to gesture the deterioration of market trend rapidly or management has hidden the real corporate risks to the stakeholders. Even they raised fund by right issues but failed to take any particular steep to overcome the situation. In April 2008 the B&B proclaim an £89 million hit which ultimately turned £142.1 million into write-downs as bad credit, did not mentioned in the previous year. But the management has until now been quite optimistic on the prospect of buy-to-let market and exposed that the quantity of borrowers failed to repayments has been getting higher enthusiastically.
In mid 2008, Bradford & Bingley was compulsory to move up millions of pounds by rights issue. The responsible bodies for underwriting the issues had lost the entire of their money with the announcement of B&B’s nationalisation. More or less 850,000 offered diminutive shareholders would also lose the entire their money by the announcement on 29 September 2008. Moreover management of Bradford & Bingley sold 200 retails outlets to the Spanish bank Santander, though the retails savers up to limit £ 35000 has been protected by the Governmental guarantee.
SWOT analysis of Bradford and Bingley
The term “SWOT” is stands for-strengths, weakness, opportunity and threats. SWOT analysis of B & B is presented in following table in the context of “Turnbull” report and corporate risk management. This report presents corporate risk management as an effective tool for an organisation. Though there occurred a few prosecutions by senior executives or staffs in UK. SWOT analysis of B & B could be ready to lend a hand to reach a new resolution, make new strategy and identify effective solution for the contemporary problems.
Recommendations
Based on prosecution reasons following are the recommendations or solutions that any company would be adopted –
- Internal conflict: first recommendation is efficient control of internal conflict among inter-administrative groups.
- Taking a huge amount of remuneration: make a restriction in taking huge amount of remuneration.
- Corruption made by top level executive: a strict inspection or monitor where any chance to create any corruption or fradulary activity caused by senior executives.
- Internal control system: it should adopt fruitful internal control system and thus the firm could control internal conflict and also manage risks efficiently.
- Ineffective revise system: – this system develops product quality system as a result product could be developed and revise whether needed.
- Internal audit system: – it creates transparency in internal audit system. This would be reduced corruption of the organization.
- Fail to manage risks: – risks management should be tactful rather than undiplomatic.
- Inappropriate risk response strategy: – strategy of risk management would be appropriate for performance evaluation, minimizing costs as well as maintain target time frame.
Conclusion
This paper describes different factors of corporate risk management, methods, and levels and also includes a case study of B & B in the context of Turnbull report. Here also present a short description of risk management according to the report. Finally, SWOT analysis and recommendation for the barriers in corporate level risk management.
Bibliography
- Associated Newspapers Limited (2009), Advice for Bradford & Bingley customers. Web.
- Brigham, E. F., and Houseton, J. F. (2004), Fundamentals of Financial Management, 10th Edition, Thomson south-western, Singapore, ISBN: 0-324-17829-8
- DeCenzo, A. D., and Robbins, S. P. (2007), Management, 8th ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Singapore, ISBN: 9812-53-171-8
- Dignam, A., (2007), Capturing corporate governance: The end of the UK self-regulating system, International Journal of Disclosure and Governance Vol 4, 24–41.
- Gomez-Mejia, L. R., Balkin, B. D., and Cardy, L. R. (2006), Managing Human Resource, 4th ed., Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi.
- Griffin, R. W. (2006), Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x
- Guillén, M. F. (2008), The Global Economic & Financial Crisis: A Timeline, The Lauder Institute.
- Holt, H. H., (2002), Entrepreneurship New Venture Creation, 6th Edition, Prentice- Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi, ISBN: 81-203-1281-3
- Hills, G (2008), Managing Principal: Business Risk Practice, Wills Technical Report.
- Meredith, J. R. and Mantel, S. J, 2008, project management a managerial approachm 6th Ed., Jhon Whiley and sons,Inc., Singapoure, ISBN: 13-978-0-471-74277-7.
- Pandey, I. M. (2006), financial management, 9th Ed., Vikas publishing house PVT Ltd. New Delhi, ISBN: 81-259-1658-X.
- Ross, S and et al, (2005) Corporate Finance, 6th edition, McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 9780073134291
- Scott, Nigel (2008), BACKGROUND: Bradford and Bingley’s turmoil – a look at the facts, Johnston Press Digital Publishing,
- Stoner, J. A. F, Freeman, R. E. and Gilber, D. R. (1995), 6th Ed, management, Prentice hall of India, PVT. Ltd. New Delhi, ISBN: 81-203-0981-2.
- Wood, F., and Sangster, A. (1999), Business Accounting 1, 8th Edition, Pitman Publishing, China, ISBN: 0273638394
- Zikmund, W. G., (2003), Business research methods, 7th Edition, Dryden Press, ISBN: 9780324320879