Introduction
Successful entrepreneurs know that planning is an important ingredient when starting a new business venture. In the current competitive business environment, an entrepreneur will need to conduct an extensive market research in order to understand relevant external forces that have positive or negative impacts on a specific business venture. With this knowledge, it would be necessary to develop a business plan that takes into consideration internal forces, and external environmental factors relating to the business operations.
According to Kraten (2010), a pre-start up business plan is a little more complex than planning for an already established business entity. The scholar says that when developing a pre-start up business plan, there may not be any referential documents that may guide an entrepreneur on a path to be taken in a particular industry. A plan will have to be developed from a scratch, with no clear information about how the new firm may interact with its external environmental forces.
This means that the planning process will have to be based on various assumptions. According to Lasher (2013), these assumptions make it difficult for a planner to draw a reliable plan because any wrong assumption made may have a devastating impact on the overall performance of the new firm when it becomes operational. This is made worse by the fact that mistakes at this initial stage can be very costly, especially if a new venture has financial constrain.
Wrong assumptions may lead to serious financial losses. For a new firm, starting with such losses may not only be strenuous to its limited resources, but may also discourage an entrepreneur, a fact that may affect the desire to press on with the investment. This explains why some business start-ups fall off soon after starting their operations. In case such a new venture depended on funding from other investors who are not directly involved in its operations, mistakes in its planning may be an enough reason to drive them away, a fact that may lead to a further financial strain. This means that the plan must be effective enough to avoid wrong assumptions.
It must clearly demonstrate an ability of the new firm to generate enough income to sustain its own operations. This will help it to attract more investors and gain competitive edge against other established competitors. This research paper will focus on how to develop a pre-start-up business plan for novice entrepreneur.
Pre-Start-Up Business Planning for Entrepreneurs
Pre-start-up business plan is a unique plan that is very different from other business plans for established firms. At this stage, a planner will be trying to create a business in a paper with all its operational structures. A planner will need to create some of the forces that a new venture may face once it gets operational. This may not be an easy task, as Kraten (2010) observes. This is so because sometimes it may not be easy to make an accurate prediction when the business is not yet operational. In most of the cases, planners are always tempted to make predictions that are beyond practical estimations.
Any entrepreneur is always optimistic of a new business venture, sometimes making a prediction out of success of an already existing firm. What is always forgotten is that the existing successful firm took a path to arrive at its current attractive status. Making assumptions that a new business venture may be as successful as an already existing one is a common mistake that has made some entrepreneurs to incur serious losses.
However, Günther (2012) says that when making predictions for new business ventures, one cannot ignore basing assumptions on the existing firms operating in the same industry. This is so because a new firm will be exposed to similar external environmental factors as the existing firms. However, care should be taken to distinguish the differences in the internal factors between a new business venture and that of an existing firm. This may also be challenging for a planner, especially defining the role of experience in defining superiority of operations and productivity.
In some cases, novice entrepreneurs- in trying to draw-up a pre-start-up business plan- experience the challenge of defining the past and present in order to predict the future. According to Lasher (2013), the best way of defining the future is by analyzing the past experiences and the present forces. This would enable a planner to develop a clear pattern of the changing factors within the environment. This pattern may be used to predict possible changes in the future so that they can be factored in during the planning process. However, a new business venture lacks the past and present data that can be used in developing the pattern.
It means that a plan will need to depend on his or her own experience and ability planner to make an accurate prediction of the forces to be expected. These are some of the issues that an entrepreneur must put into consideration when coming up with a plan for a new business venture. Minimizing errors that may arise out of these challenges is core to achieving the best result in a new business start-up.
Importance of pre-start-up business planning for novice entrepreneurs
According to Lasher (2013), a pre-start-up business plan is a document that cannot be ignored by any novice entrepreneur who intends to make a successful entry into a given industry. The scholar says that although developing a proper pre-start-up business plan has numerous challenges, it is central to achieving success for a new business organization. At this stage, it is important to define the importance of this plan to novice entrepreneur so that they can understand its relevance to them in achieving success.
One of the biggest challenges that entrepreneurs face when planning to start-up a business venture is the best way to enter a given market. According to Kraten (2010), some of the issues that entrepreneurs need to check when entering a new market include the cost of market entry, resources needed for the entry, time that it will take to make the entry, and the manner in which the existing players may react to the entry.
In most of the cases, firms may prefer the cheapest strategy that will require minimal resources and a shorter duration. It is also preferred that the strategy should not have a sudden impact on some of the existing players, especially in cases where a new start-up is a smaller firm planning to operate in an industry that has dominant players controlling the largest market share. The dominant players may react to such new threats in ways that may be disastrous to the new firm.
In such cases, they may decide to engage in price wars, something that a new start-up may not have the capacity to sustain for a long time. This means that the preferred strategy will be one that will allow a new start-up to enter the industry in the most efficient way, and in a manner that will not steer competitors into considering application of any negative competitive practices.
A pre-start-up business plan plays an important role in defining the most appropriate market entry based on various factors. A planner will need to make a survey to understand the industry and its current players. A number of market entry strategies can be chosen based on a number of factors. In case a new firm has a stronger financial power, and it has an ability to outmuscle its existing players, then it may consider an entry strategy that will create an impact in the industry.
This may involve intense marketing campaigns, widely publishes launch, and friendly pricing that will attract a large number of customers. On the other hand, if existing players are too strong to be outmuscled by the new firm, then a more silent strategy may be appropriate. A firm may consider personal selling as an appropriate strategy. This will allow it some time to gain strength into the market so that it can engage its competitors directly at a future date when it has enough experience and some financial strength to do so. The plan will also determine its budgetary allocations to ensure that the market entry approach is less expensive.
A pre-start-up business plan that is properly detailed will help an entrepreneur to understand some of the forces that are to be expected in a given industry. According to Granger and Sterling (2012), the reason why some businesses fail is because their owners did not take time to analyze some of the forces within that industry before starting operations. The level of competition within a particular industry is one of the factors that must be considered before venturing into any industry. Sometimes the level of competition can be so stiff that any mistake may lead to a firm being edged out of a particular market. The rivals could be using price wars to remain dominant in the industry.
The established firms can sustain price wars for some time because they have accumulated wealth. However, a new firm may not withstand such wars because it is depending on its profitability to sustain its operations.
When entering such competitive industries, it will be important for a new business entity to come up with a plan that it can use to avoid the war among major players. Such pre-start-up business plans are important in developing ways through which the entity will evade such stiff competition. Another important environmental factor that needs to be analyzed before a firm can become operational is the dynamism in a particular industry. Pre-start-up business planning plays a pivotal role in analyzing the dynamism in a particular industry so that an entrepreneur may know what to expect. Before drawing a plan, it will be necessary to analyze these forces so that one can understand how the changing industry pattern may affect a new business, and how the new business can manage the changes for its own benefit.
Pre-start-up business plan is very important in business forecasting. In some instances, a novice entrepreneur may need a proper channel that he or she can use to predict the future business environment in a particular industry. When drawing a business plan, it will force a planner to conduct a market research to determine trends that has been existing among the players in a particular industry. With this information, it becomes easy to develop a pattern that may be use to predict the future of a particular industry. Predicting the future trends is one of the best ways of gaining a competitive edge over other competitors in a new market.
It enables a firm to understand how such forces may affect the industry, and how the effect may impact on the individual firms. With such information, it becomes possible to plan for a mechanism that can be used to manage a change when it comes. The management of the firm will be in the best position to plan for such changes by identifying relevant change management strategies. According to Lasher (2013), some of the changes may require use of the emerging technologies to manage them.
Embracing such technologies may not only be a costly process, but also one that requires a workforce that has the right technological knowledge. Many firms have failed in their first years because of their inability to predict the emerging forces in a new market.
In some of cases, a change can be so sudden that it may prove to be strenuous to manage it within the right time. Such sudden changes may disrupt normal programs of a firm to a great extent, unless measures are taken to restore equilibrium within the shortest period of time. Having a clear plan on managing these changes may be very important because the management will know when to apply technological changes, and the right workforce to hire in order to manage the changing trends. This will give a firm a competitive edge over other market competitors.
According to Cummings and Worley (2014), the best way to succeed in a new market for a new business entity is to identify a market niche that is undersupplied with relevant products. Making an entry into a well established industry can pose serious challenges for a new firm. The best way of avoiding such a challenge is to identify a niche that it can best meet its expectations better than existing players. When developing a plan, an entrepreneur may need to understand what customers need in that particular industry. After understanding their needs, a planner will need to analyze what the industry players deliver to them.
With this information, it will be easy to identify areas that are undersupplied with the relevant products. These are the areas that should form major target market for this firm. They should be considered as the desirable market niches that the firm should determine how to meet their needs. Focusing on these niches do not only make the new firm to avoid stiff market competition by making its products unique, but they also offer the new firm a golden chance to operate in an industry that others have not operated before. This means that the inexperience of the new firm will not be an issue because it will be the pioneer in that particular industry. Other players entering in the industry will be new to the forces that play off in that particular market, making their experience irrelevant in the market.
When developing a pre-start-up business plan, Lasher (2013) says that the planner will need to conduct an environmental scan of the new business venture. This involves identifying the weaknesses and strengths of the new business venture. It is assumed that a new business start-up may not have a competitive edge over its market competitors. However, this is a misleading concept because these new start-ups may have strengths that they can use against their more experienced counterparts. The problem is that most firms rarely conduct this self-analysis in order to identify the strengths.
Identifying the strength makes it possible to develop the strategies through which they can be used for the benefit of the organization. Identifying the weaknesses of the firm will be important so that measures can be taken to address them to minimize their negative impacts on the organization.
Developing Pre-Start-Up Business Plan for Novice Entrepreneurs
Developing a pre-start-up business plan for novice entrepreneurs is an elaborate process that entails a series of activities. The planner must be aware of the important stages that the planning process should take in order to develop a document that is able to meet the expectations of the stakeholders. As mentioned above, the document is not only important in defining the path to the success of a new firm in its operations, but also in helping the firm to attract investors. An investor will need to review the plan in order to determine the viability of the project. This makes it easy for him or her to determine the relevance of investing in the firm.
Every investor only needs an investment project that can give returns after a specific period. For this reason, the document must be well prepared to convince all the stakeholders who will be needed to support the project. The following are the specific steps that should be followed when developing the pre-start-up business plan.
Stages in Developing Effective Pre-Start-Up Business Plan
Stage 1: Self-Assessment
As mentioned previously, one of the most important stages involved in the planning process is the self-assessment. Before starting up a business entity, it is important for an individual to assess the internal factors that makes the business able to operate in a particular industry. The assessment may take various approaches depending with the self-assessment tool that one decides to use. The most popular tool that is widely used is the SWOT Analysis. Using this tool, the researcher will need to identify the strengths that it has when entering a given market. This may include issues such as flexibility and vast knowledge in a particular field.
Most new business start-ups are always flexible to changes because they have not developed rigid structures that are slow to adopting the change. The owners of the business and other team of experts operating the new business may also have enough knowledge and skills in that particular field, making it easy to develop successful models of operations. Identification of weaknesses will be necessary so that the management can devise ways of addressing them before they can have any serious impact on the firm. In most new start-ups, common weaknesses may include limited resources that can be used to support the operations of the firm. Finding ways of accessing extra finance may be the best way of managing this weakness.
The external environment has some opportunities that should be exploited by the new firm once it starts the operations. These opportunities should be identified prior to the market entry by the firm. Common opportunities may be the growing economy that makes it easy for expansion of business entities. Another opportunity may be the easy access to the capital market for new business start-ups. In most cases, financial institutions are always slow when it comes to extending loans to new start-ups.
In cases where this is readily available, it should be taken as an opportunity to access extra funding for the firm. However, the firm should be keen to identify some of the threats in the market that may affect its operations in the market. Common threats that must be identified when developing the plan include issues like stiff competition from the leading players in the industry. Insecurity cases by terror groups or cyber criminals must also be identified and mitigation measures clearly stipulated so that they may not disrupt the operations of the business entity.
According to Cumming (2012), sometimes it may be necessary to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the internal and external structures that may have a direct impact on the operations of a business unit once it starts its operations. The diagram below shows some of the areas that must be given a clear focus so that any issues that may arise from them can be clearly defined.
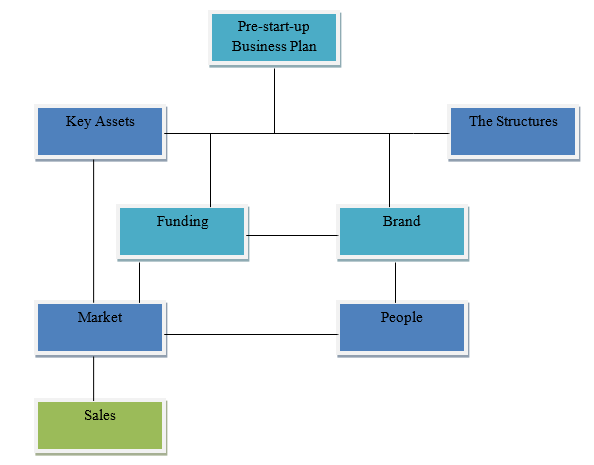
As shown in this diagram, when drawing a pre-start-up business plan, the first two areas that should be given proper focus should be the key assets of the organization and the structures. The assets include all the financial and nonfinancial properties owned by the new business that will make it possible for it to operate in the chosen industry. The structures are the strategies it has in place on how it will use its existing assets to generate value to the shareholders.
The assets are meaningless if they cannot be used adequately to generate adequate income. The next step of planning will be to identify the sources of funding for the organization, and the appropriate brand it shall use in the market. According to Finch (2013), a business plan must define the source of funds it shall use in its operations. The owner may be the major source of funds for the organization. Donations from friends and family members or loans from the financial institutions may be the other alternative sources of funding. This must be clearly started in the plan.
The business unit will need a business brand that it plans to use for its operations. The brand name must closely reflect what it seeks to offer to the customers. The name chosen should be easily memorable to avoid confusion. A brand image should also be chosen that is appealing to the eye. The next process involves the identification of the market and the people. As mentioned previously, it is important to identify the market that is targeted by a given product. The desirable market should be a niche that is yet to be exploited by other market players. The chosen market must be one in which the firm has the best capacity to satisfy its needs.
The people are the employees who will participate in the process of delivering the products to the customers. They should have the relevant skills that will make them efficient enough in their service delivery. The next process would be to make a prediction of the sales that should be made when the entity becomes operational. Making this prediction that will help the management to predict a possible income that will be generated and the expenses that will be incurred per a given period.
Stage 2: Extensive and intensive research into the industry
The next step after conducting the above internal planning processes will be to conduct an extensive and intensive market research in order to identify factors that will have direct or indirect impacts on the organization. When conducting an extensive research, focus will be to have a broad knowledge of different factors that may affect the business operations of a new firm. Analysis may involve understanding government policies that are relevant to the industry, the changing trends in a particular industry, use of emerging technology, the nature of relationship among competitors in this industry, the strength of suppliers and customers, the power of employees’ union, and many other relevant external environmental factors.
This broad analysis of these factors is crucial because it enables the entrepreneur to know all the relevant environmental forces that must be planned for in order to avoid any consequences that may arise due to lack of proper strategies on how to deal with them. Intensive research into the industry involves identifying the specific issues in the environment that have a direct impact on the operations of the firm and then conducting a detailed analysis on them. For example, the issue of market competition is an important factor that should not be analyzed casually. These factors should be analyzed to determine how they can be managed properly for the benefit of the organization.
Stage 3: Re-evaluating internal resources
When the team has successfully conducted an evaluation into a particular industry, the next step will be to reevaluate internal resources to determine if they meet stated expectations identified from the above analysis. The internal resources, including employees, may need some readjustments in order to ensure that they meet the expectations set by the external environmental factors.
Stage 4: Developing a plan that is sensitive of both internal and external factors
The last step will involve development of a plan that is sensitive to internal strengths and weaknesses; paying special attention to market opportunities and threats that external environment poses to a new firm. The plan must be effective enough to meet the vision of a firm within the desirable time.
Implementation of pre-start-up business plans
According to Blackwell (2011), good plan must be effectively implemented in order to create the desired result. The implementation process of the business plan should involve detailed activities to be conducted as per the guidelines given in the plan. This pre-start-up business plan will need to be implemented when setting up a new business entity. All the processes described in the plan must be implemented with precision, and all stakeholders identified and their role clearly stated during the implementation process. This way, all the stakeholders will know their role in this business process, and how they are expected to undertake these roles.
The top management must ensure that the finances of the new entity and other resources are used as per the plans of the organization. Any extra expenses should be made with a clear explanation as to why they are necessary, and only those that are justifiable should be authorized. During the implementation, it may be necessary to identify the new forces that were not captured in the plan, and how they may affect the entire process of implementing the pre-start-up business plan.
Conclusion
Pre-start-up business plan is important in defining the level of investment that an entrepreneur will need for a business start-up. In most of the cases, entrepreneurs always underestimate the financial resources that are needed to start up a business unit. This is common because an entrepreneur may lack the knowledge about specific assets that is needed to start up the business unit. The fees needed for the business to be authorized to operate may also be ignored by an entrepreneur if a proper plan is not drawn. This is what this pre-start-up plan seeks to address. It focuses on identifying all assets needed to start the new business, all the charges needed by various entities, and any other relevant cost that may be needed to make the new business unit operational.
To an entrepreneur, this document will provide enough information about all the resources needed, and time at which they will be needed either before starting operations or during its early days of operations. This way, cases of starting a business unit and halting operations because of depletion of resources may be eliminated. When this document has been developed, its implementation should be done with precision to yield the desired results.
References
Blackwell, E. (2011). How to prepare a business plan. London: Kogan Page.
Cumming, D. (2012). The Oxford handbook of entrepreneurial finance. New York: Oxford University Press.
Cummings, T., & Worley, C. (2014). Organization development and change. Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning.
Finch, B. (2013). How to Write a Business Plan. London: Kogan Page.
Granger, M., & Sterling, T. (2012). Fashion entrepreneurship: Retail business planning. New York: Fairchild Publications.
Günther, A. B. (2012). Entrepreneurial strategies of professional service firms: An analysis of commercial law firm spin-offs in Germany. Köln: Kölner Wissenschaftsverlag.
Kraten, M. (2010). Business planning and entrepreneurship: An accounting approach. New York: Business Expert Press.
Lasher, W. R. (2013). Practical financial management. Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning.