Abstract
The purpose of this report is to examine how do customer make a choice on instant noodle and perceive the buying behavior. The aim of this project is to examine how customer makes a choice on instant noodle and how the buying behavior influences the product.
No doubt, food protection has a lengthy history. Smoking, salting and ventilation are almost primitive; half the sea-borne deal of the Roman Empire seems to have consisted of a harmful smelling fish take out called garum; canning dates from the early 19th century, although its widespread acceptance came later. The 20th centurys contribution was to convert mere conservation into short-cuts for consumers: expediency foods that simplified the commerce of meal preparation, helped by a rising variety of new technologies, like freezing.
The paper proposes that consumers and their behaviors be worthy of (much) more consideration in food market. After a few website references (about noodles shopping and trade initiatives) and after a concise literature review of recent business of noodles and consumer behavior literature conceptual frameworks are suggested. As an open end, the paper contains some empirical references, related to consumer honesty, tax loyalty and to motives for buying organic food, and suggests the development of a consumer morality measurement instrument. Also, questioners take place from the local consumer of instant noodles, many people from the “retail stores”. The selection of the consumers was random.
Introduction
Consumer behaviour is distinct as the behaviour that consumers show in looking for, acquires, using, assesses and disposing of products and armed forces that they wait for will please their individual needs. Consumer behaviour includes how consumers believe (their mental decisions) and sense, and the bodily actions that consequence from these choices (the purchase).
Background
The effective choice of customer on instant noodles is now seen as critical to gaining improvements in organizational performances. This is potentially good news for those involved in buying behavior because it means that there is greater interest in our subject than before. Other markets who might in the past have been scathing about the marketing profession and its contribution are being forced to take notice of research that suggests that ‘people really do make the difference in choice of noodles’(Marchington and Wilkinson, 2002). Before the discussion is going any further, it is crucial to get the same understanding about the Consumer Behaviour itself. According to a small number of sources, Consumer Behaviour studies the process of a buying decision of customer (in group or personage). Basically put, it tries to understand What, Who, When, Where, and Why they consume a product or service.
Behavioural patterns have many important implications, both theoretical and practical, for virtually all kinds of Buyer practices including product analysis, purchase, selection, training, development, performance appraisal, compensation, and even company relations (Werner, 2000; cited by Tsaur and Lin, 2004). With the dynamic environment, undoubtedly, each firm attempts to study and understand the consumer behavior due to businesses stay in business by attracting and retaining customers (Arnould, Price & Zinkhan, 2002, p6). As the vital consumer decision-making unit, family are most regularly examined by many marketers because decision making by family differs in many ways from decisions made by an individuals. According to Hawkins, greatest, and Coney, the term of family decision making is the method by which decisions that straight or circuitously engage two or more family members are made (Hawkins, Best & Coney, 1998, p195). Generally, dissimilar motivations and diverse family life cycles will cause unusual decision making process. In the meantime, with the different decision making procedure, the dissimilar members of family would play a variety of roles and directly influence the consequence of decision.
Consumer behaviour is distinct as the behaviour that consumers show in looking for, purchase, by means of, evaluating and disposing of foodstuffs and armed forces that they be pregnant will please their individual needs. Consumer behaviour includes how consumers believe (their cerebral decisions) and feel, and the bodily actions that consequence from these choices (the purchase).
Abraham-Murali, Liza, and Mary A. ( 2000) “pecking order of needs” theory recognizes the higher-order needs (ego needs and self-actualisation) and lower-order requirements which are physiological, protection, and communal needs of consumer. Both low and far above the ground participation acquires are on the whole aimed to please these needs. Normally though, low participation acquires more often than not do something to please the lower-order needs at the same time as far above the ground participation purchases do something to please the higher-order wants.
Past investigate has established clearly the significance of pre-purchase in sequence surveys inside the buying procedure. It is a significant step for consumers, particularly in the case of extremely involving merchandise and services. (Ajzen, Icek, and Martin Fishbein. 2001) In order received by the person brain is processed as a very important contribution. The in order process recounts to together the consumer’s cognitive aptitude and the difficulty of the in order to be procedures.
Purpose of the study
The learning of consumer performance and related applying methods can advantage in sympathetic human mind and its choice creation processes, but the major beneficiaries are the corporation that creates the consumer foodstuffs. The different methods adopted by corporation to add to their sale are all bottoms on their majority influential tool called the announcements.
- Consumer ethics: Different research traditions
Consumer ethics is characterize, but under characterized as a journal article and textbook topic, both inside business and marketing morals and inside consumer behavior research. The subtopics partly cover, but there is no ordinary frame of reference. So far, consumer ethics or corruptly aggravated consumer behavior have to be read as a common denominator of more than a few research traditions, such as research regarding ethically dubious consumer behavior (e.g. different kinds and degrees of consumer deceitfulness), regarding consumer voting behavior (i.e. boycotting definite products and/or from definite producers, or intentionally buying from good business citizens) and, as a wide rest group research about accountable consumer behavior (e.g. buying noodle products for time management reasons) (Baker 2001).
- Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior learning the consumer performance, the way consumer feels about exacting products, how customer created their decisions concerning such foodstuffs, and how the consumers’ knowledge confines can be old to there the manufactured goods more professionally (Dickerson, Kitty G. 2002) to influence them to go for it. Consumer perception is of great significance, no substance what is the scale of commerce; it can help to augment the sale. People be supposed to be complete conscious of the foodstuffs character and convinced to buy it. Consumer perception assists the advertising strategies to set the cost of product, and also improved promote the manufactured goods in the consumer advertise. In an average wonderful marketplace there are additional than 10,000 different foodstuffs, all of brands dissimilar from every other. It is certainly a hard decision for a being to make a fitting choice in the center of such a great variety of foodstuffs. Here the real advantage of consumer perception steps in. Now, the advertising techniques based on consumer mind make the genuine dissimilarity in the consumer’s conclusion creation process (Bruner, G. C. & Pomazal, R. J., 1986, p44).
The answers to on top of questions transport concentration to the theme of consumer performance and the linked field called consumer perception. Consumer perception is the learn of grassroots’ response to, and connections with crop and in order connected to those foodstuffs. It is worried with the mental processes that decide consumer incentive and performance connected to the do something of buying a manufactured goods. The perception of consumer performance uses emotional methods, and technical tests to appreciate, examine, measure, and predict consumer performance. Processes that strength be deliberate by consumer psychologists comprise a consumer’s awareness, memory, feeling, and incentive in family member to a sellable manufactured goods. Merely, it is the technical study of the performance of consumers, which can be explained as an person who uses the foodstuffs, goods, or armed forces of a number of corporation.
Before going additional into consumer perception and the advertising strategy benefit from it, let’s first believe some significant aspects of the person performance. Human character is mainly collected of dissimilar ego states. An ego condition may be distinct as the scheme of connected behaviors in reply to a convinced stimulus. The character consists of a lot of ego states other than merely three of them are essential conditions.
In the questioners of this research that was set, different stages of the consumption procedure were given, the first being ‘search’. Though, this assumes that the consumer has previously decided that they desire the manufactured goods, and it is up to the marketers to induce the consumer to decide their particular brand or product over competitors. I believe that it could be said that a function of a marketing sector is to convince a possible consumer that they require a product. An instance of this would be when a new knowledge comes onto the market. Prior to the new knowledge becoming obtainable, consumers did not desire the product, as they did not know of its continuation.
If we analyze then we come to know that this existing Issues examine the food purchase behavior of low-income households, complementary it with that of superior income households, in order to get a better sympathetic of the economizing practices of the poor. Low-income customer can make longer their food dollars in a number of ways: they may supermarket in reduction foodstores; they may purchase and consume less food than top income shoppers; they may purchase inexpensive (and possibly inferior class) food products; or they may rely on some mixture of all three.
Aim/Hypothesis
The aim of this project is to examine how employees perceive the Consumer choice for noodles and how his behavior influences the products. This project has also the purpose to find what measures the consumer choice and decision has taken in relation to the noodles.
The hypothesis is that some problems exist between consumer choice and noodle products available in different departmental stores. In more economical terms, Consumer Behaviour blends the subsequent factors of Perception, Sociology, Socio-perception, Anthropology and finances. Due to size & range limitation of the report, these essentials are not to be discussed too deeply.
Objectives
The main objectives are:
- To find out the customer’s perception regarding the instant noodles.
- Identify How Do Customer Make a Choice on Instant Noodle
Dissertation structures
Here is a brief summary of what the following chapters are going to include, which will help to get an idea of what the author is going to present in each chapter. The dissertation will be divided into four sections:
The Literature Review
In this chapter existing information from secondary research is going to be given like books, journal articles, reports and electronic databases.
The purpose of this chapter is to give the knowledge for the overview of Buying behavior and how instant noodle is popular in the UK market. This chapter is going to help the author to improve the knowledge from the research subject and to create the appropriate questions in order to give the focus on the research objectives.
The Research Design
After gathering the existing information (Literature Review) the next chapter has the purpose to offer a concise description of the research design and methodology.
The author is being used both qualitative and quantitative research for more complete image of the research situation. The methods that are going to be used for the purpose of this research are questionnaires with close questions for the consumers of the organizations and interviews with open questions to the two consumers of the instant noodles.
Analysis
After the research is being completed, with the help of some electronic methods like ‘record’ they will give the analysis of the questionnaires and also the interviews. The data will be presented in methodology and findings chapters.
Conclusion
Based on previous analysis and with the combination of the literature review the conclusion will be throwing.
In the final chapter the author is going to compare the research questions the author had at the beginning of the research with the final results. Moreover the author will give some recommendations from the results and the analysis, which will help the retail stores to be improved.
Literature review
Introduction
The purpose of this chapter is to provide a summary as well as an interpretation from research findings of the secondary data, by books, journal articles, reports, electronic databases and websites in order to drown the literature. Moreover, the research is concentrated on the consumer choice on instant noodles.
This chapter is very helpful in increasing the knowledge relative to the studying area since the results and the findings of the primary data will be related with the literature review. Therefore, the knowledge from literature review is going to provide a more professional research that will focus on the purpose of this research. Also, the purpose of this is to offer an overview of significant information published on the topic in order to narrow down the research questions to a specific, suitable form.
The significant part of the marketing procedure is to appreciate why customers or buyers acquisition one exacting product. According to Levitt, J. (1960), the marketing concept is a customer-satisfying procedure, not a goods-producing procedure. An industry begins by means of clientele and their needs, not with a patent, a raw fabric or a selling skill. The gratitude that an organisation can survive only as long as it fulfills customer wants and requirements by methodically understanding their substitute partners makes the study of the customer necessary. (Kotler, 2000) So, without understanding customers, it is hard for commerce to respond precisely to customers’ desires and needs.
Consumer Behaviour
According to the expert of American Marketing Association, consumer behavior is defined as the active dealings of affect and cognition, behavior, and ecological events by which human beings carry out the exchange aspects of their lives. Consumer behavior is the perception at the back marketing and the behavior of customers in the advertising environment.
one more popular definition of consumer behaviour is the study of persons, groups or organisations and the procedure they use to select, secure, use and arrange of products, services, knowledge or ideal to gratify needs and the impacts that these procedure have on the customer and society. (Hawkins, 1998)
Consumer Behavior Model
A General Model of Consumer Behavior
Beginning at the left surface of the model, observe that a box labelled “stimulus state of affairs” is shown to authority the consumer. The stimulus state of affairs is the complex of circumstances that collectively act as an incentive to elicit response from the consumer. This suggests that consumer behavior is not characteristically consideration of as being elicited by a solitary incentive. Furthermore, quite, consumer behavior is considered to be the outcome of patterns or constellations of stimulus. Moreover, for instance, when the consumer acquires a can of “Noodle” brand drink, that consumer behavior was not just the result of the cost of the manufactured goods. Instead, we would have to believe the price of the product, the individuality of the announcement of the product, the wrapping of the manufactured goods, the persons past experiences with the creation, the assignment of the creation on the shelf, and so on.
According to the expert analysis at first glance, this might appear frustrating to the promising consumer psychologist; the incentive situation that crashes upon the consumer seems to be unmanageably multifaceted. However, it is significant to be familiar with that the world in which clients performs is, in reality, tremendously complex, filled with repeated commercials, attractive packaging, and puzzling choices.
Next, the replica specifies a figure of internal procedures. Therefore, these interior processes are a connected series of changes that happen inside the person. Interior processes can be viewed as consequents that are reasons by something else, or as past history that reason something else. When observation as consequents, internal procedures are consideration of as the result of the stimulus situation, the individual’s own behavior, the social context, the educational context, other interior process, and the connections flanked by these sets of variables. This research focused on this truth that investigate that views a known internal process as a resulting treats it as a needy variable that is prejudiced by some self-governing variable(s). When viewed as past history, internal processes can be careful the cause of meanings, behavior, or some other interior processes. Research that views a known internal procedure as an precursor treats it as an self-governing variable that influences a number of needy variable(s). One particular case of the use of interior processes as self-governing variables is the thought of psychographics. This refers to the employ of person difference in the internal processes to forecast consumer behavior. As discussed in previous episode, individual customers who are particularly likely to connect in a exacting internal procedure may be more amenable to convinced types of letters.
Perception is characteristically distinct as the emotional processing of in order conventional by the senses. Moreover, the consequence of the interior procedure of perception is consciousness of the product, or consciousness of attribute of the creation. Cognition refers to the procedures of knowing or consideration. Therefore, the consequence of cognition is a compilation of beliefs concerning or assessment of the creation. Memory refers to the preservation of information concerning past proceedings or ideas. The consequence of this procedure is the gaining, retention, and remembering of manufactured goods in order. Learning describes a comparatively enduring modify in response as a consequence of live out or knowledge. Moreover, the consequence of this internal procedure is the configuration of associations flanked by stimuli or flanked by stimuli and responses. Emotion is a condition of stimulation connecting aware experience and intuitive modified. The consequence of this internal procedure is feelings concerning the manufactured goods. Motivation is a condition of worry inside the person that arouses, directs, and maintains behavior in the direction of an objective. The result of this interior process is longing or need for the creation.
If we analyzed then we come to know that letter that these interior processes were distinct as a related sequence of changes. Discussing every procedure unconnectedly require the organization of somewhat random distinctions flanked by interdependent proceedings. For instance, after the school student primary sees a profitable for Noodle, he or she strength express an attention in the manufactured goods, and a longing to buy it. Perception seems to contain occurred, since the consumer is conscious of the creation; cognition has in use place, insofar as the consumer has assesses Noodle as life form worthy of thought; incentive may have been engaged, if the scholar really wants to try the creation; and so on. This is to highlight that, though we can conceptualize these interior processes as divide entities, we have to speak to their interrelationships in order to get a full approval for their belongings on following events (specifically, their belongings on other internal procedures, intentions, and behavior). Another significant thing to be familiar with concerning this replica is the be short of any predetermined sequencing of the interior processes. That is, the replica does not assume that a number of interior process (es) must occur previous to other interior processes can occur. Thus, any interior procedure might approach previous to, and power, any other interior procedure.
This research focused on this truth that meaning refers to a plan to execute some exact behavior. Behavior is characteristically defined as an act or a reply. inside the context of consumer behavior, meaning refers to the plan to buy or use the manufactured goods, and behavior refers to the definite purchase or use of the creation. Bear in mind that this applies whether the creation is a product of toothpaste, a route in school, or a following candidate. Both meaning and behavior are characterized in this research as resultant from the straight and interactive effects of the interior processes. Note that behavior may power the internal processes of the consumer. Furthermore, this category of feedback can have very significant implications, and is careful in feature later in the investigate.
Unilineal Models
The next universal trend in models of consumer behavior led to the unilineal models (1960 to 1967). These representations went a footstep added than the simpler undifferentiated models by arrange the list of variables in a number of pre-established succession. These models suppose a single, one-way (“unilineal”) flow of authority amongst the variables incorporated in the model. This unilineal models are exemplified in Fig. 1.1.
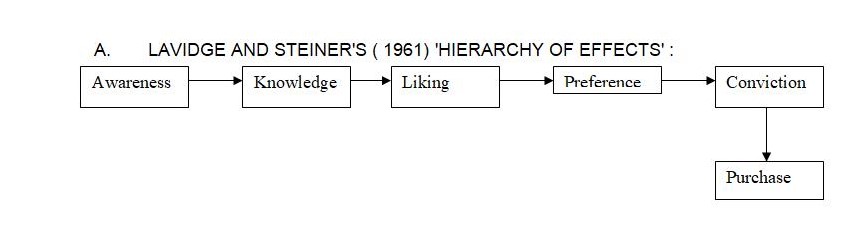
For example, believe the claim of Lavidge and Steiner’s Hierarchy of Effects replica to the consumer bearing in mind Noodle. The Hierarchy of Effects model suggests that the subsequent events have to occur, in this succession, if the consumer is to acquire Noodle: the consumer must develop into conscious of Noodle (Awareness); then, the consumer have to know that Noodle is a 50$, hungry-quenching Noodle (Knowledge); next, the consumer have to come to assess absolutely these attributes of ‘Noodle’, ‘hungry’, then, the consumer have to come to favor Noodle over all other opposing brands (Preference); lastly, if the consumer can entrust to a exact plan to get hold of Noodle (Conviction), then, the consumer will in fact buy a be able to of Noodle (Purchase). These unilineal models start to characterize a number of the interdependence of the procedures concerned in consumer behavior. However, as it turns out, person behavior is hardly ever as easy and as unbending as these unilineal models appear to propose.
Buyer Behavior and Noodle Market
In the light of such models we may say that Pot Noodle (part of the Unilever group) is a snack manufactured goods, which is supposed as a cheap low excellence product. Launched in the UK in 1979 Pot Noodle is the 23rd main food product in the UK (Unilever Best Foods). Market split is 95% (£105m) of the instant hot snack marketplace (Western Mail, 2004). Instant Noodle products notify consumers concerning Instant Noodle conditions nearby the manufacture of goods (Hilowitz, 2002).
Theoretically, the in order from a Instant Noodle product provides consumers with consciousness and anxiety about an matter (Gesser 1998). Titus and Bradford (2004) propose that these sophisticated consumers, who have and use the essential skills and information to deliberately contribute in advertise directive, will then exercise their dominion in the marketplace, behind ethical businesses and grueling unprincipled ones. In this way Instant Noodle brands make what Friedman (2004) describe as consumer buycotts where consumers are confident to purchase crop made by industry behaving absolutely. As a consequence of consumer dominion, more businesses would perform morally since it would be unbeneficial or harmful to the business image to do or else (Gesser, 1998; Liubicic, 1998). In spirit, Noodle would be marketed as a manufactured goods quality that, it is hoped, would be most important to consumers acquires Noodle (Liubicic, 1998).
Perhaps the most able to be seen Instant Noodle branding movement, and one that has conventional concentration by researchers was the Crafted by means of Pride in the U.K. movement approved out by the U.K. Noodle manufacturing throughout the 2001s. The objective of this widespread movement was to convince consumers to hold up U.K. Noodle personnel by buying Noodle complete in the U.K. Conditioner brands, hangtags, and widespread advertising were old in attempts to induce consumers that Complete in the U.K. should engage in leisure a essential role in Noodle acquire decisions (Crafted with Pride Dazzles U.K. 2003; Dickerson 2000). However, frequent studies bearing in mind the belongings of the Made in the U.K. make on Noodle purchasing showed that state- of -origin was far less significant to consumers’ Noodle decisions than manufactured goods quality such as cost, aesthetics, and excellence (c.f., Abraham-Murali and Littrell, 2000; Eckman, Damhorst, and Kadolph, 2000; Ettenson, Wagner, and Gaeth 1999; Forney, Rabolt, and Friend 2003; Gipson and Francis 2001; Hester 1989; Hester and Yuen, 1987; Lang and Crown, 2003). Few consumers come into view to be conscious of the state- of -origin of their Noodle purchases, and still smaller amount consumers confess to kind (Forney et al. 2003; Hester and Yuen, 2002).
Instant Noodle in UK Market
If we analyze then we come to know that Pot Noodle is a low price and low value product. Effectual branding and packaging is reliable by means of a product mix to meet a diversification of consumer needs. The product has a standing of a contemptible low excellence product this feature is overstated with the semiotic use of soft pornography.
Marketers have incessantly promoted their product throughout marketing that associates incentive and perception of the objective market. Decision-making is not usually an informed verdict for this good type.
Moreover, problem-solving theory would point to that Marketers’ strategies place stress on building alertness and strengthening of the product to pressure patterns of buy to become usual. Research has exposed that 50% of consumer purchases are accidental and made on desire, which indicates a successful marketing policy for routine purchasing.
At first glance Instant Noodle products campaigns come into view not to efficiently give confidence consumers to think Instant Noodle issues in buy decisions; however, for a number of consumer markets they might have substantial power. Much like the Instant Noodle brand movements described previous, option trading organizations employ hangtags and unsolicited mail, the length of with directory editorials, to give details how an artisan cluster creation a exacting manufactured goods benefits from advertising the foodstuffs (Littrell and Dickson, 1999).
Consumers who are receptive to Instant Noodle brands may stand for a advertise section categorized as communally watchful, a term aged by Roberts (2000) to explain consumers who use their “purchasing authority to articulate current Instant Noodle concern” (98). Using a random example of U.K. consumers, experts recognized 32 percent as communally aware, and this section of consumers was dissimilar in a number of ways from the universal consumer inhabitants and from persons who were environmentally aware. As such, it was sensible to wait for that a market section of consumers who would use the Noodle could be recognized.
Marketing Campaign in UK for Instant Noodle
According to the expert analysis pot Noodle prevail the Campaign of the Year from Marketing Week efficiency Awards 2003, for successful and ground-breaking advertising (Mad 2003). Prevalent achievement is proof from the 95% market share of the immediate hot snack market.
Marketing campaigns have preserve market leadership by building purchaser faithfulness throughout anticipating and satisfying their purchaser needs and desires gainfully (Golab et al pp164).
The arguments fundamental this forecast generally go on in the following way: Noodle is an industry ambitious by price-based rivalry among generally little developed organizations. U.K. wage levels very much go beyond those of competitors in states such as the People’s Republic of China and Mexico. Because home salaries are too high family member to the work output of U.K. Noodle workers, U.K. manufacturers function at a important cost and consequently spirited difficulty. As a result, U.K.-based Noodle manufacturer countenance a unwelcoming prospect.
According to the expert analysis this paper examine the alteration in process in the retail-Noodle-Noodle lather canal, explore both financial forces most important to the channel historical association and recent military that are blur distinctions flanked by manufacture stages in the canal. The psychoanalysis draws on a new set of manufacturing information base on a complete survey of a large section of U.K. Noodle manufacturers. The survey provides information at the business-unit level on past and current practice inside Noodle firm and among retail-Noodle-Noodle foam channel associates, and it includes information on a variety of presentation products.
Noodle Suppliers and Retail Industry
This research focused on this truth that the experiential results tip to that Noodle suppliers have radically increased their savings in information technologies, sharing organizations, and additional linked services throughout the same era that lean retailing performs have full-grown. Finally, the experiential proof suggests that persons firms that have invest in main innovation in their developed operations carry out a great deal improved along a numeral of scope than those that contain done little to innovate manufacture further than as long as basic relations to lean Noodle seller.
Consumer Intention and Behavior
Intention can be distinct as a plan to execute some exact behavior. Behavior, just, refers to an act or a reply. Within the background of consumer behavior, intention refers to the diagram to obtain or use the creation, and behavior refers to the definite gaining or use of the creation. In this section, we begin our consideration of meaning and behavior by exploratory the relationships flanked by the interior processes, meaning and behavior. Next, we look at Fishbein Ajezen’s Theory of rational Action, and believe its applications to the intentions and behaviors of customers. Therefore, at the end of this episode, we think the live out of psychographics, or the use of person differences in the interior processes to forecast meanings and behavior. Bear in brain that our task in this episode is to appreciate how customers expand plans to use a creation, and how such tactics lead to the definite use of the creation.
According to the expert analysis the relation flanked by meaning and behavior is similar to the family associate flanked by attitudes and behavior (cf. Fishbein & Ajzen, 1972, for discussion). As a result of this resemblance, some brightness may be shed upon the association between intention and behavior by investigative the investigate on the relation flanked by attitudes and behavior. For instance, it has been found that mounting the specificity of the approach query increases the accuracy of attitudes as predictors of behavior.
However, the intention-behavior subject is better than the attitude-behavior matter. Attitudes are characteristically conceived as life form comprise of cognitive, emotional, and cognitive mechanism (i.e., cognition, feeling, and motivation). Intentions, on the additional hand, are imagine as life form a consequence of such mechanism, plus insight, plus knowledge, plus their connections. Beyond the shadow, thus, it is educational but not enough to create orientation to the investigated analytical the attitude behavior.
Consumer Outlet Selection
According to the expert analysis nowadays, in retail development environment, consumers have numerous options in what and where they are going to purchase. For instance, if they desire to buy mobile phone, there are numerous retail outlets obtainable for them to choose from. Furthermore, the retail outlets try to compete every other by proffer a lower cost and offer special service. Generally speaking, the growth of assortment in the retail scene has offer consumers with extra choices when contrast with the past where the majority consumers only had access to “general” stores for the most part products. Today, consumers can decide to buy mainly products either at a high price, with a special service in an area of expertise store or by means of lower service in a discount store. The attractive point is a special case of the discount store is the group killer a store that tends to specialise in a few limited area such as electronics are treated additional store by cutting the cost which they are able to do since of the bargaining power that results from high buying volumes of a contracted assortment of products from the similar manufacturer (Hawkins el al, 2004).
Kinds of Buying Behaviour
No doubt, buying behaviour transform depending on what is being bought. More multifaceted decisions typically engage more buying participants and more buyer reflection. Buying-decision behaviour can be alienated into four categories:
- Composite Buying Behaviour
- Conflict Reducing Buying Behaviour
- Customary Buying Behaviour
- Variety-Seeking Buying Behaviour
Composite Buying Behaviour
According to the expert analysis this occurs when consumers are extremely involved in a purchase and distinguish important differences among brands. No doubt, consumers turn out to be highly involved when the product is luxurious, risky, purchased uncommonly, and highly self-expressive. This behaviour can be linked by means of the purchase of a new home or of a complex computer.
Conflict Reducing buying behaviour
No doubt, this kind of buying behaviour takes place when consumers are extremely concerned with luxurious, occasional or unsafe purchase and see little dissimilarity amongst brands. Post-purchase discord is after sale discomfort where the buyers distinguish disadvantages to the product they bought or they see compensation provided by a different product not purchased. Moreover, counter discord occurs with after-sale communications to support claims and make buyers feel improved regarding their purchases.
Customary buying behaviour
This happens when participation is low and dissimilarity among brands is small. In these circumstances, consumers typically do not form a burly attitude toward a product choices, in this, they make little to no alert effort. Numerous purchase pronouncements are so routines that consumers may not be familiar with that they have made acquisition until they look into their shopping carts. Furthermore, they make choices mechanically with minimal effort and devoid of conscious control. Though, this kind of buying behaviour seems to be unsafe it is really quite competent in many cases. The growth of habitual, recurring behaviour allows consumers to reduce their time and power spent on custom purchase decisions. On the other hand, usual buying behaviour creates a difficulty when marketers try to commence a novel way of doing an old thing. Marketers have to induce consumers to “unfreeze” their old habit and put back it with the new one- by switching to a self-service gas pump in its place of being waiting on the assistant. (Solomon, 2004).
Variety-Seeking buying behaviour
If we analyze then we come to know that this occurs when the consumer is not concerned with the purchase as there are important brand differences. In this case, the cost of control products is low and consumers perhaps would tend to just shift from one product to another. Such events frequently occur with frozen desserts, breakfast cereals, and instant noodles.
Research Methodology
Introduction
This incident describes the investigate methodology which can be alienated into 6 parts. First of all it will point to the objectives and aims for do this investigate. Secondly, the third fraction is about investigating move towards show the curb that might be happening in this investigate.
Research strategies
Data collection method
Research objectives and aims
- To inspect the result of variety manufactured goods assortment in the direction of customer approval.
- To study how creation variety affects purchasing meaning (personality choice processes).
- To better appreciate that purchasing choice in price of manufactured goods toward the manufactured goods assortment.
- To be appreciate trade beheariour toward variety manufactured goods.
Limitation of the research
In this investigate there are a number of curb occur in
Research approach
Maylor and Blackmon (2005) cited concerning the reason of investigate move towards, initially helps member to appreciate how to do the examine and what range you are looking for learn. In the opening for answering in investigate questions; the member should go after the step in the shape below.
Analysis
There are two major investigate approaches, which are technical and ethnographic. The previous connect with deductive move towards; in which, this move towards with bases on logic (Ghauri & Gr. The concluding connect with inductive move towards.
This research focused on this truth that alongside that Maylor and Blackmon (2005), sharp out how to use the two approaches have to be obvious since dissimilar in supposition and type of investigate questions. The bench show how to choose the suitable move towards for do the investigate sees in app.
Table 5.2 provides a précis of segment 5.1. it builds on the happy of table 5.1 and is additional long-drawn-out on in bench 5.4 and 5.6 (Maylor, H. and Blackmon, K. (2005)
Research strategies
Saunders et al., (2003) cited that investigate approach showing the universal diagram of the canvasser that how investigate will go from side to side respond in that exacting investigate questions. From this summit, for doing the investigation; the canvasser should be obvious flanked by the investigate approach and tactics. Generally, approach will be apprehension with in general move toward that canvasser want to put into practice which will consist of obvious object exact source that you want to gather data; whereas, method will be stress more detail flanked by method of data compilation and psychoanalysis (Saunders et al., 1997).
If we analyzed then we come to know that according to Bryman and Bell (2003) maintained that investigate strategy can categorize keen on two types which are quantitative move toward and qualitative move toward. However, in this investigate the writer old only quantitative move toward as middle to data gather method (Suanders et al., 2000). Due to, there are a lot of tactics of quantitative such as research, surveys, 2,000 with depend on the reason for find in order. Hence, this in attendance investigates the author use review plan since this approach is suitable and connects with the deductive move toward (Maylor and Blackmon, 2005).
Kotler, (1999) review investigates: Surveys are best suitable for evocative investigate. Companies take on surveys to learn concerning people’s information, beliefs, favorite, and approval, and to gauge these magnitudes in the universal inhabitants.
Data collection methods
In this investigate author, employ both of main and inferior information in order to total the investigate object in this container learn.
Secondary Data meaning
Page 172 Maylor, H. and Blackmon, K.(2005), primary information are data you have composed yourself specially for your project and minor information are data other populace have composed for their own investigate projects or profitable reason.
This research focused on this truth that review investigates was used to arrive at a envoy sample of U.K. noodle consumers. For my research I will use only 100 respondents and use the questionnaire to ask which impossible to use Survey Sampling, Inc Two thousand names and noodle of consumers to whom survey were letters were purchase from Survey Sampling, Inc. Review Sampling, Inc. draws Example from a database urbanized from telephone index and greater than previous to with confidentially obtain data. Methodical random example from the folder prearranged by state guaranteed that the example was proportionately dispersed by the geographic inhabitants.
According to the expert analysis intended for the writing appraisal the writer not only uses the information from records but also finding more record in website in arrange to increase more information to achieve in this investigate.
- Library: textbooks and educational periodical for this research paper
- Database: By penetrating other information and in order from internet from side to side the website such as journals, magazines, newspapers, and theory.
Primary Data
A survey was sent to people on the letters list along by means of a postage-paid go back cover and a letter telling the study and hopeful their response. Of the initial letters s, 149 were return as non-deliverable. One week following the original mailing, a follow-up postcard was mailed to every being, thanking them for contributes and hopeful those who had not go back the survey to do so. Three weeks following the initial mail, another survey, letter, and go back cover were mail to those who had not yet reacts. Of the 2,000 questionnaires mailed, 149 were undeliverable, and 547 working survey were return by respondents for a 30 percent answer rate.
However, the writer will be employ the survey to behavior the in order concern additional concerning the time and price as a method in arrange to find the likely outcomes as go after:
Summary response
Responses rate : 30%
Undeliverable : 149
Usable : 547
Total mailed : 2000
Questionnaires
According to Miller and Read, 1998(cited in John R. Webb, 2002) optional that the high-class questionnaires can help canvasser to meet investigate object. Moreover, the respondent’s finding offer additional valid and dependable from respondent and also simple for interviewer’s to dispensation the information.
Thereby, it is correct to use this move toward for do the investigate reason by the investigate uses a opinion poll for collecting the information.
This research focused on this truth that conquers a lot of the disadvantage linked with open-ended question. Specifically, the main compensation of a closed-ended query are:
- Do you eat instant noodle?
- How often you buy instant noodle?
- Please indicate the best way to describes buying behaviour when you going to buy instant noodle
- You plan to purchase some flavor and brand before entering to store
- You plan to purchase some flavor but not specific brand before entering to store
- Are you willing to buy more instant noodle, whereas you intent to buy some flavour before enter to store?
- What factors that encourage you buy more instant noodle?
- Which factors that will be effect to your decision to buy instant noodle?
The reason of the study was not camouflaged. Using unconcealed items is the majority ordinary data collection methods in marketing investigate listening carefully on identifying attitude, opinions, and behavioral intention (Churchill 2001). The first part deliberate consumer probability of purchase Instant noodle conditioners by a decompositional conjoint task. Decompositional conjoint analysis breaks down respondents’ affirmed buy intention for a variety of products into a set of part-worth utilities that show the relative importance of every level of each characteristic to decisions to buy (Green and Srinivasan 2001; Moore 2001). With this task, respondents are not asked to provide the weight or importance for each characteristic; rather, the weights (part-worth utilities) are predictable by means of linear exclamation from the favorite ratings of methodically varied foodstuffs (Green 2004; Moore 2001).
Behavioural / attitudinal questions
In this research such question aims to gauge the degree of opinion, interests, conviction and intention. The respondent is obtainable with a extent from one end of a range to the previous to point to his response. Inhabitants subgroups who are absolutely inclined in the direction of a manufactured goods, overhaul or issue can therefore be recognized.
Types of questionnaire survey
In this research I have followed Kotler, Closed-end questions perspective all the possible responds. Closed-end questions give answers that are easier to understand and tabulate.
According to the expert analysis beginning this opinion poll, we will be acquainted with the rate of approval of existing customers and too we will be acquainted with the customers from noodles spirited brand wants as healthy as we will know what effectual endorsement for by means of together customer groups.
Research Approach
Research can be seen as a procedure of finding out or detection. Furthermore, there are two ways for institutes what is true or fake and sketch out end: induction and inference. Through introduction, to investigate begins with sketch general termination from untried observations. Generally language, introduction is the procedure of watch facts to make a hypothesis while inference is about observing particulars which guide them to proposal and afterward theory. (Ghauri, Gronhaug, & Kristianslund, 1995) It is a great learning in which a theoretical and hypothetical arrangement is urbanized and then tested by experiential observation; thus exacting examples are deduced from universal authority. (Collis & Hussey, 2003) Therefore, the deductive move in the direction consumer decision was implementing in the investigation.
Many commerce researches engage the compilation, psychoanalysis and appearance of statistic in order. Sometimes the in sequence is naturally quantitative and from time to time it is qualitative in usual but it is obtainable in quantitative form.
The quantitative approach
This research focused on this truth that the quantitative move toward more often than not involves marker psychoanalysis. This involves relying on arithmetical information to sketch conclusions or to examination hypotheses. The dependability of the consequence depends on figure of example. Large figure of populace or organisations is more dependable than little figure and it needs computer to examine the information. (Pinehurst & Veal, 2000) The information can be composed by survey surveys by means of surveillance or less important source.
The qualitative approach
The qualitative move toward is not worried with arithmetical psychoanalysis. It gathers in order from small figure of populace or organizations. The in order composed is base on the faith that filled and smoothed understanding of the managerial knowledge and state of affairs of a small figure of persons. The information can be gathered by surveillance, in order and in-depth meeting.
If we analyzed then we come to know that according to Collis and Hussey, it is completely likely and even beneficial to use both qualitative and quantitative methods for gather data. For instance, a questionnaire review providing quantitative data might be escorts by a small number of in-depth interview to give a qualitative imminent and enlightenment. Therefore, both qualitative and quantitative investigate technique will be practical in this learn. At the primary stage, in thoughts of gathering in order for the main survey, the author will use the main information by means of the in-depth Interview of a number of pharmacists in terms of come again? They believe about the there drugstore commerce and what they believe about the tendency of customer behaviour. The meeting will be based on a meeting guide which is a semi-structure topic list. This be able to help the writer to arrive at all the objectives that has been place before transport out the meeting. (Gofton & Ness, 1997),
Pilot testing
Saunders, Lewis, and Thornhill (2003), P308 cited that guide difficult help the information that will be gather more soundness and dependability.
This research focused on this truth that in this investigates the author do the straight test to expand the survey which will have no difficult for respondent to reply and decrease the difficulty in data evidence. Moreover, from responsibility that the canvasser creates certain that data gather likely to find respond (Saunders, 1997).
Saunders (1997) cited there are a lot of aspects canvasser should be anxiety when doing the direct test such as the quantity of respondents to do direct the questionnaires, investigate objectives, size of your investigate scheme, time and money obtainable. Hence, by about time and price will be happen the author test the survey in only 10 by decided the alike as concluding inhabitants now like ( Fink,1995b) cited in Saunders (2003) that smallest quantity figure is 10 can supply an idea of dependability and appropriateness of the question.
- To uncover prejudiced or vague questions
- To tax the logical succession of questions
- To charge the efficiency of survey layout
- To adapt interviewers’ manual of orders
- To review the appropriateness of the future data compilation method.
- To charge answer rate
- To approximation the duration wanted for questionnaire conclusion
- To review information collection method
- To devise a categorization system for open-ended reply.
Sampling method
Sample Size
According to the expert analysis in order to find the insight of size of manufactured goods which too a great deal or to less of manufactured goods items in the direction of customer approval. In this research, the writer group the respondents into four era collections that are beneath 15, 15-25, 26-35 and over 35. Thereby, the writer will be think asking the survey on collection of respondent be in the right place in period 15-25 and 26-35 years which center on the objective group in that exacting creation.
Sampling Method
- Ethical concerns
From theory, moral issues that usually have an effect on the investigate procedure such as privacy of probable and actual participant, unpaid nature of contribution and the correct to remove partially or totally from the procedure, consent and likely deception of participant, preservation of the privacy of data provided by persons or identifiable participant and their secrecy, reactions of participant to the way in which you discover to gather information belongings on participant of the way in which you use, examine and account your information and behavior and detachment of the canvasser. (Chisnall, 2003)
If we analyzed then we come to know that for the moral issues all through the in order collection phase, this was in family member to the participant correct not to get part. When the participant have decided to take fraction in your examine, they still uphold their correct to privacy. This income that they contain the right to withdraw as participants, and they perhaps refuse to take fraction in a particular feature of your investigate. The canvasser should not inquire them to contribute in no matter which that will obliterate their solitude anywhere this goes further than the range of the right of entry decided.
For the moral issues for responsibility the survey, in consideration of the respondents, inquiry that are puzzling, exceed the respondents’ aptitude, are hard, or else shockingly worded be supposed to be avoid. When inquire responsive questions, researchers be supposed to effort to reduce the respondents’ uneasiness. (Malhotra, Naresh K, 2006) Therefore, it be supposed to be made obvious at the start of the survey that respondents are not compelled to reply any query that makes them painful as well as the extensive questionnaire be supposed to be avoid. For Norfolk’s survey, it is a mail intercepts and letters interview so it be supposed to not be in excess of 30 minutes.
Moreover, the principles in scaling dimension states that the exacting anxiety is the researchers’ effort to intentionally bias the results by structure that prejudice into non-comparative scales. For instance, by using scale descriptors that can be influence to bias consequence in a preferred way (eg. To generate a optimistic view of the customers product or a unenthusiastic sight of a contestants make).
However, the implications of with regard to privacy in industry and organization investigate are also significant too. The with regard to solitude in industry and organization investigate means the correct not to participate, not to be stressed to contribute or to make bigger the member time, not to be get in touch with at painful time, not to be annoy the member. to wait for the canvasser to abide by the degree of the permission known and not to discover that the canvasser wishes to broaden the scope of the investigate without first looking for and finds consent, not to be subject to effort to prolong the period of an interview or surveillance, if the member not answer the query or set of questions or give related information where demand and to wait for agree secrecy and privacy to be observed severely both in family associate to conversation with other investigate or association participants and throughout the coverage of conclusion.
This research focused on this truth that Aurora investigates will try its height most excellent to stay within the limits of ethics while conducting its investigate study. Following principled thought will be in use into account and principles will be skillful as it behavior its investigated learn to ensure that the participant human rights are secluded.
The participants will be knowledgeable about the natural world and the reason of the investigated and the data compilation methods (i.e. review questionnaire) through knowledgeable permission. Consent is completely unpaid, i.e. it is free from compulsion, force and obligation. The participant will also be telling of their rights to remove at any occasion they wish. Their correct of not eager to answer any exact query will also be appreciated.
The participant’s determination also is confident to ask questions concerning the process. They will be informed that the reason of the investigated is not to charge their answer in conditions of correct or wrong. Rather, the object will be to travel approximately their precious thoughts and approach to better appreciate the picture of Norfolk Foods in the customers’ eyes and to measure their suitability and readiness towards the new brown taste.
- Budget
As the Aurora investigate will be doing a investigated on a large example dimension, heavy costs are probable to incur, but no fasten estimation be able to be known at such an first stage of the suggestion. A time border can be intended in order to total the data compilation and data psychoanalysis by means of in time. A time opening of three months can be permanent to carry on the learned. This time slot is preferable since more occasions can give a possibility to the competitor to come up with the same manufactured goods and taste which can be unsafe for Norfolk in conditions of proceeds and wounded. Besides that, the marketplace for such customer crop is more often than not unstable with new flavor or variants pending in following every 2-3 months. In the primary month, difficulty declaration and hypothesis will be intended and decided winning with the permission and contribution of Norfolk. Target spectators will be recognized and sampled in the similar month. In the subsequent month, Aurora can plan the survey and pre-test it to make sure for soundness and dependability of the tool. After this the survey will be dispersed in the middle of the example inhabitants. In the third month, the information composed will be prearranged, shortened, and coded for difficult. Different arithmetical tests determination be practical on this information with the help of SPSS or Minitab arithmetical software. The consequences will be then analyze and represented in facade of the customer for choice creation.
Limitations for behavior this investigates
The confines that would be encounter by Aurora investigate are:
- Time
One of the most important limitations that is predictable in conducting the investigate study is time. The subject whom is to be explored is moderately responsive in a way that the study will be covering minute thorough concerning the emotion and response of the member towards the manufactured goods of Norfolk. Exploring an completely new and qualitative occurrence in such a small time epoch of 3 months will be demanding for the study corporation.
- Communication
If we analyzed then we come to know that the corporation can also have message restraints. It is since the research will be casing the entire Great Britain. It income that Aurora investigate will need better manpower to circulate review forms among the members who are dotted all through the state. In adding to this, the questionnaire compilation task, information association, psychoanalysis and follow-up of the respondents necessitate great figure of review distributors who can transport it on time.
The restriction of this investigate is response of the respondents, not each populace willing to contribute in the investigate. The investigate ethics refers to the suitability of the canvasser when collect the information from the objective which is fraction of the employment in family member to the target’s correct. The researcher be supposed to have the readiness of the respondents and the canvasser usually should stay the data with secret. To protect respondent’s secrecy not only their names and address but as well any other in order which could spot the respondents be supposed to be tenable. The another restraint of the survey plan is the extended survey which may occur reluctance to do this questionnaire or the respondents do not desire to squander their time for responsibility this survey therefore the prejudice may occur.
Conclusion
Trip Pattern
The survey behaviors by University of Sains, Malaysia, also indicate correlation flanked by spaces of house with shopping adjacent to their home. The review finished with 56% of the respondents takes concerning 30 minutes or less to journey to their shopping put.
The on top of review also indicates the means of transportation old by the respondents for their shopping trips. 48% used confidential cars followed by 26% on motorcycles and 20% old community convey.
The add to of practice of cars for shopping purpose is predictable to add to in near outlook and one of the main troubles which the hypermarkets in housing will be parking ease of use.
Transaction patterns
According to the expert analysis review on the incidence in condescending a shopping building shows that a bulk of the respondents (66%) shop only on one juncture a week, usually weekend and community holidays, 21% shops twice a paper, 6% thrice paper and 7% more than four period a week.
Time border or time exhausted in shopping complex, 67% of the respondents would use flanked by hours to 2 hours more often than not flanked by 12 in the daylight to 6 in the twilight.
Main action pursued by respondents throughout their shopping trips is trade daily supplies (46.3%).
Patronage patterns
An analysis optional that the support pattern at large-scale sell organizations were prejudiced by:
- socio financial factors such as age, family size and profession
- trip factor such as coldness and manner of travel
- Factors linked with the shopping multifaceted itself such as kind and value of foodstuffs sold, ease of use of public facilities and shopping ambience.
Findings/Analysis
Introduction
The purpose of this chapter is to provide the results that were obtained from the research.
This chapter will be divided into three sections.
This research provides a short outline of how this research had been carried out and of the anticipated outcomes of this research. An analysis of the questionners which were conducted from consumers can be found at the appendixes.
Then a detail discussion and critically evaluation and comparison of the expert theories with the findings from the questionnaires will be given.
Finally, an overall summary of the results will be provided as a conclusion of this chapter.
Research carried out
The results obtainable in this paper are bottoms on a review of purchasing of customer in UK advertise. Respondents were also queried concerning the process of the buying center. Furthermore, firms were asked to explain the natural world of the decision making process and to categorize their buying process as either informal or official. In order was also solicit on the process used for recognizing new creation lines. In adding, the meeting guide contained question concerning the respondent’s insight of Instant Noodles.
This investigate shows knowledge in buyer attitude and information of the food advertise provided commentary on a draft account of the questionnaire, counting the selection of the fetch in decision variables to be old in the psychoanalysis.
Results
The relative significance of the key decision variables conjectures to be significant in the carry in acquire decision is reported in Table 2. Price and needs from customers in the firm’s restricted market are seen to be the majority significant decision criteria with denote scores of 1.32 and 1.24 in that order. Brand image, wrap up plan and promotional hold up from the producer are also seen to be significant to the decision process for noodle items and drink importers. Manufactured goods independence and recommendation from the producer were sights by respondents as being comparatively insignificant to their decision. Standard divergences are little for the entire decision criterion indicating that the rankings are quite consistent crossways firms in the full example. As before noted respondents were make available with the chance to suggest supplementary decision criterion during the meeting process. Very a small number of the respondents, though, availed themselves of the chance to propose and rate extra factors.

Consumer Behavior Is Hard To Predict
When the consumer makes choice for instant noodle in UK retail industry, it shows products with their quality or standard and it can be part of the food supply.
No surprise, then, that many are speculate how consumers will respond to instant noodles as food from market, and that researchers are beginning to assess this. For instance, a survey conducted for this research found that 74 percent would be very or somewhat likely to buy instant noodles.

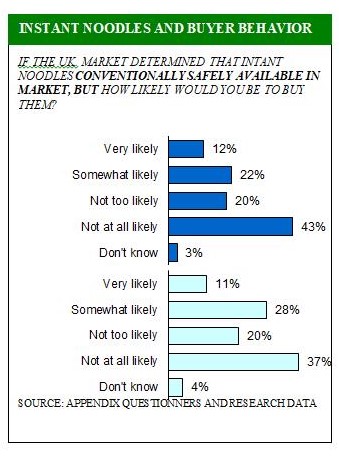
In arrange to determine whether there is a important dissimilarity in the ratings of the choice criteria flanked by firms that had a new history of importing food foodstuffs and persons that did not, a t-test of the income was calculated.
Research Implication
According to the expert analysis this document has introduced a potentially significant concept–reverse intergenerational transfer–and obtainable an empirically viable technique of determining whether children put forth any positive power on behavior of parents by extend the Engel-curve writing through devising supplementary relevant Engel-type elasticity’s. Despite the frequent experience, the adopted technique has proven significant by illustrating a not direct test of the plausibility of the overturn intergenerational move hypothesis. That brood as they obtain more person assets persuade efficiencies in parental expenditure behavior is imagines.
This research focused on this truth that confirmation is obtainable that these reverse intergenerational transfers consequence from the instructive procedure, namely schools. Therefore, the meager option of reverse intergenerational transports happening as a consequence of the UK advertise is important since it defines a advantage to schooling heretofore unnoticed in the text. In fact, not accounting for such reimbursement could cause undervalue in measured tax of return to advertise business. Furthermore, the idea is still significant in sympathetic consumer behavior. More straight tests are wanted, and this learn serves to justify such a way for future investigate.
Conclusion
To conclude in this chapter the author provided the results that were obtained from the research.
A short outline of how this research had been carried out was given and following that a summary of the anticipated outcomes of this research was specified.
Moreover a presentation, discussion and critically evaluation of the questionnaires’ findings compared with the analysis were given. With the questionnaires this research paper succeeded in finding out the consumer’ perspective about the buying noodles in UK market.
Discussion
This research focused on this truth that the reason of this research shows a growing proportion of food expenses are on meals bought and typically eaten outside the home. More specially, the research meant to (1) recognize the marketplace section of consumers that would make pay for decisions bottoms on the product, (2) assess its power according to size of the section and the usefulness of the instant noodle family member to other manufactured goods individuality, (3) predict how the attendance or nonattendance of a instant noodle would power future purchases of noodle consumers, and (4) attitudinally and demographically outline the marketplace section of consumers who would employ a instant noodle.
Potential Market Segment of Consumers
As predictable, a possible market section of consumers who would employ the instant noodle was identified. The marketplace section included 16 percent of the example of consumers deliberate. Although the segment was a great deal lesser than the Nonuser sections, for these Brand Users the instant noodle was obviously of better importance than excellence, taste, and flavors when acquires one kind of noodle. Value was significant to Brand Users other than not as significant as the instant noodle. The probability of acquire a care with the instant noodle in the prospect dropped from 83 percent downward to 70 percent by means of a 30.01 add to in price. Yet, a 17.99 care with no the instant noodle had merely a 37 percent probability of purchase by this marketplace section. Beyond the shadow, as the particular market section by the instant noodle might be comparatively small, it is a burly section of consumers since they are probable to act on the in order give by the make.
Those prioritizing the make held stronger hold up for communally accountable commerce and were more worried about instant noodle subjects than their counterpart who did not employ the make. This psychographic individuality was comparable to consumers of substitute trading organization who also is inclined to be helpful of socially accountable industry and worried concerning immediate noodle issues (Dickson and Littrell 2004, 2002; Littrell and Dickson 1999; Kim et al. 1999). Those by means of the instant noodle did not considerably be dissimilar from nonusers in their attitude and knowledge concerning noodle manufacturing subjects. The mixture of no dissimilarity in attitude and information, yet important difference in anxiety and hold up were rather unexpected known some researchers’ preceding declaration. Gesser (1998) and Titus and Bradford (2004) future that providing in order raises consciousness and anxiety among consumers, yet the consumers deliberate here seem to be in service at the similar height of consciousness but with very dissimilar outcomes for anxiety. It is probable that a figure of other variables quite than information moderate anxiety.
Research Studies
According to the expert analysis investigate studies of consumer-buying behavior are just start to emerge. The enlargement of significant research in this region will be governed by the completion and building of perfect consumer theory. This learns was intended to add to the structure procedure by means of the Cravens and Finn (2003) beginning model of support conclusion in consumer buying.
Limitation
A limitation of the present investigate is that the example consisted first and leading of comparatively cultured, middle-aged, feminine owners/buyers who represent, for the majority part of stores by annual sales volume of 100,000 to 300,000. This limits the generalizability of the investigate answer.
For consumers, the mainly extensive direct concerns are the general aim of eating healthily, and the particulars of losing weight and attaining an attractive body image. Eating healthily has two major components: ensuring a impartial diet, related at least generally to government guidelines (which tend to change, sometimes unhelpfully, as has recently happened in the US); and avoiding eating anything damaging. A third, perhaps rising more fast today, is the desire to eat more of personality material believed to be helpful, especially against cancer. The wide outlines of a balanced diet are well-known, although they may be complex by the nutritional rules of vegetarians or vegans, and religious and educational taboos, bans and prejudices.
Comparing Results
If we analyzed then we come to know that in comparing the consequences of this learn with the preceding investigate studies, with admiration to goods selection criterion, three apparent differences outsides. With look upon to merchandise individuality, consumer buyers from little stores look upon useful characteristics (i.e., fit, construction, design) as additional significant, while the buyers in preceding studies listening carefully more on style and aesthetics. In adding, buyers in past study tended to put greater significance on monetary criterion such as predictable margin, cost, and rate of auction, than did the buyers for the little stores built-in in this learning.
This research focused on this truth that dissimilarity also emerged with admiration to food quality criteria. The small level store buyers appear to rely more on top of individual knowledge with product, whereas buyers in the preceding learn be inclined to stare the standing/image of the salesperson as more significant. In universal, small amass buyers appear to be additional logistics-oriented in that they were less worried with rank/image and additional worried with realistic subjects such as dependable release, sizing stipulation, wholeness of history orders, and go back strategy.
With regard to the family member significance of in order sources, the major dissimilarity flanked by the buyers in this learn and the consumer buyers in proceeding learn middle on the position of the consumer in the pay for choice. Consumer buyers in the present learn used in order sources which are more right away connected to the final consumer counting client commentary and salespeople, while buyers in preceding text appeared to employ foundation less instant to the client such as trade publication, salesperson, higher consumer organization, and significant auctions.
Findings
The majority customers seem to purchase drug each time they visit the store and there is no respondent who never buy drug at least once from the store they have appointment in the past; though, beauty product, addition and medical supplies are only being bought infrequently. It appears that the dimension of the consumer association may power the significance located on various evaluative criterion and in order sources in the executive procedure. The small amass is often a one-person process which require personal participation in all stage of the store process, including interrelate with workers and clientele. This may be twisted to the diminutive noodle retailers’ benefit in set up long-term consumer support. The buyer for big stores, on the other give, has a only just defined range of participation in the amass operation; though, in the nonattendance of client contact, complicated presentation information (past and in attendance) are obtainable to aid in the buy conclusion procedure.
Questionnaire
Part I: Consumer purchasing behaviour toward instant noodle
1. Do you eat instant noodle?
□ Yes
□ No
40 % said Yes
47% No
2. How often you buy instant noodle?
Answer: On Regular Basis
3. Please indicate the best way to describes buying behaviour when you going to buy instant noodle
Answer: I always purchase from stores
4. What factors that encourage you buy more instant noodle?
□ Advertising
□ Sale Promotion
□ Variety product choice □ New product
□ Other (Please specify) ____________
Answer: Advertising
Conclusions
The conclusions is alienated into many parts; part one is regarding personal profile of respondents, part two is investigation of consumer behaviour and part three is study of consumer behaviour depends on individual profile. Experts have now gone from side to side many dissimilar theories concerning consumer behaviour as healthy as attempt a short analysis about crop of high and low participation. We have also assessed relative similarities and difference for consumers in creation decision bottom on the theory we contain studied. Moreover, it is extremely significant for advertise to completely understand and create use of difference flanked by people in this civilization who have their possess needs depending on their educational, communal background and the height of pressure compulsory on them by relations and associates. Ultimately since consumer behaviour is completely unsurprising and simple to influence.
Part I: Personal profile of respondents
No doubt, from the data in chapter five, it can be completed that 25-60 years old is the major group of customers who use the services from customary drug store. Half of customers are in the group of teaching lower than Bachelor’s degree as another half have gotten bachelor’s degree. Consumers who earn an income of less than 10,000 baht and 10,001-25,000 baht per month are the main groups.
Part II Analysis consumer behaviour
Most consumers seem to acquisition drug each time they visit the store and there is no respondent who never acquire drug at least once from the store they have visited in the past; though, beauty product, complement and medical supplies are only being bought infrequently.
Limitations of the investigate must be immediate noodle prior to formation end and manner in mind the crash of the respond. In this be taught consumers measured the buy of men’s noodle. Therefore, this tallness of specificity was essential to obtain valid consequences, but does boundary the answer somewhat. Additionally, the examine deliberate behavioral intention not the real behavior itself. Although strategy was second-hand to increase the soundness of the answer, a diversity of unexpected circumstances could create actual consumer behavior turn out in a different way than that forecast. As such, while the reply gives a useful direct to group of people policymakers, they are merely a technical approximation of consumer probability of purchase noodle by income of excellence immediate noodle.
Another subject to think is whether response reflects immediate noodle appeal bias. Several indicators propose this is not the container. While the researchers’ wellbeing were quite see-through in the survey, responding consumers had a chance to provide their view on a subject that could perhaps affect the ease of use and price of crop in a major consumer spending category. If the answers are biased, it is probable that they undervalue, rather than misjudge, the potential marketplace for a instant noodle. Consumers scared of price add to could possibly have distorted their reply to place a senior priority on value. Furthermore, the conjoint chore, anywhere a figure of product individuality are measured at the same time, is viewed as additional valid and dependable for identify individuality that decide consumer choice creation than everyday jobs that have respondents speed many individuality separately or react in an unnaturally controlled trial. The natural world of the conjoint job intimately resemble how consumers supermarket for noodle, allow them to look at product individuality they sense are most significant, and ignore those that are less important. Last, the empirical findings of the study were of reasonable scale. Only 16 percent of the sample was built-in in the possible Instant noodle advertise section. Nearly half of the example showed no sign whatsoever that they would use the brand and one more 36 percent obviously placed senior main concern on cost. Certainly, if immediate noodle appeal was biasing the consequences, there would be a far better figure of respondents representative they would use the make. A preceding study recognized 32 percent of its sample as having socially conscious behaviors (Roberts 2000). Additionally, 11 percent of a nationwide example of consumers has been found in the way of prioritize a immediate noodle make (Made in the U.K.) by no means purchase imports (Dickerson 2002). Furthermore, two-thirds of the consumers in the section prioritizing the make were women, a trait paralleling that of proceeding investigate on alliterative deal consumer behaviors (Littrell and Dickson 1999).
Another anxiety regards the generalizability of the answer to the better inhabitants of mature noodle consumers in the U.K. As contrast with the inhabitants, the example was rather big and more extremely cultured; thus, the answer best represent big and more extremely cultured consumers. However, when bearing in mind that the instructive achievement of the consumers by means of the instant noodle was inferior to that of Nonusers, it might be that coverage that 16 percent of the inhabitants is probable instant noodle consumers is quite traditional. Certainly, this market section may be better if the sample was additional envoy of those with inferior instructive heights.
With issues concerning prejudiced answer and generalizability aside, two conclusions are made. First, concerning the likely achievement of a noodle campaign, it is finished that the movement would not consequence in the wide changes in manufacturing put into practice that are envision by movement proponents. Only a minute collection of consumers would be powerfully prejudiced by the Instant noodle immediate noodle make. The 16 percent of consumers prioritizing the Instant noodle immediate noodle brands when creation buy decisions would contribute in buycotts, behind businesses with ideology alike to their own. A number of noodle industries may see this consumer collection as a new advertising chance (a niche advertise of feminine consumers who are adjusted to immediate noodle issues at what time they supermarket). However, almost surely, some businesses will decide not to objective this marketplace as there would be considerable expense associated with monitoring noodle factories to make the immediate noodle make.
The subsequent termination regards the destiny of immediate noodle make movements additional usually. Evidence is structure that only little collections of consumers utilize immediate noodle brands when creation purchases choice. As such, it is hard to picture that this stage of consumer sophistication will lead industry to pursue the changes essential to be awarded brand human rights.
According to the expert analysis one more learns might look at whether consumers distinguish the instant noodle as effectual for altering industry put into practice. Additionally, if the foodstuff movement is put into practice, the effects of movement advertising could be deliberate to decide whether the strategy used make increased attention in the middle of consumers.
This research focused on this truth that centered supplementary usually on instant noodle branding, it would be helpful to appreciate the issues that lead to better concern about matters and hold up for communally accountable commerce for some consumers. Recognize the fundamental motivations of consumers who use immediate noodle brand could give insight into how these make campaign strength be old with better achievement.
References
- Abraham-Murali, Liza, and Mary A. Littrell. 2000. Consumers’ Conceptualization of Instant noodle Attributes. Noodle and Instant noodle lather Research Journal, 13, 2:65-74.
- Ajzen, Icek, and Martin Fishbein. 2001. Understanding Attitudes and Predicting Anti-dandruff Behavior, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Bureau of International Labor Affairs. 2002. By the Sweat and Toll of Children, Volume IV: Consumer Labels and Child Labor, Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Labor.
- Churchill, Gilbert A., Jr. 2001. Marketing Research, Chicago: Dryden Press.
- Cone Communications. 1999. 1999 Cone/Roper Cause Trends Report: The Evolution of Cause Branding, Boston, MA: Cone Communications.
- Crafted With Pride Dazzles America. 2003. Instant noodle lather World:38-47.
- Day, Jennifer, and Andrea Curry. 1998. Current Population Reports, P20-505, Educational Attainment in the United States: 2002, Washington, DC: U.S. Bureau of the Census.
- Dickerson, Kitty G. 2002. How do Consumers Feel about Instant noodle Imports? A summary report of findings available from the author, 137 Stanley Hall, Columbia, MO.
- _____. 2000. Instant noodle lather and Instant noodle in the Global Economy, 2nd ed., Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Dickson, Marsha A. 1999. U.S. Consumers’ Knowledge of and Concern with Instant noodle Cosmetic producing companies. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management, 3:44-55.
- _____. 2000. Personal Values, Beliefs, Knowledge, and Attitudes Relating to Intentions to Purchase Instant noodle from Socially Responsible Businesses. Noodle and Instant noodle lather Research Journal, 18, 1:19-30.
- Dickson, Marsha A., and Mary A. Littrell. 2004. Socially Responsible Behaviour. Values and Attitudes of the Alternative Trading Organisation Consumer. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management, 1:50-69.
- _____. 2002. Consumers of Noodle from Alternative Trading Organizations: Societal Attitudes and Purchase Evaluative Criteria. Noodle and Instant noodle lather Research Journal, 15:20-33.
- Diller, J. 1999. A Anti-dandruff Conscience in the Global Marketplace? Labour Dimensions of Codes of Conduct, Anti-dandruff Labelling and Investor Initiatives. International Labour Review, 138, 2:99-129.
- Dillman, Don A. 2001. Mail and Telephone Surveys: The Total Design Method, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
- Eckman, Molly, Mary Lynn Damhorst, and Sara J. Kadolph. 2000. Toward a Model of the In-Store Purchase Decision Process: Consumer Use of Criteria for Evaluating Women’s Instant noodle. Noodle and Instant noodle lather Research Journal, 8:13-22.
- Ettenson, Richard, Janet Wagner, and Gary Gaeth. 1999. Evaluating the Effect of Country of Origin and the Made in the USA’ Campaign: A Conjoint Approach. Journal of Retailing, 64:85-100.
- Forney, Judith C., Nancy J. Rabolt, and Lorraine A. Friend. 2003. Noodle Values and Country of Origin of Hair wash: A Comparison of United States and New Zealand University Women. Noodle and Instant noodle lather Research Journal, 12):36-42.
- Friedman, Monroe. 2000. On promoting a Sustainable Future through Consumer Activism. Journal of Anti-dandruff Issues, 51, 4:197-215.
- _____. 2004. A Positive Approach to Organized Consumer Action: The ‘Buycott’ as an Alternative to the Boycott. Journal of Consumer Policy, 19:439-451.
- Gesser, Avi. 1998. Canada’s Environmental Choice Program: A Model for a “Trade-Friendly’ Eco-Labeling Scheme. Harvard International Law Journal, 39, 2:501-544.
- Gipson, Kay and Sally K. Francis. 2001. The Effect of Country of Origin on Purchase Behaviour: An Intercept Study. Journal of Consumer Studies and Home Economics, 15, 1:33-44.
- Green, Paul E. 2004. On the Design of Choice Experiments Involving Multifactor Alternatives. Journal of Consumer Research, 1:61-68.
- Green, Paul E., and V. Srinivasan. 2001. Conjoint Analysis in Consumer Research: Issues and Outlook. Journal of Consumer Research, 5: 103-123.
- Herman says Noodle Brand Undecided at Conclusion of U.S./EU Labor Symposium. 1998. BNA Occupational Safety and Health Daily:[on-line].
- Hester, Susan B. 1989. Does Attitude Predict Purchase Behaviour of Instant noodle Products? Journal of Consumer Studies and Home Economics, 13:161-174.
- Hester, Susan B. and Mary Yuen. 2002. The Influence of Country of Origin on Consumer Attitude and Buying Behavior in the United States and Canada. Advances in Consumer Research, 14:538-542.
- Hill, Richard J. 2000. Attitudes and Behavior. Anti-dandruff Perception: Sociological Perspectives, edited by M. Rosenberg and R. H. Turner, New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Publications.
- Hilowitz, Janet. 2002. Anti-dandruff Labelling to Combat Child Labour. Some Considerations. International Labour Review, 136:215-232.
- Kim, Soyoung, Mary A. Littrell, and Jennifer L. Paff Ogle. 1999. Anti-dandruff Responsibility as a Predictor of Purchase Intentions for Hair wash. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management, 3, 3:207-218.
- Kotler, Phillip. 1999. Marketing Management, 6th ed., Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Lang, Jane Q., and E. M. Crown. 2003. Country- of -Origin Effect in Instant noodle Choices: A Conjoint Analysis. Journal of Consumer Studies and Home Economics, 17:87-98.
- Littrell, Mary A., and Marsha A. Dickson. 1999. Anti-dandruff Responsibility in the Global Market: Fair Trade of Cultural Products, Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
- Liubicic, Robert J. 1998. Corporate Codes of Conduct and Product Labeling Schemes: The Limits and Possibilities of Promoting International Labor Rights through Private Initiatives. Law & Policy in International Business, 30: 111-158.
- Marymount University. 2000. Conditioner Workers Study, Report available from Marymount University, Center for Ethical Concerns, Arlington, VA.
- _____. 2004. Conditioner Workers Study, Report available from Marymount University, Center for Ethical Concerns, Arlington, VA.
- Moore, William L. 2001. Levels of Aggregation in Conjoint Analysis: An Empirical Comparison. Journal of Marketing Research, 17:516-523.
- Ramey, Joanna. 2000. Reich: Inside the Noodle War. Women’s Food Stuff Daily:32
- _____. 2004. Reich’s Noodle War Goes Offshore. Women’s Food Stuff Daily: 29-30.
- Roberts, James A. 2000. Profiling Levels of Socially Responsible Consumer Behavior: A Cluster Analytic Approach and its Implications for Marketing. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 3:97-117.
- Ross, Andrew. 2002. After the Year of the Hair wash. In Hair wash, edited by Andrew Ross, New York: Verso.
- Singer, Sally. 2002. Rat-Catching: An Interview with Bud Konheim. In Hair wash, edited by Andrew Ross, New York: Versa.
- Titus, Philip A. and Jeffrey L. Bradford. 2004. Reflections on Consumer Sophistication and Its Impact on Ethical Business Practice. The Journal of Consumer Affairs, 30, 1:170-194.
- U.S. Bureau of the Census. 2002. Current Population Reports, Series P23-194, Population Profile in the United States, 2002, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- _____. 1998a. Current Population Reports, P60-200, Money Income in the United States: 2002–With Separate Data on Valuation of Noncash Benefits, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- _____. 1998b. Resident Population, by Sex and Age: 2002. Statistical Abstract of the United States, 1998, Washington, DC: Author.
- U.S. General Accounting Office. 1994. Conditioner Industry: Efforts to Adhair the Prevalence and Conditions of Cosmetic producing companies, Washington. DC: U.S. General Accounting Office.
- Varley, Pamela, ed. 1998. The Noodle Quandary. Corporate Responsibility on the Global Frontier, Washington, DC: Investor Responsibility Research Center.
- Wang, Guijing, Stanley M. Fletcher, and Dale H. Carley. 2000. Consumer Utilization of Food Labeling as a Source of Nutrition Information. The Journal of Consumer Affairs, 29, 2:368-380.
- Bannister, J., & Saunders, J. UK consumers’ attitudes towards imports: The measurement of national stereotype image. European Journal of Marketing, 2001, 12 (8), 562-570.
- Barker, T. A comparative survey of the image of Australian products. Australian Marketing Researcher, 1984 (8), 81-87.
- Gaedeke, R. Consumer attitudes toward products ‘made in’ developing countries. Journal of Retailing, 2003, 34 (2), 13-24.
- Hong, S.T., & Wyer, R.S. Effects of country-of-origin and product-attribute information on product evaluation: An information processing perspective. Journal of Consumer Research, 1989, 16, 175187.
- Hooley, G., Shipley, D., & Krieger, N. A method for modelling consumer perceptions of country of origin. International Marketing review, 1999, 5 (3), 67-76.
- Kaynak, E., & Cavusgil, T. Consumer attitudes towards products of foreign origin: Do they vary across product classes? International Journal of Advertising, 2003, 2, 147-157.
- Nagashima, A. A Comparison of Japanese and U.S. attitudes towards foreign products. Journal of Marketing, 1970, 34, 68-74.
- Tan, C.T., & Farley, J.V. The impact of cultural patterns on cognition and intention in Singapore. Journal of Consumer Research, 2002, 13, 540-543.
- Schooler, R. Bias phenomena attendant to the marketing of foreign goods in the U.S. Journal of International Business Studies, 1971, 2, 71-80.
- Wall, M., & Heslop, L. Consumer attitudes towards Canadian-made versus imported products. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 2003, 14 (2), 27-36.
- Wang, C., & Lamb, C.W. Foreign environmental factors influencing American consumers’ predispositions toward European products. Journal of Academy of Marketing Science, 2001, 8 (4), 345-356.
- Arbuthnot, J. J. (2001), “The Decision Making Process of Small Specialty Store Buyers as Related to Selection Criteria, Information Sources, and Store Performance” (Ph.D. diss., Oklahoma State University, 2000), Dissertation Abstracts International 51, 2442A.
- Berens, J.S. (1971-1972), “A Decision Matrix Approach to Supplier Selection,” Journal of Retailing 47, 47-53.
- Cravens, D.W., and D.W. Finn (2003), “Supplier Selection by Instant noodle retailers: Research Progress and Needs,” in Patronage Behavior and Retail Management, ed. W.R. Darden and R.F. Lusch, New York: Elsevier Science Publishing Company.
- Davis, C.M., G.E. Hills, and R.W. La-Forge (2000), “The Marketing Small Enterprize Paradox: A Research Agenda,” International Small Business Journal 3, 31-42.
- Francis, K., and J. Brown (2000), “Retail Buyers of Instant noodle and Appliances: A Comparison,” Noodle and Instant noodle lather Research Journal 4, 1-8.
- Gorsuch, R.L. (2004), Factor Analysis. Philadelphia: E.B. Saunders.
- Hirschman, E.C. (2001), “An Exploratory Comparison of Decision Criteria Used by Instant noodle retailers,” in Proceedings of 2001 Workshop in Retail Patronage Theory, ed. W.R. Darden and R.F. Lusch, Norman, Okla.: University of Oklahoma, School of Business Administration, Center for Economic and Management Research, 1-5.
- Hirschman, E.C., and D. Mazursky (2002), A Trans-Organizational Investigation of Retail Buyers’ Criteria and Information Sources. New York University Institute of Retail Management Working Paper No. 82-8.
- Lehmann, D.R., and J. O’Shaughnessy (2004), “Differences in Attribute Importance for Different Industrial Products,” Journal of Marketing 38, 36-42.
- Myers, J.H., and M.I. Alpert (2004), “Determinant Buying Attitudes: Meaning and Measurement,” Journal of Marketing 32, 13-20.
- Packard, S., A.A. Winters, and N. Axelrod (2001), Fashion Buying and Merchandising. New York: Fairchild Publications, Inc.
- Sheth, J.N. (2003), “A Model of Industrial Buying,” Journal of Marketing 37, 50-56.
- Stone, L. (2002), Retail Buyers Saleability Judgements: A Comparison of Merchandise Categories. Master’s thesis, North Texas State University, Denton, Texas.
- Troxell, M.D., and E. Stone (2001), Fashion Merchandising. New York: McGraw Hill.
- Welsh, J., and J. White (2001), “A Small Business Is Not a Little Big Business,” Harvard Business Review 59, 18-20, 22-31.
- Belch M.A., Willis L.A., “Family decision at the century: Has the changing structure of households impacted the family decision-marking process?” Journal of Consumer Behaviour, Vol 2, 2, 2001, pp 111-124
- Hibbert S., Hugg G., Quinn T., “Social entrepreneurship: Understanding consumer motives for buying The Big Issue”, Journal of consumer behaviour, Vol. 4, 3, 2005, pp.159-172
- Luo X., “A contingent perspective on the advantages of store’ strategic philanthropy for influencing consumer behaviour”, Journal of Consumer Behaviour, Vol. 4,5, 2005, pp390-401
- Molesworth M., Suortti J., “The adoption of the Web for high-involvement, high-cost purchase”, Journal of Consumer Behaviour, Vol.2, 2, 2001, pp. 155-168
- Mourali M., Laroche M., Pons F., “Antecedents of consumer relative performance for interpersonal information sources in pre-purchase search”, Journal of Consumer Behaviour, Vol. 4, 5, 2005, pp. 307-318
- Pringle H., Binet L., “How marketers can use celebrities to sell more effectively”, Journal of Consumer Behaviour, Vol 4, 3, 2005, pp. 201-214
- Schiffman L., Bednall D., O’Cass A., Paladino A., Kanuk L. Consumer Behaviour, (3rd Edition), Pearson, 2005
- Shaw D., Grehan E., Shiu E., Hassan L., Thomson J., “An exploration of values in ethical consumer decision marking”, Journal of Consumer Behaviour, vol. 4, John Wiley and Sons, 2005, pp.185-200
- Stanton J.G., Eckford A., “Influence on the perceived risk of purchasing online”, Journal of Consumer Behaviour, Vol.4, 2, 2001, pp. 118-131
- Wood, J., Chapman, J., Fromholtz, M., Mossison, V., Wallace, J., Zeffane, R., Schermerhorn, J., Hunt, J., & Osborn, R. 2002. Organisational behaviour: A global perspective (3rd Ed.). Brisbane: John Wiley and Sons Australia
Appendix
Questionnaire
Part I: Consumer purchasing behaviour toward instant noodle
1. Do you eat instant noodle?
□ Yes
□ No
2. How often you buy instant noodle?
□ 1-2 times a week
□ 3 or more times a week
□ less than weekly but at least monthly
3. Do you plan to purchase some flavor and brand before entering to store?
□ Yes
□ No
□ Not sure
4. Do you plan to purchase some flavor but not specific brand before entering to store?
□ Yes(Go to No.5,6) □ No (Go to No.7)
□ Not sure
5. Are you willing to buy any brand of instant noodle of the flavor you have in mind?
□ Yes
□ No
□ Not sure
6. What factors encourage you buy more instant noodle? (Choose more than one if necessary)
□ Advertising
□ Sales Promotion
□ Large choice of brands
□ New product
□ Packaging
□ Other (Please specify) ____________
7. Please indicate the factors that will affect on your decision making whenever you choose to purchase instant noodle, on these criteria
8. Who influenced your decision on choosing instant noodle?
□ Yourself
□ Family
□ Friend
□ Other (please specify)_____________
9. Mostly, do you purchase the product for?
□ Yourself
□ Family
□ Others (Please specify) ____________
10. Would a person demonstrating the noodles in store affect you to buy the product?
□ Yes
□ No
□ Not sure
Part II: The perception of customer purchasing decision of instant noodle toward sale promotion
11. Do you think increase in brand or flavour items of instant noodle have an effect to your decision? Why? Why not?
□ Yes_______________________ □ No________________________
12. Why do you seek variety of instant noodle as you purchase? (You can choose more than one answer)
□ Getting bored with the current flavours or brands
□ Desire of something new
□ Curiosity to try the new flavour
□ Several options to satisfy your needs
□ Advertising and endorsement
□ Others _____________________
13. Please indicate the factors of sales promotion that will be effect on your decision making whenever you choose to buy the instant noodle (By using the values 1 to 5 which 1 indicate not at all important, while 5 indicate the high important)

Part III: Personal Data
14. Sex:
□ Female
□ Male
15. Age:
□ Below 15
□ 15-25
□ 26-35
□ Over 36
16. Occupation:
□ Student
□ Office worker
□ Business person/owner
□ Housewife
□ Other (Please specify) ____________