Introduction
This work will contain a story about the experience of working at Starbucks. This company will be shown from the inside in the dynamics dictated by the environment, large-scale decisions made by the management on the eve of global changes in the world, and the impact on the organizational structure. The uniqueness of the situation is due to the confluence of circumstances that indicate the necessary changes and the urgency of decision-making. The increased information flow has led management to make changes that affect the company’s efficiency, effectiveness, congruence, and ethics. Culture is also considered a separate important component that underlies a company’s values selling premium products. It will determine both the internal needs of the company’s components and play a vital role for the end-user.
Starbucks is an American coffee shop chain operated by the Starbucks Corporation. The headquarters is located in Washington. The total number of employees reaches almost two hundred thousand people. The structure of Starbucks includes more than 24,000 outlets and coffee houses in 75 countries around the world in North and South America, Oceania, Europe, and Asia (Starbucks – About us, n.d.). The assortment of coffee houses is represented by low-calorie and sugar-free drinks, puff and yeast pastries, quality coffee, milkshakes, light snacks, and serving accessories. Ordinary shares of Starbucks on the stock market are available for purchase on the American Exchange – NASDAQ. It is information about financial activity that best shows the dynamics of development, problems, and attempts to solve them at Starbucks in the period from 2017 to the present.
Information Flow and Decision Making
Starbucks has shown positive growth across most of its critical financial relationships through 2020. The company’s revenue grew every year until 2020, while gross profit also grew while maintaining the exact cost of goods sold (Macrotrends, 2022). By keeping revenue rates and quality at a high level, this fact demonstrates the effective management of the company’s resources, maintaining the cost of producing goods, and at the same time increasing overall revenue. However, the company’s operating expenses are growing in line with revenue, which can be said about operating income and net income.
The company’s assets peaked in 2018, as did net income and revenue. However, the increase was mainly due to a change in the long-term debt indicator, which more than tripled (Macrotrends, 2022). After 2018, its current ratio turned negative, which affected its liquidity and ability to repay short-term obligations. The company corrected the situation in 2020; however, a confident forecast for the future, in this case, is not observed for several reasons. Firstly, Starbucks has already realized its potential quite widely, which means that especially significant investments, projects, or financial injections are not expected. Secondly, the significantly increased long-term debt in 2018 quite noticeably disrupted its relationship with existing capital, increasing it by several whole units.
As it turns out, Starbucks made an important decision to take long-term, large loans to launch various projects within the company and achieve various goals. The reflection of the received loan can be seen in the significantly increased financial indicator of total liabilities and total long-term assets (Macrotrends, 2022). The company’s goals can be divided into several aspects. The first is to maintain the company’s environmental responsibility by changing the production chain to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and produce more clean water from the amount consumed (Starbucks, 2021). Secondly, the goals relate to the continuous differentiation of products and services in the premium segment for more solvent consumers. Typically, this aspect is manifested by offering new recipes for takeaway products, such as Christmas drinks dedicated to the New Year holidays in Canada (Peiper, 2021). It also includes the sale of coffee beans, utensils for storing and drinking coffee drinks, and much more.
However, plans were adjusted on the go due to the global pandemic. The restrictions imposed affected the entire global economy, including closed borders, price increases, the inability to receive guests in cafes and patios. The development of the former vector became impossible because the expected planned profit began to fall sharply, and the management had to take various measures to save the situation and treat the symptoms. In the short term, long-term lending played into the company’s hands, as it allowed it to stay afloat with the help of the received assets, comply with the law and keep temporarily closed outlets. On the other hand, risks increased in the long term, as borrowed funds were not used for the direct development of the company. It was decided to send the proceeds to the development of the delivery system, the introduction of loyalty programs, online sales, and other relevant actions at the time of the pandemic.
Efficiency and Effectiveness
The company’s management proved to be effective, as it quickly reacted to changes and, by chance, had all the necessary resources for this. It was impossible to predict the pandemic, but borrowed funds played a specific role in the new vector of the company’s development, simplifying many possible obstacles. At the same time, the company’s efficiency could be assessed only after a specific time, how correctly various actions are taken. Figure 1 reflects the ratio of these two indicators in this example.
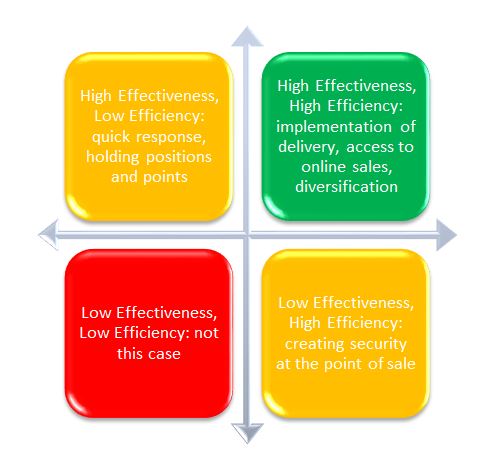
Due to restrictions, management also quickly reallocated cut spending due to the temporary closure of most coffee shops across the country. Cooperation with Uber Eats was not long in coming since it was impossible to completely stop its sales, as this would lead to highly negative consequences. During the implementation of online sales and cooperation with delivery systems, restrictions were relaxed and allowed to open outlets so that consumers could order coffee to go. Certain expenses from the maintenance of the premises were reallocated to ensure the safe interaction of the barista and the buyer, the provision of free personal protective equipment and hygiene, antibacterial products for the treatment of hands and skin. Naturally, this activity, in any case, reduced direct sales, gross profit, and net profit. However, in the context of a problematic situation, Starbucks was able to return to positive growth by the end of 2021 in most of the financial indicators that fell in 2020 (Macrotrends, 2022). It is difficult to objectively assess the efficiency of a company due to the uniqueness of the situation and the impossibility of constructing alternative examples.
The Concept of Fit
The company’s management had to adjust one of the aspects of the Fit concept – work, to maintain interaction with other aspects at a high congruence to maintain high-quality performance. Employees lost the opportunity to work for a while, but the most advanced of them returned to work quickly enough, thanks to the quick response of management. The baristas continued to make coffee, partly relieved of the burden of controlling the area where patrons usually settled down. Starbucks, among other things, is valued for the atmosphere of coffee houses, the particular design of the premises with the high quality of the drinks themselves. Consumers were involuntarily deprived of this opportunity, while employees were deprived of communication with consumers. The high culture that keeps the company’s high-performance indicators faded into the background before the need for structural changes.
In the departments within the company, the focus shifted from the indoor atmosphere to the product itself, which required a related diversification of the product line in different countries. Consumers could now only enjoy the drink at home or work, and the high quality allowed a certain level of sales to be realized to keep the company financially active. The culture was now transmitted through attitude and service through delivery: the company also signed mugs for customers, even if they did not know the names, with various pleasant wishes, offered to try other drinks, held promotions, and introduced a loyalty program. Given that culture is a vital determinant of a company’s premium products, the challenge for management was to maintain these associations with the brand. Employees of the premises themselves, according to the law, continued to receive a salary, even if they were not able to go to work so that the company could retain valuable personnel and meet the requirements of social responsibility. Here, Starbucks also optimized communication between departments, including along the vertical chain: during unexpected vacations, coffee shop employees could offer ideas, participate in discussions to solve problems created by the global crisis.
Differentiation and Integration
Initially, there was a differentiation in the company between the main offices of management and departments and direct employees of coffee shops. Communication between them was established quite well; the latter could make various proposals for the targeted improvement of their coffee shops, service capabilities, and much more. According to the strategy for which borrowed long-term funds were taken, it was supposed to introduce an even greater level of differentiation: the expansion of products, the optimization of production from an environmental point of view. In fact, the company did not wholly abandon these goals – instead of them, tasks appeared that needed to be solved in the first place. Starbucks was focused on differentiation; however, due to the pandemic, the company was forced to focus on products and technologies for its implementation in the face of restrictions. As a result, there was an integration between different departments, which were now working on one common task in a difficult situation.
There was a temporary vertical integration when the company connected temporarily idle coffee shop employees to the direct discussion. Maintaining the culture and maintaining a satisfactory level of operating revenue were the main objectives of the discussions and actions, among which the task was to return the barista to their core activities as soon as possible. The rapid transition from discussion to action required an equally rapid response to any changes in pandemic restrictions: allowing customers to enter coffee shops even without lingering at their favorite table required corresponding structural changes. A natural decrease in sales leveled the temporary cessation of coffee supplies from countries with closed borders at the very beginning of the pandemic. Integration promotes better coordination of departments among themselves, which was essential to remain competitive in the market. Decreased consumer purchasing power due to the crisis required lucrative offers from the company to attract new customers with discounted prices on premium products and please loyal customers who are deprived of the opportunity to visit their favorite coffee shops.
Contingency Theory
It should be noted that this situation is almost entirely dictated by the foundations of the theory of unforeseen circumstances. If a company is differentiated into component aspects, as in the concept of fit, then the primary and unchanging background in the whole situation is only culture. Otherwise, the company’s long-term planning was cut short by an unforeseen situation with the spread of the virus worldwide. An external circumstance completely reshaped the plans of the company’s management, shifting all sorts of accents to more important ones in this situation. Such a decisive intervention of external factors, as a rule, cannot be met ready for all difficulties since political, legal, and environmental factors are mixed here.
The path-goal theory becomes the most important of the various contingency theories. In the context of an unknown future, unknown prospects for the company’s development due to possible new political restrictions and many other aspects that are not controlled by management, setting goals becomes inseparable from the ways to achieve them. Employees of coffee shops and other vertically integrated employees see an even narrower picture of the entire company and may experience a lack of information. In this regard, it is necessary to maintain not only the setting of goals but also a clear path to achieve them on an equal basis with each employee. Figure 2 shows a diagram of the company’s contingency plan.
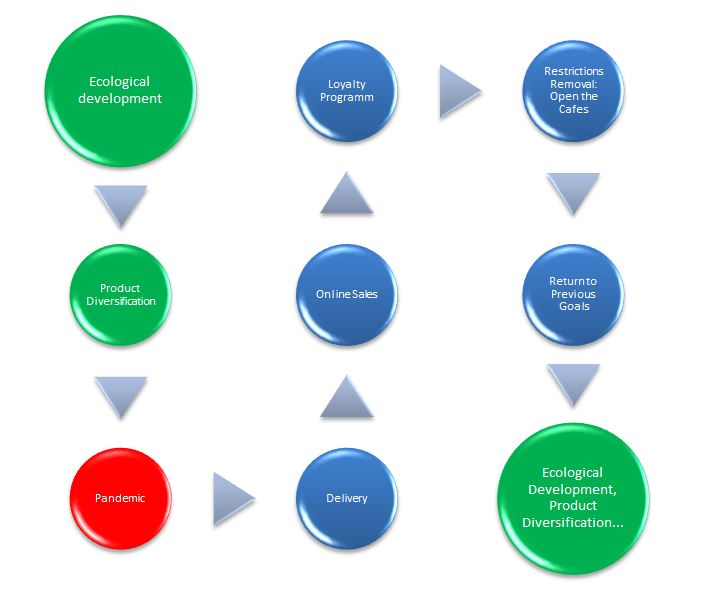
Regardless of how much management adhered to the postulates of this theory, it was to its foundations that they returned at the first unforeseen severe situation. Accompanying employees with a certain degree of integration made it possible to adjust the input and output for each goal more clearly and quickly. Sufficiently broad goals received more specific implementation thanks to the ideas of various departments. For example, product diversification supported by a high level of culture has led to the development of a line of New Year’s Eve drinks with recipes from around the world, as mentioned above. The need for delivery led to consideration and quick contact with various aggregators for cooperation. If it were not for the pandemic, Starbucks would not have improved at such a rapid pace online sales, delivery services, which are now another virtual sales channel in addition to the usual coffee shops. In addition, developed loyalty programs, discounts for regular customers were also developed under the pressure of the crisis. Consequently, this theory bears fruit if there is an appropriate response from the management.
The Congruence Model
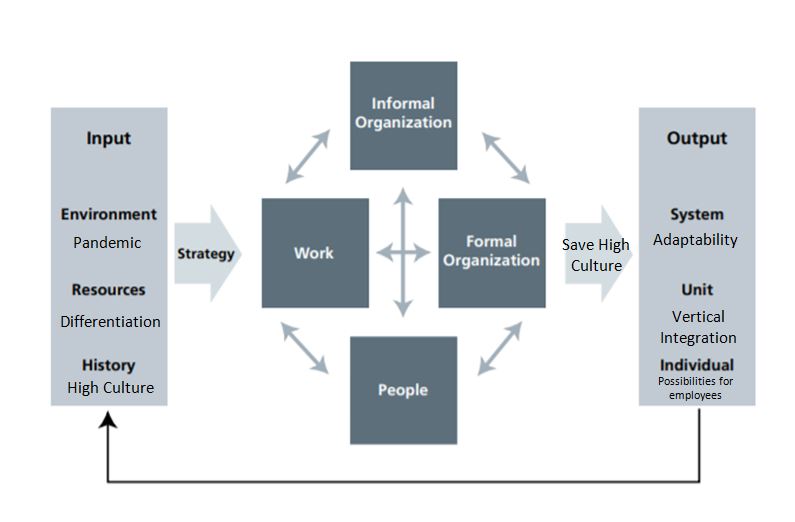
Potential problems for the company were the increased risks of a significant increase in long-term debt, the interest on which increased the company’s short-term liabilities. Against the background of falling sales, Starbucks could find itself in a highly unenviable situation, left with falling revenue, unfulfilled plans, and considerable debt. The leaders’ reactions showed a unique leadership style used in difficult situations. To build a congruence model for specific problems and symptoms, it is needed to define inputs.
The environment dictates the trends in environmental responsibility that the borrowed funds should have been directed towards. However, there is a need to cope with the problem of a pandemic that has captured the whole world. Consequently, environmental input dictates its own strict rules, which will result in a drop in sales in any case. The company has the resources and history steeped in the high culture that Starbucks is associated with in the end consumer. Human resources, as one of the company’s central values, the management unites within the framework of vertical integration to solve a common problem and find a way out in the face of falling revenue. As a result, a strategy is born that involves cooperation with delivery aggregators, the development of online sales and loyalty programs, the improvement of remote service and the attraction of new customers, and the support of old ones through loyal pricing.
The concept of fit, which follows, processes this strategy to preserve the company’s culture, both external and internal. The interests of employees are taken into account by the need to return them to work in coffee shops as soon as possible, and the formal tasks are to level falling profits due to restrictions. Determining the output for this model at different levels, one should consider the interests of employees who want to develop together with the company. Consequently, at the individual level, career opportunities, interactions with clients, as the company culture implies, and corresponding inflation and salary development should be implied. At the group level, conserving resources should be reviewed to better respond to massive global restrictions involving border closures. In addition, the experience of vertical integration will improve the communication system between departments, the positive aspects of which can be used in the future.
Finally, as a system, Starbucks will have new distribution channels that keep pace with the times, as well as a more flexible structure that is ready to adapt to various unforeseen situations dictated by a relatively harsh environment. Consequently, the company will move towards a more flexible organizational structure that, despite diversifying its sales channels, will strive for vertical integration across departments to maintain a high level of coordination and responsiveness to mitigate risks due to high debt. Figure 3 shows a diagram of a congruent model that reflects the above theses.
Conclusion
Within the framework of this work, thanks to several theories and models, a unique case was analyzed at Starbucks, when significant funds were allocated and borrowed to develop certain aspects of the company. However, due to external circumstances, the vector exceptionally swept the plans of the management. As a result, the company has achieved outstanding results against the backdrop of a crisis economy worldwide, developing new sales channels and maintaining culture as a fundamental aspect of supporting the company at a premium level. Even in the development of the strategy, all these values were applied and taken into account, which allowed both retaining employees and returning to a positive trend in financial activity as early as 2021. In this way, the company has maintained traditions by quickly adapting to the new harsh conditions, opening up opportunities for further diversification and environmental developments in production, which were postponed due to the pandemic.
References
Macrotrends. (2022). Starbucks Balance Sheet 2005-2021 | SBUX. Web.
Peiper, H. (2021). Starbucks holiday drinks from around the world. Web.
Starbucks – About us. (n.d.) Web.
Starbucks. (2021). Starbucks announces coffee-specific environmental goals. Web.