Introduction
The World Wide Web is a collection of smaller intranets and extranets as well as wide area networks, WANs, which are clustered and grouped together to form a virtual world that is known as Cyber Space or the online dimension of the Internet. The large scope of this dimension and the easy accessibility the people have to this interface has made way for a large amount of online traffic which conducts business transaction and online trade to carry out their business activities. This characteristic of the Internet has banks as well as business to employ electronic payment for their dues through electronic data interchange. ATM machines on the other hand are the automated teller machines that are used as an automated tool by banks. Currently these are being used in the developed world as a portal between the banks and the customer hosting a myriad of payment systems.
The payment systems that are currently being used pertain to those which form the manual and the automated banking utility and payment billing systems. These systems are mostly focused and built by the developed companies keeping the market for the developed companies in mind. As a result these systems are not compatible for the developing world where there is lack and restriction of basic resources that are taken for granted in the developed countries.
The following paper aims to identify the obstacles that are currently obstructing the path for Africa to attain growth and development in the ecommerce and electronic payment sector. The specific problems faced by the Africans in regard to the accessibility that they have to banks in the region. This tends to influence their ability to pay their dues and bills making way for a large number of bad debts for the government and service providing companies. The paper also attempts at analyzing the companies who are able to provide the web based ecommerce and electronic banking and payment solution for the region and states what steps can be taken to improve the development of such systems in Africa
The problems faced by Africans in the field of e-commerce
The region Africa is one of the most deprived and poor regions in the world where people are dying of starvation, hunger and lack of availability of basic necessities like water, food, shelter and medicine. In a region like this there do exist certain countries which have been able to pull them selves together and employ a civilized and formal structure for both their economies as well as for their business sand trading activities. However despite their efforts when it comes to banking and payment system these countries are still in despair. This is because of the political and regional uncertainty in the region and the lack of availability of resources.
Even though the countries in Africa like Sudan, Zimbabwe, Nigeria, Uganda other South African countries do have a central banking system. This is mostly in threat form the local activists and rebels as well as from the corrupted governments and officials in the regions Due to the high level of crime and uncertainty in this region it is almost impossible for the people in the region to be able to carry out their banking activities and the payment of their dues in public or through the branches of the banks and the financial institutions. This makes the current payment system in the region very unreliable.
Aside from this there also exists disparity in the development of specific systems for payment. This is because most of the systems that are developed for electronic commerce and e-banking are not feasible for the developing countries in Africa. The constant load shedding and blackouts as well as the breakout of disputes I the region trend to aggravate the problem faced by the people of this region concerning the accessibility to banks and branches. More over most of the electronic commerce and e-banking and payment system that are developed in the world pertain to European and American economies. In these systems majority of the payment systems are housed by the district banks and re automated and facilitated by the banking automation machines like ATM machines.
The evolution of the simple automated teller machine has made it possible for the proper to conduct their banking transactions regarding depositing money, withdrawal of money as well as payment of bills and utilities, credit transfer and balance check from the ATM machine alone. However this option is not feasible for the region of Africa as it experiences constant blackouts and electricity failures which deem the ATM machines unusable. Aside form this the long distances that are required by the individuals to travel to attain access to the branches of reliable banks are enormous and can pose problems for the population in themselves.
Another issue that has been obstructing the growth of the e-commerce sector in the region of Africa pertains to the fact that credit and debit cards that form the basis of most of the cash as well as non cash transactions around the world, specially in the united states and the European countries are unreliable and highly risky in the African region. This is because the risk of accredit card theft is very high for the regions making it a bad option for African banks to take on a bass of payment systems based on credit and debit cards.
The popular online payment systems like Google, PayPal, Skype and market places like eBay make use of credit, debit and visa cares for purpose of due and bill payment for the provision of their services. However this is not possible for the region of Africa as stated above due to the fact that credit and debit cards host a high rate of theft and fraud rate in the region. AS a result a different payment solution has to be devised that is focused on providing high level of security while making it feasible for the individual to conduct their payment and banking transactions comfortably and in privacy.
Currently the online option for ecommerce and e-banking is taking shape in Africa as most of capitals of the regions are having internet connectivity and by employing a sophisticated and secured web interface the companies have started to carry out their e-banking transactions through the internet however currently the region is facing problems pertaining to lack of specialized personnel in the technology and digital communication frilled to monitor and control this system and maintain it for the growing number of users. Additionally the equipment and software required for such a system is expensive and hard to obtain for the small and medium sector enterprises in the region.
The African companies also face problems regarding registration and statues clarification when they deal with payment service providers like PayPal, World Pay, Nexus and DataCash. This is because tin order top trade using credit and visa cards the company has to be registered with a merchant status. This status is relatively easy to achieve for the companies that are hosted in the European and the North American regions. “However if your business and bank accounts are based in sub-Saharan Africa then you face a virtually closed door. Prior to 9/11 there were loopholes. When eShopAfrica started trading on the Internet in 2000 it took advantage of one of these loopholes – the payment service provider didn’t really mind where the business was as long as it was ‘on the Internet’ and had a trading address somewhere – in this case in Accra. However new post 9/11 legislation means that the payment service providers must implement a scheme called ‘Know your Customer’. Under this scheme they must be able to visit the trading address of the company – which must be in the UK. There is a South African route which requires a business presence and bank account there – it’s circuitous but an option but the bottom line is that taking credit cards is a big barrier to trade. If you can’t take credit cards you have to rely on old world payment mechanisms such as bank transfers and checks by mail or courier.” (Eshop Africa Official Website, 2003)
The web and internet as an alternative to the current system
Despite the fact that the countries in the African region have been facing significant problems regarding the merchant status for transacting through credit and visa cards through online billing and presentment systems, this is still the most efficient the most feasible way for the people residing in these blocked regions to communicate and carry out their banking activities.
The reason for this is because the internet is available to the people through satellite and LAN/ cable based connections. Even the remote areas of the region can get access to the internet through a devoted satellite link. This makes it possible fro anyone in this region to access the internet. Aside from this the level of e-banking and billing and presentment services that are offered online are becoming more and more fool proof each day with additional security checks and authorization being out in place. As a result the small and medium level businesses in the regions as well as the individual customer/ person can also access and make use of the online and web services for dedicated to electronic banking, electronic commerce and electronic billing and presentment services.
Another factor that is in favor of such a kind of e-commerce ad billing & presentment solution for the African region is that with the technology available, it is now possible to integrate internet and communicative methodology with mobile phones making it possible for people in this region to be able to carry out their banking activities through in the convenience of their own time and secured locations through the mobile phone itself. For mobile phone banking the infrastructure required is the same as that for the operation of a mobile phone. This is already existent in most of the inhabited regions in the African countries making it possible for them to access the net and their bank accounts through the mobile phone.
This is supported by the fact that the cybercafé culture in Africa is booming. This is mostly because decimated lines cannot be delivered top all the homes in the region due to the enormous distances and the rough terrain. Instead Internet Kiosks and Cyber cafes have sprung up which offer multiple portals through which the people can access the net and use it for their personal activities like web surfing, emailing as well as for online banking and bill presentiment. More over “mobile phones represent around 90% of all telephone lines in Africa. The continent’s mobile market is consistently growing at around 50 to 60% every year. Enormous further potential remains, with market penetration standing at little more than 20%. Due to Africa’s poor fixed-line infrastructure, the mobile networks are beginning to play an increasing role in Internet service provision as well” (‘Africa – Mobile Market Overview & Statistics’, 2007)
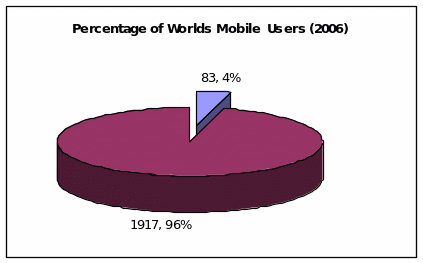
The following chart depicts the percentage of Africa’s mobile phone users in terms of the mobile phone market in the World as at in 2006. The figure is based on 83 million African mobile phone users and 2 billion mobile phone users worldwide.
Examples of companies undertaking web based payment and ecommerce
In the past couple of years many companies and state banks in the African regions have started employing online billing and presentment services and are also offering mobile and internet banking options to the account holders. Additionally the in other areas it is also possible for the general population to be able to pay their utility bills through devoted kiosks which are connected to the internet as well as through their mobile phones and personal computers. This section of the paper provides information regarding the kind of services offered by such companies and how is it helping the population of Africa adapt to e-commerce making it the basis of monetary transactions in the future.
One of the companies which is providing such service is VirtualTerminalNetwork.com. This website has formed a network for virtual and mobile payment which is specifically designed and developed for the developing economies and regions of the world. This system does not make use of the ATM machines that are highly expensive and wastage of investment in such high risk and low resource based countries. The company tested and launched its this service in Africa to check out the results while providing a realistic solution for the electronic trading and payment [presentment needs of the region. The system makes use of webs and mobile based technology to aid in the processing of transactions and for attaining access to the monetary funds across the region. With this system it is possible for the customers to deposit funds with any alliance and associate financial institution or bank and have it transferred to the personal accounts as well to other accounts in case of electronic payments. “VTN allows Merchants and Retailers to process transactions safely and securely from any computer connected to the internet and GSM Phone. With a secure login, they can complete transactions rapidly within the VTN network and receive instant authorization in real time. In addition, VTN can run in French, English and Spanish so the customer can go global while staying local. Account Holders can access their personal funds via any participating financial institutions, agents and retailers in VTN’s extensive network. Withdraw the funds easily and securely over the internet or by using the GSM phone, then pick up the funds at any participating Bank or financial institution whenever they like.” (Virtual Terminal Network Official Website, 2007).
In the year 1996 the stock exchange in Johannesburg offered the JET system to its members from which the Share Transactions Totally Electronic System evolved in 1999. This system enabled people to buy and sell shares electronically making it possible for the people in South Africa to conduct electronic transactions through the internet. This system had two purposes “to bring South Africa in line with the international practice; and to create a secure electronic settlement environment for trades in shares listed on the exchange and therefore to reduce the risk of tainted scrip and of settlement failure.”(Henning & Ebersohn, 2001).
Following the suit of such companies like VTN other well known money transferring services like PayPal are also paying specific attention to the requirements of the e-commerce market in Africa. “PayFast will soon be a new online payment system for South Africa. Late this year or early 2008 S. African locals won’t have to worry about sending, receiving or withdrawing their online funds because PayFast will allow proper e-commerce for all of South Africa.” (Mark, 2007). This payment processing will be available for free for personal users while the merchants will have to pay a low per transaction charge for the services.
In 2001 it’s the South African online bank ABSA also initiated the service of providing its customers with free internet service for online banking and bill presentment services. The infrastructure for the internet at this time as provided by the ICL and the Cisco Systems. The main target of this service initiated by the ABSA bank was the small and medium enterprise sector in the region. This service was launched to provide facilitation in e-commerce and make it easier and possible for the smaller business to conduct their business and transactions online as well.
Conclusion
Through this paper we have been able to identify the main problems that are being faced by the population residing in the African region pertaining to their e-banking and e-commerce requirements. The basis of the problem that was identified was that the services for e-commerce were not available in the region due to security and lack of control and monitoring of records. Additionally the e-commerce option that was in place which use ATM machines to conduct the transactions was almost useless and highly risky as the ATM machines suffered power failures due to the lack of electricity in the region making them redundant. Another problem that was identifies was the limited access that the people in the region had to the local banks and their branches.
As a proposed solution we have come up with a webs and internet based electronic e-banking and bill presentiment solution for the region. This option can be available to the public as well as to the business and corporations through the internet and the mobile phone. The basis for the option is that it makes it possible for anyone in the region to access the service. The success of the internet and the mobile pone and communication in the region is used to support this solution. By way of example some of the initiatives taken by private and global companies’ pertaining to providing a web based e-payment solution for the region have been depicted with examples to support the solution.
References
Molla, M., Licker, P., (2004), “Maturation Stage of eCommerce in Developing Countries: A Survey of South African Companies”, Information Technologies & International Development, Vol. 2 Issue 1, p89-98, 10p, 5 graphs, 2007. Web.
Molla, M., Licker, P., (2005), “ECommerce adoption in developing countries: a model and instrument”, Information & Management, Vol. 42 Issue 6, p877-899, 23p, 2007. Web.
Bridge, S., (1999), “SA’s second fixed-line attracting attention”, Telecommunications – International Edition, Vol. 33 Issue 2, p20, 1/2p, 2007. Web.
Benedict, K., (2006), “Taking Africa online”, Finweek, p22-22, 1/3p, 2007.Web.
Olfe, D., (2004), “Bank in South Africa Using Security Tags”, American Banker, Vol. 169 Issue 213, p9-9, 0p, 2007. Web.
“E-billing becoming the norm”, Finance Week, p42-42, 3/5p, 2007. Web.
(2002), “Electronic Payment Services”, Financial Executive, Vol. 18 Issue 9, p13, 1/3p, 2007. Web.
(2000), “Banking on the internet”, African Business; Apr2000 Issue 253, p31, 1/2p, 2007. Web.
Henning, J., Ebersohn, G., (2001), “Risks to the South African financial markets -PART 1”, Journal of International Banking Regulation; Dec2001, Vol. 3 Issue 3, p269, 22p, 2007.
Pieterse, G., (2001), “Major boosts for SMEs”, Finance Week; 2001, p38, 1p, 1c, 2007. Web.
Jones, L., (2000), “What a disappointment”, Finance Week, p56, 1p, 1 chart, 1 graph, 2007. Web.
Hogan, M., (2006), “A Global Assault on Inflation”, Business Week Online, p13-13, 1p, 2007. Web.
Jones, L., (1999), “Not so many trading live wires’”, Finance Week, p15, 2p, 1 chart, 2007.
Mutula, S., (2003), “Cyber café industry in Africa”, Journal of Information Science; 2003, Vol. 29 Issue 6, p489-497, 9p, 2007. Web.
Tenthani,R., (2000), “Malawi’s e-commerce revolution”, 2007.
“Ecommerce report: The revolution is not being televised in Africa”, 2007. Web.
“Ecommerce in Africa”, Eshop Africa Official Website, 2007. Web.
Mark, (2007), “Good News for S. African E-commerce and Online Payments”, Digital Money World, 2007. Web.
(2007), “Welcome to Virtual Network”, Virtual Terminal Network Official Website, 2007. Web.