Introduction
Fun is one of the most crucial human behaviors that affect the way they behave when accomplishing their roles. Human beings get satisfaction when something makes them happy. In fact, this is why people use a lot of money for holidays where they visit places such as comedy clubs. This dissertation, however, seeks to study the effect of fun when it is used in the working environment. This section sets the conceptual framework by exploring some of the theories that are pertinent to the use of fun in the workplace.
Organizational Change Theory about Fun
In an organizational setup, change is a critical aspect that the company must induce among its customers, employees, and shareholders among others. As a result, they develop different ways of inducing these changes, including tactics such as presenting awards and inflicting fear among the subjects (Hiriyappa, 2009). These techniques have been used to influence people’s behavior and introduce changes. Consequently, the agents of change are capable of reducing the resistance poised by those subjects. This influence makes the process of transformation more manageable and smooth.
Although these techniques have been used to induce change, they are both transactional and forceful. This condition implies that people do not adopt change because they are willing to transform the organization. Further, they do not embrace the stipulated changes because they understand the importance of the transformation (Kotter, 2010). Instead, they implement the changes due to fear of various vices such as interdiction and regulation.
Amidst a society that is seeking better methods of transforming the existing policies, the fun has been used as a tool of change. It has been discovered that making the changes fun has a profound effect on how the subjects perceive it. In this regard, when the involved people enjoy when accomplishing the new tasks, they embrace the changes smoothly and hence the transformation becomes more effective. In fact, using fun as a tool for change has been termed as the easiest way of transforming people’s behavior positively. For example, one of the British organizations encouraged people to use the stairs by transforming them into pianos.
As a result, the members of the organization found it more fun to use the stairs and hence transformed their behavior completely. In another instance, it was discovered that when people enjoy using the dustbins to dispose of trash, they were likely to take the initiative. This implies that fun can be used to initiate positive transformation and organizational change.
Positive Psychology of Fun Theory
In the near and distant past, the use of fun was considered as an informal and unprofessional aspect. People went to work to make a living. In the modern world of engagement, employees seek to become happy, productive, and meaningful. In relation to this theory, it has been established that people’s level of happiness does not depend on their genetic composition. Instead, it depends on the thought processes that take place in the mind. This process that leads to happiness helps to create a positive state of mind. The mental condition makes the human mind more productive than when it is negative or neutral. Psychologists explain that there is a chemical produced by the brain to activate the faculties of the mind. The activation makes the body alert and capable to tackle challenges and roles.
In addition, it was discovered that 75 % of the people who have successful careers are optimistic. Essentially, the optimistic spirit is informed by the level of happiness that the person holds toward the activity. In connection to this sentiment, it is suggested that positive emotions such as happiness, joy, and love help to develop resilience as well as optimism. Optimism is critical to the process of connecting with others so that the employees relate harmoniously. Moreover, the fun increases trust between the employees and the management. Understandably, the trust reduces the operational distance between the two entities and improves communication.
Transformational Leadership Theory
When it comes to the issue of using fun, transformational leadership becomes a crucial theory. In essence, transformational leadership is based on four dimensions, including intellectual stimulation, inspirational motivation, idealized influence, and individualized consideration (Hawkins, 2011). Leaders who embrace intellectual stimulation are able to develop new ways of solving problems and challenge the existing processes.
Inspirational motivation is interested in the capability of the leaders to inspire their employees regarding goal attainment for the sake of the company (Wise & Kowalski, 2010). Individual consideration is concerned with how leaders consider the employees individually. The subjects are capable of exploiting and developing their strengths to achieve the company’s objectives. Lastly, idealized influence is meant to influence people using their moral preferences.
When leaders use fun, they revoke and implement the aspects of transformational leadership. In regard to idealized influence, the use of fun helps the leaders influence the behaviors of the subjects using their preferences. When the leaders use an attribute that is preferred by the subjects, they are wooed to buy in the idea. When it comes to inspirational motivation, fun initiates happiness among the subjects of the organization such that they become motivated to tackle their respective roles.
This result shows that fun and happiness are factors of motivation that are used to inspire organizational members towards the attainment of a common objective. Individualized consideration, which is concerned with improving personal strengths, is implemented by the use of fun. Previously, it was stated that the chemical produced by the brain increases the efficiency and productivity of a human being.
As a result, the fun can increase the capabilities of the employees and hence enable them to improve their strengths. The improved personal capabilities pave way for the initiation of intellectual stimulation that is concerned with the discovery of new ideas. As a result, fun cuts across all the four dimensions of transformational leadership. It cannot be disputed that the theory of transformational leadership is pertinent to the research interest.
Motivational Theories
Mayo’s Motivational Theory
This theory suggested that workers are not only motivated by their salaries, but also the social aspects needed in the working environment. The developer stated that employees are motivated by the willingness of the managers to consider their opinion (McInerney, 2011). In other words, the acceptance of their opinion plays a crucial role in creating an interactive environment. The free interaction enables the juniors to share their problems, concerns, and proposals with ease.
Essentially, the theorist concluded that workers are motivated by good communication, manager involvement, and working in groups. This implies that fun can improve the interaction between the members, increase efficiency, and increase performance due to job satisfaction. This theory is a perfect opposite of Taylor’s concept of motivation that considers money as the only inspirer.
Maslow Motivational Theory
This is based on the premise that human life is built on continuous and hierarchical aspirations. In this regard, when people attain one of the needs, they start seeking the next hierarchical target. The figure shows the hierarchy of needs as stipulated by the theorists.
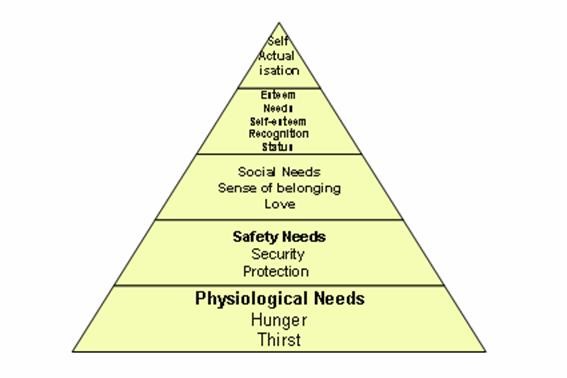
After a careful evaluation of this hierarchy, it is evident that workers aspire to get social needs, a sense of belonging, and love among others. This implies that fun can form a critical part of this hierarchy since it is an ingredient of social satisfaction. This is based on the premise that humans are social beings that are concerned with their relationships with other people. When the fun is used, the workers become socially satisfied and motivated. The subsequent motivation is important when it comes to performance.
Conclusion
It is evident that the use of fun can have profound effects on job satisfaction, performance, and collaboration among others. These positive impacts are informed by various theories, including transformational, motivation, and change concepts among others that have been discussed. Importantly, the use of fun is a crucial factor when it comes to the induction of organizational change. In this process, fun enables the employees to change their behavior because they enjoy the new policies. As a result, the agents of change do not experience a lot of resistance that can impede the process. This implies that the undertaking is implemented smoothly and the organization operates without disruptions.
References
Hawkins, P. (2011). Leadership team coaching developing collective transformational leadership. London: Kogan Page.
Hiriyappa, B. (2009). Organizational behavior. New Delhi: New Age International.
Kotter, J. (2010). Leading change. Boston, Mass.: Harvard Business School Press.
McInerney, D. (2011). Sociocultural theories of learning and motivation looking back, looking forward. Charlotte, N.C.: Information Age Pub..
Tracy, B. (2013). Motivation. New York: American Management Association.
Wise, P., & Kowalski, K. (2010). Leadership. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders.