Introduction
The concept of leadership has evolved over the years because of the changes in the socio-economic and political environment. According to Sims and Bias (2019), scholars have been drawing a parallel between leadership and management intending to integrate the two at a time when firms are struggling to attract and retain talented employees. In the past, large corporations enjoyed monopoly not only in their industry but the job market as well. It was not easy for talented employees to move from one employer to another. However, that has changed in the current competitive business environment. Skilled workers are on-demand and companies are struggling to ensure that they do not lose such resourceful workers to their rivals in the market.
Understanding the concept of human resource management (HRM) has become increasingly important for leaders in various sectors of the economy. Successful leaders understands how they can motivate their employees to act in a given way without feeling pressured or frustrated (Mello, 2018). They have to use various models, exhibits, and concepts of human management to maintain a pool of loyal and talented workforce. It means that they have to embrace unique strategies of HR management that addresses conflicting interests of different stakeholders within a firm. In this paper, the researcher seeks to discuss how leaders can use HRM concepts and theories to achieve organizational goals.
Discussion
Leaders often find themselves in situations where they have to manage conflicting interests of stakeholders within a firm. Dundon and Wilkinson (2020) argue that in a firm, shareholders often want high returns from their investment. To achieve such a goal, those trusted with leadership must maintain expenses, including salaries for employees, as low as possible as they maximize the firm’s profitability. Customers want to get the best value from the firm at the lowest cost possible, which means that the firm’s profitability and the interest of shareholders may be compromised. Employees need high remunerations and flexible working hours, which may directly affect the firm’s profitability.
The management itself is focused on fostering growth, which means that dividends to the shareholders must be low, salaries maintained to the bare minimum, and interests of customers upheld. These conflicting interests must be managed and moderated for a firm to achieve success. Successful leaders have learned how to use various HRM theories and concerns to ensure that all stakeholders remain satisfied to achieve organizational growth. They understand the fact that it is not possible to use one leadership style at all times. A leader may need to be strict when it is necessary, especially when introducing an important change that some employees may be against. On the other hand, they should be understanding and accessible enough for the subordinates to approach them whenever they are facing a challenge within the firm.
Leadership and Human Resource Management
Leaders in various sectors of the economy are facing immense pressure to achieve organizational goals with limited resources and conflicting interests. The ability of a firm to achieve success in any sector, whether it is a for-profit or non-profit making entity, depends on the effectiveness of its employees. Once policies and strategic plans have been developed, Mello (2018) observes that it is the role of employees to implement the actual actions that will achieve the intended organizational goals. From the sales and marketing department where workers regularly interact with customers to the production department where they are expected to use unique skills to lower the cost and improve productivity, employees play very critical roles in any organization. Trost (2020) observes that the still competition in the market forces companies to remain competitive. They have to understand emerging trends and develop unique ways of embracing them to remain relevant in the market.
Leadership is critical because it not only defines the creativity and innovativeness of employees but also their level of satisfaction. As mentioned above, talented workers in the modern business environment can easily leave one company for another because their skills are in demand. It is the responsibility of the leader to ensure that its talented workers are not lost to rival firms. According to Sims and Bias (2019), once a firm hires a new employee, it has to take them through some form of training so that they understand what is expected of them in their workplace. The training process not only consumes a significant amount of resources but also the time that would otherwise be used in other activities. Therefore, it is imperative to ensure that such talents are retained in the firm for as long as possible.
Leaders have to use various strategies to ensure that their employees are satisfied, motivated and empowered enough to be innovative in their places of work. Many companies use attractive remuneration as a way of enhancing employee satisfaction and reducing their turnover rates (Dundon & Wilkinson, 2020). Although the strategy is highly effective, employees also value other factors that make their work easy and enjoyable. They want to be in an environment where they feel respected and valued by those in leadership. They feel motivated when their opinions are taken into considerations when a firm is developing new policies. Having an effective communication system where they can easily share their ideas with the top management unit is another factor that creates satisfaction among employees. As such, integrating HRM principles and leadership theories is essential for a leader to overcome the numerous challenges that an organization faces.
Exhibits and Models and Their Implications on Leadership
Scholars in the field of HR, leadership, and psychology have developed various models and exhibits to help explain human relationships and how leaders can effectively influence their followers to achieve a specific goal within a given period. Trost (2020) suggests that each of these concepts and models are relevant when dealing with specific forces in the environment. it means that a successful leader cannot rigidly use one leadership model or framework and completely ignore the rest. There are cases where one needs to be tough and when they need to be accommodating. Sometimes employees need to be compelled to do something while in other cases, they are allowed to use their strategies to achieve the desired goal. In this section, the researcher discusses various leadership and HR models and theories that can help one to govern effectively.
Situational Leadership Theory
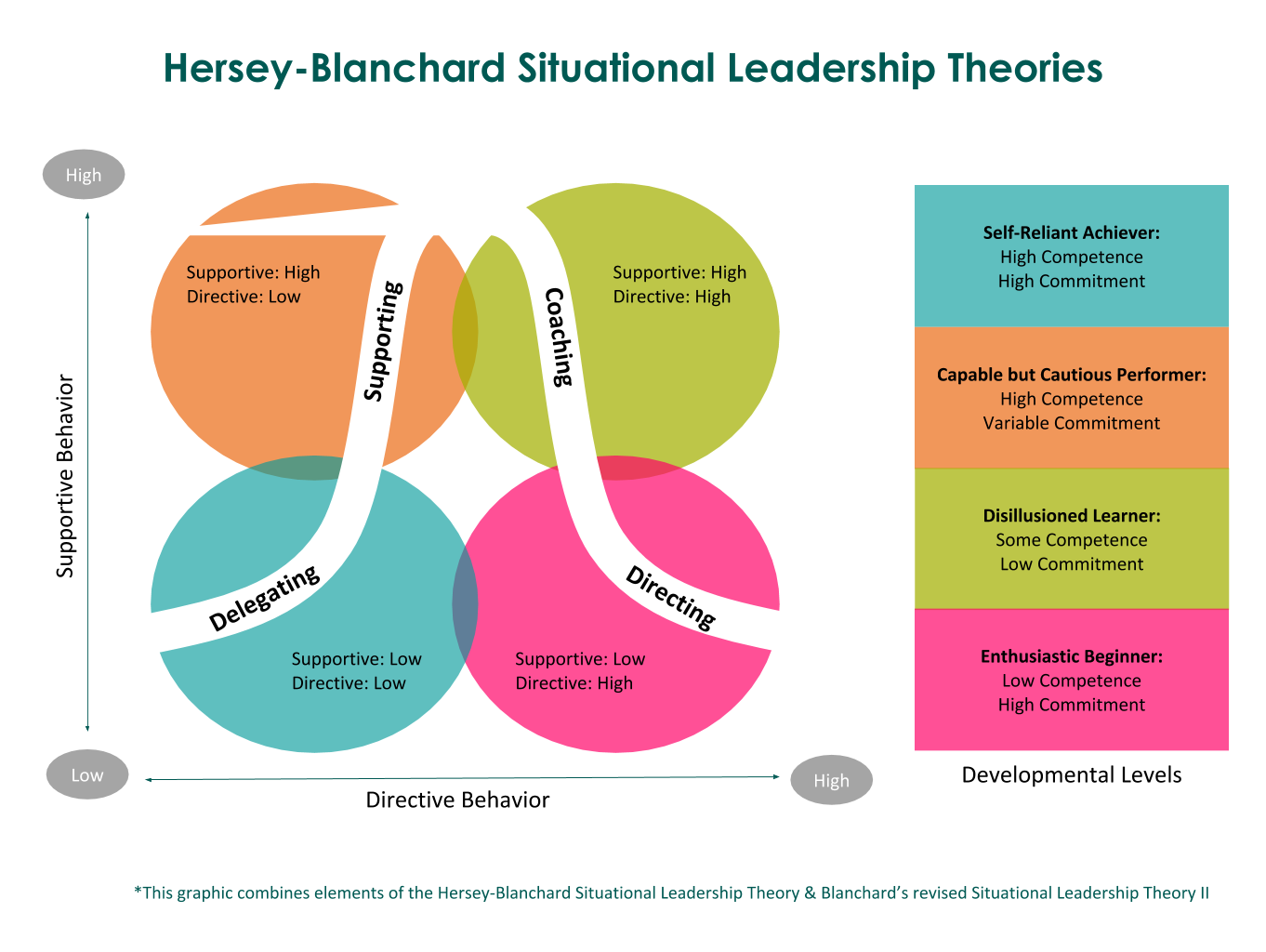
One of the most common and highly effective leadership models in modern society is situational leadership. It holds the view that leaders should apply different styles of governance depending on the situation that their company faces and the level of development of employees (Fowler, 2019). It criticizes the use of a conventional leadership style in the overall management of a firm. Successful leaders understand that each employee is unique and may require a unique approach to governance. These leaders must know how and when to use each of the four governance models proposed in this theory based on employees direct behavior and supportive behavior.
The model has four classes of employees, each requiring a unique governance approach because of their difference in traits. The first class is the self-reliant achievers who have demonstrated high competence and high commitment to the firm (Stone, 2020). Most of these employees are highly talented and self-motivated employees who have stayed with a company for a long period. They can be trusted to complete specific tasks without any supervision from superiors. They understand the vision, mission, and values of the firm, and always align their actions and decisions with them. Delegating of duties is the most effective governance approach that should be used when handling such workers. The leader will delegate specific responsibilities to them and allow them to work without any constant supervision. There will be regular communication between the leader and such employees to understand the progress and any attention that may be needed from the leader.
The second category of employees are the highly-competent workers but with variable commitment. They understand what needs to be done and have the skills and experience to achieve goals set for them (Tomal & Schilling, 2018). However, they are not as committed to the firm as those in the previous class discussed above. When handling such leaders, supporting is the most effective governance strategy that should be used. Such employees will need the support of the leader for them to undertake specific responsibilities. They need to be reminded that it is normal to make mistakes as long as there is a focus to achieve success. Such workers may need the regular attention of the leader.
The third category of employees in this model is those with some competence and low commitment. This class of workers is not as skilled as those in the two classes above. They cannot be trusted to accomplish specific tasks on their own because they are likely to make mistakes. Some may be newly recruited employees but it can also include veteran workers who never made an effort to further their education and improve their skills. They may be relevant to the firm but their performance is often in question. They are also not committed to the company, which is another cause of concern (Trost, 2020). Coaching is the most effective governance approach. It helps them to acquire new skills while at the same time ensuring that they accomplish their tasks based on the set requirements.
The last class of employees, as shown in the model above, is the enthusiastic beginners. Their main characteristic is that they have low competence but a high commitment to the firm. The majority of these employees are those who have just joined the firm from college and still lack the experience needed for them to perform specific tasks (Fowler, 2019). However, they are eager to learn and committed to achieving success with their employer. Directing is the most effective governance approach for these workers. It makes it possible for them to acquire new skills rapidly through experience. Figure 1 below identifies the different classes of employees and governance approach appropriate for each stage.
Authentic Leadership Theory
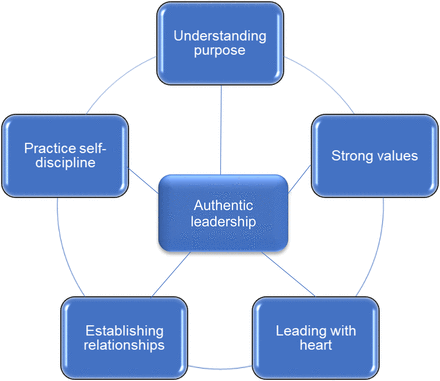
Authentic leadership is a new but rapidly developing concept of leadership in the modern business environment. It holds the view that a leader is at liberty to choose their governance strategy as long as the choice is consistent with their values and character. As the name suggests, this theory requires leaders to be as authentic as possible in their governance strategies. Authentic leader needs to avoid cases where they are championing policies and principles that they do not believe in or actions that they think cannot yield the expected results (Mello, 2018). This form of governance emphasizes the need for leaders to be real and to believe in their policies. As shown in figure 2 below, such a leader should understand the purpose of their office. They should then develop strong values, which are aligned with the identified purpose (Stone, 2020). They are then required to lead with heart, always being compassionate and trusting in their leadership capabilities.
The model also encourages an authentic leader to establish relationships. Having a cordial relationship with the subordinates makes it easy to communicate effectively within the firm. A leader can express his opinions to the subordinates with ease while at the same time receiving the views of the subordinates. It also creates trust and commitment among all the stakeholders in the organization. Finally, the model requires leaders to practice self-discipline at all times. They need to uphold the values of the firm and respect rules developed to govern relationships and actions of all stakeholders, including policies that they have helped develop. They need to exercise financial discipline, avoiding the temptation to use company resources for personal issues.
Ethical Stewardship
Companies are under pressure to maintain a pool of committed and talented employees as a way of remaining sustainable in a highly competitive business environment. Radical leadership approaches such as autocratic governance approaches that ignore concerns of employees are increasingly becoming less popular. They are being replaced with models that encourage compassion and understanding of workers. One such leadership concept, which is gaining rapid popularity, is ethical stewardship. According to Baker (2019, para. 4), ethical stewardship is “a concept that encourages fair, just and equal treatment of employees and shareholders and a management style focused on policies that work for the good of the organization as a whole.” This theory holds the view that in an organizational setting, it is common for differences to emerge.
Different stakeholders such as shareholders, customers, employees, and managers, have conflicting interests. As such, there has to be fairness when addressing conflicts or conflicting interests. When trying to reward employees as a way of ensuring that they remain committed to the firm, the management should not ignore the needs of their shareholders, customers, and the sustainability of the firm. Similarly, to please customers in the market, a firm should not ignore the challenges that workers encounter when interacting with customers. The management must be just when handling employees, especially when differences emerge. The theory encourages leaders to treat employees equally irrespective of their race, gender, religious affiliation, country of origin, or any other factor that may make an employee unique in the firm. It is based on the belief that when everyone is treated justly, they will respect others and create an environment where they can work as a unit to achieve specific goals.
Goal-Setting Theory
One of the HR theories relevant to a leader is the goal-setting theory. It holds the argument that setting specific measurable goals is critical for a firm’s success (Sims & Bias, 2019). The problem that many firms face is that their leaders set ambiguous goals that cannot be easily implemented or measured. It becomes difficult to know whether the firm is making good progress towards the realization of such goals. As shown in figure 3 below, an effective leader should take into consideration several factors when setting goals. The first factor is clarity, which refers to the measurable goal that needs to be achieved within a specific period.
The leader should ensure that the goal is clear enough to be understood by all the relevant stakeholders. The second factor is the challenge, which are the factors that may limit the ability of a leader to achieve the desired goals using the set resources and the time (Tomal & Schilling, 2018). Defining the expected challenge makes it possible to determine how they can be addressed. Commitment is the third factor, which requires all the relevant stakeholders to support the new idea. As Stone (2020) observes, such a new idea can only be supported if it is defined clearly and the stakeholders believe in it. The commitment means that it will receive the necessary support during the implementation stage.
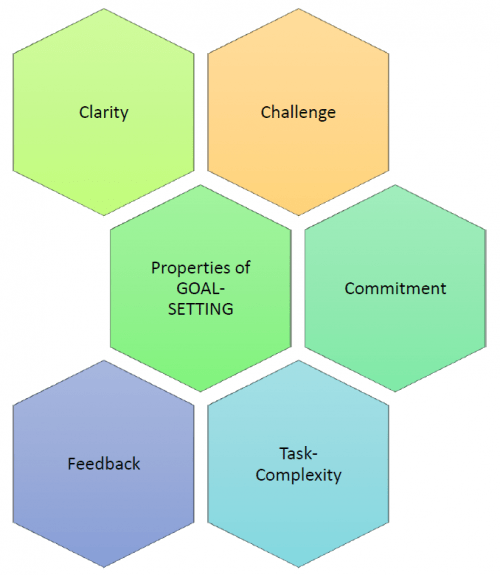
The next component for the successful implementation of this theory is task complexity. In this stage, the leader outlines specific actions that have to be taken when implementing the goal. It should also define those who need to be involved in the implementation process and the resources needed to make it a reality. The last component of the model is the feedback system. Individuals involved in the implementation should provide feedback about the progress and areas that need adjustments. Beneficiaries of the implemented goal should also communicate with the management if it met their expectations. Whenever a change is needed, a leader should have effective mechanisms of responding within the shortest period possible.
Conclusion
Leadership in the current business environment is evolving and companies are under increasing pressure to ensure that they adjust their governance strategies to achieve specific objectives. The study shows that HRM principles have also evolved in line with the changing leadership principles. HR managers are finding increasingly challenging to source for, train, and retain highly-skilled employees. It is easy for a talented worker to move from one firm to the other because their services are in demand. It means that if they feel unappreciated, underpaid, or undervalued at one firm, they can easily move to another company where they will feel their efforts are appropriately rewarded and valued. In such an environment, leaders must redefine their governance approach to lower the rate of employee turnover. The paper discusses various theories of leadership that managers can use to ensure that employees are constantly motivated and committed to the firm. As discussed in the paper, leaders should realize that there is no specific model that is universally effective in all settings. Unique situations may call for a different approach to governance that can help address what the firm is facing.
References
Baker, A. (2019). What is ethical stewardship? Business Operations.
Dundon, T., & Wilkinson, A. (Eds.). (2020). Case studies in work, employment and human resource management. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Fowler, C. L. (2019). Human resources: Best practices in church management. Paulist Press.
Mello, J. A. (2018). Strategic human resource management (5th ed.). Cengage Limited.
Sims, R. R., & Bias, S. K. (Eds.). (2019). Human resources management issues, challenges and trends: Now and around the corner. Information Age Publishing Inc.
Stone, R. (2020). Human resource management. John Wiley.
Tomal, D. R., & Schilling, C. A. (2018). Human resource management: Optimizing organizational performance. Rowman & Littlefield.
Trost, A. (2020). Human resources strategies: Balancing stability and agility in times of digitization. Springer.