Executive summary
This study specifically aimed at analyzing the benefits and limitations of online marketing from the perspective of customers as well as service providers. Furthermore, the study aimed at evaluating the impact of online marketing on customers’ behaviour towards the products and services offered on line, in addition to accessing if online marketing satisfies the customers. Lastly, it aimed at evaluating the possibility of maintaining a better online customer relationship process.
The study employed qualitative as well as quantitative research methodologies to come up with methods of data collection. Data was collected on customers that engaged in online purchases as well as on the service providers themselves. Questionnaires were administered to the customers whereas key informant interviews were administered on the online retail service providers. Probability sampling method was used to come up with the sample size for the study as all the respondents were to be chosen based on some form of random selection.
The findings reinforced the works of previous researchers as well as documented literature on online marketing that indeed the field had a massive potential for growth especially in mainland China as well as in Hong Kong. The study revealed that young people readily adapted to online marketing strategies and online buying of products and services more than older people. It also found out that majority of individuals use the internet for accessing news, searching the internet, and E-mailing. Majority of online customers mostly purchase music and entertainment accessories, followed by computer software programs, and then computers and computer accessories. These were interesting findings for the study.
According to the research findings, the internet acts as a communication medium between the service providers and the customers. Online marketing has offered consumers a bewildering array of choice of consumer products. In the same vein, the advance of internet as a distribution channel has affected the speed with which consumers and commercial buyers have adopted to the medium. The study also revealed that online marketing is convenient to customers as they can shop 24 hours a day from the comforts of their homes, besides being flexible and having the capacity to offer product related information.
In evaluating the attitudes towards online purchases, the study revealed that Individuals are always influenced by close family members and friends to participate in online buying. Also, Internet uptake is affected by socio-cultural, psychological, organizational factors. Majority of the customers surveyed were satisfied with online transactions and had trust in the process. However, a few were frustrated by the limited methods of online payment methods available in the market.
In evaluating the benefits and limitations of online marketing towards service providers, the study revealed that many retailers had indeed closed down a number of their branches or reduced their sales force in favor of internet based marketing strategies. Online marketing had also benefited service providers in the customer relationship building process. Internet marketing had effectively increased service providers’ efficiency and reduced their operational costs. Also, the study revealed that online marketing had indeed enabled retailers to access the global markets. Subsequently, the study found out that online marketing is quick, cheap, reliable, and highly effective to the service providers.
As for the limitations, the study found out that slow internet connectivity continues to affect service providers, facilitating them to loose crucial revenue as customers try to access other websites. Many service providers and customers alike have reservations about available electronic payment methods especially in this age of internet fraudsters. Also, companies dealing with bulk products are limited to transact their business online due to the heavy costs involved in delivering the products. Another limitation revealed by the study was that service providers were increasingly being faced by limitations of high capital outlays and non-compatibility with technological architecture. To the customers, online sale of products did not offer consumers the opportunity of touching, smelling, and feeling the product before purchasing. Also, majority of customers had at one time or another avoided surfing the sites altogether due to the struggle involved in downloading the much needed information
It was also revealed that online computer sales had taken root in China, led by the two online computers retailers, Dell and IBM, and that online retail sales of computers and allied products in Hong Kong had indeed gone up despite international economic turbulence. Overall, this study served to give a picture of online retail uptake in Hong Kong.
Based upon the findings of this research study, a number of recommendations were arrived at, as a way of enhancing online marketing services. First, the study recognized the huge growth potential that online marketing has. Additionally, this attractiveness also favor fraudsters who may wish to rip off customers.
For this reason, the study recommended that the Hong Kong government come up with a regulatory framework to ensure that potential customers do not fall prey to internet fraudsters. Such regulations will further offer online transactions the much needed credibility and confidence.
To achieve this, the government is called upon to ensure that all the companies that offer online marketing services are both authentic and reliable. Furthermore, it is important that such companies are secure, and this is thus the role of the government to assess and certify their security features.
Moreover, the Hong Kong government should facilitate legislation on money back guarantee on products purchased over the internet. Such a regulation has already been introduced in Germany and has popularized online purchases due to the confidence it has given to the potential customers. Such a regulation then ought to be implemented in Hong Kong. All the stakeholders’ concerned need to work in harmony to make sure that the internet access is guaranteed to potential customers.
Businesses should also be supported by the relevant authorities to increase their bandwidth to guard against slow internet connectivity, responsible for driving away millions of potential customers. Electronic payment methods need to be made more readily available and more secure for online marketing to realize its full growth capabilities.
A majority of potential customers fear to transact their business online due to the fear of insecure payment methods. A secure online marketing shall only win their confidence once they have a guarantee that they will get value for their money.
Introduction
Topic Area
The internet is one of the most sophisticated and enterprising innovations to take the world of retail marketing by storm. Considering its wide application and the immense popularity it has with consumers, it is only logical to understand its benefits and limitations to consumers and service providers alike. With the transfer of data at one’s fingertips, it is only imperative for business enterprises to maintain cordial relationship with their customers, in addition to maintaining a strong database that can help improve service delivery to customers. The internet allows a wider coverage and adds a different dimension to business altogether. In respect of this, specialized software that specifically allows retailers to retrieve and transfer data exists at the touch of a button. Such software packages include the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) package (O’Brien 2003; Elson 2006).
Barrows (2007) states that dynamic market forces such as global competition, changing customer expectations, and new communication technology and corporate restructuring have mandated continuous learning and implementation of strategies designed to beat competition. One of such strategies is online marketing, which uses specialized software packages such as the CRM to address all the requirements necessary to handle customer relations. There are two fundamental areas identified to make CRM effective:
- What are the specific needs for organization’s long-term goals, performance objectives and measures of the organization?
- What are the parameters defined by the organization for it to be termed good, and what are the capabilities required to achieve this goal (Duncan & Brown 2001, p30; Strategy 2008).
In a layman’s language, online marketing is the practice of utilizing the internet as a medium for any marketing campaign carried out by individuals, public or private entities, or government agencies in an attempt to sell products and services to customers (Aranda 2008; Shaw 2003). By any standards, internet marketing is a relatively new phenomenon. It offers numerous possibilities to retailers and customers alike to improve their lives and business. Online marketing is convenient to customers as they can shop 24 hours a day from the comforts of their homes. Internet marketing is also immediate and interactive in the fact that consumers can get to interact freely with the company’s site to find crucial information about the products and services they require, order online, and instantly download them. The service providers are able to effectively interact with consumers and study more about their lifestyles, behaviors, and attitudes. Companies are thereby able to come up with products and services that appeal to the consumers in the market place through the use of consumer data bases (Kotler & Armstrong 1998). Many more benefits and limitations of online marketing will be discussed elsewhere in the review of related software.
Customer relationship has become a prerogative to success. Customer relationship by far eclipses all the other parameters in a company’s profile. It is the function of company managers to strategize on how to retain the most profitable customers due to the value they add to their businesses. Thus, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) becomes important as it forms part of a customer-focused and customer-centric strategy to improve and succeed in today’s competitive business environment (O’Brien 2003, Ch.6, p.182).
From Australia to Canada, Africa to Latin America, the internet is increasingly replacing traditional methods of transacting business (Quelch & Klein 1994). In Hong Kong, individuals are disengaging themselves from, traditional media of the TV, newspapers, and magazines towards the internet. Accordingly, more and more of the Hong Kong’s population are looking to the internet for information and news. Due to the trend, more and more businesses are looking to the internet to market their products and services. Most companies in Hong Kong believe that online marketing gives them a leeway to include more product information to potential customers than most traditional forms of publications and broadcast. It is also cost effective. Potential customers on the internet can instantly find what they are looking for by simply searching categories, keywords, or browsing. Business too can now freely interact with their customers, and make the promotion of products and services using the internet a unique experience for potential customer (Daft 1998).
Research Purpose
With the expansion of the Internet and the evolution of e-business, business marketability has grown quite rapidly in countries like the U.S and in many western-European countries. This trend is quite noticeable in certain Asian countries such as Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and Hong Kong. Once a British colony, Hong Kong won its freedom and joined mainland China but still managed to retain a pro-western business market (Research & Markets Access 2001; Rathore 2006). Accordingly, the internet has become a vital tool in business communications in the modern competitive global market. The research aimed at analyzing the benefits and limitations of online marketing especially in Hong Kong’s retail sector. Furthermore, the study aimed at comparing and contrasting the benefits and limitations of online marketing both from the customers and service providers’ points of views. The study specifically aimed at exploring the role of the internet in supporting and sustaining high level performance in two major computer giants; Dell and IBM, and also aimed at studying its benefits and limitations on some retail giants in Hong Kong. The study was also interested in analyzing the benefits and limitations that customers get from using the internet-based shopping cartels provided online by these retailers. The paper aimed to achieve these objectives through undertaking a thorough market research study to achieve qualitative and quantitative data needed to answer the research purpose
Structure of Dissertation
The dissertation will follow a set of chapters including, the Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, Data Analysis, Conclusion and Recommendations, and the appendix section. As the name suggests, the introduction will make a brief introduction of the topic on the internet and its role in retail marketing. This will be followed by the Literature Review, which will be an in-depth analysis of the role of the internet, its various functionalities, its positive and negative impact on marketers, its uptake in Hong Kong, and its role in influencing the attitudes and buying behavior of consumers. This chapter is followed by the methodology. This Chapter serves as a framework for explaining how the research was conducted. It gives a brief description of the research design, research instruments, sampling methods, and the methods used in data analysis. The study methodology will employ both quantitative and qualitative research methods, but with foreseen limitations.
This will be followed by the research findings, an in-depth analysis of the study results in online retail marketing. The chapter will also offer an in-depth analysis of the benefits and limitations of online retail marketing from the perspectives of both the customer and the service provider. An analysis of how the internet has been used to inspire the business objectives of Dell and IBM computer retailers in Hong Kong will also be undertaken. This will be followed by a section on study conclusions and recommendations. The findings of this study will be used to answer the research objective of whether the internet is a useful tool in Hong Kong’s retail business. Relevant information that will be unavailable in the main body of the paper will be attached in the appendices at the end of the paper.
Literature Review
Introduction
This section aims at providing the basis for the research question by conducting in-depth review of the online marketing field, and its benefits and limitations viewed from the perspective of customers and service providers. It aims at looking at the origins of the internet and online marketing, theoretical frameworks in marketing, growth of the field, and the benefits and limitations it has offered to customers and service providers alike. The section will rely heavily on previous researches in online marketing to provide a conceptual framework for answering the research question.
Online marketing, also referred to as internet marketing, web marketing, basically entails marketing of goods and services over the internet (Online Sales 2008). Since its inception in the 1960’s, the internet has grown dramatically to enable a virtue market where goods and services are exchanged on a willing seller willing buyer basis (Greenstein & Hainzon 1995). In many nations around the world, internet connectivity is one of the prerequisites to economic development. This is because of the obvious advantages it brings in terms of opening up local businesses to a large pool of local and international customers connected to the internet. The marketing discipline has particularly benefited immensely following the advent of internet based solutions touching on the field.
The internet
According to Peter (2004), the internet is a “global system of interconnected computer networks that interchange data by packet switching using the standardized Internet Protocol suite (TCP/IP). In a layman’s language, the internet can be defined as a network of networks linked by fiber-optic cables, copper wires, and wireless technologies to provide connectivity to millions of public, private, business, academic, and business networks. The global phenomena has the capacity to carry various informational services and resources such as file sharing, file transfer, electronic mail, online chat, online gaming and other resources found in the World Wide Web (Quelch & Klein 1994; McNamara 2008). Through cellular routers, mobile phones, handheld game consoles and data cards, the internet can virtually be accessed from anywhere.
From its inception, the internet has become a necessary tool for the civilized world today. Not much happens without the internet, for its applications and uses are enormous to write down here. However, there is no denying the fact that the internet has made life much easier for all concerned, be it business or social. For business enterprises, the trend towards direct delivery from producers to consumers has speeded up thanks largely to the growth of internet uses and accessibility. For manufacturers and retailers, the internet acts as a communication medium with customers (O’Cass & Fenech 2003). In essence, the internet has indeed provided a large market for corporations. Through the efficient nature of low-cost commerce and advertising found in the internet, companies have been able to generate sustainable sales revenues to shield them away from harsh market conditions (Kapuscinski 2004).
The internet has greatly revolutionalized the shopping concept as it is capable of simultaneously spreading information about shopping offers to many people (Dunphy et al. 2004). Using the internet, an individual can order, pay, and download products and services online within a few seconds. The internet can also be credited with facilitating personalized marketing, a form of marketing which permits a business enterprise to market its products to specific groups of people or specific individuals more than any other advertising medium. Online communities found in internet sites such as Facebook, MySpace, Orkut, and Friendster offers the basis for personalized marketing (Online Sales 2008). Online marketing firms particularly use these sites to market their products and services based on the characteristics of these community groups.
Origins of online marketing
Principally put, online marketing is the practice of utilizing the internet as a medium for any marketing campaign carried out by individuals, public or private entities, or government agencies in an attempt to sell products and services to customers (Aranda 2008). By any standards, internet marketing is a relatively new phenomenon. When the public started accessing the internet after its inception, many companies realized that they could utilize the service to present information about their products and services to potential customers. The first known case of internet marketing made use of text websites to pass on some basic information about products and services offered by the companies (Kalokota & Robinson 2003). These websites could not upload graphics or pictures of the products on offer. With the advent of video availability, image availability, and faster internet connections in the 1990’s, internet marketing strategies evolved from providing product information to selling advertising space, business models, software programs, and many more products. Consequently, companies like MSN, Goggle, and Yahoo emerged to fill the huge demand for the provision of advertising space (Ogg 2007).
Several years later, websites became more complex as companies realized their importance in reaching the global customer audience. The websites became a source of interest for potential customers since they could successfully upload pictures of products and graphics to make them more appealing (Hitachi consulting 2008). New techniques through which companies could sell various products and services right from their websites were developed through technological advancements. In the same vein, customers could order and pay for the products right from the comfort of their homes using their credit cards. Through a simple click of the mouse, companies could reach numerous customers all over the world. Consequently, the internet marketing option has increasingly been utilized by companies and other market players to build and solidify a brand name, push direct sales, gather customer information, and encourage repeat business (Chesbrough & Teece 1996). Other marketing mediums include the Radio, Television, Billboards, and the print.
Online Marketing in Hong Kong
According to available sources, Hong Kong boasts of over 2.7 million internet users. According to a study conducted in 2006, over 87 percent of Hong Kong’s families had computers in their homes; and 66 percent of the computers are connected to the internet (Runkel 2007). One of the areas that have grown phenomenally as a result of good internet connectivity among households in Hong Kong is online marketing. Many companies are increasingly advertising their brand products and services on the internet, especially on the internet TV. In the same vein, more people are spending much more of their time online thereby creating a potential market for products and services advertised online (Sharkey & Wang 2003).
In Hong Kong, individuals are disengaging themselves from, traditional media of the TV, newspapers, and magazines towards the internet. Accordingly, more and more of the Hong Kong’s population are looking to the internet for information and news. Due to the trend, more and more businesses are looking to the internet to market their products and services. Most companies in Hong Kong believe that online marketing gives them a leeway to include more product information to potential customers than most traditional forms of publications and broadcast (Wendy 2000). It is also cost effective. Potential customers on the internet can instantly find what they are looking for by simply searching categories, keywords, or browsing. Business too can now freely interact with their customers, and make the promotion of products and services using the internet a unique experience for potential customers (Timmins 2003).
Businesses particularly in Hong Kong are fond of using the internet to communicate with customers through chats, newsletters, and online promotions (Sharkey & Wang 2003). In Hong Kong, the most widely utilized internet marketing methods includes e-mail marketing, digital Points of Sales, Search engine marketing (both pay per click advertising and search engine optimization), affiliate marketing, promotions, e-mail advertising, campaign banner advertising and interactive advertising.
Theoretical perspectives and business models
Various theoretical perspectives have been advanced to explain the phenomenal growth of internet marketing. For the purposes of conceptualizing the research questions, the Diffusion of Innovations Theory and the Long Tail Theory will be discussed. The business models of Business to business (B2B) and Business to consumer (B2C) will also be discussed.
The Diffusion of Innovations Theory
In his 1983 book Diffusion of Innovations, Everett Rogers came up with a theory of how, why, and at what rate new technology and ideas spread across cultures. “Diffusion is the process by which an innovation is communicated through certain channels over time among the members of a social system” (Wendy 2000). According to Rogers, innovations would spread within the society in an S-curve. The early adopters must first select a technology before the trend is picked up by the majority of people in the society thereby making the innovation or technology to be common. To him, companies must aggressively engage in diffusion research to critically analyze marketplace conditions that have the capacity to decrease or increase the likelihood of a new concept, product, or idea being adopted by members of a particular culture. Accordingly, the attitudes of individuals towards a new innovation or technology form the basis of its diffusion. At a glance, the theory envisages that interpersonal contacts as well as the media influences judgment and opinion despite providing information to members of a specific culture (Spooner & Kannelos 2004).
The theory consists of four crucial elements. The first is innovation or the process of introducing something new in the market. Technological advances over time have led members of the public to associate more with technological innovations found in the internet, online marketing being one of them. According to Rogers, an innovation is any object, process, or idea considered to be new by a specific group or individual. The Second aspect is the communication channels, or ways through which information is distributed to other people or groups of people. The third crucial element is the social system, comprising of group of people or organizations connected by some shared goals or purposes. Time is the forth key element. In Rogers model, time entails the length that any innovation-decision process takes, the time that elapses before other individuals or groups adopts the innovation, and finally the authentic rate of the innovation’s adoption (Spooner & Kanellos 2004).
The theory has found wide usage in the marketing field, especially in online marketing. In practical application, online marketers specifically targets the adopters as well as innovators to first adopt online marketing-based solutions before they influence the early majority as well as the late majority preferably through the word of mouth. According to the theory, the laggards are not particularly targeted as primary audience by the online marketers (Schifmann & Kanuk 2000). The theory can also be used to effectively explain how internet marketing has grown from the initial stages, not withstanding the fact that the theory could also be used to clearly locate the benefits and limitations of internet marketing.
The Long Tail Theory
Credited to Chris Anderson, the long tail theory attempts to describe the niche strategy of business entities that sell a variety of unique products in relatively small quantities such as Netflix and Amazon.com (Reynolds 1997). The theory is based on the frequency distribution concept, analyzed by statisticians since the 1940’s. According to the theory, such companies are able to realize significant proportions of profit based on the distribution of their inventory costs. Rather than selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items, these companies realize their business worth through selling large volumes of rare products to many customers.
According to Anderson, “the group that purchases a large number of non-hit items is the demographic called the Long Tail” (Reynolds 1997). The selection and buying lifestyles of the population results in a Pareto distribution or a power law distribution curve when there is a large population of customers, a large availability of choice, and a negligible distribution and stocking costs (Timmins 2003). Accordingly, a market that bears a high freedom of choice will generate a certain degree of inequality through despising the 80 percent of the items (long tail or non-hits) in favor of the 20 percent (head or hits).
This theory was further developed by Ken McCarthy in 1994 to address internet based marketing solutions. He noted that pre-Internet marketing strategies didn’t depend on potential lifetime demand or quality but rather depended on what he termed as lifeboat economics to make their promotion and distribution decisions. But since the advent of the internet, online marketing is particularly gaining precedence in informing consumer choice. According to Anderson, products that have low sales volumes or are in low demand can communally make up a market share that exceeds or rivals the relatively few block busters or best sellers if the distribution channel or the store is large enough. In developing this theory, Anderson relied heavily on earlier works by Michael D. Smith and Erik Brynjolfsson that sought to reveal how Amazon.com remained profitable though online selling of obscure books that could not be found in other bookstores (Blane 1997). Online marketing has thereby created a potential market (Long tail) through the numerous sales and distribution channels or opportunities offered by the internet. Through online marketing, business enterprises have fundamentally succeeded to tap the market and fulfill its requirements.
Business models
The business of internet marketing is innately associated with a variety of business models. According to Kotler and Armstrong (1998), the most used business models in online marketing are the Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Consumer. B2B entails business entities that conducts business with each other, while B2C basically entails business entities that directly deals with the end consumer. The B2C model was the first to emerge with the advent of internet marketing. This means that business enterprises were increasingly dealing with end customers during the initial phase of internet marketing. Business to Business internet based transactions came later as they were more complex. Subsequently, both business models have been applied in online marketing to further its cause of being the best advertising medium (Wendy 2000).
Online marketing in retail sector
Online retail marketing involves the “sale of goods or commodities in small quantities directly to the consumers using the internet” (Timmins 2003). A recent survey by Forrester Research (1997) contrasts the growth in internet shopping in 1997 and 2000. According to the research, all categories of retail businesses are expected to grow, especially those of PC hardware and sales, travel and entertainment. But overall, the retail sector performs dismally when it comes to internet marketing as it lags behind all the other sectors. The financial services industry, especially the banking and insurance industries are viewed as the best performers when it comes to online marketing. A recent study conducted by Crafted Media in the US revealed that more than one-third (38 %) of the retailers interviewed do not basically exploit available online marketing opportunities.
The retail industry in global market trends is considered as a major player. In the United Kingdom, over 2.9 million individuals (11. 5 percent of UK’s total labor force) were employed in the retail industry in 2005 (Morton 2007). In the same year, UK’s total retail sales amounted to over 260 billion sterling pounds. This serves to reinforce the fact that the retail industry is crucially important to business enterprises. The retail industry is often perceived as a stepping-stone to other profitable business sectors.
In 2005, almost 7 percent of the total retail sales in the UK were made up of online retail selling. From 2002 to 2005, the value of online retail sales per month in the UK rose from under 82 million to 1,373 million pounds. Available forecasts projects that online retail marketing will represent above 20 percent of all retail sales in the UK. Online retail business in the UK alone will have the capacity to achieve expansion of up to 320 percent to effectively conduct business worth over 60 billion pounds by the end of 2012 (Morton 2007). This shows that internet retail marketing has got a huge potential for growth. But does this growth results to more benefits or more limitations to consumers and the service providers alike? This research aims at specifically answering that research question.
In their attempts to remain competitive in the market place, retailers must shun their traditional approaches to marketing and embrace online marketing to achieve greater productivity (O’Brien 2003). In this respect, the electrical’ retail sector has effectively utilized internet shopping to net over 6 billion pounds in sales collection. Through online retail marketing, customers are able to search, find, and compare online offers and product market information much more easily, quickly, and reliably. A successful online retail company understands their customers better, the market, and the importance of strategically locating their entities on the internet (Oracle Corporation 2005).
Benefits of online marketing
According to Kotler & Armstrong (1998), the benefits that accrue from internet marketing to consumers are almost the same the world over. Thanks to the advent of computers and the internet, some retailers have closed a number of their branches, or reduced their sales force and instead offered customers access to their product range through their website on the internet. Several UK suppliers of books, music, computer games, and flowers have developed their business on the internet. Car manufacturers have realized the impact of the internet on their dealership-based channels of distribution, with evidence that the internet is increasingly being used for selecting, negotiating, and ordering new cars, says Morton (2007).
While the internet may facilitate direct communication between service producers and end consumers, the chances of direct interaction taking place among them is considerably lessened by the proliferation of content on the internet, even though it presents a bewildering array of choice to consumers. This has led to the development of a new brand of information intermediary, or ‘informediary,’ which gathers information about customers and products and uses it on customers’ behalf to enhance business operations (Quelch & Klein 1994). Screening commercial messages for customers, representing their interests to marketers who seek access to information about them, and finding vendors who can deliver the best product at the cheapest price are some ‘informediaries.’
The advance of internet as a distribution channel has affected the speed with which consumers and commercial buyers have adopted to the medium. There is considerable evidence that young people readily adapts to this medium than older people. In a study using a technology acceptance model, it was found that consumers’ perceived ease of use was affected by a range of factors, including age, opinion leadership, impulsiveness, shopping orientation, and perceived web security (O’Cass and Fenech 2003)
It is not just in business-to-consumer markets that the internet is reshaping distribution channels. In business-to-business channels, the internet (and intranets and extranets) have replaced previous EDI systems in handling transactions between businesses. Many government and non-profit organizations have also incorporated the internet into their distribution channels, both for procuring purchase (Timmins 2003) and for making services available to users.
Online marketing is convenient to customers as they can shop 24 hours a day from the comforts of their homes. Internet marketing is also immediate and interactive in the fact that consumers can get to interact freely with the company’s site to find crucial information about the products and services they require, order online, and instantly download them.
One of the benefits that accrue to service providers in Hong Kong is customer relationship building. Through online marketing, business entities are able to effectively interact with consumers to study more about their lifestyles, behaviors, and attitudes. Companies are thereby able to come up with products and services that appeal to the consumers in the market place through the use of consumer data basis (Kotler & Armstrong 1998). This is a huge plus for the service providers. Another benefit for the service providers is that internet marketing effectively increases their efficiency and reduces their operational costs. According to Blane (1997), online marketing reduces or do away with rental costs, physical store costs, utilities, insurance, and numerous other expenses. Indeed, printing and mailing paper catalogues is more expensive than preparing digital catalogues.
To service providers and consumers alike, online advertising offers greater flexibility. Rather than using a printed paper catalogue whose prices and products are preset until the next printing, digital cataloguing offers the service providers the opportunity of adjusting their prices and products on an hourly or daily basis, and adapting promotions, prices, and product availability to match the changing conditions in the market (Kotler & Armstrong 1998). Consumers are more flexible based on the fact that they can be able to shop around for products and services at any given time 24 hours a day.
The service providers are also given the benefit of accessing global markets through online marketing since the internet is a worldwide medium that allows consumers and businesses to conduct business by clicking from one nation to another in just a matter of seconds (Kotler & Armstrong 1998). The service providers are ensured of a wide market reach due to the millions of individuals that are connected to the internet.
In Hong Kong and the greater Asia, internet marketing can bring rich dividends if the main players adopt reasonable online marketing strategies. In that respect, many service providers has also benefited from the opportunity to showcase their products and services to millions of potential international customers. Online marketing is also quick, cheap, reliable, and highly effective. Internet marketing is also lightning fast and quick. It allows the service providers to change their company, products and profile online and the changes are replicated almost instantaneously (O’Brien 2003). Another crucial benefit for the service providers is that payments can be made immediately on line using major international credit cards such as MasterCard or Visa.
Despite online marketing serving the respective companies well, it also benefits consumers by offering product related information such as promos, pick-up services, and come-ons, thereby putting both the consumers and the stakeholders at a distinct advantage over their challengers (O’Cass & Fenech 2003). However, there is no doubt surrounding the fact that the Internet has made a mark as a marketing tool. This is because of the numerous company Websites seen on the internet providing little or no real value-added information or services for customers. There are however, many sophisticated websites available, which provide customers with an expanded range of products and services, enabling the smooth communication between businesses and customers. What is striking is that the internet allows B2C and B2B even if there is the barrier of distance and location (geography), time zone differences, and cultural differences (language and customs). To this end, the Internet has the potential to transform retailers from their traditional marketing role as product-led merchants to consumer-driven marketers. This is important given the market saturation that exists in many mature market places in North American, Europe and SE Asia, to name a few. What is critical in the area of on-line shopping is that websites must offer customers an interesting and value-added service, possibly one which can transfer cost savings onto the customer (Ganeshan & Harrison 1995).
Limitations of online marketing
The limitations of internet marketing are also the same the world over for both the consumers and the companies or service providers. For the consumers, internet connection can become a daunting task as websites require greater bandwidth to open due to their complexity (Marx, 2008). If business entities develop complicated or excessively large web pages, internet users may avoid surfing the sites altogether due to the struggle involved in downloading the needed information especially if they are relying on mobile devices or dial-up connections. This is not good for internet marketing as fast content delivery is a prerequisite in the field of online marketing. While convenience and comfort is the basic reason why individuals are switching to online transactions, this aspect of slow internet connectivity is worth noting (Quelch & Klein 1994).
Another limitation of internet marketing is that it doesn’t allow consumers to smell, touch, try-on, or taste tangible products prior to purchasing the product online (Marx 2008). Indeed, some products and services advertised on the internet end up deceiving and confusing people more due to lack of that “physical presence” (Adrian 2004). Even the two-dimensional representation of images may be a poor substitute for a three-dimensional representation of a product in real life. This is especially true in cases where customers select clothes, fresh vegetables, or soft furnishings. Even in the automobile sector, a customer would like to see a car first hand and test it before making the purchase. This is not possible in the virtual world of the internet. However, even though online marketing does not permits potential customers to touch or smell a product, some countries like Germany offers a return policy on specific commodities purchased over the internet. This perhaps explains why online marketing has grown phenomenally in Germany (Gordon & Delimar 1997).
Also, Internet users particularly from the poor parts of Asia, Africa, and Latin America are inhibited by lack of secure electronic payment methods such as MasterCard, Paypal, Visa, and electronic cheques (Marx 2008). This translates into lost business for the service providers. Many buyers have doubts about the security of financial transactions carried out through the internet. This is also true in the case where personal information collected through an interactive dialogue with a company may inadvertently be disclosed elsewhere.
Companies dealing with bulk products are inhibited to transact their business online due to the heavy costs involved in delivering the products (Chesbrough & Teece 1996). As such, particular market segments may never find their way into internet marketing on a global scale. Also, Systems often require high capital outlay, and there may be a slow return on such investment. Compatibility within the technological architecture can be a further limitation, with new technologies continually requiring additional investment from companies. The disaster of the ‘dot.com’ is still fresh in the mind of consumers. Given the history of failed web initiatives, raising capital for next-generation technology can be a challenge.
Another limitation for the stakeholders is their preparedness to internet connectivity. Companies experience complaints and subsequent loss in revenues if they engage in full-blown online marketing campaigns haphazardly and without prior preparation (Marx 2008). Many companies have been keen to move communication with customers to the internet and away from other more expensive media. Research undertaken by Oxford Associates in a number of US-based industries suggested that most companies achieved a 20-40% reduction in transaction costs when selling through distributors and partners, 40-45% when selling through call centers, and over 50% when selling over the internet. However, any cost reduction strategy must take into account a buyer’s behavior (Palmer 2004, Ch.11, p.512-513).
E-Business and E-Commerce
E-business can be simply defined as the use of internet to connect with suppliers, customers, and partners. More conceptually, the term refers to the exploitation of information and communication technologies to support all business activities. E-business basically goes hand in hand with E-commerce, which entails the exchange of commodities and services between individuals and business groups online. Hence E-business and E-commerce are processes that utilize ICT to facilitate relationships and external activities of the business enterprises with other businesses, individuals, or groups of individuals (Greenstein & Feinman 2000).
E-commerce accomplishes business processes that support the complete life cycle of buying or selling of products and services (O’Brien Ch.5, p.220). E-commerce has grown considerably to such an extent that a customer can sit in the comfort of his/her home or office, choose from a wide range of products by browsing the internet, and make the payments on an order. Computer giants Dell and IBM have gone the e-commerce way to improve their target audience worldwide. E-commerce supports Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-Commerce, Business-to-Business (B2B) e-Commerce and Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) e-Commerce. In simple terms, e-commerce supports any and every business process that is operational in any part of the world.
Role of E-commerce in Business Applications
When one talks of Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and Internet Relationship Management (IRM), one is drawn to the positive advantages of these internet-based software packages in business development.
An important feature of e-business is that every aspect of the sales process is considered critical to obtain a successful order, and IRM and CRM are personalized sales platforms which assist in servicing potential customers and act as interactive modules for deriving revenue. How does this happen? Both, IRM and CRM act as the front-office of a company (Greenstein & Feinman 2000). IRM is interactive software that has provisions for free e-mail, discussion boards, and up-to-date product content, while CRM specifies the specific needs for the organization’s long-term goals, performance objectives and measures of the organization. The software also draws the parameters defined by the organization for its cosmetic outlook so as to achieve its goals. For example, for a realtor, IRM could address questions normally put up by customers regarding sales and mortgage of property, project development cost and time, structural features and so on. A customer who can avail all required information through such software will undoubtedly be impressed and initiate the order process. Legal opinions, blue-prints, property purchase and lease agreements, mortgage details and price listing will help make a customer more than confident of making a firm decision. Also the fact that the internet helps reduce process time will benefit the realtor in concluding sales early and efficiently (McWilliams 2003).
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) has become an important tool in customer-centric strategies today (O’Brien 2003, Ch.6, p.182). It not only enhances the quality of service, but also adds more strength to compete in the highly competitive service industry. Be it the Front Office, F&B, Room Service, Stores and Inventory, Supplies or Maintenance, CRM can improve the efficiency and reliability of systems and performance. According to Dong (2007), CRM systems are enterprise applications that support and integrate customer-oriented business processes such as marketing, sales, and customer services to manage business interactions with customers. CRM analyzes and distributes a customer’s personal details and needs to the concerned departments within an organization for personalized services. CRM can also help initiate guest preferences, by which customers feel elated for being recognized without a formal introduction. Their personal preferences, billing details, method of payment, and eating habits can be optimized to create an atmosphere of being a very important person. The guest could use this to impress his/her guests too, and recommend the resort to others on behalf of the company (Daft 1998).
By implementing CRM, organizations can minimize contingencies arising out of staff behavior. Siebel Systems, Oracle, PeopleSoft, and SAP are leading CRM software vendors, which offer solutions that integrate and automate customer processes to allow fast, convenient, reliable, and consistent services to their customers (mySAP 2005). These software packages delivers customer-inspired innovations and state-of-the-art, Web-based user interfaces that enables the organization to delight its customers, empower their support team, and improve their business. SAP solutions and applications support a wide range of business processes related to Customer Relationship Management applications, including:
- Category management
- Multi-channel retailing
- Price management
- Price optimization
- Sales order management (SAP.com)
The following Figure 1 gives a fair idea of how a CRM system design would look like.
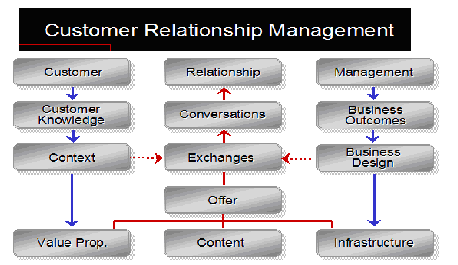
While many companies have realized that the traditional approach of introducing CRM is purely a tool for front-office operations, many have gone a step further to include not just data from front-office, but also enterprise-wide information about customers’ buying habits and profitability. Moreover, fast and flexible deployment to focus on strategic business priorities is critical for any CRM implementation. CRM provides a platform for business agility, enabling a company to adapt its processes easily to constantly changing business dynamics, manipulate business processes across and beyond the enterprise, and transform itself into a customer-centric enterprise.
In a nutshell, CRM will:
- Evolve as business grows with support for end-to-end business processes.
- Empower Users with Role-Relevant Customer Insights.
- Gain Immediate Value.
- Increase Customer Satisfaction.
- Reduce Cost of Ownership (mySAP 2005).
The service industry of late has seen unlimited scope for professionalism in streamlined operations leading to better customer care and services. In the years gone by, retailers used electronic data interchange systems for communicating between manufacturers, suppliers, and tracking. The trend has given way to a more advanced and sophisticated brand of software that not only enhances performance and efficiency, but cuts costs, raises customer fulfillment, and controls long-term supply positioning (Valdero Corporation, 2002). Many innovative software packages have been introduced in the market lately to bridge the gap between planning and execution. E-Commerce is perhaps the solution to a lot of problems facing man today. Business transactions, reports, analysis, planning, execution, payments are all part and parcel of organizational strategies to compete and excel in their respective fields. The internet and e-commerce allows for free flow of data and instruments much needed by industries to survive competition. MasterCard and Visa jointly promoted the Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) with the intention of providing customers a secure payment option through transmission of data electronically. This is secure and helps prevent thefts. The most conspicuous benefits derived from such schemes is the reduced operational cost, reduction in processing time, increased interoperability, and increased payment options (Greenstein and Feinman 2000, p. 295-322).
For corporate giants like IBM and Dell, e-commerce business has held prominence, as it has reduced operational costs and brought customers closer through direct interaction. The internet allows customers to choose the various options available to them before making an online purchase. Product availability status, delivery schedule, payment options, service and spare availability status make their choice of investment easier and most conspicuous. IBM and Dell have both gone online marketing with the idea to help customers choose from products of choice rather than enforce it on them (Ogg 2007).
Customer Purchase Behavior
Consumer behavior is the “study of how people buy, what they buy, when they buy, and why they buy” (O’cass & Fenech 2003). It combines aspects in psychology, social psychology, sociology, economics, and anthropology. Consequently, customer purchase behavior attempts to analyze the buyer decision making processes, both in groups and individually, As a discipline, customer behavior involves studying individual characteristics of customers such as psychographics, demographics, and behavioral characteristics in an endeavor to understand the wants of individuals (Online sales 2008).
The discipline of customer behavior also evaluates influences on the customer from specific groups such as reference groups, family, friends, and society at large. As such, customers purchase behavior depend on two components only – the consumer and the organization. What needs to be understood here is whether the internet-based marketing strategies offered by organizations meet customer needs. If they satisfy the needs of the consumer, the strategies can be termed as a success (Schifmann & Kanuk 2000). The following Figure 2 shows what organizations need to provide and what customers expect and offer in return:
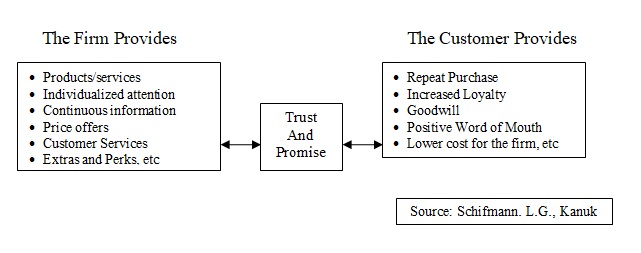
It is imperative that any form of marketing strategy offers customers the choice of options. When choosing an internet-based marketing of buying portal, the arrangement should be such that customers should be able to get all relevant information about a product or service before they place an order. Factors like socio-cultural, psychological, organizational influence make up a sales process and unless the internet is able to satisfy these clauses, it becomes difficult to manage a positive sale. This is true in the cases of both manufacturers and retailers (Schifmann & Kanuk 2000).
It has become increasingly vital for marketers and advertisers to gain a sympathetic attitude from their online target consumers (Wendy 2000). A previous empirical study revealed that the attitudes of internet users are directly related to their apparent interactivity of the internet. It should be the function of business managers to ensure that their websites elicits the right mix of feelings to induce a potential consumer into online shopping (Yrjola 2001).
The Chinese Retail Computer Business
Introduction
IBM sold its PC division to China-based Lenovo Group and took a minority stake in the former rival in a deal valued at $1.75 billion in 2004. The two companies formed a complex joint venture that made Lenovo the third-largest PC maker in the world, behind Dell and Hewlett-Packard, but still gave IBM a hand in the PC business (Spooner & Kanellos 2004).
Under the deal, IBM took an 18.9 percent stake in Lenovo, for which Lenovo paid $1.25 billion for the IBM PC unit. Based on both companies’ 2003 sales figures, the joint venture’s annual sales volume was around 11.9 million units, generating revenue of $12 billion (Brandchannel. Com 2002). Lenovo is the preferred supplier of PCs to IBM, allowing IBM to use its brand for five years under an agreement that includes the “Think” brand. IBM promised to support the PC maker with marketing and via its IBM corporate sales force. Dell continues to enjoy the first place in PC sales all across the globe, reports Gartner.
While Lenovo has a strong client base and sales infrastructure in the Chinese market including Hong Kong, IBM will rely heavily on its comprehensive network in PC sales on a global basis. Yang Yuanqing, Lenovo’s CEO, said that during the first phase of the integration process, Lenovo’s and IBM’s PC operations were independent of each other, but later they used a common brand. He added that IBM’s R&D center in Japan continued to be important to the company (Blumberg partnership 2005). The following figure ranks the computer firms in china in relation to their market share.
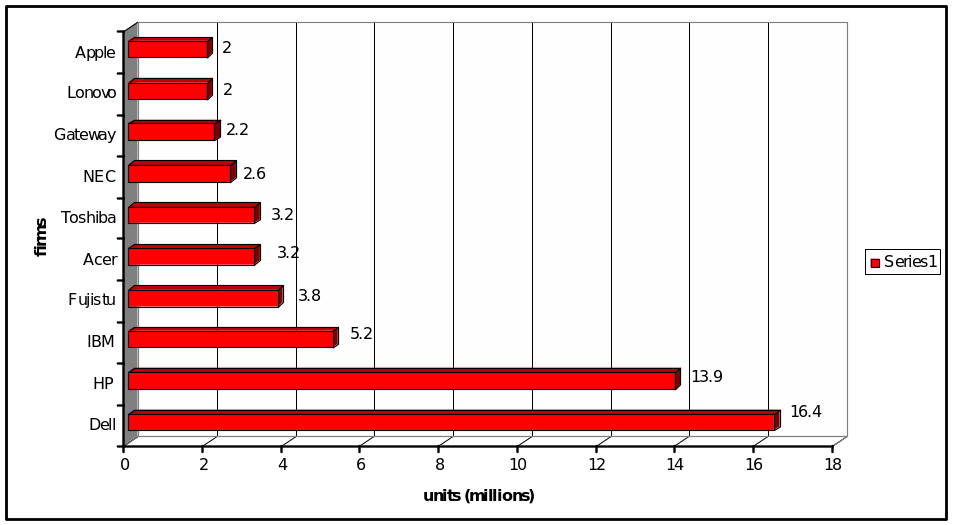
Lenovo is the largest PC maker in China. The company, founded in 1984 as a distributor of IT products, started its own PC business, growing to be No. 1 in China. During 2002, it opened a Silicon Valley office and started selling laptops in Spain under its QDI brand, but was beaten back by competition from other multinational PC makers, such as Dell, which has been growing in popularity China. Dell won a $10 million contract with Beijing’s municipal government to supply Optiplex to primary and middle schools. Lenovo responded to the irrational price competition among second-tier PC vendors and increased effort of foreign brands with price cuts of its own. IBM is also eyeing new inroads into the Chinese market by working with Lenovo to gain an edge in selling servers and services in China, a fast-growing market targeted by a number of U.S. tech giants. Financial analysts have gone on record to say that IBM’s joint venture with Lenovo would be profitable to it, and could add more than 5 cents per share to IBM’s earnings in 2006, or $85 million in net income.
A strategy which this joint-venture hoped to achieve is for Lenovo to collaborate with IBM design teams and assume control of manufacturing, said Steven Fortuna, an analyst with Prudential Equity Group. This could be a sure way to confide in customers their product (Spooner and Kanellos 2004).
Market Trend
In contrast to the gloomy global economic outlook, the IT sector in Asia is a contrast. The industry is experiencing positive growth despite turbulent times in the west. According to GfK Asia’s 2008 Mid-Year Pan Asian IT Retail Data Summary, which covers personal computers (PC), both desktop and notebooks; monitors, printers and multifunctional devices, data from nine Asian countries show mid-year figures for 2008 rising against the same period in 2007 (Anjum 2008). Hong Kong was one among the nine countries covered by the survey for both, PCs, monitors and Single function printers, and multi-functional devices. What was striking was that retail sales of computers and allied products went up despite international economic turbulence.
GfK Asia’s retail PC market findings for the first half of 2008 showed that retail sales were up an average 19 per cent in volume across the nine countries surveyed, with sales totaling about 8.7 million units. This region’s total retail sales value increased 21 per cent over the same period, last year, to over US$6.7 billion (Anjum 2008).
Singapore and Hong Kong showed an unprecedented increase in retail sales volumes for the first half of 2008, with Hong Kong retail sales of PC’s increasing 26 per cent year-on-year. Desktops continued to be the main attraction, with retail sales at nearly 4.75 million, more than 55 per cent of total PC sales in the first half of 2008. “Contrary to popular belief, desktop sales are not at a dead end,” said Gerard Tan, commercial director (IT), GfK Asia (Anjum 2008). Despite the negligible drop in the average price for the desktop for over 12 months; Hong Kong saw a slight drop of about 4 per cent, yet retail sales figures remained solid.
Surprisingly, the sales of Notebooks weren’t far behind either. According to the report, notebook sales have narrowed the gap, coming in with an unprecedented 4 million notebook purchases; a 50 per cent increase over units sold in Asia against the same time last year (Anjum 2008).
However, there was some not-too-good news for stand alone monitors. The report stated that there was a -2 per cent drop in unit sales of stand alone monitors across Asia. According to its figures, the total market segment generated just over US$312 million in the first six months of 2008 with total retail unit sales nearing 1.4 million, a nine per cent increase over the same period in 2007. Hong Kong sadly, reported significant retail sales drops (Anjum 2008).
Dell Retail Promo
‘Buy For Charity’ unveiled a fundraiser discount card that allowed shoppers to save money on their purchases while generating a revenue stream of much needed funds for non-profit organizations. ‘Buy For Charity’ utilized its relationship with online retailers from their charity mall to put together a novel concept that would, apart from raising funds for the much needed, offer discounts of up to 40% off from hundreds of major online retailers including Barnes & Noble, Amazon.com, Target, Home Depot, Dell, Sharper Image, Overstock.com, and many more (Kapuscinski et al. 2004).
The scheme was sure to be a success as it offered an average online shopper, hundreds and even thousands of dollars in saving. The card gave access to a website with all of the online discounts which they could avail. Purchase of Airline Tickets from Expedia, Office Products from Office Depot and Office Max, cosmetics from Avon, gifts from Sharper Image, Electronics from Circuit City, and computers and printers from Dell were some of the exciting offers up for grabs. This scheme is extended to just about every major online retailer one could think of and is no different in the many countries where Dell sells its products. Since this Online Shopping Discount Card was relatively new, it gave Dell’s exclusive clientele the privilege of getting something which was not available earlier (Free Press Release 2006).
Dell changed tactics to address the concerns of many consumers who felt that online shopping robbed them of touching and feeling products before they bought them. It officially signed up Best Buy as a retail partner in December 2007. With this tie-up, Dell would be able to showcase several models of its XPS and Inspiron PCs. These products can now be seen at 900 Best Buy locations after Christmas, and will also include Dell’s consumer-friendly XPS M1330 notebook, Inspiron 1420 notebook, and the XPS One desktop (Ogg 2007).
For a company that built its fortune and reputation on selling its products directly to consumers for more than two decades, the Best Buy deal marks a major historical shift (Ogg 2007). Perhaps this is in contemplation to what many marketing strategists having said could be a major drawback in online shopping. Richard Shim summed up the theory saying that, it was like going from being committed to one religion to being pagan. The PC industry analyst at IDC continued that, Dell was very much in need of a distribution centre, particularly in consumer retail, and Best Buy came as a blessing to them (Ogg 2007).
There is no doubt that this move can be seen as a huge cultural shift for Dell. Among them, it’s the way the company will deal with their customers in selling them products. This will be more than an experience for many at Dell, for most of the people in the company grew up on the direct model, with less experience in the PC retail marketing (Ogg 2007).
Conclusion
The PC retail market holds a lot of promise for Retailers. Available information from earlier research papers and reports suggested that the market in Asia, especially in Hong Kong, was alive and kicking. With IBM aligning with Lenovo, the combination did extremely well in closing the gap with Dell and Compaq. Lenovo however, scored over others in terms of total sales in Asia. Dell’s move to tie-up with Best Buy was an attempt to negate the drawbacks attributed to online shopping, and this has helped increase Dell’s market presence considerably in the US market. In Hong Kong though, the company continues to market its products online, and while it has made an impression of late, the plan to introduce a concept on the lines of Best Buy cannot be ruled out. It is the customer’s prerogative that must be answered and despite many positives, online shopping will remain, virtual. Dell’s move to be different will pay off in getting more customer loyalty if it rigorously pursues a pro-customer marketing strategy.
Methodology
Introduction
This research undertaken to evaluate the benefits and limitations of online marketing offers from the perspective of customers and service providers adopted both a quantitative and qualitative approach of study since the main objective was to measure the attitudes and perceptions of individuals and stake holders towards online marketing, and its benefits and limitations. To this end, a quantitative research design is viewed as the most ideal methodology that would assist in the interpretation of the research questionnaires. Moreover, the quantitative research would enable the researcher to compare the benefits and limitations of online marketing with traditional marketing using a descriptive questionnaire. The key informant interview utilized a qualitative approach as it was concerned with generating the attitudes and perceptions of online marketing from the service providers. Creswell (2008) suggests that qualitative approach is the most applicable in studies focused on “people’s attitudes, behaviors, value systems, concerns, motivations, aspirations, cultures, and lifestyles”.
Thus a quantitative study in the outline of a semi-structured consumer – service providers’ attitudes survey through questionnaire was applied. In more broad terms, this study intended to further explore similar issues addressed by previous studies in the discipline as suggested in the literature review, focusing specifically to Hong Kong where extensive research in online retail marketing is yet to be carried out. Given that no evaluation have been extensively carried out in Hong Kong towards internet marketing, the research intended to evaluate the benefits and limitations that the industry has brought to the residents and online marketing service providers in Hong Kong, and if online marketing meets the satisfaction levels of the consumers. In this regard, questionnaires and interviews specifically designed to accommodate open-ended questions were viewed as the best tools to use in the data collection process. The methodology utilized in conducting the research is shown below.
Primary Research
Research Aims and Objectives
The overall aim of this research was to evaluate the benefits and limitations of online marketing from the perspective of consumers and service providers in Hong Kong. Specific objectives included the following:
- Evaluating the benefits and limitations that both the customers and service providers experience from online retail marketing.
- Evaluating if online marketing satisfy consumers
- Evaluating the impact of online marketing on customers’ behaviour towards the products and services offered on line
- Evaluating the possibility of maintaining a better customer relationship online.
Research Design
According to Creswell (2008), a research design is a framework for collecting and utilizing sets of data that aims to produce logical and appropriate findings with great accuracy, and that aims to adequately and reasonably rest a research hypothesis. As mentioned in the introduction, a quantitative study was conducted. This permits the research to meet its objectives by comparing, analysing, evaluating, and measuring the benefits and limitations of online marketing as well as the impact online marketing has occasioned on customers’ attitudes and behaviours towards products and services.
This study utilized a descriptive research approach to accurately describe the variables that were under examination, and determine the degree through which the variables could be related (Malhotra 1993).According to Kumar (2000), exploratory research is undertaken when a researcher is seeking insights into the broad nature of the problem, the possible substitutes, and the appropriate variables that need to be evaluated. Casual research is undertaken when the objectives of the research are to understand the causal–effect variables and their effects on a phenomenon. Causal research also involves determining the nature of the association between causative agents and the effects of a phenomenon. This study is basically a descriptive study since it is aimed at evaluating the benefits and limitation variables of the online retail marketing especially in Hong Kong. It is concerned with the frequency with which something occurs or the relationship between variables (Kant 1999).
Data Requirements
The data collected for this study was limited to the benefits and limitations of online marketing offers from the perspective of consumers and service providers, evaluation of if online marketing satisfies the customers, the impact of online marketing on customers attitudes and behaviours towards products and services, and evaluation of the possibility of maintaining a better online customer relationship particularly in Hong Kong.
Research instruments
Questionnaire
According to Creswell (2008), the best method to minimise the measurement error is to “use a good [research] instrument” (p. 394). Therefore, one of the research instrument used in this study is an open ended questionnaire. The use of open ended questions will enable individuals to express their views freely without having any limitations (Cohen, Manion, & Morrison 2002) based on their “cultural and social experiences” (Creswell 2008, p. 399). Cohen, Manion and Morrison (2002 p. 255) furthermore states that “closed and open ended questions can catch the authenticity, richness, depth of response, honesty and candour which is […] the hallmarks of quantitative data”. Therefore, in order to evaluate the benefits and limitations of online marketing, the most appropriate method of data collection is by using an open-ended questionnaire and key informant interview.
The questionnaire was to be administered personally. According to Creswell (2008), personal administration has the obvious advantage of making the respondent understand the questions and concepts involved. Personal administration also gives a respondent the opportunity to ask for clarifications. Personal administration also yields the lowest refusal rate among respondents. It also allows for detailed, longer, and more complicated interviews to be undertaken (Lee & Johnson 1999).
Key Informant Interview
Using a questionnaire alone could not give the desired results of the study. Therefore, a key informant interview was also undertaken for the purpose of collecting data. According to Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (2002), individuals have different significations to the same question given in the questionnaire. It is therefore important to offer an interview to dig deeper into the subject. In addition, an interview is the most appropriate method used to obtain respondents beliefs and attitudes, according to Cohen, Manion and Morrison. According to Knight (2002), face to face inquiry presents a possibility to change the direction of the interview by probing to accommodate new comments and insights made by the participants (p. 50).
Sampling
According to Creswell (2008), sampling is one element of the statistical practice that concern itself with the selection of unique observations that are anticipated to surrender some knowledge about a population in question, specifically for the purposes of forming some statistical inference. Before primary research is conducted, a researcher must be clear about the category of respondents it wants to interview. In most instances, it is virtually impossible for a researcher to interview the whole population to get their views and opinions about a research question as this would be unfeasible and costly. In that respect, a representative sample of the population was taken to assist in conducting the research.
The population for this study included consumers of online marketing products and services in Hong Kong and the companies and corporations conducting their businesses online. To this effect, probability sampling method was viewed as the right one for this research as respondents were chosen based on some form of random selection. According to Creswell (2008), probability sampling ensures that the different units in the research population have the same probabilities of being selected.
After the required sample size of the consumers and service providers of online marketing had been calculated, systematic sampling technique was employed for the purposes of collecting data for the study. This sampling ensures that each individual in the population has an equal and known possibility of been selected to participate in the research (Creswell 2008). However, any researcher using systematic random sampling must first ensure that chosen sampling interval in a population does not conceal any pattern as this would threaten the randomness of a sample. Consumers that engage in online buying and online marketing service providers are homogenous and thus systematic sampling can effectively be used to study systematic sample units of consumers and service providers uniformly distributed over the population. Every 10th consumer entering selected online stores in Hong Kong was selected for the study. Systematic sampling was also conducted on the online marketing service providers to come up with the required sample size.
Questionnaire design
The questionnaire developed for this research was a self completed research tool, consisting of 18 questions including those asking on demographic characteristics of respondents. Majority of the questions included were closed-ended thereby implying that the questionnaire was highly structured. Only several open-ended questions were used in the whole questionnaire. According to Leung (2007), factual data is best collected using questionnaires and thus appropriate questionnaire design is crucial in making sure research questions elicits valid responses.
The questionnaire developed for this research mainly recorded the attitudes of consumers towards online products and services on a five point category scale, asking consumers of online products to state their status of disagreement or agreement towards a set of variables. According to Creswell (2008), putting the variables under study in a category scale is very effective in measuring the attitudes and behaviours of people towards that variable. By utilizing the Likert scale of agreement or disagreement, critical information on a variable under study can be revealed. The categories mostly utilized in measuring attitudes are the strongly disagree, Disagree, Neutral, Agree, Strongly Agree.
Data analysis process
Data collection
Hong Kong is a territory located on the Pearl River Delta, facing South China Sea to the east, south, and west, and bordering Guangdong province to the north. It is one of the most densely populated areas, with a population of over 6.9 million individuals. Hong Kong maintains a highly capitalist economy and has a higher level of autonomy under the policy of one country, two policies. Renowned for its natural setting and expansive skyline, Hong Kong is a major cultural and business hub, and one of the leading financial capitals of the west (Research & Markets access 2007).
Although Hong Kong is densely populated, the study was concentrated in the Kowloon Peninsula located along the northern edge of Hong Kong Island. A sample of 110 respondents was selected to respond to the questionnaires, and 25 business professionals were picked for the key informant interviews. The small sample size was due to traveling costs and constrains of time. A more comprehensive study would have shed more light on the benefits and limitations of online marketing campaigns to the consumers as well as to the service providers.
Data editing
Of the 110 returned questionnaires, 8 were discarded since they had been partially completed. For the remaining 102 questionnaires, data cleaning and editing was undertaken to ensure that the data received was of very high quality. This is a general prerequisite for any research undertaking. The 25 Key Informant interviews conducted to collect qualitative data on major online industry players were also edited for mistakes.
Data analysis
Once data was collected, data for the study was analyzed using various statistical packages namely SPSS and Excel to generate frequencies and percentages needed to answer the research objectives. Analysis would be carried on the benefits and limitations of online marketing especially in the retail industry and the attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards online consumer products and services.
According to Creswell (2008), data analysis is the technique of gathering, transforming, and modeling data with the purpose of suggesting conclusions, highlighting useful information, and supporting decision making. Data analysis has manifold approaches and facets, encompassing varied techniques under a variety of names in different social science, science, and business domains.
Study Limitations
The phenomenon under investigation by this study is very extensive and therefore limitations were experienced in designing the questionnaire questions to limit themselves to the field of online marketing. Another study limitation was that this study objective had only been undertaken in Hong Kong at a very narrow empirical perspective. No solid data existed to show how individual attitudes and behaviors were affected by online marketing of products and services in Hong Kong. This therefore presented some difficulties in trying to form the basis of the study’s objectives.
Other study limitations include traveling costs, inadequate budgetary allocation, and a small sample size. The researcher however could not extend the size of the sample to be used in the study due to budgetary challenges. A more comprehensive study would have properly enlightened the stake holders on online marketing trends and the attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards online products and services.
Ethical considerations
Informed consent, confidentiality and privacy have been identified as the foundations of ethical research on humans (Frankel & Siang 1999; Jones 1994). A full comprehension and identification of a possible violation of any one of these key elements when carrying out research studies into online marketing are proving to be quite difficult owing to a rise in the implemented measures for computer security, hazy boundaries between both the public and private communication space, as well as web tool functionality advances.
With respective to the research design for this specific study, it was the goal of this researcher to ensure that the information sought was not likely to jeopardize the privacy and security of the respondents. Furthermore, the research design also ensured that the respondents were not coerced to give the needed information fro the research in question. During this research study, the data that was used was for the purposes of this research only. Furthermore, the information obtained was held in the strict confidence.
Results
Introduction
This section presents research findings to the questionnaires administered to online marketing customers and the key informant interviews administered to the retailers of the service. The findings were used to inform the conclusions and recommendations of the study. The first section presents the findings under four headings namely: demographics and usage of online marketing; benefits and limitations of online marketing to customers; customer purchase behavior; and online computer sales in China. The second section presents the findings of the key informant interviews that targeted the service providers, and will include: uptake of online marketing among retailers and the benefits and limitations the concept has elicited towards retailers. Below are the research findings.
Customer demographics and online marketing
The study reinforced the position taken by previous studies that online marketing had indeed taken retail customers by storm. A 2006 study conducted by the Forbes magazine revealed that Chinese internet users spent in excess of two billion hours online on weekly basis. This is far more than the 129 million hours logged on by American users per week (Pace, 2006). Of the 102 respondents interviewed in the study, more that two-thirds (66.7%) spent over 8 hours per day browsing the internet while another 15.7 % spent around 5 hours each day browsing the internet in Hong Kong. This reinforces the findings of other previous studies that the internet brings obvious advantages to online retailers of products and services through opening up local businesses to a large pool of local and international customers connected to the internet.
The study revealed that young people under the age of 35 years had formed the habit of utilizing the internet to know the product information of the commodities they wished to purchase. Indeed, over 55.5 % admitted to purchasing some online products and services in their lifetimes. The 18-35 age category is viewed as crucially important for marketers as this age-group has greater spending power and more independence. According to the literature review, there is considerable evidence that young people readily adapts to this medium than older people. In a study using a technology acceptance model, it was found that consumers’ perceived ease of use was affected by a range of factors, including age, opinion leadership, impulsiveness, shopping orientation, and perceived web security (O’Cass and Fenech 2003). Judging by the huge uptake of the internet-based solutions by individuals in China, online marketing has a huge probability of growth in mainland China as well as in Hong Kong. Many individuals are finding comfort in the internet as other forms of gathering information; especially the print media is state-controlled. As such, the internet comes in handy to fill that void (Pace 2006).
Overall, more than half (52.8%) of the respondents interviewed used the internet to gather worldwide as well as local news. The rest of the distribution on internet usage is shown in the following pie chart.
The above figure shows that the Chinese population is hungry for information and thus online marketers can utilize this situation to market their products and services online. Nearly all respondents (90.2%) had the information that the internet is being increasingly used by business enterprises to market their products online. Of those who had participated in online buying, 35 % had bought music and other entertainment accessories over the internet, while 30 % had bought computer software programs. A smaller number (20 %) had participated in online buying of computer and computer products from the two leading computer companies in Hong Kong, namely Dell and IBM. This reinforces the assertions made in the literature review that the internet acts as a communication medium to the customers, providing a large market for corporations through the efficient use of low-cost commerce and advertising found in the internet. Companies have been able to generate sustainable sales revenues to shield them away from harsh market conditions.
Benefits and limitations of online marketing to customers
The study was successful in confirming assertions from previous studies that online marketing had indeed offered many benefits to the customers. Of the 102 respondents, nearly two-thirds (64.3%) revealed that their lives have been revolutionalized by the advent of the internet, and could not survive without the internet. To the customers, online marketing had facilitated direct communication between the service providers and the end consumers, as well as offered them with a bewildering array of choice of consumer products. Nearly 80 % of the respondents believed that internet purchases are almost instant, with half (50.5%) arguing that purchasing commodities online was very secure and hustle free. According to the literature review, the advance of internet as a distribution channel has affected the speed with which consumers and commercial buyers have adopted to the medium (O’Cass and Fenech 2003). A further 48. 7% of the respondents believed that online marketing is convenient to customers as they can shop 24 hours a day from the comforts of their homes. According to Pace (2006), Internet marketing is immediate and interactive in the fact that consumers can get to interact freely with the company’s site to find crucial information about the products and services they require, order online, and instantly download them. Another 12.7 % argued that they benefited from online marketing due to the flexibility it offered to consumers.
This study revealed that online marketing indeed had many benefits to offer to the emerging class of online consumers. A further 33.3 % argued that online marketing benefits consumers by offering product related information such as promos, pick-up services, and come-ons, thereby putting the consumers at a distinct advantage over other consumers who follows traditional methods of purchasing goods. According to Kotler and Armstrong (1998), there are many websites on the internet today providing customers with an expanded range of products and services, and enabling the smooth communication between businesses and customers. Below is a graph representing the benefits of online marketing according to customers.
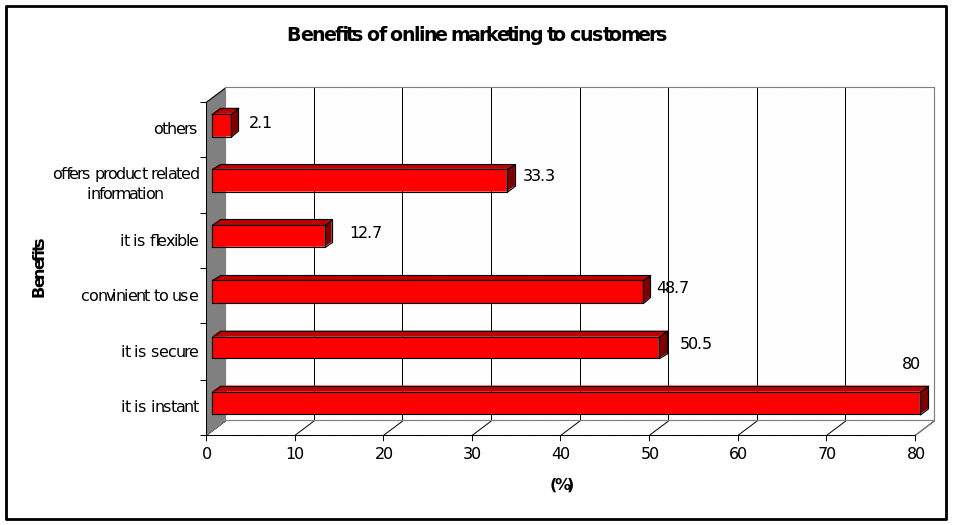
Any technological advancement has its own benefits and limitations. Online marketing too had its own limitations towards consumers. Of the respondents surveyed in this study, 20.1 % believed that online marketing did not offer them the opportunity of touching, smelling, and feeling the product before purchasing. This was highlighted in the literature review, and the way governments across the world were facilitating a regulation on money back guarantee on products purchased over the internet (Pace 2006). However, Hong Kong had not passed such a policy to protect online consumers. A further 15.1% of the respondents did not trust the money transfer methods used in many online business transactions. The fear was that credit cards such as the Visa and MasterCard were subject to being penetrated by international hackers thereby occasioning huge financial losses. 8.7 % of the respondents had at one time avoided surfing the sites altogether due to the struggle involved in downloading the needed information. However, 5.5 % of the respondents believed that the online service was not easily accessible to them.
Customer Purchase Behavior
Customer purchase behavior attempts to analyze the buyer decision making processes, both in groups and individually, As a discipline, customer behavior involves studying individual characteristics of customers such as psychographics, demographics, and behavioral characteristics in an endeavor to understand the wants of individuals.
As such, almost two-thirds (65.7%) of the respondents said they had been influenced by close family members and friends to participate in online buying. This shows a very important consumer market trend that company managers have to follow in order to maximize their sales online. Behavioral studies on reference groups, family, friends, and society at large, is of paramount importance for any online marketing strategy to succeed (Hitachi consulting 2008). Other respondents believed that they were influenced by the complexity and artistic beauty of the websites into participating in online marketing. These are some of the important consumer behavior trends that online advertisers need to study in order to make it big in online marketing.
Factors like socio-cultural, psychological, organizational influence make up a sales process and unless the internet is able to satisfy these clauses, it becomes difficult to manage a positive sale (Hitachi Consulting 2008). This was proved right as more than half (55.5%) of the respondents said that they were influenced very much by socio-cultural and psychological factors into participating in online buying. Such factors include the spending power, religious orientations, personal beliefs, and cultural values. It has become increasingly vital for marketers and advertisers to gain a sympathetic attitude from their online target consumers. A previous empirical study revealed that the attitudes of internet users are directly related to their apparent interactivity of the internet. It should be the function of business managers to ensure that their websites elicits the right mix of feelings to induce a potential consumer into online shopping (O’Cass & Fenech 2003).
Of all the respondents who had participated in online marketing, 70 % were satisfied with the transactions and had trust in the process. However, some respondents said that they had experienced problems trying to access online services. A few were frustrated by the limited methods of online payment available in the market. The most popular funds transfer methods in the market were MasterCard, Visa, Western Union, and PayPal. Many respondents believed that E-marketing had some distinct advantages over traditional marketing strategies in that it is fast, convenient to use, flexible, and reliable. Overall, over 63 % of the respondents believed that online marketing had a great potential for growth.
Benefits and limitations of online marketing to service providers
From the perspective of service providers, online marketing had many benefits as opposed to traditional marketing strategies. To gather their views and attitudes towards online marketing, 25 key informant interviews were administered on several companies offering online marketing services. For purposes of time and space the names of the firms will not be revealed.
Many retailers interviewed admitted to closing down a number of their branches, or reducing their sales force in favor of internet based marketing of their range of products and services. This has translated into profits in reduced overhead costs for their businesses. Another benefit for the service providers was that online marketing facilitated direct communication between the service providers and the customers. This relationship has been beneficial to the service providers since it has enabled them to learn more about consumer behavior and attitudes which is crucial in informing current market trends (O’Cass & Fenech 2003). In this respect, online marketing had benefited service providers in their customer relationship building process. According to Kotler and Armstrong (1998), business entities are able to effectively interact with consumers to study more about their lifestyles, behaviors, and attitudes through online marketing. Companies are thereby able to come up with products and services that appeal to the consumers in the market place through the use of consumer data basis.
Furthermore, key service providers interviewed argued that internet marketing had effectively increased their efficiency and reduced their operational costs. Financial statistics from five firms revealed that online marketing had indeed increased sales revenues by between 10-18 percent, while at the same time reducing overhead operational costs by between 8-13 percent in 2007. According to Kotler and Armstrong (1998), online marketing reduces or do away with rental costs, physical store costs, utilities, insurance, and numerous other expenses.
Majority of the online retail service providers interviewed in the study argued that online marketing offered them greater flexibility. Rather than using a printed paper catalogue whose prices and products are preset until the next printing, digital cataloguing offers the service providers the opportunity of adjusting their prices and products on an hourly or daily basis, and adapting promotions, prices, and product availability to match the changing conditions in the market (Kotler & Armstrong 1998).
Perhaps one of the greatest benefits that online marketing have been able to offer the service providers based on the study is the ability to access global markets. According to Kotler and Armstrong (1998), the internet is a worldwide medium that allows consumers and businesses to conduct business by clicking from one nation to another in just a matter of seconds (Kotler & Armstrong 1998). The service providers are ensured of a wide market reach due to the millions of individuals that are connected to the internet. Many service providers believed that the internet had indeed offered them an opportunity to showcase their products and services to millions of potential international customers. Hong Kong-based computer companies had indeed benefited immensely from this facility.
According to the key informant interview findings, online marketing was also quick, cheap, reliable, and highly effective to the service providers. This reinforces the literature review’s assertion that online marketing allows the service providers to change their company, products and profile online and the changes are replicated almost instantaneously (Kotler & Armstrong 1998). Majority of the service providers interviewed were happy that payments could be made immediately on line using major international credit cards such as MasterCard or Visa.
The study brought forward several limitations that continued to dodge the service providers. First, a few of the service providers interviewed were concerned about the slow internet connectivity experienced when customers try to access their websites. It is a well known fact that majority of consumers avoids interacting with websites that connects at very low speeds. Often, this translates into lost revenues. Majority of the service providers had reservations about the electronic payments methods especially in this age of internet fraudsters. However, this was a perceived threat as none of the companies interviewed had lost money on internet transactions. Some of the electronic payment methods mostly used by service providers include MasterCard, Paypal, Visa, Western Union, and electronic cheques (Kotler & Armstrong 1998).
Another limitation noted by the service providers was that, companies dealing with bulky products were limited to transact their business online due to the heavy costs involved in delivering the products. As such, particular market segments may never find their way into internet marketing on a global scale. Other limitations noted by stakeholders include high capital outlays and non-compatibility with technological architecture. Given the history of failed web-based initiatives, raising capital for next-generation technology can be a challenge for modern companies (O’Brien 2007).
Online computer sales in China
Just like in other parts of the world, online computer sales had taken root in China, led by the two online computers retailers, Dell and IBM. The online computer retailers interviewed reported that online marketing had effectively increased their sales revenues in the business. Indeed, one company indicated that online sales in computers and computer accessories had plummeted from 2% of the total sales revenues in 2004 to over 18% at the end of 2007. This is a positive growth path for the industry. A recent survey done on Hong Kong’s computer industry revealed that retail sales of computers and allied products had gone up despite international economic turbulence.
The study reinforced the literature review’s assertion that Desktop computers were the most heavily traded items in the computer industry, representing 45 percent of the whole industry. Laptops were second, with a 30 % market share in the heavily saturated computer market. Computer monitors took a partly 7 % of the total market share.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
The study was an eye opener in the field of online retail marketing. All indications pointed to the direction that online marketing had completely revolutionalized the way business used to be done. Companies that had embraced the technology had reported increased growth in revenues. Individual customers had reported increased efficiency and greater freedom as key benefits brought about by online marketing strategies.
Benefits
The research study concluded that Young people readily adopt online marketing strategies and online buying of products and services more than older people. Many of the online customers mostly purchase music and entertainment accessories, followed by computer software programs, and then computers and computer accessories. The internet acts as a communication medium between the service providers and the customers.
Online marketing has also offered consumers a bewildering array of choice of consumer products. The advance of internet as a distribution channel has affected the speed with which consumers and commercial buyers have adopted to the medium. Online marketing was also discovered to be convenient to customers as they can shop 24 hours a day from the comforts of their homes.
Moreover, online marketing is flexible to both the customers and the service providers, besides benefiting consumers by offering product-related information. Many retailers admitted to closing down a number of their branches, or reduced their sales force in favor of internet based marketing strategies.
Online marketing has benefited service providers in the customer relationship building process. Furthermore, internet marketing has effectively increased service providers’ efficiency and reduced their operational costs. Due to online marketing, advertisers and other business professionals have been able to access the global markets.
Online marketing is also quick, cheap, reliable, and highly effective to the service providers. Online marketing was also discovered to have a huge probability of growth in mainland China, just as it has in Hong Kong. A Majority of individuals were also shown by the study to use the internet for accessing news, searching, and E-mailing.
The sale of computers online has taken root in China, led by the two online computers retailers, Dell and IBM. Online retail sales of computers and allied products in Hong Kong had indeed gone up despite international economic turbulence. Desktop computers were the most heavily traded items in the computer industry.
Limitations
Nevertheless, online sale of products did not offer consumers the opportunity of touching, smelling, and feeling the product before purchasing. Majority of customers have at one time or another avoided surfing the sites altogether due to the struggle involved in downloading the much needed information. Most of the individuals, the study revealed, are always influenced by close family members and friends to participate in online buying.
Additionally, internet uptake is affected by socio-cultural, psychological, organizational factors. Although a majority of the customers are satisfied with online transactions and had trust in the process, there are however a few who are frustrated by the limited methods of online payment available in the market.
Slow internet connectivity continues to affect service providers, facilitating them to loose crucial revenue as customers try to access other websites. Many service providers have reservations about available electronic payment methods especially in this age of internet fraudsters.
Moreover, companies dealing with bulky products are limited to transact their business online due to the heavy costs involved in delivering the products. At the same time, service providers are increasingly being faced by limitations of high capital outlays and non-compatibility with technological architecture.
Recommendations
The study came up with a number of recommendations, and which if implemented adequately, have the potential to enhance online marketing. Owing to the huge potential for growth in online marketing, the Hong Kong government should come up with a regulatory framework to ensure that potential customers do not fall prey to internet fraudsters.
Such regulations will further offer online transactions the much needed credibility and confidence. The government should also facilitate legislation on money back guarantee on products purchased over the internet. Such a regulation has already been introduced in Germany and has popularized online purchases due to the confidence it has given to the potential customers.
There is therefore a dire need to formulate such a regulation need to be formulated in Hong Kong. All the stakeholders’ concerned need to work in harmony to make sure that the internet access is guaranteed to potential customers. Businesses should be supported by the relevant authorities to increase their bandwidth to guard against slow internet connectivity, responsible for driving away millions of potential customers.
Electronic payment methods need to be made more readily available and more secure for online marketing to realize its full growth capabilities. A majority of the potential customers fear to transact their business online due to the fear of insecure payment methods, and so the more reason why there should be an authentication and surveillance of online marketing companies by the government so that such customers are protected from fraudsters.
Reflection
As already mentioned elsewhere, this study gives an analysis of the benefits and limitations of online retail marketing from the perspective of customers and service providers alike. It has highlighted the many benefits that customers get from online marketing ranging from its ability to be flexible, convenient, and a dependable communication medium, to its ease of use and ability to provide product related information online. Online marketing has also benefited customers by giving them an array of consumer products choices. Retailers has benefited in the customer relationship building process as well as in reduced operational costs and increased efficiency. Despite online marketing being a quick, cheap, reliable, and highly effective method of communication, it has also given retailers the ability to access global markets. However, several limitations continue to face the industry including slow internet connectivity and insecure electronic payment methods to name just a few.
The study was largely successful despite the usual challenges faced by numerous other research undertakings. The process of booking interviews for the key informant interviews with the retailers was faced with problems since many of them were busy. However, the research time-table was altered in a way to accommodate the reservations of the retails. Other challenges included inadequate time and traveling costs. Travel logistics for the data collectors was viewed as a challenge during the initial stages of data collection but it was immediately dealt with. Otherwise, the study was well planned and executed.
Both the qualitative and quantitative research methodologies used in the study had been previously evaluated and passed as the best for the data collection exercise. The questionnaires and key informant interviews were especially critical in collecting the attitudes and values of customers and service providers towards online marketing. The sampling procedures employed made it possible for the research team to come up with a representative sample size. The method of data analysis chosen was specifically aimed at coming up with critical success and failure stories of online marketing.
Overall, the research objectives were met through the study findings. The benefits as well as the limitations were analyzed to the fore. Through the various methods of data collection utilized, the attitudes and behaviors of customers towards online products were well analyzed. Most of the study findings or outcomes helped to reinforce the initial expectations presented in the literature review. The study helped reinforce previous study’s findings that online marketing has indeed recorded impressive growth in recent years. Online marketing had the capability of offering many more benefits to consumers and stakeholders alike if it is well developed.
The study brought a variety of experiences to the researcher based on its depth of study. But in future research studies, it is imperative that adequate time is allocated for the successful completion of the project. Lack of time to conduct in-depth interviews was a major challenge that faced the research team.
References
Adrian P 2004, Introduction to Marketing-Theory and Practice: Distribution, Oxford University Press, London
Anjum Z, 2008, Asia IT retail market strong despite global economic crisis: GfK Asia’s data shows substantial growth in retail figures in the region. Web.
Brandchannel.com 2002. Brand Features: IBM vs. Dell: The winner is…, Web.
Blumberg Partnership 2005. Dell vs. HP vs. IBM. Web.
Chesbrough H. W & Teece D. J 1996. When is the Virtual Virtuous? Harvard Business Review, p.65-73.
Cohen, J.P., Manion, C.W., & Morrison, P.M 2002. Handbook of Qualitative Research. London, International Educational and professional Publisher.
Creswell, J.W 2008. Educational Research: Planning, Conducting and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research. (3rded). New Jersey, Prentice hall.
Dunphy, G., Griffiths, A. & Benns, S 2007. Organizational Change for Corporate.
Sustainability for Leaders and change Agents of the future. Taylor & Francis, Inc. ISBN: 9780415393300.
Elson, P.R 2006. “Tracking the implementation of online marketing in medium-based agencies.” The international Journal of Not-for-Profit Law, vol. 8, no. 4.
Daft, R. L 1998. Management: Academic Service, 6th Edition, Thomson Press Gordon, M.E., & De Limar-Turner, K 1997. “Consumer attitudes towards internet advertising: A Social Contract perspective.” International Marketing Review, vol. 14, no. 5, pp 362-375.
Kalakota R. & Robinson M 2003. Identifying the Problem: Disconnected Front-Office Systems, Page 2-3, E-Business 2.0: Roadmap for Success. D. McWilliams Blane E 1997. Sizing Intercompany Commerce. Forrester Research MA.
Ganeshan R., & Harrison T. P 1995. An Introduction to Supply Cha Management. Web.
Greenstein M. & Feinman T. M 2000. Electronic Commerce: Security, Risk Management and Control, McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, London.
Hitachi Consulting 2008. Customer Relationship Strategy. Web.
Kapuscinski, R., Zhang, R. Q., Carbonneau, P., Moore, R, and Reeves, B 2004. Inventory Decisions in Dell’s Supply Chain, Interfaces, 2004, Vol. 34, No. 3, 004, pp. 191–205, ISSN 0092-2102 _EISSN 1526-551X _04 _3403 _0191.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G1998. Principles of Marketing (8 ed). Prentice Hall. ISBN: 0139570020.
Marx, D 2008. Limitations of internet marketing. Web.
McKissick, F.W 2004. Strategic capability: Ensuring the growth of your Business. Prentice Hall.
McNamara Carter 2008. Online Marketing. Free Management Library.
Miller, M 2006 Media Visionaries. Web.
Morton, R 2007. “Some Pick-up in Online Sales…however, most customers still prefer
to buy from showrooms.” Financial Times, March 4, p.5
MySAP 2005. Customer Relationship Management: Solution Overview. Web.
O’Brien, J 2003. Management Information Systems (6th Ed). The McGraw-Hill Companies.
O’Cass, A., & Fenech T, 2003, “Web Retailing Adoption: exploring the nature of internet users’ web retailing behavior.” Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 10 (2), p.81-94.
Ogg E 2007. Dell: Not the PC Company you used to know. Web.
Online Sales 2008. Internet Relationship Management, Transforming Customer Contact into Revenue: Selling-Chain Management. D. McWilliams
Oracle Corporation 2005. “How Best to Measure Your Supply Chain Today.” Oracle monthly Review. Web.
Quelch, J. A., and Klein, L. R 1994. The Internet and International Marketing. Sloan Management Review, spring, p.60-75
Rathore, M 2006. Customer behaviors and attitudes: A representative study. BNET.
Research and Markets Access Asia Ltd 2001. Telecommunication Services in China: A Market analysis. Web.
Reynolds, J 1997. “The Internet as a Strategic Resource: Evidence from the European Retail Sector.” In L. Willcocks, D. Feeny and G. Islei, (Eds), Managing IT as a Strategic Resource, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Runckel, C. W 2005. The Internet in China – cutting through the hype. Web.
Schifmann, L. G., and Kanuk, L. L 2000. Consumer Behavior. Prentice Hall.
Sharkey, C., & Wang, M 2003. An Overview of the Telecommunications and Broadcasting Market in China. Market Research Reports, 2003.
Shegetomi, S 2006. Building proper online customer relationships distribution: A case study of Japan retail sector. Institute of Developing Economies (IDE) Japan
Spooner, J. G., & Kanellos, M 2004, IBM sells PC group to Lenovo. Web.
Strategy – Analysing Competitive Industry Structure 2008. Tutor2U. Web.
Shaw, B.A 2003. Business environment: Strategic capability. Oxford University Press.
Timmins, N 2003. “Online Auctions: e-commerce has arrived in the public sector as a way to reduce the civil procurement bill.” Financial Times, Valdero Corporation 2002. Valdero’s Intelligent Supply Chain Control Selected by Extreme Networks. Web.
Wendy, Currie 2000. The Global Information Society, Market as Opportunity: Developing Business-to-Business Internet Commerce, John Wiley & Sons, West Sussex, UK.
Yrjola, H 2001. “Physical Distribution Considerations for Electronic Grocery Shopping.” International Journal of Physical Distribution and Logistics Management, 31 (10), p.746-61.
Yu, C.H 2008. Competitive Advantage. Web.
Appendices
Questionnaire used to interview customers
Demographic information
- Age of Respondent in completed years………………………..
- Area of residence………………………………………..
- Religion Catholic
- Methodist
- Protestant
- No Religion
- Oriental
- Traditional
- Occupational status of respondent
- Formal employment
- Informal employment
- Student
- Not employed
Internet use
- Do you use the internet or browse the world wide web
- Yes
- No
- How many hours do you spend browsing the internet per week……………….
- Have you ever spent your time looking for product information on line?
- Yes
- No
- Have you ever bought a product or service online?
- Yes
- No
- What do you use the internet for most of the times
- Reading News
- Searching information
- E-mailing
- Listening to music/ videos
- Other
- Do you know that the internet can be used to market products and services online?
- Yes
- No
- List the products and services you have purchased online over the past one year?
- Music and other entertainment accessories
- Computer software
- Computer hardware
- Beauty products
- Phonographic materials
- Others
Benefits and limitations of online marketing
- Can you be able to live without the internet?
- Yes
- No
- Please list some of the benefits you like about online marketing……………….……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Please list some of the limitations you have experienced with online marketing……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Who introduced you to online marketing?
- Self
- Friends
- Family members
- School mates
- Work mates
- Others
- Are you satisfied with the process of online marketing?
- Yes
- No
- Please briefly explain your response in Q15 above?………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Do you believe that online marketing has a huge potential for growth?
- Yes
- No
- Please explain your response in Q17 above?………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
End.
Key- informant interview used to interview service providers
- Name……………………………………………………………..
- Retail Organization………………………………………………
- Position……………………………………………………………
- Age in completed years………………………………………….
- When did your company start operating online marketing services…………………………….
- in a few words, can you explain how your business has been influenced by online marketing strategies in relation to traditional methods of marketing……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- In a few words, can you sum up the benefits that online marketing strategies have brought to you renterprise?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- In a few words, can you sum up the challenges that your enterprise continues to face through online marketing?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- In your own view, how has online marketing influenced the attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards purchasing online products?………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Which are the two leading online computer retailers in Hong Kong according to you?…………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Please explain your choice in Q10 above……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Any other comments relating online marketing?………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..