Introduction
The Microsoft Corporation has subcontracted its customer support function. Mambo Graphics has outsourced its entire manufacturing process. After profiting from this outsourcing decision, Mambo Graphics later subcontracted the distribution of its products also. Marks & Spencer’s competent suppliers are its competitive edge (Domberger, 2002). All of these are top companies of the world. One of the factors of their success lies in the question of what to produce themselves and what to get manufactured (Domberger, 2002).
“Outsourcing and globalization of manufacturing allows companies to reduce costs, benefits consumers with lower cost goods and services, causes economic expansion that reduces unemployment, and increases productivity and job creation” (Elder, n.d).
The world is becoming a global community and therefore the business conglomerates throughout the world are in constant search of increasing their competitive edge without compensating their profit margins. Keeping up with new technology requires resources, time, money, effort and risk. Therefore many new companies are now seeking the option of outsourcing.
Key Objectives of the Study
The purpose of the dissertation is to identify, evaluate, and validate the critical steps that affect outsourcing decisions and their effects. Outsourcing is a dependent decision. It is dependent on various independent factors which determine the outcome of this decision making. In this study, the independent variables are cost reduction, improved service, better quality, business secrete, product knowledge, intellectual property etc which are the determinant factors set as evaluating criteria to make the decision to outsource or not outsource.
There are certain extraneous factors also. These factors might not affect the outsourcing decision directly, however are responsible for influencing the decision maker. The Literature Review of this report will be based on four research Questions. The Methodology takes these questions a step further and discusses the main objective of this report i.e. identification, evaluation and validation of steps of the outsourcing decision. Various surveys and studies will be analyzed in order to find out the best model of this decision making procedure.
Research Questions
The main research question in this study is what are the critical steps and reasons that affect outsourcing decisions? Specifically, it will support the following research questions:
- What are the different factors involved in the evaluation of outsourcing decisions?
- Identifying and analyzing what factors should be considered before outsourcing and what types of process and methodologies should be used to evaluate them
- Identifying what to outsource and why
- Selecting the best product life-cycle stage to outsource
These research questions will be answered in the literature review section. A hypothesis is formulated in the methodology section which will discuss with the help of several surveys and studies, various steps that affect the outsourcing decision.
Assumptions and Limitations
Data in this report has been taken from various sources all of which have been mentioned. Surveys etc have all been taken on their face value and no changes have been made. Due limitations, a proper survey could not be conducted on our behalf hence no first hand information is available. This report discusses the outsourcing decision in general and cannot be applied to only one function of any one organization. It has been assumed that all the data provided in the reports is true and does not contain any discrepancy.
An Overview of Outsourcing
Outsourcing is the transfer of organizational activities or subcontracting of company’s processes (Greaver II, 1999). Sometimes these are recurring internal activities and sometimes these are processes, factors of production and sometimes even decision making rights. The factors of production can include human resources, facilities that the company might lack, any equipment or technology the company might not have or other assets (Venture Outsource, n.d).
Almost every organization is involved in the outsourcing process in one way or the other. Usually core functions of the business are not outsourced. The management of the business itself takes care of these important strategic elements of the business. Other noon-core functions can be sub contracted in order to reduce load from the management, improve quality and customer service or reduce costs and increase profits. For example; in case of an insurance company, it can outsource or subcontract its janitorial and housekeeping functions. These functions are not related to insurance, which is the core element of the business.
However, these are also important as without these many other functions might suffer. For example if there is no janitor it will be a hassle for the staff to keep the unwanted people out and in turn their work will be affected. Secondly, it is a minor function and spending time and money on how many people to hire. Taking interviews of each person and describing job specifications of each is not worth it. In such cases the outsourcing company or the third party service providers come in handy (Sourcingmag, 2008).
History
Outsourcing emerged quite a few thousand years ago. It has been there since work specialization was innovated. Outsourcing started as soon as the production and sales of food, tools and other materials began. Communities were formed and people started to exchange products and services. It was a more sophisticated form of the barter system. Later when the industrial revolution came, workers who specialized in a specific function started to offer their services as a third party service provider. However, the companies at that time did not indulge in much outsourcing. Most of the companies were vertically integrated with their own manufacturing and production, their own retail outlets and even their own insurance and tax lawyers (Cyber Futuristics, 2004; Sudhian, 2006).
It was when specialization became common, outsourcing was also developed; with companies now sub contracting various functions of their organization. After the boom of industrial revolution many industrial sectors were developed. Services like insurance, architecture and engineering were taking more interest in outsourcing. However it was still onshore outsourcing which was taking place (Cyber Futuristics, 2004).
Onshore outsourcing was used to make low tech items. As technology became more advanced, a search for outsourcing services which provided lower costs began. With this offshore outsourcing became common. Companies now outsourced from firms which provided low costs, be it from any other country. Another reason for this change was the development in transportation and logistics. In 1980s companies started outsourcing their payroll, billing and other such activities to offshore service providers (Cyber Futuristics, 2004).
In former days companies were always able to attain cost reduction. The reason for this was there huge and complex organizational structures and design. As it was a very cost friendly design, even many years after his companies still used to use this complex structure to reduce their costs. Organization had a pyramid structure of tasks and activities, all of which were combined in to more specific ones.
A lot of time and money was invested in the functions of organizations, therefore it was difficult to outsource. Outsourcing companies at that time might not have done this well, as already mentioned, the business were used to operating on their on basis and for this reason had done a lot of investment. At that time the cost of technology, transportation and other communications was very expensive. These costs were no centralized hence it was difficult to manage them.
As today communication, transportation and technology costs are relatively lower than in the former days, hence it is easier to outsource the functions. Secondly this reduction in cost has removed the large management team which had to take care of the huge complex organization. A centralized organization does not exist today. Even big names like Boeing outsource many of their projects. A centralized structure is now not needed for better functional operation of the organization. According to MacVaugh (n.d);
“An organization might not monitor year-to-year changes in transaction costs, but they do respond to commercial and competitive pressures, from which changes in organizational structure follow. Looking back 15 to 20 years, the forces of international competition and western economic recession only served to exacerbate the pressure on organisations to cut costs and link any capital expenditure to measurable returns on the investment. This is the background from which the debate over the role of HRM begins”.
Today, outsourcing is not just about payroll, billing and call centers. Many big companies outsource their entire manufacturing process. The biggest example in this case is Marks & Spencer, which has a very long term relationship with its supplier. Another example is R&D, which outsources many of its medicine to subcontractors in India.
There are many forms of outsourcing. Some organizations hire subcontractors for doing small daily functions, while others have the outsourcing companies taking care of the entire business. The most common example is the outsourcing of information technology. Business process outsourcing is yet another example. BPO consists of call centre outsourcing, HRO, finance, accounting etc. These are huge contracts which run for many years. IBM, HP and ACS are a few examples in information technology outsourcing (Sourcingmag, 2008).
Companies which are new, sometimes outsource their entre projects. This is feasible for them as they get more expertise, knowledge, better market information and latest technology. On top of this a good outsourcing company usually provides projects on lower costs.
New companies get their projects from designing to distribution, subcontracted. Many companies also get their marketing and sales function outsourced.
The main emphasis of this repot is on the evaluation and validation of critical steps that affect the outsourcing decision. The outsourcing process has several steps. They can be described into four stages. The first one is the strategic step of deciding what to outsource. In this step the management defines the affect of outsourcing in their organization. The second stage is the strategic thinking. In this stage the management has to see from a list of service providers, which offer them the best service with feasible cost.
The contract is also formulated in this stage. The last stage is after the contract has been signed. This is the maintenance and management of the outsourced project. The management has to see if the outsourcing company is fulfilling their task properly. If the business and the service provider both are satisfied, this relationship can become stronger and the sub contractors can become the official suppliers of the business (Sourcingmag, 2008).
There are many factors which can affect the outsourcing decision. The first and the most important one is the support from the top management. If the executive level mangers do not support the idea of outsourcing business functions to a third party, then it is most likely that the staff will also not support this idea. Hence it will become very difficult to implement it. Effective communication is the key to success. The implementers of this plan should see that the employees, who get affected, know and understand the plan.
Moreover, the understanding of the contract and negotiation are also important factors. Lastly, it is always difficult to adapt change, hence it should be seen that the employees are willing to accept this change in their organization. The outsourcing project becomes more difficult if there is a cultural difference between the business and the outsourcing firm. This usually happens in the case of offshore outsourcing (Sourcingmag, 2008).
“Competitive advantages from information no longer accrue naturally to institutions that have internal technological ‘resources.’ Rather, the benefits accrue to institutions with the flexibility to tap the source of the best technology at an acceptable price” (Huber, 1993).
Outsourcing has brought many changes in the organizations. Companies have not only accepted but adopted outsourcing as a new and better trend of performing non core functions of the business (Greaver II, 1999). Below are some changes brought by the outsourcing process.
- In former days a bigger organization was considered to be better. These days a bigger organization just means more hassle. Hence it is not a competitive advantage. Businesses now have establishments which are enough for performing core business activities; other non-core functions of the business are usually outsourced. However, this does not mean reduction in sales. The profits might be going up, but the business will not hire new people and buy new technology, rather it will outsource the required personnel and technology.
- Small competitors can now bring a revolution in the specific industry. A small and agile company can be changed easily, rather than a big company. Therefore, small companies can usually change the cost structures and affect their competitors. When a change has been brought in a specific industry, it is usually very difficult for big companies to accept it and hence incur losses.
- Due to outsourcing now quicker responses are demanded from the buyers. Due to many functions of the organization being outsourced, it becomes easier for the management to respond to a situation. It will just need a note to various suppliers. However, if the company is large and handles all operations on its own, it will become difficult for the mangers to take care of the entire company at once.
- Multi outsourcing has also reduced cycle times. Due to different suppliers in different time zones, it is practically possible for the business to operate 24 hours a day. This contributes to reduction in product and lifecycle times.
- Usually the investors are looking for a more focused management team. A team which focuses only on the core activities of the business and outsources other non-core functions is more successful one.
- Today, size and growth are not important factors determining the success of a business. Hence investing in more human resource or technology is not a feasible idea.
- In order to survive long term, financial improvements are important. This can be achieved via low costs, which in turn can be achieved through outsourcing.
Apart from outsourcing what other options are available to the management. The table below summarizes some other alternatives.
What is the rationale behind the outsourcing decision? Many companies take outsourcing as a quick fix; however this usually leads to the failure of the outsourcing decision. Other companies use it for various strategic and tactical reasons. The table below shows various strategic and tactical reasons of outsourcing.
Even though outsourcing has a lot of advantages associated with it, however many citizens dislike it due to the fact that this phenomenon takes away their jobs and gives it to people outside their country. The table below shows the jobs loss.
Outsourcing has many advantages as well as many disadvantages. A few pros and cons of outsourcing are listed below
Pros
- Planning and controlling now has a new meaning. The management understand this new meaning which helps them identify better ways of operating functions of the business
- Outsourcers usually follow the best practice. If the management works hand in hand with the outsourcer they achieve better results than if they worked on the function themselves.
- There are limitations to increase in productivity and decrease in cost. If the management gets and outsourcer to do the same job, they will come up with new and better ideas which can help the organization achieve better rate of return
- This helps the management focus on their core competencies. The non core activities now being handled by the outsourcer helps the management find their competitive advantage and hence create a niche in the market.
- It helps the management develop an understanding in similar projects. In future if any such projects have to be handled, the management might be able to do it faster at a lower cost.
Cons
- Even if external resources are used in a project it is difficult not to commit to the internal resources. Hence sometimes at a time both are being used
- If the relationship between the outsourcer and the business is not worked upon properly, it will be difficult to manage the project properly. Moreover the management might not be able to develop the project management skills they need.
- You do not own the resources instead the outsourcer does. For example, if you outsource the human resource function, without an investment people can just leave.
- The start of the project is very crucial. If proper management and planning is not done, a lot of money can go waste.
- As the company will have to share its secrets and highly confidential company information, there is always a risk of it being leaked out.
Literature Review
Many of the world’s largest companies have outsourced many of its functions. Some have even outsourced the entire manufacturing process. There are many reasons why a company would outsource. Some sub contract their processes to reduce costs, others do it because they do not have up to date technology and relevant expertise. It not only reduces the project timelines but also helps saves labor costs. In offshore outsourcing, where the outsourcing is usually done from a firm located in low waged countries, the business can considerably reduce labor cost and hence increase its profits.
There are as many disadvantages and challenges associated with the outscoring process, as are the advantages. Even though after the outsourcer is once selected and the business gets its business functions operational without having to hire and pay the employees; before the selection process the business has to spend time and money in selecting the best vendor. Sometimes a proper management team has to be formulated in order to evaluate various factors associated with the process. Then there are legal costs attached to the contract, transition costs and apart from all this sometimes the supplier is not competent enough to complete the project and by the time you find out it is already too late.
In order to outsource any part of the business the business ahs to go through various possibilities, strategies and options before actually taking the decision. So in order to have a proper transparent process of deciding whether to outsource or not, the management should first list all the reasons which has resulted in this decision. These should be then ranked according to the priority. For example, if the company’s business is expanding and now it needs to hire more people in order to insure smooth operation of the business. The main reason in this is the fact that the business needs more skilled people. For this reason it can outsource the new staff that ahs to be hired.
It can also outsource the technology which needs to be updated as the business is now growing. The priority list in this case will contain ‘attainment of new skilled worker’ on the very top. The reason why the business is outsourcing new equipment and human resource is because it wants to save costs on the process of hiring new personnel and buying new equipment. Hence second in the priority list is the cost. The cost cannot come on top because even if the business cannot find any outsourcing company which can take care of the growth in sales and business, the business will have to hire new people and buy new technology as this is the far most important factor which can foster the growth of the organization (Batta, 2008).
After this management will evaluate other factors which can affect the outsourcing decision. In the end the outsourcing company is evaluated based on the evaluation strategy of the business and the best supplier chosen. The management will also have to provide sound reason for their decision. If proper evaluation of the vendors is not done, wrong supplier may get chosen, which instead of helping the company can become a nuisance for them. Not only the money and time will get wasted, the employees will also get de motivated (Engardio, 2006).
When a business outsources any function of the organization, it should make sure that the decision is well communicated in the entire company. The workers who are affected and the ones who are not affected, both should know what the management is planned. Communicating with the staff usually builds up their morale and motivates them. The workers recognize their importance to the organization. On the other hand if proper communication is not present then the workers might believe that they are not important to the organization and hence get de-motivated.
Even though outsourcing seems like an easy way to get out of difficult things yet the businesses should understand that it is not a panacea to all the problems. Sometimes if the problem is not studies and evaluated properly, the outsourcing decision can result in disaster also. Management should first find out the root of the problem. If the problem is very big and complex and has a huge historical background, then the managers should first unfold it themselves. It should be realized that the business managers can understand the problem better than the outsourcing employees. The reason is their relationship and knowledge about the company (Batta, 2008).
Factors Affecting the Outsourcing Decision
“The outsourcing issue should be part of a larger question regarding how the function being evaluated… fits into the organization and what types of services it offers”(Jones, 1997).
The outsourcing decision is affected by various factors. Therefore it can be called as a dependent process. The independent factors which are related to the outsourcing process determine the outcome of the decision. In this study, the independent variables are cost reduction, improved service, better quality, business secrete, product knowledge, intellectual property etc which are the determinant factors set as evaluating criteria to make the decision to outsource or not outsource. There are certain extraneous factors also. These factors might not affect the outsourcing decision directly, however are responsible for influencing the decision maker.
Why Outsource?
The main reason for outsourcing is to perform various functions of the organization in a better way at a lower cost. This is sometimes also used to enhance the product value also. According to Earl (1996), a careful selection of processes and functions which have to be outsourced increase the strategic competitiveness of the company. This he calls as ‘smart outsourcing. According to him smart outsourcing helps the companies get closer to their customers. This provides a competitive advantage to them. Evaluation of the outsourcing decision helps the manager other important aspects of their organization.
First it helps them to evaluate the threats and opportunities presented before their company. The threat is any other company making a better product at a lower cost. Lower cost to the company means lower selling price and hence more customers. Opportunities in the sense that now the same product can be made at some offshore location without any hassle. If an offshore location is selected properly, products can be manufactured even at a very low cost.
Secondly the managers now know what functions they can perform efficiently and in what areas they will need help. The managers also develop a cost and operations structure which will help them sort out the functions according to importance. They will also find out which functions require more money than the others. If high cost functions are non core functions they can be outsourced to a cheaper offshore location.
Evaluating the supplier’s competencies is also important as this gives a general idea of what businesses require from these vendors. Doing business with well known and accepted suppliers helps them create a niche in the market. Many customers are very concerned about where and by whom the product is made. So care should be taken in selecting the best vendor. Another important aspect of outsourcing is that it helps share the risk with the vendor. In certain industries risk level is very high; in such case a proper contract usually distributes the risk between the outsourcer and the company seeking the outsourcing option.
Technological and human resource can also be made available via the outsourcing option. Many companies outsource because they do not want to make huge investments in updating their technology and hiring new human resources. In such case they outsource certain functions which are affected by the advancement of technology. Human resource is usually outsourced from low waged countries. Moreover, management is also able to learn how to maintain a good business relationship, as their relationship with the vendor affects the outcome of their processes directly (Elliot & Torkko, 1996).
Why does any company decide to outsource? Below are some of the factors which can affect the outsourcing decision (Bragg, 2006).
New Skills
A company cannot have expertise in all functions of its business. There are always some functions where the company might lack or might not be able to fulfill the given requirement. In order to overcome this problem the company can handover this function to the supplier which has expertise in this area. Such suppliers who specialize in a certain area have proper trained staff and updated technology for the purpose. For example: certain engineering and computer services require high level of expertise, which are usually outsourced to a well reputed supplier (Bragg, 2006).
Better Management
Sometimes due to poor management even a good staff cannot perform well. Poor management leads to absenteeism, poor wok, missed deadlines and high turnover. Sometimes it is not easy to formulate a management style which improves the functions of the organization. In such case the company can hand over the management to any supplier who specializes in this area. Sometimes the entire management of the organization is outsourced in order to obtain the optimum results (Bragg, 2006).
Better Control
Every company is concerned about having sufficient control over all the functions. This control sometimes helps in better performance. In order to reduce pressure on the management, sometimes a few functions are outsourced. For example some companies take the help of chartered accountants from suppliers in order to work on the accounting section in their firms. This helps the management to have better control of other functions in the company and hence develop a pressure on them to perform better (Bragg, 2006).
Focusing on the Strategy
Every day the managers have to hand out each day’s job to the staff. Along with this they also have to manage the tactical aspect of their job. Handling out the tactical parts to the outsourcer, the management can benefit a lot. By doing this they can focus on the strategic issues of their organization and spend the time on what they do best. For example, if a manager focuses on simple day to day jobs in the organization, he will have little time to focus on the product positioning and marketing strategy (Bragg, 2006).
Importance to the Core Functions
There are many functions of an organization; however the core functions of an organization are the ones which keep the organization running. Failure of even one would mean failure of the entire company. Hence in order to focus all its energy in to these functions the company usually hands out it smaller and less important functions to a supplier. Sometimes, as the nature of the business changes, the core functions might become less important and the management would want to outsource them too. It not only helps the company to focus all its energies into the core functions but also helps the company perform better by handing out other functions to a supplier who has expertise in this area (Bragg, 2006).
Avoid Major Investments
Sometimes a certain department or function in a company does not perform better because not much investment has been done in that area. No technology updates have been installed and no new staff has been recruited. Even with new updates, a certain function of any company needs constant and time to time updates in order to keep with the technology. In such case the company might consider to outsource that particular function as the suppliers who specialize in a certain department usually have best updated technology and expertise in that area. This will help the company avoid investment costs. The supplier usually does not mind investing in new technology as this is one area a company looks at in order to outsource its functions (Bragg, 2006).
Assist Fast Growth
Sometimes when a company is growing very rapidly, the management of the company might need additional help in order to run the day to day chores. In such case the company sub contracts its various functions and the rapidly growing transactions and sales, so that it can focus on the core functions of the company. However, the company has to see that the supplier it chooses has already dealt with large number of transactions or a fast growing company.
Handle Work Over Flow
Sometimes the work load upon the company is so heavy that it is difficult for even the managers to take care of the situation. There can be many reasons for this exceptionally large amount of work. For example in the peak seasons the sales are usually more and the work load is more too. In such case the management of the company has to take the decision of outsourcing some of its functions so that other functions of the company do not suffer.
Strategic Change
In order to bring a good strategic change the management usually has to outsource majority of its functions in order to let the employees get acquainted with the new situation. This also helps in getting the message across that the management is serious about the change and that all employees will have to work accordingly. If the management just announces a change and no serious action are noticed by the employees, then these employees will not take this seriously (Greaver II, 1999).
Risk Reduction
Outsourcing any function reduces the risk to a great extent. How much risk is reduced is usually dependent on the type of contract. However, one important thing which the outsourcing company shares, is responsibility. Once the agreement is done and the company hands over its functions to the supplier, then it is the responsibility of that supplier to finish the work. Hence sometimes in order to reduce the amount of responsibility and risk the company outsources its various functions (Greaver II, 1999; BTQ, 2006).
Cost Reduction
Due to supplier’s better performance, time efficiency and better productivity the company can reduce its cost by outsourcing. This works for both, the company and the outsourcing supplier. The suppliers want to reduce their costs so that more companies get interested in outsourcing their projects to them. The companies are interested because sometimes companies want to avoid huge investment costs in new technology and prefer reduced operational costs. The outsourcing companies are usually providing the same kind of service to many companies; hence economies of scale also contribute to the cost reduction factor. The bigger an outsourcing firm is, lesser can be the cost of operation (Greaver II, 1999).
Increase Flexibility
Outsourcing functions of the business helps the company become more flexible. It is not easy to bring change to the entire organization. However, due to globalization and ever changing business conditions, it is usually easier for the companies to outsource areas where the change has to be brought (Greaver II, 1999).
Acquire New Ideas
Sometimes in order to have new ideas and innovations the company simply outsources its functions. The supplier might have a new and different and even better way of performing that function. This usually brings in new ideas in the company. If the company has a designing section it can subcontract the entire designing department and just work on the already created new ideas by the supplier (Greaver II, 1999).
Improved Customer Service
A good customer service is very important to the business. Technology is developing at a very fast rate, faster than the customer can interpret. Therefore, it is very essential to have a very efficient customer service which is updated and has the best technology. These days many companies have outsourced their customer services centers. Many have outsourced call centers in order to deal with customer’s queries. The suppliers keep these call centers up dated with information and technology.
Improve Credibility
Outsourcing via a big firm means improving your credibility. Sometimes it helps to outsource your projects through a big reputable outsourcing firm. This improves the image of the business and attracts more customers. However, it is also true that outsourcing firms might also help in improving the quality of service or product.
Enhance Sales and Foster Growth
Sometimes when the company itself does not have the capacity to grow, it can always subcontract its various functions. An outsourcing firm which can handle big projects can help in the growth of the company. This growth naturally means growth in sales and hence the profits of the company. Having a good long-term relationship with the supplier also helps in gaining access to markets which were formerly unfamiliar to the company.
This list does not exhaust all the reasons why a company would outsource, however it does give a general idea of what makes the companies subcontract various functions of their organization.
The outsourcing institute has given almost ten reasons why a company would outsource (The outsourcing institute, n.d.).
- Reduce and control operating costs.
- Improve company focus.
- Gain access to world-class capabilities.
- Free internal resources for other purposes.
- Resources are not available internally.
- Accelerate reengineering benefits.
- Function difficult to manage/out of control.
- Make capital funds available.
- Share risks.
- Cash infusion.
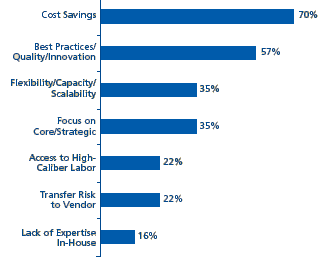
Deloitte has conducted a survey on the realities about the management phenomenon outsourcing. According to this survey almost 70% of the people said that the cost factor was the most important factor in the decision of outsourcing. Getting better quality and performance was yet another factor. Almost 57% of the businesses said that they outsourced their projects in order to get better performance.
Looking at the above figure we can outline various factors which can affect the outsourcing decision, however, there are some problems and challenges associated to these factors too.
Almost 38% of the respondents in this survey said that even though the main reason why they outsourced was to reduce costs, they had to pay hidden additional costs which the outsourcing company claimed was included in the contract. These costs were shown after the business had signed the contract.
Almost 57% of the respondents said that the main factor which affected their decision to outsource was better quality and performance. Almost 31% of the respondents said that once they had signed the contract, the outsourcing company became complacent and did not come up to their expectations.
The third most important factor was the fact that outsourcing is flexible and can mould according to the business needs. However many of the respondents said that once they have signed the contract they are bound by the supplier. The supplier usually does not accept any last minute changes. Hence outsourcing any function with a thought that this will make it flexible can prove wrong, as sometimes the outsourcing methodologies and contracts are usually very rigid and instead of helping the business in any way, it becomes difficult to get rid of the outsourcing partner (Deloitte, 2005).
Sometimes it is not just the supplier who makes a mistake. The businesses usually define some activities as non core activities which do not affect the business directly. Many of these activities are outsourced. After these are outsourced the management realizes the importance and brings it back in the strategic functions of the business. Hence again it becomes difficult to get rid of the supplier, as both are bound by the contract. The management looses control over these functions and hence cannot monitor them (Deloitte, 2005).
Another major factor which affects the outsourcing decision is the high level of skill and expertise the business requires. In the survey conducted by Deloitte consulting, almost one out of five respondents said that after the functions are handed over to the outsourcing firm, the employee turnover of the supplier is more than the turnover of their own employees. Most of the expert and skilled staff leave the job before the project is completed and hence the main factor which fostered the business management to take up the outsourcing decision has now failed itself. Almost 44% of the respondents said that after they realize that the vendor has no expertise or majority of them have left, they have to bring back the functions under their control (Deloitte, 2005).
Many businesses where the risk factor is quite high, the management usually outsource majority of their functions so as to share or transfer the risk. However, this methodology also fails when the vendor incurs loss and blames the business management for this. The business company usually ends up paying for the losses (Deloitte, 2005).
Shalabi et al (2007) conducted a survey and took a sample of almost 915 manufacturing firms. 55% of the respondents of this study were from the automotive industry, 36% were from the chemical and the rest were from the electrical industry. The table below shows the number of respondents according to their respective company size.
Table: the distribution of participating firms according to size. Source: Shalabi, 2007.
It was found that the best firms, or big firms usually outsourced more than the smaller ones. The gap between the two was also noticeable. The table below shows the number of firms which have conducted the outsourcing process. It was found that almost 80% of the best firms outsource, however only 64% of the rest of the firms outsourced their manufacturing products.
Table: outsourcing of the manufacturing process. Source: Shalabi, 2007.
Later the companies were asked why they preferred outsourcing over their in house production. Different companies gave different answers. The increase in levels of production was the main factor which fostered the outsourcing decision among all the firms. The next important factor was cost. Significant reductions in cost of the manufacturing process lead the managers to take this decision. Other factors and the percentage of the respondents’ answers are given in the table below.
Table: 3: Criterion for making the decision to outsource the manufacturing of product. Source: Shalabi, 2007.
However, there were many firms which were not outsourcing at all. There were many big firms also who did not like to loose control over what they were doing and wanted to work on the functions themselves. The table below shows certain reasons why many firms do not outsource.
Table: reasons for not outsourcing the production function. Source: Shalabi, 2007.
It was then asked, which department or function in the organization initiated the outsourcing function. Most of the respondents believed that it was the research and development function which first initiated this process. Respondents were asked to rank the functions which initiated the outsourcing decision. The table below shows the answers of the respondents.
Table: Function responsible for initiating the outsourcing. Source: Shalabi, 2007.
Later the respondents were asked which factors affected their decision to choose a vendor. The best firms said that World class market Knowledge was the most important thing as far as choosing a supplier was concerned. However other firms believed that technological knowledge was the most important thing. The respondents have ranked their answers according to importance. The factors which are most important in selection of a vendor were given more preference, whereas the factors which did not affect the decision making much were given the lowest preference. The table below summarizes the criteria for selection of the best vendor.
Table: Factors involved in the choice of outsourcing partners. Source: Shalabi, 2007.
Where to Outsource?
Onshore Outsourcing: It is also known as domestic outsourcing. As the name suggests, in this type of outsourcing the outsourcing services are obtained from somebody within the country. For example, for United States, getting the products manufactured from companies inside the country (European Information Technology Exchange, 2004).
Offshore Outsourcing: In this type of outsourcing, the headquarters of the company is usually several time zones away from where the product is to be manufactured. For example if any company with the United States wants to get its products made in India or Pakistan. Even though there might be time and cultural difference between the two, there are other factors which motivate the company to take the outsourcing decision. For example, in Pakistan and India the labor costs are relatively cheaper than in United States. Thus getting the product manufactured in these countries means increased profits (European Information Technology Exchange, 2004).
According to Deloitte Consulting (2008);
“2 million jobs will move from the United States and Europe to cheaper destinations in the financial services business alone. The emigration of service jobs across all industries could be as high as 4 million. The consulting firm also forecasts that in the next five years 3/4 of major financial institutions and investment banks will allocate tasks to low labor cost countries and that India will be at the top of the list. Global financial institutions are predicted to invest $356 billion in India for outsourcing projects”.
According to estimations “3.3 million U.S. jobs and $136 billion in wages could be moved to such countries as India, China, and Russia by 2015”.
Near shore Outsourcing: In this type of outsourcing, the headquarters of the company is near the base of operation. This means that for a company outsourcing its product manufacturing from United States, will look at the nearby countries like, Mexico and Canada. In this type of outsourcing the cultural difference and the time difference is usually less and accessibility is more.
After the management has decided to outsource, certain factors should be considered before actually carrying out the outsourcing process.
It is not usually easy to identify the best vendor. For this the management has to develop a proper team which identifies and evaluates the factors which can affect this decision. After the identification of these factors the management team evaluates each vendor according to these criteria. There are different methods of evaluation of these factors. Either the management can ask the supplier or the outsourcing firm questions regarding these factors, or it can do a comprehensive research in the market about this supplier. The later is an expensive method and hence the businesses usually use the first one. In this way they can question the supplier if he has made any claims which are proved wrong afterwards.
Apart from the factors which decide which vendor to select, there are also some extraneous factors. These might not affect the decision directly but it does have some influence on the decision maker’s ability to decide. Some of these factors are discussed below.
Customer’s Choice
Even though most of the customers are not concerned where the product is manufactured, but there are some customers who might not buy the product or boycott it if it is made in some country they do not prefer. For example: after the press of Denmark released the cartoon image of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH), Muslims all over the world have boycotted Danish products. In such case, any business will incur loss if it has been getting its products manufactured from that country. Many customers also believe that if a product is made in a low waged country, than the quality of that product will not be good. Even though the cost reduction factor always persuades the business to find vendors in such countries, the management should make sure that they do not compromise the quality of the product (Reid, 1996).
Political and Legal Factors
The political and legal factors also have an impact on the decision maker. For example; for many years Kosovo was under a civil conflict. None of the businesses in the world considered vendors or suppliers from that place as the political situation of the country was not stable, even though it was providing low costs. This political situation also affected the legal factors which in turn affected the contacts and agreements between the two. Hence the management of any business tried to avoid suppliers of that area as the future was uncertain (Drezner, 2004).
Employees Response
Employees of the company which is considering outsourcing feel very insecure. Some of them seek jobs else where as they think their position might be taken away. The management’s decision to outsource or not is therefore also affected by employees’ response to this news, as a company would not want to loose its old, skilled expertise.
Cost
Cost is one of the most important factors of the outsourcing decision especially human resource outsourcing. According to Klass (2003),
“Economies of scale make it difficult for SMEs [small and medium size enterprises] to maintain a professional HR staff and to internally develop required HR programs and services”
This is not just the case of small and medium enterprises, but the large corporations also try to cut down cost by outsourcing their human resource. Many company functions like payroll and pensions were initially outsourced; however with the technological advancements companies can easily administer these functions. However, even today companies, who do not want to invest in technological advancement, save cost by outsourcing even pension and payroll.
Human resource department of any organization defines the core functions of the company. Core functions are usually not outsourced, as the management does not want to loose control over them and also develop them strategically in order to be competitive. According to Barney (1999), core functions of an organization are very important to the business. Therefore outsourcing them is not a good option. These days companies are trying to reduce costs to such extent that they outsource their entire manufacturing process from product design to promotion and delivery.
Organizational Capabilities
Even though cost is a very important factor in determining the outsourcing decision, there are other factors which tend to influence this decision even more. Outsourcing is usually done depending on the capabilities of the organization.
If the organization does not need to outsource any function, it is very rare that a management will outsource just due to the cost factor. Sometimes it is also important to work without outsourcing just to prove the organization’s worth. It was also noted by Rasheed (2000), that reducing the cost and outsourcing functions usually does not have any effect on the capabilities of the organization. Depending on the organizational capabilities it is argued that companies should always work on core functions themselves and outsource the non core functions (Klaas et al., 2001; Lepak et al., 2005).
For example the recruitment and selection agencies practice attracting and selecting a very large pool of candidates. Even huge multinational companies cannot attract and hire employees on such regular basis, therefore the companies should focus on their core activities and let the outsourcers who specialize and have expertise for certain functions work on their non core activities. Therefore it can be concluded that organizational capabilities to perform the functions of it business directly affect the outsourcing decision. More the company is capable of performing its own functions, lesser is the outsourcing option considered. However if the organization does not have much resources to work on any project it will be better to get it outsourced.
Nature of Function to Be Outsourced
Outsourcing also depends on the nature of the function to be outsourced. Hence the management should first evaluate and examine the nature of function which has to be outsourced. For example, before outsourcing any function, the management should see if that function will have a positive affect on the core competencies of the business or will just take up important management time just to evaluate the outsourcing decision.
Therefore a proper evaluation of the functions should be done. For example; in case the management is deciding to outsource its human resource function, it should first determine the dependent factors of this activity. According to Carrrig (1997) the human resource activities are of three types, transactional, traditional, or transformational. The transactional part of the human reousce activity is the payroll. Strategic planning of the human resource of any organization can be called its transformational activity as this will decide the future of each and every employee. Recruitment is the traditional portion of this function. According to Lepak et al (1999);
“In this vein payroll administration might be considered transactional, recruitment as traditional, and strategic planning as transformational…. ‘At a general level, a parallel exists between the transactional-transformational HR activity continuum and core-peripheral continuum…Consequently, we anticipate a greater reliance on outsourcing for transactional practices’ but note that it ‘is the manner by which HR practices are used that determines whether they are transformational or transactional, rather than the practice itself”
Personal Reasons
The decision to outsource and which buyer to choose is also dependent on the personal choice of the person taking this decision. This decision is usually taken from the executive level management; hence if the top management feels strongly about any vendor, it is more likely they will choose it ignoring any problems associated with it. Or if the outsourcing decision is not affecting any major functions and still the management prefers to sub contract any part of the function, they might do it. For this reason the business company should always formulate a decision making team. This team will properly analyze each factor and deduce the results based on everybody’s evaluation.
Before outsourcing the management should find answers to a few questions which will help them take a better outsourcing decision (Weisman, 1997).
- What are our core competencies in the organizational function which has to be outsourced?
- What support functions found in any business do we require?
- What necessary functions (core and support) could potentially be done more efficiently and more cost effectively by a supplier?
- What are our overall objectives for outsourcing?
- What barriers exist to outsourcing?
- What is the potential functional impact of outsourcing?
- What can be improved internally before outsourcing is considered?
- What are our requirements for each of the functions to be outsourced?
- Who are the major suppliers (world-class companies) in each of these functional areas?
Whom to Outsource?
All of factors listed below are represented as the evaluation criteria for the selection of the best vendor. After explaining each factor, in the end methods of evaluation are also given. These factors will help the management select he best vendor. Moreover the evaluation criteria will help them assess various suppliers and find out who stands in the market.
Outsourcing Commitment
Outsourcing is a unique and different process. In order to outsource the supplier should have required expertise in that area and people who are able to understand the nature of business and importance of that function to the business. Without this understanding it will be difficult for the third party to help in controlling that function. It should also be noted that outsourcing is not just system integration, but is more than that. The commitment factor is by far the most important aspect of the supplier.
There are several ways to evaluate whether the outsourcing company is really committed to the job. For this reason answers to the following questions should be determined.
- How long the supplier has been in this business?
- How is the company organized in terms of commitment to customers?
- What percentage of the total revenue of the suppliers company comes from outsourcing?
- Approximately how many customers can the company deal with at one time?
It should be noted here that if the answers to the above questions show that the vendor has not been in the industry for a long time, or it has many failed projects the management will automatically assume that the vendor is not suitable. Hence we can see a direct relationship between this factor and the decision to outsource (Rothman, 2003).
Flexible and Tested Approach
Once the outsourcing company takes over the specific function of the business, an already proven methodology will come in handy. For this reason before actually outsourcing it should be seen that the outsourcing company has a proper well defined method of approach. Outsourcing companies usually have predefined criteria of approach as they are dealing with similar functions. In order to work, that methodology should be flexible.
A very rigid form of rules will not work as situations can be similar in any two organizations but not same. Moreover, when the outsourcing team takes over the current management of the business usually loses control over that function of the company. The action is usually fast and if the managers are not updated from time to time they will loose track of changes happening in the organization. Therefore, in order for the methodology to work and up to date information, the outsourcing team should be asked the following questions.
- Do you have a standard methodology or criteria of approach?
- Is your methodology fully documented and accessible to all?
- In how many cases have you used this methodology?
- How many times it has proved to be successful? Did it ever fail?
- What was the reason for that failure?
- What is your approach to changing it according to the situation?
- Is it difficult to make changes without affecting the basic framework of this methodology?
In order to check the factors, the business can present a hypothetical situation and see how the outsourcing company deals with it. This will help the company determine what level of flexibility the outsourcing firm has in its approach. If the methodology fails, the business can either base its decision on this particular factor or ask the outsourcing firm to take a corrective measure.
In such cases it is always better to outsource from a bigger firm, as such firms not only have a proper framework which they have been using for years, but also have tested it.
This is also and important factor as it will directly influence the outcome of this decision. In order to validate this factor, the outcome of the above questions should be analyzed. If there are one or more failed methodologies of the vendor, than there is a chance that the management will not commit with that supplier.
Expertise and Talent
One of the basic reasons why companies prefer outsourcing is the level of expertise available in the outsourcing firm. This knowledge and talent is used in operation of the functions which are outsourced. If the outsourcing firm is not able to apply this, then the basic reason of outsourcing is not fulfilled. Moreover, the business also expects to have a low cost expertise, if it has hired an offshore supplier from a country where wages are low. In order to determine whether the outsourcing company has expertise to deal with critical problems and has skills and expertise the business requires, certain questions can be asked to the outsourcing team.
- How big is your outsourcing staff? How many personnel in the consulting staff? How many in the analysis and design staff?
- What level of education and years of experience does the outsourcing staff have?
- How many personnel in the documentation, implementation and telecommunication function?
- How do you train your employees?
- How do you integrate them with the present situation?
In this case the business can test the employees by presenting them with hypothetical situations and then testing their level of expertise. If a long term relationship has to be establish then the business can also take some measures in training the staff according to their requirement and helping them learn more about the function they are going to work on. In a short term relationship this will not be feasible.
This is also an important factor. The casual relationship of this factor can be noticed due to the fact that lack of expertise at the vendor’s side can result in rejection of that supplier.
Intellectual Capital
If a company is outsourcing its human resource, this mean that the business will not have any expertise or people who have in depth knowledge about that particular industry. Some industries undergo vigorous legislative changes. If the supplier does not have knowledge and projections about this area, then it is most likely that the management of the business will not be able to justify sub contracting to this vendor.
As time passes by the management usually loses its original skilled staff due to outsourcing. At this point the business relies on the supplier’s team. So it is crucial that the supplier’s team has in depth knowledge about the political, legal and other changes which affect such an industry. For other industries this might not be an issue, however many companies are affected by governments regulations.
The relationship between the outsourcing decision and this factor is also a casual relationship. This means that the outcome of this analysis is dependent on the evaluation of this factor. For this reason the management should ask the suppliers the following questions in order to find out their knowledge in this area.
- How much knowledge do you have about this industry?
- Do you think you can call your self superior than other suppliers in terms of this knowledge?
- Do you think this knowledge is enough for you current and future industry needs?
- What connections do these hold with the current organizations present in this industry?
International Presence
If the company’s business is spread in many countries then it should seek a vendor which has international presence too. This will be helpful in the context that the business will not have to coordinate with various different languages and time zones. If the company wishes to test interfaces on different platform, then this will be and added point. Hence if the company is looking for a vendor who can cater its global needs than it is better to choose the one which has an international presence. For this purpose the management should make sure that the a few questions about the vendor are answered.
- What experience and resources do you have outside this country?
- Where are your offices located other than here?
- What treaty are you a member of?
Financial Power of the Vendor
The financial power of the outsourcer is vey important. Many lawsuits have been filed against such vendors who were not able to fulfill their claims. Due to a legal agreement binding the two nobody can step back and dismiss the contract in just a day.
The vendor usually has all the information about the business and the company. It knows what technology you have, the finances, how you function etc. In order to this outsourcing work, careful analyzing of each supplying candidate should be done. Many outsourcing companies start the business, take order, but do not have the finances to carry on and eventually shut down. Filing a lawsuit will cost more money and nobody can confirm if the verdict will be in your favor. During the selection process the business management should check the financial statements, stock offerings, reports etc in order to make sure that the company has enough resources to carry on the operation and will be able to meet the future needs if the business wants to offer more contracts to the same outsourcer.
This is also an important factor in the decision to outsource or not. An outsourcer with very poor finances will probably not get selected for the contract. Moreover, the strategic plans of the outsourcing company can also reflect its ability to perform various functions. Though you can ask questions regarding this issue, however the best way is to check the finances yourself, the strategic plans, corporate culture and history of the organization.
References and Alliances
Another important factor in the outsourcing decision is the customer referral base of that outsourcing company. It is usually easier to attract new customers than retain the old ones. Hence an outsourcing company with a large base of customers can be helpful, as the business management can contact the old customers to find out about the company, their way of operations and their adherence to the business.
However, it is very rare that a person admits his /her mistakes. Same is the case here. If their experience was not good, it is more likely that they will deny it. However, if the person talking is sharp he can ask various questions like; was your organization performing better before or after the outsourcing decision? What would you do differently if you outsourced again? Etc. These questions will help the business determine whether the outsourcing decision is worth investing or not.
Successful outsourcing companies usually develop a relationship with other parties providing services to them. For example any outsourcer might be strategically allied with the consultancy firms; tool set providers and testing houses.
These parties provide the outsourcing firms with immediate access to materials and resources which might not be possible on a short notice from anybody else. So in order to find out more about the outsourcer the business management should contact these suppliers. It also helps in finding out what kind of relationship does the outsourcer have with the allied parties, as a poor relationship might mean that they will not provide those resources on time, or in worst cases completely deny the access. In such case out business will suffer as out outsourcer will not be able to operate without those resources.
In order to determine what kind of relationship the outsourcer has with its strategic alliances, the following questions should be asked before any contract is singed.
- What kind of relationship do you have with your alliances?
- How do you use this relationship?
- Do you have any plans of extending this relationship or taking it further in the future?
- How have you used this allied relationship?
- Is it very important to your business?
Commitment and Resources for R&D
As mentioned in the previous section that many companies outsource because they do not have the resource to update and develop their information technology system. When outsourcing decision is made, the management should see that the firm being considered has proper strategic plans for research and developments. Not only plans but it also has the resources and finances to do so.
As the time passes and the business grows, there will be a need to bring in new technology and update the old ones. If your outsourcer does not have the resources to do, it is most probable that your company will also lag behind as the outsourcer is working on business functions of your organization. Hence the research and development ability of the outsourcer should be checked in the beginning.
Quality of Contract
The agreement or the contract should be well read and understood before acceptance. It is better if a lawyer or a person who understand such terms reads the contract so that there are no hidden costs etc in the document. It should be seen that all the clauses are clear and that there are no one sided clauses. If the contract is so too good that you cannot believe somebody can provide so much with this amount of money, than probably he is lying. Ask yourself the following questions.
- Are these good people?
- Is it worth starting a business with them?
- If you have plans of building up this relationship with more future contracts, of they have the resources and ability to fulfill them?
A good and flexible contract has the following properties:
- Terms of the agreement (the trend is to shorter-length contracts)
- Detailed description of supplier’s obligations and services to be provided
- Company’s responsibilities and obligations
- Performance measures and expected service levels
- Rates, fees, and any incentives or penalties
- Ownership rights if the agreement is terminated, including intellectual property rights
- Warranties
- Disclaimers
- Annual reviews
- Option to renegotiate
- Means for conflict resolution
Negotiation
When you start negotiating with the outsourcer, it will give a fairly good image of what it will be like doing business with him in the future. It is always difficult for both the parties to agree on different terms which might or might not be in favor of the other. Therefore, how does the buyer respond to difficult issues in the contract, is he willing to change something according to your needs, is he ready to listen to your side of the story, are questions which will help determine the future relationship with that buyer. In order to develop a good relationship, the following steps should be followed (Weisman, 1997);
- Evaluate core and commodity functions.
- Determine requirements and analyze internal capacity.
- Investigate potential partners.
- Select the right partner or partners.
- Negotiate a win-win agreement.
- Make the transition.
Insurances and Legal Actions
Looking back at the insurance and litigation history of the buyer will tell you about his past mistakes. All wins and losses, all legal actions, lawsuits should be checked. This will give an idea about the outsourcer’s mistakes made in the past and what he has learned from them. If he making one mistake again and again, it is most probable that he will make that mistake in your case also. Hence the past trends can be used to forecast the future behavior of the outsourcer.
Another important aspect is security. As the outsourcer usually has access to all your information, it is possible that he leaks your business secrets to other people he might be doing business with. Hence the past record of the outsourcing firm should be checked.
Many people have had problems with outsourcers. This is due to not clearly setting out a guideline before the selection of a vendor. A survey was done by Deloitte consulting company. According to this survey many business managers said that they would define realistic service levels that align with business goals, if they had a chance to re do their outsourcing strategy (Deloitte, 2008).
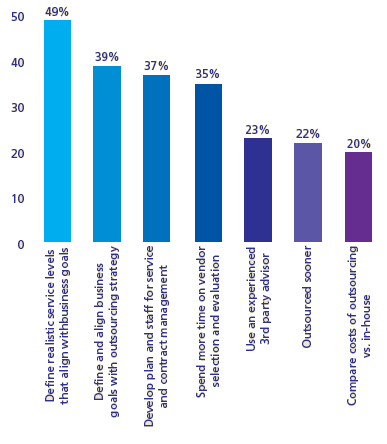
Looking at the above figure we can see the mistakes people had made in deciding which factors were important in the outsourcing decision. The lowest number of people almost 20% people made mistake in costing. It is quite predictable as cost is usually the main element which fosters this outsourcing decision. Almost 22% of the people said that they had taken the outsourcing decision too late and that they should have outsourced sooner.
Many people did not consider planning as an important factor, which resulted in many other possible faults. Management did not set up realistic goals which were according to the businesses needs and demands and hence goals were not achieved. Moreover, management also did not consider vendor selection as an important part. According to them whoever they will select will be bound by the contract and will definitely work on their project. However, they did not predict that many outsourcers run out of resources in the middle of the project and are incapable of finishing it. Therefore careful evaluation of everything from the financial resources to the human resource of the outsourcer should be done.
According to the Gartner group;
“… 20% of outsourcing deals do not produce cost savings…10% of those deals actually wind up increasing costs.”
“… This year alone 50% of all outsourcing projects will fall short of delivering expected value and will be deemed unsuccessful” (Gartner group, 2003).
Product Life Cycle
Every product lifecycle has four stages. The first stage is conceptual and preliminary design study. At this stage. The second stage is detail design and development. The third stage is production phase. This stage includes production, distribution and repair service. The fourth stage is product phase-out where product obsolescence and disposability process takes place.
If the outsourcing is done in the early years of the production life cycle, it can benefit the organization in 2 ways.
- Access to frontier global technology
- Ability to write detailed procurement contract
Before the actual date when the product ahs to be launched, an evaluation can be done of the cost and prices associated. If the product is outsourced in a later stage the organization is bound in many ways. Now if the outsourcer has a problem and does not work for any reason, the products coming form the back will create a backlog and hence many issues such as storage, depreciation etc will arise. Hence the best option is to outsource the product in an earlier stage.
Organizations have to include product outsourcing alternatives as apart of conceptual design review to determine if the product is a candidate for outsourcing. If it is, then at which stage of the product lifecycle should be outsourced. Evaluation the following inherent traits of the product will help to determine the candidacy and the stage of outsourcing compliance.
- The type and level of importance of product’s intellectual property, product secret and unique manufacturing techniques required to manufacture the product, and any feature that differentiate the product from similar products that manufacture by competitors.
- The impact of losing knowledge and expertise about the product due to experienced employees who were let go during outsourcing.
- Outsourcing cost benefit analysis.
- Product and process complexity.
- Product documentation level and detail requirement.
Methodology
Pre-Implementation Steps
There are certain things which are very important while making the decision of outsourcing. The plan I have created below contains critical steps which can affect the outsourcing decision. Careful implementation of each step can result in a successful implementation. However there are certain factors which have to be administered properly in order to have an effective outsourcing decision. The outsourcing decision does not end where the implementation takes place, even after the implementation there are many things the management has to take care of.
- The outsourcing implementation and evaluation team should be well organized. Any discrepancy between the members can result in problematic situation. Moreover the team should be expert and should have proper knowledge of what afctors can affect their decision.
- Necessary management commitment should be attained. Without the commitment of the management it will be impossible to implement and have a good relationship with the outsourcer.
- The corporate needs of the business should be clearly defined and known to every member of the team. The members should know why they are outsourcing
- Proper alternatives should be identified and evaluated.
- Risks associated with the outsourcing decision and general risks associated with the industry should be identified. Moreover benefits and opportunities should also be identified.
- Each function should have its own alternative
- A proper outsourcing contract should be created. This should be read by every member of team so as to find out the problems if any.
- The team should evaluate and administer the contract in order to remove those problems. A careful evaluation and corrective action can lead to a good contract.
Critical Steps That Affect the Outsourcing Decision Organize a Team
The very first step is to create a top management team. This team will not take care of little operation but will act as a path finder. The members of this team will be the board members or the executive management members. These members are the ones responsible for taking the major decision of the organization. Therefore, obviously without these members it will be impossible to implement the outsourcing plan. These members also help the organization in the transition process. These members will make the final decision of the vendor selection as they will be the ones who are sued by the stakeholders if any information leaks out of the system due to a bad decision of vendor selection.
Team Up for the Outsourcing Decision
The above members should now choose different members of the organization which are most suitable to work on this outsourcing project. These members will be responsible for the evaluation of the factors which affect the outsourcing decision. It will be better if the management selects the members who have some experience in making the outsourcing decision or have specialized in this area. These professional should understand the needs of the business and should be able to administer the outsourcing project even after the implementation.
They should also be skilled in problem solving and negotiation. At least one member should be able to understand the legal terminologies used in the contract and who should be responsible for majority of the contract negotiation. In order to the relationship to work, both the sides should have a clear understanding of a realistic approach to this decision. A biased contract or demands will lead to a unhealthy relationship, which will hinder all the future relationship the company might want to have with the outsourcer, moreover it will also result in a deteriorated present relationship.
Identification of Internal Resources
Identification of critical internal resources is very important. If necessary appoint a person who has the knowledge of the function being outsourced and can help the outsourcing staff get acquainted. He should also be an expert negotiator in order to maintain a good relationship between the two.
Identification of Problems in Your System
Identify any problems which you currently have with your system. For example, high cost, backlog, delivery problems, time management problems etc. these should help in assessing the strengths and weaknesses of the business. The management should identify and evaluate these problems. Moreover alternatives to solve these problems apart from outsourcing should also be mentioned. A proper matrix formulation always helps in understanding such problems and a brainstorming session can give various ideas of how to solve these problems.
Business Plan Updating
The strategic business plan should be updated accordingly. A typical period of any outsourcing is almost 8 to 10 years. However this usually changes depending on the function being outsourced. Therefore the business plan should be amended accordingly. The management should note the expected changes brought in due to outsourcing. These can be later on compared with the actual results.
Identify Long Term Needs and Amend the Plan Accordingly
The long-term needs of the business should also be identified. As mentioned above the strategic business plan should be worked upon accordingly. All new application should be identified. Some these requirements might need implementation; other might need discontinuation after sometime. So a time plan will be needed. New hardware and tools which are required should also be brought in to the company.
Cost Structure
The current cost structure of the firm should be thoroughly understood. Moreover the future costs associated with the company should also be evaluated. This is probably the most difficult task. The management should keep in mind the inflation, technology change etc while cost estimations are made. Expenditure from the outsourcer which he might ask later should also be determined. The cost estimations should be made for a minimum of 5 years.
Identify Your Current and Expected Use
Moreover, the management should make calculations about the anticipated and current operations’ function. These might increase or expand over the time. For example in peak seasons the sales might be high hence a proper integration of invoices, cash inflow and backup should be made.
SWOT Review
The strength and weaknesses analysis has already been done before, but they need to be reviewed from time to time. As the time passes new opportunities come up, company achieves competitiveness in one area and loses in the other. The outsourcing alternatives which have already been mentioned above should be evaluated here. It should be noted if the any alternative is better than the outsourcing decision. These steps are not to implement the outsourcing decision but to find out what is best for the company. Long term benefits should be kept in mind while the evaluation is done. The best team should identify the alternatives as this is a very critical part of this decision making process and will affect how the business operates in the future.
Outsourcers’ Information
Identify the strengths and weaknesses of your outsourcer. The team should even study the corporate history in depth. Information about new, old and current customers is also essential as they might be a reference and will help in the evaluation of the outsourcer. The outsourcer’s market value can be estimated by reviewing the number of contracts it has and with what companies. The type of relationship it has with its customer can also tell a lot about that outsourcer.
What to Outsource?
During the strengths and weakness analysis the company ahs found out its functions which are in a need of outsourcing. In this step these functions need to be reevaluated in order to find out the one or ones to outsource. For example for a typical IT company, there can be various things which can be outsourced. For example;
- The first option is to outsource all the activities in a specified area
- Equipment
- Applications software
- Systems software, tools, etc.
- Personnel
- Consulting services
- Systems integration
- Development of new programs and systems
- Data conversion
- Live system operation, management, and control
- Communications equipment, software, and interfaces
- Daily and periodic processing and reports (accuracy; timeliness; formats)
- Responsibility for troubleshooting
- Compliance with applicable laws
- Audit trails
- Pickup and delivery
- Physical security
- Data and program security
- Backup procedures for programs, data, etc.
- Disaster recovery capabilities
- Data entry
- Maintenance
- PC service
- PC installation of hardware, software, and modifications
- Help Desk
Request for Proposal
A proper request for proposal should be formulated. This will help the management compare different outsourcers. Management should specify to the outsourcer that they should be very specific about the costing issue and that there should be no hidden charges. Pricing or costing can be of various forms. It can be monthly, bi monthly, yearly or depending on per unit cost. The management should accept the model which suits them best and negotiate accordingly. There can be other charges such as training fee, seminar fee, disaster recovery fee etc. all prices should be taken into account and then pricing should be done. Acceptance criteria for the bidding should be made. Reports generate and downtime should be evaluated.
Invite Bidders
Now is the final task of inviting the concerned parties. The management should give each bidder a tour of the site and the management team should meet with the outsourcer’s team. In order to maintain a good relationship it should have a good start. The management should have at least half an hour meeting with the team explaining them various aspects of the function they wish to outsource. Even if it looks that this proposal cannot be accepted, even though decisions can be made without evaluation, the management should be polite and should not show signs of rejections at this point.
Evaluation of the Proposals
All the proposals should be evaluated now. This should be done with the help of a predefined and properly documented criterion. After the evaluation the management should be open to discussions and negotiations. The outsourcer should know where he lacks and negotiations should be held if feasible. The management should be very polite and careful in rejecting any proposal so that the relationship between the two does not get affected. The bidders should be ranked accordingly, so that if due to some problem the management cannot work with the first one the second option can be chosen. In the end the alternatives should be established.
The management should see that the negotiation should be tough but polite. Every thing should be crystal clear and there should be no hidden things on both ends. The outsourcer should be given the confidence to have negotiations on any basis. It does not matter how good the outsourcer looks apparently, if he does not meet the minimum requirement then he should be out of the list.
Reference Checking
After the best few vendors have been selected, reference checking should be done. The management should contact and if possible visit the site and see the outsourcer’s previous project. A huge referral base does not necessarily mean that the outsourcer is good, but a long term relationship does specify the effectiveness of an outsourcer. If the experience of any customer was ot good it is more likely that he will not accept that he made a bad decision. However, if the person talking is sharp he can ask various questions like; was your organization performing better before or after the outsourcing decision? What would you do differently if you outsourced again? Etc. These questions will help the business determine whether the outsourcing decision is worth investing or not.
Successful outsourcing companies usually develop a relationship with other parties providing services to them. For example any outsourcer might be strategically allied with the consultancy firms; tool set providers and testing houses.
These parties provide the outsourcing firms with immediate access to materials and resources which might not be possible on a short notice from anybody else. So in order to find out more about the outsourcer the business management should contact these suppliers. It also helps in finding out what kind of relationship does the outsourcer have with the allied parties, as a poor relationship might mean that they will not provide those resources on time, or in worst cases completely deny the access. In such case out business will suffer as out outsourcer will not be able to operate without those resources.
Monitor, Manage, Modify, and Steer
The contract and the outsourcer should be monitored and worked in the right direction as required. The contract usually needs amendments from time to time. With the proper negotiation from the outsourcer the management should modify and negotiate the new and updated contract.
Functions to Outsource
Below are some functions which organizations are outsourcing these days:
- Payroll
- Pension administration
- Information system and technology
- Telecommunications
- Document processing (mailroom, copiers etc)
- Accounting
- Tax compliance
- Internal audit
- Materials/supplies inventory stocking and distribution
- Facilities management and maintenance
- Food services
- Janitorial services
- Management services (construction, hotels etc)
Lindholm (n.d), in his study has given what type of functions businesses outsource. He has given the present and future percentage evaluations of those functions.
Table: services outsourced. Source: lindholm, n.d.
Evaluation
The qualitative approach to evaluate the factors which affected the outsourcing decision ahs already been discussed. In this section we will discuss the quantitative approach to the evaluation process.
Evaluation should be done on the basis of:
- Impact on the firm, i.e. on its organizational structure, financial position and human resources;
- Time horizon, i.e. the period of time in which the relationship with the external sources of technology is planned to go on;
- Level of control over activities, i.e. the possibility/right of the company to define the way in which the output is to be achieved and the resources to be used for this aim;
- Level of control over results (output), in terms of property and exploitation rights;
- Start-up time and costs needed for selecting the partners, defining their relative contribution, determining the game rules;-
- Level of reversibility, i.e. the extent to which the characteristics of the relationship can be modified and the easiness to abandon the collaboration.
Different criteria can be used for evaluation
- Functionality
- Platform Utilization
- Survival Probability
- Initial Cost
- Annual Cost
- Annual Benefits
Discussion and Analysis
Historically the main factor which fostered the outsourcing decision was cost. Even today, it remains the main motivational factor. If outsourcing is done from low waged countries the optimum cost saving model can be achieved. However, care should be taken so that the cost saving does not come from using cheap materials, which can reduce the overheads in general (Quint and Shorten, 2005). When outsourcing is done through a big company, the cost saving can be achieved through economies of scale. Hence a careful combination of the above factors can help any company achieve a low cost functional model of business. This will increase the potential profit and even help in business expansion.
Looking at the above report, it can be said that outsourcing also helps improve business’s financial flexibility. This is accomplished by paying only for what you really require, hence changing the fixed costs to variable costs (Teems, 2003). This means that the money which initially used to be tied up in fixed assets is now free and the company can use it as it requires (Drtina, 1994). The financial flexibility helps companies allocate their resources based on their competencies. Initially these companies were just trying to move the product out of the door.
Apart from the monetary benefits outsourcing also helps the company in getting access to new technology and updates. Outsourcing firms usually have very up to date and latest technology. Gaining access to this creates various other opportunities for the business. New technology also means betterment in product and hence a satisfied customer (Welch and Nayak, 1992). An external provider helps comparison of its supply chain with the outsourcer. This helps the business to improve. The business can also compare itself with other buyers of that particular outsourcing firm and hence gain a competitive advantage.
Apart from all these benefits of outsourcing, we also found out that companies, who outsource non core activities to the supplier, are strategically better than other companies who do not. The main reason for this is the fact that outsourcing non core activities gives them time and energy to focus on strategic and important functions of the business. Therefore such companies can strengthen their competitive advantage and create a niche for themselves in the market.
Along with these benefits there are some risks associated with the outsourcing process. According to Simhan, almost 50% of the outsourcing activities fail (2002). In another study Barthelemy and Adsit (2003), discussed various reasons which caused the failure of any outsourcing decision. According to them the outsourcing process usually fails because:
- Companies outsource important functions of a business which should not have been outsourced
- The selection criteria for the outsourcer is not right or they have collected the wrong supplier
- They accept a contract which is not beneficial or has many hidden things or costs. In other words signing on a poorly written agreement also results in the failure of an outsourcing venture
- Companies usually loose total control of the outsourced function.
- The hidden costs are not discovered until its too late
- A proper exit strategy is not planned
The above list has given various reasons which are responsible for the failure of any outsourcing venture. These reasons can also be termed as the risks associated with any outsourcing process.
Selecting the best vendor is not an easy job and if a proper procedure is not followed, can lead to disaster. The very main issue regarding this selection process is that many companies fail to plan the selection process properly. Moreover, after the selection of any vendor, steps should be taken for building future relationship (Barretto, 2004). After the selection, when the contract negotiations have to take place, care should be taken that the management is very explicit about their demands and requirements. Any vagueness in the agreement can lead to differences in the middle of the project.
This can lead to a loss for both the parties. The outsourcing companies should also be clear about what will they provide; not only in terms of operations but also in terms of inventory, time and resources (Hogan, 2004). Companies, businesses and outsourcers both should also define a clear exit strategy. This means that if anything goes wrong, how each will leave without creating conflicts. Therefore not only the agreement should be clear, but each and every point in the agreement should be clear. These risks which were deduced from the above report are present even before the outsourcing implementation has taken place.
After the negotiations have been done and the plan is executed, there are other types of risks which get associated to the process. The main risk however is that of flexibility. Outsourcing usually does not accept any changes after the outsourcing implementation has taken place. This again goes back to the negotiations where it was not clearly defined that the business might have some fluctuations. Therefore during the contract development stage, it should be clearly defined that there might be operational issues etc. A realistic timeline also helps in overcoming this risk.
Apart from this any product or service which is produced outside the four walls of the company, usually has some other kinds of risks associated with it. For example, regulatory risks, legal risks, reputation risk etc. It is difficult to predict how a buyer will react to outsourcing. Some buyers are not concerned where a product is manufactured whereas others are very particular about this issue (Beasley, Bradford, and Pagach, 2004).
After the implementation stage is the relationship stage. In this both the parties have to communicate effectively in order to build a good relationship. It is better to have a meeting in which the business can lay down what it wants next and if there are any differences, similarly, the outsourcing company can also communicate things which were otherwise missed out in the contract. If the business intends to outsource other functions of in the future and the outsourcing company has the potential to fulfill those, then it is always better to use the same outsourcer.
The main reason for this is that the outsourcing company has already worked with this company and has a lot of information about, how this business works? What are the operations and functions? Which are the important and core functions and which are under their supervision (the outsourcer’s). All of this information can prove helpful in the future contracts.
One of the most important things in the outsourcer and the buyer relationship is strong communication. If both parties understand the needs, demands and requirements of the other then it will be very easy to do business. However, it was also found out that without the collaboration of both the parties this outsourcing relationship might not go far. A clear-cut understanding of the costs associated with the project can make it easier for both the parties. Therefore, in order to have a long term relationship, understanding and communication are two important tools (Hodges and Block, 2005).
One major problem which usually arises after the implementation of the outsourcing project is the affect it has on other functions of the business. None of the functions in a business are independent and have some affect on each other. Changing one can bring changes to many other functions. A precise knowledge, understanding and prior study in this case is very important. Many companies implement the outsourcing project without analyzing what affect it will have on the organization as a whole. These companies also fail to analyze specific risk which are associated to their company (“40 Risks” 2004).
Therefore, proper planning is very important for any outsourcing project. Before even deciding to outsource any project, the management team should first jot down the adverse and positive affects this can have on the organization as a whole. Later, the influence on each and every department which can get affected by this decision should be noted. A proper planned out and well defined outsourcing project can never fail.
Summing up, the list below will give an overview of the above discussion and point out few other factors of risk involved in such decisions.
- Transaction costs: Quite a good amount of cash can go in the administration of the outsourcing project. This cost is apart from the payments made to the outsourcing firm.
- Hidden and additional costs: Hidden costs are not necessarily what an outsourcing company hides from you and later on demands. It can also be the cost which the company has to pay, even though the outsourcing firm did not demand. For example: with the bringing in of new staff by the outsourcing company, the old employees in the firm can feel threatened and hence leave for any better option. This can be an additional cost for the company as now it has to place and add, conduct tests and interviews in order to select a suitable and experienced candidate.
- Lack of flexibility: as already discussed above outsourcing results in lack of flexibility in all senses.
- Loss of control: As per the previous discussion, loss of control in the company means you can alter lesser things and cannot have them your way.
- HR problems: with new people now becoming in charge of various functions in the organization, the older can feel threatened and hence serious human resource differences can arise.
- As mentioned before an exit strategy should be planned. Moreover the cost associated to such a strategy should also be evaluated. Having the very same vendor just to avoid the hassle for getting a new one can get the business into more hassle. A supplier should always be evaluated very carefully and the plan should be aborted if does not go according to time or cost plan. However exceptions are present.
- Privacy and confidentiality issues should be mentioned in the agreement. This is important not only for the company but also for the customers. For example, if a bank outsources its phone banking service it will then have to provide complete information to the outsourcer. The outsourced employees can always misuse it. Therefore everything should be mentioned in the contract. Another thing which is important and should be present in the contract is the intellectual property rights. Limitations of access should be defined. For example in case of IT outsourcing, accessibility of LAN should be defined.
- The very first question a business should ask before outsourcing is whether it should outsource or not. The opportunity cost and alternatives should also be defined. This will give a fairly good idea of how much the business needs to outsource.
Conclusion
Many changes in this and past decade have made this era probably one of the most important one in the history of the world. Rapid globalization indicates the improvements and technological advancements mankind has made.
Outsourcing is one phenomenon which has attracted a lot of attention. Business Week, The financial Times, Forbes, Fortune, The New York Times, Time Magazine, The Wall Street Journal, almost all magazines and every newspaper is talking about off shoring, even though it is just one part of the greater outsourcing phenomenon. Why people are interested in this and what kind of rewards does it offer? What kind of outsourcing strategies are businesses using these days? All of these questions have been answered in this report.
Outsourcing has many advantages. However we can classify these in to four main categories. Cost saving and technological advancement are probably the most important ones. Two other factors which foster the outsourcing decision are strategic enhancement and financial flexibility.
A detailed discussion and analysis of these factors indicate that companies consider outsourcing as a quick fix to their needs and minimum one of these factors are definitely involved in the outsourcing decision. Many businesses have a very strategic approach to outsourcing. Many of them develop a long term relationship with their supplier, which is not only beneficial for them, as the supplier now knows a lot about the business and is easy to deal with them, but is better for the supplier as now they have a permanent customer.
The management should always consider all risks associated with the outsourcing project. This will help create a better relationship, and it is not possible to create a long term relationship without a good understanding.
This paper has outlined and explained in detailed critical steps of the outsourcing decision. These steps are critical due to the fact that missing out even one can result in the failure of the outsourcing plan as a whole. Each and every step is important in its own way. Various studies have also been quoted in order to emphasize on the importance and provide a logical background to the information provided. The study answers the where, how, what and when of the outsourcing decision.
A comprehensive analysis to the outsourcing decision will help companies develop a clear and concise outsourcing strategy. Many studies have discussed the outsourcing steps. Others have discussed what and where to outsource. However very few have discussed the factors which can affect an outsourcing decision, more importantly even fewer studies have discussed all these factors in detail.
This study also discusses how a healthy vendor and company relationship is important for the future business. With the rise of globalization, many companies are now outsourcing their entire production and manufacturing process. Many companies use this option as a cost saving model.
This is particularly important when outsourcing is done via and offshore firm. Offshore outsourcing helps in cost reduction if the vendor is present in a low waged country. Many companies have now shifted to offshore outsourcing and have relocated their entire businesses. However care should be taken as there are risks associated with outsourcing. As discussed above, one wrong step can lead to the failure of the entire decision.
Usually the managers search for the cheapest possible offshore vendor. Countries like India, Pakistan and China provide one of the cheapest outsourcing solutions. Companies like IBM, Microsoft etc outsource many of their business functions from these countries. Smaller businesses usually use freelancing as an outsourcing tool. However freelancing cannot provide a long-term relationship with the vendor, but can provide cheapest possible solutions.
As the technology becomes more advanced and with dot com generation taking hold, more and more companies are now switching towards online outsourcing. An online business can be setup within a week with the lowest possible investment. For this reason many large companies feel threatened due to internet outsourcing.
Outsourcing has brought many changes in the organizations. Companies have not only accepted but adopted outsourcing as a new and better trend of performing non core functions of the business.
References
40 Risks Purchasing Pros Must Address for Outsourcing Success. (2005). Supplier Selection & Management Report.Vol.5 No.3, pp. 4-6.
Barney, J. (1991) ‘Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage’ Journal of Management, Vol. 17, pp. 99-129.
Beasley, Mark, Marianne Bradford, and Don Pagach. (2004). Outsourcing? At your own risk. Strategic Finance. Vol. 86, No. 1, pp. 22-29.
Barthelemy, Jerome and Dennis Adsit. (2003). The seven deadly sins of outsourcing; Executive commentary. The Academy of Management Executive. Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 87-100.
Barretto, Charito B. (2004). Weekender: Labor & management. BusinessWorld. p. 1.
Batta, Mike (2008). Factors influencing the outsourcing decision. Web.
Bragg, Steven M.A Guide to selecting; Negotiating the contract; maintaining control of process. the correct business unit.John Wiley and Sons. Hoboken. New Jersey. United States of America. ISBN-139780471676263.
BTQ (2006). Bet On Governance To Manage Outsourcing Risk; strategic outsourcing. Web.
Cyber Futuristics (2004). History of Outsourcing. Web.
Centre for American progress (2004). Outsourcing Statistics in Perspective; Domestic and economy. Web.
Carrig, K. (1991) ‘Reshaping human resources for the next century – Lessons from a high flying airline’ Human Resource Management, Vol. 36, No. 2, pp. 277-289.
Domberger, Simon (2002). The Contracting Organization; A strategic guide to outsourcing. Oxford University Press. ISBN-0198774583.
Drezner Daniel W (2004). The Outsourcing Bogeyman. Foreign affairs. Web.
Drtina, Ralph E. (1994). The outsourcing decision. Management Accounting. Vol.75, No. 9, pp. 56-62.
Deloitte (2005). Calling a Change in the Outsourcing Market; The Realities for the World’s Largest Organizations.
Deloitte (2008) Why Settle For Less? Deloitte Consulting 2008 Outsourcing Report.
Earl, M. (1996). The Risks of Outsourcing IT. Sloan Management Review. 37. 26-32.
Elliott, T.L. & Torkko, D.E. (1996). Word Class Outsourcing Strategies. Telecommunications. American.
Engardio, Pete (2006). Outsourcing job killer or innovation boost? Business Week. Web.
Elder, Larry. “The sage from South Central” American radio Speaker, b.1952. Web.
European Information Technology Exchange (2004). Key Outsourcing Terms. Web.
Greaver II, Maurice F (1999). Strategic Outsourcing; a structured approach to outsourcing decisions and initiatives. AMA publications. ISBN-0814404340.
Gartner Group (2003). Outsourcing statistics. Web.
Hogan, Jane. (2004). Managing strategic outsourcing. Medical Device Technology. Vol. 15, No. 10, pp. 12-13.
Hodges, Mark and Duie Block. (2005). Business process outsourcing: Current trends and best practices. Contract Management Magazine. Vol. 45, No. 1, pp. 8-17.
Huber, R.L. (1993). How Continental Bank Outsourced Its “Crown Jewels.” Harvard Business Review. 121-129.
Jones, W. (1997). Outsourcing Basics. Information Systems Management. 14. 66-69.
Klaas, B.S., McClendon, J., and Gainey, T. (1999) ‘HR outsourcing and its impact: The role of transaction costs’ Personnel Psychology, Vol. 52, pp. 113-136.
Lepak, D.P. and Snell, S.A. (1999) ‘Virtual HR: Strategic human resources in the 21st century’ Human Resource Management Review, Vol. 24, pp. 31-48.
Quint, Mitchell and Dermot Shorten. (2005). The china syndrome. Strategy + Business. Web.
Reid, Warren S. (1996). Outsourcing; the 20 steps to Success. Articles from WSR Consulting Group, LLC.
Rothman, Johanna (2003). 11 Steps to Successful Outsourcing: A Contrarian’s View. Computer World top stories. Web.
Rasheed, A. (2000) ‘Making More by Doing Less: An Analysis of Outsourcing and its Effects on Firm Performance’ Journal of Management, Vol. 26, Issue. 4, pp 763-790
Sourcingmag.com (2008). Outsourcing; what is outsourcing?. Web.
Sudhian (2006). A brief history of outsourcing. Web.
Simhan, Raja. (2002). An inside view of outsourcing. Web.
Shalabi, Ammar. Omar, Muhammad. Rundquist, Jonas. (2007). Outsourcing and organizing of NPD; A survey of Malaysian Industry. Paper presented at EIASM Product Development Management Conference in Oporto,Portugal.
The outsourcing institute. (n.d). Top ten outsourcing survey. Web.
Teems, Yvonne. (2003). Outsourcing offers some pros, along with a few cons. Business Insurance. Vol. 37, No. 30, p. T13.
Venture Outsource (n.d). Terms and definition. Web.
Welch, James A. and P. Ranganath Nayak. (1992). Strategic sourcing: A progressive approach to the make-or-buy decision. Academy of Management Executive. Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 23-31.
Weisman, Joan. Pirkey, Kevin E. Outourcing;Plannign for strategic partnerships. The Sheridan Press.
Appendix
Questionnaire
- What is approximate gross annual revenue of your entire company?
- <£50,000
- £50,001 to £100,000
- £100,001 to £250,000
- £250,001 to £500,000
- £500,001 to £1m
- >£1m
- What is the approximate number of employees in your company?
- 1 to 9
- 10 to 20
- 21 to 30
- 31 to 50
- 51 to 100
- >100
- What is the estimated annual value of the outsourcing project(s) your company is currently outsourcing?
- <£1,000
- £1,001 to £5,000
- £5,001 to £10,000
- £10,001 to £50,000
- £50,001 to £100,000
- >£100,000
Depending on the framework your organization has chosen to help implement the outsourcing project, answer the following.
- Does the framework provide the following features?
- Quantitative measurements
- Qualitative measurements
- Financial costing methods
- Core and non-core classification
- Performance benchmarking
- Are there any factors crucial to outsourcing which the framework has not addressed? (If yes, please briefly elaborate)
I. General questions about the firm
The purpose of these questions is to provide a general picture of the firm and the activities in the firm. Please answer the questions as a representative for the whole firm, and not as a representative for a single business unit or a geographical location.
- Firm:
- Address:
- Telephone/e-mail:
- Homepage (www):
- Name of the respondent:
- Position of the respondent:
- Average number of employees during 2004
- Firm’s total turnover in 2003/2004
- Please describe the new-product success for your firm compared to your competitors. Do you estimate that you are:
- The most successful in your industry on your most important markets
- In the top 1/3 of your industry on your most important markets
- In the middle 1/3 of your industry on your most important markets
- In the bottom 1/3 of your industry on your most important markets
- In what industry is the main activity of the firm?
- Mechanical industry
- Chemical industry
- Food industry
- Textile industry
- Electronics industry
- Paper, wood and forest industry
- Computer industry
- ICT industry
- Biotechnology industry
- Building & construction industry
- Other
- For your new product development program, provide the following estimates:
- A) New product sales as % of total sales (average for past 5 years): __%
- B) New product profits as % of total profits (average for past 5 years): __%
- C) % new products considered as successes in the last five years: __%
- D) % new products considered as financial successes in the last five years: __%
- Estimate the share of the firm’s turnover generated by export sales: __%
- How would you describe the development during the last two years of the markets where the most important product lines of the firm compete?
- rapidly increasing
- increasing
- stable
- decreasing
- rapidly decreasing
- Approximately what share of the firm’s turnover was generated by the three largest customers?
- less than
- 25%
- 25-50% 5
- 1-75% 7
- 6-90%
- more than 90%
- Our new product development program meets the performance objectives set out for it.
- disagree
- neutral
- agree
- Overall, our new product development program is considered a success.
- disagree
- neutral
- agree
- Does your organization have a specific strategy for the development of new products regarding the choice of product lines or areas where new products shall be developed? Yes/No (If you answered “No,” please go to question 14.)
Is this strategy based mainly on information from…
- Management group/board ______%
- Marketing department ______%
- R&D department ______%
- Production department ______%
- Other ______%
- Does your organization have a specific strategy for the development of new products based on product platform thinking? (A product platform is a joint basic design or a number of joint key components which can be combined to form many different products.) Yes/No
- Does your organization have a specific strategy for the development of new products based on a module system? (Module thinking means that a small number of modular products can be combined to form many different products.) Yes/No
- Does your organization have a specific strategy for selecting the activities in product development that will be subject to outsourcing? (Outsourcing of product development means that the main part or the most important parts of the product development process are conducted outside the firm.) Yes/No
- Does your organization have a specific strategy for continuous improvements of product development activities and the product development process? Yes/No
- The process of developing new products is often considered as a number of phases. Please consider in this question the latest large new-product development project in which you were involved. To estimate the time-to-market, please indicate an estimated (a) starting point and (b) finishing point for the activities below. Time should be expressed as months before market introduction:
- Concept development
- Project planning
- Product development
- Production planning
- Pilot production
- Please choose one of the five options which best describes your firm´s product development process (check only one):
- We do not have any formally documented process for new product development.
- We do not have any formally documented process for new product development, but we have a series of activities that are informally accepted as the way we conduct product development in this firm.
- We have a formally documented process where one function completes a set of tasks, management reviews the results and then passes the results on to the next function which completes another set of tasks.
- We have a formally documented process where a cross-functional team completes a set of tasks, management reviews the results and gives a go-ahead for the team to complete the next set of cross-functional tasks.
- We have a formally documented process where cross-functional teams use a staged process with overlapping, fluid stages, but where the phases interact and management takes decisions when they are needed and in dialogue with the cross-functional group.
- Other (please describe).
- How do you reward project managers and project members upon new product development? Please mark every method of reward that is used, and estimate to what extent the method is used for project managers and project members respectively. (Please mark all methods that are present in your firm.)