Abstract
The real option valuation analysis in the business is the option in the business scenario, which can be selected and analyzed from the various alternatives. The decision-making and the analysis of the real option is the main aim of the study. The real value of the option is the replacement from the traditional method of the decision making and there are traditional models of the real value options like the NPV of cash flow that does not perform the work up to the mark for the reason that they disregard the flexibility management decision. The main intention is to construct the model for real options valuation and to have a complete analysis of the real options in assessing the conditions of the business or the company. The study in this deals mainly with the real options analysis and how it can be analyzed by the various tools and techniques.
Introduction
The real options theory or the real options analysis is vital in the decision-making process of the business organization. A real option can be defined as a certain valued theory that is supportive in the commencement of several business decisions. The real option can be described as the valuation method in the strategic decision in the new way of analysis. The real value analysis depicts the advantages and disadvantages of the same.
The real options analysis is not the equation or the mathematical derivation to be pointed out, the real option is a two-way valued approach by the analysis and the description mainly with an intention in the decision making. The major contribution of the real option is from research and thought process and the rest are as the result of the same from the decision making by the managers and by the analysis of the particular models. The study of them deals mainly with the new upcoming trends in the business scenario.
The study in the paper mainly deals with the traditional views of analysis and the new conditions where the theory can be applied in practice. The use of the real option is in a variety of technological applications.
Objectives
The real value in this study mainly aims at the analysis conducted by them and the various decision-making approaches and the valuation of the real options. The document explicates that the valuation of the Real Option technique, indulges in the forecast of the returns on investments by assuming that the asset evaluation is strongly associated with asset management. They are an alternative to discounted cash flow. The real option value accentuates the significance of the flexibility management in the decision-making process of the project. The real options combine the strategic planning options. As a prevention against errors.
“Real options is the extension of financial option theory to options on real (no financial) assets. In contrast to the valuation of financial options –where decision-making is a matter of shopping for the best deal on a specified contract — the valuation of a real option requires that it be identified and specified. Moving from financial options to real options requires a way of thinking, one that brings the discipline of the financial markets to internal strategic investment decisions” (Managing Strategic Investment in an Uncertain World: Tell me more about Real options 2004).The other aims of the research methods are the descriptive analysis of the real options, the programmed real option seeking methods by using the process of optimization and the discounting of the cash flow economically and determining the cost generated and benefits in the cost analysis. The aim of this research is to sketch foremost factors in operation of real options for the various operations in research.
The real options Analysis
A real option is “An option or option-like feature embedded in a real investment opportunity” (Financial Glossary 2005).
The real options include the tangible assets, financial assets and the physical assets of the cash flows in business. The real options can also be defined as the suppleness that managers should become accustomed to the changes in the decisions regarding the capital budgeting.
The real option is voluntary and it does make any kind of obligation in verifying the price and the time. The real options are just an optional method in spreading out the business or enlarging it depending on the preferential conditions of the market. Real options are important in escalating the value of a project as there takes place lots of discarding in the unfavorable outcomes which may lead to the risk in the project. The understanding of the real options method in the organization is very vital and after the determination, it makes use of the capital budgeting prospects AND techniques in choosing the right method for the evaluating the value. The NPV (net present value) and the DCF (Discount cash flow) are the methods used as the forecast tools of real options.
Real options analysis is a beneficial tool for motivating attitude about a collection of achievable options and choice to take up a decision on investment. Specifically, ROA facilitates to maintain investment options release, and initiate riskier approaches to be explored, by shortening the commitments and the devotion of long term, It permits various choice of options available in present and future, to determine the cut off’s.
The chief driving force of ROA is that it allows a number of investments to take the investments at a certain time helps in identifying for the future forecast and imagine a little will succeed. The suppleness means that, at the each future instance, the decisions can be arrived depending on which to be used and neglected.
The real option is found as a very much useful tool in the decision making and in the applying of the various kind of the market-based approach and in the generation of the finance and the market values that are applicable in the building the public utility and the results mainly based on the various policies by the public.
The real options analysis plays a vital role in the increased growth of the business and the contributions for the government in the making the information much available using the various techniques that are applicable and in supporting the decisions in the public utility projects.
Steps in real value analysis
The various steps in the real value analysis are the:
- Qualitative management screening
- Base case net present value analysis
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Real options problem framing
- Real options modeling and analysis
- Portfolio and resources optimization
- Reporting
- Update analysis (Dr. Mun 2006, 27).
Quantitative screening
The quantitative screening is the first step in the real options analysis and this screening depends on the various kinds of the decisions that are to be taken on the projects, company policies and the objectives and the various strategies that are taken up by the company. The screening takes place with the much of the globalized issues and the management principles.
Net present value analysis
For the each criterion that passes the quantitative screening they have to have a clear estimation of the present value of the project in detail. The net present value is the traditional approach in comparison with the Real option.
Monte Carlo simulation
The Monte Carlo estimation is the typical analysis of the data and the sensitivity analysis is being conducted in each discount flow method and they mainly deal in the setting of the net present value.
Real option problem framing
The problem framing is an important step in the real options analysis and this is the process where the strategic optional ties come as the contract method and it mainly includes the identification of the strategic option and the list of the options can be chosen in detail.
Real option Modeling and analysis
This is the modeling and the analysis of the forecast of the various methods that are in the forecast and they use the Monte Carlo estimation in the analysis and in the data formation of the same. The net present value and the cash flow are used in the process.
Portfolio and resource estimation
Portfolio analysis is not an important step in the project analysis, this can be as a result of the correlated data that can be having the various projects and the optimization of the value differs.
Reporting
The reporting consists of the analysis and the presenting of the process in the each of the analytical methods and they depend on the various mathematical and financial charts and the reporting methods for the analysis.
Update analysis
The updated analysis is very important as the future is a set of uncertainties and these have to be treated and made in a proper formatting and each time it has to be updated.
Methodology
A methodology is a systematic procedure or the step-by-step process in achieving a certain task or objective. A methodology uses diverse ways in accomplishing the final result by incorporating different methods. The methods used for the analysis of the real options are the qualitative and the quantitative methods of the research. “Design Methodology refers to the development of a system or method for a unique situation. Design Methodology stresses the use of brainstorming to encourage innovative ideas and collaborative thinking to work through each idea and arrive at the best solution. Design Methodology also employs basic research methods, such as analysis and testing” (What is Design Methodology? 2010).
The methodology design will be helpful for the evaluation and analysis of real value options in the business. Data collection is an important part of the design of the methodology. It facilitates the acquiring of data so that decisions can be taken on the significant problems.
Research Design
The research design is useful in identifying and analyzing the various methods in conducting the research and involves the decision-making after the analysis of the data collected. The research design forms the building block of the research proposal. The research on the real options in business can be both qualitative and quantitative. The research design is a conceptual structure or the blueprint of the information which the customer wants to execute for business forecast.
Research Appropriateness
“Research design provides the glue that holds the research project together. A design is used to structure the research, to show how all of the major parts of the research project — the samples or groups, measures, treatments or programs, and methods of assignment — work together to try to address the central research questions” (What is the appropriate research design for ‘Effects of Poor Economy on the Development of Qualitative Educati 2010).
Quantitative Analysis
The quantitative research is the organized analysis and investigation of the quantitative data. The quantitative data make use of the various statistical models and the theories of the quantitative data. There are too probable achieves from the more quantitative feature of real option. In making the decisions with projects to sustain, Government can observe the fundamentals of the real options as a buying option for the UK economy. For Government, the risks will primarily be technical ones in contrast to the political market risks. The suppleness of ROA resources is when things go erroneous the disadvantage happens at an initial investment. The analysis of the real option is much dependent, if circumstances are favorable, the beneficiary side of the investment can be retrieved from the capital investment.
ROA as a quantitative tool is likely to have greatest impact in helping Government to make decisions on larger, complex multi-stage projects and where appropriate proxies can be found for inputs, outputs and risk
The idea of the quantitative method is the employment of the mathematical and statistical model and the analysis of the hypothesis. The quantitative link is the main link among the empirical methods.
Qualitative research
The qualitative method investigates the why and how in decision-making approach. In the current scenario, the key value of ROA for the Government is likely to be in two ways in shaping a successful course for selecting the mechanism of an investment program, and second for observing and rebalancing investment decisions in the light of emerging information about project progress and commercial possibilities. Using ROA as a discipline is very valuable in stimulating thinking about the range of investment options that are available in the each stage, how these might change with time. This is much helpful in the various identities of the future data.
ROA as a qualitative and quantitative tool
Government ought to initiate integrating ROA into the decision-making processes for business and technology innovation. Its prior consideration of applying ROA will lead to the various kind of the different kinds of decision-making and in the setting of the various strategies.ROA has advantages over the NPV and the DCF method; it is helpful in the measuring of investments and in the future prediction of the same.
Example of real options
“Suppose an R&D project requires an outlay of £3m now to enable the investment of £80m in a new product after successful R&D. Suppose further that the certain value of the cash flow from this asset is £100m. If the R&D is believed to have 10% chance of success, a standard valuation, taking into account the technical uncertainty in the R&D assigns to this project a value of:
10% x £ (100m – 80m) – £3m = – £1m”. By the analysis it seems to be worth and selectable. (Johnson MP 2005).
Real option as powerful alternative
The real option can be considered as a powerful alternative in comparison with the DCF and the ROI techniques, the various kind of the technology means the implementation of the business by the various means of standard techniques mainly like the net present value and the return on investment, There are certain environments to continue the various kinds of the missing values,
There are many uncertainties that are to be considered in the project and in the analysis of the real value options, the real value option are Project managers and designers are engaged in production with the uncertainties and planning up with very best choices in the development of good production system. There are many traditional approaches in the planning and in deciding on the investment decisions. The various tools of the assessment are the payback, simple interest rate, discount or net present value (NPV), and rate of returns.
Real Options Analysis and decision making
The section of the study focuses mainly on considering the real options analysis is dealing with and the approach of them. To establish with, certain information on options valuation is made available. The fundamental call options agreement is clear as a concurrence in which the consumer (holder) has the power to implement by buying or selling the benefits or prosperity at a desired price.
In the future date of the contract the buyers keep in tact with the terms of the agreement. Options evaluation began from the financial sectors wherever the options are bought at an assured cost and implementation only if advantageous. The option holder has the authority to take up the call option and not the obligation, regarding the stocks and the bonds with the specified time taken for the cost which is pre-determined. To state an example the
Bob may purchase a 1-year option to buy 100 shares of company X at $50 per share. If company X’s shares trade above $50, Bob is likely to exercise the option. In doing so, Bob gets a net payoff equal to the price of the share at the time of option exercise, less the $50 he’ll pay per share. If company X’s shares trade below $50, Bob is not required to exercise the option and his losses are limited to the purchase price of the option. More information and examples of financial options can be found. “Real options are similar to financial options, except that it applies the theory of options to real life projects.” (Babajide 2007, 15).
Method of decision making using real options
The various price drivers for the real value options are the present value of the cash flows that are forecasted for the future and the total cash invested and the uncertainty in the projects carried out and the various arising opportunities in the project and the risk-free rate in the analysis of the same, the intense competition among the various players in the market.
“The financial markets are adept at calculating the value of an investment under uncertain conditions–exactly the challenge faced by business strategists. By applying the discipline of the markets, executives can avoid basing important decisions on subjective judgments about the future. The application of market discipline to strategy involves three components. First, the decision is framed in terms of the real options it creates. Second, in evaluating an investment, all the relevant information on value and risk available in the financial markets is taken into account. Third, actual financial transactions are used, when appropriate, to acquire options or otherwise mitigate risk”. (Amram & Kulatilaka n.d. 8)
Analysis
Real options valuation is one of the monetary methods used for assessing saving under the certain circumstances of doubt, but this doubt is linked with various variables in the marketplace. For example, the need for product in future or worth of an asset in future etc… In valuation of real options, the universal thoughts from monetary alternatives of pricing hypothesis are utilized together with a number of mathematics. Valuation of the Real option has previously concerned various investment judgments by business establishment and is broadly taught as area of the up to date prospectus in company investment study. The real options solution is a principal advantage. This information is observable for a monetary alternative with the intention of can be sold on a public alternative switch over for a vested workers encouragement alternative that can be implemented. “Real options technique can conceptualize and value managerial flexibility to alter initial operating strategy in order to capitalize on favorable future opportunity or to react to mitigate losses. Recognizing a particular capital budging project as a real option has value, particularly as the business environment becomes more uncertain.” (Alleman 2002, 35). The Valuation of the Real option is one of the most attractive investigations in the area of the Finance nowadays. The various reasons for increasing the relevance of the Valuation of the Real options are due to a variety of causes. That is, initially, due to the disadvantage of the DCF technique the a large amount universal techniques in Business Finance have turned out to be increasingly clear to the practitioners and as a result of this they have put great force on academic study to develop customary valuation. The next cause is that various writing on the valuation of the real options such as pricing procedures and all have turned to be more available to community so that this will sharpen the consciousness for assessing asset schemes with the valuation of real option scheme.And lastly, the extremely unstable world financial state of affairs and still the superior elasticity being put up into asset schemes entitles for assessment techniques with the intention to corporate this instability and elasticity and form it more precisely. Valuation of real option tool provided better-quality than any other customary valuation technique. “The real options analysis needed in the following situation, (1) when there is a contingent investment decision. No other approach can correctly value this type of opportunity. (2) When uncertainty is large enough that it is sensible to wait for more information, avoiding regret for irreversible investment. (3) When the value seems to be captured in possibilities for future growth options rather than current cash flow. (4) When uncertainty is large enough to make flexibility a consideration. (5)When there will be project updates and mid-course strategy corrections.” (Schulmerich 2005, 22). The various five measures to take care of the real options in the management of finance is business. That is (1) Make use of the discounted cash flow evaluation method and avoid any real alternatives by assessing their worth as zero. (2) Make use of the discounted cash flow evaluation method and consist of a qualitative acknowledgment of a real alternative value. (3) Make use of the resolution tree examination. (4) Make use of the customary form for a financial alternative. (5) And finally build up an exclusive, project exact form using monetary business method. There are some fundamental techniques that are necessary for real options. This assessment begins with the capability to recognize real alternatives and construct qualitative evaluation on the subject of a real option worth. So a Decision tree becomes one of the most important tools to make the valuation of real assets.
In view of the fact that, they need a clear recognition of the embedded alternatives. This is very much necessary for making decision-making procedures. “The management of real options requires corporate decision-makers to take a portfolio view to evaluate how strategy adjustments can enhance individual option value as well as the aggregate value of real decision-making flexibilities at the level at the level of the firm” Kopel & Kursten 2004, 29).
The real option situation can be used in many situations, such as; alternative to invest in a novel know-how based manufactured goods or any of the services as the outcome of the flourishing Research and development attempt, in the case of trade mark or any of the other intellectual property possessed by the industry and all. But the same time analysis valuation of the faced so many difficulties too. At the time of valuing the real option a lot of the inputs for the alternative pricing form are hard to acquire. For this example Research and development plans. “The Real Option Valuation model encompasses a suite of option pricing tools to quantify the embedded strategic value for a range of financial analysis and investment scenarios. Traditional discounted cash flow investment analysis will only accept an investment if the returns on the project exceed the hurdle rate. While this is a worthwhile exercise, it fails to consider the myriad of strategic options that are associated with many investments.” (Real Option Valuation 2009).
So that we can see that the analysis of the valuation of the real options model offers the capability to recognize what options may subsist in the new plan and the apparatus to estimate all these aspects. One of the main advantages of using the value of the real options model is that customary assessment measures cannot correctly capture the organization’s elasticity to become accustomed and modify afterward decisions in reaction to unforeseen developments such as aggressive/technical/marketplace growths. And at the same time this particular model method can help to value the organizations’ elasticity to modify its preliminary working strategy with the intention of taking advantage of positive prospect enlargement opportunities or to act in response so as to diminish certain losses occurring in the organizations. “Real options also tend to mitigate project risk, since the project owner has the right to modify strategy midcourse. This can help avoid the worst outcomes for the project, providing a kind of operational hedge against downside risk.” (Shimko n.d.). The changes in the market conditions and the changes in other factors which will obviously affect the future profits therefore, there must be timely information with respect to these aspects. The need for such timely information for maximizing profits has made real options analysis more effective and valuable.
Case Study
XYZ and software electronic company are considering the economic and financial feasibility for setting up a production unit for hand-held devices that could be used for wireless internet connections. However the main issue that is continuing to plague XYZ is that its demand profile is uncertain and it would be difficult to predict, or forecast, with reasonable degree of accuracy, regarding how many units could be sold. However, their budget managers have made estimates as follows:
There is 25% chance that high demand could occur, leading to a cash flow of $33M per year for 3 years. Again, there is a 50% chance of average demand, with cash flow of $25m per year, and finally there is also a 25% chance that demand may be low and annual cash inflows could be $5m. This project, according to risk management experts, carries more than average risks and thus attracts 14% cost of capital. A tabular representation of the tentative demand forecast would be as follows:
Moreover, the annual cash flow is expected around $22M, the cost of capital of the project works to14%, with life of 3 years and required investment, or cost of project valued at $50M.
Since more market data is needed to reach a final conclusion, Murphy is also toying with the idea of delaying the decision by a year, by which time a clearer picture would emerge. However, expected cash flows would be delayed by one year if such a decision is taken,
It is now necessary to consider the real options as follows:
First option – Discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis ignoring timing choice :
The expected cash flow of this proposed project is $22 M based on this calculation:
- 0.25($33) + 0.50($25) + 0.25 (S5) = $22M.
- NPV is calculated- $5= + $22/ (1 + 0.14) + $22 / (1 + 0.14)² + $22/ (1 +.14)³ = $1.08
If a decision is to be taken based on just the above DCF, it is possible that it should be accepted since the NPV is positive and is not negative. However a deeper analysis would yield as follows:
Second option – DCF with a qualitative consideration of the timing option.
The project gains an expected but risk-filled NPV of 1.08M. Now the critical question that arises is that whether an immediate decision needs to be taken, or the decision could be deferred for a year or so. If the deferred decision could yield a higher NPV of $1.08 it needs to be deferred, but if it is feared less, then, an immediate decision needs to be taken without further ado. Another aspect that arises is whether a call option with an exercise cost of $50 on a stock with a current price of $50 is worth more than if the price were $20. If the value of the underlying asset is close to the purchase price, such an option should be honored. As testified by the expert risk managers, this is a proposition which entails a large degree of risk, and therefore the risk option value also needs to be high.
Thus, the case would hinge upon whether XYZ Software would like to make an immediate decision or would consider delaying it for a year or so, in order to get better understanding of market and its trends, etc. It would thus be the risk and responsibility of the Board of Directors, in consensus to decide which course of action would be most valuable for the company at the present juncture. Opt for the option right away, at an NPV of 1.08 or wait for a year, to get a higher NPV.
Another Case study
XYZ is a FMCG company and is launching a new product and the initial investment is $ 50000. The company expects that this new product will be generating a future cash flow of $ 600 yearly for the coming three years. The cash flows in the firm XYZ predict that the standard difference of the generated cash flows would be by 10% on a yearly basis. The discount-free rate for XYZ is 3%. The cost of capital for the launch of the new product is 5 %.
XYZ has the option to launch and develop the product within the time span of the next three years.
- I – Initial investment = $ 50000
- N – no. of years = 3 yrs.
- V – The present value of the future cash flows @ 5 %
- D – Deviation = 10 %
- F- Future cash flows = $ 600
Therefore the present value of the investment in the new product can be calculated as below:
- PV (I) = 50000/ (1.03)3
- = 50000 / 1.093
- = 45745
Therefore, PV (I) = $ 45745
The present value of the future cash flow is at 10 %
- = 600 x 5 % x 3
- = $ 54000.
Under the traditional net present value the profit is $ 54000 – $50000 = $ 4000.
Under this system there is a profit of $ 4000.
So this product can be launched but it is also beneficial to check if deferring the launch of this product for the concerned period of three years will generate how much amount of profits or loss for the firm.
Therefore,
- = 54000 / 45745
- = 1.18
- = 10 % x (3)1/2
- = 10 % x 1.73
- = 0.3
Therefore exercising the call option product’s value becomes 10.3 %.
So, the value of the new product launch is calculated as below:
- = 54000 x 0.103
- = $ 5562
Therefore it is lost and is better that XYZ launches the product after some time.
Analysis of Real options
All the assets whether it is financial or real, will have a particular value. But in order to understand the best ways to productively invest in and manage these possessions depends on the method of perception made not only as to the value of the property but it should also be seen to it that the value of the resources should also be understood in a better way. All the assets are capable of being valued but there is only difference in the techniques and methods which are used in assessing the value of these assets. The method for the assessment of the value of different assets is different. Therefore the assessment of a real estate possession needs diverse information and a diverse plan is used when compared to the assessment of the value of a business supply. But even though the methods used for valuation are different, there is likeness in certain fundamental principles used for valuation. The degree of the likeness in the different principles is a distinct factor. “Options analysis appeared to offer the tool necessary to overcome the tool necessary to overcome the perceived deficiency in the Net Present Value approach.” (Ryan 2006, 340).
A recent study in the United States says that the value of real options is not widely accepted and that many of the industries are of the opinion that the method is not practical.
Real options hand over a worth to elasticity in production of the firm. For instance, an electricity-producing corporation can devote a sum of money to a power plant that is kept unused for some part of the period and bring into production in the other part of the period when the demand for electrical power increases and the cost of electric power has gone higher. Similarly an industry that does gold mining may possess a gold colliery which is kept unused at present but there is a possibility that the said mine may be brought to use if the value of gold goes higher than a certain level. To asses such manufacturing ability solely in expressions of the net current value of their anticipated production would be to lose the advantage of flexibility. The elasticity in manufacturing levels adds up to real options. Flexibility can be assessed and the assessment which has been made can be considered as the value of real option. Elasticity can bring up the profits of the company and eventually the anticipated income also. Hence the anticipation of payments and income has to consider real options.
“Real options valuation is a financial technique for evaluating investments under conditions of uncertainty, particularly uncertainty associated with market variables such as future product demand or the future value of an asset.” (Ruan et al 2008, 641).
The changes in the market conditions and the changes in other factors which will obviously affect the future profits therefore, there must be timely information with respect to these aspects. The need for such timely information for maximizing profits has made real options analysis more effective and valuable. In the present day, real options theory is broadly recognized as a novel mechanism for investment development and quality assessment which has also been accepted by researchers and academicians in this field. The real options approach signifies that various investments make significant opportunities that can or cannot be used by the industries in the future. “Real options are useful not only in valuing a firm through its strategic business options but also as a strategic business tool in capital investment decisions. For instance, should a firm invest millions in a new e-commerce initiative?” (Leggio et al 2006, 85).
The result of incorrect judgments can be dangerous or it may even bring an end to the life of an industry. By using the traditional methods, these questions cannot be answered appropriately since while making judgments, they take into account static factors and without giving required importance to the changing circumstances. In such circumstances, the decision once taken would suit only the present situations and would become ineffective in the long run. The real options aid in making logical decisions as to whether a business should devote a huge sum of money to a novel e-commerce scheme. It also helps make decisions as to the infrastructure and the other related projects. The conventional methods which were used for value assessment could not maintain elasticity in order to make upcoming decisions and there was a failure to take in the liberty to prospective incomes. The conventional methods also are unsuccessful in properly quantifying the assessment created by novel know-how. These methods also do not give the required signatures to the various data and information required in order to make the right decisions which give better output with respect to the probable incomes and prospects of the business. Due to the loopholes in the traditional methods of value assessment, the new theory of valuation of real options was welcomed by the academicians and also by various industries. The real option looms in assessing investment has drawn higher consideration from various businesses in the latest periods. It has also gained significance with respect to strategic management in the present day. This theory has gained significance since it highlights the joint requirement of uncertainty and ad ministerial prudence and it also expresses an active view of business assets and administrative decisions. The valuation of real options methodology was accepted because it was easily adaptable to different business conditions, to novel technological know-how and to different business situations.
This approach regarding premeditated administration and judgment is used as a method that aims at bringing down exposure to risks and improving opportunities. It rests between pure finance and various fields of judgment. It emphasizes a structure of mind and makes use of methods that are accepted by various managers and eventually gives a familiar language. The theory is applied in numerous fields which are central to modern industries. The new approach has become widely accepted because it has proved to be effective and successful and it has also been adhered to by distinct managers and entrepreneurs. Since there have been various changes in the trade and business, and novel technologies have been used in order to see to it that the challenges are overcome and the competition is met, it is not possible for the businesses and industries to follow traditional methods for value assessment. It has become the need of the hour to adopt the new methodologies that provide better results. Therefore the valuation of real options has been adopted by the businesses to get better results not only for the present period but also for the future benefits of the company. It has been accepted by the entrepreneurs in the present days to a greater extent because of the capacity of the method of valuation of real options to work by giving regard to the uncertainties which occur not only in the present but also in the long term.
The benefits of valuation of real options can be achieved only if the administrators and the managers of the industries become well aware of this way of thinking. The industries which are successful in the present years always give importance to valuation of real options and educate their managers and other members regarding this aspect through various ways.
Determination of real options valuation assumes more significance when its outcomes are uncertain. The method of valuation of real options is of more value when the uncertainty with respect to potential results is greater. In normal circumstances, there would be an expectation of a higher stage of instability to bring down the assessed value of the scheme to the business and hence the when there is a lack of development option an industry company may better select to choose a higher rate of reduction concerning its weighted standard expenditure of investment in order to pay recompense for the point of assessed loss.
The business environment and market conditions will never remain static. It keeps changing rapidly especially in the present day. Today drastic changes have been undergone even in the matters of investments. The new methods such as mutual funds, stocks and other options have been followed rather than direct investment method which was followed in the earlier days. Hence these changes should also be considered while doing the valuation and the traditional methods cannot be sought for assessing the values. Therefore the tactics and methods used in the earlier years cannot be used in the present business conditions, and even if they are used, they will not be in a position to provide successful results. The value assessment methods used today by various businesses need proper consideration of deviations in the government policies, rules, regulations and also the changes which are occurring in the use of technology. It also needs to offer market changes from the existing circumstances. There is also another requirement that is offering a factor that justifies the administrative capability to affect various circumstances and also the capacity to stop, sell or alter the strategic decision. Valuation of real options has been accepted by the managers as the only method which has been successful in incorporating the uncertainties prevailing in arriving at the proper final value.
The basis of the theory of valuation of real options can be traced back to 1980s and the promotion of a model that is the foundation for various present applying of the real options theory. In the recent years, this area has tremendously developed and has become rich due to high research works in this area. Making a judgment as to whether a valuation of real option has to be followed in a particular business depends on various factors and arriving at a proper decision is a bit difficult. But the entrepreneurs in the present businesses have always welcomed this new concept because of the numerous benefits that it provides.
Analysis of how an acquisition project valued through Real Options is beneficial than the DCF method used in determining whether the acquisition will be beneficial or not:
The value of an organization is determined by combining the assets and the options. The valuation of a business by the option of real options is more beneficial because the valuation of business through their NPV does not take into consideration the value which is created by managerial flexibility and secondly while determining the NPV a project’s future uncertainties are not analyzed. “Real options are opportunities embedded in projects or investments that are likely to exist and have a material economic impact on cash flow and risk.” (Real Options (Strategic Options) in Financial Modeling 2010).
The idea of valuing a business by the real option is more flexible than judging a business through its NPV. Decisions made on the basis of the theory and practice of real options are more flexible than the decisions made on projects on the basis of their NPV. The valuation of real options is beneficial in investment decisions. “‘In ten years, real options will replace NPV as the central paradigm for investment decisions’ Tom Copeland & Vladimir Antikarov, Real Options, A practitioner’s Guide, 2001.” (Brach 2003, 9).
Illustration for analysis
Firm A is a manufacturing firm for bags, shoes and all leather goods and Firm B is a firm which produces leather. In this case the firm A proposes an acquisition proposal of firm B to its shareholders. The shareholders being the owners of the company asked to evaluate how the acquisition would be beneficial. Therefore it was decided to value the investment of the acquisition. The Discounted cash flow (DCF) method was first used in the valuation since The DCF method has been used for many decades in analyzing whether an investment in the form of acquisitions or mergers is beneficial or not. DCF methods have been used priory for making the decisions of capital budgeting in an investment.
In the DCF method it is calculated as to how much of the investment is backed by the net cash flows over the number of years. The present value of an investment is determined by the following formula:
- PrV = PrC/ (1 + I) y
When the amount PrC is invested at I% then for y number of years then it yields the principal value of PrV
Where PrV = principal value, PrC = original investment amount I = the interest rate or the discount rate, y = the number of years.
The current value is determined by:
- CrV = 1/ (1+I) y.
Where CrV = Current value, I = the interest rate or the discount rate, y = the number Of years
The discount rate or the interest rate is based on the capital costs incurred by the firm A in the acquisition project. In the calculation of DCF the potential expenses and proceeds were first anticipated and then it is tabulated. The cash flows that will be generated were estimated. In the DCF technique the currency’s future worth is taken into consideration while making acquisitions. The cash flow is determined by taking into consideration the operating profit, the income tax rate the depreciation etc. the cash flows at the end of the three years of firm B was determined and it was ascertained that the NPV was beneficial or the NPV indicated that the acquisition would be beneficial or profitable. The NPV through the DCF method indicated that it was a very profitable business acquisition for firm A. while some of the shareholders agreed the others did not converse with the idea and wanted the business to be valued through the real options and pointed out that the NPV analysis through the DCF method had certain limitations. The major problem with the DCF method of ascertaining the value of an investment project is “DCF discounts the cash flows at a higher rate by adding a risk premium to the risk free rate” (Kodukula & Papudesu 2006, 48).
Which implies that when the risk is higher then the risk premium added is also higher? One of the prime limitations in using the DCF technique it was found was that the DCF method in the acquisition project was that the DFC approach shows only those assets of the firm B which are utilized or the assets which is generating revenue. If the firm has unused assets then those assets do not generate any cash flows and thus the value of these assets cannot be depicted through the DCF method. The DCF method also did not answer to the question as to whether it would be feasible for firm A to acquire Firm B’s management also by not changing the equity and the preference share capitals and the holding shares. This simplifies that the DCF analysis ignores the real situations involved in investing in a project. It purely judges investments on the basis of the NPV ignoring the real elements like the managerial viability of the project for the company, the project cost with respect to the changing time etc. Therefore the DCF approaches cannot be used in firms that are in the process of restructuring or the firms which are making new acquisitions because simply ascertaining the NPV through the DCF method will not prove whether Firm A can acquire Firm B. Thus a lot would depend upon conjecture and how Firm A and Firm B perceive their chances of survival in the competitive environment, especially when there were real risks of using DCF when these techniques are neither appropriate nor suitable under the circumstances.
Therefore it was decided to value the acquisition through the real options method because in the real options framework it can be determined whether to expand or reduce the acquisition business on the basis of the acquisition’s productivity for Firm A. The main idea of the real options framework is the proper treatment of the project appraisal process. Therefore the real option framework offers a number of real options like the investment timing option, the growth option, the abandonment option and the flexibility options. “Acquisitions often contain certain embedded options such as the ability to accelerate growth by adding to initial investment (i.e., expand), to delay the timing of the initial investment (i.e., delay), or to walk away from the project (i.e., abandon).” (DePamphilis 2007, 332).
Therefore firm A is more in an advantageous position using the real options framework in the acquisition deal. One of the important reasons for adopting the real option framework was because in the real option framework there are no long-term commitments therefore in case if the acquisition project is not satisfactory then it can be withdrawn even after the process of acquisition. Firm A can also analyze the individual stages in the real options to understand whether the acquisition process is beneficial or not. In the acquisition process the cut-off points can be determined and after analysis it was identified that Firm A can go for the acquisition process. Therefore Firm A decided to adopt the Options according to the capacity of this acquisition project.
The different types of real options available to Firm A in the acquisition process of Firm B by which it can determine whether the acquisition of Firm B will be beneficial or not beneficial, or whether it could result in value addition, are as follows:
Proper Investment timing options –The Investment timing options are such a type of real option in which the investment decision is delayed till the correct time. “Acquisition opportunities can be modeled as real options, whose value creation depends on uncertainty, exercise or investment timing, price and (idiosyncratic) target value” (Berg 2007, 114).
Using the investment timing option of the real option Firm A started investigating whether it can delay the acquisition option till all the minute questions involved in the acquisition process are answered. When the answers of the acquisition investment are satisfactory and all doubts about the acquisition are clear in the minds of firm a then it implies that the investment is made at the correct time and this is called investment timing options. It was analyzed that in this acquisition bid there were several competitive bidders who were also manufacturers of products using leather. Since there were several bidders the value of Firm B went up to 300 million pounds and so Firm A started analyzing whether it would be beneficial for it to pay the extra premium which the bidders will be accruing on firm B. It also needs to be identified as to whether the acquisition of Firm B at the premium price would be supported by Firm A’s financial resources and capabilities because investment options made at the correct timing increase the investment project’s profits. It was understood that the CEO turnovers in Firm B were high and there were several financial issues that were not in records of firm B which existed due to the high rise of CEO turnovers in the organization. The owners hid these reports especially of the financial issues like the case of bank overdrafts. It was also identified that due to the bank overdrafts its supplier base was creating enormous problems. Considering all these factors the NPV of the firm was estimated to be of negative 1 million pounds. So Firm A in this case decides to wait for the NPV to be at a positive figure and therefore delay the acquisition process. The Investment timing option leads to the minimization of risk in the real options. Sometimes in the investment timing option when the project gets too much delayed then it leads to the loss of the project to a competitor company. This investment timing option is very much suitable for Firm A because it is a proprietary firm where delay of decisions is of less threat. Because if the acquisition price paid is more than the value of the venture will be reduced for firm A. In the case of the Investment timing option the decisions can be put on hold and all angles of the decision process can be studied and then the project can be invested at the correct timing. Therefore Firm A decides to put on hold the acquisition deal considering the investment timing option.
Next Firm A also tries to analyze the acquisition deal through the growth real option.
Growth Option – the growth option is a category of real option in which a company’s growth option can be augmented by reviewing the marketplace situation. The growth option in the real option of a company can be categorized into three parts. The first one is the growth option where the company’s existing product line is further enhanced meaning the capacity of the existing product line of the company is increased. The second type of growth option is such a type of real option in which the products of the company are extended to penetrate into newer physical markets. The third type of growth option is to the addition of new products or innovating new products for the company which increases the market share of the company. Firm A analyses the growth options available in the acquisition deal. Because Firm B produces leather therefore and since firm A produces leather items therefore it would be of immense benefits when firm A takes up firm B because then Firm A will be a total hub of both leather manufacturers as well as leather items manufacturers. “Acquisitions involve a substantial interaction between growth options in the purchasing and acquired firms” (Schwartz & Trigeorgis 2004, 408).
Therefore according to the growth real option firm A can acquire firm B n addition create its own market share of both the producer of leather as well as leather items. Analyzing the growth option if the Firm A spends 200 million pounds to acquire Firm B it can always generate more revenue because Firm B has the technical know-how in the production of leather and therefore acquiring firm B will also lead to the acquiring of technical know-how of firm B which can generate huge revenues for firm A. the acquisition of firm B will effectively increase firm A’s growth option value by around 50% considering the huge amount of new physical markets that it can create and establish.
The next existing real option that firm A can consider is the abandonment option in other words discarding the acquisition transaction. This type of option is available to firm A even after it acquires Firm B because in case after acquisition firm A finds that firm B is not generating enough value as expected then Firm A can always exercise the abandonment real option so that firm A does not face future negative value.
Abandonment options – the abandonment option is a category of real options where the acquisition can be dumped if the value of the project declines. This type of abandonment option allows Firm A to abandon the acquisition deal of Firm B if the market conditions are not found to be satisfactory and if the project needs to be abandoned before the economic life cycle of the project is completed. It is not necessary that all the projects should be implemented till the full economic life cycle. “if the acquired firm does not operate up to expectations, an abandonment option can be executed where it can be sold for its intellectual property and other tangible assets.” (Mun 2006, 35).
When the cash flows generated from Firm B are not as positive as projected by Firm A in the acquisition process and the NPV of firm B becomes negative then it is time for Firm A to abandon Firm’s acquires share. Therefore using the real option firm A has the option to abandon Firm B even after the acquisition process is over in case Firm B is not proving to be beneficial for Firm A after the acquisition because Firm A can use its right to sell the acquisition to another buyer.
Advantages of real options valuation
The limitations of DFC analysis like that in the standard DFC projects the decisions of the projects cannot be delayed, If the NPV of an investment is negative then the investment cannot be adopted. In the standard DFC the projects have fewer growth options like new addition to product lines, capturing new market share etc. The DFC analysis requires that a project cannot be abandoned till the completion of its life cycle. The Abandonment option in the real option allows a project to be abandoned in case if the investment project is not beneficial before the project’s complete life cycle.
Limitations of real option
There are mainly three options the option to delay the decision, the growth option and the abandonment option. The growth option and the delay of investment decision are contradictory in the sense that firms have confusion as to whether they should opt for the growth option or wait for the NPV to be positive. In the meantime of making decisions another competitor might bid away the project.
Considering the limitations and advantages of real options over the standard DFC analysis Firm A prefers to use the real options theory in the acquisition of firm B.
This could be evidenced that real option is a right, not a commitment to take necessary action like deferring, abandoning, expanding, or contracting on an underlying non- financial asset at a recommended cost, or before a pre-determined date. The decision whether to exercise real options would lie with the Chief Finance Officer (CFO), or the Board of Directors, in co-ordination with the other members.
There are several myths that surround the valuation of real options and these could be seen as follows:
- It is widely believed that more complicated the process of valuing real options, the more accurate and scientific the valuation would present itself. Nothing could be more distant from the truth. Actually the fact is that the minimum quantum of inputs needs to be used to value assets. Often it becomes necessary to make “tradeoff” in that benefits of using more advanced mathematical and statistical calculation could make it noisier, and could also lead to higher degree of errors. (Damodaran 2002, 5).
Life cycles are also key factors while determining the valuation of options, since there is the huge element of having to estimate future values and estimations also, thus leading to greater reliance on conjecture and future possibilities. Again, there are also aspects of correct estimation based on correct interpretation of data, more so, due to impacts of variables and other impacting factors. There are several factors that impact the business of real options valuation and this could be that the values need to treat as correct, until and unless this has been proved wrong. Thus by optimistically analyzing the real options, it is possible to gain many benefits. Moreover, it is widely believed that the most accurate figures for the worth of a firm are market price of its stocks, since the market prices take care of both positive and negative aspects of business, and thus there is real detriment caused by its negative aspects and benefits accruing from positive. Some of the main aspects regarding valuation of real options could emanate from the fact that there is no such thing as a perfect valuation method and a lot would depend upon the facts and characteristics surrounding the cases and the actions or inactions of key players and estimators. Thus while DCF takes into account the discounted cash flows as adjusted for interest rates at current prices, the present value analysis needs to consider the present values of future cash inflows to determine the positive aspects of the project. But both the DCF and NPV do not consider the fact that a project may envisage large cash inflows after a certain period of gestation that would more than compensate for earlier losses. And negative cash flows.
In the foregoing chapters, the positive and negative aspects of Discounted Cash flow (DCF) as a means of evaluating potential projects have been established, including appropriate theories like Black and Scholes’ Model, etc. DCF and NPV do provide inputs for managerial decision making, but fall short of providing alternative solutions in the event, at later point of time, the said project needs to be postponed, delayed or shelved due to supervening circumstances. This could also happen if more inputs must be necessary for taking a final decision on the fate of the project under review. Thus, through the exercise of real options, it could be gainfully possible to evaluate investments, indulge in valuation of firms, identify lucrative investment opportunities, expansion of firm and also take scientifically based decisions on matters of company sale, corporate restructuring (external or internal) or mergers.
Liquidation option
“Shareholders always have an option to abandon their investment through liquidation. When a company reports a loss, shareholders may exercise the option to liquidate to avoid further losses and to recover the liquidation value of net assets” (Sin and Watts 328). The option of whether to exercise liquidation or not is dependent upon the thought process and conjecture of the equity holders. In most cases, shareholders wait for some time for the companies to recover and start posting profits before they dispose of their share holdings through exercise of options. This is especially so of companies who have successfully staged economic turnabouts creating expectations in the minds of optimistic equity holders that could be done again. Another aspect that needs to be considered in the case of exercising options of liquidation would be as follows. Based on the previous performance of corporate and the robustness of assets and reserves, there is a minimum share price below which the shares would not tumble, no matter what. What is important is whether the equity holders consider this minimum price as suitable for them too; in which case, they would adopt a wait and watch attitude and not hasten to exercise a liquidation option.
The market value of a firm could also be seen in the context of its constant earning stream. Shareholders could enforce liquidation to outside buyers at a price that is at par with liquidation or exit values of the assets. Below the liquidation value, it is uneconomic for shareholders to cling onto their share holdings for the simple reason that asset holdings do not justify it.
How can we improve the real options valuation?
There is real need to broaden the decision making capacities of real options valuation from the fundamentals of expansion and switching options to advanced options problems such as valuing timing options calculated with optimum use of models
Improvements in real options could introduce a whole new vista of real ,specific and highly scientific options that managers need to enforce in their decision-making processes. Particularly, real options valuation could recommend, with collaborating data whether they need to consider in right earnest the following possible outcomes for the proposed project under scrutiny:
- Option to Abandon
- Option to Expand
- Option to Contract
- Option to Choose
- Compound Options
- Barrier Options
Scholastic assessment provides a novel view of evaluating business decisions, projects, and strategies by taking into consideration a unified strategic portfolio analytical process.
The analysis need also delve into the liquidation option which could be exercised viz. withdrawn from the project any time it is felt that the project has ceased to offer viability or profitability to investors. It is believed that real options development in terms of profits and balance sheet analysis by research analysts, which underpins the theory and practice of real options. Conclusively, considering the intricate nature and complexities associated with real options, we decide to conduct our study based on real options available to firms namely the option to dissolve, or liquidate or abandon a firm’s present activities.
Thus the liquidation option may be exercised when the management has strong and valid reasons to back out from the project once they find that it is no longer economically attractive to continue pouring investments into it, or certain supervening reasons have compelled the company to withdraw participation and funding of such projects. Thus could be in terms of commencement of hostilities, outbreak of epidemics or war, or man-made or natural calamities which have made the subject matter of option untenable, or unsustainable. Perhaps the need for keeping an option open for liquidation happens in the case of a valuation of a distressed firm.
“The parameters of equity as a call option are as follows:
- Value of the underlying asset = S = Value of the firm = $ 50 million
- Exercise price = K = Face Value of outstanding debt = $ 80 million
- Life of the option = t = Life of zero-coupon debt = 10 years
- Variance in the value of the underlying asset = 2 = Variance in firm value = 0.16
- Riskless rate = r = Treasury bond rate corresponding to option life = 10% “ (Applications of Option Pricing Theory to Equity Valuation: A few caveats on applying option pricing models n.d.).
When considering valuing equity in a distressed firm, we need to follow the Black-Schools Model the calculations of which yield the following results as depicted below:
- d1 = 1.0515 N(d1) = 0.8534
- d2 = -0.2135 N(d2) = 0.4155
While calculating the value of the call it is observed that:
- Value of the call = 50 (0.834) – 80 exp (-0.10)(10) (0.4155) =$30.44m
Therefore, calculating the difference between the value of bond and the value of the call yields the following results:
- Value of the bond = $ 50- 30.44 = $19.56m
Therefore, it is evidenced that the bond has lost 39% of its value.
It needs to be seen that again, the flexibility option offers optimal security that could, in effect, not only reduce financial costs but also ameliorate the level of risks inherent in the project. In effect, the analysis needs to go deep into the study of liquidation, flexibility and other options that are some of the innate benefits of real options, especially when compared to other financial evaluation exercises as expounded in other chapters of this study. In the real option valuation an option which does not generate any profit in the future period is denoted by the formulae : v(t,T) = exp ( -r (T-t) ) E [max (o,W (T))]
The value v is the real option while t is current time and E denotes the risk-neutral expected value and r is the riskless discount rate The proposed value of the cut-off function could hardly be calculated analytically. On most occasions W, or another version of could be employed to assume to follow random procedure and suggested methods like Monte Carlo could be employed to approximate its full probability distribution time. The option value can be achieved after deducting from the average worth obtained from the duplicated pay-offs. As mentioned earlier, management must be able to identify and understand which are the real valuation that needs to be done and concentrate on them- therefore, valuations should be carried out that best suit the purpose and provide the necessary inputs that could allow the management to reach a correct decision regarding real options and how it could aid management in making the right kind of investment and appraisal choices. Moreover, it is also believed that the interest rate is also an important factor, and unless the interest factor is correctly assessed and implemented, the real option valuation may be inaccurate and may present problems later on. Another thing is that choosing too low a rate may produce a real options decision that may not be currently applicable and too high a rate may also not really serve the purpose- therefore it is important that the current and correct interest rate factor must be known before embarking upon real options valuation and its mathematical calculations etc.
Interpretations
The analysis part of this project first dealt with the deficient aspect of Net Present Value (NPV) in terms of its future cash flows as discounted by the discount rate or the rate that reflects the riskiness of expected cash flows. Normally it is seen that if the NPV is negative, it is not considered. The NPV is usually enforceable only if the NPV tests positive. However, NPV does not seem to consider a situation wherein the future cash flows after the estimates are good and could be taken into account. It is quite possible, according to the assessment that the future cash flows over a period of time, may increase such that the negative options could be wiped out completely.
However, there is also a third option that may seem discreet in many ways. This could be delaying the project until a clearer picture emerges. This could be used when the market growth is not known, or more market and financial data are in the process of being collected. The fact remains that project delays may be constructive when the cost of delay is valuable only if it more than tradeoff the harm that may occur due to decision delays. For instance, this analysis speaks about the fact that delays in decision making may make one lose one valued customer, and also the impact of items like licenses, patents, technology etc, which may cause detriment not attended on time. Not only are such delays intrinsic when market systems are uncertain and volatile, but also when delays could cause wide fluctuations in the interest and other impacting rates, thereby causing hardships to many.
The analysis of real options seeks to consider the following aspects:
- Using the DCF valuation and ignoring any real options by assuming that they cease to have any value or have zero value
- Using the principles of DCF valuation and also including a qualitative recognition of any real value of options
- Utilizing the benefits of Decision Tree Model.
- Using a standard model for a financial option
- Developing a bespoke project-oriented model using financial engineering processes.
There could be different options when it comes to investment options for new lines of products, according to the analysis of this study,
- There are are25% probabilities that demand for products may be very high
- There are 50% reasons to believe that demand may be moderate
- There are also another 25% fears that this may be moderate to low.
In the case of the first option, according to the analysis conducted the element of timing is ignored and the formula considers only the positive or negative aspect of business. Therefore, there is need to understand that traditional NPV needs to consider the total effect, and accept this if profitable. Market conditions and customer trends are important considerations, as is the need for maintaining proper records and movements of stock.
The next aspect that needs to be considered is with regard to DCF analysis. The basic factor to consider in this case is whether a call option with an exercise cost of $50 needs to have current underlying assets of more than this amount. Again, we also know that the value of an option increases with the risk of the underlying assets. There are many critics of this postulate who argue that there is no hard and fast rule that with increase in underlying assets, option also needs to increase.
Coming to decision tree analysis, average –demand branch in middle has a positive and high NPV, while it is quite possible that the NPV of low demand may be a negative figure, and this adds to risks to be taken by the owner.
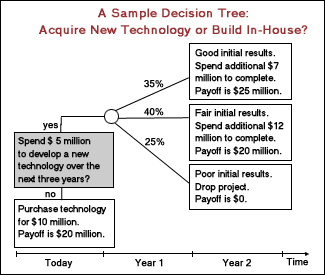
Thus, clearly, the decision tree analysis as advocated (D’Souza 2002).To get the correct assessment, it is necessary for the three outcomes the in-house be assessed. You need to reduce the costs of payoff and increase the outcome by the chances of success. After undertaking all the computation, the expected value is seen to be $6.3 million. The weighted average of outcomes is used to mix together the worth of the three outcomes into a lone number. The discount rate could be set at 10 percent cost of capital.
This assessment shows the valuation of the in-house alternative to be $7.14m, or, in other words, less than 75% of the values of obtaining outhouse technology.
Thus it is reckoned that even in the case of decision tree analysis, there are areas by which it is possible to size up the entire prospects of business and reach a correct decision. Some factors could endorse the viability and economic suitability of units and how these could be utilized for better and more value-based and critical thinking. There are ways and means by which the positive aspects of business analysis and decision making could be strengthened and reinforced, keeping in view its effect on business prospects.
Coming to the standard model for the financial option, it is believed that one middle option for real options and a judicious one at that is to delay the decision making until all data and information are available. Moreover, there are also real concerns about how these could be better implemented, considering that many variables and impediments may be present in one form or the other, either incorrect data, wrong processing or sometimes of that kind. When these kinds of impacts are present, it becomes necessary to conduct a sensitivity analysis which could determine, inter alia, that the NPV of delaying is higher than that of immediately taking decisions, since taking hasty and impetuous judgment may cause regret later on.
The next available option is that of valuing timing option using the Black-Scholes Model which is premised on the following assumptions:
- Lending and borrowing is carried out at regular risk-free interest rate
- There is a certain amount of volatility inherent in the equity
- It is characterized by no element of transaction costs
- There is no question of dividend payouts
- There are no fractional holdings of shares
- There are no short selling or arbitrage
Thus, the aspect of real options with regard to the application of Black-Scholes would need to consider the price of a European call option. This Model tends to determine the price of a European call option. This Model forecasts that invariably, prices of heavily trade assets adhere to geometric Brownian motion with constant price changes of stocks, time value of money, the exercise price of the option and expiry time.
This is perhaps considered the best model of determining the fair prices of options. Further, the analysis part of this study would mainly be concentrating on options in the valuation of the firm, especially with regard to the use of liquidation option which equity investors possess, based on the value which real options create, especially in the context of risky firms. Besides, the option of liquidation, this analysis would also deal with real option of flexibility. How the option could be used for designing security mechanism which would, in effect, reduce financial costs and alleviate default risks.
This assessment drives home the fact that valuation of real options as a critical financial procedure is undertaken to estimate the values of future demand trends and expected value of assets.
The market factors like the anticipated demand and anticipated market value of the project need to be considered in the financial valuation of real options. This is of wide application for investment decisions in industry, and also scholarly taught as part of syllabi in classrooms of business investments. Perhaps real options fill the gap managed in NPV.
During times of vague and undefined economic conditions, it is best to adopt a wait-and-watch approach until the uncertainty gets resolved.
When there is improbability in the future circumstances flexibility of a project is dependent on the ambiguity of the project and the project is flexible only after the ambiguities are removed. The management has the option either to wait, increase or decline the project depending upon the real option to be exercised. Thus, the analysis has indeed undertaken in-depth studies on real options and how it impacts business. There are also issues relating to how real options could be exercised during the times of falling prices when it would well not be possible to accurately judge conduct, especially under stress.
Further, it would be known which kind of real options need to be used and why. The correct assessment of real options needs to be correctly identified and endorsed in order to call for business. The main aspects of real options would be the judgment and assessment of risks, and the final analysis. This analysis also seeks to consider the impact of real options in decision-making and also for pursuing the right valuation of real options. Recommendations: As a result of this survey, It has become necessary to identify areas of deficiencies and drawbacks and take necessary steps for its eradication, or containment. The structure that could cross gap between practice of real-world capital projects and higher mathematics associated with formal option pricing theory.
It is evident that there needs to be considerable amount of future research on this subject in order to gain a complete knowledge of real options since its complete data cannot be seen and since this would probably need more extensive research to be undertaken at home. Besides, there is also nexus of the formation of right kind of data that is amenable and agreeable for future research. The main aspect that needs to be kept in mind is interim and final results and quantitative views on the balanced sheet. This could be utilized by the Company for making investment plans as deemed necessary that could not only make future call options a safe option but also better ones. The need for making scientific and calculated measures for call options, especially regarding the valuation of real options is of extreme importance and needs to be actively controlled and monitored. The recommendations also need to consider the value of underlying assets which may not be traded and thus makes it difficult to estimate value and deviations for underlying assets Next it is possible that the price of the asset may not follow a predetermined course as a result of which it would be difficult to set up option pricing models and use that assumptions deviation or variation may not be obvious and may undergo major vicissitudes thus adding to the complexity of option valuation. It may be necessary to make complex calculations to determine the real option valuation which may not be comprehensible for a layman. Again, it is also possible that although the valuation may be suitable, its application and deployment may be fatuous and misappropriate. Thus, it becomes necessary to consider how best these issues could be addressed, especially in wake of major economic upheavals and recessionary trends wherein the valuation would need to be different from what it is under normal circumstances.
There are also other considerations like exclusive advantage for taking the second investment based on the first. If this is answered in the positive, the firm is entitled to take into account the full value of real option; otherwise it needs to consider only a part of the value of real option with the degree of aloofness provided by the first investments. If the second investment provides the necessary returns and incomes that could boost its incomes it may be taken. Moreover, there are aspects that this pattern could also sustain the future option valuation. Moreover, there is also real trepidation that in the event real options do not work positively, there could be adverse effects on real options.
The next aspect in this recommendation section is that in the event these do not work there needs to be alternative means for valuation of real options.
Conclusions
This dissertation on real options does present interesting challenges since it becomes necessary to determine value of investment under unfavorable conditions and where there are no major determinants for true appraisals. There are several aspects to be considered. In the first place, managers would like to make decisions based on the real option an investment creates.
Next, while assessing an investment, it is necessary to consider all suitable data on value, risks and hazards. Next, it is also necessary to acquire options through financial transactions to mitigate risks/
It is therefore necessary that in context of real options, there is need for clarity and strategic direction and goal-setting real options can be a powerful tool for quantifying the value of strategic and operational flexibility associated with uncertain IT investments. Nevertheless, it also makes up a novel method of thinking about how projects could be organized and planned to maximize upstream powers while reducing downstream risks.
In order to know the real difference between real options and NPV analysis it is necessary to make a comparative study. On the one hand, NPV has all or blank approach, real options are exercised along the path of the progress of the business. Another very interesting aspect stems from the fact that real options work better insomuch power industry, process and product industry, etc whereas in the service sector its efficacy may be reduced due to transduced factors. Thus, it would be in the fitness of thing to conclude that to a very larger extent it is necessary to first understand and appreciate what kinds of benefits need to be gained through real options deployed and how to mobilize the infrastructure to gain these benefits. For one thing, it is necessary that a professional and not punitive approach be taken, which is in the best interests of all since a negative approach may cause do more detriment than good. Besides, since a large number of direct and indirect variables are involved, the impact of each such variable on the determination of real options should be identified and the best method or technique should be used. To gain the best and optimum usage value from Real options, it is also necessary that the same procedures be used over and over again, so that comparisons could be made and also improved versions of real options, more in tune with current needs could be evaluated and used. Another factor that comes into play is that of industry comparison in the real option valuation which is also important. There is a need for industry comparison to know where one company stands vis-à-vis others and how the deployment of real options could be conducted in a manner that could bring more benefits than challenges. For one thing, more than real options per se, their actual handling is more important and which contributes to the overall growth and well-being of the corporate that uses these tools in the first place. For another, the technique of using real options plays a significant part in the overall success of the firm or enterprise.
Bibliography
Alleman, James. The new investment theory of real options and its implication for telecommunications economics. Springer, 2002. Web.
Amram, Martha & Nalin Kulatilaka. Real Options: Disciplined Decisions: Aligning strategy with the financial markets. D Harvard Business School, n.d. Web.
Applications of Option Pricing Theory to Equity Valuation: A few caveats on applying option pricing models, n.d. Web.
Babajide, Abisoye. Real Options Analysis as a Decision Tool in Oil Field Developments. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2007. Web.
Berg, W A van den. Private equity acquisitions. Rozenberg Publishers, 2007. Web.
Damodaran, Aswath. Investment valuation: tools and techniques for determining the value of any asset. John Wiley and Sons, 2002. Web.
DePamphilis, Mergers, acquisitions, and other restructuring activities. Donald. Academic Press, 2007. Web.
D’Souza Fabian. Putting Real Options to Work to Improve Project Planning – Project Analysis? Climb the Decision Tree: Deciding on in house. Working Knowledge, 2002. Web.
Dr. Mun, Johnathan. Real Options Analysis versus Traditional DCF Valuation in Layman’s Terms: Critical steps in Performing Real options. Real options valuation, 2006. Web.
Johnson MP, Alan. Real Option Analysis: ROA Compared with other methods. Dear Secretary of state, 2005. Web.
Kodukula, Prasad & Chandra Papudesu. Project valuation using real options: a practitioner’s guide. J. Ross Publishing, 2006. Web.
Kopel, Michael & Wolfgang, Kursten. Real Options. Gabler Verlag, 2004. Web.
Leggio, Karyl et al. Managing enterprise risk: What the electric industry experience implies for contemporary business. Elsevier, 2006. Web.
Mun, Johnathan. Real options analysis: tools and techniques for valuing strategic investments and decisions. John Wiley and Sons, 2006. Web.
Real Options (Strategic Options) in Financial Modeling. Financial Modeling Guide, 2010. Web.
Real Option Valuation. Shareware Connection, 2009. Web.
Ryan, Bob. Corporate Finance and Valuation. Cengage Learning EMEA, 2006. Web.
Ruan, Da et al. Computational Intelligence in Decision and Control: Proceedings of the 8th International FLINS Conference, Madrid, Spain, 2008. World Scientific, Web.
Schulmerich, Marcus. Real options valuation: The importance of interest rate modelling in theory and practice. Birkhauser, 2005. Web.
Schwartz,Eduardo & Lenos Trigeorgis. Real options and investment under uncertainty: classical readings and recent contributions. MIT Press, 2004. Web.
Shimko, David. Real Options: Opportunity from Risk. Q Finance, n.d. Web.
Sin, Samantha and Watts, Edward. The Information Content of Losses: Shareholder Liquidation Option and Earnings Reversals. Australian Journal of Management (2003): 25.3. Web.