Introduction
The service industry is highly competitive, it as player domestic, local and international; there are different sectors in the service industry but always one main characteristic that cuts across the industry, the secret to succeed (Skålén, 2009). The secret to succeed in the service industry rests on the differentiation of one’s services, differentiation comes with ensuring that the services are unique, of high quality and are continually improved to ensure that the company holds a competitive advantage over others in the same industry. When a company has some differentiated services, then it stands to enjoy differential advantage that will distinguish their offer from competitors. However, it is easier said than done, unlike in the product sector where the product of a company can be seen, felt and touched to see whether it is any different from that of the other company. In the service industry, it is more of the feeling, the experience and the interaction that a customer has with the company. The challenge is magnified further in the fact that there are individuals who will have to participate in the entire process: they may be required to offer the differentiated services but their personality may offer a limitation to the attainment of the differentiated service (Riedl, Bohmann, Rosemann & Krcmar, 2009). This paper discuses how a company in the service industry can differentiate its services from those of its competitors; it will look into the general approach applicable in all companies in the sector.
Methodology/method of approach
The paper will be divided into three main parts; the first part will aim at discussing and defining the meanings of service, differentiation and offer some living example of companies in the service industry, which have differentiated their services effectively.
The second part of the paper takes an in-depth literature review and the views of scholars in the industry have to say about differentiation in the service industry.
The third part of the paper will be recommendation on the best approach, from the literature review conducted, that a company can implement to differentiate its services.
What is service?
According to Karl, 2000, service is defined as “intangible equivalent of an economic good,” the definition above gives the shape of a service in that it has an economic value despite the fact that the service receiver has nothing tangible to show. The main difference between a service and a product sales is that in the case of a service, the buyer does not attain any exclusive right of ownership of the service paid for; however in the case of products sales, the ownership of the product in question shifts from the seller to the buyer. The service industry has its task in trading on services they offer; some service sectors that can be said to be purely service while a number of others have service inclined in their main line of business. Pure service businesses include, law firms, accountants and auditors services, architectural services and cyber café business. Other businesses considered to be in the service industry include the airlines industry, the hospitality industry and medical services provision industry; in both pure and impure service sectors, the list is endless (Kumar, Kee and Manshor, 2009). There are some characteristics in services, they are:
Intangible
Services have no tangible mass, they are provided and the buyer pay for what he does not hold. The service is commissioned to the service provider and cannot be re-sold, gripped, handled, looked at, stored, stocked, substantiated, smelled, transported, tasted or heard. After it has been offered, the provider remains with the exclusive benefits of the talent and have it all along; the highest likelihood is to become sharper and offer better services in the future.
Perish-ability
The Perish-ability of service can be seen in three angles: when the service has not been used, when the service is being offered to someone else and when the contact of offering service has ended. For example, when a hairdresser has no customer, then he has his expertise and has the service to offer, then according to him his services are perishable- they have no value. If the same hairdresser has a client, when attending to the client, he is held and can only attend to that one only to any other customer coming when this one is being made the service has become perishable. Finally, when the hairdresser is going home, after alighting from his public means of transport, where he has paid for the service, then the service has ended and no longer useful, it becomes perishable. To define whether a service is perishable or not depends on the angle that it is looked through; however, if service is not adding value to the giver or the receiver, then it is regarded as stale (Solnet, Kandampully, 2008).
Inseparability
The service provider cannot be separated from the service despite having offered the service for a number of times, actually the more services he provides, the better skills he attains and get improves his skills the in-separately characteristic denies the service receiver any tangible material after paying for the service. For example after tourists gets is toured by a guide, the tourist has nothing to should about it , the guide does not lose anything because of offerings the service.
Simultaneity
Services are delivered and consumed at the same time, they do not have the transportability and the storage characteristics, for example when a customer is getting services from a hotel, he cannot wait and use the services offered today tomorrow. Incase he want to consume the services tomorrow, the he will have to wait for tomorrow and get the services then.
Variability
Although service may be said to be the same, when repeated, it gives a different feeling and it is different in time, location, circumstances, and conditions; in the case of a product, it can resemble another 100%, however services cannot. for example when an airline has offered transport services, they may be good and of high standards, however if the same people where to repeat the same, then there would be differences in the way its approached and felt (Kumar, Kee and Manshor, 2009)
Service differentiation
Different companies in either service or products industry has the standards and the kind of commodities or services that they aim at offering. In the service industry, the services offered has some similarity, thus a customer getting into a company has some basic expectation. For example when someone is approaching a hotel facility, he has the expectation of getting a waiter and the waiter will serve him. The difference that a customer feels or gets after consuming the services of a certain company, which is different from the services of another company, is what is referred to as service difference. Service differentiation is the efforts undertaken by a company to make its services unique, different and have a better touch on the consumer for a long-lived remembrance (Treacy & Wiersema, 1995).
Let us discuss an example of a customer who buys a sandwich at McDonald and another time buys one from Subways: the kind of approach that he is going to get in either of the two joints is different; they have their way of approaching the customer. The customer is left at free will to decide the services he feels better and the one that makes the two companies unique. Differentiation in the service industry is rather difficult since there are no products that the customer can designate and state that this came from this company while this came from another. It also involves the services and efforts of the service provider. If a company sets a limit and structure of how service should be offered in its company; it has to rely on the real people who are offering the service to improve it; this is different with if it was a product where the company would just need to align production and the final differentiated product is derived.
Characteristics of differentiation in the service industry
Ordering ease
This defines how easy a company’s products can be accessed: some companies have made it easy to order and get delivery of products at the doorsteps: for example with the proximity of 2 kilometers radius, a customer can call the nearest McDonald and get a sandwich delivered.
Delivery
The speed, the tone, the way and the customer service that the customer has when delivering the service pays a major role in determining the differentiation. For example when customer has ordered for food, a restaurant with good service will advice the customer precisely the period of time that he will have to wait for the service to be delivered (Stanton, Etzerm & Walker, 2007).
Installation
This is the quality and the approach that the services has been offered, for example when an engineer is offering services, he should offer services of high quality and offer the expertise he has to create a peasant feeling on the consumer.
Customer training
This involves the rate of customer involvement in the service provision; for example after making an order, it is unique to have some restaurants seeking advice from the customer on how they want the food made.
Customer consulting
When offering service, despite that the service provider having the upper hand in knowledge and experience, the consumer may need to be consulted and his input considered when offering the service.
Maintenance and repair
Services needs to be maintained, repaired and improved to make them better and attract more customers as well retain the existing ones (Sichtmann, Selasinsky & Diamantopoulos, 2011).
Examples of differentiation within a services context
As have been stated earlier, the in differentiation, the uniqueness of a service play the major role; what a certain company is offering which is better , unique and different than other players in the same industry. For example, Baxter Healthcare has integrated their services with the internet that a consumer does not need to attend physically a super market and order for the company’s products but can do this at the comfort of his home and he will get delivery of the commodities. To do this the company uses systems like peapod and net grocer.
General Electric, is a company that installs Xrays machines in hospitals, however after installing the machines, it stays on the ground for a whole week to oversee the proper functioning of the machine and ensure that staffs have been trained on how to use the machine despite them being experts in the sector. The company is also a phone call away when the machineries installed has a problem. Such service are not available in other installers, it leads to a different unique service and offer the company an upper hand in the sector.
JetlBlue airways company has implemented measures that ensure more satisfied customers; the service offered by the company are different than other low cost planes for example the company installed video players in their planes and XM radio was installed by Live TV; this improved customer service.
Customers are offered online help in case there is an issue, booking and checking in can also be done online. Customers are also entertained when aboard a plane. This is aimed at developing a strong brand name and customer loyalty. Another move that the company has made is to have an online help support desk where a customer can chat with the provider via the internet and get solution for the burning problems that he might be having (Babakus, Yavas, Karatepe, Avci, Babakus, 2003).
Literature review
In the service industry the ability and willingness to provide quality services is seen as an essential strategy for success and survival; a service can be defined as an encounter between business and a customer that has supporting facility and using facilitated goods. According to Neal and Quester, the initial point in the provision of quality, maintenance and improvement of quality service starts with a company having a service charter, this offers the base line through which a customer and the service provider has to abide. The charter defines how the service should be at the minimal state; with the charter, anything that improves the service is seen as the differentiating factor. For example in the banking industry, a bank may have the target of processing a loan facility within one week; this may be what the central controlling authority. if a certain bank is able to process the loan facility in a day and still offer quality loans, then the bank is said to have high deferential policy; this quality has two visible strong points; it has offered quality, and at the same time with minimal time (Neal and Quester, 2006).
Metters, Kathryn, Madeleine and Steve, 2006, are of the opinion that businesses have customers as the most important stakeholder; they aim at creating good cooperation through the service they offer. Customers on the other side are motivated by factors within their psychological core, the consumer environment, and by marketer-controlled activity. Success in a business is attained when management can understand effectively the expectation of their customers and align their services and duties to satisfy those needs. As the saying goes, “a happy customer tells another while unsatisfied customer tells two others” (Metters, Kathryn, Madeleine and Steve, 2006).
In the diagram below, the major components of a service differentiation has been discussed; differentiation is not a single process, however it is the result of a variety of services and action within the industry; it is never at the maximum so there is always a room of improvement and efforts of making it better.
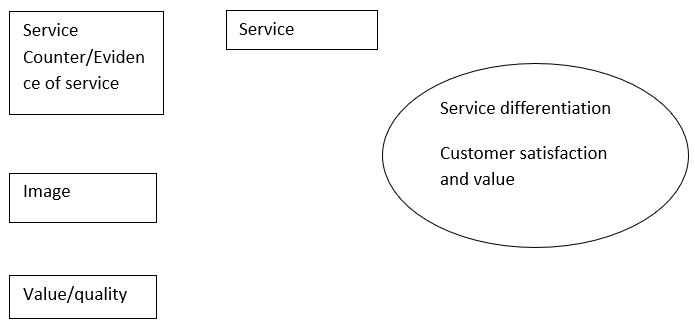
From the above diagram, it can be seen that service quality is an element of a number of elements that need to be implemented in an organization. According to Cook, 2008, organizations that offer service responsive to customers’ need perform better than those who do not care or are rigid to change. In the service industry, there is high contact of service providers and the customers, the high interaction need to be strategically managed if it will be differentiated with that offered by competitors. The experience that a customer gets now of service encounter has a wide influence on the attitude, perception and the feeling that he delivers from the institution. (Cook, 2008)
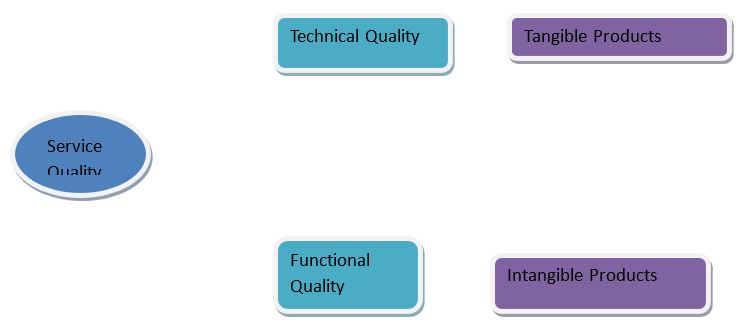
When a customer gets a certain service, he pays for the utility derived from the service, the much he or she is willing to commit is a show of the level of satisfaction that the customer has attained form the service. Kotler, Bowen and Makens, 2003 find no single definition of service quality since it is more of the receivers’ perception that determines whether he will be willing to trade with the company in the future. When concerned on the quality of a service, there are two most important deviations: technical quality and functional quality. Technical quality deals with what is delivered while functional quality is all about how it has been delivered. Technical quality is tangible while functional technical is not (Kotler, Bowen and Makens, 2003).
The chart below summarizes the service quality phenomenon:
Moment of service is the moment that a customer and the service he is receiving interact; it ranges from the general perception that a customer gets with the mention of a certain products or a certain business. The moment of service gives the immediate reaction and creates a feeling to the customer; it is the interaction that makes a customer know whether the services offered are quality, and if they can be differentiated with services offered by other companies. At this point, the company has the chance to offer its differentiated service for its competitive advantage. Kandampully in 2002 says that a company can only differentiate its services when it offers quality services to the customer than he can get form competitors: when a customer is within the premises of the business, the service offered, both tangible and technical should be of a high class that improves the general feeling derived by the customer. This is the way that the organization can strengthen its brand name (Kandampully, 2002).
According to consumer preference, theory for a customer to buy a certain product, the product or consumer a service it must be outstanding among the options that the market offers. To be outstanding, there must be continuous products innovation and an innovation that ensures that products can be differentiated (Hartline, Wooldridge, and Jones, 2003). When consumers are aware that a certain company has an improved service every time they visit the joint, then the company gets some differentiation on its products. The way customers feels about a certain company has an impact on how he will be willing to communicate and do business with the organization, thus there is all reasons that a company should invest and have an improved service all the time a customer visits its company. When a customer is able to differentiate a certain company’s products then the company is able to self-market itself and lead to increased customer satisfaction. Creativity and product innovation comes handy in creating product differentiation. A continuous program of training of staffs should be implemented as it will assist the company offer the much need service quality (Grönroos, 2000).
To remain competitive and maintain efficiency in today’s service industry, comapnies must focus on the kind of employees that they deploy. They should vet new entrants; good human resource manager should ensure that he should understand their human capital capabilities and the best method to utilize them for the benefit of the company. To have an effective sales team, they must be enthusiastic and hold a positive attitude at all time. This will only be attained if the managers develop measure to assist his team to be enthusiastic and positive minded. In the words of Ralph Waldo Emerson “nothing great was ever accomplished without enthusiasm”. As much as possible staffs that can influence or persuade effectively should be deployed (Craven & Lamb, 1993).
Since to make a good sales person it involves in-born traits and nurturing, training and development should be done continuously. To persuade easily, previous success stories should be explained to the potential customer; any extra services offered by the hotel should be used as a tool of persuasion. An example of extra service may be a professional talk at a staff meeting offered free by the hotel for a certain period. Secondly sales associates should be taught on how to keep in touch past success. They should understand what is happening in the trade of their past customers and visit them regularly (Kotler, 2000). At the visit they pose as business partners as they discuss what the customers trade is doing and establishing any assistance that their hotel can accord to the customer; this calls for a lot of research on the part of sales people. There are established customers, loyal customers, an assumption should not be made that they will remain loyal, but they should be visited. In the visit, general things are discussed in line with the business. Although the reason for the visit is actually to keep truck and sell, it should not be seen on the face. If there is anything that the hotel can do to improve the current condition of the loyal customer, an offer to do so should be given (Normann,1991)
Customers are the main force behind the success of a company; there is need for a company to understand its target market and the kind of motivation that can be used on the customers for better results. In the service industry, the case is not different where customers increasingly are demanding for more satisfaction. This is attained if companies are willing to produce consumer-focused goods (Blomme, Rheede and Tromp, 2009).. To ensure that a company in the service industry maintains its stand then it has to utilize its available opportunities well. Opportunities for the company are dependent on both the internal and external assessment criteria of the company’s profile of operation. The company can still optimize on the various opportunities available to bring about sustainable growth through effective competition. The environment they are living in as well as the internal processes of a company shapes customer’s perception; in the case of service industry, companies should ensure that they improves its internal process in terms of product differentiation and offering fresh approach to the system and the way they do things. Consumers are affected by the general perception that people who have had an experience with a company have. This calls for efficient and satisfactory services from service industry always (Normann,1991)
Recommendation and the way forward to the problem faced by service industry when differentiating its services
According to Blomme, Rheede and Tromp, 2009, when developing a certain service differentiation strategy, companies in the service industry need to undertake an elaborate internal and external audit analysis, the analysis will offer the company with the right approach to improve its services (Blomme, Rheede and Tromp, 2009). Three questions needs to be answered genuinely:
- Where the current position as far as service provision is concerned; if there is data on the level of service that other company in industry has offered?
- What level of service quality does the company aim at offering?
- What are the expectations of the customers and what level are our competitors offering
When the above three areas have been addressed effectively, then a company can develop objective and goals with the aim of improving and differentiating its services despite the specific companies in the industry (Blomme, Rheede and Tromp, 2009).
Some difference appears between differentiation of products and services; when differentiating products, managers and the producing team can come with other formulae’s of production, then implement them, the results then becomes the differentiated products. When it comes to the case of service, human resources in the organization are the major players, they need to be trained and coached on the new methods that need to be adopted (PIZAM and SHANI, 2009). When coaching employees to improve their services, the management must not only address the technical skills but should also focus on attitude, perception and personal traits; they will go a long way in ensuring that the services are optimal and efficient (Bebko, 2001).
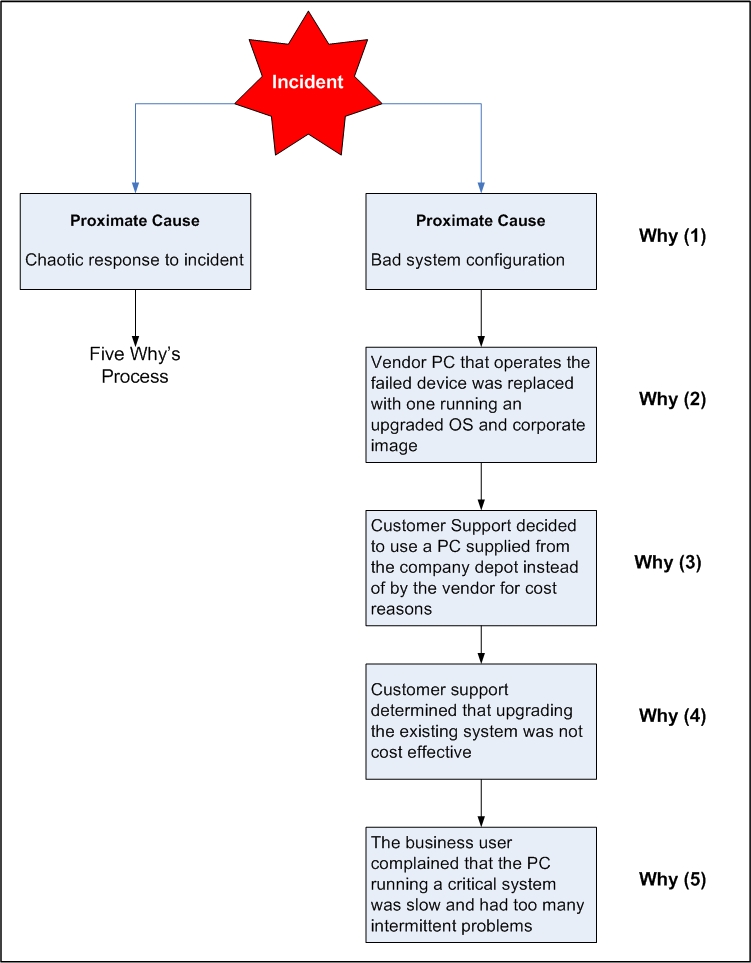
Operations managers have the role of overseeing service delivery system are effective, they are the ones who make policies that target the improvement of the system. They should observe the way service is offered and get responses from consumers on how they feel about the offered services. In most case, customers have very informative information on the quality they receive and others may give good advice on areas of improvement. In an outlet of the operating management can be seen on three levels, outlet manager, daily managers, and supervisors; they should be working as a team to maintain and uphold high service delivery. When they are enforcing the laid down rules, they should be open for additions and improvement areas of deficiencies, they should from time to time undertake internal and external audit to gauge the success of the outlet (see the appendix on 5whys of service improvement)
To implement and maintain high services operation manager should adopt quality management systems like the use of TQM (total quality management system), adoption of Six sigma polices and the use of lean thinking; the spirit of Kaizen (continuous improvements) should be embarked on. With such polices that aim at improving the internal operations for efficiency developed, then the company will maintain and attain high service delivery (McCluskey, 2004).
The effects of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in preventing disasters in the future
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) department in a company is responsible for establishing and managing activities aimed at social and environmental welfare. Oil/ Energy industry, one of most lucrative industry whose processes and products are not environmentally friendly, requires strict governance, and sustainability models cannot be overlooked; it was last hit by BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. The case of BP was an eye opener on the need for businesses to be accountable for their actions and always aim at offering the best to the world; the spill affected human and animals and its effects is of great concern to environments and other players. BP management is having issues trying to convince the world on the cause of the problem since it is ethically believed that they needed to take full responsibility. CSR section of management aims at ensuring that there is Good Corporation between the universe and the company. When the policies are embarked on, then companies will be accountable for their actions thus reducing future chances of disaster.
When companies have embarked on CSRs, they have no option than considering ethics and good governance in their business, when these two have been attained, then future disasters are likely to be prevented. In line with CSRs operations, companies make efforts geared toward social enabling efforts like developing infrastructures, providing primary health care, developing education systems among others in developing countries. In wakes of disasters, the company will be ready to assist. Internally, it will also aim at making operations safer and enhancing disaster recovery. These efforts will not only benefit community and environment but also enhance the organization image, thus increasing business. Corporate social responsibility manager establish frame works to enhance compliance with internationally recognised CSR standards like Triple Bottom Line (TBL), People, Planet & Profit (3Ps strategy); if companies can be genuine and embark on CSR supported by ethical business and good governance, then the world can stand free of disasters, resulting from companies operations.
Reflective Report
This section of the report discusses how the investigative report above on service differentiation was conducted; it aims at adding more input to the quality and the best approach as adopted in the study. The information was derived from secondary sources of material; the materials were gotten from the library, the internet and shaped by knowledge and observable facts on the service industry.
A number of materials exist in the library, the materials were used to get information and data; was on those materials written by professionals in trade and businesses more so those in the service industry. All material to be used will be vetted for relevance and the qualification of the writer (Thomas, 2004). The focus will remain in service but to get a deeper understanding, review of journal s and academic articles written for other sectors was done. Different materials were seen to contain some information that were conflicting and they seemed to have different suggestions; the researcher always harmonized the materials to ensure that the information used was the right one and one that could be generalized. After developing the materials to use, the writer focused on the topic where he compared different ideas, research and viewpoints as brought about by the texts, he ensured that he used current materials since the trend in the issue is changing and needed updated information. He then came up with the draft that had major points and learnt objectives; from the draft, he developed the final draft (Fisher and Buglear, 2004).
When the materials to be used were gotten, the next crucial moment was to compile the report; before writing the report, the writer ensured that the right tone, mood and language have been set to produce an augmentative/investigative/descriptive paper. The paper was n investigative paper and called for massive literature review on the topic ; the writer needed to collect data from secondary sources and form base of my augment. The topic of discussion, how to attain differentiation in the service industry, had numerous materials in the library and the internet addressing this issues, however the sources has different reputation and the ones to be used needed to be well scrutinized (Collins and Hussey, 2003).
In the internet, there are a number of personal comments and documentaries on the issues; however, these sources were disregarded since their quality could not be guaranteed. The main sources that were used came from institutional information, government press news, government institutions, scholar books and journals and peer reviewed journals. After using the materials, they were cited using Harvard system effectively (the entire paper was formatted as according to requirements of Harvard style).
The main problem that was uncounted when writing this paper is determining the material that had the most current and quality information; the figures given from different sources were different and the researcher had to make a personal decision on the figures and specific materials to use (Lancaster, 2005).
From the research conducted, there is an area that has come-up that need further research, the area is on the role that sales repetitive plays in modern competitive service industry; technology and people expectations have been shaped by globalization, enlighten, development of technology. The changes have influenced the level of effectiveness that a company in the service sector stands to get. Much research needs to be conducted to evaluate how the service industry can benefit from change of approach by sales people.
Conclusion
Service industry is highly competitive; companies in the industry need to develop strategies that assist them differentiate their service from those offered by competitors. To expand an organization’s customer base and probably get customer loyalty, the leaders within the organization should look into service delivery mechanisms; they should focus on maintaining, repairing, and improving the services. High quality service should look into the products quality, speed of service and the general outlook of the company. There is no one point that a company should relax and believe it has attained the best as far as differentiation is concerned, there is always something more that can be done to improve customers experience with the company.
References
Babakus, E, Yavas, U, Karatepe, OM, Avci, T, Babakus, E.,2003.The effect of management commitment to service quality on employees’ affective and performance outcomes. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 31(3),PP. 272-286
Bebko, C. ,2001. Service encounter problems: Which service providers are more likely to be blamed?Journal of Services Marketing, (15)1, 6,pp. 480-495.
Blomme, R., Rheede, A. and Tromp, D.,2009. The hospitality industry: an attractive employer? An exploration of students’ and industry workers’ perceptions of hospitality as a career field. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Education, (21) 2, pp. 6-14
Collins, J. and Hussey, R.,2003. Business Research: A Practical Guide for Undergraduate and Postgraduate Students. Hampshire:Palgrave Macmillan
Cook, S.,2008.Customer Care Excellence: How to Create an Effective Customer Focus. New York: Kogan Page Publishers.
Craven, D., & Lamb, C. 1993. Strategic Marketing Management Cases. Boston: Irwin.
Fisher, C. and Buglear, J. ,2004. Researching and Writing a Dissertation for Business Students. Harlow: Prentice Hall/Financial Times.
Grönroos, C. ,2000. Service management and marketing: A customer relationship management approach. Chichester: Wiley.
Hartline, M., Wooldridge, B. and Jones, K. ,2003. “Guest perceptions of hotel quality: determining which employee groups count most”. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly, 1(1),pp.43-52.
Kandampully, J. ,2002. Services management: The new paradigm in hospitality. Melboune: Hospitality Press.
Kotler, P. 2000. Marketing Management: Millennium Edition. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Kotler, P., Bowen, J. and Makens, J. ,2003. Marketing for hospitality and tourism. Upper Saddle River: Prentice-Hall.
Kumar, M., Kee, F. T., and Manshor, A. T.,2009. Determining the relative importance of critical factors in delivering service quality of banks: an application of dominance analysis in SERVQUAL model. Managing Service Quality, 19(2), pp. 211-228.
Lancaster, G.,2005. Research Methods in Management: A Concise Introduction to Research in Management and Business Consultancy. Oxford: Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann.
McCluskey, M., 2004.How Mature is Your Service Operation?” Supply Chain Management Review, (8) 5,Pp. 17–20.
Metters, R., Kathryn, K., Madeleine, P., and Steve, W.,2006. Successful Service Operations Management. Thomson South-Western: Mason.
Neal, C. and Quester, P.,2006. Consumer behaviour: implications for marketing strategy.NewJersey: McGraw-Hill.
Normann, R., 1991. Service management: strategy and leadership in service business. New York: Wiley.
PIZAM, A. and SHANI, A,. 2009. The Nature of the Hospitality Industry: Present and Future Managers’ Perspectives. Anatolia, (20)1, pp. 134-150.
Sichtmann, C, Selasinsky, M, & Diamantopoulos, A.,2011.Service Quality and Export Performance of Business-to-Business Service Providers: The Role of Service Employee- and Customer-Oriented Quality Control Initiatives. Journal of International Marketing, 19, 1, pp. 1-22
Riedl, C, Bohmann, T, Rosemann, M, & Krcmar, H., 2009.Quality Management in Service Ecosystems. Information Systems and e-Business Management, 7, 2, pp. 199-221,
Skålén, P., 2009. Service marketing and subjectivity: the shaping of customer-oriented employees. Journal of Marketing Management, 25, 7/8, pp. 795-809.
Solnet, D., Kandampully, J. ,2008. How some service firms have become part of service excellence folklore: an exploratory study. Managing Service Quality ,18(1),PP. 179-93.
Stanton, W.J., Etzer, M. J., & Walker, B. 2007. Marketing Management. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Thomas, A. B., 2004. Research Skills for Management Studies. London: Routledge
Treacy, M. & Wiersema, F. 1995. The Discipline of Market Leaders. New Jersey: Addison Wesley.
Glossary of terms
Service: an intangible product that the buyer pays for; after the transition, the buyer does not diminish the service from the seller and neither do he get something tangible in return
Service differentiation: refers to the unique service that a can be used to differentiate a company from its competitors
Intangible: means having no mass: services have no tangible mass, they are provided and the buyer pay for what he does not hold
Perish-ability: can become stale and lose its value
Appendix
The diagram below shows how a business can improve its service delivery: