Labedo Berries is a small business entity run by a family of entrepreneurs. The main activity of this company is the collection and processing of strawberries. In the course of its work, Labedo Berries contacts the farmers, receives their supplies, sorts strawberries, and uses the chocolate blend to add a unique flavor. The ultimate goal is to attract customers and sell them the final product. Execution of these tasks requires using cloud services as the primary type of business infrastructure.
There are two options for a business network and storage. It can be a physical server within the company’s possession or a cloud service which is stored somewhere else. Smaller-sized entities will find cloud storage more available to them, as the procurement of a physical computer is only viable for large businesses (Attaran & Woods, 2019). In the case of Labedo Berries, there is no need to single-handedly maintain server hardware; therefore, using the cloud services is more than necessary to support the company.
Organizing a business infrastructure can take two forms, the first of which is having everything set before the organization starts working. Such an approach is beneficial when management knows exactly how much information they will require to be processed. The drawback is the necessity to buy a new server in case the storage is not enough. The second form is better suited for cloud-based databases. In this case, a framework gradually expands, as the organization needs more storage. According to Khan (2019), the expansion of the IT limit does not require staff training, new hardware installation, or programming. The cost is the risk and danger behind virtual servers because they are recent technological discoveries. Nevertheless, starting with a small cloud framework and enhancing it is a better choice for Labedo Berries.
The reason why cloud-based tools are more viable than traditional ones lies in the cost of hardware. When an organization employs a machine for storing data, the subsequent implication is the necessity to maintain the equipment. Khan (2019) points to such tools as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS as more economical alternatives to physical servers. However, they do necessitate occasional upscaling as, beyond a certain point, sales and inventory cycles will need more storage to be adequately monitored. Therefore, Labedo Berries ought to consider its expansion and update their online services as frequently as the need arises.
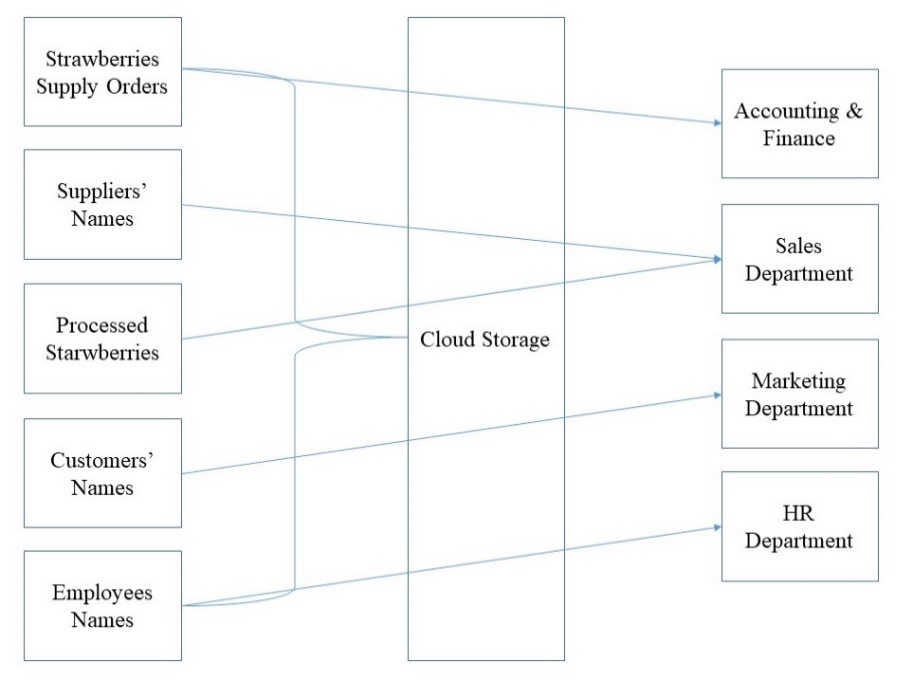
Choosing cloud services means storing all major information systems on virtual servers. Diagram 1 in Appendix A shows the information flows in Labedo Berries with the inclusion of an online tool. First, the company has to process all supply orders from farmers. It requires information about the details of received strawberries, which are accessed by the Accounting & Finance Department. The names of suppliers and the number of strawberries, which have been dipped in the chocolate blend, are intended for the sales department. The marketing department is accountable for the names of customers. Finally, the employee roster is critical for HR Department’s analytics. The major change from the original design is that all departments have to work with the cloud storage to upload and retrieve the needed information.
Altogether, cloud services are the most appropriate type of infrastructure necessary to support the activities of Labedo Berries. Virtual servers are more flexible than physical ones and allow expansion with minimal loss of resources. The database has to be upscaled as the number of business operations increases. By having all vital data on the cloud storage, the company allows its departments to access the relevant information without being physically present in the office. Overall, cloud services are the most cost-effective solution for a small-sized enterprise, such as Labedo Berries.
References
Attaran, M., & Woods, J. (2019). Cloud computing technology: Improving small business performance using the Internet. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 31(6), 495-519. Web.
Khan, S. (2019). Cloud computing: Issues and risks of embracing the cloud in a business environment. International Journal of Education and Management Engineering, 9(4), 44-56. Web.
Appendix A