Executive Summary
Apple is a US-based company operating in various states across the globe. One of the main markets for Apple’s products is China. The micro-environment of Apple shows that it has the financial strength, effective leadership, a powerful brand, and strong research and development team. The macro-environment shows that Apple’s main problems are the trade wars between US and China and intense competition from local companies. The trade war creates a hostile environment for the company to operate in China effectively. For example, high tariffs on US products make it challenging for Apple to compete effectively. The recommendations to solve the problems identified are engaging with the US Department of State to handle the conflict. In addition, the CEO of Apple and other leaders should consider sending a message explaining the problem and potential consequences. If the problem persists, the organization should leave the market and focus on other markets. However, if there is hope for a shift in the trade war, Apple should consider further differentiation to compete with the local companies.
Introduction
Apple is one of the companies that have benefitted from globalization. It is a multinational organization flourishing in the technology sector. China is one of the main markets across the globe for Apple products. The company has become popular and more successful in this market over the years. Apart from its quality and competitive pricing, mobile applications for services like banking and shopping are particularly popular with Chinese consumers, creating the potential for Apple’s success. However, for the company to make strategic decisions, it is important to understand its business environment and identify the challenges that it might experience causes, and possible solutions. The company’s micro and macro business environment can be examined effectively by conducting a SWOT analysis, PESTLE analysis, Porter’s five forces, and many more.
Company Assessment
Overview
Apple is one of the best-performing companies in the world. They make and sell consumer electronics, computer software, and other online services. It was established by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak back in 1971 in California, the United States (Zacharakis and Bygrave, 2019). Even though the company started making and selling personal computers, it has now moved into other areas. In addition, it is known for making new hardware, software, and services (Podolny and Hansen, 2020). Offices: The company has offices in the US and other countries across the globe. They also have offices in Asia and the rest of the world. In addition, iPhone, iPad, Mac, iPod and Apple Watch are all sold under its brand name. Therefore, the success of Apple is attributed to its high-quality products, strong innovation and application of effective marketing strategies.
Financial Health
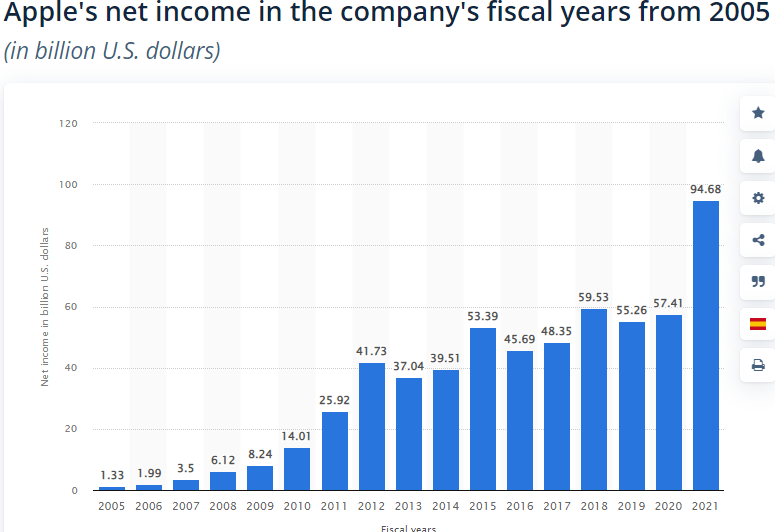
Apple has sound financial health due to its extraordinary performance in the market. The company reported a steady rise in net income starting from 2005 to 2021, as shown in the figure below (Statista, 2022). For example, the company reported a net income of $94 billion in 2021 compared to $1 billion in 2005. In terms of revenue, the company has experienced a steady rise in revenue over the past decade. In 2021, Apple obtained revenue of $365 billion compared to $13 billion in 2005 (Statista, 2022). Apart from revenue and net income, its financial strength can be observed through its balance sheet. For the year ending 2021, Apple has total assets of $351 billion, total liabilities of $287 billion and total shareholders’ equity of $63 billion (Statista, 2022). As a result, the company has strong financial strength.
Mission, Vision Statement, and Values
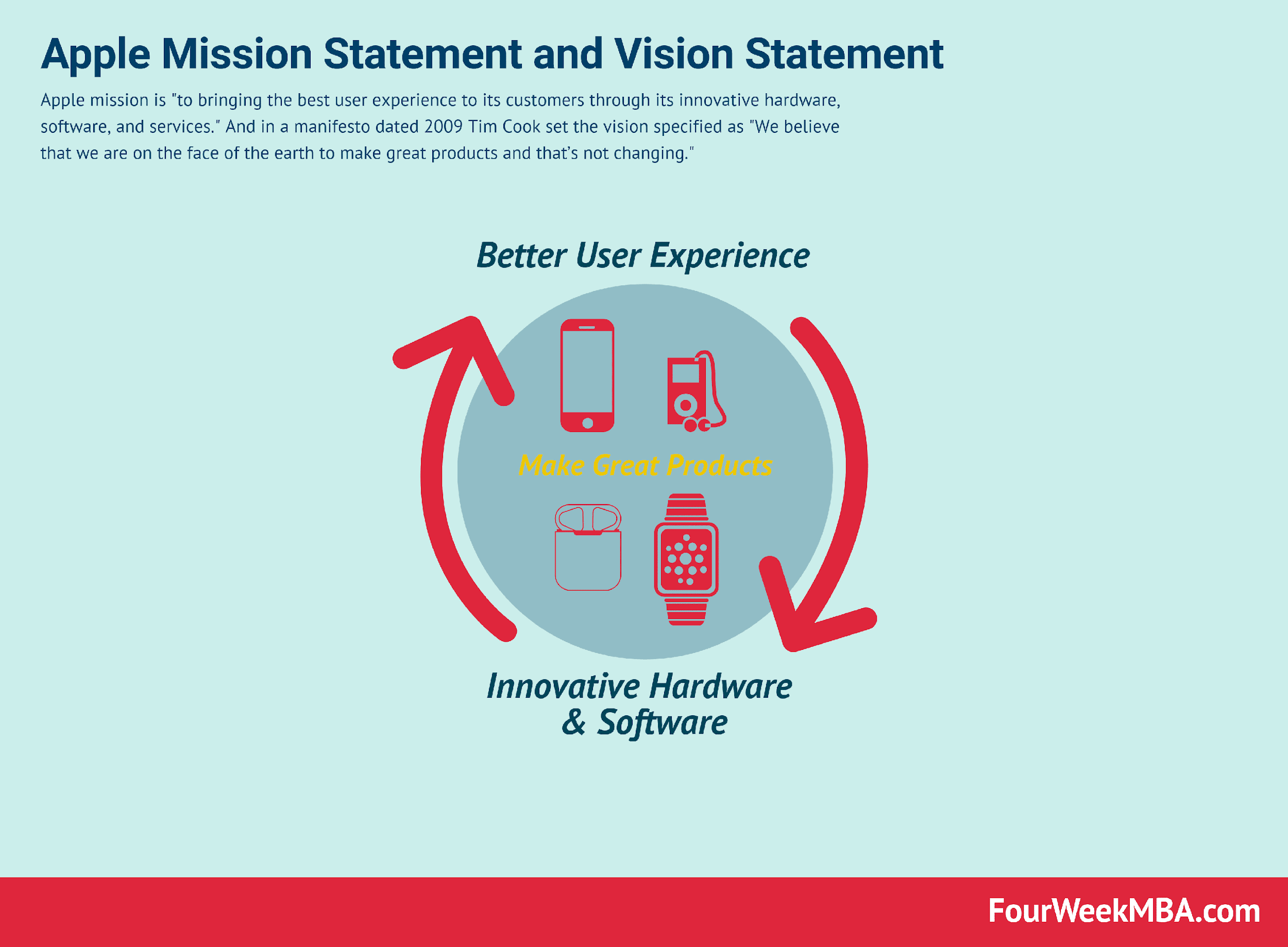
Mission and vision statements provide a company’s purpose, goals, and values. For example, Apple’s vision, as found on their website, is “Apple is committed to bringing the best personal computing experience to students, educators, creative professionals and consumers around the world through its innovative hardware, software, and Internet offerings” (Cuofano, 2021). In this statement, it is evident that the company is determined to provide quality products to its customers. On the other hand, Apple mission statement is “to bringing the best user experience to its customers through its innovative hardware, software, and services” (Cuofano, 2021). In this statement, the company highlights the scope of its operations and intends to satisfy its customers’ needs in the market. Therefore, the statements are integral because they provide strategies and direction to its stakeholders.
Apple’s core values are inclusion and diversity, education, accessibility, the environment, supplier responsibility, privacy, and inclusion and diversity. It shows the company believes that it is important to be a technological and innovation leader (Cuofano, 2021). Apple is mindful of the principles that have helped it become a company that cares about the quality of its products. These principles have made Apple what it is today. All of the company’s activities must be in line with these values, which the company says are its core values (Cuofano, 2021). For example, the values create a conducive work environment for its employees. Thus, values such as environment and supply responsibility sell the company as environmentally conscious and attract many customers.
Macro Environment Evaluation
SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis is a framework used to evaluate an organization’s external and internal implications. It can assist in examining the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats faced by Apple. The analysis also presents the strategic aspects that influence the decisions of Tim Cook and its managers in developing the company. It provides crucial information such as the strengths that the company should build on, the weaknesses and threats they should eliminate, and opportunities they should consider in the market. The following is the SWOT analysis model for Apple Company.
Table 1: SWOT Analysis
Table 2: PESTEL Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of buyers influences Apple because it determines customers’ purchasing power and preferences. Consumers’ purchasing power is moderate due to few individual buyers (Onyusheva and Seenalasataporn, 2018). This indicates that the number of customers who can afford Apple’s products is few in the market. When customers are few in the market, they raise their stake, and organizations’ actions ensure that their interests are considered to survive in the market. The other reason for moderate purchasing power is low switching costs. It is relatively easy for a customer to switch to other brands in the market, such as Samsung. This makes it challenging for Apple to meet customers’ needs from every aspect.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers of Apple in the market is low. This indicates that they have a weak influence on the company and its rivals (Onyusheva and Seenalasataporn, 2018). The weak influence on Apple is attributed to a high number of suppliers in the market. As a result, the ratio of company concentration to supplier concentration is high. This makes it easy for Apple and its competitors in the market to access spare parts. This shows that Apple and other companies in the tech industry can easily switch from one supply to another. Therefore, the bargaining power of suppliers in the market is a small issue to Apple and its rivals due to the existence of alternatives.
Threat of Substitute
Apple faces a low level of threat of new entrants due to the high level of capital required and the strength of the existing companies in the sector. To establish a firm in the tech industry, there is a need for a large amount of funding, making it challenging for new firms to enter (Onyusheva and Seenalasataporn, 2018). Without adequate funds, the business is prone to failure due to the inability to fund operations such as research, development, and production. In addition, the existence of established companies in the industry, such as Samsung, Xiaomi, Huawei and many others, act as a barrier to new entrants. Brand development is extremely costly and challenging in the presence of existing giants in the market like Apple. The threat of new entry is not an issue for a company of the caliber of Apple.
The Rivalry of Existing Players
The rivalry among existing players in the China market is high. The sector is characterized by very high and fierce competition against players (Onyusheva and Seenalasataporn, 2018). In China, Apple faces intense competition from Chinese smartphone brands like Huawei, Oppo, and Xiaomi. The competition is high due to the companies’ aggressive advertising, extensive research and support from the government and locals. In addition, the existing players in the Chinese market, such as Huawei, have a good understanding of the market. This gives them the ability to make products that meet the customers’ needs. As a result, product differentiation is low because the existing products are almost the same and perform the same functions.
Threat of Substitute
The threat of substitutes is relatively low in the Chinese market. A low threat of substitutes is due to technology, online services, and consumer electronics. For this company, substitutes have a weak force due to the scarcity of available substitutes in the market (Goyal, 2020). There is also a low performance of alternative products such as landlines. The advancement of technology has rendered these alternatives unusable. The use of landlines in offices and homes is declining due to technological disruptions. In addition, the existing substitute performs poorly in the market because of limited features. As a result, Amazon is not worried about the existence of substitutes in China market.
Overview of Apple in China Market
One of the main markets for Apple products in China. Apple entered the market through a deal with China Unicom for the exclusive sale of the iPhone 3. The high traffic in the Chinese market contributed significantly to Apple’s high revenue (Xing, 2019). Consumers in China were attracted by the technological advancement of the iPhone, iPod, and iPad. However, things began. to shift at the start of the US-China trade war. The increase in tariff for US products reduced Apple’s competitive advantage in the market. In addition, the growth of local companies such as Oppo, Xiaomi and many more has reduced the performance of Apple in China (Xing, 2020). Therefore, Apple’s performance in China is adversely affected by trade wars and intense competition from local companies.
Problem Identification
The first problem is the escalating trade war between the US and China. The poor relationship impacts both countries economically due to an unfavorable business environment. The high tariffs on US products by China contributed to the increase in their prices. With high prices, it becomes challenging for Apple to compete effectively with local companies such as Xiaomi, Oppo and others (Xing, 2020). In addition, the poor relationship makes China market hostile to the operations of Apple and its products. The consumers in the market are likely to avoid purchasing Apple products due to a lack of diplomatic relationships between China and the US. The stringent rules and long bureaucratic processes make it hard for Apple to function effectively. Therefore, the company is likely to lose its market share in China because of trade wars.
The second problem is the rise of local firms in China market, leading to intense competition. One of the impacts of competition on a company is reduced market share (Bal and Errand, 2019). For example, China is among the main market for Apple products due to its population and economic strength. However, the market shift is caused by intense competition from local companies. The other impact of intense competition is a decline in the customer base. As a result, the company is likely to reduce its prices to remain competitive, reducing its return in the market. Amazon is prone to failure in the China market due to intense competition originating from existing companies such as Huawei.
Recommendations
Table 3: Problems Identified and Recommendations
Implementation
The following are ways to implement the proposed strategies that Apple should use to solve the identified problems.
Table 4: Implementation
Reference List
Bal, H.Ç. and Erkan, Ç. (2019) ‘Industry 4.0 and competitiveness.’ Procedia Computer Science, 158, pp. 625-631. Web.
Barston, R.P. (2019) Modern diplomacy (5th ed.). Routledge.
Chu, X., Luo, X.R. and Chen, Y. (2019) ‘A systematic review on cross-cultural information systems research: evidence from the last decade.’ Information & Management, 56(3), pp. 403-417. Web.
Cuofano, G. (2021) Apple mission statement and vision statement in a nutshell. FourWeekMBA. Web.
Gu, X., Hasan, I. and Zhu, Y. (2019) ‘Political influence and financial flexibility: evidence from China.’ Journal of Banking & Finance, 99, pp. 142-156. Web.
Goyal, A. (2020) ‘A critical analysis of Porter’s 5 forces model of competitive advantage.’ A Critical Analysis of Porter’s, 5. Web.
Liu, M., Zhang, H. and Huang, H. (2020) ‘Media exposure to COVID-19 information, risk perception, social and geographical proximity, and self-rated anxiety in China.’ BMC Public Health, 20(1), pp. 1-8. Web.
Li, Y. (2021) ‘Apple Inc. analysis and forecast evaluation.’ Proceedings of Business and Economic Studies, 4(4), pp. 71-78.
Onyusheva, I. and Seenalasataporn, T. (2018) ‘Strategic analysis of global e-commerce and diversification technology: the case of amazon. com Inc.’ The EUrASEANs: Journal on Global Socio-Economic Dynamics, 1(8), pp. 48-63. Web.
Podolny, J.M. and Hansen, M.T. (2020) ‘How Apple is organized for innovation.’ Harvard Business Review, 98(6), pp. 86-95. Web.
Shen et al. (2021) ‘Spatiotemporal change of marsh vegetation and its response to climate change in China from 2000 to 2019.’ Journal of Geophysical Research: Bio Geosciences, 126(2). Web.
Statista. (2022) Apple’s net income 2005–2021. Web.
Xing, Y. (2020) ‘Global value chains and the innovation of the Chinese mobile phone industry.’ East Asian Policy, 12(01), pp.95-109. Web.
Xing, Y. (2019) ‘How the iPhone widens the US trade deficit with China: the case of the iPhone X.’ National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies. Web.
Zacharakis, A. and Bygrave, W.D. (2019) Entrepreneurship (5th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Zhou, Q. (2022) ‘Decoding China’s 2021 GDP growth rate: a look at regional numbers.’ China Briefing News. Web.