The presence of information technology (IT) in accounting arena especially spread out due to the rapid organisational changes across business houses throughout the world. These organisations are rapidly shifting their value chain by incorporating IT. Accounting information system (AIS) is a part of the IT incorporation of the accounting world. Every system has a set of two or more interconnected components those work together to attain a goal or a set of goals.
AIS also includes various elements such as people, measures, information, software, information technology (IT) infrastructure those work together to fulfill accounting information which needs for an organisation. Emergence of information and communication technology (ICT) raises the necessity of AIS in the organisations. Therefore, the International Accounting Education Standards Board (IAESB) developed the regulation for accounting education worldwide to achieve accounting professionals’ competence with IT capabilities. It further aimed to achieve the outlook and echelon of continuing professional education considered necessary for the accentuating professionals.
Chayeb, L., and Best, P., (2004) stated that IT has changed many aspects of accounting fundamentally. They further argued that accountants’ position becomes more complicated for usage of information-systems in analysis & design activities. Skidmore S., (2002) pointed out that accountants have to face the challenges of the global economy, IT, issues of accountability, e-commerce, tax planning, analysis & design etc so IFAC provides new guidelines to integrate IT in Accounting Curriculum. However, AIS dictates to incorporate it in the curriculum for the enhancement of accounting professionals’ competencies.
Moreover, there has been a lot of software designed to apply in accounting practices. Application of internet, IT peripherals and emergence of e-learning has shaped a radical change in accounting teaching methods. Since organisations are incorporating enterprise resource planning (ERP) more rapidly, it further necessitates the implementation of AIS. Furthermore, the usage of computer in teaching and learning process in higher education has been encouraged by different policy and regulatory initiatives in USA and UK. For instance, EQL is used as a CAL component when EQL has applied like a self-tutoring system in the management school as such as a machine tutor.
To discuss the IT Integration in Accounting Education of higher institutes in Kuwait, this term paper will consider the curriculum, IT infrastructure and facilities of accounting education of four Kuwaiti universities, which provide high demand degrees on accounting. The Kuwait is favored by rapid technological development and government’s direct investment in IT sector etc which prove the country’s ability to implement IT in higher accounting education. In this respect, the country faces problems with legal basis, bilingual effects, bureaucracy and so on. However, in Kuwait, the appearance of multinational companies is enhancing AIS in higher education.
Significant of IT in accounting Practice
In general, IT has profound impact on accounting practices. It has transformed the nature of the organisations, organisation’s value chain, and the accounting practices. To make available all accounting information in a unified manner, IT has to be incorporated with existing accounting practices. Further significance of IT in accounting practices are as the following:
- Enhancement the speed of accounting processes: traditional accounting procedures is the manual accounting measures which are less speedy in terms of dealing out because manual jobs required physical labour that is lagged behind by various limitations. On the other hand, IT based accounting processes are more speedy because of having less limitations. It has more working capacity, rapid data mining facility, high processing power and the least manual labour requirements. Therefore, application of IT in educational accounting practice speeds up the accounting processes and thus the decision-making courses of action of its users get unpredicted speeds.
- Reduction of labor costs: The labour cost is one of the main curtail factor for the originations’ profit. Since manual accounting practice requires more workforces, therefore, the organisations have to incur more costs associated with its labours. The application of IT in accounting processes requires less labour and thereby organisations incur less labour costs.
- Rich information in the place of lean information: Rich information is the combination of the information substance along with the audiovisual signals those the dispatcher gives while notifying and communicating. To reduce ambiguity and uncertainty in the data set, it is required to produce rich information. Due to the failure of existing inefficient information system, management fails without having prior notifications. Therefore, organisation requires IT based accounting system known as AIS. It enables an organisation to produce more rich information according to its external and internal user’s requirements. AIS can produce both situational derived and systems supplied information to its users. All these only can be happened by the implication of IT.
- Ease of data extraction: The manually kept data is very complex to extract with ease. In manual book keeping, the major job of accounting processes required to use huge data books. However, these data books are not readily accessible always. Moreover, data mining from the aforesaid is also a time consuming and labour intensive task. Since the IT has relatively more data extraction capabilities, it extracts data with ease and provides data in time on requirement.
- Accuracy of accountancy: There is a jargon that man may do wrong, but the computer does not. However, the jargon is partially correct because it has problem within itself since human produces the IT systems. If and only if the IT infrastructure has been made accurately, it will work indefinitely accurate over a long time period. Manual labour has no such capability of performing any job indefinitely correct because it has several limitations such as fatigue, illness etc. Since the IT is free from these limitations, it has more and more accuracy.
- Comprehensive set of reports: by employing IT in the form of AIS, an organisation can easily create a comprehensive set of reports since the IT has capacity to produce rich information. In the organisation, which is noncompliant of IT events are very difficult to derive situational reports. Because in such an organisation, the preparation of a comprehensive set of reports is very time consuming and the arrangement relevant data is complex.
- IT as the most significant haulers of accounting systems and information: in the present days, IT works as the most significant haulers of accounting systems and information. Today’s business organisations are incorporating IT very rapidly in their business operations and value chains. As it has described earlier that the IT has transformed organisation and thereby information processing and information grabbing throughout the organisation become very easy.
- Making faster processing and decision-making: As it is said earlier that the information system (IS) has significance advantage over manual labour, therefore, it enabled the firms for faster information processing and quick decision making. It further facilitates the managers to hold various managerial roles through its ease in data processing and decision-making.
- More reliability: From aforesaid discussion it is clear that the IS has more capability than manual labours, therefore, it has the capacity to produce more reliable information. Moreover, a slight change in any IS can destroy the whole system, bringing any little manipulation in the system would result completely irrelevant data. As a result, it is less catchy to fraud by changing the IS and thereby IS has gained more reliability.
Significant of IT in Accounting Education
UNESCO (2008) pointed out that the stipulation to right of entry to higher education has been increased with modern trend towards a knowledge-based culture and the rapid growth in information technology has fashioned new opportunities to boost quality of education in higher level. The pioneers among the higher educational institutions are using IT to design and develop their curriculum and course materials, distribute and sharing the complete course content, providing lectures and projection of assignments and presentations, smooth the progress of communication among teachers and students, carrying out research and endow with administrative and supervision jobs.
The accounting educators have derived with aims is to ensure the easy access to the best educational facilities essential to prepare young learners to play occupied roles in modern society and to generate build blocks for knowledge based financial management. With this view upholding a capacity to integrate latest upgrade of information technology in optimal balance with local circumstances and older educational technologies, the higher educational institutes are assisting to develop educational software, web portals, e-library, distance learning facilities, online examination system integrated with assessing the examination papers and materials that imitate the local and regional cultures with relevance to the key components of accounting practice.
Anderson, J. et al (2002) argued that the first emphasis to spell out an accounting curriculum with integrated IT for higher education would be linked with current global context when the second priority is to put forward a programme for professional development for students essential to implement the specified IT curriculum effectively. Moreover the IT tools also provide a sensible and practical approach to curriculum and teachers could development their lectures and learning materials addressing the individual student’s needs that could be put into practice quickly and cost effectively with existing resources.
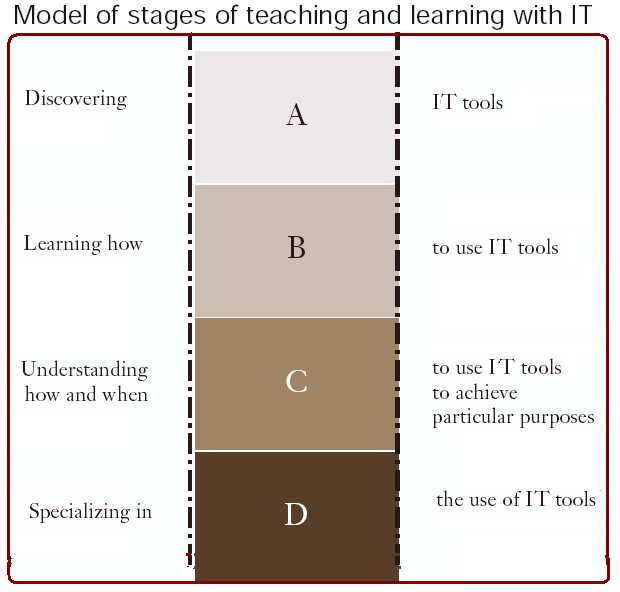
Anderson, J. et al (2002) also pointed out the first stage of IT tools to be integrated in curriculum is to identifying the required tools, second stage is to learning the application of the tools, in third stage is to applying the tools in relevant fields and finally gaining specialization on the tools. For the accounting student whether he enrolled for a class-based or distance learning environment application of the tools would facilitate the educators to build competence for settle on why, when, which and how the IT tools would contribute to achieving teaching objectives and how to define the most appropriate IT tools that would encourage-
- Web based software facilitate to getting entry to the academic resources and quality assurance,
- Online portal provides learning materials and communication facilities with teachers
- Databases provides capabilities to solving learning dilemmas at once
- Spreadsheet gives the ability for automation
- Word process helps to generate assignments
- Online resources facilitates to participating and contributing in group discussions on the use of IT.
- Other IT tools like conferencing, email, forums and bulletin boards contribute to work together for the enhancement of learning as well as management of learning processes.
- Multimedia presentations help to get lesson materials in accordance with the major goals of teaching method
- Hardware like PCs, CD-ROMs, video and audio helps to performing courseware;
- The most remarkable contribution of IT tools is to facilitate to address individual student’s requirement.
Accounting Professionals Market Demand
Eshai M., (2002) pointed out that the bookkeeping based accounting profession has changed due to development of technology, changes of financial analysis system in stock market and for increasing the Computer systems in audit process. Eshai M., (2002) identified that in the job market people with IT skills form non-accountant background are replacing the traditional accountant those who are not yet achieved ICT skills. In order to compete in traditional job market, it is essential for Accountants to have IT skills and to do this the Regulatory bodies have to take initiatives to remove all loopholes.
Dillon and Kruck (2004) and economists predicted that by 2010 the majority of American personnel will have a high level of IT competencies because successful companies require qualified and experienced IT employees including accountants as well as financial executives. The demand of accountants who is equipped with IT information is increasing as the organizations started to hire the persons who have competency in IT.
They also added that the basic three competencies such as acquaintance, dexterities, and capabilities will be the entry-level requirement for accounting jobs and accountants should comprise the application and combination of IT into the accounting procedure along with principles of financial and managerial accountancy. Moreover, several reports published that there is huge gap between the remunerations of traditional-accountants and specialist-accountants.
Accountemps (2007) mentioned that comparing to the previous years, from 2007 non-technical skills such as verbal, written and interpersonal skills turn out to be most important skills. It further stated that the demand of finance and accounting professionals was increasing in such a way that fresher need not to wait after graduation completion and professional accountant’s salary is also increasing noticeably. Globe University and Minnesota School of Business (2009) recommended that accounting degree is a win-win scheme for the demand of accounting professionals.
Both in the economy’s slugging and booming, the need for accountants remain stable because in both of the case, businesses have to focus more and more on tracking profits and expense. Though accountants are still working with numerical terms but they are also building image of supporting strategic management and decision-making. Auditing, financial and tax accounting, and management accounting are the three professional accountants’ working arenas.
Association of Chartered Certified Accountants of Hong Kong (2008) reported in the survey that 36% of responding workers think that there had no change in the accounting & financing jobs market, 25% believes that these jobs are going to better position and rest of them provides completely different view. Besides employees, employers also provide different views for example 29% of responded employers believe that more job opportunities would be created for IT skilled accountants who are furnished with various technical-knowledge because demand of such professionals still is sheathing behind the demand..
There were also signs of increase in salary of accounting professional though the economy was shrinking. In the survey 79% of responded employers projected that they got resignation letter from their accounting professional. It happened due to better offer for payment or better fringe benefits. Therefore, the organizations saw offering rise pay or better fringe benefits as the strategy to retain its employees. The picture shows how much demand of accounting professionals is at hand in present market worldwide.
Badenoch & Clark (2009) expressed that though there is news of recruitment freezes and redundancies but commercially equipped accountants those can act in response swiftly in a unpredictable market (for instance in the present economic downturn accountants require to reforecast in every single month) and supply onward looking study of data are in demand. Highly qualified accountants equipped with experience of risk, regulatory and compliance still have available job opportunity. To fulfill the requirements of IFRS, central government, and NHS, there is demand for public sector experienced auditor. The personal bankruptcy and corporate recuperation experts linger significant and required after skills determined by present global economic scenario.
Press Release.com, (2009) pointed out that 65% of the accounting & finance professionals believed that job opportunity for accounting professionals is increasing or remain stable. It also added that both for accountants and auditors, the US Labour-Department anticipates an 18 percent growth (within 2016) in the jobs, which is the fastest increasing rate of all occupations. That department also anticipated that extra 226,000 accounting jobs will be evolved by the next 10 years.
Information technology in Kuwait
There are various studies have been taken place on the application of IT and ICT in Kuwait. These papers have several commonalities in these issues; National Profile of the Information Society in Kuwait (2007), Kuwait Information Technology Report Q4 (2008), and Kuwait Central Agency for IT adopts ICDL digital literacy programs within the government and society (2007) has presented the following results:
Kuwait is the regional leader and the third major IT market in the Gulf region because of its moderately minute but well-off and IT cultured population. King, M. (2008) agued that it is expected that the worth of the Kuwait IT market would boost from US$ 539 million in 2008 to approximately US$ 833 million in 2012 because there was an economic growth due to bloated oil revenues and government spending. The IT market is blessed with government’s direct investment and spending though consumers retain their spending for IT. The country has been updating its hydrocarbon sector IT infrastructure by using revenue from ever heightened oil prices.
To enhance broader change in the government structures, it has transferred Central Agency for Information Technology (CAIT) to communications ministry. The CATI was working for e-governance in the country. It aimed to developing the e-governance portal, a single site for all governmental services, along with mobile platform technology. Due to the extreme officialdom and sheathing education systems, the country’s e-development remains a challenge. Foreign vendors have dominated the country’s PC market and furthermore, they are stressing local value chains.
The marketing conditions of IT of the country seek more distributors within the country and from overseas. The enterprise system segment of the market is highly competitive, thus SAP and Oracle are fighting to hold the most customer base. The Microsoft is also fighting in the market segment.
In 2007, computer sales totaled up approximately US$ 185 million, third after the two market leaders of which 60% was the notebooks sales. The ease of use of wireless admittance technologies was pouring demand between small and medium businesses and at the same time as high-end amusement features also draw customers. More intuitively, the IT market was facing with a rate of 62% software piracy. The government aimed at reducing the software piracy.
Almost every homes of the country is equipped with DSL or wireless internet access. The government like past still is rendering its hand to force IT advancement with its fresh broadband access plan. The State Ministry of Communications (MOC) of Kuwait has involved Alcatel to provide gigabit passive optical network (GPON) service to cover the total roll out made by the ministry.
Kuwaiti Central Agency for Information Technology (CAIT) and ICDL GCC Foundation has recently agreed an agreement to actualise ICDL and e-Citizen programs across the government bodies and societies. It has further aimed to force the government performances and teach people to take advantage of new technologies and online services. The Kuwaiti Central Agency for IT is empowered to take responsibility for mounting the country’s e-Government competences, taking advantage of the utilisation of IT-enabled services to rationalize government activities, lessen expenses, and abolish technical difficulties coming from inaccurate use of technology.
It has been also working for developing education and training systems for IT advancement that will advance implementation of eServices and endorse the eCitizenship program, which tries to offer citizens with IT skills and permit them to whole utilisation of numerous eServices, for instance, utility bill payments, different bookings, electronic trade or e-commerce, visa issuance, and employment.
The Ministry of Education took several realistic steps to enlarge ICT’s educational reimbursements more of just computer training. It also set up the e-learning project to initiate new educational functions that could put in to the expansion of education. The project includes scholarly books over the Internet infrastructure, CD-ROMs, and unique learning software, appoints the teacher, their student, and the parents of their students in the educational program. Remote learning and e-learning are also in the verge of growth because of its adoption in some universities and colleges though in a minimal level. The Civil Service Board (CSB) has developed a site for e-training to develop its work forces.
The Governmental institutions have been arranging annual development training programs to adopt ICT benefits. These trainings are designed either to realize any software or IT issues in the jobs or to increase the productivity of the employees. To compete in the competitive market, the private sector is incorporating ICT more rapidly to increase employees’ productivity in the workplace.
In the Governmental arena, Electronic transactions are still partial though almost every governmental institution has their own websites. A limited number of governmental institutions are offering government to individuals (G2C transactions) services, for instance, data revitalisation. However, government to business level transactions (G2B transactions) has not been developed yet. Telecom companies and financial institutions are enjoying the ICT security as like as the government institutions.
The NGOs in the country are working to educate people about the benefits of ICT but there is no program to lessen its misuse. Moreover, there are also no regulatory measures to de-motivate the misuse of ICT. However, the private sectors in the country are rapidly increasing their data security by employing various high tech technologies. The security for information and network is also highly enabled through the means of continually updated measures. Even so, the country has to train up its human resources for the very purpose.
Kuwait requires developing laws that will direct the governance of the sector to be widely used in the country. By 2007, a draft law emerged to govern electronic transactions. In 1999, Kuwait had passed an intellectual property protection (IPP) law to protect the integrity and the owner of software, IS, and electronic contents. Due to the regulation by 2006, the software piracy lowered from 95% to 64%.
Since the online storage and archiving are increasing day by day throughout the governmental and non-governmental institutions, the security measures are also required for these aspects. And due to over emphasis of delivering e-services, standardization requires to get the most attentions in the IT sector of the country.
Reduction of the gap between academia and practice
Anderson, J. et al (2002) addressed that the IT curriculum for accounting in higher education institutes of Kuwait has always driven to follow is a state-of-the-art curriculum. But Al-Atiqi, I. M., & El-Azma, M., (2007) pointed out that the Universities of Kuwait has to follow the Law 34 of 2000 for which Universities bound to follow the policy decisions taken by the regulatory body. Thus to integrate latest updates of IT in accounting curriculum needed to follow the regularity decisions and academic council’s approval which is a time consuming process.
On the other hand the practitioners of accounting arena are always follow open end solution to integrate the most updates of IT without bothering for any regulatory bindings. Consequently there would raise some gap among academia and practice, when the offers academies suffer from regulatory bindings, the practice always attempts to facilitate fruitful application of IT tools evolving the advancement rapidly.
Thus in every set of IT integration in accounting, there are always gaps between the academia and practice. Usually academia remains traditional in form and relatively unrealistic in accordance with time frame. On the other hand, practice is completely realistic and more evolving day by day onward. The recent survey on various organisations of Kuwait showed various gaps between academia and practice in accounting. Tribunella et al. (2005, pp-36-8) confirmed that these gaps corresponded to the explanation to various dilemmas among academia and practice of accounting practice and IT incorporation are as follows:
Practitioner versus Academic Points of View
Practitioners are seeking more mobility in their data and more security of the data. Data mining along with database and application incorporation depicts the aspiration of getting a greater return on investment (ROI) by reusing data in later applications. They are also craving for data warehouse that will support the management decision making. They are more practical and directed by competitions. Most importantly, they focus on gaining competitive advantage by using systems for strategic purposes but they do not focus on system development.
On the other hand, academies are focusing on the system performance and system development since they are concerned in designing and networking matters. The computerised transaction processing (TP) has greater importance to academics along with interest in intelligence systems such as decision support as well as expert systems etc.
The joint workshops, seminars and conferences on issues those would bridge academia and practice should be helpful to reduce the gap. Moreover, having a rigorous common research agenda, collaboration of academics and practitioners, may end result reduction of the gap.
Rapidly Changing Practitioner Interests
There have been radical changes in practitioner interests. Though they are consistent with security questions but are letting out new issues to rise. So it demonstrates is a gap between what practitioners need their fresher has to know and what academics are agreeable and capable of teaching their students. The educational systems are not readily changeable but the industry’s scenario is rapidly changeable and it is being changed to gain competitive advantages over rivals.
To resolve the gap, it is required to enable students in the so called “learn how to learn” process to make them life long learners. Because, it would enable them to know the tactics of evolve with emerging technologies (ET). The process helps to know new technologies and skills and therefore, enables the students to become capable with new demands correspondingly. The students should be capable of using analytical thinking skills of one application in other applications because academics are not able to teach every of the software packages, accounting systems (AS), and computer languages used in the practitioners arenas. Furthermore, the students must shift ahead of acquaintance of the technology and into intellectual capacity, application and examination of the technology.
Process versus Static Thinking
The electronic reporting system, named as animation, does more than just preparing conventional reports. Management should be aware of reengineering of processes while bringing in new technology into the organisation. Academia and practice must be recognised with database procedures to ascertain a suitable acquaintance of accounting and enterprise systems. Due to the practitioners’ inability to comply with the notion the organisation would cost extensively. Furthermore, the formation of languages such as XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) lets swift exchange of data among organisations, their systems and networks and consequently affects financial reporting.
Thus, the accounting profession is a highly regulated, for the very reason efficient data collections, storage of common format data, reporting effectiveness of greater value and these must be acquired by the accounting practitioners.
The Effect on Practitioners, Decision Making and the Accounting Profession
The gap between academia and practice results practitioners to expend resources and time to train up fresher students. Moreover, if the fresher students are given to incorporate complex data into the system, there is a risk of misstatements of data and thus produce inappropriate business decisions. Therefore, the students must focus more on data rather on decision-making. The blend of strategic decision with the systems would provide competitive advantages.
Since students are less acquainted with professional and judgmental issues and new issues, therefore, there is a necessity to incorporate more case studies to enhance students’ critical thinking skills.
IT as core competencies of professional accountants
IAESB (2006) argued that the IT is omnipresent in the present business arena which requires the competency of the professional accountants in the technology. Information Technology for Professional Accountants, IEPS 2, states that the all professional accounting aspirants need to have an acquaintance and understanding of at least any of three roles – manager, assessor or designer of IS, or a amalgamation of the three roles.
Harrison, D. et al. (2004) stated that the practitioners placed accounting profession would to be acquainted with the achievement and manifestation of definite competencies and unique selling of proposition in the place of the conventional achievement of the body of knowledge. So the core competency as a USP of professional accountants is competency in IT.
Dillon and Kruck (2004) stated that the present day’s organizations mostly require the new accountants who need to know the present AIS systems and have the ability to prepare tomorrow’s. For the very purpose the accountants must have technical dexterities and theoretical acquaintance of AIS. CIty Iloilo, (2007) pointed out three most significant competencies of accounting professionals and these are knowledge, skills and professional values. The knowledge further encompasses general acquaintance, organizational and business awareness, IT and accounting acquaintance. To set unique selling proposition of a fresh accounting professional, IT knowledge needs to be considered as the most valuable.
Manoharan, T. N. (2009) stated that the IT is omnipresent for the present accounting and business world. Now-a-days globalisation has been changing the business environment and e-commerce is getting more significance. The application of IT in the present business environment needs sufficient knowledge base. Competence in professional accountants is required to be able to execute various roles with reference to a given standard in any given environment. It defines the way of organizing, operating, and managing the organizations. Businesses have been developing their business strategy with incorporation of IT strategies, because IT plays the role of enabler in business commencements. The IT has been changing the environment and financial side of accounting activities. Professional accountants need to execute significant roles as managers, advisors and assuror of the implementation, exploitation and execution of various IT.
Therefore, there is an importance of pre-qualification and post-qualification education on IT to make the professional accountants competent for assuming and executing the IT and evaluative related services.
Accounting Software for Professional
ICAEW, (2009) stated that the professionals are those who study and work accordingly with their ultimate set goal, do whatever possible to achieve the goal and after the achievement of the goal start to accomplish a new task. In case of accounting professionals, now they are used lot of professional accounting software(s). Mostly of these software(s) are used for:
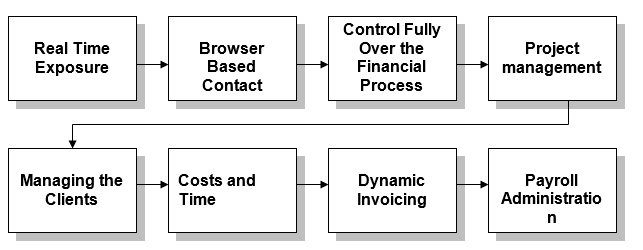
Shepherd, John, (2008) added that software those are largely used by accounting professionals has termed as professional accounting software(s). These are the tools used by any type of firms to reduce the costs and time of general and special accounting and bookkeeping process. Thus these software(s) can help to increase the profit margins of a firm.
Jayaraman, B., (2007) mentioned that the designs of these software(s) are mostly of two types: Manual and web based. This software is dedicated to make ease the accounting and bookkeeping system of a firm and help increase the performance and output level, modernise operation and to achieve success in the business. Through using professional accounting software, all financial information and transaction related updates can be maintained in a perfect way.
The daily transactions and period basis transaction can be easily coordinated with the help of these software(s). The three most important task of professional accounting software(s) are-Monthly reporting, budgeting and accurate balance keeping of any period.
Jayaraman, B., (2007) also added to select effective and efficient software at first the total idea about the need must be clear. That is for what purpose the software(s) will be use must be clear. Then the capacity of expense must be identified. There are lots of software(s) in the market. Collection of data of each and every kind must be gathered to mach with the capacity and need of the firm. Then the suitable type could be differentiated.
Many of the firms try to use powerful software(s) where thy do not need it. Thus, the cost of buying the software(s) will reduce the profit margin and hampers the total accounting process. Thus the clear idea about the needs and functions of the software is important in case of professional software(s) buying process. Professional accounting software(s) (s) can help in basically five sectors. These are:
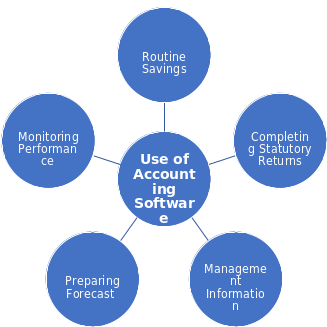
While using PAS1, the entry of any debit or credit account is done only one time and the software(s) automatically update it. So, in all time the pro-forma invoices and bills can be updated every time. Routine bookkeeping and other routine works are thus become easier. The updated and actual cash position is ready for all time and some times these software(s) present additional payroll management systems.
Saatçıoğlu, Ömür, (2004) argued that completion of statutory returns is one of the most key features. The VAT, revenue and customs and other tax oriented works become easier by using PAS. Management can be able to extend their control to the credit by using PAS. Establishment of a cash control system, detail sales information and stability in the stock position can be done easily through PAS.
Again, these software(s) are helped to forecast about the cash flows. Thus, budgeting, auditing and detection of cash patterns become much easier. PAS can also help to show what resources to use in what sectors. Finally, the easiness in performance monitoring system can be achieved through PAS. Management can decide with flexibility about the performance.
Accounting Software(s) for Learners
Niece Jennifer, and Cheryl Amantea, (2004) emphasised that the learners are not essentially students. People who are attending any kind of training programme are also treated as a learner. Accounting learners are of different types. Certainly they have no age limits. From students to professional trainees, all use different types of accounting software(s). Both quantitative and qualitative works are done by the learners. For the wide spread use of web based education system, accounting teaching and learning are also become software centred. Differentiation and uniqueness are the mostly asking features for the learners accounting software.
IQMS, (2009) stated that in almost every level of accounting learning, ICT are now used in a meaningful way. But there are some challenges to incorporate the useful software in the classroom or in the training place. In the early age of ICT it was not very easy to completely solve an accounting problem by using software. After that the wide range of accounting activities were spread out and many of the ICT sector oriented firms tried to mention out the easy and dependable software for making the accounting learning process easier.
Jones, David and Nona Muldoon, (2007) explained that the appropriate uses of these software(s) are depending on some key issues. Firstly, the knowledge about the software of the trainer or the teacher, it will be very embarrassing to fail to use software in front of the learners. In some cases various types of difficulties in using software has arise in the class room. As because accounting has no identified dimension of problems, these types of problems may arise time to time. Then, the idea of e-learning can not be successful without the proper functioning of the technological advancement. Finally, the capacity of the learners to acquire certain functions from the software is also important.
Jayaraman, B. & Gupta, G., (2009) pointed out that in case of educational software designing, the technological design is important. Thus, the learning process must be of purpose driven. To design the purpose driven software the organisational structure must be of technologically user friendly. The shortcomings of the technological approach declare nine attributes to design software like accounting learning software. These are: ultimate purpose, intermediate goals, design focus, designers, design scope, design process, design problems, management and control.
Ultimate purpose represents the certainty of feelings of why the software has designed for. Besides, if the stability and predictability of the problem can not be clear, the software can not be helpful for the learners. The intermediate goal is the set of ultimate goal for which a learner can use it. Other factors are mainly related with the design of the software.
Deng Jiangao and Yijie Bian (2007) addressed that the accounting learners are generally sophisticated and the design of the accounting learning software(s) are basically maintained in a manner to use in many languages, like English, France and Arabic which would help the learners to use manually the software more smoothly.
Policy Initiatives of Information Technology by Local Legislation
Calvanese, Diego, et al. (2009) stated that like most of the countries of the world, Kuwait is also using their legislations to ensure the proper use of the information technology. As because the world is becoming information based economy, important logistics must be imposed properly. Not only in the developed countries but also the developing countries, like Kuwait are constantly taking policies to use effectively and efficiently their information technological powers without any mistreatment though it is not only a critical but also a difficult task.
Calvanese, Diego, et al. (2009) also added that Kuwait has an open economy. So, if it wants to become IT based, it has firstly ensured that the IT has matched with its economic policies. After the war with Iraq, Kuwait becomes mostly US driven policy holders. The US-Kuwait relation kept constant pressure to open Kuwait’s market to foreign invest and also in information technology sector. The industry of Information technology is a unique one in Kuwait and they are Internet hosts, computer hardware sales, software sales and some of the e-business related functions.
Harris Glynn, (2009) argued that the number of internet hosts in the economy is now capable to link with the network of the other countries of the world. The government in this case takes a liberal views. Thus one host can provide the access to several internet networks. The recent collapse of oil price keep barrier to increase the IT spending in Kuwait. But the policies are making the country to be a lucrative market for IT business. In 2008, the Kuwait cabinet approved a bill named CAIT (Central agency for information Technology). The e-government programs and the budget are influenced crucially by CAIT. CAIT2 drives to build the IT industry in a meaningful way.
The computer sales of the country are mainly of notebooks and Desktop computers of globally famous brands. The recent computer hardware sale of Kuwait makes it the third largest market of computer hardware. In case of software, the increasing regional competition and liberal policies of trade worked as a barrier. But the Business software association (BSA) estimated that the paired software rate is 60%. The most recent initiative of the government is to use broadband access. Kuwait’s ministry of communication recently assigns Alcatel to provide a gigabyte passive optical network. Now, Kuwait has a policy to accept the IT sector as a useful one. Their e-readiness is a success its open IT policy.
Standardisation of Information Technology by Accounting Professionals
Shepherd, John, (2008) addressed that globalisation emphasises on the borderless economic activities and the accounting profession is also accelerated this view. The accounting professionals are trying to standardised the Information technology in a manner which is suitable for them. Both the accounting professionals and the accounting educationalists are trying to increase the capabilities and skills of the accountants.
Besides, the globalisation argues to make some common pattern for the all accountants worldwide. For this, International accounting standards, International standards of auditing, IFRS and many accounting standards are designed to help a common function of accounting learning. The accounting standards are acting as the driver to direct the professional and learners of accounting in a suitable and a practical way.
These standardisations results in some ultimate outcome. Firstly, it provides flexibility in the work of the accountants and the learners of accounting. The easiness comes to maintain some common tasks. Then, these standards give accounting a cosmopolitan nature. All over the word, all accountants use same way to keep financial records and to show the balance. After that, accountant of one country can easily get access to another country as because the same standards are practiced by him earlier. Finally, the accounting professionals use these standards as a way to compare one firm’s financial condition to another, whether it is within the same country or outside the country.
The accounting professionals thus try to standardise the IT to match these standards with the web based accounting practice. KPMG Accounting advisory service states that the accounting software(s) use the standards as a parameter and thus shape the information technology. In different countries, accounting professionals create their own standards which are suitable for their country and also matched with international standards. In Kuwait, the accounting professionals also shape the information technology to bring flexibility in their accounting standards.
Popular Software Used in Kuwait
There are some popular software(s), like ERP3, CAL, EQL4 and many more. Some of them are used in Kuwait, discussed in below:
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
CAL (Computer Assistance Learning) Software Code Review (2002) presented that the Enterprise resource planning is used mainly for the advancement of the enterprise management. An enterprise’s resources are of various types. These various types of resources must be based on integrated information of the highest level of system of utilising the optimum level of enterprise’s resource. Implementation of ERP is a key issue. These issues are some of the maintenance and functionality issues such as troubleshooting of a new business process, want of new report in any time, managing interfaces, dealing with scale, quick and effective apply, assistance to the users, performance maintaining and security.
CAL Software Code Review (2002) also addressed that there is a key knowledge related issue in ERP. The implementation of ERP is basically knowledge driven. There are two types of this knowledge based implementation such as explicit knowledge and tacit knowledge. But there are some success factors also. These are:
- At first focus must be upon the process and requirement of the business
- Achievement of a good return on investment of ERP
- High degree of importance on project management and resource planning
- Highly committed executives
- Plan up front
- Frequent effective training schedule and change over all level of management
- Clear idea regarding the need or implementing ERP
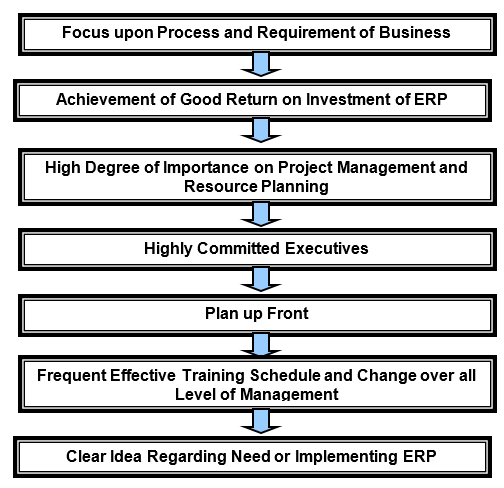
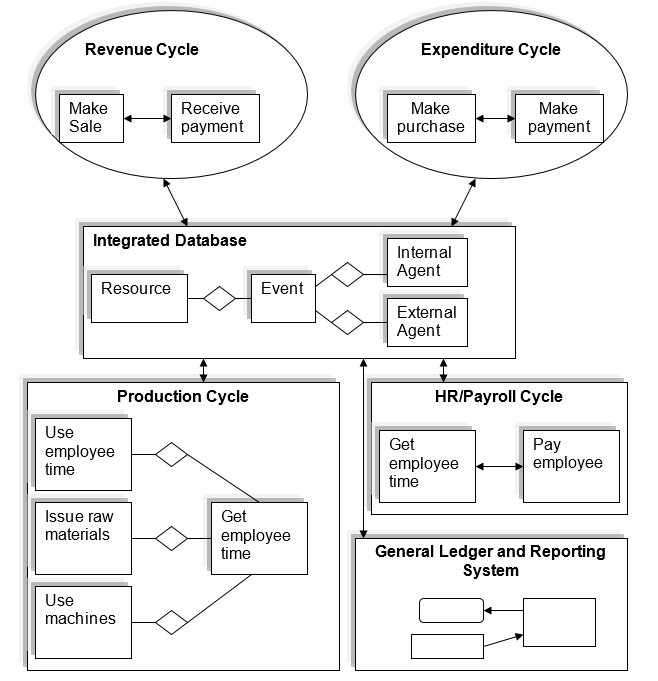
There are many benefits of using ERP. It reduce the cost, cycle time, financial close cycle, inventory level and improve revenue, better logistic use, cash management, interaction with suppliers, timely delivery, interaction with customers, order cycle and IT infrastructure capability.
Besides, there are some risks also. ERP may cause boom of cost, conservation of trained people, higher level of organisational change, reduced user acceptance and loss of control over the total software system.
CAL (Computer Assistance Learning)
Jayaraman, B. & Gupta, G., (2009) mentioned that CAL (Computer Assistance Learning) is documentation and code related software. There are various types of software(s) such as, CalDigi, CalDigiAlg, CalCluster, CalClustersAlg, CalXtalRecData, CalXtalRecAlg and many more. In case of documentation, it is used to make a summary of a document. But CAL codes are needed to be updated frequently. Modification must be implemented and constant development of documentation is a key issue.
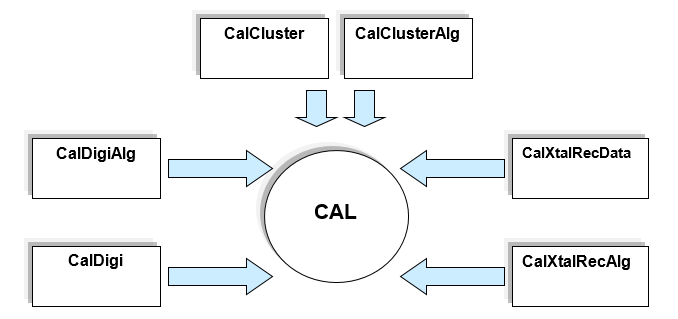
IQMS, (2009) emplasised that to make CAL as a successful tool, self imposed teams must be designed. They must use the correct geometry to correct the coefficients of the algorithm. Another task is to implement calibration. New designed algorithm must be done through cluster search, minimum energy correction and corrections of position. The documentation and program tools have to be designed to optimise and o frequent possible changes. To implement CAL segmentation must be matched with plan. Initiatives are essential to direct the fit and to determine these.
CAL is a way to deliver an integrated business system offered to the customers. But its ultimate use is in the B2B problem solution. But as because the firm’s ultimate goal is to maximise profit, CAL has to be designed in a low cost featured manners.
EQL (Epistemic Query Language)
Bossong, Julian. (2009) reviewed that EQL stands for Epistemic Query Language which is one kind of general purpose language which have the combination of functional capabilities and logical language of programming. In EQL the rules are conditional and blueprint directed. Here the conditions are directed in combination of equations. The blueprint is made of data constructors and core values. Equation solving is the basic computational concept in EQL. The major features, the non-determinism, overdue assessment of primitives and rational variables are important aspects of EQL. Mostly, assemble time gratifying of equations; run time equation hold-up and final equation optimization are the major features of EQL.
EQL language is treated as a driver in language of prototype system description. EQL language can be transformed easily in any other programming languages such as C or C++ programming language. Here many types of timing analysis tools used to acquire implementation of time related information.
EQL is the presentation of formal semantics of a fresh language. Mainly this is used for primary level of functional order and key logical programming. This equation programming software offers almost complete solution and creates the possibility to refinement. In primary level of functional order, EQL is used as a querying language. Many of the firms worldwide faced problems with querying. Again, many of them have lack of complete information and creating information database. Here the feature of equality and a one operator in the model helps to simplify problems. Many research found that, EQL is much appropriate in case of query related problems.
In case of the educators, these accounting software are being used as a primary tool to introduce the learners with the different accounting techniques. In the class room educators use these software as an easy way to convey their sayings along with these software and their experiences. This process has happened because when they try to deliver a specific subject the specific software manage the structure of that subject, help to create the effective environment for the delivery of that matter and match the framework with the basic lessons of the educators.
In most of the cases the learners enjoyed to using of these software. They enjoyed it because of two reasons. Firstly, the use of technology seems it to become effective whenever they are applied in the professional life of the learners. Secondly, this software makes an easy and formal way to acquire accounting subjects. Thus, students are feeling that the integration of IT and accounting bring an additional scope in the fields of accounting like tax or audit. This is in the way that, the integration of IT and accounting makes it easy to maintain standards accordingly, apply accounting theories and formulas effectively and to offer the higher level of accuracy. Students can now get these benefits for the presence of IT along with the lectures of the educators.
Concept of accounting
Accounting is a systematic process that accumulates financial information and communicates through this with the managers of the organisation for production decision making and for financial decision making investors and creditors. As well as basic academic learning, accounting program has also taught about adequate professional certification. Some professional certificate accounting courses are- CPA (Certified Public Accountant), CA (Chartered Accountant), CMA (Certified Management Accountant), CIA (Certified Internal Auditor) etc.
Objectives of accounting department in Kuwait
Proper execution of accounting missions following are the common objective taken by almost all colleges and universities of Kuwait-
- Considering the working atmosphere academic institutes are focused on- professional competency improvement, ethics, values and attitudes, monitoring the globalisation effects and its fast movement, improvement in technology and diversity management. Coordinate among features are the core theme to teaching and learning curriculum.
- Universities have responsibilities to the society. So, their study programs have to understand and recognise both the professional communities and local academic communities to promote the tasks of public, private and social responsibilities.
- Develop the contribution in society psychology students have to prepare- working in a group or in a team, capable in articulate communication, problem analysis and solution and efficient technology utilisation.
- Finally, in the course of professional and academic research and through join into any profession skill of the faculty members would be progress.
Kuwait Universities and Colleges who offer Accounting Degree
All over the world teaching of the accounting degree requires a high and efficient qualification both the teachers and the institutes. Some of the most renowned universities and colleges of the Kuwait those offer accounting degree are- College of Business Administration under Kuwait University, the American University of the Kuwait, the Gulf University for Science and Technology, the American University of the Middle East, the Australian College of Kuwait, the Public Authority for Applied Education and Training etc.
Four universities
Kuwait University
In 1967, Kuwait University established its business administration department that offers multiple courses as follow. These courses are available both for the bachelor degree and the masters program.
- Finance
- Accounting
- Economics
- Marketing
- Management science
- Management Information System (MIS) and
- Public administration
The Mission of Kuwait University is: following are the statements of the mission of Kuwait University-
- Scientific and cultural heritage of the country turn dynamic
- Community service participation
- In order to boost productivity and efficiency utilise the human resources
- Among the Arab regions both local and global institutions extend and improve both the cultural and scientific ties
Following are the prime issues those build the aim of the University-
- Benefited the students through the fruits of knowledge
- Culture
- Civilization
- Creation of intellectual and heritage
- Cultivate the human resources efficiently
- Improve the productivity of the human resources
- Improve both the social and cultural level of the people
- Involve and contribute self custom in the development of the society
Sequentially and systematically execution of these forces Kuwait University made a prominent image of them both in locality and in international market.
With the flourish of the business administration in Kuwait, they pay more attention in forming of the above departments in their university. CBA (College of Business Administration) of the Kuwait University has officially started their international AACSB (Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business). CBA of the Kuwait University is stayed Shuwaikh Campus along with abundant facilities both for professional and academic researchers.
Hospitability provides by the department infrastructure nursing the dream of the future business leader of a student. As par essential feature of the third millennium CBA of the Kuwait University focus mostly on the IT improvements for all the departments continues in the CBA. Digital computing in the 21st century is a great challenge for CBA (College of Business Administration). In view of this challenge CBA sketch their vision, mission, goal and objectives in the course of following road map-
- For easier communication and connect the faculty, students and staffs in the same circle establish indispensable IT infrastructure.
- CBA already has finished their new campus network.
- So as to access the WWW (World Wide Web) they continue the connectivity and speed of the Internet. Application of this networking involves in- e-mail (electronic mail), electronic global directory among the student, faculty and staffs.
- For all level of users, CBA already has executed the Internet Services that attached by the global University connectivity.
- For both of academic and administrative IT users there have adequate training and technical services and consultation conveniences.
- Another significant aim is that CBA is committed to standardize their information architecture.
- All colleges under the Kuwait University are managed effectively and efficiently in the course of their networking and College computing.
- Their networking atmosphere is secured for all categories of IT users.
Accounting department in CBA of Kuwait University
In the area of auditing and accounting prime mission of the Accounting Department is to nursing academic and professional education. With the purpose of achieve this, their teaching curriculum continue their effort in the class duration and also at the end of the classes. Under the program of study students of the accounting department get enough capability in making decision and utilising IT infrastructures properly in practice.
Another significant point considered by the authority of CBA is that- “focus on essential views relates to human and profession those build an elegant professional career.” Regarding all of these, both in public and private areas student of the accounting department could integrate their highly innovated thoughts. Recommended courses of the accounting department is- principle of accounting, financial accounting, cost and inventory management accounting, accounting information system (AIS), accounting reporting and auditing. All of these courses are taught with the aid of IT (Information Technology) infrastructure. In addition, for every 10 student there have one PC.
The American University of Kuwait (AUK)
For higher education in liberal arts the American University of Kuwait (AUK) has contained following features-
- Independency
- Privately owned
- Equal opportunity
- Co-education
The American model of the higher learning is the tool to execute their education, culture, outline of the administration and also in evaluating methods and standards of their services. All of the courses they endow with are instructed by English language. In 2003, with the support of an Amiri Decree the AUK was established and two times accredited in 2006 and in 2008 respectively. All of these processes have been processed by the Council for Private Universities under Ministry of higher Education State of Kuwait.
IT infrastructure and the Accounting department: In order to execute the University community with the aid of computing infrastructure and services the AUK provide their accounting education services. Application of IT is not for only the students but also for the faculty and staffs. The AUK campus adopts the latest state-of the-art technology infrastructure in the period of establishment. In addition, 3000 network points and wireless coverage are connected with the optical fiber backbone. The network points involves in following dynamics-
- Firewalls
- Server for authentication and auditing and
- Intrusion detection system
Moreover, a complete IP along with a voice mail competency communication process of the AUK has also an efficient and strong server including following vibrant-
- High end specifications
- Effective and reliable operation guarantee
- Operate a secure storage atmosphere
- Redundant technology
A significant issue the AUK’s has been also provides a set of major enterprise solutions as following table. Not only for the learning and teaching purpose the AUK has also provided IT support for the research purpose.
The Gulf University for Science and Technology (GUST)
During July, 2002 Executive Office of the Private Universities approved GUST charter and throughout this GUST has started its journey as first private university of Kuwait. From the inception period, GUST enrolled about 1500 students and their campus stayed at Hawally. In 2002, Ministry of Higher Education was also approved their charter by the Amiri Decree of 156.
History: Owner of the GUST is Eyas Company SAK. Investors of the GUST are-
- Excellent Education Foundation
- Aref Investment Group
- Kuwait Establishment for educational Services
- Kuwait Awqaf Foundation and
- Public Institution for Social Security
Owner of the GUST have got their license to operate this university in 2000 along with a number of colleges, high schools and vocational training. Since the starting of the university GUST offer semesters for fall, spring and summer session.
GUST Vision: Vision of the GUST stands on following three grounds-
- American style establishment
- Accredited and
- Degree
Be more focused on students positive attitude educational process of the GUST emphasize on-
- Excellence in academic custom
- Draw the education base on a liberal platform
- Considering students succession forces sketch all of the academic programs
- Adopt ad utilise advance information technology (IT)
Match the steps with the new millennium GUST train their students so that they become an efficient leader as well as a creative thinker. Other focusing points of the GUST for their students’ efficiency creation are as bellow-
- Make the learning atmosphere to understand the alteration of the world
- Continuous improve the process of the information development
- In order to adopt diverse culture abstraction of skills
- Develop basic values for the development of the Kuwait and also fabrication of a strong inner sense
- In the learning atmosphere of the GUST they grasp a mixture of Western and Kuwait Islamic culture
- Prior on individual learning acceptability and requirements
- Not only for the academic performances GUST provide such facilities so that a student can get efficiency in their professional life
- “State of the art” is the approach through which they cultivate their students for the 21st century and focus on individual learning requirement.
Mission statement of the IT Center: the Gulf University of Science and Technology architect their IT Center (ITC) by means of the mission of as long as both communication and computing infrastructure at once. Feature of the Gulf ITC are- planning support, continuous improvement, conveniences integration and employment, learning oriented infrastructure and services, well defined administrative goals, teaching and research equipment in an adequate form.
Objectives of the Gulf ITC: Following are the objectives of Gulf ITC accounting department as well as other-
- Gulf ITC is always continuing their academic and administrative programs with the aid of reliable and fast technological infrastructure.
- Consider those categories of approaches so that they could provide efficient and effective IT services.
- Library database collections are available for faculty and all the students to access.
- Teaching and learning both are technology oriented.
- For easy communication among the faculty, student and the staffs there have sufficient technological support like- receive and sending e-mail, download books and necessary files, made academic papers, view academic results etc.
- GUST (Gulf University of Science and Technology) also have the appearance on web.
- For both of academic and administrative support ITC featured with- continuous improvement and maintaining, highly efficient and effective, safe, secure and reliable guarantee, innovative and versatile characterized information system.
The American university of the Middle East
Another renowned private university in Kuwait is – the American University of the Middle East (AUM). During 2005, by the Amiri Decree no. 304 the AUM issued their license both from the Kuwaiti Private Universities Council (PUC) under the Ministry of Higher Education. In addition, as an independent institution, AUM has offered its own decree as well as licensed and authorised.
The AUM has focused more on versatile study approach rather than an individual career path involving both theoretical and general education. 4 years graduation courses of the business college’s are- finance, accounting, MIS (Management Information System), industrial management, HRM (Human Resource Management) and organizational leadership and supervision.
Accounting department and IT: With the aid of lean IT staff the AUM has nine staffs and among them one is director and the total number of IT users are almost 1500. Eight staffs out of nine are grouped into two forms-one is worked for system development and another execute the technical operations and support system. Though compare to the number of stuff is too low than its users, the authority of the AUM has took initiative to adopt fully migrating to Banner 7.3 for the student of business college specially for the accounting department.
Two two-year colleges
The Australian College of Kuwait
In Kuwait, for the first time the Australian College of Kuwait provide vocational education college as private program. A student of ACK got the most qualified facilities in this university such as- international stuff, sound vocational courses etc. Other than these there have the opportunity to seek attitudes, skills, knowledge both for t5hev academic and professional life.
The Department of Business: Besides bachelor degree in business administration, following are the three vocational programs that a student can get from here-
- Diploma of management
- Diploma of marketing
- Diploma of Business (Hospitality)
Above courses are designed through a four semester program those evaluate and improve a student’s attitude to learn, skills and knowledge. All of these courses are for entry level position of a business administration. After end of the program, students of the marketing could join themselves as a marketing consultant in a bank or retail business. On the other hand, against limited seat diploma of business (hospitability) is offered. In following chart, mention all the areas that a student need to learn-
Workplace supervisors and the ACK instructors supervise all the learning modules and attached IT infrastructures at the best of their effort along with a hospitability atmosphere. As for example- they provide course links through an Adobe Acrobat PDF Format. Students have both the opportunities either just read the document and save that through download.
Practical Training: Almost all the courses provide by the ACK are designed and practice through Competency Based Learning. At the beginning of each semester this learning method alters from each other due to the course diversification.
The Business Plan: In 3rd and 4th semester business plan program for practical oriented and make the students innovative and dynamic following are the effective initiative taken by the ACK-
- Choose a business idea
- Evaluate the effective opportunities that would be launched in Kuwait or abroad as the host firm of Kuwait
- Analyze and evaluate marketing scopes for the chosen business
- Analyze the market research approach for the target business
- Sketch a effective business plan for the preferable business
- Draw a HRM (Human Resource Management) functions like- recruitment, employee benefits, selection etc.
- Build a operating strategy for all the level of the proposed business
- Outlined a marketing communication or the marketing channels for the proposed business plan
At the end of the above steps supervisors of the ACK would chose seven best business proposals and these would presented to a panel of industry leaders. Panel is featured as follow-
- HR managers
- A banking representative
- Representative from manufacturing and hospitability area
- Expert from finance and investment
Task of this panel is to guide the students and encouraging feedback to motivate them.
Computer Labs: The ACK campus has composed of three annex building long with eight computer laboratories. Major equipment of the computer lab is-
- Latest hardware
- Software
- Multimedia infrastructure
Each of the laboratories also surrounded through following features-
- By self-paced tuition e-learning is well capable and featured
- Have both the upgraded business and management software
- Adequately capable with multimedia accessories
- For the engineering and graphic design courses there have CAD (Computer Aided Design)
- Three of the eight labs featured through oil and gas simulation software at high end
- 3D graphic design software for solid works
The Public Authority for Applied Education & Training
In December 28, 1982 PAAET (Public Authority for Applied Education and Training) was established in Kuwait with the aim of following reasons-
- For the industrial and economic development of the country cultivate the manpower
- Develop the manpower being upgrade them so that they could successfully accept the challenges of the 21st century
This institution is foundered by the Law no 63. Due to exploration of the oil initiation as well as production and export in Kuwait education ministry felt necessity of applied education. Especially for the oil industry Kuwait at the beginning of its establishment in 1950, started to build manpower development training centers. At the end of establishing sufficient basic educational institution, education ministry pay attention in building skilled manpower development training centers as well as the other ministries have build training centers in their own area of activities. Therefore, it can be said that PAAET is established both for the education and training of the manpower. PAAET is based through following four colleges-
- College of basic education
- College of business studies
- College of technological studies
- College of health sciences
Training institutes established and controlled by PAAET are as bellow-
- Telecommunication and navigation institute
- Electricity and water institution
- The industrial training institute
College of Business Studies under PAEET
Formal term of the PAAET’s college of business studies is- “Business Institute”. Academic year of this institute was stated in 1986 though the PAAET has started its journey in 1975.
Objectives: Objectives of the PAAET is as bellow-
- In all departments of the government like- finance, administration, commercial areas, both private and public corporate areas prepare and supply skilled manpower
- Prepare the unemployed manpower for involve themselves in business specialization
- Not in quality but increase them in quantity as the requirement of work specimen
Specializations: program provide by the Business institute are as follow-
- Materials management
- Cooperatives management
- Postal administration
- Administration
- Secretarial
- Medical secretarial
- Accounting
- Banking and insurance
- Computer
Study System: The entire aforesaid program composed of four semesters followed by a credit system. At the time of course continuation students needs to complete 68 credits and in each semester 17 credits. Duration of each semester is 14 weeks and following are the factors entire into each semester-
- Registration
- Attendance of the exams at the end of the semester
- Avoid time set and prefer guidance
Field training: Field training is essential for each and every continuing program under PAAET. Students of the PAAET have an opportunity to enjoy an intensive summer semester that lasts for 7 weeks. Aim of field program are-
- Develop the students so that they could gather applied knowledge in their studying
- Skilled them both in theoretical and practical field
Concept of e-learning: The term e-learning defines the form of teaching that executed through a network utilisation regarding to delivery, facilitation or interaction. Modes of network are as below-
- The Internet
- Local area Network of the university
- Corporate Wide Area Network
Utilisation of these modes e-learning would be in following one of the ways-
- Individual learning
- Taught as a part of a class
- Utilise a computer for guide or instruct
Recent most of the Kuwaiti universities facilitate both the Internet and the university network for networking and e-learning. In addition, universities facilitate not only in class room but also any time, anywhere students have the opportunity to connect Internet to their computer.
Reasons for providing e-learning in accounting department
In this information era, there is no doubt that worlds become more competitive and smart. Regarding this circumstance besides affection of technology and information networking it’s difficult for anybody to be isolated towards the global village. For an accounting department following are the facts to attach with IT (Information Technology).
- Quick learning is the prime quality to be developed and innovated. In all categories of industries as well as in education, new developments need to adopt as fast as one can. Thus, the game of innovation through learning would be occurred effectively and efficiently.
- Today e-learning is the most widely used approach in AIS (Accounting Information System) learning. Hopefully, in recent next few years that would be broader than now.
- Most of the college, institute and universities make opportunities for their students be acquainted and master in e-learning at the beginning of their student life and hold this for a long time in future.
- Furthermore, e-learning is an approach that moves towards to self-motivation and independence. Regarding this it helps those who eager to continue seek knowledge by own self.
- At last for both of the learning and teaching would be effective and highly satisfied if in the classroom have adequate advance educational technology.
Required quality of the e-learning facilities
For AIS required e-learning facilities have to be rich in quality and also be recognised by the international benchmarks. Required high quality of e-learning have to ensure following atmosphere-
- Teaching materials should be same in category and repetition of these materials have to ensure that not loosing of any element.
- All of the students should be facilitated by the same categories of teaching materials and for this they don’t need to be in the same session’s classroom.
- Last requirement is that all of the online courses have to be modified and upgraded as par requirement of the student and alteration of the worldwide information and technology.
Scope of AIS implementation in Kuwait
Kuwait has the fourth largest crude oil reservoir of the world. Due to high volatility of oil prices, the country’ economy is also much volatile. Withholding the fact, the country has been doing well in its information technology (IT) infrastructure developments. It has also proven its strength to implement information and communication technology (ICT) throughout the country. Though ICT has not been developed well enough (let alone e-business), the country has further scopes to implement accounting information system (AIS) in higher education which are as follows:
- High Per Capita Income and Disposable Income: Kuwait is a member of High Income Oil Exporting Countries (HIDOECs) so it has a very high per capita income. For instance, in 1987, the per capita GNP of Kuwait was around 14,610 US dollar. It was the second-highest among the Gulf region HIDOECs countries. It was $30,630 in 2006, which turned $33,391 at present time. Therefore, it is clear that the country has a trend of rise in per capita income. So, the country has also a relative degree of growth in its people disposable income. Since incorporation of AIS education would increase the cost of accounting education, thereby the country is ready to welcome the implementation of AIS in higher education. Moreover, when people see rise in their income, they usually spend more on education. In both senses, there are good signs for such an implementation.
- Emergence and influence of Multinational Corporations (MNCs): Yapa and Wijewardena (1995) argued that the appearance of MNC with severance of administration from its possession made it necessary to initiate the usage of contemporary accounting tactics to have power over the possessions and to apply them effectively (doing right things) and efficiently (doing things right). That means the inauguration of MNCs in Kuwait has initiated the accounting education which has shaped the curriculum. Yapa and Wijewardena (1995) further argued that the major sources of force on accounting systems and schooling in Kuwait were the multinational corporations, multinational and international accounting institutions and professionals body and émigré accountants. These trends are also present since the oil boom continues; therefore, implementation of AIS has a bright future.
- IT adoption made by some educational institutions: though e-learning or e-business has not been well established in the country due to some limitations, there are some educational institutions which offering online learning facilities and IT incorporated accounting education. For instance, The Gulf University for Science and Technology enabled itself with IT and is able to render higher education in AIS.
- Rapid technological development: various technological developments are available throughout the country. Both the government and the private sectors are rapidly investing in the IT sector. For example, the mobile network system of the country is 3G enabled. The country had gigabit bandwidth of its own. Both wireless and wired means of internet communication are highly available in all area of Kuwait. Since the AIS implementation requires high demand of the technological development of the market, it also seek educational infrastructure with expertise by which the country Kuwait can easily implement AIS in higher education.
- The Oil boom: the oil boom in the HIDOECs took place after 1970s. Yapa and Wijewardena (1995) stated that prior to that period of oil boom, Kuwaiti people were engaged in traditional works and therefore they did not need to know accounting. However, the business environment of the country has completely been changed later on the oil price hike. They further argued that the accounting procedures in the HIDOECs are still changing and working since the oil boom. The giant financial resources of these countries are also the reasons behind the alteration of accounting systems. However, since the income of Kuwait from its major sector is still booming it also has the capacity of implementing AIS in the country. Furthermore, Kuwait can manage to pay for costly modern computers, overseas specialists and other necessary components required for this rapid revolution.
- Government’s direct investment in IT sector: as it is implied earlier that the IT sector of the country is the most blessed sector by the government’s help. The government has been investing in the sector as a thrash sector. Moreover, to enhance IT education in Kuwait, the government issued its propaganda and furthermore, has taken a project of implementing e-learning. Different types of IT literacy programs are also being run by the government’s agency and by the Kuwaiti Central Agency for IT. All are the signs of government’s willingness to implement AIS in higher education.
Barriers of AIS implementation in Kuwait
Though the Kuwaiti government has taken IT sector as a thrash sector and they are continuously providing necessary helps and investments but still there exists various barriers. Since, the IT sector the basic of AIS is in problem, the AIS also lagged behind by the following barriers:
- Lack of legal base: the emergence of AIS would require a high level of inter industry and inter organisation data sharing. Furthermore, there should have some laws and regulations for keeping accounting information accurately as this information is valuable and very urgent for strategic business decision. National Profile of the Information Society in Kuwait (2007) argued that Kuwait requires to have related laws to govern electronic transaction on the national level and on a diverse collaboration. There was a drafted law in 2007 on electronic transactions for the use of giving definition of electronic files, determining the files, files’ identification and signatures, along with protection of electronic data and their privacy. In 1999, the country had passed a law on intellectual property to protect software piracy, plagiarism etc. Even so, the adoption of AIS requires more legal supports than available. Furthermore, implementation of AIS in higher education also need government regulations and laws related to curriculum. These inabilities make the implementation lagged behind before its adoption.
- Bilingual effect: the people of the country are Arabic spoken. But the higher education and IT literacy are usually of English spoken. Though the students will easily adopt the AIS in company but the organisations might not easily get on AIS in this respect. Therefore, bilingual effect will be enhanced among the accountant professionals. Moreover, to render AIS education for the mass people, Kuwait need to adopt Arabic IT literacy that is time consuming and a tough job to do. Portaneri and Amara (1996) stated that in 1985, Arab Standards and Metrology Organisation (ASMO) and the Arabization Coordination Bureau jointly started working on Arabic computer standardized code (ASMO-449). However, because of political and budgetary problems, the code has not been updated and therefore, there are explosions of various new codes. Thus, bilingual problems remain same as earlier days.
- Unwillingness of students: since the accounting education is completely new in the HIDOECs, therefore, the students are regarded as unwilling to be educated in the education system. Unless the multinational or national companies show their interest in recruiting accountants from Kuwait, the students would not become willing to have AIS education. Yapa and Wijewardena (1995) argued that the students of HIDOECs are not willing to have education on accounting and finance which it is also true for Kuwait.
- Lack of expertise in the field: the country has been lagged by itself due to lack of expertise in accounting and IT, let alone AIS. Therefore, where expertise in IT is still not up to the mark thereby implementation of its sub part is also a difficult job. Moreover, due to the lack of expertise in the field the MNCs and national corporations use accountant professionals from overseas. Since these corporations do not seem to patronage the AIS implementation, there remains some vulnerability about the implementation of AIS. Moreover, to enhance expertise in AIS, the government needs to have a multi stage and a very time consuming training effort.
- Less number of business institutions: there are very few institutions those provide higher education in accounting. Therefore, implementing AIS throughout the country is not possible. Moreover, since there are a few business schools for accounting education, the competition between them to incorporate a new technology seems less. Thus, these institutions may not try to implement AIS in higher accounting education because such an implementation would cost a substantial amount of money.
- Social supports: Palloff and Pratt (1999) stated that the requirement for social support is an aim that roughly authentic to the content-orientated aims for the technology literacy. The social support of the educating process was vilified in how students joined with the technology literacy. For having big power distance in the society, students of this country may not get such a support from their instructors. Moreover, the students those require more support on learning may be deprived because of less number of instructors.
- Bureaucracy: Kuwait is highly under pressure of bureaucracy from the rest of the world. Since the implementation of a new curriculum in any country requires a high level of paper works and approvals from different secretariats, therefore, the implementation of AIS in all part of Kuwait can not be made within few days. Thus, the corporations do their business in Kuwait will recruit from outside of the country.
- Economy’s dependence on single sector: Kuwaiti economy mostly has been depending on oil sector, there are too many government initiatives to flourish other sectors that possibly would contribute the national economy. In nineties the government has introduced the Offset Programme by which investment to and from Kuwait has been encouraged. So many multinational companies derived their operation in Kuwait including educational institutes. Thus there is an insisting requirement to design and put into practice a wide-ranging action plan for global standard accounting curriculum strengthening and upgrading the traditional accounting education. As long as the country is depending on the only oil sector, there is a high uncertainty of the industry’s boom. Therefore, pursuing people to adopt the AIS may fail. On the other hand, non oil sectors have very significantly lower employment opportunities; thereby, the implementation of AIS in higher accounting education is in question mark.
Recommendations
The leaders of accounting profession and academics of Kuwait alleged that accounting education is mandatory to explore with an extensive assortment of knowledge and analytical capabilities with the modern IT application. On the other hand, accounting programs through the Kuwaiti Universities have widely emphasised IT training with standard of IAESB rather then CPA certification preparation. IFAC (2009) stated that IAESB has developed the regulation in order to progress the standards for accounting education all over the world that aimed achieve an unified aspirations through out the globe.
Kuwait as a pioneer of Gulf region IT, the higher educational institutes should be recommended for the vital rudiments of accreditation of accounting curriculum with realistic experience as well as assessment of professional competence with IT capabilities.
This recommendation would go for the stakeholders of IT integration in Accounting Education in higher educational practice of Kuwait. The Kuwaiti government, higher education institutes, educators, students and social groups interested in IT integration in accounting would be significantly benefited from this recommendation to up to date the higher education systems. With this research this author has identified that the AIS have a moment ago restructured very a few of the faculty committees of Kuwaiti higher educational institutes, but not allover the universities. But a large number of institutes not yet run accounting courses where IT integration is a fantasy, thus the paper would recommend for-
- The education Ministry of Kuwait would be needed to assimilate a separate moderator team or faculty committee to compulsory incorporation of accounting education with IT integrated manner starting for undergraduate program to master’s, as well as PhD level complying with the educational standards identified by IFAC. This moderator team would look after the progress and gradual development and change the existing faculty governance structure of accounting education to allow full-time educators nourishing the appropriate respond from the institutes.
- All the Kuwaiti Universities in AIS department needed to have a senior faculty member on the chair who would oversee the accounting curriculum for undergraduate and post graduate level. It is predictable that such a senior faculty member would be capable to increase the involvement IT in accounting education in the course of his amplified charisma in accounting teaching. All the other faculty members would report their progress and dilemmas to the chair to resolve the major obstacles in IT incorporation in accounting education.
- Kuwaiti Universities has been encouraged to introduce AIS courses both in part time and full time with distance learning facilities with most modern IT tools. Universities would interchange their ideas and information along with the teaching personnel all over the world which would be a vital development for higher education in accounting and promotes scope of further research. The Kuwaiti accounting educators of higher-education institutes are encouraged to their careers by participating in international conferences, seminars, and higher researches and allowed to travel overseas without any hindrance and facilitated to exercise speedy Internet connectivity for video conferencing as well as exchanging views.
- It has been recommended to propagate more widely to create awareness among the people about the necessity of human resource skilled with AIS in modern Kuwaiti society especially with look upon to the student interactions and their career advising in global context. This social awareness would also enhance to the quick IT integration in accounting education from the undergraduate level.
To make further recommendation for integrate IT in accounting education of higher educational institute of Kuwait, this paper of would go to recommend to addressing educational standards of IFAC with amalgamation on self-assessment in evaluating ethical sensitivity, local legislation, academic standards, real fife judgment and decision-making. Moreover the Kuwaiti local values from the traditional practice of higher educational institutes to which people are more interested should be incorporated with the IT based accounting education. There should be online scopes and opportunity for the students to judge their capabilities by means of self assessment.
Conclusion
Information technology has shaped the modern education system in a new dimension by means of easy communication, data process, data storage and data presentation and the learners and academia specialists have driven voraciously to amalgamate it in the education system. King, M. (2008) addressed that the Kuwaiti IT market has been flourished with a volume of US$ 539 million in 2008 and targeted to jump US$ 833 million in 2012 under the global recessionary economy, engorged oil revenues and public spending. The significance of the Kuwait IT market is that, with US$ 24000 per capita income it is the third largest IT market in the gulf region. Thus it is quite natural to influence the education system of Kuwait and the Universities are ready to face the challenge of IT incorporation in their education system.
Al-Essa, A. A. (2007) stated that the aim of the Kuwaiti education system is to endow learners with the knowledge and skills those would be helpful for them to contribute the society as skilled professional. Within the Gulf region, Kuwait is the country that spends lower of its GDP for education which is 13% of public expenditure and a large part set off to the vocational and tertiary education including accounting education. The practitioners and academics of Kuwait have condemned the existing accounting education due to backward sketch, lack of persuading technological development and constricted entrants and argued for quick changing with expanding profession and information technology integration.
This paper would reviews the prospect and predicament of IT integration in accounting education in the State of Kuwait and mark out the beginnings of this initiative in a broader and more noninterventionists accounting education with support and inception of the Kuwaiti universities programs on information technology incorporation for a better outcome from accounting education around the country. It would also present the trend of Kuwaiti corporate houses to recruiting accountants with IT know how as well as accounting information system, distinction of their performance and practice with old professionals and argue to draw a conclusion that would facilitate scope of further research.
Bibliography
Accaglobal, Professional development trends analysis. Web.
Accountemps, Demand for Accounting and Finance Professionals Remains Strong. Web.
Anderson, J. et al 2002, Information and Communication Technology in Education: A Curriculum for Schools, Division of Higher Education, UNESCO, Paris, French. Web.
Association of Chartered Certified Accountants, Survey Finds the Employment Market in Accounting & Finance Sectors Cautious but Steady. Web.
Badenoch & Clark, Who’s in demand in accounting & finance? Web.
Bossong, Julian. Managing ERP Applications for Strategic Advantage. Web.
Calvanese, Diego, et al. EQL-Lite: Effective First-Order Query Processing in Description Logics. Web.
CBA, Department of Accounting: College of Business Administration. Web.
Chayeb Lwana, & Best Peter, The Accounting Information Systems Curriculum: Compliance with IFAC Requirements. Web.
CIty Iloilo, Core Competency Framework for the Accountancy Profession. Web.
College of Business Administration, Department of Accounting. Web.
Cooper Barry, Accountant of the future. Web.
Dr. Louis, Information Technology (IT) Skills and Education for Accountants in the New Millennium. Web.
Deng, Jiangao and Yijie Bian, Constructing the Knowledge Model in ERP. Web.
Emory, CAL Software Code Review Report. Web.
Eshai Mujahid, Information Technology and Accountants’ Education. Web.
Globe University and Minnesota School of Business, The Accounting Job Market is Expanding. Web.
Granlund Markus, On the Interface between Management Accounting and Modern Information Technology – A literature review and some empirical evidence. Web.
Gulf University for Science and Technology, What is E-Learning?. Web.
Gulf University for Science and Technology, Welcome to E-Learning Center of Excellence. Web.
Hadi Mahdi, The Importance of Accounting Information to the Investors in Banking sector: Kuwaiti Evidence. Web.
Harrison David, McPeak David, & Greenberg Sandra, Validating Competencies Underlying a Professional Accounting Credential. Web.
Harris Glynn, Cal Software. Web.
IAESB, Information Technology for Professional Accountants, Proposed International Education Practice Statement 2.1, International Accounting Education Standards Board, Exposure Draft, 2006. Web.
ICDL GCC Foundation, Kuwait Central Agency for IT adopts ICDL digital literacy programs within the government and society. Web.
ICAEW, Using accounting software. Web.
IQMS, Manufacturing ERP software selection demystified: How to evaluate ERP platforms. Web.
Jayaraman, B. & Gupta, G., EQL: the language and its implementation. Web.
Jayaraman, B., Semantics of EQL. Web.
Jones, David and Nona Muldoon, The teleological reason why ICTs limit choice for university learners and learning. Web.
Kennedy Helene, IFAC’s International Accounting Education Standards Board Releases New Practice Guidance on Ethics Education and IT Knowledge Requirements. Web.
King Mike, Kuwait Information Technology Report Q4 2008 – companiesandmarkets.com adds new report. Web.
KPMG, Accounting Advisory Services. Web.
Link recruitment, Accounting Market Trends. Web.
Manoharan, TN., Equipping future accountants. Web.
Ministry of Information, The Public Authority for Applied Education and Training. Web.
Msbcollege, The Accounting Job Market is Expanding. Web.
NZQA, National Qualifications Framework Levels 1–3, Accounting: National Moderator’s Report. Web.
Niece Jennifer, and Cheryl Amantea, The Use Of Professional Portfolios For Accounting Students And Young Accounting Professionals, Journal of College Teaching & Learning, Volume 1, Number 5. Web.
PAAET, The Public Authority for Applied Education & training: College & Institutions. Web.
Palloff Rena M. and Pratt Keith, Building Learning Communities in Cyberspace: Effective Strategies for the Online Classroom (The Jossey-Bass Higher and Adult Education Series), 1st edition, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, 1999, ISBN: 978-0787944605.
Portaneri Franck and Amara Fethi, Arabization of graphical user interfaces, Del Galdo Elisa and Nielsen Jakob (Eds.), International User Interface, John Wiley & Sons. Web.
Press Release.com, The Accounting Job Market Is Robust, Says AccountingCrossing; Job Site Seeks to Increase Job Count to Help Accounting Professionals, 2008. Web.
Romney, Marshall & Steinbart Paul John, The Accounting Information Systems, 9th edition, Pearson Education, ISBN: 81-7808-816-9, 2003.
Saatçıoğlu, Ömür, What Determines User Satisfaction In ERP Projects: Benefits, Dokuz Eylul University. Web.
Shepherd, John, Accounting Learners Impact Public Library Operations. Web.
Skidmore Steve, Information technology in the accounting curriculum. Web.
The Australian College of Kuwait, Programs and Courses Department of Business Studies. Web.
The Australian College of Kuwait, Campus Facilities. Web.
Thompson Anthony, Accounting Adds Up. Web.
Tribunella Thomas, Neely Pamela, & Tribunella Heidi, Academic and Practitioner Interests Regarding Emerging Technologies In Accounting. Web.
United Nations, National Profile of the Information Society in Kuwait. Web.
United Nations, National Profile of the Information Society in Kuwait. Web.
UNESCO, ICT for Accessible, Effective and Efficient Higher Education, © Ron Ashore. Web.
Wessels, PL, Information Technology and the Education of Professional Accountants, University of Stellenbosch, Meditari Accountancy Research Vol. 12 No. 1 2004: 219–234. Web.
Yapa Senarath and Wijewardena Hema, The development of accounting systems and accounting education in high income oil exporting countries: An overview, The University of Wollongong. Web.
Footnotes
- Professional Accounting Software.
- Central Agency for Information Technology.
- Enterprise Resource Planning.
- Epistemic Query Language.