Introduction
A foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to a sale of an interest in a corporation by another company or an investor normally situated outside its borders. It involves a company’s decision to obtain a substantial stake in a foreign nation and purchase it outright to expand its business to a new region. The primary purpose of this report is to choose a multinational company that intends to expand its current operations within Finland. In addition, to describe the organization’s FDI’s opportunity in the selected country, give brief background information of the business environment and analysis of the business scenario.
Below is an Amazon Scout:

The chosen company
The company of my choice is Amazon Inc., a multinational technology organization in America that focuses on cloud computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and digital streaming. The business is one of the leading big five in the United States’ information technology industry, including Apple, Google, Microsoft, and Facebook. Additionally, it is the most valuable, influential, cultural, and economical brand globally (Alassaf et al., 2020). Initially, the organization began as an online retail for books but later expanded to sell video games, electronics, jewelry, software, food, and furniture. Moreover, Amazon is the largest internet business by revenue internationally and provides AI assistants and live streaming platforms.
The FDI opportunity that Amazon is looking for in Finland
The Amazon Company wants to establish a Scout Development Center in Helsinki in Finland to focus on autonomous delivery technology. The technology center will conduct research and survey of the organization’s fully electric independent delivery service in America (Oitzman, 2021). Its scout equipment is inherently secure, small in size, and rolls along sidewalks at a walking pace. The team deployed in Finland will be tasked with developing 3D software to simulate the complexity of real-life and assure Scout can safely navigate barriers while making deliveries.
The decision aims to establish philanthropic relations, create job opportunities, and minimize the effects of climate change on the generations to come by creating a sustainable business. Amazon is expanding its activities to this nation to create quality jobs for thousands of jobless and invest billions in local economies, increasing its profit margins. The choice of my company is motivated by the fact that Amazon does not have a receiving center in Finland, and establishing one will lower its shipping costs. The organization deals with huge volumes of products. These centers will facilitate the smooth distribution of orders to different companies.
Background Information on Amazon
Size of the company
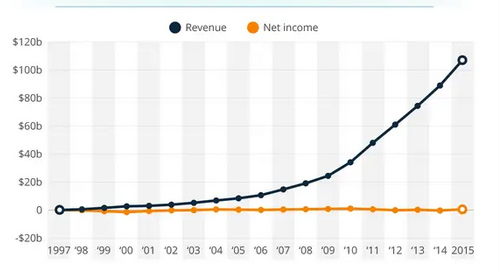
In 2021, Amazon Inc.’s net income reduced to $3.2 billion in the third quarter compared to $6.3 billion in 2020, as labor expenses and other costs declined for the period ending 30th Sept 2021. In addition, the firm is said to have increased the number of workers by 30.5%, from about 1.125 million to nearly 1.46 annually (Conley, 2021). Furthermore, its fulfillment expenses were up 25.8% from the comparable year. Moreover, its first-party and third-party sales hit $92.39 billion in the third quarter of 2021with 360 estimates of digital commerce, an increase of 9.8% year over year. With high estimates in total America’s e-business reaching $210.35 billion, the corporation accounts for about 43.9% of the United States e-commerce market share in the year 2020.
The sellers in the marketplace account for 56% of units sold on Amazon’s international sites in the third quarter of 2021, up from 54% a year earlier. The firm expects net sales of between $130 billion and 140 billion, rising between 4% and 12% compared with the fourth quarter of 2020. Even though the operating income and rising costs could be as low as zero, the organization is warned. The corporation’s fears concerning the holiday season have surprised Wall Street, which anticipated that the e-business powerhouse would have enough inventory and logistics expertise to richer supply networks crisis. Consequently, online stores’ sales rose by 3.3% to approximately $49.94 billion in an earlier year when Covid-19 forced its closure of many of its stores. The revenues from third-party seller service, which includes commissions on sales by merchants in the segments and the charges they pay for their fulfillment centers in Amazon, rose by a margin of 18.7%.
Research indicates that executives and members of the board own about seventeen percent of the total stock in Amazon. They have confidential information that is unavailable to the general public. In addition, individuals and institutions outside the firm own up to about five percent of the company’s stock. The largest shareholder, Jeff Bezos, owns 16.3% of the business; BlackRock and Vanguard investment institutions have earned nearly five percent. More than sixty percent of the organization’s shares are under the authority of the investment bodies that generally sell mutual finances. They also sell exchange-traded funds (ETF) and govern investment portfolios for several organizations such as university endowments, pensions funds, wealthy individuals, and college savings schemes. The investment institutions aggregate the finances deposited with them, purchase inventory and exercise the stakeholder voting rights on behalf of the depositors. The leading fifteen institutions based on Amazon holdings manage twenty-nine percent of the common stock.
Furthermore, approximately a third of the stock is held by mutual funds and EFTs, most provided and controlled by the investment bodies named above. The rest of the shares, 20-22%, belong to independent individuals who purchase the shares in the stock market and hold them in their portfolios. However, the firm encourages and discourages certain forms of investing, partly due to its business model. Currently, the firm has not yet issued dividends, and it has opted to allow its stock price to continue to rise, about $1500 per share, without dividing it. That makes the company a growth stock but not an income stock as people are purchasing it with hopes of increased prices and ultimately selling it in the future to profit from the price differential. Stores that provide dividends are attractive for investment portfolios that demand cash yearly, such as retirement funds.
The intensified stock in Amazon discourages small investors because various consumer-grade investment firms require transactions to include a minimum set number of shares. While its retail business yields plenty of cash that can be distributed as dividends, its business model dictates that those funds are plowed back into business for expansion purposes. The retirement framework in the organization is heavily invested in a Russell 1000 index fund; thus, the company’s success is contributing a lot to the city’s employees’ future retirement.
Legal form/ownership structure of Amazon
The ownership of Jeff Bezos represents a great fortune, where the company’s management is diffuse. No small group of individuals or institutions collectively own enough of the voting shares of 50% +1 to control the decision-making process. To acquire the majority control, one would need to organize a coalition of Bezos together with dozens of institutional investment managers and persuade them to vote in the same way. Additionally, there is no back-room cabal of wealthy aristocrats pulling all strings. So, the executives and directors in the firm should articulate a compelling vision and deliver results. Both the stakeholders and individuals at their private capacity who own shares are allowed to attend the company’s annual meetings and vote.
Current international operations
Amazon is the largest and most successful retailer globally because it built the best consumer experience. As an international e-business organization, it operates in thirteen nations with specific sites devoted to purchasers in America, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Germany. The Amazon Prime is a great popular subscription service that provides lucrative benefits like extensive online streaming access and free two-day delivery for its consumers. Many of its top tech items and in-demand shipping alternatives are exclusive to its prime customers. Currently, the business has grown to be the most renowned marketplace globally, progressively expanding into more and more new market segments. In 2017, the corporation’s sales totaled about $180billion, 40% of which was generated outside its native country, the United States.
Unsurprisingly, the company is one of those that has become synonymous with international success. Through its broad selection of goods, it offers or the technology it uses to enhance customer satisfaction, Amazon remains one step ahead of the rest, staying the master of the online world. One of the factors behind its success is the team’s time to research the markets they are considering entering into. As a result, this means having great knowledge of holidays, lifestyles, seasonality, and tax regulations. The firm is the winning choice for many, and in fact, the retail giant that delivers to more than 200 markets and territories internationally. Another success factor is that Amazon utilizes international address verification to guarantee that buyers across the entire globe can quickly and easily enter their billing and delivery address details with ease. In addition, it ensures that the captured international address information is accurate and delivered to the right address. Its worldwide stores allow domestic and non-domestic consumers to conveniently buy products from America and offer a seamless end-to-end shopping experience. Its success is mainly attributed to its dedication to implementing great technology and researching the market.
Background Information on the Business Environment in Finland – PESTLE Analysis
Political Factors
Finland is a parliamentary republic government mainly with a multiparty system-based nation headed by a president. The head of state holds an office for six years with a maximum of two consecutive terms elected by the Finnish (Piironen, 2016). In addition, the prime minister and his deputy are nominated by the president following the parliamentary elections. Women in Finland represented thirty-eight percent of the seats in the two hundred members of parliament and are treated fairly great. The country has established strong confidence in all foreign investors and motivates them, increasing profitability in the long run.
Economic Factors
The nation is highly industrialized with a gross domestic product (GDP) of $181.4 billion in the year 2009; over about 40% of GDP are from the contribution of exporting products.
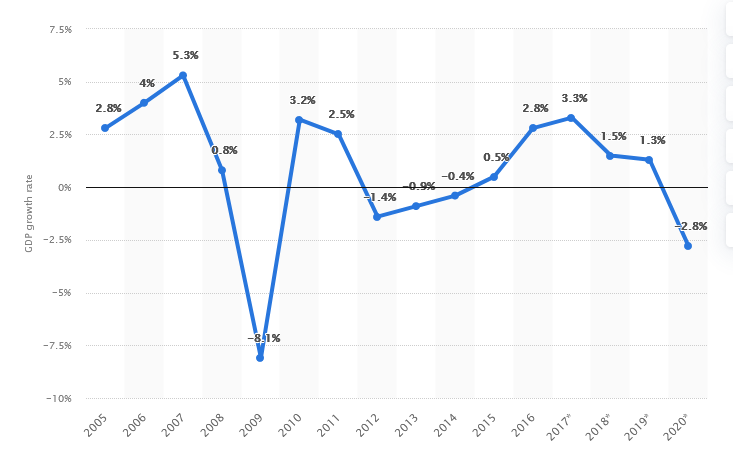
The main economic sector in Finland is the service sector which contributes about 65.7% and follows by the manufacturing industry in producing chemicals and metals. The nation holds its tax card to prevent the cardholder from getting exploited by the government. Those citizens without the card have imposed a levy of 60% from all of the income they obtain. The leading industry in the country is Nokia which deals with mobile phones. The government finances, prospects of growth and stability, and international transactions of the state might affect the development of the country’s economy. Its economic risk is low, and most economists anticipate that the current recession could affect businesses negatively.
Social Factors
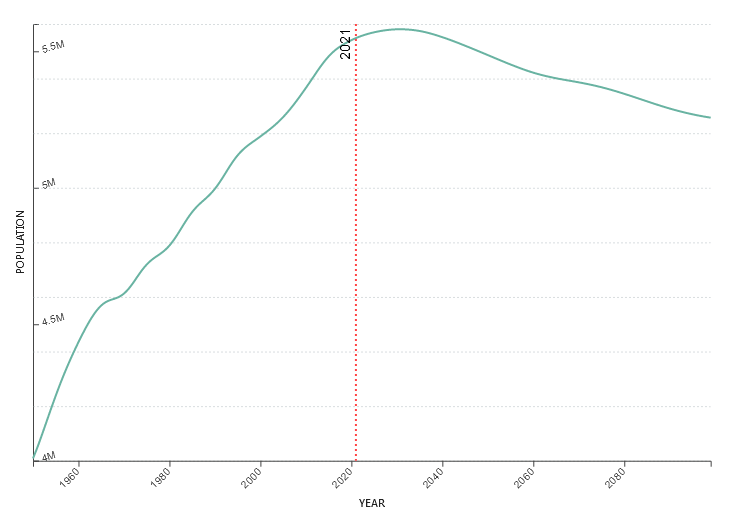
The state holds a population of over 5.32 million residents, out of which 2.7 million of them are workforce, and 2.5 million are employed.
Social security has been cut back nowadays, and its health care system is one of the most decentralized and highest levels internationally. Medical care covers the entire country’s population, and it is mainly provided by the government and the public sector and all financed through general taxation. The municipalities take the whole responsibility for organizing and taking all the financial responsibility for the entire range of municipal health services.
Technological Factors
This nation’s science and technology are very well known and excellent ones globally. It has advanced from playing catch up to being at the forefront of advancement in technology. After the invention of Nokia, the state has emerged as a place where multinationals like to recruit and erect labs. Currently, the local entrepreneurs and the government, in general, are preparing the development of clean technology, where it intends to spend 3.5% of its gross domestic product in the development of R&D. The nation maintains strong relations with both private and public investors. For example, almost two-thirds of the R&D funding comes from the private sector and one-third from the government.
Environment Factors
The nation is the eighth largest area across Europe, although it is a sparsely populated nation in the European Union and most of its citizens reside there. It is well known for preserving the natural environment using its technological skills and wide-ranging and detailed environmental data. That helps the nation formulate ecological protection policies and function more effectively. In addition, the government has invested a lot in solving pollution problems to create a conducive business environment. The air quality around the industrial areas has been improved, and polluted lakes and rivers cleaned up. Furthermore, every citizen in Finland is entitled to equal rights and the right to have their cases heard by the court system.
Legal Factors
The general court mainly deals with civil suits and criminal cases, whereas the administrative courts regulate the administration’s actions and litigations between individuals and the government. The foreign entities can acquire shares and assets in Finnish companies without any approval or permission from the state authorities. Finland has an Employment Contract Act that regulates all the matters between employers and their employees, who interpret individual employment contracts, basic rights and duties of parties such as equal treatment and compensation for groundless termination, and claims based on personal contracts.
Demographic Conditions
The country has an average population density of seventeen inhabitants per square kilometer, making the nation the third most sparsely populated country in Europe after Norway and Iceland. Population distribution is uneven; the population is concentrated on the small southwestern coastal plain, with one million living in Helsinki and about 64% in towns and cities. The country is ethnically homogenous, the dominant ethnicity being Finnish people, and official languages being Swedish and Finnish.
Analysis of the Business Scenario – Porter’s 5 Forces
Competitive Rivalry
Amazon faces an intense competitive rivalry in its online retail industry that it has to adopt competitive strategies to create the technology center in Finland. The competition results from an increasing number of players and traditional brands that provide online sales and increase their technological advancements (Sadq, Sabir, and Saeed, 2018). Reduced switching costs and readily available substitutes exert more pressure on Amazon since clients can move from one retailer to another at a low price. So, the firm should invest a large amount in providing high-quality products and services to its consumers and gain an advantage over other players and exploit this business opportunity in Finland.
Threat of New Entrants
New entrants in mail order and catalog bring innovation and advanced ways of doing things. As a result, this puts pressure on Amazon through reduced costs, a low pricing strategy, and a new value proposition to the shoppers. The company should manage all these challenges by building economies of scale to lower the fixed cost per unit and establish effective barriers to safeguard its competitive advantage. Innovating new goods brings new customers to the fold and gives the old consumers a reason to buy from Amazon.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
There are different types of suppliers who supply raw materials to Amazon. The suppliers in the dominant position can lower the margins the company earns in the market. The overall effect of increased supplier bargaining power is that it minimizes the overall profitability. Considering the business opportunity for Amazon in Finland, the former should develop third-party manufacturers whose business solely depends on them. In addition, it should establish an efficient supply chain with multiple suppliers as this creates a scenario where the producers have significantly less bargaining power.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The shoppers demand a lot as they wish to purchase quality offerings available by paying the minimum price possible. In the long run, this puts pressure on Amazon’s profitability. The smaller and more powerful the consumer base is, the higher their ability to seek increasing offers and discounts. Concerning the business opportunity that Amazon has identified, it should establish a vast base of clients. Ultimately, this will provide an avenue for the organization to streamline its sales and production process.
Threats of Substitute Products or Services
When a new item or service fulfills a similar customer need in diverse ways, industry profitability suffers. The danger of a substitute product is great if it creates a unique proposition that is specially different from present offerings in the market (Greenspan, 2021). Amazon should tackle this by being service-oriented rather than just product-driven. Additionally, the company must comprehend the core demand of the consumers instead of focusing on whatever they are purchasing and increase the switching costs for the end-users.
Conclusion
In summary, if Amazon utilizes its foreign direct investment decision well, ultimately, it will be able to offer millions of jobs and, in turn, obtain huge profits. The firm should continue its technological advancements to gain a competitive edge amongst its competitors and maintain its image. Furthermore, the company must familiarize itself with the business environment within Finland to know whether it is compatible and look at the areas of improvement. One of the suggestions to Amazon is to address the strong forces of competitive rivalry by emphasizing the comparative advantage and strengths of the e-commerce organization. Moreover, it must address the external factors associated with the strong influence of the bargaining power of buyers by focusing on service quality. Finally, the organization must counteract the substitution threat by making its service more attractive.
References list
Alassaf, D. et al., (2020). Amazon: Industrial/international corporation and dynamics. In Innovation Management in the Intelligent World (pp. 67-80). Springer.
Conley, P. (2021) Amazon’s Q3 sales rise modestly but profits plunge amid rising costs. Web.
Greenspan, R. (2019) Amazon.com. Inc. five forces analysis & recommendations (Porter’s Model). Web.
Oitzman, M. (2021). Amazon Scout development expands in Finland. Web.
Piironen, I., 2016. A Marketing Strategy for Foreign Startup Charities in Finland. Web.
Sadq, Z.M., Sabir, H.N. and Saeed, V.S.H., 2018. Analyzing the Amazon success strategies. Journal of process management. New Technologies, 6(4).