Executive Summary
This report presents a detailed analysis of the performance of Apple. The analysis focused on the company’s market share, business strategy, and financial performance. Product differentiation is the main business strategy that Apple pursues. This involves developing high quality products that are sold at a premium price. Nonetheless, Apple’s market share has been declining steadily since 2011.
Currently, Samsung has overtaken Apple in terms of sales in the global smartphone market. Apple expects to regain its lost market share by launching new products in 2014. Although the company has been losing market share, its revenue and net income have maintained an upward trend in the last five years. The company is financially stable and is likely to maintain its high profitability in the medium term. Consequently, a significant amount of money should be invested in Apple.
Introduction
The purpose of this paper is to provide a detailed analysis of Apple Company. The objective of the evaluation is to inform decisions concerning the suitability or viability of investing a significant amount of capital in Apple. In this respect, the analysis will shed light on Apple’s performance in three areas namely, business strategy, market share, and financial standing.
Apple is one of the leading technology companies in the world. The company owes its success to innovation and effective marketing strategies. Apple specializes in the production and distribution of high-end computers, entertainment products, and smartphones, as well as, software packages. The most successful products of the company include iPhone, iPad, Mac, and iPod (Apple). These products have historically enjoyed a huge market share, thereby enabling the company to earn high profits. However, the company is increasingly facing high competition from firms such as LG and Samsung whose products are relatively cheaper.
Business Strategy
Apple’s business strategy is to compete in various markets based on product differentiation. The company achieves differentiation by implementing the following strategies. First, Apple focuses on producing and selling a narrow range of products in various markets. The aim of this strategy is to enable the company to channel its scarce resources towards the production of a few, but high quality products that meet the specific needs of customers (McCray, Gonzalez and Darling 240-255).
In this respect, the company achieves differentiation by developing new products to satisfying needs that have not been satisfied in the market (Apple). Nevertheless, focusing on producing a narrow range of products denies the company the chance to serve customers who are interested in a variety of products that satisfy their unique tastes and preferences.
Second, Apple focuses on the production of high-end products. The company’s smartphones and computers are positioned as superior products that provide elegance and advanced functionality. This strategy emphasizes differentiation through innovation to make the products unique and attractive to customers. The products are differentiated in terms of quality by combining advanced technology with art (Apple).
In the mobile phone market, Apple produces stylish and ergonomically designed smartphones. In addition, the smartphones have reliable and user-friendly operating systems, which make their functionality unique. In the computer industry, Apple produces the hardware and the operating systems for its computers. The benefit of this strategy is that it allows Apple to manufacture the hardware that can best run its software. As a result, the company has eliminated the quality problems that often arise when computers are assembled using parts and software packages from different suppliers. Generally, the company’s products are not only technologically superior to their competitors, but also provide unparalleled attraction and user experience.
Indeed differentiation is one of the strategies that have enabled Apple to defend its market share in markets were competitive rivalry is ever increasing (Apple). However, the strategy forces the company to serve a niche market that consists of only the rich who can afford high-end products. This means that Apple is missing the opportunity to increase its revenue by ignoring the mass market.
Third, Apple achieves differentiation through its branding strategy. The rationale of brand differentiation is that customers must understand the unique features of a product in order to buy it. In this respect, Apple focuses on conveying very simple marketing messages that customers can identify with and remember easily. The company’s brand promise highlights the features of its products that are most important to the target market.
It also emphasizes the fact that Apple’s products are meant to address needs that have been ignored by the competition. Apple as a brand exists in the mind of customers who associate it with stylish designs and superior functionality. The strong brand image has enabled Apple to achieve differentiation by owning the two most important benefits to customers, namely high quality and reliability. As a result, the company benefits from a strong brand preference and brand insistence. For instance, iPhone users believe that Apple’s ecosystem is the only viable solution to their communication and entertainment needs.
Thus, they are not willing to pursue substitutes when Apple’s products are not available. Brand preference also allows Apple to charge premium prices for its products. The benefit of the premium pricing is that it allows the company to realize huge profit margins. As a result, investors benefit in terms of high returns on their investments. However, the premium pricing exposes the company to the risk of losing its market share to competitors such as Samsung, LG, and Google, which are able to offer high quality products at low prices (He 112-120).
Market Share
Prior to 2011, Apple was the world leader in the smartphone and high-end computer market in terms of sales volume (McCray, Gonzalez and Darling 240-255). The strategy for maintaining market leadership involved developing a new innovative product that enabled the company to gain quickly the largest share of a market that it did not serve previously.
For instance, the company developed iPod, thereby gaining the largest share of the MP3 player market (McCray, Gonzalez and Darling 240-255). Similarly, it gained over half of the smartphone and tablet markets by developing iPhone and iPad respectively. In order to maintain the largest market share, the company has to guarantee its customers of unique product designs and access to a strong ecosystem that include iTunes and App store. The role of the ecosystem is to improve product relevance and usability.
Since 2011, the company has been defending its market share in highly competitive markets such as China while increasing its dominance in mature markets such as the US and Europe. This involves using creative marketing tactics to attract and retain customers (He 112-120). Specifically, the company sells its products and those of third parties through a variety of distribution channels to increase brand visibility. The channels include the company’s retail shops and online stores, as well as, selected independent distributors. The company’s stores enable it to offer excellent customer service, thereby retaining customers. On the other hand, independent distributors enable Apple to gain market share in countries where it does not have its own stores.
However, the company has found it hard to maintain its leadership position. In 2014, Google increased the market share of its Android operating system to 73.3%, thereby overtaking Apple’s iOS system whose market share has fallen to 11% (Pattie and Rogers). Although Apple still leads in terms of the value of sales in the high-end market segment, Samsung has already overtaken it in terms of volume or the number of units sold (Pattie and Rogers). Overall, table 2 shows that Apple has dropped from position one with a market share of 18.8% in 2011 to position two with a market share of 11.7% in 2014 in the smartphone industry. By contrast, the market shares for Samsung, Huawei, and Lenovo have steadily increased in the last three years.
One of the reasons for the decline in the market share of Apple’s main products is its inability to maintain high standards of innovation after 2011. The company has focused on improving existing products rather than developing new ones that serve emerging needs. Poor innovation has partly been attributed to the company’s low investment in research and development in the last three years. As a result, Samsung and Google have developed products that are superior to those of Apple.
For instance, iPhone 5S is technologically inferior to its competitors such as Nokia Lumia 920 (He 112-120). Another reason for the decline in the market share is maturity of the markets for most of the company’s products in the US and Europe. In this case, companies that have focused on reducing their prices while maintaining acceptable product quality have gained market share at the expense of Apple.
The implication of the declining market share is that the company’s revenue and profits are likely to reduce in future. The decline will negatively affect investors in terms of low earnings-per-share and dividends. Currently, the company has increased its investment in research and developed to design improved products. Thus, the company expects to regain the lost market share in the medium term after introducing new versions of its iPhone in the fourth quarter of 2014 (Apple).
Financial Standing
Trend analysis
Apple’s annual revenue and net income have been increasing steadily in the last five years. Figure 1 in the appendix, shows that the company’s revenue increased from $42,905 million in 2009 to $170,910 million in 2013 (Apple). This means that Apple’s revenue increased by nearly 298% in the last five years. In the third quarter of 2014, the company realized $37.4 billion in revenue, which is slightly higher than the $35.3 billion that was posted in the third quarter of 2013. The significant increase in the company’s revenue is a manifestation of the popularity of its products and the effectiveness of its marketing strategy.
The company’s net profit increased significantly from $8,235 million in 2009 to $41,733 million in 2012. This shows that net income increased by nearly 407.8%. Nonetheless, increased competition in the smartphone market coupled with declining demand for personal computers led to an eleven percent decline in the company’s net income in 2013. In the third quarter of 2014, Apple realized $7.7 billion in net income, which exceeds the $6.9 billion realized in the third quarter of 2013 (Apple). The upward trends in revenue and profitability show that Apple is a reliable company where investors can expect high returns in future.
Ratio Analysis
Apple’s profitability ratios for the last six years are summarized in table 1. Earnings-per-share increased from $0.77 to $6.19. This means that the amount of the company’s net income that was allocated to every common stock increased by 803.9% in the last six years. Profit margin increased from 14.88% in 2008 to 26.67% in 2012. However, it declined to 21.67% in 2013 (Apple).
The decline reflects the high competition that has forced the company to reduce the prices of its products to maintain its market share. Return-on-equity (ROE) increased from 22.99% in 2008 to 31.20% in 2014 (Apple). Apple’s return-on-assets also increased from 12.22% in 2008 to 17.92% in 2014. These ratios clearly indicate that the company’s profitability has significantly improved in the last five years.
Apple has been able to maintain its current ratio above 150% since 2010. This means that the company is liquid since it can meet its current liabilities using its short-term assets such as cash. The company’s debt-to-equity ratio was 0.00 from 2008 to 2012 (Apple). However, it rose from 0.14 in 2013 to 0.24 in 2014. This shows that the company has very little debt. Overall, the liquidity ratios show that Apple is financially stable. Thus, it can easily attract external capital to expand its operations and profitability.
Conclusion
The analyses in the foregoing paragraphs indicate that Apple is a reliable company with effective business strategies. The company focuses on producing high quality products, which it sells at a premium price. As a result, it makes high profits. However, the company has been losing its market share to its competitors since 2012. The downward trend in market share reflects the fact that the company is facing difficulty in competing based only on product quality. However, new product development and marketing strategies are being implemented to regain the lost market share.
Increasing the market share of the existing products is expected to improve Apple’s revenue and net income in the medium term. The financial analysis shows that Apple is a very profitable company. The company’s revenue and net income have maintained an upward trend despite the decline in market share. In addition, the company is financially stable due to its high liquidity and low debt levels. These insights show that Apple’s investors are likely to realize a high return on their investments in future. In this respect, the company should consider investing in Apple in order to improve its future income.
Appendix
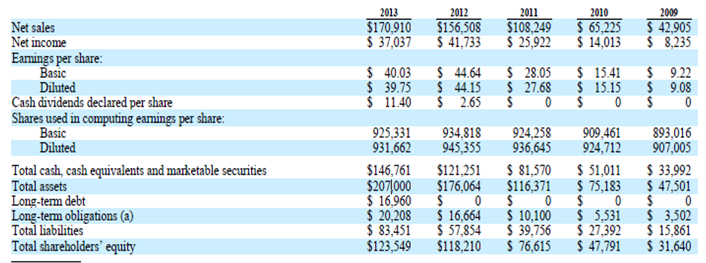
Table 1: Profitability ratios
Table 2: Market share in the smartphone industry
Works Cited
Apple. Apple Inc. Annual Reports 2014. Web.
He, N. “How to Maintain Sustainable Competitive Advantages: Case Study on the Evolution of Organizational Strategic Management.” International Journal of Business Administration 3.5 (2013): 112-120. Print.
McCray, J, J Gonzalez and J Darling. “Crisis Management in Smart Phones: The Case of Nokia vs. Apple.” European Business Rview 23.3 (2011): 240-255. Print.
Pattie, L and Rogers, P. Galaxy S5 Attracts some Apple Customers in Europe, but Sales Lag in Great Britain 2014. Web.
Peterson, M. “iPhone and Apps: The Brand Management and Marketing Aspects of Apple’s iPhone and Associated Applications Software.” Strategic Direction 27.3 (2012): 12-45. Print.