Introduction
Employee unrest is on the rise in Saudi Arabia, putting pressure on the country’s economy and companies and their workers. Although past studies have concluded that labor relations affect the performance of an organization, they have not defined the nature of the relationship between labor relations and business variables such as revenue, losses, and value of equity. This paper discusses the relationship between labor actions and the performance of Uber Technologies Inc. and explores some possible strategies out of the problem.
Purpose of the Study
To investigate the relationship and correlation between labor relations and financial and business performance of Uber Technologies Inc.
Methodology
Type of Research
In this research, Qualitative Research and Quantitative research will be used. Qualitative research will be used to study human behavior and the reasons for certain behaviors for different members of an organization. It will analyze the different reasons that lead to employees feeling that they are unfairly being treated in the workplace. It will also be used to analyze response strategies to curb labor action. Quantitative research will be used to measure the losses that arise from the employees’ actions and the cost to counter the loss in revenue.
Sampling Method
For a more scientific outcome that can reflect the entire population, random sampling will be employed as the research sampling technique in this study. Drivers from the Uber Company and its competitors (Lyft) will be selected randomly to participate in the research. From all Uber drivers in Saudi Arabia, 100 will be selected using a random sampling method to become respondents. A letter will be sent to Uber subsidiary head offices to obtain their consent for their drivers to be utilized in this research. Data Collection was done in public areas where Uber and its competitor drivers operate.
Respondents
Those that participate physically in this study will all come from Riyadh. To conduct the study, the researcher picked Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, because of its socio-economic circumstances and suited the researcher’s time and resources. Experts’ opinions will also be sought to explain respondents’ newborn feeding methods and behaviors in this study. Other participants will be contacted via telephone communication and email.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire will be used to obtain information on the reasons for labor action among drivers. They will also be used to seek information on office staff opinions on the ongoing labor strikes. And finally, the questionnaire will help obtain information on expert thought of what the labor action means for the IPO, which is almost due.
Findings
The surveys found that most customers prefer Uber more than other online taxi services to other taxi services. According to the questionnaires, most Uber drivers felt that the company did not favorably consider their welfare. 54% of the drivers felt that the company did not treat their staff fairly. 44% felt that the company treated its drivers well, while only two percent felt that the company did not care for their welfare at all. According to surveys, Uber was the most popular company among taxi companies in Saudi Arabia, with a 60% market share.
Many of the respondents, at least 50, felt that the popularity of Uber was because it was the first online taxi service to be introduced to the country. In telephone interviews, 50% of the managers felt that there was still room for improvement in labor relations and customer satisfaction. Most of them explained that human relations are ever-changing and, therefore, it is an ongoing process. Investors who gave their opinion, 44% of them thought that the drivers’ strike was less likely to impact the IPO process and anticipated capital raise. On the other end, 15% thought that it would, and the remaining were not sure of the effect of the strike.
Practical Implication
The sources from which data was sourced were deemed as reliable as at the time of the study. There is likely to be a change in the data in the future. However, the data was reliable for this research as the paper is only focused on the current situation before IPO. The data on customer satisfaction was primarily applicable for the study and is subject to change in the future. The company can use the information gathered in this study to make further changes to its strategies to improve on areas that call for improvements.
Structure of the Paper
The paper starts with an introduction of Uber Technologies Inc. An insight into the nature of the business of the company. Then there is a corporate reputation issue which is the Drivers’ Strike. Next is an industry analysis of the company. A press release is given after that. Then there is the PR strategy that the company can explore to enhance customer relationships and public relations. Then finally is a look into the future of the company.
Background Environment
Uber Technologies Inc. is one of the most captivating firms to surface recently due to its fast growth and persistent debate. Founded in 2009, the worldwide ridesharing app was the first of its kind and has since grown to be one of the world’s most valuable private startups. In 2019, Uber went public. It is a major play in the rideshare industry.
Analysis of Current Situation
PESTEL Analysis
The media has regularly covered Uber. It’s recognized as the fastest-growing taxi-hailing app startup in the world today. However, it has also been the subject of debates over the taxi business, minimum wage issues, and bans in numerous nations throughout the globe.
Political Factors
Uber has been the subject of debate. A lack of rules marred Uber’s early stages. It was difficult to determine where the insurance fraud was taking place. France filed a lawsuit against Uber’s advertising model, the Netherlands decided against Uber since its drivers did not have Taxi licenses, and Portland issued a stop and desisted order for Uber (Smith et al., 2019, p. 600). Political debates concerning taxi sector minimum wage legislation and whether Uber was adhering to these guidelines (Dudovskiy, 2021, para. 2). Uber is required to show government-issued business licensing papers as well.
Economic Factors
Factors of the sharing economy have a role in Uber’s business model. In other words, they share physical or intangible assets. When a consumer requests a ride from Uber, a driver is sent to pick them up and take them somewhere. Uber and Lyft are often seen as more cost-effective options for getting about than taxis (Dudovskiy, 2021, para. 9). Uber’s popularity has skyrocketed since its inception. People are trying to figure out whether this market creates new job prospects or eliminates old ones. Alternatively, bringing in new employment prospects, although at a reduced wage. Uber’s rapid expansion shows the market’s economic potential, and that’s a given. However, as Uber expands, other platforms like Lyft are forced to compete for market share.
Social Factors
Using the app on cellphones, scheduling an appointment, and picking it up is a breeze. It just needs a few button pushes and doesn’t require any communication. As a result of the lower cost, Uber’s growth has skyrocketed worldwide. During their trips, customers took to social media to share their experiences (Frue, 2017, para. 9). The word spread swiftly by word of mouth. However, with the rise in popularity, the cost of living in big cities increased as well.
Technological Factors
The testimonies of people who have gone to the internet to share their experiences with others have spread. Users who had previously done so were asked to do so as well. Uber provides a solution for customers who were searching for more economical ways of transportation (Frue, 2017, para. 11). Uber depends significantly on its app.
Legal Factors
Uber faces lawsuits, accusations, and other legal issues. Uber Technologies Inc. must adhere to technology usage laws, patent laws, labor and employee safety laws.
Environmental Factors
It is a common belief that Uber causes an increase in traffic congestion. Research shows that Uber has had little impact on traffic congestion (Li et al., 2021, para. 1). Instead of using the bus or train, some people may choose to utilize Uber. The ultimate sum may be affected by a wide range of variables.
SWOT Analysis for Uber
The Strengths of Uber
Uber Technologies Inc. has several qualities that will help it succeed in its primary market. Because Uber developed ridesharing, they have a monopoly on the market. This company makes more than 40 million trips each month, which has a 77% share of the market. Lyft, Uber’s primary rival, occupies ten percent of the market (Brown, 2020, p. 125). Uber’s excellent brand recognition has made it simpler for the firm to expand into other markets.
One of Uber’s best features is its dynamic pricing model, which considers several criteria to determine the price of a trip. Uber has invested in self-driving vehicles and partnered with Aurora Innovation to expand its engagement in autonomous transportation technology (Colquitt et al., 2017). Uber has been an enormous success with its capacity to make ridesharing more convenient and affordable than hailing a taxi (Sepelova et al., 2021, p. 530). With a simple phone call, you may reserve a low-cost transport. Uber’s business model is well suited to customer-driver interactions.
The Weaknesses of Uber
Even though it has no direct link with its drivers, Uber is a company that depends on its drivers. Several Uber passengers have complained about unpleasant or intoxicated drivers at pickup places. As a result, their reputation has been damaged, and competitors have undermined their market share. Lyft and Uber have been accused of imitating one other’s business models. It’s impossible to claim that the ridesharing sector doesn’t have any patented or protectable features (Sepelova et al., 2021, p. 530). Due to the firm’s aggressive policy of rewarding drivers with incentives and discounting clients to surpass its rivals, the company cannot generate profits.
Opportunities for Uber
As a result of the government’s support for economic growth, new markets have been created. Unorganized taxi companies that have been out of business for an excessive amount of time have lost their appeal among the public. It is possible to find the best drivers by monitoring their performance (Mohlmann, 2017). With autonomous vehicles on the road, Uber Technologies has great promise and a big problem ahead. Uber is a business that may deliver a large variety of current goods and a vast range of future products.
Threats to Uber
Uber’s customer-centric strategy involves low commission rates, resulting in limited profits. To this day, there is a lot of debate about whether or not Uber must treat its drivers as employees or independent contractors (Rubin, 2017, p. 163). OLA, DIDI, and Lyft are a few of Uber’s rivals in the transportation sector (Korabova, 2019, p. 6). Long-term, lower industry rates might be the result of more competition. Uber has a hard time meeting regulatory standards in many countries and locations it operates in.
Uber Marketing Mix
The Product Element
As a service provider, Uber doesn’t offer any goods. Using Uber instead of taking a cab has obvious benefits. These features include a detailed price breakdown before requesting, tap trips, customer driver tracker on the map, online payment, and fare split feature.
Uber’s marketing mix includes Element
There are 71 countries where Uber is offered. The service is concentrated in a certain area. There are eight smaller markets where Uber Eats will be shutting its operations in May 2020. Specific activities were terminated in the Czech Republic, Egypt, Honduras, Romania, Saudi Arabia, and the United Kingdom. Careem, the company’s wholly-owned subsidiary, took over operations in the United Arab Emirates (Verschoor, 2017, p. 23). To remain competitive on a worldwide scale, the ride-hailing behemoth implemented these adjustments.
Price Component
Geographic pricing is one way to characterize Uber’s pricing method. The cost of an Uber journey relies on three factors:
- The base fee.
- The charge for expected duration and distance.
- The demand for rides in the region where you live.
According to the economic theory of supply and demand, Uber’s price approach may be classed as dynamic pricing (Santos, 2020, p. 240). The more people who need a cab at a certain time and place, the more expensive it is.
Press Release

Executive Summary
Company and Stakeholders’ Communication Background
Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp founded Uber Technologies Inc. They gave it a domain UberCab.com. Both Uber and Lyft are ride-hailing services that compete with taxis and other long-established modes of private transportation (Hoffman, 2021, p. 15). The nature of their business is an advancement of the traditional taxi transport services. Rather than customers manually searching for a cab, Uber and Lyft allow their customers to reach cab services from their smartphones.
Uber Technologies Inc. runs a ride-hailing service and gets a part of the fare revenue to earn money. Uber also operates a food delivery service and a freight transportation service, Uber Freight. In cities throughout the globe, Uber and Lyft drivers are logging off their ride-hailing applications to protest working conditions and compensation. Before the projected IPO on Friday, Uber’s value was projected to reach as high as $91.5 billion, resulting in demonstrations in cities around the country (Cordina et al., 2021, p. 200). The issues that lead up to the strikes are likely to put the company’s reputation at risk. CEO Dara Khosrowshahi is one of Uber’s most notable stockholders, Tony West and Nelson J. Chai of Nelson Chai & Co. After a 12-month (TTM) period, Uber’s TTM revenue was $13.0 billion, with a net loss of $6.9 billion, and the company had a market valuation of $89.1 billion as of January 27, 2021 (Harrison, 2020, para. 1).
Industry/Market Review and Analysis
Uber Technologies Inc. has operations within the Rideshare industry. The main stakeholders here include; drivers, management, investors, government, and customers. The Stakeholders connect via Rideshare software. The customers, management, and drivers interact through the software to exchange services and income. Its main competitor is Lyft. However, Bolt Grab and Snapp are also offering similar services like Uber Technologies Inc. Its woes benefit its competitors (Harris, 2017, p. 269). However, their weaknesses include limited resources to conquer Uber’s market share.
The Uber company’s target market includes those who dislike public transportation yet have a restricted budget. Between the ages of 20 and 40, the vast majority of Uber clients are using the service (Schaller, 2021, p. 1). For Uber Eats, bachelors who prefer not to cook, and sometimes everyone else, is the designated target markets.
Rideshare firms saw a drop in sales when people were ordered to stay in their homes to prevent the spread of the coronavirus. In October 2021, Rideshare expenditure is still dominated by Uber, which takes in 69 percent of the total. Although most Uber Eats transactions are excluded from Uber’s market share starting in August 2017, some remain unidentifiable. Customers seem to be paying more for trips as ridesharing continues to recover from the plague. Uber’s average sales per client in October 2021 were $80, a 28% year-over-year rise and a 6% year-over-year increase (Feix, 2021, p. 117). Most ridesharing services have a single user base throughout the country.
During the first week of January that year, the #DeleteUber hashtag became popular, and Uber’s market share decreased five percentage points in a single week (Pendegraft, 2021). In June 2017, the company’s former CEO, Travis Kalanick, stepped down after a slew of scandals, among them accusations about the company’s workplace culture. Since then, a new CEO and a redesigned brand in 2018 have helped Uber improve its image and stabilize oscillations in market share.
Setting Goals and Objectives
This marketing strategy aims to increase Uber’s customer experience while reaching out to new ones to increase market share. The objectives include determining the needs of customers based on their experience with Uber. The marketing strategy will also establish the effectiveness of the previous and current marketing structures. The third objective will be to determine the factors causing the customer experience at Uber to decline. It will seek to highlight key areas of focus as the company heads to the revenue increase in the future. With this revenue objective, we shall measure the revenue projections and their achievability. And finally, the strategy will help set new strategies for increasing customer satisfaction using Uber services. We measure customer reviews in different categories.
Strategies and Tactics to Achieve Objectives
Uber Taxi Application Design
The current Uber site design is easy to use by many people. However, the app does not offer pictures of the car models which will be offering the ride. Considering that many people may not know car designs, a picture of the car would help customers select the car they would like to take a ride in. The application could be customized to reduce the prices of poorly rated drivers in the review icon charge fewer amounts. While they are still going to make incomes from the application, they will be pushed to improve to charge more. That way, customer satisfaction is increased.
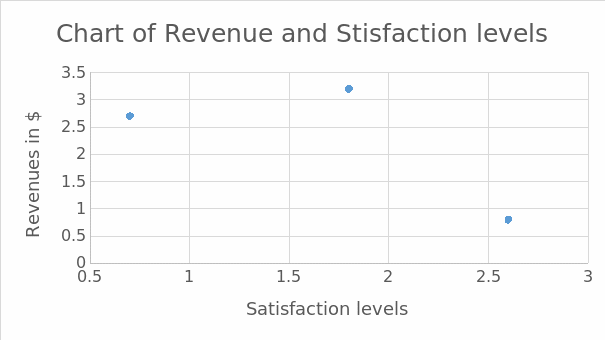
I will use a chart to rate and monitor the efficiency that may be achieved using the strategy. I will make a scatter chart for the revenues and satisfaction levels before and after implementation. This will be as follows:
Scatter chart before implementation:
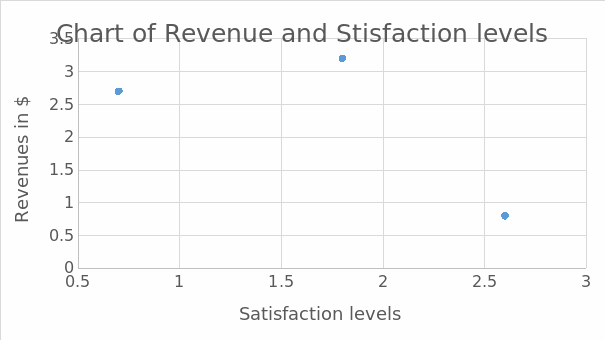
Pie chart after implementation:
Uber can create a search engine marketing plan whereby paying up for search engine prioritization packages. Uber should pay for potential Uber customers to obtain information about its services easily. I would recommend some examples of search engines are Google, YouTube, Baidu, Facebook, Twitter, and Yandex. Uber will use click rates for Google, Baidu, and Yandex and views for Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube to monitor usability.
The marketing strategy will be targeting internet users. The potential customers in this area are well vast with social media use, especially youths.
The brand values include accessibility, user-friendliness, and simplicity. In this area, the company can create an automated system of sending emails of new offers and promotions to existing customers and potential customers. The contacts of potential customers can be saved whenever they click on Uber products. This system can be integrated by making upgrades and adjustments to the existing Uber sites and applications.
Additional revenue can be generated by partnering with other companies to introduce new products to the customers. For example, partnering with stores to do delivery of shopping and groceries to the customers for convenience. The company could also introduce a service to connect its customers to airports and other transport modes.
Customer Service, Relationship and Loyalty Plan
Uber’s current customer relationship strategy is composed of three elements. Customer satisfaction, quality service delivery, and reliability. On satisfaction, it ensures that customer needs are satisfied by providing services as advertised to ensure customer expectations are met. The drivers and cars employed for Uber services are qualified based on customer need criteria. On reliability, the company ensures that the services of Uber are available at the convenience of the customer.
To retain customers, Uber uses promotions and offers to ensure that customer loyalty is maintained. Existing customers are offered vouchers and discounts reflecting their usage of Uber services (Raina, 2018, p. 351). The company offers new customers welcome gifts to establish healthy relationships. The company uses incentives to ensure the loyalty of customers. Uber uses the SAP customer data platform.
Time Frame for the Strategies
The strategies will be implemented within a period of one to three years. While customer retention strategies will be commenced immediately, user application strategies will be implemented within two years. Customer feedback action strategies will be implemented in three years.
The Future
In about five years, Uber may adopt structures to offer more advanced services and products. There will be a total of 100 percent zero-emission cars, public transportation, or micro-mobility for every trip by 2040 from Uber (Cao, 2021, p. 180). Besides providing transportation, Uber focuses on self-driving technology and urban air transport; enabling consumers to order meals quickly and economically; reducing obstacles to healthcare, building innovative freight-booking options, and assisting corporations with seamless staff travel.
Reference List
Brown, A.E. (2020) ‘Who and where rideshares? Rideshare travel and use in Los Angeles,’ Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 136, pp. 120-134.
Cao, Z. et al. (2021) ‘E-scooter sharing to serve short-distance transit trips: a Singapore case,’ Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 147, pp. 177-196.
Colquitt, J. et al. (2017) ‘Driverless cars: how innovation paves the road to investment opportunity,’ The Invesco White Paper.
Cordina, R. et al. (2020) ‘The IPO of Uber-a classroom case,’ International Journal of Teaching and Case Studies, 11(3), pp. 191-207.
Dudovskiy, J. (2021) Uber PESTEL analysis: a brief overview – research-methodology. Web.
Feix, T. (2021) ‘Ride-hailing: is sharing the new owning?’ in Valuing digital business designs and platforms. Cham: Springer, pp. 115-171.
Frue, K. (2017) PESTLE analysis of Uber. Web.
Harris, B. (2017) ‘Uber, Lyft, and regulating the sharing economy,’ Seattle University Law Review, 41, p. 269.
Harrison, J.S. et al. (2021) ‘UBER: a great disrupter or not?’ Journal of Marketing Development & Competitiveness, 15(2).
Li, Z. et al. (2021) ‘How do on‐demand ridesharing services affect traffic congestion? The moderating role of urban compactness,’ Production and Operations Management.
Möhlmann, M. and Zalmanson, L. (2017) ‘Hands on the wheel: navigating algorithmic management and Uber drivers,’ 38th ICIS Proceedings.
Pendergraft, G. (2021) Should we #deleteUber? London: SAGE Publications.
Raina, A., Rana, V.S. and Thakur, A.S. (2018) ‘Popularity of online food ordering and delivery services-a comparative study between Zomato, Swiggy and Uber Eats in Ludhiana,’ International Journal of Advanced in Management, Technology and Engineering, 8(1), pp. 350-355.
Rubin, E. (2017) ‘Independent contractors or employees: why mediation should Be utilized by Uber and its drivers to solve the mystery of how to define working individuals in a sharing economy model,’ Cardozo Journal of Conflict Resolution, 19, p. 163.
Santos, F.A.D.N., Mayer, V.F. and Marques, O.R.B. (2020) ‘Dynamic pricing and price fairness perceptions: a study of the use of the Uber app in travels,’ Turismo: Visão e Ação, 21, pp. 239-264.
Schaller, B. (2021) ‘Can sharing a ride make for less traffic? Evidence from Uber and Lyft and implications for cities,’ Transport Policy, 102, pp.1-10.
Šepeľová, L., Calhoun, J. R., & Straffhauser-Linzatti, M. (2021) ‘Sharing economy business models: informational services innovation and disruption in Uber and Airbnb,’ in Developments in information & knowledge management for business applications. Cham: Springer, pp. 521-540.
Smith, N.C. and McCormick, E. (2019) ‘Uber and the ethics of sharing: exploring the societal promises and responsibilities of the sharing economy,’ in Managing sustainable business. Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 575-607.
Verschoor, C.C. (2017) ‘Uber culture causes big losses: harassment and mismanagement have led to steep losses for this high-flying company,’ Strategic Finance, 99(3), pp.23-25