Abstract
Derivatives are financial instruments traded in capital market. The underlying assets for derivative trading are most commonly bonds, stocks, etc. Derivatives greatly influence movements of debts in an economy which will lead to total economic slowdown. Derivatives have high rating values but in this case have been at the receiving end of criticism due to vagaries and uncertainties in the bourse and commercial money markets. The purpose of this study is to understand the extent, if any, to which derivatives have impacted present global financial crisis.
An economic crisis is one in which the values of some assets held by certain financial organizations loses its value. During a financial crisis, total assets or part of asset values are depleted. Stock market crisis also affects the economy. There are different challenges posed before businessmen and financial specialists, especially with regard to derivative business, and a decision could be taken only after a deep and comprehensive study of this topic. However there is need for taking “best use of available and potential resources” (Florincua & Thonqsawai 2010).
In the first part, the reader is introduced to the topic of derivatives and its various ramifications including aspects that were not mentioned in earlier research studies. The second part takes the reader into deeper waters in terms of what derivatives, its various hues and colors and how its impacts business, especially in financial markets. The third part is the crisis as such, the research design that is to be put into place and the methodology of research to be adopted. Part four deals with the analysis and interpretation and finally the study rounds off with the conclusion and recommendations. This being a hypothetical research study and not backed up by actual empirical research, the deficiencies that go along with a hypothetical study are present.
It is however believed that more detailed and comprehensive research work on derivatives needs to be the subject matter of another research, although this may be premised on the present study.
Introduction
The unprecedented financial crises precipitated by a crisis in the sub-mortgage sector and the failings of major banks like Lehmann’s and credit institutions have brought down the entire financial world right on the doorsteps of a major catastrophe, the likes of which was not even felt during the Great Depression in the forties when even essential commodities like common bread were sold at premium rates and were not affordable by everybody. In this case, it is seen that the crisis was not due to one factor or even several, but the effect of many adverse situations that were not checked and remedied over many years. Perhaps derivatives also played a major role in this crisis, but to attribute this to derivatives alone would not be judicious.
The impact of derivatives on the global financial crisis
The role of derivatives in the present economic crisis is indeed controversial, in that whether the present derivative scenario is the cause of the crisis or the result of it. There has indeed been a great deal of manipulation, unethical practices and badgering in the capital and money markets, but whether this has been capable of causing such extensive damages is indeed debatable. This is more so in the context of various other intermediary factors that have also caused havoc during its presence in the bourses and markets through uncalled speculative trading and dubious trading activities. When businesses and individuals trade-in imaginary assets, or funding not backed by robust underlying assets, a situation of this kind is bound to happen, one day or the other. Besides, fall in demand, interest rate declines and general lull and slump in activities including banking, insurance and real estate, to name a few, have also been principal contributors for this crisis to develop and accelerate.
Researchers who have had occasion to study the bourse and how derivatives impact upon it are unanimous in their opinion that such massive damages could not have been caused by a few instances of indiscretion– perhaps this has been the aftermath of detrimental actions and loss of controls that have been going on for quite some time, even years. The innate solidarity and resilience had overcome this to a certain extent, but now things had crossed the limits and had thus triggered a crisis. The very fact that this economic downturn is showing no signs of abatement is enough indication of how deep its impact has been and how damaging its effect on the global economy has been, despite strong remedial and abatement measures taken by the US and other European countries to tide over the situation.
Purpose and objective of this research
The main purpose of this study is to understand various features that constitute derivative trading and to determine if derivative trading has contributed to the present economic global crisis, and if so in what measure. In the recommendations part, this study shall also take up the matter of suggesting ways and means by which derivatives shall seek to play a positive role in the economic renaissance of the world.
What are derivatives?
Derivatives are financial instruments traded in the capital market. Derivatives can be defined as “a financial instrument whose characteristics and value depend upon the characteristics and value of an underlier, typically a commodity, bond, equity or currency.” (Derivative n.d.)
In the context of developed nations, derivatives have emerged as an imperative tool for risk management. Their astonishing growth has been one of the outstanding improvements in the financial markets. Derivatives assist corporate to undertake risks and maintain their profits. Derivatives are monetary tools that obtain their worth from some fundamental variable. They are also known as delayed-release or deferred payment instruments.
Forward, Futures, Options and Swaps are some of the easy, ordinary and extensively used derivatives across the world, particularly in nations where the derivative marketplace is rising. US, UK, Japan, etc. are the developed markets, one can spectator a selection of composite derivatives like range forward, credit derivatives, etc to declare a few. The materialization of the marketplace for the derivative instrument can be illustrated back to the readiness of risk-averse corporate shareholders looking to defend their funds from the uncertainties occurring out of the variations in the value of the investments.
There are confirmations that traders during the Twelfth century used to enter into forwarding contracts with one by one for the potential release of a particular amount of commodities at a specified price. In order to reduce the possibility of the huge price swings in the market forward contract is too essential commodity futures in1865, various markets have been studied at different time periods. The concern over how trading in index futures and options affects the spot market has been an interesting subject for investors, academicians, regulators and exchanges. Studies proved that derivatives significantly influence different economies.
Background of derivatives
There is potential scope for discussing the history of derivatives when studying derivatives. The future market that existed for what was one of the first derivatives markets. The market came into existence as a result of the concerns and worries of farmers who are much conscious of the price that they receive for their cultivated wheat. Sometimes they may receive more than expected some times they may receive less than they expected due to falling in the price at the time of sales compared to the price at the time of planting. When they receive much less than they expect, there are a high amount of risks. In order to protect from these unexpected, they decided to enter into an agreement in advance for fixing the price of the crops. This can avoid the risk of paying a higher price by the millers and the risk of receiving a very less price for their crops.
The system is worked in such a way that, both parties, that are buyer and seller, will fix a price before the cultivation. Therefore the farmers can grow the crops with no tension of the price at the time of sale and at the same time the millers also need to be tense about paying a higher price for the crops. (Brigham & Ehrhardt 2002, p.918)
This was considered the beginning of derivatives trading. However, the derivative market that we see now is started wherein there are middlemen started later. One of the first middlemen was The Chicago Board of Trade. The Chicago Board of Trade was started in the year 1848 by a group of merchants in Chicago. Initially, futures trading was applied for trading agricultural commodities. Later, it started to apply futures trading to other businesses also (The Chicago board of trade 2000).
This market arranged a facility for the farmers and millers to enter into a futures contract for the agricultural crops. Here the farmers can sell futures and the millers can buy futures. Later the practice of futures trading became common in capital markets of different parts of the world. The main objective of derivative trading is to minimize the quantum of loss during uncertain bourse transactions and deal with credit and debt instruments. In derivatives, the underlying assets play a very important role and undertaking derivatives without proper underlying assets or assets entails a lot of risks and contingencies. In the worldwide scenario, especially in the US derivative trading was taking place without having underlying assets to underpin them and this impacted when stocks value started sliding and losing heavy value.
Types of derivatives
There are different types of derivatives such as forwards, futures, options, swaps, warrants, leaps, structured notes, inverse floaters, baskets and swaptions (Types of derivatives n.d.)
Forwards
Forward contracts are agreements between two parties in which the buyer agrees to buy a product and the seller agrees to sell the product for a fixed price. The prices are fixed at the time of agreement and the actual delivery of the goods are taken place at a future date as per the agreement. It can be defined as “a contract that specifies the price and quantity of an asset to be delivered on in the future.” (Forward contract 2008).
There is a high amount of risk involved in the forward contracts, as there is the highest possibility of the breached agreement by any one of the parties that is either buyer or seller. The reason for the breach of agreement may be the possibility of high variations in the price of the commodity after entering into the agreement.
The following diagram shows the operation of the forwarding contract.
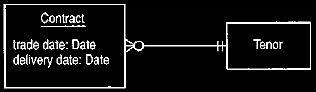
In the diagram, tenor refers to the difference between the date of trade and the delivery date.
Futures
A futures contract is also a derivative contract which is almost similar to a forwards contract but there are some differences like trading on a daily basis, the existence of a standardized clearing house…etc. A futures contract can be defined as “a standardized, transferable, exchange-traded contract that requires delivery of a commodity, currency or stock index, at a specified price, on a specified future date.” (Futures contract n.d.).
Options
Options are a type of derivatives and are different from futures or forwards contracts. Here a right to buy or sell is created. An option can be defined as a derivative which “gives the right but not the obligation to buy (call) or sell (put) a certain amount of an underlying commodity or financial instrument by or at a certain date in the future.” (Define options: definition-investing 2008).
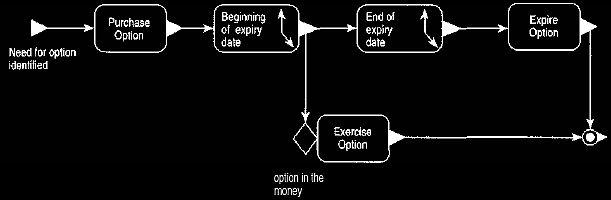
Options trading is very important for those who deal with risk management. Option pricing is used as a derivative tool in order to efficiently manage the risk. In financial terms, the buyer in the options contract will have the right to buy the dollars at a prefixed exchange rate. Banking institutions deal with options contracts of different parties thereby managing the risk of exchange rate difference. The diagram below shows how an options contract operates.
Warrants
Warrants are derivatives that give the holder a right to purchase a fixed number of shares of a company upon a time condition. Warrants can be defined as “a security that permits its owner to purchase a specific number of shares of stock at a predetermined price.” (Warrant Definition- the business: warrant 2009)
For instance, permitting the holder of the warrant to buy a fixed number of shares say 10 shares at $40 before September 2, 2010. Warrants are issued certificates.
Leaps
Leaps are just like options that give the right to buy or sell a specific quantity of commodities. The difference is that in leaps there is enough time for maturity. Leaps can be defined as “long-term equity anticipation securities, long-term stock options, with expiration, dates up to three years away.” (Leaps n.d.).
Structured notes
Structured notes also are a kind of derivatives that are used as a security for the payment of debts. It can be defined as “a debt security with one or more special features, such as making payments based on an underlying index.” (Structured note n.d.). As high complexity is involved in this kind of contract, there is a higher chance of getting back a larger return.
Inverse floaters
These are a kind of derivatives and they have an interest rate that fluctuates according to the fluctuations of the index of a few interest rates. Inverse floaters can be defined as “a fixed income instrument which has a coupon rate that varies with a short-term interest rate index in such a way that the yield is inversely related to the market rate of interest.” (Inverse floater n.d.).
Baskets
These are a kind of derivatives used to hedge against securities. It can be defined as “a group of several securities created for the purpose of simultaneous buying and selling.” (Basket n.d.).
Swaptions
A swaption is a kind of derivative in which the parties enter into an agreement for an interest rate swap. Interest rate swaps are covenants between two parties for transacting in certain specific deals. Here the writer of the agreement of swaptions is treated as a seller. (Swaption 2004).
Importance of derivatives
Important factors accountable for the enlargement of financial derivatives are:
- High fluctuation in the financial market: Derivative causes make high fluctuations in the market. The reason is that derivatives have every market all over the world and also derivatives are used to transfer risk from one party to another.
- There is a connection established between the national financial market and the international financial market: Derivatives help to create a connection between the national financial market and the international financial market. The reason is that derivatives contracts have international acceptance.
- IT and communication improved to a great height: The advancement of the Information technology and allied branch also led to increased the significance of the derivatives. The development of information technology results in becoming the financial market more competitive and risky and thereby increasing the need for derivatives contract. Also modernizations in financial markets, which present a combination of risk and return over a number of financial resources leading to higher proceeds, lower transaction costs but enlarged risks.
Derivatives are kind of collaterals whose prices are determined by assets that underpin it. It is based on the contracts between two or more parties, as an underlying asset. Pricing can be caused by vicissitudes in value of collateral assets.
Essential asset backing for derivatives are most common paper securities, traded shares, currency notes like sterling, interest linked bonds, trading in commodity trading and market indicator.
The rapid growth of derivatives trading throughout the world in this recent years because of the internationalization of capital markets, technological advances and by fierce competition among big banks and security houses to sell the products. (Meaning derivatives marketing n.d.).
The relationship between derivatives and different terms
Derivatives are financial instruments such as options, forward contracts, MBS. They are value based on the value of securities, commodities etc. Investors interested in underlying assets are Hedgers. Speculators are concerned with exchange of contracts in profit motive. Listed Derivatives are traded in exchange markets and others are done in over the counter and private transactions.
The growth of derivatives started from the last two decades. Financial institutions and investors took full advantage of derivatives.
Semi annual Over-The-Counter Derivatives market statistics is to provide information regarding the size and structure of derivative markets in the G 10 countries. They provide a comprehensive picture of global financial markets also. Statistical reports on forwards, swaps, interest rates and options of foreign exchange.
Derivatives can be used for three purposes, hedging, speculation and arbitrage
Hedging
It means controlling or reducing risk. The process of taking a position in the future market with the objective of reducing risk or controlling of risks associated with price fluctuations.
Speculations
Investors who analyze the direction of movements of prices of shares and investors buys them when there is upward trend. The counterparty of a speculator is a hedger. Without a speculator, hedger can’t insure by himself.
Arbitrage
It is the exploitation of price differences between markets. It is performed by professional market participants. Derivatives have the role in price discovery. They are combined with other financial instruments in order to eliminate price inefficiencies between markets (Hrovatin, etal. 2009).
Types of Derivative businesses
- Publicly traded Derivative market
- Over-the-counter derivatives market.
OTC derivatives are such as,
- Foreign exchange derivatives
- Interest rate derivatives
- Equity derivatives
- Commodity derivatives and
- Credit derivatives (CDS)
The Main participants of OTC are
- Investment banks
- Commercial Banks
- Government-sponsored enterprises and
- Hedge Funds
Derivatives are dangerous
Derivatives at the heart of crisis and many losses raised such as EU doomed, CDS forms main problem, money values declined. Half of the derivatives were listed and the remaining was unregulated.
As mentioned earlier fund managers, bankers and insurers provide derivatives whose underlying strength is gained from underpinning assets. It was created to help the farmers and manufacturers for the loss insured against. Most of the derivatives are sold over the counter through private sectors. Analysts and regulators can’t find the liabilities of the company.
Derivative-based swaps and securitization consolidated the corporate power through mergers and acquisitions. Public should make control over the management of credit, and they must promote the banking system. The problem is the complexity and lack of control by buyers and sellers. Public should overcome from the pressures of derivative associations and special interest lobbies (Dangerous derivatives at the heart of the financial crisis 2008).
Bespoke
In the context of securities, bespoke securities means those assets which are President Barracks Obama of the US has come up with a plan called for plain vanilla derivatives. But the standard one was not the cause for the collapse of the financial system. It was also called as bespoke derivatives-created by financial institutions like AIG. It is a kind of product that when customized generated enormous profit in the beginning. Finally, it created enormous damage to the financial system.
Treasury authorities created clearinghouses to analyze the trading of derivatives. The expert opined that regulators must maintain the derivatives in a uniform and standardized manner. It should also be seen that it is under the cover of regulators. Firms have to go for some more capital and proper controlling may help the concern to improve once the crisis completes. (Nocera 2009).
Bespoke Market studies
The study may supply details with a range of studies for the purpose of business planning, strategic analysis, commercial due diligence. (Bespoke market studies 2009). Derivatives have come to mean the ultimate in debt management, interest rates, foreign exchange rates and commodity price controls and equity exposures. It gives an idea for the investors who are really studying the market fluctuations.
There are different investors who wish to be the part of the investors in a company. The investor who takes risk is different from those of the other. The person who takes the risk may, or may not be the beneficiary. As the economic catastrophe gained pace and force, housing and mortgage banks went bust and negative aspects of derivatives exasperated the impact of the crash. The customers in international groups were linked with one another by derivatives. The Wall Street firms have always been linked with one another in one way or the other (E g) Lehman Brothers, Bear Sterns were eradicated by Wall Street during this crisis.
But the reason for the crisis was not ultimately the derivatives but derivatives played a role in the story of Lehman. For banks, hedging their situation in the money market seemed a more obvious choice rather than selling them straightaway. These markets provided the kind of leverage that banks were seeking. CDS and other derivatives are another problem part of the banking system (Davi n.d.)
Capital Market and its importance
The capital market or the wealth market is one of the most significant sectors of the financial structure of any nation as it has a straight impact on the economic progress of the country. As one of the legislature of open economy resources markets serve as a significant connection between the requirement for and the delivery of long-term capital funds for creative investments in manufacturing and profit-making units. A well set up capital market can analyze savings of the people towards gainful investments. It has been observed as the large proportion of funds remains inactive and there is no appropriate medium of investment. It is mainly because of this information that a resourceful capital market is an essential obligation for the rapid economic development of a country.
“Around the world, business organizations, small to large investors, financial organizations, and governments of different nations are all major participants in stock market trading activities.” (World stock markets and exchanges n.d.).
Studies show that the derivative contracts were widely used by firms in the developing nation to hedge the risk. However it will be like an insurance pact for safety against terrible future. The financial institutions are using the instrument in the form of interest rate swaps, forward foreign exchange contract and currency swaps. The speculation is considered as gambling on the future price movement. However the speculation plays a major role in the market and the liquidity is available to other investor by the derivative instruments.
Arbitrages also have a very important role in the market. They simultaneously having positions in two different markets and looking forward to the changes in the two markets to make profit. When the stock price of a commodity is different in different markets, the arbitrages assist to get market price back to its original position.
Functions of Derivatives market
The derivative market performs a number of economic functions like,
- Serving in significant current and future prices of resources.
- Facilitate to the relocation of risk from indisposed risk takers.
- Encourage entrepreneurial activities.
- Inform savings towards investment.
- Development upon the allotment of recognition by sharing of risk.
Derivatives permit investors to control relatively small amounts of funds over an extensive class of assets and thus expand their portfolios. Derivative value reveals information to investors and offer more strength to the financial markets.
The uncertainty related with derivatives depends upon how these marketable securities are used in a meticulous market and profitable atmosphere. Though, recognized derivative market survives, where consistent derivatives are traded on proper legally recognized exchanges. There are informal unorganized and officially unrecognized marketplaces where numerous privately discussed, modified financial contracts are traded, which are acknowledged as Over the Counter (OTC) derivatives. Such OTC trading monetary contracts represent markets to a large amount of financial, operational, counterparty, liquidity and lawful risk.
Role of derivatives in the economy
Derivatives play a very important role in the economic or financial decisions of a country.
Investment decisions
The investment decision is a challenging task for the management team of any kind of organization. It is evident from the success or failure of different organizations, there is one or more decisions in this success or failure. While making investment decisions like different factors like internal rate of return (IRR), net present value, payback period, accounting rate of return and profitability index…etc are to be considered. Sometimes new ideas might be seen as a failure in the short run but it can give a better return in the long run. Therefore while making investment decision the long run return should be given much preference and they are to be made into action first. The managers also have to consider different other factors like the nature of the organization, cash flow and feasibility.
Investment decisions in times of recession
Utmost care should be taken while taking decisions in times of recession. Apt decision can only ensure survival in this period of economic slowdown. The studies show that, the recession has adversely affected the manufacturing industry in the United Kingdom. The out put of the manufacturing organizations have come down recently due to the economic slowdown. Also the industry did mot meet the expected percentage of growth. “David Page, a UK economist at City bank Investec, said the manufacturing slump, combined with a larger than expected fall in the wider production sector that includes energy, would cut GDP to 0.1 per cent.” (Thornton 2003).
The topic risk management is of great relevance in today’s recession affected world. In relation to the business operation and management the tern risk management means identifying, analyzing and taking necessary steps for managing the occurrences or situations which may negatively affect the business organization. Taking new investment decisions during recession period involves high amount of risk. The reason is that there is a greater possibility of becoming the project a failure. The recession has because the failure or closure of number of manufacturing concerns in the United Kingdom which means that situation is much worst. Therefore it is better to not go ahead with major investment decisions in this period. (Geroski & Gregg 1993).
Do derivatives really help in hedging the risk?
Derivatives help to shift risk from one party to another. The derivatives were originally meant for transferring or reducing the risk, but now it has become a riskier as more and more people started to come towards derivatives contracts (Derivatives n.d.).
Overview of Global Crisis
An overview of present recession
It is the growth of GDP but it is in the negative sense.
The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) defines recession as a “significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy lasting more than a few months normally visible in real GDP real income employment industrial production and whole sale retail sales.” (The NBER’s recession dating procedure 2003).
Recessions are not frequent events. In the past there are only four in last 30 years. According to NBER, (National Bureau of Economic Research) recession begins from the zenith of each business cycle and terminates in the bottom. US have experienced 10 such cycles. This situation can go for a period of months or years.
The recession that the world is experiencing now caused serious impact on almost all economies of the world. Developed countries like United States of America and Britain are the most affected by the recession.
Management of compensation packages
Many reputed banks in these countries fell down to the loss. Also the recession caused many people to lose their job. The severity of the recession can be understood from the following chart.
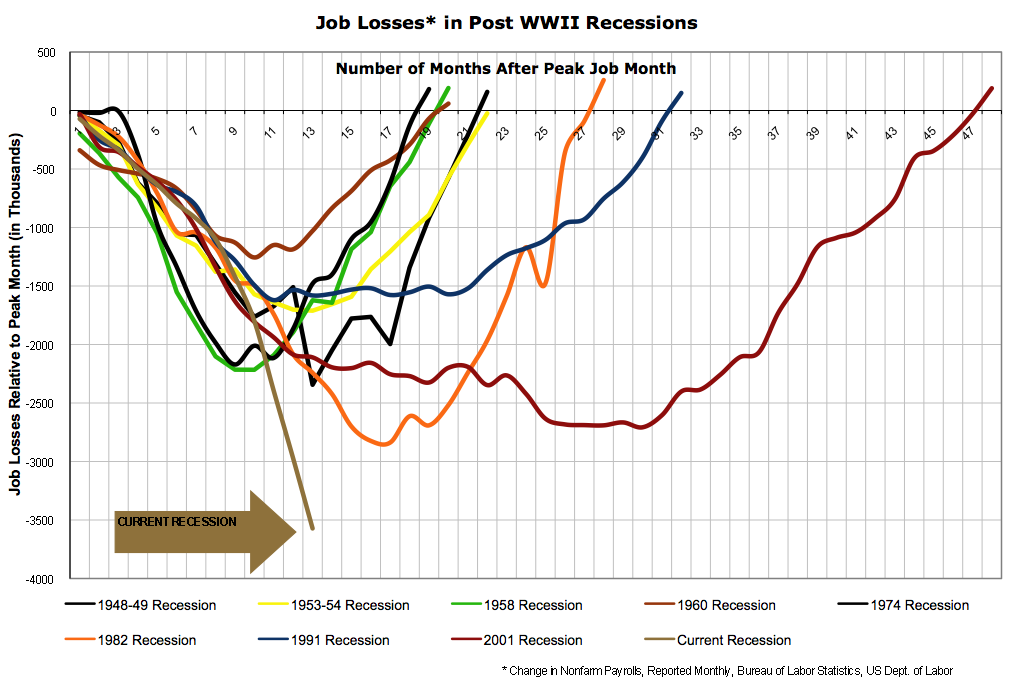
From the above graph it is clear that in the current recession have indicating that the recession created a serious hurt in the global economy. Employees losing their job means companies are not able afford to pay the salaries to them or unable to use them productively due to fall in business.
York, the CEO of the company Harwinton Capital told that present recession would be worst, last longing and deep recession that the world has ever seen. He also added that, as a result of crisis the housing sector stooped into losses and so many banks. (Reason & Mintz 2008).
Recession caused to decrease the GDP of the countries like United States of America and United Kingdom. The following graph shows the GDP of United States of America for the recent five years.
Recession is good or bad
All economists are worried about recession going to be a great depression. Governments and reserve banks work to control recession. This situation declines GDP of the economy. The trading communities and ultimate consumers hold their savings instead of spending for business development or purchase of goods and services. Unemployment goes up and salaries drops downwards, many lost jobs.
Recession is some what good, many mismanaged companies failed and many businesses were sent out. But the employees in those concerns lose their livelihoods. There are good opportunities for surviving businesses and newly formed business. Now competitions become lesser so that many concerns thinking of expansion. Typical companies like private education companies, service industries, bond business, law firms, mortgage companies expand during this time.
When recession started Fed reacts by lowering of interest rates and they have increased their money supply. Businesses and common people took advantage from this. Prices fallen due demand for goods and services dropped. Oil prices decreased, Stock prices dropped which made investors to buy more. Investors look for safe place for investment in recession.
Business cycles are normal where there are growth, boom decline, recession and recovery stages. No one can control the flow; it is a kind of wave in the ocean. There may be calm and storm situations. There is a limit for the governments, they can cut the rates of taxes, can create a business environment and they cannot make private companies invest in areas where required. Entrepreneurs and investors must come which can change the situation. (Seitz 2009).
Financial crisis
Monetary losses: These are scenarios in which a financial crisis may precipitate losses of values. Today’s crisis is considered as the most serious crisis since the great depression. With this crisis there are global effects such as failure of key businesses, decline in consumer wealth, financial commitments by governments and the decline of whole economy. Due to this crisis many lost their jobs their holdings and many lost their belongings.
The decline of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for the consecutive two or more quarters of a year is Recession. Whenever there is a continuous economic growth for the period of 6-10 years there will be a decline and that’s recession. But recession today had affected every part of the economy.
Financial occurrences in the US affected other global economies as well. The larger economies which basked in growth and development for long were now feeling the pinch of goods lacking demands.The expenses of the consumers are decreasing drastically which in turn leads to less production and all these raises unemployment. Quite a large number of industries and corporate needed to cut down the strength of their workforce.
Stock markets are the major indicators of the economy. Most economies of the world are forced to cut back on staff strengths and governments are constrained to provide bailout packages for closed industries. The global economic crisis is getting worse. Recently in the banking industry citi bank has been bailed out with several hundred billion dollars in cash and guarantees from the authorities
Some people fall down while some make profits, some feel danger while a little found as opportunities. Mergers and acquisitions appear among luxury brands in the world.
Since 1974 Americans faced a huge job loss around 6.7% highest in last 15 years. Experts opined that this will be the worst recession period since the 1930s great depression. The recession in industrial countries overwhelmed the forecasting abilities of many institutions (IMF). similarly, it has been affecting the other two big economies Japan and Europe.
China’s stature in the world economy has gained as a consequence of this financial crisis. The aim focuses the attention on the international community. The crisis will not diminish or eliminate the growing hope in between the people. The recovery can be achieved earlier rather than later. Appropriate and coordinated are to be implemented. (Recession: India’s prospects in 2009 2009).
Global crisis and stock market
Stock market crashes collapsed the stock prices across all around the markets. Crashes created panic in between investors by the underlying economic factors. This made the market participants to sell their stocks. It is because of social and psychological phenomena.
Investors lost their confidence in global financial crisis. All the stock markets of whole world declined during the financial crisis. Banks, mortgage lenders, and insurance companies failed. Crashes are often associated with Bear markets. Bear market periods declines the stock prices over a period of time. (E.g.) Crash in 1987 and crash of Japanese Nikkei in1990. Crashes occurred when rising of stock prices over a period of time, excessive economic confidence; price of earning ratio exceeds long term averages, extensive use of margin debt, and influence of market participants.
Failures of large financial institutions due to loans and credit default swaps which are issued to insure these debts resulted in failures, in turn diminishes the stock prices. More than 15 banks failed in US some are taken by other banks and governments rescued others. In October 2008 the fall was around 21% which was compared with 1987, but this shocked and named as “panic 2008”by the traders in the in market. By the end of October all stock exchanges was totally destructed. Both US dollar and Japanese yen rise against other currencies particularly on British pounds and Canadian dollars, but they were considered as safe in the market
Stocks markets around the world are suffering big losses as a result of global credit crisis. Sub-prime mortgages where those people with poor credit histories. (Stock market crash 2009).
Crisis and Insurance industry
The main role of insurance companies is to help the other sectors to manage risks. Insurance companies support corporate and household sectors. Reinsurance companies work similarly in relation to primary insurers enabling risk. The insurance companies aims to make underwriting profits and use investment income against claims. (Current financial crisis and insurance companies 2009).
The liabilities of non-life sectors are related to the likelihood and severity of losses in real economy. Insurance companies’ assets are mostly marketable securities. Everyone were thinking of their insurance money will be affected by the present crisis. Insurance companies are monitored by state regulations to ensure that customers are fully protected. Besides, one more protection for insurance clients called guaranty funds is available. The industry has been able to ward off the challenges created by the collapse of sub-mortgage meltdowns and effective risk management strategies.
Life insurance industries are quite safe in this crisis- AIG is the biggest insurer collapsed, strict regulations are made on derivative products. Banks and securities and insurance companies are the three pillars of the financial industry (Ja-Young 2009).
Impact by the crisis
- Credit loss on sub prime mortgages
- Financial institutions with specific exposures such as CDS and financial guarantee business.
Insurer’s contribution to a rapid end to the financial crisis
- Promote financial stability and security
- Encourage productive investments and innovations
- Mobilize savings
- Efficient use of capital (SC2: insurance and finance 2008).
The Role of Derivatives in the East Asian Financial crisis
- Derivatives have been developed for the growth of private capital flows in developing economies. Capital flow through unbundling the risk involved in bank loans, stocks, bonds, and direct physical investments.
- At the Macroeconomic level, derivatives lead to the financial crisis but when the crisis started. Later it quickened and deepened to the downturn.
- Derivatives play an important role in the economy. They help in hedging and risk management in developing economies.
- It can also make fixed exchange rate systems and then later quicken the pace and deepen the impact of devaluation
- The accounting rules, capital requirements and risk management requirements of financial institutions should be updated such that it forms as a regulatory safeguard in the financial systems.
- Both the derivative markets exchange-traded and over–the–counter, must become transparent in reporting for the transaction.
- Proper regulations should be made for shaping the structure of derivative trading. (Eatwell & Taylor 2002, p.447).
Right path for encouraging derivative industry
- In a bid to achieve higher degree of standardization, reforms were put into place
- Refocussing customer needs and acting on it.
- Corrective and remedial measures in the economy must be supervised by authorities who are able to identify and hone in the correct solutions for market issues.
- The OTC derivative industry particularly CDS (Credit Default Swaps) is moving forward with new solutions.
Diagnosing the root for financial crisis
For the last several months world economy was suffering from great problem- Financial Crisis. Many policymakers’ researchers working to find out the real root for the financial crisis. But the problem is extremely severe, complex, and very urgent to find the roots and proper solutions. Getting out of this crisis there are many problems to be faced. There are two related factors that cause to the financial crisis.
- Through a regime of excessive lending, customers were constrained to invest in property that was heavily overvalued.
- To a large extent the presence of excessive land used drives land use to penury.
Excellent workforce, excessive land use and a plethora of workforce, excessive industries and land use regulations in metropolitan markets such as urban growth, building moratoria, leading to severe mortgage exposures.
However, land laws were not harsh in Texas, Georgia and in Midwest and South US which were conventionally well-controlled markets.
Causes for the financial crisis
US Housing Market
It is considered as one of the causes for the severe financial crisis since great depression. These have been spread all over the world economy.
Excessive lending
It is one of the macro-economic factors which has affected all markets in USA. The availability of mortgage funding lead to greater demand for housing in the minds of people. The present condition of failure to meet is seen in Bear Steam, and is concerned with how and through smaller investments. The present condition of failure to meet is seen in Bear Steam, and is concerned with how and though Smaller values are in good health.
Excessive land regulation
Greater offerings of quantum of loans led to falloff demand for housing loans in urban segments. Apart from the restrictions man wants their house in the metropolitans and they pay huge amount for it. This leads to the relative increase in the house prices. But at the same time it didn’t affect those areas where there are traditional regulated markets. (Cox 2008).
Credit derivatives are not the only factor responsible for the crisis in Wall Street. It is not the only factor which collapsed Bear Stearns and Lehman, but this made the financial world more complex and opaque. Financial institutions and regulators were too late to understand and find solutions to them. US treasury came out with a largest bailout in the American history-Regulating Credit Derivatives.
During the Asian Financial crisis in 1997- Morgan’s derivative project ways of protecting banks from bad loans, there are two victims Bear Stearns and Washington Mutual-still under the credit derivatives.
Credit Derivatives- created only a decade ago is more responsible for the global financial world. (Eisinger 2008).
Derivatives in mortgage crisis
The global financial crisis lost the confidence in investors in the value of securitized mortgages results in liquidity crisis. Mortgage-backed Security is a good example for derivatives. Derivatives are complex financial product that derives their value on the basis of underlying assets.
Process in M B S (Mortgage-backed Securities)
The process of begins from providing Interest only loans to the owners. Then bank sells mortgages to Fannie Mae-buys mortgages’ from banks and converts them in to MBS and resells to the investors in market. Fannie Mae motivates the housing market, which comprises 10% of the economy and supports the owners with high priced houses and also supports the medium and low income groups. When Fannie Mae sells the values are derived by the value of mortgages in bundle. MBS are bought by the Hedge Funds.
Hedge Funds
The Owners of Hedge Funds are Public Corporations. These are privately owned investment funds. There is no such regulation that prevails in mutual funds.
Hedge Fund Managers use highly reliable Derivatives such as options, forward contracts, and puts. Normally they use small amounts and promise higher stocks and commodities. They will deliver the stocks and commodities at the right point and at right time. The process continues until housing prices decline or interest rates reset. (Amadeo 2008).
Participants of mortgagers
Banning investors’ law suits and indemnifying mortgagers both cost substantially. Investors can claim or sue against breach and indemnification makes tax payers liable for any damages. (Jakabovics 2008).
From the above graph it is clear that the economy of United States of America is facing a drastic decline in its Gross Domestic Product.
The recession caused to come down the GDP of United Kingdom also. The following graph shows the GDP of UK in recent years.
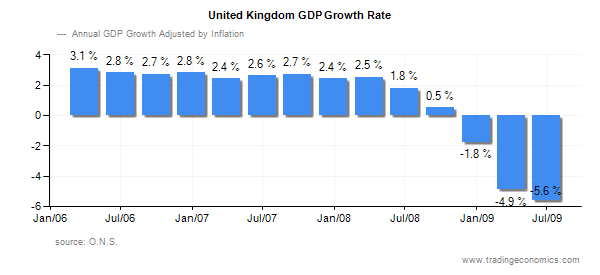
It is clear from the above graph that the GDP growth rate of United Kingdom is showing a declining trend as a consequence of the recession. The GDP growth rate in 2006 January was 3.1% and in 2006 July it came down and till first quarter of the 2008 it was almost constant. However, after that it started to came down falling below zero.
As a result of the recession, the interest rate in UK has come down which shows the severity of the recession. The following graph shows the UK interest rate from 1999 to 2009.

From the above graph it is clear that there is a variation in interest rate from 1999 to 2009. Interest rate in 1999, it was around p percentage, but when it comes to 2009 it came down to less than twp percent. The recession affected very badly the financial market and banking industry.
Consumer behavior during recession
This is the study that represents the behavior of consumers during times of a weak economy or recession period. Here, there is a report which consists the information about the consumer’s shopping or buying behavior during the weak economic year. “The report is also supported with online shopping traffic data sourced from Market Reporter, a statistical database that tracks actual consumer shopping behavior on PriceGrabber.com. PriceGrabber.com is a major shopping comparison engine, with more than 26 million unique users per month and up-to-date daily pricing of products supplied by more than 12,500 sellers.” (Consumer Behaviour Report 2008, p.2).
Consumer spending trends in a recession affected economy
During the quarter of the year 2008 the surveys were conducted to analysis the consumers spending behaviours and the economic downturn. The tax rebate survey contains 1260 respondents of consumers from March 25 to April 19. Consumer spending survey includes 3359 respondent surveyed consumers and the economic stimulus survey contains 2483 respondents’ surveyed consumers in the year.
- Among the 1260 online shoppers surveyed from March 25 to April19, they planned to use tax refund in the recession period. Among them 65 percentage of consumers are interested to spend their tax refund. 35 percentages of respondent consumers are planned to save their money.
- Among the 3359 respondents surveyed from April 29 to May 23, 2008. The survey revealed that 56 percentages of consumers accepted the cutting back price policy as per the impact of weak economic crisis. A few reasons of the cutting price are; 57 percent increasing inflation and 25 percent causes due to the lack of confidence in the economy.
- From June 13-30, 2008 survey including 2483 respondents, among them 69 percent of consumers decided to spend their stimulus check. 39 percentages indicated that, they will pay the existing debt as economic stimulus check.
- From the above information we can have an idea regarding the consumers spending behaviour based on the surveys conducted on various individuals, as per the weak economic down turn. (Consumer Behaviour Report 2008).
Recession- causes and effect
There are so many reasons for the present recession and derivatives trading are the one of the reasons for the recession. Some of the main reasons are explained below.
Unwise spending by the people
The people spend money without any control which was regarded as one of the causes of the present recession. People did not think about tomorrow when they spend money.
Liberalized credit policy of banks
Banks liberalized loan procedures which caused to increase the number of people who take loan. Most of people borrowed money without thinking that they have to repay the loan. They failed to repay the loan and ultimately that lead to the failure top banks.
Increase in mortgage loans
An increase in mortgage loans in the United States in different names is treated as one of the causes of financial recession. These mortgage loans were issued without asking to submit any documents income proofs. The people money without any control, in such a way that those who already have one home bought one more house using the mortgage and people, are more interested to become the holder if different credit cards even if it is not affordable to them. This lead to an infinite increase in the number of persons who do not repay the mortgages and this ultimately lead to economic slowdown.
Regulation lacking derivatives trading
There were no proper regulations for derivatives. For those who argue that derivatives are one of the causes of present economic meltdown has a proof a country which went bankrupt due to its extensive involvement in the world derivative market. Recently, different investment funds in the world started leave the relationship with derivatives.
The recession still continues to exist due to different reasons and one among these reasons is the attitude of the people. People are feared of making further financial movements and which made the situation worst. There was not enough flow of money into the economies. (What in the world happened? 2009).
Now a day every one is talking about recession in the global economy. Before studying recession deeply, we have to understand the meaning of GDP. This means the aggregate dollar value of all Gross Domestic Product of all final goods and services produced in an economy during a particular year. Final goods remain the same and have not changed identity into other kinds of goods. Ultimate goods are computed on the base of present market value of goods and services.
Recession could be a state in which there are sliding rates of all ultimate goods and utilities produced by an economy for two consecutive quarters.
“As per NBER (National Bureau of Economic Research), there have been ten recessions since 1945. From mid 1940s till 2007, the average recession lasted 10 months, while the average expansion lasted 57 months, giving us an average business cycle of 67 months or about 5 years and seven months.” (Bijlani 2009).
Mainly there are various factors that turn an economy into recession, among these factors; inflation plays a predominant role to change the economy into recession. In the simple sense, we can say that inflation is the situation occurred due to continuous price rise. It could be said to be the state of an economy wherein prices of goods and services cannot be reined in. Inflation occurs in the economy, due to the increased rate of production costs, higher energy, etc… It can change the overall functional aspects of an economy. When the rate of inflation increases, the people spend low amount of money for purchasing and other basic needs. The people tend to cut the rate of total expenditure of spending. Automatically, it makes the companies to cut their overall production costs and brings unemployment in the particular situation
Following factors also can are the factors, which can turn an economy into recession.
- Lack of sufficient fund
- Falling house prices
- Uncontrollable rate of Inflation
- Reduced disposable income etc….
Recession creates major effect on the economy over a particular period. The following are the causes and effect of recession. It influences the standard of living of people in a particular country, and creates the unemployment during the specific financial years.
Are derivatives a cause of the present recession?
In a blog Spin Doctor points out that derivatives helps managers who are dealing with money to hedge against the risk. He says that derivatives caused to make changes in the decision-making of the investors. The investors are now ready to involve in risky investment ventures as they are confident that they can mitigate or hedge the risk using derivatives. He also argues derivatives are one of the causes for the present recession as there are not enough regulations for controlling and coordinating the operation of derivatives. (Recession watch 2009).
Some experts argue that, the attitudes of the leading banks in the developed countries were the real cause of the recession. Banks gave out loans to people without asking any security or like that, even they allotted loans to job less people by ignoring the possibility of non-re-payment by these people. When allotting loan the banks even did not check the credit history of the loan applicants. These all caused to increase the amount of unpaid back loan, thereby pulling the banks into loss. These ultimately lead to recession. (Whitney 2009).
Finding solution
When the governments understood that, the unregulated derivatives market is the one of the causes of the present economic crisis, they started to find solution to overcome these issues. In United States, the treasury department passed a new bill for controlling and regulating the private derivative markets. According to the bill, a fresh unit is created in the treasury for co-ordinating, the derivatives market regulation, with Securities and Exchange Commission and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission. (Treasury has prime role in derivatives bill 2009).
Also, the new government of United States led by Obama proposed rules for regulating credit default swaps, which are kind of contract for hedging the risk, as there is no authenticity in this kind of swap contracts.
The real danger of the derivatives is seen when securities which are backed by assets fall down. Some organisation had an illusion that derivatives could give them a better even if the marketing is showing a declining tendency. But when market started to fall down these believes and illusion proved wrong. Derivatives were unable to any thing. Therefore the government decided to regulate the operations of derivatives market. (Hamilton 2009).
There is no single solution to the effects of financial crisis on middle income countries. Economists opined that improvement in the economy. Both export products and markets need to be diversified by middle income states. Exports and local demand need to be well in harmony. Unemployment will be remaining in middle income countries.
The board of International Accounting Standards and its counter part FASB issue proposals to replace their financial instruments with a common one. The two boards were considered as the standard setters. Now they find it difficult to reconcile the differences in existing standards. The fiscal steps are most effective to defuse current crisis. Six central banks around the world did not respond. Governments are finding creative ways to deal financial crisis. US real-estate markets and overall economic financial crisis crisis can be solved very quickly and successfully if the US government takes right steps In emergency and radical legislation. It is believed it would take few more years for this crises to resolve. (Grant 2009; Foxley 2009).
World economic crisis needs two years to recovery
Experts opine that the recovery from the financial crisis needs around few more years to be mitigated. The employment rate is still in a declining range whereas the GDP rates are improving. In a symposium held in Kuala Lumpur. Expert opine that US has begun to recover from the technological crisis. Governments are playing their role in preventing from falling to great depression. Fiscal policies and monetary policies can be manipulated to motivate economic growth. (World economic crisis needs two year to fully recover 2009).
The global financial crisis started showing its effects from the middle of 2007-2008 All the markets have been fallen many financial institutions were collapsed; banking sectors faced a lot of problems. Developed countries faced more than the developing or under developed. Many countries came out with rescue packages to bail out financial systems. The packages may save financial institutions but it does not solve livelihood problems which are interconnected with the world economy. The crumple of Mortgage Market and the boom situation in housing in industrialised economy had a current effect around the world. The mortgage markets crisis came about with securitisation of financial instruments.
Banks convert their loans to sellable assets. They want avoid the risk from those loans. Even more money has been borrowed to lend out and convert them in to securities. Sometimes they borrow from other banks for lending. This made Lehman Brothers into a big fall. Some banks gave more excuse to the loans in order to securitize them. Some banks bought securities from others. Collateralised Debt Obligation (CDO) was complicated and too risky. Investment banks who are not dealing with buying, selling and trading risks, but they are caught in home loans and uncontrolled management.
When crisis started people began panic and lost their confidence. Assets have been losing their values. So some collapsed quickly, the problem here was quite large so the government came out with bailout packages. (Shah 2009).
The Treasury have limited ability to control over the mortgages that create trouble in the market. They should buy the MBS and their derivatives from all financial institutions. There should be proper control over the mortgages such that the plan of buying the troubling assets will fail.
Legal Modification
Changes made in the governing political system for collateral loans on basic homes facing liquidation claims. But the current law of bankruptcy must be modified or loans of primary residence should be modified.
Purchase of Mortgages
Treasury authorities purchase not only the residential and commercial mortgages but any other financial instruments which needed. The positive effect on housing markets helped house owners. Once the treasury had acquired the mortgages they will divide them in to current and wrong ones. Loans would be sold and make them in a liquid form. Other offending mortgages would be analyzed and restructured. Treasury would resell them.
The Role of Government and IMF
A financial crisis occurs in the exchange market and stock market. Controversies raged. Some argue government intervention is unnecessary. The signs of recovery started showing in the southern part of Asia. Investors in foreign countries have begun to take up the acquisition of Asian debt and equities in the reforms package of these countries. IMF supported countries like Indonesia, Korea, and Thailand. Local governments and global agencies should help during need. The world economic agencies along with interrelated agencies are striving to set higher standards for the world. IMF needs co-operation from governments, financial institutions, and other social communities. (Boorman 1999).
The financial crisis and Banking sector
In highly regulated environments banks and security firms are facing complex challenges. Financial institutions are mostly affected in this financial crisis. Stock market slowdown has created a lot of problems in the economy as a whole. Everyday there is demand for managing the risks. It is quite hard to satisfy the divergent interest of stakeholders. The US banking system is on the border of disaster. It started with sub-prime mortgage losses from 2007 which caused this huge crisis.
Banks in small towns and cities are busy with auctioning of houses. Merrill Lynch and citi group has to look in to Asian and Middle East to shore up the balance sheets.
Both banks in Europe have been as adversely affected as their Swiss, German, Britain and French counterparts in terms of losses of billions of dollars. These losses are not only those of banking sectors. The largest insurance company in the word, American International Group was affected during this crisis and has currently reported losses on account of the ensuing sub mortgage crisis. A combination of credit crunch, declined house market, increased energy prices, threat of rising inflation totally declined the American economy.
The crisis did not spare any financial sector like pension and mutual funds, insurances etc. The Central Government resorted to emergency strategies like stimuli plans, tax cuts, freezing interest rates preventing institutions from total collapse through bailout packages.
Traditionally banks operated on the base on deposits from the customers and lending money for interest. The difference between interests paid and received forms profits to the banks. If the loans are not repaid the banks are responsible to depositors. Before providing the loans banks finds the repayment capacity of the customer who seek loans. To increase their profits banks used customer’s money for securitisation. This involves the procedure of converting mortgage into notes and offering the same to investors like pension funds, mutual funds, insurance companies and other banks. Banks earned through fees for having put together. They earned much better than before.
Many customers do not satisfy the standard lending procedures, loans were provided to all the applicants (Sub prime customers). There are no screening procedures. The financial crisis started from 2007, the surplus of homes, problems in mortgages. The crisis has deepened and investors have assets that cannot be indemnified. Banks now find more difficult to sell additional bonds, thus bank fee income dried out making capital deficiency. Banks have controlled their lending. (America’s banking crisis 2008).
The Impact of the Crisis Varies by Business
The financial crisis has different strategic implications for different businesses:
- Retail Banking- Banks faith remains in the deposits they acquire and their functioning of branches.
- Corporate Banking- Increase in Corporate loans leads to relocate pricing and productivity.
- Investment Banking- Many moves from risk-takers to risk facilitators
- Asset Management- More amounts of withdrawals. They have to look in trust rebuilding and cost-cutting.
- Wealth Management- damages to brand and trusts. (The financial crisis has slashed the banking industry’s market value by $5.5 trillion 2009).
Interviews of Managers in Derivatives and the Brokers associated with the stock markets are conducted. There were 10 questions asked. The participants answered sincerely. These questions are framed to make investors aware of the crisis and reduce their panic about investment.
Overview of global crisis
Perhaps the derivative crisis arouse due to overtrading, banks dealing in securities and assets which were either non-existent or heavily overvalued.
Resulting in massive downscaling of securitized assets and investment holdings. The cumulative effects of massive asset erosion could not be borne by bourses and factors like sub-mortgage loan crisis, falling interest rates and loss of market confidence all led the snowballing crisis to develop. Thus, the problems of the derivatives in the current situation were like lack of liquidity, opaque system management and credit ratings that did not match with actual ground realities and data. Thus it became necessary to create reliable, genuine and high liquid derivative markets, bring ratings in tune with actual performance and create a legal framework that could support or sustain business.
Add to this, liquidity crisis also arouse, which prompted many banking companies to become bankrupt, almost overnight. The loss of market credibility of World.com, Lehmann Brothers and many other European banks precipitate their downfall, which was only obvious considering the kind of risks they were exposed to and minimum levels of risk management that were enforced during those periods.
The various ramifications and implications of these factors would be analyzed next.
Research methods
In this part of the research paper different sampling methods, selection of variable, selection of the population, reasons for the selection, way of analyzing collected data, etc. are discussed. The research method adopted here is statistical research of secondary data. Sampling refers to the process of choosing the unit from the available population like people, organizations, etc. using different methods and techniques. The chosen units are called samples. Each item in the samples is called a sample unit or simply unit. The process of measuring or counting together with recording of results is termed as data collection. (About national statistics & ONS: What is data collection? 2005).
Methodology
Methods of data collection
The data may be a primary data or secondary data. The primary data refers to data collected for the first time by the investigator for his own purpose. There will be originality in the nature of data. The primary data can be collected by direct personal interview, indirect oral investigation, telephone interview and questionnaire by post. The secondary data refers to the data collected by others for some other purpose and used by the investigator. In other words the secondary source of data refers to the use of those data which have been already collected by some other persons for their purpose.
The different sources of secondary data are internet(which includes published articles in different websites and public documents like books, reports of surveys done by other researchers and organizations), regular publications of the government, occasional publications of the government, Publication by various agencies, Private agencies, articles in news papers and magazines, research organizations, research scholars, international agencies…etc. In this paper both the primary and secondary data are used. The data collected from various sources are analyzed focusing on the reasons for the fall in oil price. The research method is designed with most care as the result is being affected by the research method. (Primary & secondary data – what’s the difference? 2007).
Sampling process and its method
When data are collected from a representative part of universe or population, it is called sample method. Sample method is based on the assumption that the sample selected from the population is likely to possess almost all the characteristics of the population or universe. (Mugo n.d.).
All the units or items which come under the boundary or limit of the study are called the universe, or population. When the sample size increases reliability also increases. Sample should be selected in such away that it should have almost all the characteristics of the entire population, the size of sample should be sufficient and also there should not be any bias in selecting any item as sample. The main merits of sample method of data collection are it is economical in terms of cost and time and also as it is a detailed information results are more reliable. The demerits of sampling are that it requires the service of the expert and also if the information is needed from each and every unit sampling techniques cannot be used.
Research design
The various data collected from different sources of information are analyzed with the help of different statistical techniques. The analysis will help to understand the behavioral pattern of the industry and also to frame a valid proposition on the research question. As the entire industry is kept understudy under this method of research, it facilitated in understanding and analyzing the complex factors covering all the aspects of the research question.
They are as follows:
- What were the problems of the derivatives in the current crisis? The lack of Liquidity? The absence of transparency? The false ratings? …
- What should be done to prevent that crisis?
- Create reliable and liquid market für derivatives?
- Enhance the rating? Enhance the legal framework (a better international coordination)?
Analysis of collected data
The data that is being collected by various methods are analyzed with the help of various statistical techniques.
The Methodology that was being pursued for this study would be in terms of personal contacts established with people who are actually indulging in the derivatives market and who have first account knowledge of the current market conditions and the impact of derivatives upon the global recessionary trends
The main objectives of this derivatives study are:
- First and foremost, to evaluate the current trend of derivatives trading in the country and suggest ways and means by which these could be overcome.
- To analyze the effects of derivatives trading upon respondents and how they view derivative trading in view of the current scenario.
- To probe the risks, threats and negative aspects associated with derivative market and seek avenues through which they are resolved.
Survey Paper
It is repeated that this derivative trading business would depend upon open ended questions posed to select group of respondents as major part of the survey.
This Study used the help of open-ended questionnaires were drafted and electronically mailed to individual respondents who formed the Core Study Group. The Study was conducted through Online Interviews and Structured Questionnaires which was distributed to samples selected for derivative study.
Mode of survey conducted
A Sample of 500 respondents were selected through random sampling in which 300 respondents had limited derivative trading experience whereas the other 200 were regular and active players in the derivative markets.
All the responses for this questionnaire were treated with utmost confidentiality and privacy.Prior permission of employers of respondents were taken before they were requested to participate in this survey. It was also deemed that only concerned persons who were directly involved in the survey regarding derivatives had access to the reports and submissions and all matters concerning this survey was treated with utmost privacy.
The kinds of questions that were asked and sample answers that were received have been sent with this study which forms part of the Survey. The prior permissions of the required administrative bodies and authorities were sought and received for the conduct of this online survey. Prior appointments with executives who agreed to anonymously pose as respondents were also made. The main idea for a survey of this kind was to assess the impact of derivatives on industry, and what experts have to say on this topic.
The survey results of open-ended questions posed to respondents are mentioned in a separate attachments.
Ethical considerations
The ethical issues regarding the use of the responses only for the purpose of current and future business prospects, and not for any other commercial usage underpinned the study and this was followed. The permissions of the employers of the derivative market firms in which the respondents were working as traders and brokers were also sought and received to avoid later issues arising from the survey.
The online survey method was considered better than other forms, since it is necessary to gain a broad-based and total picture of the present scenario and how it impacts the general public. Besides,” Internet surveys lend themselves to certain types of survey because respondents know how to use e-mail or the web, have the technology to reply, give their permission to participate and have an interest in completing the survey.” (Internet surveys 2009).
Moreover, such a large number of respondents could not be possibly personally interviewed and results obtained in such a short span of time, and the costs, time and efforts required for conducting a physical survey would be immense and beyond the scope of a study of this kind. Moreover, it is also seen that the internet survey method provided quick, accurate and genuine results, with lower degree of bias, or statistical errors, since the questions are posed to experts in their respective fields, and also the feedbacks received would be appropriate and in tune with the needs of the survey. It is observed that for a survey of this kind, internet survey could be the most plausible method when the respondent population is representative of the internet population.
While the internet survey methodology may be representative of the sample that are needed for a survey of this kind, it is also to be ensured that the results are plausible and question specific. This is because, in use of open ended questions respondents have wider choice and may sometimes prefer rambling answers that do not serve the purpose of survey. “Open-ended questions are questions that encourage people to talk about whatever is important to them. They help to establish rapport, gather information, and increase understanding.” (Open-ended questions n.d.).
Thus, standardization of answers to arrive at final conclusion may sometimes be a difficult proposition that needs to be suitably addressed to.
However, it is felt that for a survey of this kind, involving a highly technical subject like derivative trading and its impact on the current global economy, the internet survey method would be most suitable, considering the fact that it addressed issues to those who are directly connected with it, with least costs and maximum convenience and ease of performance. Coming next to the fact whether there could be a more suitable method, it would be difficult to say so, considering the fact that a topic of this kind needs to address several crucial aspects of derivatives trading before forming a final consensus on the subject. Use of alternative methods would not best serve the purpose of this research, since telephone interviews, or even face to face interviews have not been considered necessary or suitable for this kind of research.
One of the primary reasons has been that derivatives trading are a highly specialized and technical subject, known not to the general public, but only to people who are actually in the field as brokers and consultant managing portfolio or wealth management. Thus, a research study of this kind needs to address to the specifics of the case study and deal with the problem in hand and the remedies and solutions that could be found after research.
Another aspect that needs to be considered is that this research could substantiate and underpin further detailed research on this subject, lending more evidence-based information and data on a crucial and significant subject in modern times.
The methodology used also considers the fact that future research study on this subject may based their research on information and data gleaned from this report.
Analysis and interpretations with survey results
Why companies manage risk
It is common knowledge that the investors of securities will not be interested in bearing many risks. They will analyze different portfolios and make investments in portfolios where here is least, or no amount of risk. There are different reasons for managing risk by the companies. Some of them are explained below.
Increases debt capacity of the company
Risk management helps the company to increase its debt capacity as it makes the cash flow more stable thereby reducing the chance of bankruptcy. Through this company can properly manage and reduce the operating risk. These all will result in increase in the debt capacity and ensuring the higher price for the stock of the company. “The stockholder/bondholder conflict can be resolved by managing the risk of changes in the value of the firm.” (Culp 2001, p.150).
Risk management helps to keep best possible capital budget
Most of the companies are interested in financing its capital requirement by using debt capital than external equity due to high cost and other market problems. The companies try to maintain finest capital budget by using capital from internal sources like ploughed back profit or depreciation. The cash flow can be smoothened by using derivatives. If there is a proper risk management system in a company, it can ensure efficient implementation risk reduction techniques like derivatives. Also a proper capital budgeting can help in efficient risk management (Froot & Stein n.d.).
Ensuring financial safety
If there is a proper risk management system in a company, it can ensure that there is enough cash flow in such a way that the risk management team will efficiently deal with interest rate fluctuations, problems associated with customers and other financial problems.
Helps in hedging operation
It is impossible for the most of the individual investors, to hedge against the risk of fluctuations in price, unlike the companies which effectively involve in hedging operations. First firms generally have lower transactions costs due to a larger volume of hedging activities. Also the managers will have the clear picture of the risk and related factors of the company than the investors from the outside the company thereby making hedging operation more effective.
Economy in the cost of capital
The companies can reduce the cost of capital, if it efficiently made use of the derivatives. This can ensure a strong financial position.
Tax benefit
If the company has stable earnings it can ensure tax savings. The reason is that the corporate rules are favorable to those companies whose earnings are non volatile or stable. These companies enjoy tax credits. If the earnings of the company are volatile it cannot enjoy much tax benefits.
Management of compensation packages
The stability of the earnings of a company influences its compensation packages, especially incentive plans. Some companies may fix a target of monthly or
annual income, if the company achieves this target it may give extra incentives or bonuses to the top management. Risk management can ensure proper management of compensation packages. (Brigham & Ehrhardt 2002, p.917-918)
The main causes of the derivative crises could be attributed to fiscal indiscipline, inability to regulate and rein trading in the bourse, market money and credit instrument markets deficiencies and above all the failing of major banks business in US. In effect lack of liquidity, absence of transpareny and false ratings all combined to precipitate a financial debacle that could not be arrested effectively even to this date.
Coming to the remedial measures, it is believed that a combination of injecting liquidity into the economy, creation of a reliable and liquid market, making genuine ratings and enhancing the legal framework of the business could create a better scenario for improving the situation
According to the survey results, it is seen that 90% of the respondents believed that.its effects would be felt till the next decade, which is 2020. This is not only because it is one of the most powerful recessions after the Great Depression, but also it has wide ranging economic effects on several economies in many parts of the globe. Although most economies are recovering fast, it would take some time for them to be fully recovered from the aftermath of the recession.
There have been plethoras of reasons, according to 86% of respondents, and derivatives perhaps belonged to one in this list. One of the major contributions of derivatives is that it triggered the collapse of many sub-mortgage businesses, which, in turn, devastated major corporations and banking institutions in the United States and in other parts of Europe. Nearly 84% respondents felt that derivatives alone cannot be held responsible and yet its role cannot be denied, or downplayed. The other 16% did not think it necessary to drag derivatives into this crisis scenario.
To the question whether this financial crisis has made it presence felt throughout the globe, 88% of the respondents felt that it had, but some countries felt its impact more than others, given the kind of vulnerabilities they possess and the innate lack of resilience and robustness of their economies. Others failed to comment on this.
The role of Derivatives as a tool, or technique was the next argument by 79% of the respondents, who felt that its competence could only be judged by the positive results it produces and the risks that it was able to thwart effectively. Just as the effectiveness of a tool is contingent upon the skills and dexterity of its users, so also, to a very large extent, according to 87% of respondents, this could dampen, or enthuse business prospects. The dangers in derivative trading are inherent and need to be converted into opportunities by skillful traders.
According to 95% of the respondents, the impact could be seen in terms of falling stock prices, greater degree of market fluctuations and real uncertainties about future stock movements, and the future of derivatives is indeed unknown at this juncture of time.
Coming to the sixth question, according to 68% respondents, solution would be in terms of stopping book trading without concrete underlying assets and pumping a great deal of liquidity into the economy.
Regarding the seventh question, according to 90% of the respondents, the derivatives could be controlled by setting up a high powered Watchdog Committee that would not only exercise overall control over its day- to-day operations, but would also enunciate the policies and procedures that need to be strictly and vigilantly followed by these derivative traders in each case transactions.
According to Answer to Question 8, nearly 86% of the respondents felt that it was the financial and banking sectors (FBS) that were most affected by this derivative crisis. Another 13% also felt that all industries and businesses that were dependent upon FBS were also affected, perhaps at a lower scale.
Coming to the last question, 88% of the respondents believed that there is indeed a great role for the authorities to be able to arrest declining trends and usher in better growth prospects
Most of the survey results seem to concur on the fact that the importance of derivative trading in contemporaneous business cannot be underemphasised. In the US it is believed that the OTC traded derivative market works out to $450 Trillion (DeCarbonnel 2009).
This works out to be larger then GDP of most countries. The results of the survey showed that although derivatives were not the fundamental cause of the present global financial crisis, it may have been a contributory factor, since derivatives are linked with interest factor and underlying assets and the fall in interest rates may have been a factor. “I think derivatives helped but it is a little simplistic to say derivatives are the cause of the problem. They definitely made it worse because they allowed risk to hide in places and risk became fragmented and also they assisted in creating leverage and complexity in the system and that complicated the crisis and it is also complicated how we are going to have to deal with it“ (Derivatives not the root of financial crisis: Satyajit Das 2009).
Again another factor could be leveraged operations which accounted for derivative trading with a high degree of risk taking and non accounting of losses as and when they occur. Glaring examples of derivatives being the primary cause of failures have been the failure of Barings Bank in the United Kingdom and the insolvency of Lehmann Brothers in the United States, which have been due to huge losses accumulated through speculative derivative trading, which such companies were unable to bear.
Most of the respondents believed that the high degree of international leveraging has to be brought down. The fiscal and monetary system has to find ways and means to de-leverage their risks activities. It is seen that nowadays “Credit creation and lending is pretty much at a standstill. This will, in turn, force companies and consumers to de-leverage by selling assets or deferring investment and consumption to reduce borrowing levels” (Atulbull 2008). “The leveraged operations are said to have generate an “irrational appeal” for risk taking, and the lack of clearing obligations also appeared as very damaging for the balance of the market” (Derivative trading: a boon to Lankan financial market n.d.).
Most of the respondents were of the considered view that although the main economic crisis began as a result of the sub-prime mortgage crisis, it was fuelled by ambitious derivative trading on it. Although in the beginning, the sub-prime mortgage loans were resold to low risk borrowers, gradually they were also transacted with high risk borrowers, thus adding to complexities of the crisis, since even with derivatives in place, the creditors were not in a position to repay their mortgage loans on demand. “They produced various derivative financial instruments that consisted of loans and mortgages with different risk levels so as to serve all kind of investors, from risk-lovers to risk-averse ones” (Sesric monthly reports on the current global financial crisis 2009, p.4).
What most respondents felt that, although not a precipitating cause, the present crisis could have been exacerbated by the derivatives trading business? It is no secret, according to respondents, that most derivatives in these cases are fictitious and not underlied by real and robust assets. The numerous players in the game, its diversities and complexities and above all, lack of transparency and strong control elements, all led to the crisis. “In fact, until the outbreak of the current financial crisis, most of the people were not aware of these derivatives although this kind of financial instruments makes up the largest financial market in the world. Indeed, financial derivatives have no intrinsic value” (Sesric monthly reports on the current global financial crisis 2009, p.6).
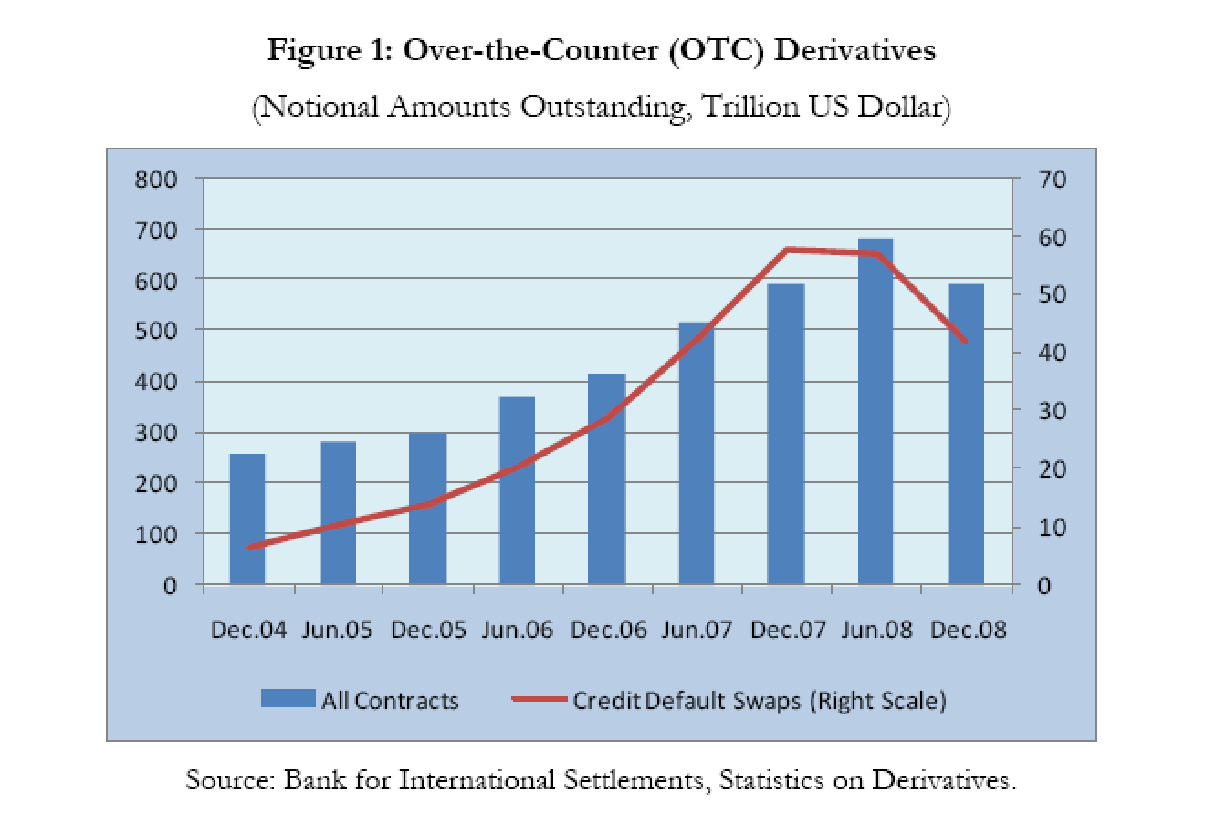
The respondents state that “Analysts say there is insufficient liquidity in the credit default swap market to be able to extract enough information about default probability for pricing purposes. There is no model for pricing because the information about default probability isn’t there“(Chapman 1998).
It has been pointed out by the respondents that there were reasons to believe that derivatives could create future losses. This would definitely have a detrimental effect upon the financial institutions who dealt with such instruments. Further they had reasons to worry that “derivatives allowed companies and investors to gamble with others money” (Das 2006, p.20). This, according to most respondents, over trading in deratives without asset backup and strong financials could be one of the major causes for the economic recession, although not the primary ones. It is well documented that over trading, and over speculative transactions could lead to situations wherein, prices may crash and therefore, the probability of buyers selling off their assets (houses for instance) at higher prices, to pay off the mortgage cannot be surmised.
Thus, under such circumstances, where foreclosure is not possible, nor is it payable to pay off the loans, the bubble bursts and affects the economy dramatically and drastically. According to the respondents, there is a drastic shortage of liquidity since all transactions have been mere book transactions, and thus ready cash to bulwark the economy is not possible.
Coming to the remedies that could be made available, it could be said that greater control needs to be exercised. Control measures over the flow of capital, the investment processes and role of traders and financial consultants need to be reviewed. It is now proposed to have Clearing house for derivative instruments, which in effect could substantively control derivative operations and ensure liquidity and asset-based transactions. “The interposition of a clearing house (or an exchange) and the requirement to post standing or initial margins is intended to eliminate counterparty credit risk. (In some markets, price limits or capital-based position limits are also used to address financial risk.) “(Introduction n.d.).
The use of clearing houses, according to most respondents would not only act as a stimuli to business development in derivatives, but also seek that wrong use of derivatives are not made and it is channelised for common good of the economy. “The use of central clearinghouses is viewed as key to removing systemic risks posed by the contracts, should the failure of a large dealer spark a chain of losses globally. The issue arose after the collapse last year of Lehman Brothers and insurer American International Group” (DeCarbonnel 2009).
Moreover, it is also seen that injecting liquidity into the economy, one of the principle action plans that have been taken up, including government bailout packages’ for ailing companies, may have only limited advantages, since the economic crisis has been a culmination of many factors, intrinsic and external that has led to the present situation.
Arbitrageurs influenced in the derivative markets by buying the undervalued assets in one exchange and sell it another exchange. So they would be risk free profit through this transactions. So emergence of uncontrollable players in the derivative market affected the financial crisis. Another reasons uncertainty in derivative contracts. Derivative contracts undertaken for reducing the risk. When uncertainty arise in the derivative contract lead to huge loss to the participants. for egs: natural calamities, weather condition, breach of contract etc.. this caused financial crisis.
Derivative lead to financial contributions in developing economies. The sectors relating to bank loan, stocks, bonds and direct physical on investments.
Derivatives play an important role in the economy. Recession lead to decline the performance of derivatives and it lead to huge loss to the parties. Excessive land use regulations which increase the prices in impacted market. Excessive lending without any restrictions or without submitting any documents lead to increase the bad debt and inflation in the US. Variation in the interest rate was another factor caused the financial crisis. Increasing mortgage loans without submitting any documents lead to supply of uncontrollable money within the market. it al so lead to inflation. No regulation on derivative contracts lead to huge loss to parties.
Consumer attitude changed due to recession caused decline the economic activities within the market. Falling real assets prices, lack of liquidity, high inflation, reduced earning, un employment are the related factors cause to financial crisis. High bad debts lead to bankruptcy of the financial organization.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
It has been sought to detail how derivative market influenced the current financial crisis. Actually derivative contracts used to reduce the risk within the financial transactions. There were dramatic changes in the financial industry after evolution of the derivative contracts. Most of the corporate depend on the derivative contracts for their overseas transactions. Derivative could reduce the risk in their transactions. But after the technological developments in the financial markets caused to increase the derivative contract participants in the industry.
It could create some complexity in the derivative contracts. According to the situations there were developed different types of complex contracts. It also worsens the market. Finnov research in the context of the current international crisis mentioned that “highly leveraged derivatives such as credit default swaps and collaterized debt obligations, are not properly valued” by the financial institutions. (FINNOV research in the context of the current international financial crisis, n.d.). It lead to some complexity in the financial market.
In order to cure the deflation immediately US treasury and federal reserve undertaken the different uncontrollable policy which was the main reason behind the inflation in the economy of US. (U.S. economy risks hellish prospect of hyperinflation, 2009).
Investors always aims how can maximize the return with less risk. But return and risk are direct proportional factors. When the risk of the investment is high, return would be high. If the risk is less, return al so less. With every good return investment there would be appropriate risk. So the question is how can maximize returns using less risk. Investors always look in to these factors. Derivative is the good tool for reducing risk.Derivative assets changed the financial markets. It established the relation between domestic financial markets and international financial market. Emergence of IT lead to financial markets more competitive and it lead to increasing the demand for derivative contract. Rapid growth of the derivative market leads to internationalization of capital market. Hedging, speculation and arbitrage are the fields used in the derivatives
Derivatives are market through over- the- counter (OTC) and exchange traded market. The derivatives that constitute OTC are typically- known as exchange rate, equity, commodity, interest rate and credit rate genres of derivatives.
Over the counter derivatives are the exchange rate derivatives, equity derivatives, commodity derivatives, interest rate derivatives and credit rate derivatives. Investment decisions are important factor in the derivative assets. Different techniques are available for decision making. Non discounted cash flow methods and discounted cash flow methods are major used investment techniques. Net present values, (NPV) internal rate of return (IRR) and profitable index are discounted cash flow (DCF) methods. In discounted cash flow (DCF) techniques considered the future money value of present money. While considering the non cash discounted techniques didn’t consider the future value of present money.
Pay back period and accounting rate of returns are the non discounted cash flow techniques. So rational investment decision is important one in this present recession period. In some extent derivative helpful to reduce the risk. It can act as a protector for the asset in the stable economy. But it will difficult to make commitment in his duty in the fluctuating market. Because lot of uncertainty event may occur in this market. There may be huge loss by the parties through entering the contract.
There are different risks associated within the market. Systematic risk, unsystematic risk, credit risk, exchange rate risk, market risk, political risk, country risk and interest rate risk. Systematic risk can not be controlled by investor.
This are external forces and beyond the control of the investors. Egs: natural calamities. While considering the unsystematic risks can be controlled by the investor through rational decision making. Exchange rate is the risks associated with the exporters or importers. Credit risk is relating to lender. Political risk is relating to the rules and regulations of the government. Market risk is related with fluctuations of the market. How will be effect unexpected changes of the interest rate in investment return? This is the interest rate risk. Country risk is relating to growth rate of the investment country. If the growth rate of the country high investment returns will al so high.
Risk management is the one of the panacea for reducing risk in the investment. In this recession period important of risk management is high. It will helpful to increase the efficiency in decisions and activities if the investment firm or individual. There is lot of benefits through risk management. Judicious mixture of debt and equity increase the profit maximization of the firm. Risk management can implement this. It can ensure the safety of investment, tax benefits through maximum uses of debts in the investment.
Exchange rate decisions of the central bank important one for controlling the fluctuations within the market. Hedgers may be farmers or manufacturers. They enter to the contract with parties in order to reduce the risk of the future transactions. Inflation, unexpected decline of the GDP or natural calamities may be the reasons for entering the systematic errors. This may cause to increasing the uncertainties and huge loss to the parties. This leads to financial crisis.
Arbitrageurs influenced in the derivative markets by buying the undervalued assets in one exchange and sell it another exchange. So they would be risk free profit through these transactions. So emergence of uncontrollable players in the derivative market affected the financial crisis. Another reasons uncertainty in derivative contracts. Derivative contracts undertaken for reducing the risk. When uncertainty arise in the derivative contract lead to huge loss to the participants. For egs: natural calamities, weather condition, breach of contract etc. this caused financial crisis.
Recommendations
Investors should take a rational decision before undertaking the investment. He should have the complete knowledge regarding the investment. he should analyse the cashflows by using quantitative techniques. There are different techniques.net present values, profitability index,accounting rate of return etc…it would be helpful for making decision.if the investors have no adequate knowledge he should approach financial consultancy or brokerage firm. Rational decisions helpful to reduce risk and losses. it creates a strong financial position and achieve the objectives of the organization.
Exchange Rate Feasibility
There should be exchange rate feasibility. Exchange rate fluctuation increases uncertainty. If uncertainty increases the risk will al so increase. Central bank decision bear an important role in the exchange rate feasibility. Whether the exchange rate is fixed or based on demand and supply of domestic currency or managed float rate. A fixed exchange rate means the central bank will fix the exchange rate. If the exchange rate below or above the fixed exchange rate, bank will purchase or sale the foreign currency from the international market in order to maintain stability in the exchange rate. Stability in the exchange rate lead to a decline the speculation.
So derivative market players especially speculators can control. But the government has to spend huge cost in order to maintain the fixed exchange rate. If the exchange rate of the country is according to demand and supply there would not need to spend huge amounts in order to maintain the fixed exchange rate by the government. But there would be high fluctuation within the market. It leads to an increase the players of speculators and high uncertainty within the market. there would be huge risk in the investment of this type of market. When we look in to managing float government will allow to fluctuate on a certain level from the fixed exchange rate. If the exchange rate is beyond the limit central bank of the government will intervene in the foreign exchange market to maintain the fluctuation within the limit.
Strengthen the Financial Policy
As derivative assets are complex, the government should strictness in the rules and regulation of derivatives transactions in order to strengthen the financial market. This will helpful to remove of complex derivative transactions that will harmful to the financial market.
Proper Regulation
Proper regulation should be made for the smooth flow of the financial transaction. avoid to give the loan without proper documents helpful to decline the baddebts.i twill strengthen the finance industry. Regulating credit default swaps al so essential factor for strengthening the industry.
Regulate Private Derivative Market
Even a derivative contract bears the risk, if any uncertainty arises within the market lead to huge loss to the parties. it will cause to the financial crisis
Improvement in the Economy
A healthy economy leads to confidence to investors. They would like to participate in economic activities in this healthy environment. Government should undertake appropriate financial and monetary policy in order to develop the economy. Balance of payments should be stable. Government should undertake the appropriate policy when the changes in balance of equilibrium. For egs: if deficit occur in the balance of payment following decision will helpful to restore the economy
- Stimulating exports
- Reducing unnecessary imports
- Control the expenditure
- Provide the incentives for exports product
- Increase the customs duty for unnecessary imports items
If the balance of payment is facing surplus, the following decisions will help to restore the balance of payments
- Increasing expenditure
- Reducing exports
- Increasing imports
- Encourage foreign investment
- Increase the grant to undeveloped countries
Stimulate The Packages For Crisis Banks
Government should provide financial support to the crisis banks in order to overcome bankruptcy.
Invite Foreign Institutions For Financial Support
IMF and world banks can provide funds for assisting balance of payments recovery Risk management tools help to reduce loss in the investment. Port folio management is a useful weapon for reducing the risk in the investment. Risk is high on the stand-alone basis investment. As far as considering the investor they would not interested to invest in high-risk investments. Important of portfolio management essential in this present crisis period. Two important factors involved in the portfolio analysis. Covariance and correlation coefficient. Covariance is used to measure the nature of the movements of two stocks at a certain period. If stock A and stock B moving simultaneously covariance would be positive otherwise negative. It difficult to specify the magnitude of the two movements. The correlation coefficient is used to measure the degree of co movements between two variable.
Portfolio standard deviation is the simple equation used for measuring the risk of two assets in the port folio. The importance of this equation is used for the selection of efficient portfolio. Efficient portfolio can lead highest expectation of return in any risky market environment.
The equation is
Port folio SD=root of {squres of WA & SDA +squares of (1-WA) & SDB +2WA (1-WA) rAB SDA SDB}
- WA –Fraction of the port folio invested in security
- (1-WA)-Fraction invested in security B
- SDA-Standard deviation of the asset A
- SDB-Standard deviation of asset B
- rAB-Correlation between asset A and asset B
Thus, it is seen that the derivatives business needs to be controlled and monitored and new innovative ideas and solutions need to be injected into it. Besides, it is necessary that government policies and stringent rules are not very strictly enforced that could bring about more rigidity and lack of flexibility in derivative market operations. The concerned authorities need to be open and transparent to new ideas and concepts that could develop the derivative business better and take steps to better the administrative and control aspects of the overall derivative business to avoid the occurrences of such financial mal functioning and economic crises.
Appendix 1
Questionnaire
- What is your general opinion about recession? Do you think that it will last for a long period?
- Do you think Derivatives played a role in this crisis?
- Did financial crisis affected throughout the world? How was it?
- Do you think Derivatives are dangerous in financial markets?
- What is impact of crisis in stock markets?
- What do you think will be the solution for this crisis?
- How can these Derivatives be controlled?
- Which sector was mostly affected by this financial crisis?
- Is there any role for the authorities in the crisis?
- What is the difference between OTC derivative and exchange traded derivative?
- What were the problems of the derivatives in the current Crisis?
- What should be done to prevent those Crises?
Reference List
About national statistics & ONS: What is data collection? 2005, national Statistics. Web.
Amadeo, K 2008, Kimberly’s US economy blog: role of derivatives in creating mortgage crisis, About.: US Economy. Web.
America’s banking crisis: a financial tsunami approaching! 2008, The Real Truth: A Magazine Restoring Plain Understanding. Web.
Analysis of derivative contracts in trading business: Forward contracts 2008, Open Frame Technologies Inc: Derivative Contracts. Web.
Analysis of derivative contracts in trading business: Options 2008, Open Frame Technologies Inc: Derivative Contracts. Web.
Atulbull 2008, Trading psychology: Derivatives business in full of beautiful lies: where do you think the sub-prime mess will end, The Equity Desk. Web.
Basket: Definition 1 n.d., Investor Words. Web.
Bespoke market studies 2009, CTR: Center for Telecoms Research. Web.
Bijlani, D 2009, Recession – its causes & effects, Ezine Articles. Web.
Brigham, E.F. & Ehrhardt, MC 2002, Financial Management theory and practice, 10th ed. South-Western.
Brigham, E. F. & Ehrhardt, M. C 2004, Financial management theory and practice, 10th ed. Thomson Asia Pte Ltd.
Boorman, J 1999, Asian crisis: world must cooperate to find solutions. Web.
Bowers, C 2009, Another frightening recession graph, Open Left. Web.
Chapman, R 1998, The derivatives mess. USA Gold Gilded Opinion. Web.
Chapter 6- investment decisions- capital budgeting. n.d., FAO Corporate Document Repository. Web.
Consumer Behavior Report: Spending trends in a weak economy 2008. Web.
Consumer Behavior Report: What is the “spending trends in a weak economy” report? 2008. Web.
Cox, W 2008, Root causes of the financial crisis: a primer. New Geography. Web.
Culp, CL 2001, The risk management process: business strategy and tactics: Increasing Debt Capacity and Reducing Borrowing Costs with Risk Management, John Wiley and Sons.
Current financial crisis and insurance companies 2009, Quotes R Us. Web.
Dangerous derivatives at the heart of the financial crisis 2008, Eurodad: European Network on Debt & Development. Web.
Das, S 2006, Traders guns & money: knowns and unknowns I the dazzling world of derivatives: financial WMDs- derivatives demagoguery, FT: Prentice Hall. Web.
Davi, C n.d., Derivative Dribble. Web.
DeCarbonnel, C 2009, About the 14 trillion collateral behind the 1.144 quadrillion derivatives market, Market Skeptics. Web.
DeCarbonnel, C 2009, About the 14 trillion collateral behind the 1.144 quadrillion derivatives market: central clearing of derivatives seen adding risk, Market Skeptics. Web.
Default risk 2004, The Free Dictionary. Web.
Define options: definition-investing 2008, Kitchaloo. Web.
Derivative: definition n.d., Investor Words. Web.
Derivatives . n.d.. Web.
Derivatives not the root of financial crisis: Satyajit Das: how much would you say that derivatives were the root of the financial crisis 2009, Moneycontrol. Web.
Derivative trading: a boon to Lankan financial market n.d., The Nation on Sunday. Web.
Eatwell, J, & Taylor, L 2002, International capital markets: systems in transition, Oxford University Press US.
Eisinger, J 2008, Wall street: the $58 trillion elephant in the room, Portfolio. A Bizjournals property. Web.
FINNOV research in the context of the current international financial crisis, n.d. FINNOV: Finance, Innovation & Growth. Web.
Florincua, G R, & Thonqsawai, P 2010, Support for small business and its perceived influence on project success: A study of projects a small business in a Swedish Science Part, essays. Web.
Foreign- exchange risk: What does Foreign- exchange risk mean. 2009, Investopedia: A Forbes Digital Company. Web.
Forward contract 2008, The Free Dictionary. Web.
Foxley, A 2009, Recovery: the global financial crisis and middle income countries. Carnegie Endowment: For International Peace. Web.
Froot, KA & Stein, JC n.d., Financial institution center: risk management, capital budgeting and capital structure policy for financial institutions: an integrated approach, Wharton. Web.
Futures contract: definition n.d., Investor Words. Web.
Geroski, PA & Gregg, P 1993, Coping with Recession, National Institute Economic Review, no.146, Questia: Trusted Online Research. Web.
Grant, P 2009, Standard setters seek swift solution to financial crisis. Accountancy Age. Web.
Hamilton, J 2009, Administration unveils legislation to regulate derivatives, including credit default swaps, Wolters Kluwer: Law & Business. Web.
Hrovatin, S etal 2009, Derivatives in crisis: policy7 choices for Europe, ISPI Policy Brief. Web.
Interest rate risk: what it is 2009, Street Authority: Independent Guidance for Profitable Investing. Web.
Internet surveys: January 2003: how appropriate is an internet survey? 2009, Snap Surveys. Web.
Introduction: Features of derivatives instruments with implications for regulatory regimes n.d.. Web.
Inverse floater: definition n.d., Investor Words. Web.
Jakabovics, A 2008, Real solutions to the financial crisis, Center for American progress. Web.
Ja-Young, Y 2009, Life insurance companies safe from financial crisis, The Korea Times: Biz/Finance. Web.
Leaps: definition n.d., Investor Words. Web.
Market risk: definition n.d., Hedge Funds Consistency Index. Web.
Meaning derivatives marketing n.d., Economy Watch. Web.
Mugo, FW n.d., Sampling in research. Web.
Nocera, J 2009, Only a hint of Roosevelt in Obama’s financial overhaul, Green change. Web.
Noun: Uncertainty n.d., WordNet Home Page. Web.
Open-ended questions n.d. Web.
Primary & secondary data – what’s the difference? 2007, Adfoster: Fine Facts For Flourishing. Web.
Reason, T, & Mintz, SL 2008, Capital markets: York: A Long, Ugly, Deep Recession, CFO. Web.
Recession graph 5 . 2009, Opencast project- A Blog. Web.
Recession: India’s prospects in 2009. 2009, Rediff News. Web.
Recession watch: What’s the point of derivatives? 2009. Web.
Ries, J 2007, Country risk definition. Credit Worth: Credit Topics. Web.
SC2: insurance and finance: research on finance issues in insurance 2008, The Geneva Association: Risk & Insurance Economics. Web.
Seitz, M 2009, Can a recession be a good thing?, Conservative Today. Web.
Sesric monthly reports on the current global financial crisis: Islamic finance & banking system a potential alternative in the aftermath of the current global financial crisis: the conventional baking system and the outbreak of the crisis 2009, Organisation of the Islamic Conference Statistical, Economic and social research and Training Centre for Islamic Countries. Web.
Shah, A 2009, Global financial crisis. Global Issues. Web.
Stock market crash 2009, Absolute Astronomy.com: Exploring the Universe of Knowledge. Web.
Structured note: definition n.d., Investor Words. Web.
Swaption 2004, The Free Dictionary. Web.
Systematic risk: what does systematic risk mean 2009, Investopedia: A Forbes Digital Company. Web.
The Chicago board of trade 2000, IPO. Web.
The difference between risk and uncertainty 2009, Robust Decisions: Decision Management Solution. Web.
The financial crisis has slashed the banking industry’s market value by $5.5 trillion-equivalent to 10 percent of global GDP-says the Boston consulting group 2009, Market Wire. Web.
The NBER’s recession dating procedure: business cycle dating committee, national bureau of economic research 2003, NBER: National Bureau of Economic Research. Web.
Thornton, P 2003, Manufacturing Industry slumps back into recession. The Independent Business. Web.
Treasury has prime role in derivatives bill 2009, Reuters UK. Web.
Types of derivatives n.d., Maps of India. com’s: India Business Directory. Web.
Unsystematic risk: definition n.d., Investor Words. Web.
U.S. economy risks hellish prospect of hyperinflation, 2009. Global Economic Crisis. Web.
Walayat, N 2009, UK recession watch- Britian’s great depression: UK interest rates. Global Reasearch. Ca: Centre for Research on Globalization. Web.
Warrant Definition- business: warrant 2009, Your Dictionary. Web.
What in the world happened? 2009, Stimulus package Details: Simple Details About The Most Complicated Economic Stimulus In American History. Web.
Whitney, M 2009, This is not a normal recession: moving on to plan B, Global research. Ca: Centre for Research on Globalization. Web.
World economic crisis needs two year to fully recover 2009, News: China View. Web.
World stock markets and exchanges n.d., Economy Watch. Web.