Introduction
Employees play an excellent role in the success of an enterprise. In particular and in the light of competition, we are in the era of new knowledge economy, the weight assigned to the role played by an employee in a hotel and hospitality enterprise is given greater importance and concern than before. Their contributions lead to overall development of the hotel and hospitality industry. With respect to sustainable competitive advantage, employees take credit in providing this advantage within hotel industry. The ultimate success is attributable to the level of employee retention within the industry. It is a clear fact that hotel and hospitality industry has access to human resource at high frequency than any other industry. Conversely, this industry is therefore exposed to a higher possibility of brain drain than other enterprises (Jones, 1996). The paper starts by reviewing past literature on hotel and hospitality industry, then the methodology applied in conducting the research data collection and analysis, results discussion and finally conclusion and recommendations.
Within the global market, hotels have become an important force in economic development of countries such as China. However, compared with larger enterprises aside from the hotel industry, there is a weaker competitive advantage in the hotel industry with regard to employee turnover. This has a negative impact to the health and stability of hotels within China. This has been more profound in the quality of service rendered by the hospitality industry. Provisions of remuneration and development of opportunities for employees presents activation of employee outfits expected to result into direct losses.
For the purposes of reducing the turnover within hotels therefore, the management should look for ways of curbing this tendency. It is evident that the hotel industry is a service industry. For this reason the people more likely to be employees in this field are common people, who include; cleaners, waiters’ connectors and many others. Although their description in terms of the work they perform may suggest minority, their service delivery due to job satisfaction is key to the success and profitability of any hotel enterprise. The issue of turnover within these enterprises therefore draws a discernable attention both from scholars and managers in this industry. Retention of employees is not only good for cost reduction, brain drain control, and morale boosting. One problem that requires to be addressed in the light of employee turnover is the causes.
This study therefore, investigates the causes and how to address them for the purposes of helping the Hotel and hospitability industry with Sheraton Haikou Resort as the case study. It is not an entirely negative experience to have some turnover in the hotel industry. There is an exception under which turnover, especially, voluntary turnover is accepted. This occurs under cases where an employee is involved in fraudulent incidences where the company’s property becomes the target. In such a case, laying-off could have an immediate alternative although it does not address the causes of fraudulent activities. Although not directly involved with this study is the relationship between the employee and his/her employer is also a substantial contributor to the retention or departure of employees from one firm to another (Cascio, 2002).
As it shall be discovered later in the course of this case study, the location of a hotel premise also matters in terms of determining whether an employee is motivated towards staying or leaving. Business dictates that, strategic location of a business is of critical influence to its success. Workers have a tendency of linking satisfaction of their work to what and where they would prefer to have their place of work located. To give weight to this argument, in recent years, there has been an increase in hotels located on the beaches along seas and oceans. Such ideas become embedded in the minds of employees and ultimately acts as a determinant of their stay within a given hotel enterprise. Location of the business also has much to do with employer’s prediction of continuity and profitability as a result of its location. An employee derives morale for work when the probability of long term stay in the organization is assured. If the stay is questionable due to lack of customers resulting from poor location, an employee’s reaction would be looking for another firm which would guarantee better services (Meyer and Allen, 1997). Most of the hotels all over the world irrespective of their sizes, have well laid strategies on the processes of retaining skilled and talented employees, this is due to rising demand and competition within the market.
Maslow theory focused on the psychological needs of workers, and argued in the perspective of five levels of human needs which employees are considered part of and hence the need to satisfy these needs. The theory argues that unless one need is fully met, it presents some difficulty for the employee to be motivated towards next level. This call for hotel industry to offer some kinds of incentives to individuals that could enable fulfilment of their needs. However, workers are motivated at different levels leading to differences in pace of movement up the hierarchy. This means that different set of incentives could be offered depending on the nature of the employees. Maslow argued that the highest state of human level is characterized by several human virtues which include integrity of character. “His prescription for human salvation is simple, but not easy: ‘Hard work and total commitment to doing well the job that fate or personal destiny calls you to do or any important job that “calls for” doing” (Edwards et al, 1998, pp 28-67). However, Literature review of employee and hotel industry needs are very crucial and influential in the process of making innovative suggestions which could bring required changes or modifications to the hotel and hospitality industry as a whole.
Aim of the research
This study aims at finding out the major causes of employee dissatisfaction within organizations and the necessary working environments and job structures appropriate for specific employees.
Objectives
- To critically review secondary literature on human resource management, with the purpose of bringing into light factors that leads to job satisfaction and turnover in the hotel industry
- To investigate the causes of high employee turnover in the hotels
- To critically investigate the impact of various techniques used by Sheraton Haikou Resort in order to motivate and retain its staff
- To analyze and report on probable alternatives and recommendations that could be used by management to enhance job satisfaction and curtail turnover.
Literature Review
This chapter focuses on the various views of authors concerning employee turnover within hotel and hospitality industry. The literature review discusses the whole issue of employee turnover based on its economical impacts, motivational aspects, conditions of the working environments, the overall importance of employee management and the resulting consequences. The mentioned topics bring to the realization that human assets are not limited but require variety of considerations to be made. The study seeks to identify and give clear effects of work policies and environment on employee turnover. Employee turnover could be viewed as outflow and inflow of employees between or within industries in the market environment (Van Dam, 2004). Each time an employee leaves an organization either voluntarily or involuntarily, there is always a vacancy created which always demand for replacement, through hiring and training of other employees appropriate for the positions. However, before any replacement is made it is important for hotels to consider restructuring various sections for the purposes of retaining employees.
The idea of attracting and maintaining employees leads to creation of some form of interconnectivity within the employment field, hence making the issue be of interest to many researchers. According to Pavesic and Brymer (1990), employee satisfaction is an employee’s general attitude and acceptance of work, its environment and time to time changes. This reinforces the level of retention within the hotel and hospitality industry. Such incidence generally describes individual’s employability nature, as well as ability to adapt to changing environments.
Economic Impacts
Employee turnover has drawn a substantial attention from both academics and managers from the hotel and hospitality industry, particularly in the light of its causes to the whole economy (Bockerman and IImakunnas, 2009). According to Pavesic and Brymer (1990), issues concerning employee dissatisfaction within hotel and hospitality industry revolves around relating academic credentials with the level of salary an employee is offered. According to Archer (2006), the high turnover and dissatisfaction is as a result of seasonality of the business within hospitality industry. There are higher costs incurred by the industry concerning employee turnover rates, which could be attributed to numerous expenses spent on employee requirements. These costs could be traced back to expenses incurred during recruiting, training, and retention of employees. However, such spending has proved rather beneficial since the process ensures recruitment of experienced employees to the industry (Corporate Leadership Council, 2003).
Motivational aspects
The achievements of individuals and organizational goals are independent process linked to employee work motivation. Individuals motivates themselves to satisfy their personal goals, therefore they invest and direct their efforts for the achievements of organizational objectives hence also meeting with their personal goals. This is a full proof that employees at times share same principles as with organizations they work for, and such applies in the hotel and hospitality industry. Archer (2006) reported that the manager’s job is to ensure the work done through employees is possible, if the employees are self motivated towards work rather directed. Managers’ involvement within the hospitality industry is not so much important in the process of motivating employees. Employees should have the capability of motivating themselves towards hard work. Management finds it challenging to offer efficient services under competitive environment and at the same time motivate employees towards offering efficient services to customers’ expectations. Employees’ motivation, their enthusiastic and energetic behaviour towards task fulfilment play key role in successes of any organization (Khan, 2005).
According to Archer (2006) managers should bear the responsibility of encouraging employees towards performance. Human resource managers should have the capability of employing and retaining. They could also help in developing employee’s enthusiasm regarding their respective responsibilities hence creating a highly motivated team. Within the hotel industry, employees’ enthusiasm could be boosted by matching them with the kind of work they have trained for and at the same time creating for them conducive working environment. The performance is poor if the employee is not satisfied and happy (Khan, 2005).
Work plays very important role in people’s lives and brings about crucial influences on their general response towards health and environment. Salaried employment has contributed much to people’s day to day livelihood. Employment sometimes become very wonderful experience to individuals and at times presents some level of stress. Stress produced from work; always demand more energy and time. This means that all employees irrespective of their status are subject to either good or negative aspects of employment within the hotel industry. Relationship exists between work, mental and physical health which is an essential part towards career adjustment as well as productivity within various hotels (Cohen et al, 1997).
Working Environment conditions
There are several causes of problems at work place some of which include; threats caused by poor working conditions, fear of dismissal from the work place, the rate and certainty of change. The level of relationships within hotel working environment also causes stress since it could sometimes lead to junior employees being harassed by their seniors. Employee dissatisfaction could also be caused by pressure due to unreasonable deadlines and acquisition of new methods of management or technology. These conditions often demands employee’s adaptation and acceptance which sometimes comes with unnecessary conditions (Driskell and Salas, 1996).
The nature of the conditions within the hotel industry is further attributed to compliance with tough proposals from frequent meetings and the means and ways of responses upon performance feedback. Sometimes stress amongst employees arises from frustrations caused by poor communication links and lack of motivation from the senior employers. Overlooking employees small improvements and often fail to acknowledge them is also contributor to low self esteem. This may also be as a result of poor training on particular management positions. However, major employee problems within the hotel and hospitality industry could be caused by emotional losses and fear of some unknown physical danger (Cohen et al, 1997).
The manner in which managers handle employee related problems influences the duration of employees’ retention and any arising costs. Handsome salaries given to employees’ within the hotel industry acts as incentives used to encourage them towards rendering their services wholeheartedly. Part of the payment is always related to time off work, and training services. Possible agreements and resolutions should be made prior to occurrence of problems. But most importantly, effective managers within hotel industry have applied deep understanding of particular employee activities and appropriately linked it with the right kind of stressor. This has helped in reducing the chances of causing lots of harm on workers hence encourages them to stay put. The nature of attention given to employees by their managers determines the level of success within the human resource department (Edwards et al, 1998, pp 28-67).
Employee troubles within hotel industry could be responded to by increasing and triggering immediate series of physical and internal changes. These changes may either be adaptive, as with increased energy and performance or maladaptive as with increased turnover, increased health-related benefit costs, increased absence, or increased aggression on the part of employees. Various problems within the work environment weakens the immune systems, life satisfaction and decreasing level of happiness, the risk of heart related diseases, and also increases the rate with which cancer develops (Cohen et al, 1997). For these reasons, we need to better understand how organizational choices influences individual stress (Harrison, 1985).
Research on the effects and causes of employee retention or quitting within work place was considered since it led to clear creation of roles and duties. Since then, many current theories have been offered to guide researchers interested in the relationship between organizational or occupational stressors and resulting strains or illnesses, between stressors and coping choices, the underlying psychological appraisal processes, and the causes of organizational burnout (Harrison, 1985). There exists a relationship between organizational stress and a post-stressor outcome or response. This relationship enables slow reaction towards stress preventive measures within an organization leading to strengthening of the issues.
Different variables influence employee turn-over levels. These comprises of factors such as personality differences, perception and social support. Employee related stress arises as a result of emotional interference, physical activities, social and economic situations that require rapid responses to change. Some levels of stresses within hotel industry are considered healthy since they enable individuals to discover new things and crucial areas in life (Driskell and Salas, 1996). The danger lies when stress comes in magnitude too big to handle. Workplace stress can be attributed to the demands between emotional and physical within specific roles. This requires some level of control for which when exceeded leads to individual stress. These combinations of high demands can sometimes lead to harmful responses both to the individual and the organization at large. An individual’s personality conflict with other people within social set-up contributes to some percentage of workplace problems sometimes leading to mental illness. There are indeed several causes of stress within the workplace which can cause negative effects within working (Driskell and Salas, 1996).
Generally the common inception is that issues concerning employee dissatisfaction within hotel and hospitality industry revolve around the environmental set-up as well as relations between employee and their employers. It is necessary to solve employee related problems in order to avoid stressful circumstances undergone by employees. Workplace dissatisfaction often leads organization and its employees’ towards poor performance.
Importance of managing employee problems and resulting consequences
Management of employee problems is important since it helps in the identification and addressing of workplace related issues. The management helps employees come to terms with the reality of facing some unexpected events within the work place. For instance, good number of employees may refuse to accept that they are stressed or fear losing their current positions within their respective hotels. However, this could result into more damage to personal life and even the working environment at large (Driskell and Salas, 1996). Scheduled training in which multiple sessions are involved is necessary. Organizations should regularly schedule training sessions throughout the year, varying time, location, and format. This may help in reducing unnecessary overall stress if these training sessions are locked together in a single time frame in a common environment and following common structures.
High level of stress within working environment is one of the causes of low employee turn-over since it leads to significant health effects. These are also experienced in jobs done on shifts and those done part-time as experienced within hotel and hospitality industry. The kind of job one is exposed to, determines the kind of health an employee is exposed to. Research has revealed that taking some rest from work results in high quality of work done. Those who always perceive their workdays to be stressful take at least frequent one day off within a period of one month. Straining jobs results into poor health conditions, and ultimately reducing performances. Majority of the people link active performance with less work and this at times become more insecure in terms of rewards (Chen and Spector, 1991).
Motivation and morale at the work place could at times be affected through the use of inappropriate means such as use of drugs. Individuals who use these negative means are often prone to low productivity since they tend to take frequent leaves on the basis of health. Constant short leaves are only appropriate for those with jobs demanding psychological alertness. However, certain aspects of work stress diminish with the increase of protective factors. On the other hand, negative coping behaviours increase the likelihood of taking short-term rests (Edwards et al, 1998, pp 28-67).
Employees within hotel industry are often prone to stress when they are subjected to vigorous working conditions. This may be contrary to other industries’ experiences having the ability to make their employees cope with such situations (Geary, 1998). They should be subjected to some light training on effective management of their working hours without being subjected to unnecessary stress. At the same time they should be discouraged from using drugs as means of lowering stress from work place (French, Caplan, and Harrison, 1982).
Summary of main findings
Hotel industry should actually improve on the nature in which they render their services taking into account the different areas of expertise an individual could serve best. There are several reasons which could cause employees to show their willingness to leave or stay within an organization. However, employee concerns presents important aspect within workplace which could be utilized in the process of enhancing the level of productivity through the impact created on employee relationships, creativity and effectiveness (Coulter, 1996).
The literature review applies an analytical approach whereby the results deduced from various authors revealed in-depth experiences that employees within hotel industry undergo while undertaking their duties. This is of importance to the research since it provides a very good ground for application of appropriate methodology for accurate results.
Methodology
This chapter tends to explore the various research paradigms and design used. The process of research instrument and questionnaire development as well as appropriate sampling technique used during the research and finally the various limitations encountered from the methodology applied. Rationale for using in-depth interviews is also applied.
Research Paradigm and design
This study utilizes the use of qualitative research method which deals with non-tangible aspects including perceptions, experience and behaviour among humans. The variables used have no standard numerical measurements and therefore they are assigned codes for analysis and interpretation (Atkinson, 1995). Various schools of thoughts emerge from the kind of research method chosen which includes positive and interpretive view. This school emphasizes on maintaining objectivity in avoiding biasness in data acquisition so that findings could be generalized to similar scenarios through prediction.
Development of research instrument and questionnaire design
During the exercise a list of questions was prepared which helped as guideline towards obtaining relevant answers required for the exercise. This was used as part of the basic outline for the entire interview process. The interview started by asking simple questions before the respondents were engaged in more sensitive questions, this was preceded by introduction and the understanding of the interviewees’ background. This includes a brief story on what they feel about the hotel industry particularly where they worked. One typical question used was “What can you say about the type of services provided by the industry to employees”. However some respondents at times found themselves stating responses that were outside the questions asked, prompting some adjustments to majority of the questions depending on the interviewee responses.
Within the questionnaire were included questions focusing upon employees’ personal information, and this comprised of four questions in total. Then one question focusing on the level of employee satisfaction. In addition, there were a total of twelve questions dealing with the employee characteristics as well as their general concern about the perceived characteristics. On the issues of retention, employees were asked to give response on their current working environments and their confidence level with their current employers. The questions were based on the authors’ views concerning nature of responsibilities, level of motivation, environmental concepts as well as personality issues (Archer, 2006; Khan, 2005).
Sampling Technique used
Random sampling method was applied in this research which involved non-systematic collection of samples from whole population within the hotel. Advantage of this method is that it provides opportunity for participation of all subjects. This approach was preferred over others because it provides chance for general results. Every member within the hotel was given an equal opportunity to be included in the sample. However, the sampling size used within this method was indefinite but helped in building conclusion through data collection, coding and analysis enabling researcher to decide where to collect data and the type of data to be collected. The sampling was based on purposive and on judgmental basis enabling thorough study of participants with relevant experience and knowledge (Glaser, 2005). Empirical data collection was done through primary data collection involving interviews (Strauss and Corbin, 1990).
The target respondents of this study were 58 employees of Sheraton Haikou Resort. They were sent to the questionnaires through their respective email addresses after permission was granted by the hotel management two weeks earlier (see appendix I for a copy of the questionnaire). The participants returned 33 representing a response yield of 60%. The investigation was done based on the knowledge by the people that there would be an investigation. The investigation consisted of the following three phases which included; preparation stage, the actual field work involving collection of data and finally the follow-up stage done for the purposes of ascertaining the level of accuracy of the results obtained.
The method used to generate data in this research was both flexible and very sensitive to the area where data was collected. The method adopted in this research was the use of distributed questionnaires (Minichiello, Sullivan, Greenwood and Axford, 2003). Interview was conducted amongst the same individuals to establish on the validity of their responses. Before the start of the interview, each interviewee was requested to sign a consent form after reading and agreeing with the written conditions. Then the interview process was audio-taped and transcribed for confidentiality purposes. Each respondent was given a code name which was used instead of their real names; this ensured that there was no possibility of linking individuals to any information given. In-depth interviews were conducted immediately to find out on individual responses which could be possibly shared with others. However, there was not enough time to gather all workers within the hotel together for the completion of the group interviews; therefore the focus was shifted to questionnaires and individual in-depth interviews which assisted in the generation of timely data.
Rationale for using in-depth interviews
In-depth interviews were used to help gain an understanding on the employees’ responses and how they interpret their interactions based on the entire hotel social environment. In-depth interviews are considered flexible and easy to understand since they are generally open-ended, neutral, sensitive and very clear to the respondent. The structure provided by the method allowed for open conversations that provided detailed information about the interviewees’ general experiences. In-depth interviews were used to help in deep understanding of the social and physical settings of the environment where it is undertaken, the traditions, values, effects and roles practised by the respondents. Using in-depth interviews enabled collection of sufficient and crucial data information that could not be otherwise shared in group settings. This also reinforced trust between the interviewer and the interviewee and made the respondents to be willing to contribute more and more (Whyte, 1982).
Limitations of methodology chosen
The method used, in-depth interview, offered very flexible and detailed data. Despite all these, there were some limitations associated with it; first it required too much time and a lot of resources hence the research could not cover large sample of people. So much time was required to conduct interviews since the respondents needed assurance on the type of questions asked, also time to transcribe the interview and analyse the data was limited.
Much effort was required to make the respondents comfortable, secure and interested in the responses they were giving. There was also the challenge of using acceptable and workable techniques which includes appropriate body language. There is no possibility of generalizing the results because of the use of small samples. The method was more theory based and also reduced the ability to speak in clinical terms for understanding to be established between interviewer and the respondent. Despite all the limitations this research method is easily monitored step by step.
Analysis of Data
The data was analysed using various techniques such as inductive coding which was used to reveal the consistency of the research with the information given. The data was broken down and re-organized to achieve the intended objective. The grouped data was then categorized for the purposes of comparison that helped in providing practical reality of the research (Strauss and Corbin, 1990). For quantitative analysis Chi-square analysis test was utilized. The critical alpha level that was used to measure discrepancies was 0.05.
Empirical research design was developed in order to help in exploring the theory discussed in this paper. Individual calculations was measured based on the interviews conducted and previous data collected and statistically analyzed. Available database having track details on the nature of the effect of policies on employee turnover and environment based on race was also analyzed. Meta analysis was conducted to include all the effects of public policies on inequalities within the industry down the previous years. This research sought to establish an understanding between the research objectives and findings from the interviews (Strauss and Corbin, 1990).
This research employed the use of Grounded theory which was used for the purposes of interpreting the data collected. Collecting, interpreting and understanding of data was done best in grounded theory, where the collection of data, its analysis and theory were closely related bringing some relevance to the research undertaken (Strauss and Corbin, 1990). There was the utilization of peer debriefing which ensures that the required consistency is achieved. For the purposes of coding, the interview scripts were scrutinized to ensure identification of similar or different opinions, the similar ideas were identified, substantiated and all the comments highlighted within the transcript margins. Two different evaluators were used each making his own coding frame for sampling the sub-transcripts (sub-sample used n=2). The different findings were then compared to ensure accuracy of the coded data. From this a coding frame was produced that is appropriately utilized on the whole data which was collected. The data was then thoroughly compared and analysed to tally with the requirements as per grounded theory approach. Data collection was also followed by the process whereby the data was grouped into themes which assisted in detailed description of the research based on the social and environmental settings. The validity of the research was based on transparency and viability of message conveyed. Individual narrative interviews were conducted concurrently with the process of transcription and coding of data which was later concentrated and categorized for analysis.
The analysis of the reasons discussed connected the theory and the academic facts and this could help the Hotel draw from the findings, an action plan that may change the employees’ attitudes hence more attraction to the hotel industry, with employee motivation being varied under specific circumstances. Since the respondents needed not sing on the questionnaires, it is a strong belief that the opinion given by the employees was theirs and therefore actual about their job. The table below shows relationship of the research topic with age, gender amongst other important considerations such as academic background of the employees. The age structure was found to be 18-50 years, with no respondent reporting an age lower than 18 or higher than 50years.
The age profile 18-28 representing 47.5% of the respondents, 28-38 age bracket representing 30% of the population studied.
Table1: Demographic characteristics of the respondents
The majority of the respondents are the common staff in the hotel, ranging from waiters to cleaners. From the table, more of the staff had a high school certificate, followed by college degrees and just a handful had bachelor degrees. There were also no staff members with master’s degree. This reveals the level of expertise required within the service industry. The hotel is composed mainly of single people but the married are not fewer in description. From the results, it is true that the hotel industry is a service industry and therefore, managers within the hotels are under obligation of knowing how employees feel at work and what they want. The amount of effort or commitment an average employee inputs at work, depends on whether the employee believes on his level of satisfaction and therefore determines the ultimate way the hotel’s goals and targets are achieved.
People get satisfied concerning issues if at all their expectations are met. However, the result from the above analysis shows correlation between job satisfaction and age. This has got much to do with relationship between management and the junior employees. This means that, older people have different relationship to authority compared younger people, such that young people are likely to grab and embrace new dimensions under which they seem to lack enough experience hence making them expect more than the requirement. The results of the table also show there are few divorced or separated employees in the hotel. Maybe this as a result of life making a little meaning to them therefore this group translates same as low job satisfaction. The same results above can be analyzed as in the chart below.
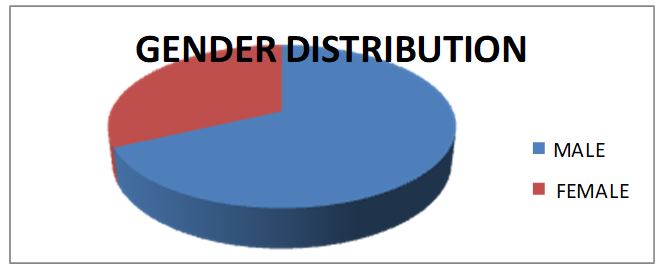
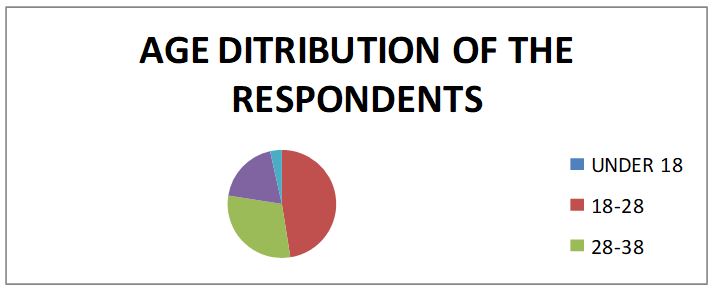
Table 2: Major determinants of employee satisfaction and turnover intentions (n=55)
Potential sources of dissatisfaction were discovered to be; lack of clear focus and objectives, poor internal relationships and unrealistic timing and deadline. According to the analysis provided in the table above, it is revealed that the rate of employee dissatisfaction within the hotel is viewed in the perspective of more dissatisfied and less dissatisfied groups. More dissatisfaction come as a result of high level of stress owing to frustration and work overload (Cordes and Dougherty, 1993).
Results
The given results present Sheraton Haikou Resort with an opportunity of employing relevant strategies so that they can tame employee turnover. Retention of employee through monetary incentives alone does not guarantee satisfaction of an employee at work. The results reveal that all employees need to be acknowledged on their behavioural responses concerning specific duties within the hotel. The scenario where the manager designs and selects handful of employees for recognition should not be applicable since it demoralizes others. This shows some kind of favouritism on the side of senior managers, since it creates a formality picture amongst employees hence do not allow them time to think outside the box. The recognition should consider some basic information concerning employees’ reactions and contributions towards duties and the organization in general.
The management could also set up a way which encourages its employees to purchase shares and stocks of the company to enhance employee’s involvement in the company. The costs of implementing the above strategy may look prohibitive but its effects are long term. In most cases these costs seem prohibitive but it is an ideal way of taming turnover within the hotel industry. The use of service providers within transition channels provides the hotel with considerable clientele. Employees might find it challenging using new technologies in marketing as this is not core part of their daily business. Organizations like Sheraton hotel could outsource customer care services through dedicated information communication companies so that the company maintains effective touch with consumers. In their quest to expand globally and nationally the organization will have to interact with employees at personal level and intelligently shift them to channels which are convenient to both consumers and the business.
Employees’ personalities
Changes to enhance the employee’s personal identity at the hotel should comprise actions such as enhancing effective communication channels between management and the employees. Removing barriers to communication enhances self esteem and behavioural component such that views of all employees are articulated. This could be enhanced through establishment of regular meetings. Secondly, is the review of their extrinsic rewards including payment rewards as well as opportunities of advancing their studies as per job descriptions. A system in which employees are paid according to performance provides good base for hardworking culture within the institution. Lastly there should be a provision for career advancement among the employees including promotion granted within their line of duty. This enhances self sufficiency and sense of appreciation from the organization.
Training and development is the most important method that could be used to equip the employees enabling them to cope with the change, competition and some of the business challenges. Training needs analysis need to be conducted for the purposes of determining areas where training is required, what need to be taught, and who needs to be trained. In this case study, those that need training are maids manning the front office section. They need to have adequate induction and proper training with respect to their work. Induction should be implemented in the hotel for the purposes of educating staff members and giving them basic knowledge necessary for running the organization. In the process of induction the management should monitor and check closely the abilities of the new employees, their behaviours and humble reactions towards the working environment (Hollander, 1986).
Best management styles
According to the results the best management style which could apply is the hybrid leadership style. Views of employees expressed wholly and decided based on their welfare will imply that the organization values everybody for their contribution and as such cultivate a sense of belonging to the organization. This motivates them that the organization is sensitive to their needs (Hollander, 1986). Management leadership should have the ability of motivating and uniting employees working in all sections within the hotel. The managers should possess the ability to control and cope with major changes and challenges within the industry. The management need to adopt the Sheraton Haikou Resort espoused values in line with valuable information on the current trends, and avoid relying so much on their past performances. They need to improve on their level of interaction and communication with maids in various departments (Charness and Rabin, 2002).
Transformational management should be implemented whereby management team should take employees through all the risk items within the hotel and give each member opportunity to think of possible solutions. Employees should be taught on ways of decomposing scopes to appropriate depths, ways of building and integrating programs and ways of developing master plan documents. They should also be taken through efficient estimation processes, costs calculations, ways of drawing schedules and making appropriate decisions (Hollander, 1986).
Good management should focus on training the employees on ways of building group cohesiveness by working as a team based on the principles of humility, honesty and integrity. Exposing employees to mandatory training on a regular basis could guarantee improvement in the level of skilled manpower. This could be used to enhance marketing effectiveness as well as the level of performance. Recruiting experienced maids ensures that proper tactics are implemented in winning the confidence of customers (Charness and Rabin, 2002).
Management done in a democratic way has to be hybridized with administrative leadership and non-discriminative rules, where the leader gives specific instructions within the scope of work and keeps close supervision to ensure that the instructions are followed. As much as the employees are accorded democratic space the management should have a system which closely monitors their execution of roles in conformity to the hotel’s culture. This will ensure that work is effectively performed and well rewarded. So long as employees have a feeling of belonging they will always strive to work to satisfaction.
Motivation
Intrinsic motivation arises when one does an activity for personal satisfaction. They move into action for the purposes of fulfilling individual goals and rewards (Deci and Ryan, 1985). The maids at the hotel seem not to be intrinsically motivated because of the low morale producing low grade and careless approach to job leading to loss of room charges by customers. They do not find internal satisfaction in their roles at the hotel such that even repeat customers never bother to acknowledge and appreciate them for their exemplary services, a sense that will show to them that they have grown in knowledge and skills.
Extrinsically motivated behaviours are those executed because they are instrumental to some separable consequence (Deci and Ryan, 1985). Clearly one extrinsic motivational factor lacking is attractive wages as a benchmark in the industry. The maids want to feel appreciated for their hard work in terms of monetary compensation. When this is factored they will instead shift their goals in offering excellent services to the institution as they will be introjected to perform flawless duties in respect to their financial rewards. When this is achieved it will be internalized as part of their roles in performing tasks.
In this scenario, extrinsic motivation is the most appropriate. Indeed considering that they are identified as professional in the hospitality industry intrinsically they feel there is no more room for exploration and will need external factors to perform for satisfaction. Provision of external factors will always make the maids to develop an attitude of performing their duties with diligence so as to prove their worth for the payment. Consequently when this is met they will strive for self satisfaction within their various duties of which intrinsic factors will be part of them.
Organization Culture
The organizational culture at Sheraton Haikou Resort seem to be non cohesive and seems to have significant impact on the overall performance of the organization, this results into cognitive dissonance on the part of employees. There seems to be no overall core values for the employees which could help in checking their behaviours at work place. This has since resulted into careless approaches by the maids as they perform their work, and also the manner in which management handles their issues. Since maids form an integral part of the hotel their work execution displays the hotel’s culture and image to the public.
The overall culture at the hotel does not seem motivating to the employees. This could be viewed in terms of better working conditions and competitive remuneration owing to the kind of services rendered by employees. These external factors are critical since they determine to greater percentage, employees perceptions about the hotel. This determines the level of self satisfaction and in turn self esteem which enhances productivity and ultimately overall revenue (Khan, 2005).
Organizational culture defines the way members of an organization work towards specific goals. This could be derived from the principle objectives the organization operates under. Other values attached to these, determines intrinsic behaviours among individuals. Several dimensions towards culture within organizations include social and task oriented dimensions. Culture is ultimate determinant in the process of rewarding employees and management should focus on critical sources of motivation including good pay, enhanced working environment and opportunities for growth. These factors should be closely integrated for the benefit to an organization’s productivity (Khan, 2005).
The use of cross-functional management teams assist in the process of deciding the kind of aspects which requires close monitoring and measurement. Organization culture provides perfect framework for realization of progress within the business since it incorporates all the sections under the hotel. The culture could also be used in reorganizing the organization towards achieving its mission, provision of accurate responses on performance levels and also identification of areas requiring improvement. Sheraton Haikou Resort could use contingency approach by incorporating the use of business score card within its culture as a management tool; this could be used for the purposes of motivating employees towards increasing the value of the organization. This helps in giving the organization the ability to appeal to shareholders and all employees.
Communication
Good interpersonal skills and relationship between workers is vital for effective management and running of any business. Communication is a very important factor which ensures smooth running of activities within the company. This must be encouraged amongst all employees regardless of the positions they hold. This may as well act as a very important tool for designing communication marketing mix outside the business premise.
Selective perception plays vital role in communication of any kind, this is since people react differently towards information. Barriers to effective communication comprise people’s actions which interrupts smooth information flow. These hindrances could be reinforced through stressful circumstances. They easily interfere with other’s self-esteem and could lead towards dependency, withdrawal, feelings of defeat, or of inadequacy. They lower self or corporate drive towards achievement and solution to problems (Lahlry, 1991).
In this scenario communication between the administration and hotel employees could be improved through listening to their concerns. This ranges from job conditions and having predetermined perspective on employees needs. This could be identified on the verbal reaction of one of the managers who claimed that the whole idea was “just a waste of time and money” in relation to the employees concerns. This if not checked could lead to stress at work with underperformance as the ultimate result. Utilization of proactive integration could help in improving communication. Proactive personality and integration relates to communication because it involves exchange of information from one source to another. For information to reach the desired target, communication channels have to be utilized. Conveying information concerning programs could be done either through writing or speaking (Hollander, 1986).
Conclusion/recommendation
From the study, there is a direct relationship between job satisfaction and turnover. The relationship is such that when we achieve an increment in job satisfaction, we reduce turnover. It is therefore more costly towards turnover in the company than remuneration and a growth opportunity to employees, since there is a time lost before an employee is replaced. Another cost associated with this is training attached to the incoming employees. Ways such as mentoring programs could help in cases concerning employee turnover.
Employees capable of interacting with businesses over multiple channels prove more loyal than an employee who does just small kind of duty. Some key strategies for effective working environment with employees are development of un-parallel responses network. It is important that Sheraton hotel develops a department in the marketing section endowed with responsibility on customer care. Such sections require management by professionally trained experts who ensures that quality services are delivered and never compromised. Sheraton could realize quality services from employees when they resort to communicating on personal basis through modes like e-mails. This makes it easier for consumers to be informed of new range of available products and current offers available. This creates an impression which considers employees as the most valued asset within the business.
In the struggle to retain employees and reduce turn over within hotel industry several factors are considered of major concern to the management. Employees are considered as individuals coming from different backgrounds, having different educational experiences and at the same time different family classes; these could be used to deduce are all the factors from which their needs could be located. The primary interest of employees is always satisfaction of their personal needs, ambitions, desires and goals. Employees require basic needs satisfaction which is linked to survival and security concerns and a desire to belong. This is essential in generating positive feelings from within and from others, hence leading towards full satisfaction.
Most employees require fair and consistent concern of companies in matters affecting them directly. They also need to serve under management which they could respect and trust in terms of offering adequate working relationships. At the same time they require reasonable salaries as well as good working environment and assurance of job security alongside favourable job status. Business today does not entirely focus on the brand but rather on employee-customer satisfaction and customer care. As competition increases, and for transformation to be realized, there is apparent need in maintaining loyal customers for the purposes of building respectable market share. However, employees need to be recognized and appreciated so that they could be considered as part of the company’s success. The above therefore determines the cause of turnover or retention taking place within the hotel industry, the results depends largely on the management’s willingness to accept their presence and proper action plan after concerned review.
Recommendations
Other key factors should be used in communicating the condition of the Sheraton Haikou Resort to employees; this comprises several aspects discussed below. Sheraton hotel’s intention within the industry looks very attractive for competitive purposes. This is because they face low pressure from suppliers and moderate pressure from customers within the Chinese market. The Hotel industry is highly competitive with many substitutes available, this makes it essential for Sheraton hotel to develop business and marketing strategies which will help them do well against pressures from the global forces and ultimately attract and retain consumers. Research undertaken using qualitative method has great influence on decision-making and designing of strategies. The level of competition within the market determines the development of products and services which would grant them competitive advantage. The high purchasing power of buyers determines the level of sales and ultimately the profits. It is essential for Sheraton hotel to focus on consumer tastes and demands.
The enterprise should seek to diversify its services other niche markets. This should be for the purposes of adding onto their current performance concerning employee recruitment. Sheraton hotel should indulge into offering fast foods. These fast foods could include; sandwich, cakes and crisps. This could prove of great benefit for the purpose of satisfying those employees used to working with fast foods. The rationale to this is that by diversifying products to consumers, the business reduces risks associated with venturing in one brand of products and further offers an opportunity for additional revenue and employees.
Sheraton hotel should intelligently opt to renting business premises rather than buying those premises which are rather averagely costly. Renting is comparatively cheaper to acquisition and this provides an avenue where the business breaks even its operations within a short time, a factor responsible for quick profitability, hence creating avenues by significantly reducing costs of business set-up. Distinctive ways in selling products based on continental aspects are always associated with high customer turn-out. The hotel should as well offer products to consumers in a relaxed environment and not the typical fast food environment of eating and drinking while standing as enshrined in American culture, and mostly practiced by major competitors. This in essence brings some sense of relevance to both employees and consumers who view themselves as part of the organization’s valuation.
Level of employees’ aggressiveness in sales and retention of customers through loyalty cards should be considered while hiring employees. This strategy ensures that the business has substantial clientele within the market despite the intensive competition; this ensures that revenues are assured at certain benchmarks. It also acts as a form of advertising since loyal customers are offered discounts, a situation which prompts new customers to the business because of their sensitivity to consumer spending.
Necessary physical changes
Physical changes should be initiated at the hotel, several attributes which includes wages increments, excellent working environment and job security should be considered. Basic needs are essential for survival hence requires preference compared to other needs including secondary needs (Schultz & Schultz, 1994). Employees at Sheraton Haikou Resort operate at lower levels of hierarchy needs; hence improvement in their wages should be reviewed. This is because money always presents one of the superior motivating factors to employees of this cadre. Payment for performance strategy should be incorporated since this might ensure work is done diligently and more productively.
Conducive working environment at the hotel enhances the ability and instils self esteem amongst workers. This could be provided through provision of free meals and use of Institution’s facilities for the purposes of creating some sense of belonging amongst the employees. On the other hand job security could be enhanced by putting maids on permanent terms and accord them incentives like access to credit facilities which accrue to the status. One is more comfortable working for an institution if there is a guarantee of job security.
Management need to employ people with common values and share the same vision with the organization. This could help in preventing un-productivity and reduce the amount of money used in training. Secondly the management needs to develop a culture which could encourage employees to focus on higher level achievement as they perform their work. This could be implemented through the belief that everyone has got something worth contributing to the organization and decision making should involve people at all levels within the organization (Mason, 2001).
Information concerning work place improvement needs to be clearly communicated to all employees. This makes them accountable towards making every employee comfortable. These expectations should be supported by actions, whereby managers are required to lead in every section on a regular basis, and alert people on the progress of the organization through daily meetings. The organization should assign duties in accordance to employees’ areas of interest and training (Khan, 2005). This ensures that the organization operates responsibly towards achieving its goals and objectives. The study helped in bringing out positive reactions which in turn could help in the creation of encouragement systems which target satisfaction improvement for the purposes of encouraging employee retention thus improving on performance and reducing on hiring costs for replacement of employees in a hotel organization.
References
Archer, J., 2006. Discover the Hawaii of China. Travel Weekly: The Choice of Professionals, (1837).
Atkinson, P., 1995. Some Perils of Paradigms. Qualitative health research, 5(1), pp 117-124.
Bockerman, P., & IImakunnas, P., 2009. Job Disamenities, Job Satisfaction, Quit Intentions, and Actual Separations: Putting the pieces Together. Industry Relations, 48 (1), pp 73-96
Cascio, W., 2002. Responsible Restructuring: Creative and Profitable Alternatives to Layoffs. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler.
Charness, G. & Rabin, M., 2002. Understanding Social Preferences with Simple Tests. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 117(3), pp 817-869.
Chen, P. Y., & Spector, P. E., 1991. Relationships of Work Stressors with Aggression, Withdrawal, Theft and Substance use: An exploratory study. Journal of Occupational & Organizational Psychology, 65 (3), pp177-184.
Cohen, S., Kessler, R. C., & Underwood Gordon, L., 1997. Strategies for Measuring Stress in Studies of Psychiatric and Physical Disorders. In S. Cohen, R. C. Kessler, & L. Underwood Gordon (Eds.), Measuring Stress: A Guide for Health and Social Scientists (pp. 3-28). London: Oxford University Press.
Cordes, C. L., & Dougherty, T. W., 1993. A review and integration of research on job Burnout. Academy of Management Review, 18(4), pp 621-656.
Corporate Leadership Council, 2003. Linking Employee Satisfaction with Productivity, Performance and Customer Satisfaction. Web.
Coulter, M., 1996. Find management. Bellingham, WA: Prentice Hall College Division.
Deci, L., & Ryan, M., 1985. Intrinsic Motivation and Self-determination in Human behaviour. New York: Plenum.
Driskell, J. E., & Salas, E., 1996. Stress and Human Performance. Mahwaw, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Edwards, J. R., Caplan, R. D., & Harrison, R. V., 1998. Person-Environment Fit Theory. In C. L. Cooper (Ed.), Theories of Organizational Stress (pp. 28-67). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
French, J. R. P., Caplan, R. D., & Harrison, R. V., 1982. The Mechanisms of Job Stress and Strain. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Geary, D. C., 1998. Male, Female: The evolution of human sex differences. Washington D.C.: American Psychological Association.
Glaser, B.G., 2005. Basic Social Processes. Grounded Theory Review, (4), pp1-27.
Harrison, R. V., 1985. The Person-Environment Fit Model and the Study of Job Stress. In T. A. Beehr & R. S. Bhagat (Eds.), Human Stress and Cognition in Organizations. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Hollander, E., P., 1986. The Central Role of Leadership Processes. International Review of Applied Psychology, 35 (1), pp 39-52.
Jones, G. R., 1996. The experience of work and turnover intentions: Interactive effects of value Attainment, job satisfaction and positive mood. Journal of Applied Psychology, (81), pp 318–325.
Khan. A., 2005. Matching people with organizational culture. Khan organizational culture. NY: Newport Beach.
Lahlry, S., 1991. A blueprint for perception training. Journal of Training and Development, 45 (8), pp 21-25.
Marchinton, M. & Wilkinson, A., 2005. Direct Participation and Involvement in Managing Human Resources: Personnel Management in Transition. (ed. S. Bach). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Mason, L.J., 2001. Retaining Key Personnel. Plus: Top 10 Retention Tips. Stress Education Center. Web.
Meyer, J. P., & Allen, N. J., 1997. Commitment in the workplace: Theory, research and application. New York: Sage Publications.
Minichiello, V., Sullivan, G., Greenwood, K. & Axford, R. (Eds.). 2003. Research Methods for nursing and health sciences (2 nd Ed.). Australia: Sydney
Pavesic, D. V., & Brymer, R. A., 1990. Job satisfaction: What’s happening to the young Managers? Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly, (12), pp 90-96.
Schultz, D. and Schultz, S.,1994. Theories of personality. (5th Ed.). Pacific Grove. CA: Brooks/Cole.
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J.,1990. Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory Procedures and techniques. UK: London.
Van Dam, K., 2004. Antecedents and consequences of employability-orientation. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, (13), pp 29-51.
Whyte, W. F.,1982. Interviewing in field research. In: R. G. Burgess (Ed.), Field Research: A sourcebook and field manual. London.
Appendix I