Introduction
Goldman Sachs is an American financial company which offers various financial solutions at the local and international markets (Rumelt, 2011). It is one of the leading financial institutions in the United States of America. The external environment where this firm operates offers a number of opportunities, but there are negative forces too that this firm must be able to manage. In this paper, the researcher seeks to analyze the market where this firm operates.
Key terms
- Industry rivalry- competition among different firms in the same market
- Market forces- factors in the market that affects operations of a firm
- Market segmentation- classification of the customers in the market based on their taste, age, purchasing power or any other relevant demographical factor
SWOT Analysis
When analyzing the external market for this company, it is important to look at the opportunities and threats that this firm has to deal with in the market.
Opportunities
The market offers a number of opportunities that Goldman Sachs should take advantage of to achieve the desired success (Scherf, 2014). The growing economy in the United States and other markets where this firm operates means that customer base is increasing. It also means majority of the population has the capacity to repay their loans. Increased security, expanding size of the middle class, and emerging technologies are all opportunities that can help this firm.
Threats
Stiff market competition remains one of the leading threats for this firm. There is also a problem of unfriendly policies in some foreign countries that makes it difficult for this company to succeed in these foreign markets.
Five Forces Analysis
It is important to look at the Five Forces analysis and how they affect this firm. The forces are summarized in the figure below.
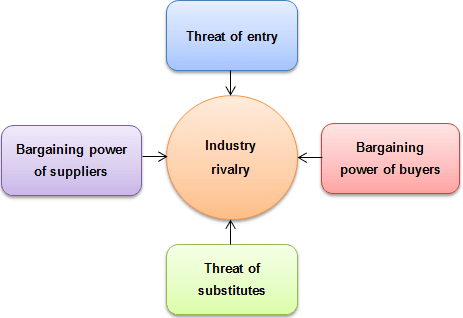
The industry rivalry is very high in the finance and banking sector because of the emergence of numerous local and international firms struggling for the same market (Sinn, 2014). The threat of new entry is real as the American market is open to new entrants from all over the world. The bargaining power of the buyers is also relatively high because of the numerous options they have whenever they are looking for financial products such as loans in the market (Williams, 2016). The suppliers (those who deposit their money in the bank) also have a wide range of choices from which they can make hence they have a strong power. Threat of substitute products such as those offered by Sacco is also growing in some of the market.
Strategic Group Map
It is possible to determine the current position of Goldman Sachs in the market in terms of ability to access services immediately and availability of tailored services. The map is useful when conducting market segmentation. The figure below shows the map.
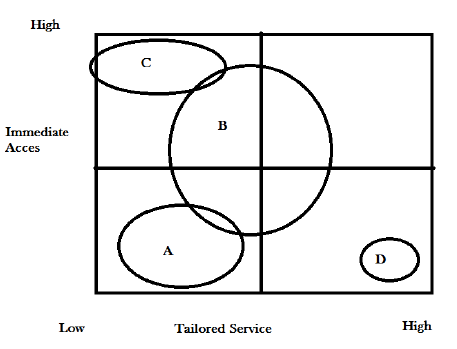
Goldman Sachs falls in the Quadrant C as shown in the figure above. Its services can be accessed immediately whenever clients need them given that it is currently offering online banking services. However, most of the services are universal, not tailored.
Conclusion
Goldman Sachs is currently enjoying a relatively stable market in the United States and Europe following the end of the recent global economic recession that affected numerous financial institutions. The management of this firm must remain aware of the emerging market forces and how they may affect its operations
References
Hall, D., & Yip, J. (2016). Discerning career cultures at work. Organizational Dynamics, 45(3), 174–184. Web.
Mandis, S. G. (2013). What happened to Goldman Sachs? An insider’s story of organizational drift and its unintended consequences. New York: Cengage.
Rumelt, R. (2011). Good strategy, bad strategy: The difference and why it matters. London: Profile.
Scherf, G. (2014). Financial stability policy in the Euro zone: The political economy of national banking regulation in an integrating monetary union. Wiesbaden: Springer Gabler.
Sinn, H. (2014). Austerity, Growth and Inflation: Remarks on the Eurozone’s Unresolved Competitiveness Problem. The World Economy, 37(1), 1–13.
Williams, E. F. (2016). Green giants: How smart companies turn sustainability into billion-dollar businesses. New York: Cengage.