Executive Summary
This dissertation effort with ‘Comparison of marketing strategies of two mobile operators Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) to becoming the Market Leader of Belarus’ has dealt with the marketing strategies of two mobile operators working in the same geographical area of Belarus and their drives to becoming the market leader. The paper has chronologically developed with problem statements, Literature Review, methodological approach, finding, discussion, and finally drawn conclusion and recommendation on how the companies gain and sustain the market leader position in Belarus.
The market leader of an industry indicates the market power and influence of a company with its product and service by using strategic tools to achieve a competitive landscape. For the same category of product and services, the methods of calculating market power to assessing the market leader position is to determine the percentage of market share while the highest percentage of market share, that company would called as the market leader. The next largest would possess a lower scale of market shares and some other companies might have very little though economics has presented the dominance index (D) explaining as a Strategic tools.
The paper has organised with the introduction to marketing strategies, target market, competitive analysis, positioning strategy, and marketing mix with the literature search, discussion of macro and micro environment of the company, Ansoff Matrix, organisational structure, different level of strategies, seven P’s analysis, distribution channel, consumer behaviour of Belarus market. The research has examined the framework of being market leader and the way of measuring the effectiveness of marketing strategies and then empirical evidence of marketing strategies has been presented from the performance of mobile operators Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS).
Problem Statement
Introduction
This dissertation will compare the marketing strategies of the mobile operator Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) with the aim to explain and investigate how the marketing strategies of the organisations have contributed to become the market leader based on their current market position. This paper would be organised in six major sections and these have demonstrated as below-
- Problem Statement: Problem statement or introduction is the first chapter of this dissertation, which provides the overview of entire paper with the background of the research and rational of the research. In addition, this part will raise research questions, enlighten the scopes and drawbacks of the research and research objectives.
- Literature Review: The second chapter has deliberated with the appropriate theoretical arguments on marketing strategies supported by the most recent authors and remarkable researchers recognised by the global marketing institutes. This literature review would argue to answer the research questions with theoretical framework first then it would also fit the literature on the marketing strategies of two mobile operators Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) with the aim to compare the marketing strategies of these two mobile operators. This chapter would start on coherence with the introduction to marketing strategies, its target market, competitive analysis, positioning strategy, and marketing mix with the theoretical discussion of macro and microenvironment of the company, Ansoff Matrix, organisational structure, different level of strategies, seven p’s analysis, distribution channel, consumer behaviour and so on. This chapter also addresses the theoretical framework of being market leader and the way of measuring the effectiveness of marketing strategies. Then empirical evidences of marketing strategies have presented from the performance of mobile operators Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS).
- Methodology: The third episode of this dissertation makes it available that the justification on how the current research on the marketing strategies of two mobile operators Life and MTS would take place and the paper would argue for qualitative research. Malhotra demonstrates the difference between quantitative and qualitative research to collect and analyse the data in different way, for example, qualitative research methods may be direct (focus group interviews) and indirect. Therefore, this dissertation will explain the data collection processes such as direct interviews of the subscribers and managers of Life and MTS, significance the primary and secondary sources. Besides the data collection, limitation on data collection, reliability, and validity of the interviews will also be illustrated.
- Key Findings and Results: It is important among other chapters as this part based on the practical data and evaluation to bring the suitable solutions for measuring the effectiveness of their marketing strategies to become the market leader of Belarus. The tools of strategic analysis will briefly explain by using the several models and the collected data to measure the market risk factors, opportunities, and external environmental influences. In order to compare the marketing strategies of Life:) and MTS, it should be required to evaluate target market, market segmentation, SWOT analysis, PESTLE analysis, and porter five forces, BCG matrix and other strategic tools for the two mobile operators Life and MTS.
- Discussion: The basic differences between the strategies of Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS), which effect to increase the subscriber will be discussed to compare the data. Both of these companies would like to expand its business in European market, therefore, international business entry strategies should develop to show how they analysis the market.
- Recommendation and Conclusions: finally, chapter six of this dissertation will scrutinize all the discussion of previous chapter to draw significant conclusion and to point of key recommendations.
Background of the problem
Belarusian telecommunication market has turned into an emerging market of Europe with introduction of cellular technology and drawn the attention of multinational mobile operators. With the historical perspective of Soviet Socialist Republic, the telecommunication market of Belarus has practiced sate monopolistic control but with the political change and technological development, it has driven into perfect competition among the operators to become market leader.
Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) and Life are the two mobile operators of Belarus market striving to become the market leader with their different marketing strategies. Lisitsyn, et al (2006) argued that MTS1 the telecommunication company of Russia has targeted Belarusian market to address subscribers demand with their entry strategies and competitive advantages with GSM service and extending of its network largely. While MTS emphasising on more technological improvement to achieve lion market share, the marketing strategy of Ukraine mobile operator Life has aimed to capture the Belarus market with different value added services and strong strategic network of vendors.
While both companies are efficient with their organisational structure, strategy, and much more aware about the corporate social responsibility, MTS and Life both companies are following acquisition strategy to expand their business in neighbouring countries and help to obtain comparative uniqueness in terms of market shares, customer services, selling its products, networking, and annual financial development. Nevertheless, the implication of different marketing strategies in the Belarus market has generated a dissimilar outcome in context of gaining competitive advantage and ROI 2 measures while both of the companies faced more amplified dilemmas from the market with other competitors. To overcome this significant problem, it is essential to have an elevated study on how efficient the marketing strategy to contribute the companies to become market leader.
Rationale for the Research
Dekimpe & Hanssens (2004) argued that marketing strategies are not a rigid framework of hypothesis that would respond same outcomes in different market or in the same market in long run though the organisations set up their marketing strategies at the core of their business to generate a sustainable competitive advantage for that organisation or brand. Marketing strategies is thus a dynamic discloser of a modern business that necessitates a continuous responds with the shift of technology, demography and market test with the key challenge though the short-run outcome of the marketing actions are enthusiastically observable, the must be a huge gap in long run. It is thus essential for the marketing professional to observe the marketing strategies of different companies and the continual outcomes.
Hirschhausen (2006) pointed out that the Cellular Market of Belarus & CIS is an emerging market where the traditional structures of telecommunication are diminishing and the multinational cellular operators are extending their presence in this region. Lisitsyn, et al (2005) added that both the companies target local and foreign mobile operators are struggling in these markets with their different their strategies of internationalisation pave the way by growth and spreading out within the individual national boundaries of CIS from 2001-2002, when the key local telecommunication markets were under control of Russian Federation. Thus, there is some space among the marketing strategies of mobile operators in this region that is required to have a study with this market.
Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) is a Russian originated cellular operator working Belarusian and most of the CIS market. The company has reported that it has revenues grew of 24.2% and accounted over US$ 10.2 billion in 2008 under a global financial crisis it has generated strong growth which is very significant. According to the annual report 2008 of Turkcell, its 55% indirect subsidiary Astelit LLC had launched its GSM functions in Ukraine under the brand name of Life, which has successfully amplified its revenue up to 10.1%.(profits enlarged from US$ 6.3b to US$ 7.0b) by increasing number of subscribers 27.3%. Both the companies are working in the same market with different marketing strategies and significant financial outcomes. Above data demonstrates huge gap among the return on investment and thus, it is rational for this researcher to investigate with marketing strategies of these two companies how they contributed to become the market leader of Belarus.
There are huge studies on marketing strategy, but there is enough gap in the area of which marketing strategy variables would explain the differences in performance with elevated scale of operations, which marketing strategies have substantially with better use of shared facilities and enable the companies to achieve extended economics of scale to becoming the market leader. To address these gaps it is rational to have a study on this dissertational topic.
Research Aim and Objectives
The main objective of this study is to examine the performance of marketing strategies of two cellular operators working in the same market and to understand why differences would exist among the business entities of different countries of origin but working in the same market and how their marketing strategies contribute to become a market leader. Life is a Ukrainian Cellular operator when MTS is a Russian Cellular player, both are working in the Belarus market with their own marking strategies, and there are noteworthy differences among their marketing strategies as well as their levels of performance in terms of financial outcomes and marketing measures. There are crucial differences between the marketing strategies of two companies served in the Belarus market in Cellular industry concentration and there are other competitors’ in the market with their own rates of new product and services while Belarus Cellular market environment is with high degrees of attentiveness and particularly argued privileged levels of profitability.
This dissertation has aimed to explore the effectiveness of marketing strategies by considering strategic tools and parameters and assess how these two companies manage their company as both companies are trying to capture Belarusian market to become the market leader. To do so, this dissertation also deals with few imperative questions for instance what is the company’s pricing-strategy or what are its policies for dissimilar markets, what distribution channels is the corporation planning to exploit as well as how does this contrast with the competitor as well as what are the company’s advertising, public relations, and promotion plans.
Research Questions
This dissertation has intended to answer the following research questions to support the topic. The main objective of this research is to analyse what is the relationship between the marketing strategies of two companies and how the marketing strategies influence the development of Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) and to do so this paper would raise four research questions and these are –
- How does the theoretical framework of marketing strategies contribute to become a market leader?
- How the effectiveness of marketing strategies would be measures?
- How MTS & Life have designed their marketing strategies to become a leader in Belarus Mobile Market?
- What extent do the MTS & Life assessed on competitive advantage to implement their marketing strategies?
The raised research questions are important to examine the marketing strategies of the two mobile operators, and these questions would ultimately assist to draw the conclusion of the dissertation.
Scope and Limitations of the Study
Projected scopes
- The topic of this dissertation is unique as it identifies that there are no previous research on comparison of strategy on two Belarus mobile companies. However, many researchers and scholars have take attempts to research on mobile industry and different companies but they only consider the multinational companies like Nokia, Vodafone, Airtal, Hutch, Samsung etc.
- Discussion on Belarusian mobile companies is also prospective in judging the core problems of the region along with some fruitful solutions;
- The study has the opportunity to acknowledge the business environment by considering social, political, economical, legal and technological factors;
- Most importantly, this dissertation will address the different strategy especially the acquisition strategy. Because, Turkcell has purchased 80 percent of the total shares of Belarusian Telecommunications Network (BeST), which changed the brand of it as Mobile services operator Life:), which helps to compare the strategy of the company before and after the owners were changed.
Projected limitations
- Lack of adequate information: As the main purpose of the study to compare the strategies between Mobile services operator Life:) and Mobile Tele Systems (MTS), it should require adequate information about these two companies. Moreover, this dissertation has to rely on secondary resources but there are no annual report, relevant important data, strategic company history or company profile can be found for Life :). However, all the information for the MTS and press releases for Life are available in the internet.
- Ambiguous and cluttered with irrelevant data: Turkcell is the parent company of Life:), so it is difficult to separate the data for Life:). In addition, government owned company Belarusian Telecommunications Network (BeST) had very limited information on websites; therefore, it is quite difficult to provide all the relevant and updated data.
- Constraint of time: due to lack of information sources, the author has to dedicate more time for searching relevant data by interviewing people and field working, which creates this problem of time crisis.
- Limited scope for proper expression.
Summary
Introduction provides the background of the study including research aims and objectives, research questions, the scope and limitation of the study and rational of the research to observe the marketing strategies of different companies and the continual outcomes.
Literature Review
Kotler & Armstrong (2006) argued that the overall marketing strategy of an organisation is a standard approach that it takes to achieve the organisational objectives and the marketing strategy would determine the tricks those the organisation will embark on to catch the attention of customers and retain them. Marketing strategy is the core tools of an organisation that completely devoted to attracting, retaining, and amplifying customers while the other strategies have focused internally and externally on the overall business but very a few on customers.
Theoretical framework of being Market Leader
Sladew (2004) pointed out that the market leader of an industry or market indicates the market dominance or market power of a company that is the measure of the dynamism of a brand or product or service even of a market player in context of competitive offerings. To defining the market leader of a geographical region indicates to what degree of a product or brand or a company controls over his product group at the market where he sustain with the strategic element of competitive landscape.
Kwoka (1977) argued that there are few methods of calculating market power or market dominance to assessing the market leader and the most influential method is to determining the market share. The market share of a brand or a company would present as a percentage of the aggregate market serviced by that company or brand. When a company possess highest percentage of market share, that company would called as the market leader and the next largest would possess a lower scale of market shares and some other companies might have very little.
Ruekert &Walker (1987) added that market share is not only the suitable alternative of determining the market leader or market dominance when there are influences of customers, bargaining power of suppliers, threats of new entries and competitors existing industries with government regulations are significant to take into accounts. In Economics, there are rich literatures to determining the relationship between market share and market leader, here some general criteria of market power or dominance would explained.
Rhoades (1985) explained that, when a company possesses a market share of about 60% with its brand or services, positively it would indicate strong market power and market dominance but a market share of above 33% and lower than 60% with same product or services possibly indicate a good market strength nevertheless not essentially any dominance. At the same time a market share of less than 33% gained by another company with same product or services do not point to any strength dominance.
Nissan, E. (2003) pointed out that the concentration ratio of market or industry would be taken as a measure of the market leader in relation to other leading firms of the industry as a whole or hundred percent where the superior concentration ratio holder possesses the greater market power and termed as leading firm or the market leader.
Kwoka (1977) has presented the dominance index (D) explaining it as the summation of the squared difference connecting the each company’s share with the subsequently biggest share of the market and modelled as:
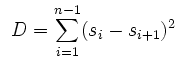
Where
![]()
Pickford & Haslett (1999) has reviewed the process of Kwoka (1977), modified the dominance index as (ID), and emphasised on the Herfindahl index, which is also termed Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) where ID is the summation of squared contributions of all companies in the market:
![]()
The significant difference among the biggest and the second-biggest shares of the company can point toward that the biggest company has the dominant location in the market though the market shares do not robotically provide control of the market while there are huge gaps among the location of the market leader company and its neighbouring competitors.
Sustainability of Market leader
Ward & Stasch (1986) added that the position of market leader is not a rigid thing that may sustain for long term, rather than longevity the market leader always be attacked by the competitors to descent his position. A spontaneous growth of business, trimly addressing to innovative technology and investment to research marketing can sustain market leader. The competitors attacks to the market leader is associated with circumstances where they are achieving more market share and makes encounter from the point where the market leader’s weakness lies on.
Nissan (2003) presented strapping argument that raising market share rather than concentration ratio is the driving force to turn a market leader as a monopolistic power within the industry while lower concentration ratio indicates that there is some market power problem. Large firms always try to get more market share even drive for in conglomerate mergers to spread out into a new market with the aim to achieving market power and dominance to be the market leaders.
Trebing (1998) explained that maintaining competition is not just a theme of antitrust or anti-monopolistic enforcement, every industry has its inherent structural attributes that let it to use concentration and practice of market power to be the market leader of that industry while the of public policy endow with maximum access and boost rather than confine customers choice. Although the general process of public domain deregulation may not guarantee any outcome, key players of the industry would aggressively move to ascertain positions of dominance but the guidance and regulatory initiatives can linger and make more difficult to sustaining the goals of market leader to turn into monopoly.
Influence of marketing strategy to turn into a market leader
Implementation of appropriate marketing strategies is important to become the market leader as customers like innovative products with new facilities (such as new devices and solutions for video camera, games, internet and others), and mobile companies strive to incorporate technology convergence strategy to integrate different features in its mobiles and upgraded them. In addition, competition is too high in global mobile phone industry as well as in Belarus market, so, if a renowned company fails to provide the above-mentioned services by their new invention, then other manufacturers will capture the market by introducing several new models or applying marketing strategies. Such as, MTS became the market leader in Belarus and Russian market by rolling out cutting-edge 4G wireless data services, Vodafone captured the global market by using two strategies- the direct investment and the partnership, Nokia accomplished the success in the mobile phone industry by assessing the external threats, the new market opportunities, and its internal strengths (Krause, 2009). From the annual report of Nokia, it can found in 2000, Nokia failed to measure the rising demand for its products; as a result, LG, Samsung and other Chinese manufacturers introduced new model phones at better prices to become the market leader in Chinese market. However, in 2005, Nokia retrieved its position (the market share of 19.7%) by measuring the marketing strategies of its competitors and adopting new policies.
Teece & Pisano (1994) and Sanchez, Heene & Thomas (1996) stated that organisation’s main aim is to become the market leader in the mobile phone industry in terms of both market share and profitability by developing distribution network. They further added that these organisations want to develop committed sales teams to amplified profitability by reducing the dependence on retailers and other distributors.
Wit & Meyer (2004) and Smirchich & Stubbart (1985) mentioned that organisations should asses the market opportunities, resources and capabilities, external environment, organisational structure, customer behaviour, and competitors’ attitude to choose their own marketing strategies. Teece, Pisano & Shuen (1990) and Prahalad & Hamel (1990) argued that in order to dominant the market share, companies should build on the strengths of their resource bases and activity systems’, support-branding strategy with aggressive marketing and enhance brand portfolio.
Life became a market leader in Ukraine by implementing innovative services and it has presented more than 150 value added services, for example, it introduced the EDGE technology, EDGE+/GPRS+ technology, which provides the maximum possible data transfer speed MeloRing, Voice SMS, Push-To-Talk, Mobile TV, and so on. It also suggests new and easy ways of paying for mobile services, and develops products, services and tariff plans considering subscribers’ needs, and it provides high quality services at most attractive prices. On the other hand, to maintain its position as a leading wireless operator, in 2006, Mobile TeleSystems adopted a new corporate strategy, and to become the market leader of Belarus market in 2007, it introduced 3+2 Strategy. According to its marketing strategy, 3 indicates capture growth potential in its core markets, value creation in developing markets (CIS region) and development of mobile broadband in the CIS (in 2008, MTS was first presented pan-regional 3G network) and 2 means cost efficiency and MTS Group development.
Effectiveness of marketing strategy
According to the survey report of Stewart (2009, p. 6), 79% of people responded that increased Sales is the main metric for measuring marketing effectiveness, and Stewart believed that increased sales is an objective of marketing, which measures the whole business. He strongly argued that traffic to the website is not effective metric to measure though 71% people support this strategy, for example, website visits may boost for many reason do not indicate company’s good position. He also pointed out that marketing can make dramatic contribution for the success of business and sales revenue is an excellent measure of the effectiveness of the distribution network, where as, website visits are the superior gauge of the brand awareness. Colne (2009) and Rajagopalan, Rasheed & Datta (1993) stated that effectiveness is defined as doing the right things.
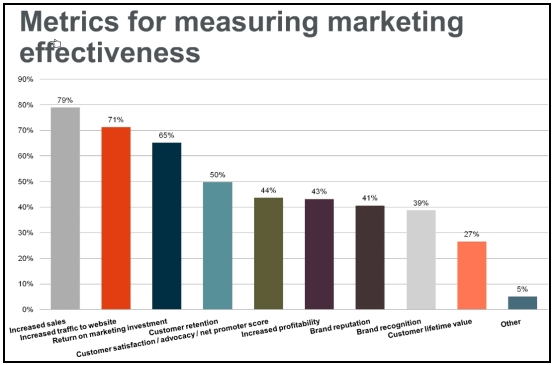
However, there are many other measures besides sales, such as, return on marketing investment (68% of people suggest this measure), measuring marketing performance, strategic marketing analysis, purchaser retention, goodwill, loyalty marketing, lead nurturing, customer satisfaction, brand status, and so on.
Colne (2009) argued that marketing research assists to evaluate the effectiveness of marketing strategy in terms of return on investment and can keep striking contribution to gaining the success for achieving the position of market leader. Massey & Dawes (2004) and Colne (2009) addressed that most common measures are assets, customers, distribution channels, promotional activities, technological development, financial capabilities, etc. Menon, Bharadwaj & Howell (1996) stated that many companies would like to consider net present value and managing marketing assets. However, other measures are focus on the key business drivers, which strengthens the company (to service provider’s customer care and to manufacturer production line speed is the key business drivers), compare marketing strategies with competitors, assessing the production techniques, allocation of resources quality controls, and stock management.
Elements of marketing strategy
Zeithaml & Bitner (2006) pointed out that before setting up marketing strategies; the firms have to keep in mind about the strategic objective of the organisation, its vision that it would like to achieve within short term and log run as the marketing strategy is a consistent part of organisation’s ultimate strategy. Moreover, marketing strategy would incorporate not only the strategic objective but it also takes into account of financial and management strategies. Marketing strategy is the canter of target marketing that argues on how to attract prospective customers, keep hold of them, and gradually gain the target segment of the market. (Zeithaml & Bitner 2006)
Drummonda, et al (1998) added that the marketing strategy would be consist of six components such as:
Target Market: Kotler & Keller (2006) mentioned that not all the products and services of a company always match in every market and address the needs of all customers but those products and services possibly would match some of the customers in a particular market. Thus, the foremost pace to developing a marketing strategy, it is essential is to identify the target market by classifying the overall market and make out its different subgroups as well as market segments. After this identification, it is necessary to weigh up them and decide on the market segment that will bring into being of the best outcomes for the business, it is the primary market segment, and there would some additional market segments, which possibly will create advantageous outcomes. Prior to identifying market segments it is also mandatory to consider how to define the market segment, what would enable to make a distinction among the market segment and generate the understanding to identify the exact potential customers those have to attract.
Positioning Strategy: Zeithaml & Bitner (2006) explained that to developing a positioning strategy, it is crucial to consider the competitors how they have positioned themselves in the marketplace and how the organisations would like to build up its strategy as well as position close up to the competitors, as a result consumers can make a straight judgment when they will purchase. On the other hand, the organisation may wishes to enlarge a strategy that positions far away from their competitors offering a more enhanced benefit than the competitors do and it depends on a great deal of the marketing mix strategy that the organisation going take up. Thompson, et al (2007) added that the pricing strategy have to reflect the advantages offered while the promotion strategy would correspond that benefit and all the positioning would focus on is how they want consumers to distinguish their products and services as well as which strategies would implement to gaining the ultimate goal.
Competitive Analysis: Drummond et al explained that a competitive analysis is a recognised assessment of business organisations by which a firm would review the strategies and outcomes of the businesses of other firms with its own strategies who are directly or indirectly compete with that firm. Most of the competitors have the scopes to access to one another’s business information as well as marketing activities but there are some initiatives, which are not easy for others to achieve and this special scopes would allow the firm for even greater opportunities to get advantages commencing from competitive analysis data for further strapping marketing drives. Competitive analysis is thus look for how can firm improve its marking drive by analysing its competitors, what is the most excellent way to put into practice a methodical competitive analysis, what are the payback of carrying out a competitive analysis.
Through a competitive analysis, a firm would capable to identify who are competing against it, and the firm would capable to evaluate the threat intensities offered by the other firms in the same market. At the same time by this analysis, the firm would able to identify its own weaknesses and without pay attention to the competitors it is not possible understand whether it is doing right or wrong for not to having framework of reference. Hitt, Ireland, & Hoskisson (2006) argued that competitive analysis also facilitates to evaluate competitors offers and gives an ideal chance to recognize how the firm can show better performance for its customers.
When the weaknesses have identified the firm will be capable to get better of its business in many ways that are determined by the analyses of competitors. The firm would also identify its strengths through comparing its own presence to the target market with its direct competitors; it would determine what sets of its business are far away from the competitors and these unique qualities would emphasised in its marketing efforts. Moreover, through this process of competitive analysis a firm will be capable to recognise its own UVP 3 that is particularly most significant constituent of the business that sets the firm apart from its competitors. Competitive analysis also allows a firm to validate its market test by categorising of products, lowest product prices and best customer service and this validity would assist the firm to enlarge its UVP and argues to determine what factors carry out its success in the target market.
Marketing Mix: Kotler & Armstrong (2006) argued that organized with Product, Promotion, Pricing, and Fulfilment of a marketing drive, which is a foundational marketing perception that set up the test of time as well as for good reason and It is crucial piece of marketing strategy that makes sense to works. The stated strategy when the marketing mix is any amalgamation of marketing functions and method of a company that applies to attract and keep hold of its customers. The spirit of raising a marketing strategy is to come across accurately the correct marketing mix for the target market that consists of a variety of elements but grouped into four classes such as (I) product; (ii) promotion; (iii) pricing; and (iv) fulfilment. To get the highest outcomes all rudiments of the marketing mix ought to ground in firmly on the positioning strategy to ensure effective use of the resources and to address properly in the target market.
As the marketing mix has aimed to attract and retain the customers, it is more significant to keep a vital attention to the customer’s point of view, their satisfaction, and recognition for decision-making.
Seven P’s analysis: Kotler and Keller (2006, p. 19) argued that there are 4 P’s in marketing which are common for both products and service. These are Product, price, place, and promotion. Nevertheless, Zeithaml and Bitner (2006, p. 25) stated that there are three additional P’s in case of Services. As Mobile Telesystem and Life both are providing telecommunication services, the analysis of 7 P’s should be argued here.
Product: Product or service is the core offering of a manufacturer or service provider where the variety, quality, design, features, brand name, packaging, sizes, warranties, and returns are concerned (Kotler & Keller 2006, p. 19). According to Willson and Gillian (2005, p. 7) product means the management of production, new product development or service differentiations, and the branding of the product or services. According to Kotler & Armstrong et al (2005, p. 34), the product is any kind of offering, which can be a physical object, service, person, position, firm, or thoughts, targeted to a market for gaining concentration, acquisition and utilization, which has the ability to satisfy the needs of customer.
Price: Johnson, Scholes & Whittington (2008) argued that price is the amount of money that a firm charges for a particular unit of its product or services. It also includes the exchanged values of the customers, which they exchanged with the benefits of getting the product or services. Kotler and Keller (2006, p. 19) stated that these prices are of different types like list price, discounts, allowances, and payment period with credit terms. All these have controlled with three strategies, which are pricing strategies, discount structures, and terms of the business (Willson & Gillian, 2005, p. 7). Zeithaml & Bitner (2006, p. 518) said that there are some costs related with the pricing of the service. These are time costs, search cost, convenience costs, and psychological costs.
Place: Kotler & Armstrong et al. (2005, p. 34) argued that place means where the activities of a company run to make its offerings are available and attainable to the customers. The key aspects of a place related with service providing are the channel type, exposure, intermediaries, outlet locations, transportation, storage, and managing channels (Zeithaml and Bitner, 2006, p. 26). Willson and Gillian (2005, p. 7) has termed place as the function of three aspects distribution channel management, quality of customer services and physical attributes of the service providing. Livelock & Wright (1999, p. 14) stated that place are the management decisions related with when, where and how the service will be delivered to customers. Time is also a type of pose, which dictates the when question. Place is influences on the decision making of the consumers.
Both Life and MTS mobile operating companies are not only distributing their services to not only Ukraine and Russia, their local territory, but also expanding their distributional networks to other countries, like Belarus United States and other developed countries to expand their roaming business. In that sense, two companies are moving aggressively to place their services with international recognition. (Life, 2009), (MATS 2009)
Promotion: Livelock and Wright (1999, p.14) argued that promotion means the all efforts of the firm to communicate with the consumers which will influence the consumer preferences to consume the services. Three roles have played by the promotion and these are providing needed information and advice, persuading the consumers to buy the service and introducing the attributes of the service. Belch & Belch (2004, p. 16) termed promotion as the integration of efforts used by the service provider for establishing an efficient channel of information which will result to the persuasion of the consumers and triggered the ultimate consumption of service. There are different forms of promotional activities such as advertising, sales promotion, public relation, personal selling, merchandising and sponsorship (Willson & Gillian, 2005, p. 7).
Life is focusing on promotion for its individual and business life services only, not implementing strong promotion to life platinum services. (Life, 2004-2010) On the other hand, MTS is promoting both subscriber and corporate subscriber services in same manner.
People: Zeithaml and Bitner (2006, p. 26) indicated that, people as all the human actors who has some specific role in the service delivery process and whose actions and attitudes influence the perception of the buyers. These humans are the personnel of the firm, other customers in the environment who come to get service, and the customer himself. On the other hand Willson and Gillian (2005, p. 7) termed all the Human resource related functions as people like employee selection, employee training, and recruitment and employee motivation. However, Livelock and Wright (1999; p. 14) stated the interaction between the personnel and the customers and the customers within the service place as people. They argued that the perception of the customers massively influenced by these interactions mainly.
Life mobile operating company is managing its people both practically and virtually. It is making unified services to its customers by maintaining proper network among people within the company to every level of business. MTS is also managing real and virtual groups of people, from employees to other stakeholders in this company. The management of MTS is developing group of people to build synergies according to organisational structure for exploit the business
Physical Evidences: Hitt, Ireland, & Hoskisson (2006) stated that the environment in which the customers receive the service and where the interaction between the customer and the personnel has occurred is termed as physical evidence. It also includes the tangible components, which facilitate the performance or communication of the service. (Zeithaml and Bitner, 2006, p. 27) The evidences, which ensure the quality of the service and provided by the visual and the tangibles elements of the place where the service has provided, are also termed as physical evidences. Example of physical evidence includes the building, landscaping, vehicles, interior designing, equipments, signs, symbols, and printed materials. All these are important because they can change the impression of the customer (Livelock & Wright, 1999; p. 15).
Both Life and MTS are service-oriented companies, so physical evidences or infrastructures are not main terms of their business. Corporate offices and customer care points are only physical evidences of these two companies. Therefore, for Life, the physical evidence is on Russia and Ukraine for MTS, but his common market for both is Belarus.
Process: Steps are the methods of service delivery operation and series of actions, which occurs in a sequence of creating and delivering the service elements to the customers, are termed as process (Livelock & Wright, 1999; p. 15). The judgment of the customer is depended on the processes as the procedures, mechanisms and flows of the activities to deliver the service have observed directly by the consumers. The complexity of the service is a critical issue here (Zeithaml and Bitner, 2006, p. 27). The process of handling the customers this includes the managing of the first interaction with the customer, which last for the last moment of the consumption of the service, is also termed as process. (Wilson and Gillian, 2005, p. 7)
For Life, the company is focusing on to become profitable and productive with efficient process maximisation of their services according to customers. The process of running business of Life is also flexible and control on market need with smart and fast decisions of managers (Life, 2009). On the other side, MTS is adopting evolution process to its business with new strategy and management structure for delivering effective services to customers by meet up goals and objectives of MTS itself. (MTS, 2010)
Market Trends: Trends are the course and the progression of events, which has some force and durability (Kotler and Keller, 2006, p. 77). Market trends means the analysis of the long-term underlying patterns of sales growth or decline which is actually the result of major changes in the locality, population, major information and information flow and technology. These are the attitudes of the target customers, which have intense influence over the service designing and delivery. There are many mechanisms and techniques available in analysing the market trends like Moore’s law. All these are reflection of what were the consumer’s attitude in past and what are the present attitudes. Based on these two, the attitudes of the consumers in near future could be projected (Kotler & Armstrong et al., 2006, p. 370).
Life is developing market trends in unprecedented manner in Ukraine by meet up million of customers demands according market trends. Mobile operating services have mainly subscribed with intelligent wireless system, where, Life is successfully adopting this market trends for its customers, by adjusting customers demand according to proper market trends of efficient services. The growth of sales of Life is showing the trends of market with rapid growth (Life, 2009).
In other sense, MTS is committing with core market trends to deliver super quality of its services and to feel customers about the USP by giving different experiences from its competitors. From market trend of sales of MTS and its competitors, it can see that, it is faster and greater than its competitors do in terms of capturing and covering market trends of Ukraine. Therefore, both these companies are focusing on market trends by their USP and customers demand of their services (MTS, 2009).
Market Growth: Market growth means the increase in the sales and profit available or probably attainable within a target market. There are three types of growth. These are:
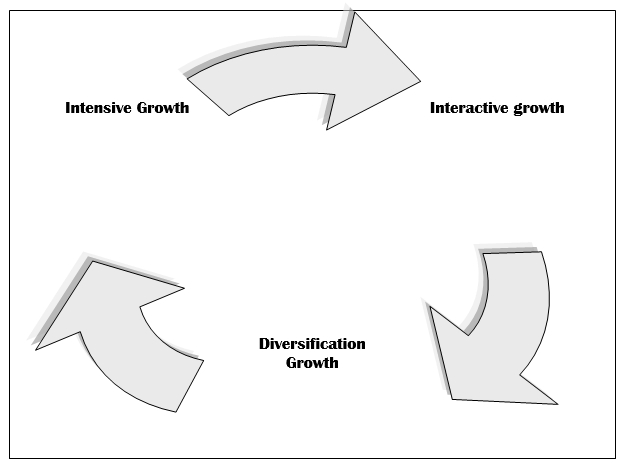
Intensive growth is the growth where the management is only concern for the betterment of the present businesses. Interactive growth is the growth where the growth has dictated to the forward, backward, or horizontal integration within the existing industry. Kotler & Keller (2006, p. 49) argued that diversification growth means the entering in a new business operation in the new or existing target market. However, marketing growth analysis is important for many reasons, such as –
- It is related with achieving market share,
- It creates extra investment opportunities (Wilson and Gillian 2005, p. 565-566)
From TeliaSonera (2008), it is argued that, the market growth of Life is increasing day by day, which is focusing by 20% market share of mobile market in Ukraine with 10,700,000 subscribers in the market. The sizes of customers are giving the market growth of Life in its regional market in the year of 2008. By giving efficient services to its customers, market growth of Life is expanding day-by-day (Life, 2009). MTS is continuing market growth in CIS region and evaluating its business opportunities with 100% market portfolio to its customers. Additionally, MTS is capturing commercial areas and geographic territory of local area to increase its market growth. (MTS, 2008)
Market Segmentation: Kotler & Armstrong et al. (2006, p. 31) termed market segmentation as dividing a market into some distinctive group or clusters of customers where the customers of a group has similar needs, characteristics, attitudes and demographics but the different groups have difference in these criteria. Here the customers of a group require similar products or marketing mix. Kotler and Keller (2006, p. 242) stated that the base of the segmentation is the preferences and the consumers of a segment must have the same preferences. They differentiated the market segment based on three preferences. These are Homogenous, diffused and clustered preferences. The rationale for segmentation is by doing so; the marketers can satisfy or attract all of the customers with only a single product. (Wilson and Gillian, 2005, p. 318)
Life has mainly segmented its target market in terms of young generation, business class people, and high-class people. Therefore, Life is segmenting its market within income groups of customers (Life, 2009). On the other side, MTS is making its segmentation in terms of geographic location of customers by extending network services in Russia, Uzbekistan, and America with different products and services for subscribers of the market. Therefore, these two companies are focusing on two different market segments, in terms of income and geographic location of customers (MTS 2009).
Promotion:
Advertising:
Advertising is a way of promotion, which is a paid form of non-personal communication about an organisation, product, service, or idea initiated by a sponsor who has individual identity. (Belch & Belch, 2004, p. 16) An advertisement must have three qualities. These are:
- Pervasiveness: the facility of repeating an advertisement for many times,
- Amplified expressiveness: Use of art and sound, which increase the dramatisation of the organisation and its offering,
- Impersonality: It must not force the audiences to pay attention but to attract the customers to pay attention.
Various media has used in advertising now a day. Some of them are television, radio, newspaper, and internet (Kotler & Keller, 2006, p. 555). However, if the mode of advertising is discussing, then it can say that, both of these companies are not focusing on only real advertisements methods, like TVC, broadcast media etc. but also they are focusing on virtual and online mode of advertisement by representing with different websites etc.
Research and Development:
Business research is the systematic and objective process of obtaining, recording and analysing business related data, which facilitate the decision-making in business. Zikmund (2003, p. 6) pointed out that there are two types of research done in business and these are basic or pure research and applied study, whereas development means the implementation of the findings resulted from a business research.
He further added that mobile business need to develop market research and development according to research to be flexible, innovative, and technological advanced to its customers. Both Life and MTS are above from this situation, they also develop market research of customers demand and technological movement of wireless services in market trends.
Marketing Research:
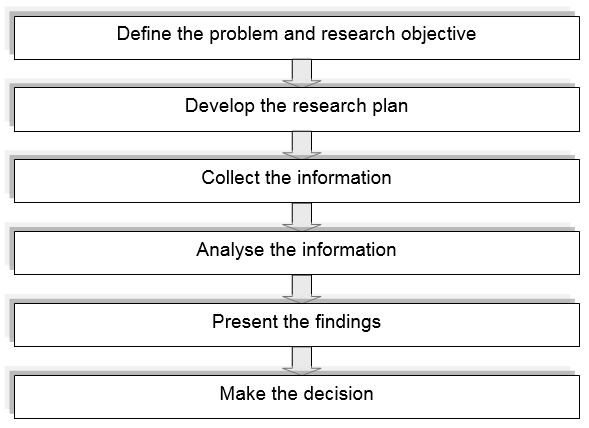
Marketing research is the approach to hook up the end user, shopper, and mass people with the marketer by the information flow that has engaged to make out and classify the market opportunities, its difficulties, including facts those prolonged and get rid of impurities of marketing drive. It also engender evaluates the marketing the drive and its functionality and monitors the market awarding whether to improve or diversify connecting by the assist of clear understanding (Kotler & Armstrong et al.; 2006, p. 344). There are six steps in doing the marketing research. These are:
Distribution Channel: Distributions channels are the ways marketers use to display, sell, or deliver the product or services to the customer. (Kotler and Keller, 2006, p. 26) Companies who have their operation internationally must take a whole channel view. In this view, there are three major nodes of channels. These are the seller’s headquarters, channels between different countries and channels within the nation (Kotler & Armstrong et al 2006, p. 344).
Life and MTS are both first moving companies in terms of market share and customers of their own. For this reason, both of these companies are developing proper distribution channel not only in Ukraine, but also in other part of Russia, Uzbekistan, and America as extension of their business in all over the world. (MTS, 2009)
Influence of Buyer Behaviour on Decision Making: In case of marketing, consumer behaviour is the key issue to make the ultimate purchase decision. The consumers not only try to maximise their benefits by purchasing a product but also try to get the cost-benefit advantage. Researchers proved that, many times the consumers behave so strangely that the ultimate purchase decision becomes an intuitive one. The decision-making has not only influenced by the friends and family, advertisements or role models but also by mood, situation, and emotions of the consumers (Schiffman & Kanuk, 2007, p. 35).
Life is giving three types of products to its customers, on the other side; MTS is giving various options to its customers to choose various types of products. However, by this, customers may get confused to choose right product for them, and Life is giving smaller and easier options to its customers. So, customers may influence on Life’s products, rather than MTS.
Methodology
Research Methodology
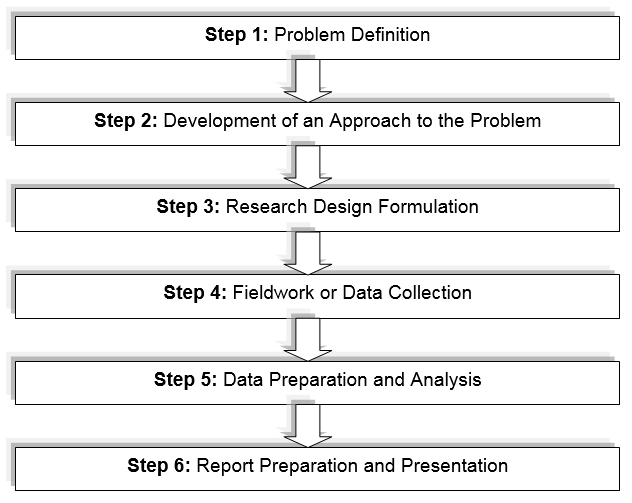
The foremost intention of this chapter is to discover the route how the selected research methodology would comply with the key objective of this dissertation subject matter and to finding the way of gaining the ultimate goal. Malhotra (2009) mentioned that essentially, there are two types of research methodology and these are qualitative and quantitative research while the quantitative research would be carried out to obtaining primary data by means of questionnaire and the qualitative research is the research that would be conducted through interviews and observations as well. For that reason, this research method would enable the researcher to investigate the details of his individual perceptions over phenomena of marketing strategies of two mobile operators Life and Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) to becoming the Market Leader of Belarus. The researcher will apply the following steps:
Research Design
Research design is a significant stair in the marketing research procedure and offers a structure for performing the market research and this step procedure are essential in order to acquire the required information and to establish chain of command among objectives, accomplishments, and analysis.
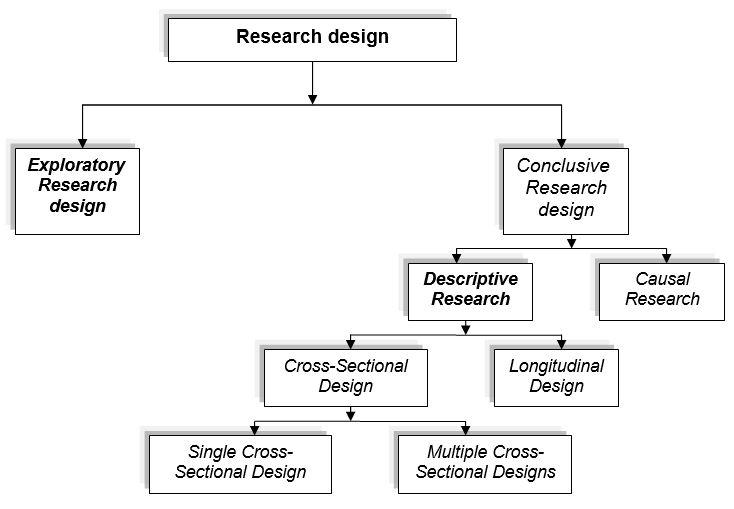
In order to formulate the study, the researcher will apply both exploratory research and descriptive research method. Exploratory research will help to originate a problem or describe it more accurately, develop theories, find out research questions, and ascertain priorities for further research etc. On the other hand, descriptive research method will assist to determine the perception of product or relevant groups and to describe market characteristics or functions by analyzing secondary data, surveys, panels, observational and other data.
Here it is important to mention that using secondary data is the main advantage of exploratory research as these data are easily accessible, reasonably inexpensive, and promptly obtained etc. The author will use internal data, which are ready to use or requires further processing and the author will also apply external data, which are published materials or computerized databases.
For the present research at the primary stage, qualitative methodology has born up by utilisation of the proper execution of research approach principles as well as by nursing of its significant strategic regions. In addition, the research approach has also outlined the research design varieties along with the data collection techniques and unambiguous coherent under the course of action.
This researcher has emphasised to communicating with the raised research questions and to do so, the current research section has required to working out during a variety of reliable mode of data to establishing information quality. Here the impact of data collection has proportionally gone through “applicable collecting data” and the “adequate collected data”.
Here the researcher apply the viewpoint of qualitative research approach including inductive justification along with deductive loom is a significant appliance universally where the inductive research rationalisation looked after the queries, and aim to illustrate it. On the other side, deductive research explanations have deal with the limitations of operating areas that turned the overall practice backward. For more clarification, comparison of marketing strategies of two mobile operators Life and Mobile Tele-Systems (MTS) has typically cultivated inductive rationalisation while constructing the theoretical profile to reach potential conclusions to diverse the firms’ marketing functions in Belarus.
Research Strategy of Fieldwork
This research framework addressed on the two prevailing methodologies of fieldwork study, such as traditional and scientific with different endeavour contained within them where the traditional approaches present fieldwork excursion with the objectives entrenched within the progress of satisfied knowledge. At the same time scientific approaches of data collection, testing of theories and field inquiries prolonged with the learning opportunities, which presents and encourages the appropriate purpose of learning objectives from the fieldwork by means of the scientific methodology; learning outcomes from the fieldwork turns as painstaking rather than the classroom as a setting up standpoint (RBFSC 2010).
This research has added that both the approaches would be complimentary where scientific approaches facilitate to have an elevated value of analytical thinking skills, when more expended humanistic fieldwork approach put emphasis on the development of accuracy and literacy issues of the research topic.
In order to conduct fieldwork for the present research, this researcher would categorise in accordance with the degree of student-centeredness and further traditional teacher-centred features of fieldwork, such as note taking from the supervisor as well as directed observation, description and explanation that espouses problem-solving focus for field survey in Belarus Mobil Market.
Interviews
There has been research in comparison of marketing strategies of two mobile operators Life and MTS that has allowed the researcher to understand more about how the offered services affects on customer. Interview is the best process to gather knowledge about the actual scenarios as “interview” would address as a communication mode that has contained both the features of consistency as well as the legitimacy. To conduct the interview on the strategy of Life and MTS, the approach of an interview has sketched either through several predetermine questionnaires or by a set of themes those would be covered the questions as well as would persuade the thirst of interested areas. This paper has assembled through semi structured interview technique due to focus on the mobile subscribers and current manager’s view and the advantages of this tool are that it has suitably conveyed required aspects, perceptions, and initiatives. Following are influential features, which the researcher has considered.
- What variety of data or information should be crafted from the interviewees?
- What are the objectives to illustrate the interview?
- Where and when the interview would take place?
- What are the dynamics of the interview?
- How the interview would be analysed?
The researcher of this dissertation would go to Belarus to interview more than a hundred mobile subscribers of Life and MTS and some of the managers to generate primary data concerned with the subjected area. The researcher will interviewed 50 participants breaking them down into two categories for two companies. The first category of participants is the managers and employees of Life and another is management of MTS.
Questionnaire Design
The researcher will design questionnaire to motivate and encourage the respondent to complete the interview because incomplete interviews have limited usefulness. To formulate the study without error, it is necessary to design a questionnaire, which will minimize response error, such as without questionnaire respondent may provide wrong answers or their answers are misanalyses.
However, the author will not adopt any scientific method to prepare this questionnaire, as there are no specific theory about questionnaire design and it has to develop by utilizing own experience and skills. Firstly, the researcher will apply few steps, for instance, identifying the required information, and interviewing method for this dissertation, determine the content of questions, formulate the question structure and so on.
For the researcher it is a comparatively trouble-free step to make out the residents of Belarus and to decide to conduct survey on the focus group of the population while the structured questionnaire itself has designed in so easy way to answer the questions by the respondents those would cover for the most part of general research questions. In addition, the questionnaire has designed and developed with aim to bring out the information upon the both demographic and psychographic features of the respondents as needed.
Moreover, the demographics have integrated the age, gender, and ethnic background along with employment status as well as psychographics towards the mobile phone usage categories and attitudes to the mobile operators especially on Life & MTS. Which age, gender?!!?
The questionnaire has been alienated with four divergent segments such as demographics, mobile phone operators, usage patterns, and attitudes towards Mobile Operators and the questionnaire layout is given in the Appendix-1.
Reliability & Validity of Interviews
It is crucial to assess what are the facts that have enacted behind to prefer an interview with the subscribers of Life and MTS and few operational manager rather than supplementary resources of the data collections. The most significant motivation of such an interview is that, according to this author’s believe, their involvement with the companies would make proper sense to the responds. Moreover, a discussion, which intends to take place with one of the member of management team of the companies, such as operators Life and MTS, would be further rewarding than any other potential sources. In view of the fact that these subscribers and employees would be at the top awareness of comparative to the research concerns, such as what are the marketing strategic difficulties of the organisations that has to overcome, and how do Life and MTS plan to face future complications to become market leader of Belarus.
Data Analysis
Data analysis for this research in the same geographic region, all potential data collection for interview has pre-approved by the regional research executives along with their superiors without any authentic data or information analysis and whenever the approval has taken place all of the redundant information gathered for interview questionnaires would have wipe away due to protect unfairness. However, the qualitative data generation technique is most reliable and valid for all type analysis while interviews and research of the historical documents need to conduct by utilising the qualitative research module.
Consequence of the aforementioned discussion, assemble of the interview has set of every event of the required attributes and its chain of order as well as ethics and values. While the change of managerial strategies, the inductive research approach has illustrated the overall feature of environmental dynamics and tend towards to a developed and flourished business market. On the other side, with the change of overall organisational business strategies and values have treated as empirical evidence and hence accomplished outcomes.
Further the researcher emphasis on data grounding and incorporated with editing, coding, recording and verification in order to refine them from errors that possibly will have taken place throughout the data assortment process where the next pace is data analysis from the contained information covered by questionnaires and turned into relevant knowledge.
In this research, collected data has brought together for scrutinising by using computer programs such as Microsoft Excel. In the questionnaire, the author has applied a number of ranking scales with very simple questions categorised with multiple-choice single response where the author is interested to adopt Likert scale for further analysis.
Contingency Plans
The contingency plan would explained that the company analysis and strategic decision-making interviewed questionnaires and collected data or information would not enough sufficient for the overall analysis if there is no option to make termination or pointed any potential rationale to overcome limitations. In this case, the research techniques have to transform compare to previous guidelines or principles, for instance, here the qualitative scheme would be better as well as easier to collect data for the analysis of the selected mobile operators.
As the qualitative research tactic would be applied for this study, several off-line observation tools like the questionnaires, different publications, survey reports etc are useful tools. However, practice of this guideline cannot but help to reduce time limit as well as proportionately increase the accuracy of the outcomes. Moreover, observation of both the existing products, services and the subscribers have enriched the researcher’s perceptive. To avoid biased or favouritism, head of the research team would be assembled numerous questionnaires by utilising magazines, journals, books, articles, which have written by renowned researchers and enthusiastic authors
Secondary Research
The researcher will use secondary data sources in order to support primary data to compare the marketing strategies between Life and MTS to become the Market Leader in Belarus. The justification to use secondary data is the researcher could able to collect processed data rapidly and inexpensively from external sources, such as, from the website of MTS and Life, books, previous researches etc. The researcher of this dissertation identified that there have an abundant supply of secondary data sources, for example, annual reports of the companies, several journal articles, previously published research papers, e-books, management journal and management books, relevant research books, and magazines and so on. However, the collection process is simple, cost effective, reliable, and helpful to interpret secondary data.
Primary Research
The researcher will use primary data for the clear-cut purpose to address particular research problem, research questions, and research dilemmas, and in order to do so the researcher would draw attention upon a focus group and equipped with a survey questionnaire with aim to generate primary data. The researcher of this dissertation has prepared a questionnaire to collect primary data from mobile subscribers as well as the management of Life and MTS. However, gathering of the primary data is more expensive as well as time consuming whereas the secondary data is frequently available quickly and economically from the valid sources. In addition, the researcher has to modify these data, as it is not free from errors.
In this study, the researcher has gathered primary data from field survey in Belarus with a focus group from viewpoint of the subscribers and managers of the Life and MTS through questionnaires. The questionnaires would be assembled and taken forward with consequence that has been possible for the mass people to assess the entire company as well as to generate a broader sense. For present study, the primary research has competent to assemble the views of younger generation and middle age group (18 – 45 years) of the Belarusian.
Limitation of Data Collection
The employees of the mobile operator Life and the Mobile Tele-Systems (MTS) were enough friendly to represent their company profile but the researcher of this dissertation had not enough time for the overall execution. The key secondary source of data collection was their annual report that was not left clear perception about these mobile operators. On the other hand, confidential barriers, as well as information gap was other major constraints to complete this paper.
Ethical Issue
This dissertation would keep its keen eyes on two ethical issues, which are diverse nevertheless interrelated with each other and laid on the central point to the conduct such any qualitative research together with research in strategic comparison and these ethical issues are the representation of truth as well as confidentiality. The ethical issue of representation of truth affects the exceptionally on the procedure of carrying out qualitative research including data gathering and data analysis and ultimately gaining the outcomes. The other ethical issue is the confidentiality concerned with respondents and the services triggered by the said companies. Both the ethical issues engross an influential relationship among the researcher and respondents and it carries consequence for other ethical issues such as susceptibility and corporate social responsibility.
Limitations of the Research
To conduct this research, this researcher has faced several limitations regarding this particular research where the results are limited as the sample group was restricted among the employees of the two mobile operators who owned mobile phones. This grounded a particular degree of unfairness where it is very difficult to draw in the least general inferences concerning the total population of Belarus. The presumption beleaguered from this research will facilitate the readers to differentiate the essential cellular market trends of Belarus including the strategies of the two mobile operators but the research does not make available any conclusive evidence regarding perception of the aggregate population of Belarus.
Sample
The sample group has been selected from the population of Minsk, the capital of the of Belarus but not other parts of the country where the larger part of sample have resulted with an elevated confidence gap and chosen from the people of two mobile operators interested to attending the interview. In addition, the research has focused on subscribers of the two mobile operators who re familiar with the strategies of the two operators and the employees who are acting with the major differences between them. Point to be noted that the survey has conducted along with a sample group rather than the entire populace of Belarus but it is not straight proportionate to the whole population and the data possibly will consist a marginal of error.
Findings and Results
Current Market Position of MTS & Life
According to the respondent’s view, the mobile telephony market of Belarus has gone through a gradual development due to regulatory labialisation for foreign entrepreneurs interested to bring their investment in the country. Within this drive, the Russian MTS formed MTS Belarus with a 49% share where 51% goes to the government. The small operator BeST 4 has integrated G3 technology with Ukraine’s Life and droved in to the market with the brand name Life, where the Turkish operator Turkcell has acquired an 80% share. The most recent development in the market is that the core second largest mobile operator of Belarus, the Velcom is going to be owned by the Telekom Austria which demonstrates liberalisations of the mobile sector of Belarus’ mobile telephony markets.
In September 2008, the Belarus Ministry of telecommunication and Information has presented the statistics that the mobile telephony market of Belarus consisted of 7.886 million subscribers open-handed a saturation of 81.9% with an annual growth of 16.5% where Turkcell apparently proclaimed that it has been targeting one third of the mobile market at the end of 2009. Even though the growth has so far downcast, it is expectant that the Life would show more strapping growth in 2009 by its re-branding of the operator and amplify its marketing investments to enlarge the network exposure with competence of 3G services. Following is the current market position of Belarus Mobile market:
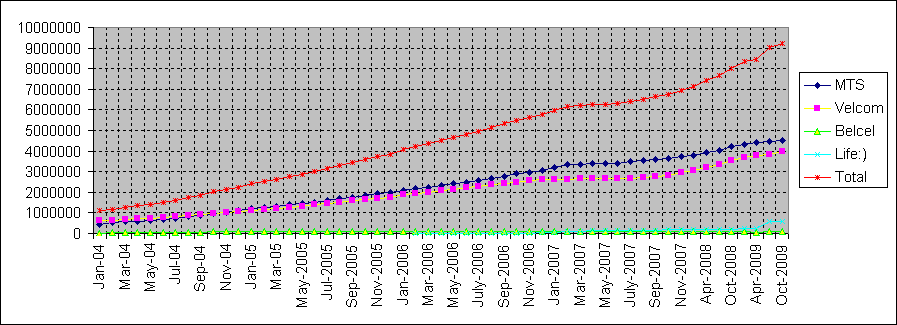
To analysis the mobile telephony market in context of the marketing strategies of MTS and Life of Belarus it is essential to address the LAN 5 phone market where the Beltelecom has an inherent monopoly on the fixed-line telephony market and has been intensifying the fixed-line network infrastructure with the aim to gaining the leading telecommunication market share where the respondents reported that there are more than 3.7 million fixed-line subscribers as per statistics of September 2008 and has estimated to be increased up to 3.749 million. This forecasting of LAN line subscriber enlargement would influence the mobile operator’s market share as the rising mobile market also impact on the LAN line subscriptions and Beltelecom would be unable to sustain its monopoly for both local and overseas calls.
It has also argued by the respondents that the present stage of Belarus mobile phoney market has scored 10 to 20 ranking out of hundred while it still vestiges at the lowest gain, the mobile operators would be optimistic that the Belarus government would continue its efforts to liberalising its regulatory legislation to engender the telecoms market. Moreover, there are huge positive initiatives taken by the government such as adoption of new telecommunication legislation taking into account the EU standard norms effective from January 2009 and come forward that the Belarus government has allowed to provide licensing ISP with broadband wireless access of internet through WiFi technology breaking the previously monopoly of Beltelecom.
The respondent also pointed out that there is a broadband subscriber pedestal of 250,000 in December 2008 with an annual growth of more than 127% where the mobile operators have opportunity to capture this emerging part that forecasting to be grown up to 1 million within 2013 with a market penetration of 10.4%. The monopolistic dominance of Beltelecom in the internet sector would be shared among the mobile operators and the both MTS and Life is ready to gain a remarkable market share though there are some small alternative ISPs are struggling in the Belarus market just like cable operators. Taking this advancement as a threat, Beltelecom has already decreased its internet access connectivity charges around 30% in 2008 and it would facilitates the small alternative ISPs to carry on trespass on the current market share.
MTS
The marketing strategies of MTS has faced a catastrophic lose of US$ 794.8 million foreign currency in 2008 to replicate the book value of the firm’s foreign denominated liability caused for the week currency Ruble but there are abundance of evidence that MTS is the biggest mobile operator has guts to investing at present situation with revenue growth of 4.0%. This percentage has amounted US$ 2.42 billion, which was $2.33 billion in previous year and this is enough satisfactory under the present recessionary economic when the Ruble has devaluated about 16% aligned with the US dollar at the end of 2008, this is fact has evidenced that MTS is an exceptionally robust player in the Belarus market.
Some respondents added that the marking strategy of MTS has complied successfully to market its mobile services all over the CIS 6 including Belarus and its marking strategy has targeted to the foreign markets like India and more and looks forward to kept it market leader position in Belarus serving the higher end user. In the first quarter of 2009, MTS has recorded highly increased subscribers all over its market while its subscribers increased 11.9% in Belarus. Due to the success of its marketing strategy MTS subscriber’s base amplified 44.8% in Armenia, 8.7% in Russia, 141.4% in Turkmenistan, 67.9% in Uzbekistan, and 8.5% in Ukraine and it turned the aggregate subscribers figure of MTS around 93 million satisfied end users.
With the current marketing strategy of MTS, its present market capitalisation of US$ 13.1 billion and sale revenue amounted over US$ 10.2 billion in the preceding financial year and MTS looks forward that it would be capable to tune-up its US$ 2.9 billion debt by means of net income of US$ 1.9 billion without facing any extra burden of liability.
The forward-looking marketing strategy of MTS going to promote plain that would to sustain its position of market leadership in Belarus with cost reduction and expansion in the course of offering VAS 7 and partnering with Vodafone that should convey most interesting features of services like CAPEx optimisations, network deployment, 3G based services, and CRM services pedestal on Vodafone Global platform. The MTS marketing strategy has proved a good evidence of sucking up new subscribers with data transmission plans via a mobile broadband internet connectivity offering while it has potentiality of entering the LAN line market with a new invest plan of US$ 1.5 billion of capital expenditures with other US$ 450 million infrastructural develop.
Life
Some respondents added that, the marketing strategy of Life has positioned it in the third when it is the brand name of Belarus state owned Mobile service provider BeST and 80% share of it has acquired by Turkcell the Turkish company for US$ 500 million and willing to pay more US$ 300 million following the first payment. Turkcell also pay for Life US$ 100 million for the financial year 2009 and 2010 with a customer base of 187,000 subscribers in 2008. Life has generated a profit of $1.2 million at the end of financial year 2008 while Turkcell pointed the business environment of Belarus, as an isolationist ex-Soviet state may be difficult to sustain.
There is a government influence on the marketing strategy of Life and the Belarusian government is adamant not to trade the enduring 20% shares of Life for the next five financial years. Meanwhile the government has pronounced a far above the ground of privatisation scheme in 2009 and sold out 70% shares of Velcom, which is the 2nd prevalent mobile service provider of Belarus, and by purchasing this shares Telekom Austria has taken entry6 in the Belarus market as a strapping competitor of Life.
Thought the mobile market of Belarus concerned with high competition, Life has given a boost to following the market entry of Telekom Austria and Life is going to enjoy radio frequencies allocated by regularity authority to build a 3G network due to the acquiring agreement with the major stakeholder Turkcell.
The most exciting significance of the marketing strategy is that still now Life is offering the lowest call transmission charges in the Belarus. Thought there are five major players in the Belarus mobile phone market, but none of them is capable to compete with the call rates of Life. For instance, when MTS is charging 180 BYR/min for the calls to LAN line, Life is charging only 94 BYR/min. Only this strategic criterion has seriously influenced the mobile users of Belarus, subscribers of all other operators are gradually shifting their choice fro Life, and thus Life is dreaming to become the market leader of Belarus in near future. The following table demonstrates the unbitten call rates of Life:
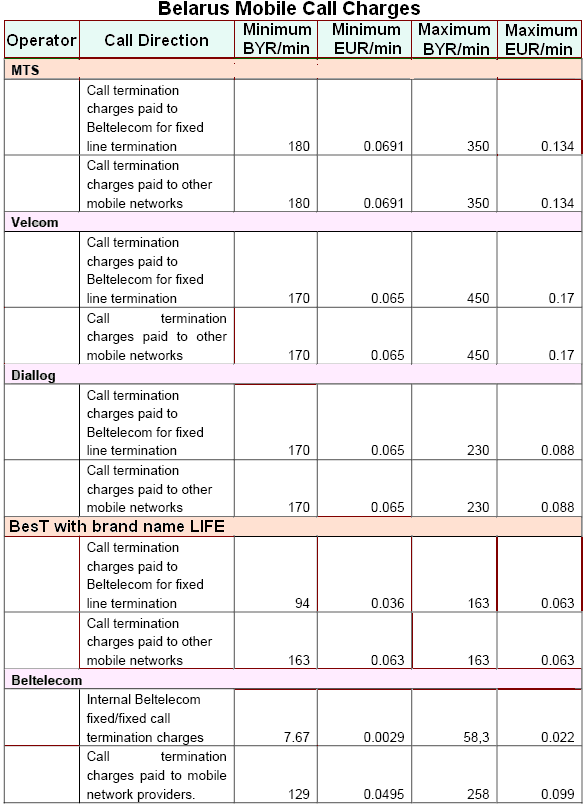
The economy of Belarus has enjoyed strapping growth in spite of significant government participation that reflects by the progress of its telecommunications market especially mobile phone sector. The global recessionary economy has seriously influenced the Belarus economy and the mobile operator Life has taken the great opportunity of getting amplified number of subscribers due to it attractive and most lowest price.
The strategic analysis of MTS & Life
MTS
In terms of strategic focus, the overall operations of MTS has emphasised on two aspects (Nikita, et al, 2005). Those are describes as following-
Market Entry strategies: There are many ways in entering into a foreign market such as incorporating exporting, joint venture, FDI (Foreign Direct Investment), licensing, franchising, acquisition etc. Among such options, the historical framework of MTS shows that it would like to make joint venture and acquisition as overseas market entry strategies in most of the cases (Annual report, 2008). Thus, the acquisition statistics from 2006 to 2008 can be presented as-
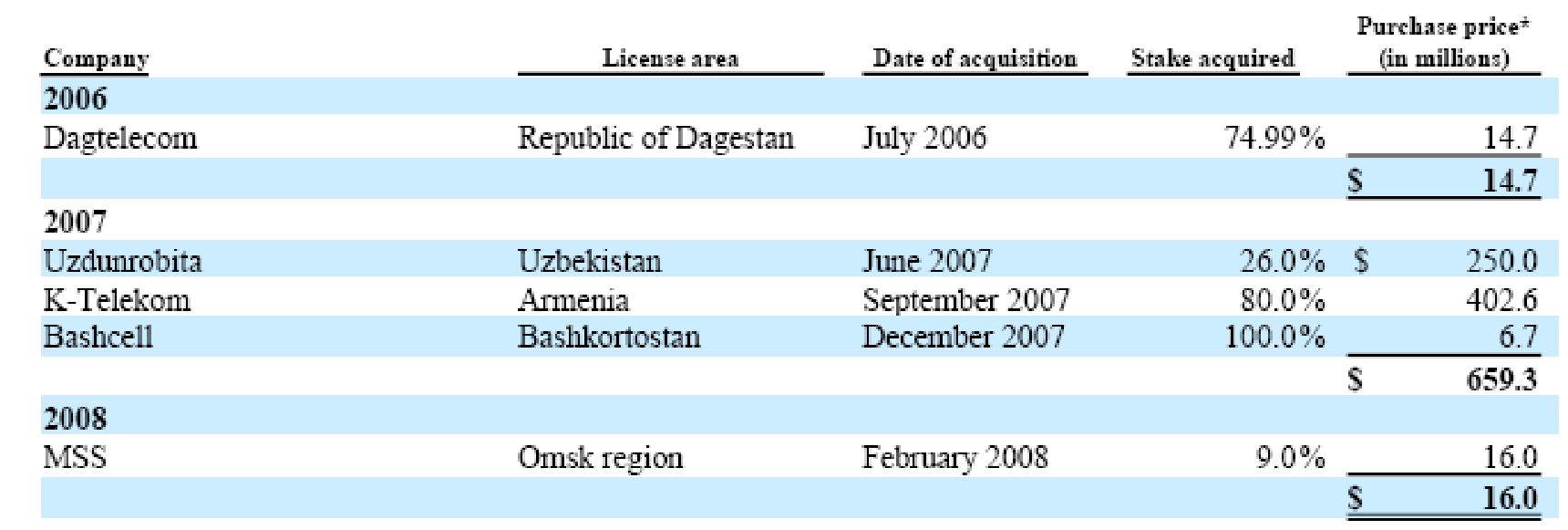
Almost in all telecom operators in Russia, such entrance strategies are widely influenced by legislative and technological circumstance. Thus, in 2008, a joint venture of Sistema and Shyam Group of India named as SSTL has been formed with a taking over of PAN- India license, which has later introduced MTS Company in Tamil Nadu that has been resulted into 8 circles among 22 cell phone circles of the country. In 2002, June, the company has begun a network regarding a junior counterpart in Belarus. Later, in 2004, 17th December, NTT DoCoMo from Japan and MTS have declared to form a strategic partnership through which MTS would initiate i-mode in Russian and other CIS regions along with making a high accessibility of this technology via 13 operations (NTT DoCoMo, 2004). Additionally, the company involved in global i-mode agreement considering Germen E- Plus Mobilefunk GmbH and Co. KG, Italian Wind Telecommunicazioni SpA, Greek COSMOTE Mobile Telecommunications SA, French Bouygues Telecom SA, along with some Australian, Germen, British, and Irish companies. In 2002, MTS has also determined for entering into the Belarus region through a joint venture partnership with a local entity. From June 2002, it has begun Belarus functionality with Mezhdugorodnaya Svyaz in terms of mutual stakes of 49%- 51%-combined ownership. At the same year, it has entered in Ukraine market through a buying of leading UMC of 58% shares, which delivered an outcome of 99% ownership of that domestic company. Similarly, in 2004, it has acquired an Uzbek company’s three quarters share for US $ 120 million named as Uzdunrobita with an addition requirement of purchasing the rest shares at more than US $ 40 million. Market expansion in Turkmenistan also followed by that technique but Kazakhstan is the single country where MTS could not be successful by keeping up with that trend (MTS, 2009).
Life
In the Belarus market, Life has extensively applied market entry strategy and pricing strategy for its focused growth. Life’s strategy construction drives have gone through flexible tariff plan, greater customer value, and product and service differentiation (Life, 2010)
Market entry strategies: At the beginning of entry in Belarus, Life’s vision based on the philosophy that is everything is possible. On the other hand, market entry strategy stands on-“everybody would be welcomed to Life”. Every one subscriber’s idea and cooperation has appreciated here cordially. Life’s platform is conveying through call forward, SMS, MMS, IVR etc. services. In following diagram, Life developed four key market entry strategies. Considering Michael Porter’s theory, strategic specialists of Life emphasised on generic business strategies to enjoy greater competitive advantages. At the first step, operation managers of Life made trade-off between narrow and broad business activities. In the second phase, they pay attention to the product differentiation and cost leadership. For instance, in 2008, Life offered 1 billion bonuses for their subscribers. On the hand, for new school year they have a gift package and send traffic update SMS six times during a day. In Kyiv, subway Life has a unique media project. Another marketing strategy- for the Ukrainian disable sponsor “National Sports Committee” that reflects their corporate values (Life 2010). Following figure demonstrates the logical drives of Life for its Strategic analysis in to its scope of business in Belarus market:
Figure 11:
Few of the respondent pointed out that, Life has designed its market entry strategy and segmented as bellow considering above-mentioned scope of business in Belarus.
- Target market: Life has segmented its target market through- VIP clients, corporate, and pre-paid.
- Customer needs: It has addressed customer’s needs with simple function and value added services rather than single package.
- Integrated marketing: Life has been well equipped with all level of skill employees at its marketing drives.
- Customer satisfaction: Rather than profit generating, Life prefers customer satisfaction.
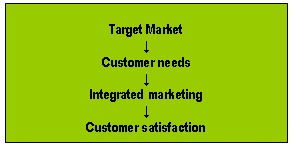
Pricing Strategy of MTS & Life
MTS
It is general perception of the mobile operator MTS that, price is the amount of charged for a product or service or the sum of values that the customers exchange for the benefits of using MTS product and services. Through pricing, MTS tends to charge some financial values for their delivering mobile phone operating services to their network subscribers but before setting a standardised price and adoption of an appropriate approach, the company considers some external and internal factors those are affecting such decision making process and they as:
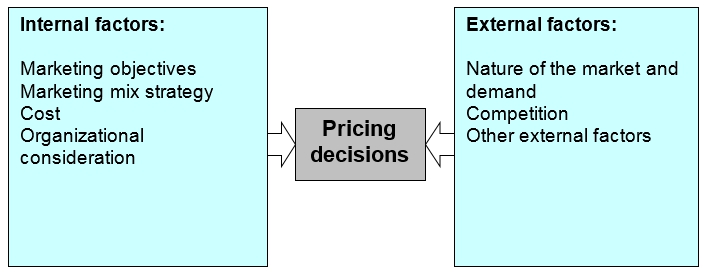
Regarding the inner variables, MTS considers the following:
- Broader marketing goals of meeting customer demand with wider expansion network,
- Better combination with service quality, valuation process, distribution and promotional activities,
- Identification of total costs regarding fixed and variables of establishing the widespread network, accumulation of necessary tools and equipments, hiring and bearing of expertise assistance and other employees etc.
- By considering own organisational contexts, MTS sets price through the interaction of marketing and sales unit.
For better understanding the nature of market and demand, it incorporates pricing in various market patterns as treating Russian telemarketing under monopolistic competition, customer perception towards price and value of their services, price elasticity, and demand integration with it. The pricing technique of other mega competitors, costing and offerings are examined with an additional concern for other economic disasters or strict regulatory movements by government are also taken into account by the Belarus mobile operator MTS.
Among the three alternative approaches of pricing regarding cost- based, value- bases and competition- based pricing; MTS generally follows the last one. Another name of this strategy is going-rate pricing where MTS bases its price largely on major rivals’ prices (Annual report 2009 of MTS). Here, it may charge the same, more than or less than those target competitors. This approach is a winning factor in this pattern of industry while user demand is enough difficult to measure. It also works effectively in terms of company’s effort to holding the existing price to prevent harmful price wars. At the same time, for introducing a new service like- offering free talk time or internet package, MTS follows penetration-pricing approach with a low initial price to penetrating in the target market quickly and deeply in order to gain huge market share (MTS, 2010).
Life
Due to the significant amount of share has owned by the state and perception of previous welfare state characteristics the pricing strategy has generated with the viewpoint of offering rock bottom price for all the communities. Through pricing, Life tends to charge lower financial values for among the other mobile phone operating services to their network subscribers but before fitting a standard pricing strategy, the company considers several external and internal factors.
To structure pricing strategy Life has considered the nature of market and demand; it incorporates pricing in various market aspects under open competition rather tan monopolistic antagonism with customer perception, services quality and price elasticity.
Among the different approaches of pricing Life has taken into practice the value- bases and pricing strategy from its beginning but Life always consider competitors’ pricing strategy and global financial downturn (Life, 2010). This approach is a well-built winning factor in the Belarus mobile industry while user demands are enough rising day by day. Life also works effectively in its own effort to holding the existing price and to preventing any unparallel price competition (Life 2010). Evidence of Life’s major pricing strategy has plotted bellow-
- Free service offer: by Utilising 1 MB of WAP Life offers 1000 free SMS which worth only 10 UAH. Within one-year validity, other operator charge is 0.50 UAH/min but for the same service, Life charges zero kop/min. Any subscriber could exchange free SMS in terms of Internet information.
- UAH 2000: in Kyiv 2007, LG Prada phone buyers have gotten UAH 2000 bonus talk time of Life.
- Dual SIM card and free talk time: For multi SIM users, Life opens communication freedom. Subscribers could use their two SIM at once along with a great offer free 500 UAH for each.
- Tariff plan and promotion: tariff plan has divided into three phases. They are in sequence as- free Life, simple Life, and super Life. On the other hand, subscription term has served through one world and free world.
Challenging and competitive factors of MTS & Life
MTS
In the present era of intensive pressure and competitive telecommunication industry, MTS is facing different options of challenges in its daily operations (MTS, 2010) and some of the major challenges are:
- Pressure for continuously developing the technological skills in rendering telecommunication service offerings,
- Adoption of wise acquisition planning in order to get free from intended risks associated with that business.
- Maintaining satisfactory level of cost- effectiveness in relation with other market partners for delivering competitive prices,
- Adoption with local and overseas government inflexible rules and regulation for expansion, networking and servicing strategies,
- Maintaining of tight control over the movement of fees of frequency spectrum practices for avoiding reverse impact on the brand,
- Assurance that the delivered 3G networks will be qualified enough, priced perfectly, accessed timely, commercially viable, pre-emptive and free from any sorts of public legislative effect (MTS, 2010).
- An entrance of Russian community Mobile Virtual Network Operators is posing a high potential to face more intense competition and whipping of users with an anticipated threat for market share and profit.
Life
Following are the major challenges faced by Life (Life 2010):
- First, Life is the fourth largest mobile company in context of Belarus market but third GSM service provider and now market leader in Ukraine and for this reason getting hold of subscribers in Belarus is their first challenge.
- Second, making variation in product and services or providing value added services are also another challenge. In Belarus, other operators provide only single unit service but Life has successfully traced its customers’ test. Now with more than 150 VAS, Life is able to deliver its services to the most of the areas of Belarus.
- Third, data transfer speed is another constrains of Life’s growth. As other challenges, Life has overcome this dilemma by five times speedy data transfer facility EDGE/GPRS roaming. Now EDGE has covered 66.2 % of the whole network connections.
- Forth, tariff plan and pricing strategy are other key challenge. Get rid of this complexity Life’s customer segmentation, pricing strategy and tariff plan is enough flexible for the consumer and also enough smart to retain and grow potential customers.
- Fifth, compare to other competitors it was hard for Life to provide easier mobile function but today, Life’s mobile operating system is easier than others are.
Core competencies of MTS & Life
MTS
Since MTS is being positioned as one of the largest telecommunication operators within the operating regions of Belarus, it can be said that several basic competency of the company are contributing for holding such level of operational performance (MTS Annual report, 2008). Thus, some most notable competencies are-
- Innovative approach,
- High growth and emerging operational areas,
- Stringer brand value,
- Global recognition for extensive corporate governance and higher intensity of information transparency is another significant core competence of MTS.
Life
The Core competencies Life differs from their rivals. Business size is ignored here and general usage is used widely. Concept of core competencies has left by corporate strategy of Life’s operation. Customer benefit, threat to competitor and value added services are three central issues of Life’s core competency. Besides differentiate from rivals, competitive advantages and long-term success are two effective outcomes. Life’s competency performed through- bright marketing strategy, build skill human resources, superior customer services, innovative, and value added services. Entire competencies of Life have marked through above-mentioned areas (Life 2010).
By new horizon of professionalism, every day Life’s operation tried to win customers’ trust. On the other hand, their corporate value produce through- team spirit, passionate for better outcomes and customers at hurt. Operators’ activities are also evaluated daily. However, Life is comparatively new player in this market but it has won numerous awards in several sectors. For instance, advertisement project, corporate solution in telecommunication, world’s fastest growing operator etc. are areas Life’s progress is better than its rivals are. Moreover, value added services and faster data transfer utilities are another two central issue of efficiency (Life 2010).
Competitive advantages of MTS & Life
MTS
It refers to the features those are singularly practices and mostly possessed by MTS (MTS Annual report, 2008). Some of such advantages are-
- Application of innovative motive in regular life in terms of thoughts, beliefs and stimulations for developing community growth and personal welfare;
- Comparatively lower fixed- line penetration.
- Opportunity for using multi- SIM cards,
- Adoption of unique CSR policy, which is assisting the company in creating positive public attitude about their offers and services,
- Unique networking facilities than other industry partners has provided competitive advantages of MTS.
Life
Life has enjoyed several competitive advantages in their business episode. To enjoy grater competitive advantages Life follow generic business method and TQM (Total Quality Management) philosophy. Utilisation of TQM Life gathered enormous success in following areas-
- Cost reduction: In comparison to other mobile operators, Life’s tariff plan is cheap and smart.
- Large number of product and services: In relation to another four competitors, Life provide only single package but they offer plenty of customer service centre as well as innovative value added services.
- Innovative products: In case of speed and utility, Life has a set of innovative mobile functions and GPRS facilities.
- Flexible supply chain management: Contract with outsourcing parties is enough flexible for supply chain management.
- Skill supplier: suppliers are skilled to meet customers demand.
- Skill management team: Both operational and functional management teams are able to get complement.
- Customer satisfaction: key success and enjoy competitive advantages are mostly comes from high customer satisfaction.
Discussion
Comparing mission and vision between MTS and Life
Mobile TeleSystems Operator or MTS is a Russia and CIS based mega cell phone Company running its ongoing national and international operations based on some core corporate objectives. In this regard, the company is running upon the broader vision of keeping its leadership functional orientation over the Belarus and some other especially Central Asia, Eastern Europe and CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States) regions. Motivated by such vision, corporate missions can be summed up as offering standard customised value, obtaining the top communications entity in CIS nations and generation of exclusive vale for the stakeholders. Thus, in short, MTS aims to incorporate completely all of its financial and non- financial responsibilities in terms of maintaining an interactive mode with customers, workforce, co- operatives, and legislators (MTS 2008).
January 2005, Mobile Operator Life was born in Ukraine and introduced by GSM operator, the Astelit Company. A set of mission and vision from the early stage, their passage is segmented through entire philosophy everything is possible. In order to enrich lives of general people, its vision mostly focuses on individual communication (Annual report 2009 of Life). For each subscriber, their customised services aimed to afford latest technologies with new opportunities and qualitative mobile communications. All of these inspires them invent modern shared experiences and connect people through a simple and significant mode. On the other hand, mission of Life connected their subscribers by qualified value added services for a long time. Consequence of above now Life is the fourth GSM operator in Belarus.
Environmental analysis of MTS and Life
PESTEL analysis of MTS
Under this concept, the related political, economic, socio- cultural, technological, environmental, and legal issues affecting MTS can be explained (MTS Annual report, 2008). Such as-
- Political factors: The widely accepted privatisation procedure has mostly assisted by the political background of Russia. Additionally, the most vulnerable political instability of CSR countries also highly influences the intended operational criteria of the company.
- Economic factors: Low per capita income, increasing demand of matured and emerging markets, huge competitive pressure from both neighbourhood and European entrants are several economic variables affect the growth and expansion rate of MTS from one region to another. It also poses a strong political and economic intimacy with the entire Soviet area.
- Socio- cultural factors: The historical socio- cultural background of its target regions, general infrastructural arrangement, and trading practices along with improvement of reinforcement technique etc. assist the company in implementing their skills and present situations as a basic theme of forward development in other CIS zones.
- Technological factors: MTS has considered as one of largest cell phone generated service providers in Russia, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, and Ukraine in terms of offering the sophisticated level of GSM technology. Additionally, it uses GSM 900 infrastructure, GSM 1800 equipment, UMTS 2100 networks and LTE etc. forms of ICT technology.
- Environmental factors: Corporate consciousness toward maintaining social responsibility and sustainable environmental issues with satisfactory level of ethical attitude reflects in capitalization for community health and growth, stable partnership agreement, obeying the rules and regulations of domestic and international marketing and enhancement of standard of living etc.
- Legal factors: The popular monopolization and globalisation viewpoint of the company is highly emphasised by legal telecommunication laws within the operating regions. Besides, Russian legislation for required inter- relationship in networking, Ministry of Communications and Mass Media for controlling telephone numbers and other technological and financial legislative bodies are comprehensive elements of such factors.
PESTEL analysis of Life
The status and current position in marketplace, external environment feature, and required initiatives are treated under PESTEL examination of Life. Both organisational and individual relation to the environment is also crafted here. Under PESTEL analysis, at first Life has to select most significant issue. Forces of PESTEL analysis has describe below from view point of Life –
- Political factors: The drivers of the political forces in Belarus are domestic and international organisations condition, tax strategies, institutional policies, government rules and globalisation issues (Life 2010);
- Economic factors: offering low price in global financial downturn, low operating cost to sustain in the market, internal funding models, financial support mechanism, profits creation objectives, budgetary margins, and industry directives etc. are economic dynamics for the Life (Life, 2010).
- Socio-cultural factors: Change of general lifestyle, employment opportunity, social view to education, government relation to particular relation, change in demography and population, mix culture impact are the key dynamics of socio-cultural forces that influence the strategy of Life in Belarus (Life 2010).
- Technological factor: Research, lack of emerging and recent technological knowledge, administration etc has treated under technical forces of Life.
- Environmental factors: Local environmental influences, global warming, deliver of socio-political forces etc. waved through environmental forces those persuade the strategy of Life in Belarus.
- Legal factors: Both national and international legislation has serious impact to designing the strategy of Life (Life 2010).
Competitive forces analysis of MTS and Life
Porter’s Five-forces model of competition for MTS
Under this model, the competitive environment of MTS could be examined with five factors as below:
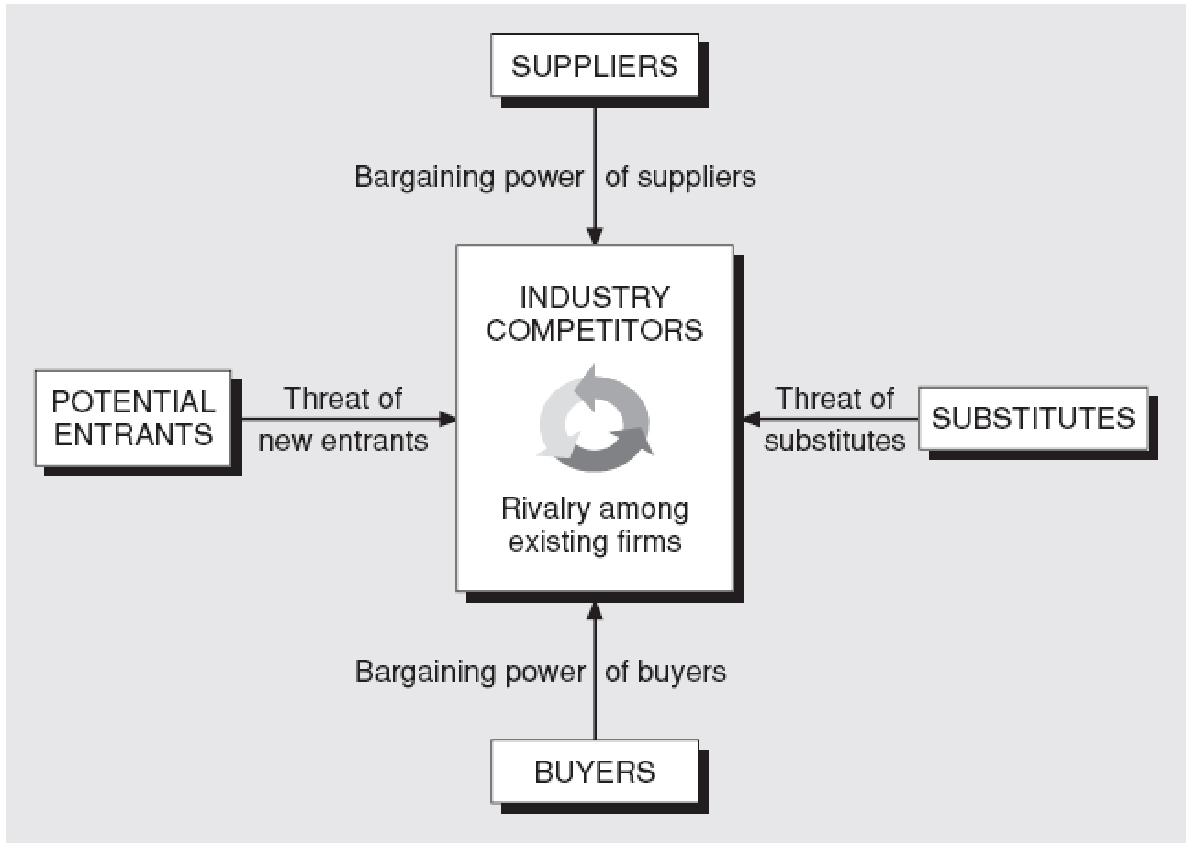
- Threats from new entrants: Recently, although the company has successfully sustaining among other competitors because the local ones do not pose technological and operational efficiency like it along with little bit attention of western agents in CIS region, many other new entrants are showing their interest gradually for emerging public demand in this sector. In addition, in Belarus, taking over of local entities formed a significant entry mode with huge contribution of Russian cell phone operators.
- Bargaining power of suppliers: Cell phone suppliers are those vending bodies from whom a cell phone operator buys network equipments and software. Since MTS is continuously purchasing such network tools and software from overseas supplies, maintaining a sound and mutual relationship is a crucial factor.
- Bargaining power of buyers: In telecommunication industry of CIS and Russia, subscribers pose adequate bargaining options while they are continuously demanding more and upgraded requirements from the intended servers.
- Threats of substitute products: Online chatting, e- mail, landline etc. are some substitutes of mobile phone although the industry is not facing a higher competition from those substitutes because of limited expansion of internet in many zones and other benefiting features of cell phone.
- Rivalry among existing firms: Some major industry competitors of MTS in Belarus market are Velcom, Belcel, and Life, who are targeting and operating at the same market in terms of engaged themselves in stronger price, market share, and penetration and technology war. On the other hand, competition among Russian cell phone companies has been intense enough so that they are seeking for new development scopes. Recently, MTS is facing a little bit competitive pressure from Life Telecom, which is particularly a Belarus based mobile phone operator.
Porter’s five-force Analysis for Life
In case of Life, Porter‘s five force analysis is another popular way of analysing competitive advantages. Life has taken this analysis as most significant field to address and termed as an environmental audit. Following are five key areas that Life is eager to discover under this approach (Life 2010).
- The threat of new entrants: Economies of scale, entrance of low cost technology, government policy, rigid distribution channel, avoid learning curve effects and harmful champion of branding etc. are threats for Life (Life 2010).
- Bargaining Power of buyers: Since Life is third mobile operator in their national GSM services, customers have greater scope to bargain though Life’s services are easiest among five mobile operators.
- Threat of Substitute Products: Due to numerous advance technologies, lot of network infrastructure played as substitute and would make threats to current product line.
- Bargaining Power of suppliers: greater bargaining powers of suppliers than consumers have negative impact to hold consumers. In addition, most of the cases it’s the chief issue to customers’ switch.
- Competition among the Industry: rival’s competition is high where entrance of new firm is flexible. In addition, Life is the third domestic mobile operator in Ukraine has faced a tough competition in their playground (Life 2010).
SWOT Analysis of MTS & Life
SWOT analysis of MTS
This analysis shows the corporate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of MTS such as:
- Strengths: Some stronger issues of MTS are:
- The external international policy serves as the key issue for the company in terms of high growth factor in the targeting Russia, Belarus, and other CIS countries, which facilitates the company in twin ways regarding development of modern communication devices and introduction of belligerent marketing operations.
- Long- term with NTT DoCoMo has enriched MTS as a successful i- mode provider, GMS/EDGE/GPRS network holder, and famous brand associate and diffused technical expert. For this, MTS now can easily manage subsidiaries through a wider expansion of i-mode technology in Uzbekistan, Ukraine, and Belarus along with satisfying its huge customer base regarding a number of differentiated and desired quality services. It also acts as an extra revenue generator with ARPU growth, which pulls customer’s attention by well-situated interface, greater options, and affordable value of consumption.
- Weaknesses: some vulnerable issues of the company are:
- In ending quarter of 2008, MTS had to lose about $794.8 million foreign currency, which had reduced the book value of this organisation’s overseas debt for the lower value of ruble. It had also negatively affected the growth rate of expected revenue.
- Lower wireless saturation rate in Uzbekistan market in 2007,
- The company incorporates a number of independent dealers, which does not pose adequate control by the company.
- Opportunities: Some optimistic issues are:
- The increasing trend of total number of users noted as 8.7% in Russia, 8.5% in Ukraine, 67.9% in Uzbekistan, 141.4% in Turkmenistan 11.9% in Belarus and 44.8% in Armenia offers the company with a greater potential of obtaining more revenue and market share in the forthcoming fiscal years (MTS 2009).
- Introduction of several 3G oriented offerings in the less advanced internet efficient areas of Russia would be resulted in discovery of more stable- line market featured by broader cell phone internet background as Omlet that will also pose entertainment option for Russian youth.
- Threats: Several challenging issues faced by MTS are:
- Different forms of economic, legislative, taxation and political instability of the developing operative nations are creating numerous challenges and pressures for the smooth operation of MTS.
- Any fall in existing dealership handling of the company would cause an uncertain fall in total subscription rate, industry share and consolidated income.
- At present, the intellectual assets owned by the company are expensive enough and thus critical for protection, which would lead it to move in quite inefficient way.
SWOT Analysis of Life
For Life, SWOT analysis is an effective tool in support of marketing strategy planning where strengths and weaknesses are dynamics that are more significant rather than opportunities and threats. Life’s SWOT analysis has presented bellow consecutively as strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats.
- Strength: Within last four years following are key driver of Life’s strengths. (Life 2010)
- Dynamism: In terms of subscription, Life is the world’s fastest growing mobile operator. For instance, in Ukraine they able to attract 1 million customers within first 8 month and now they are serving 11.8 million subscribers. Moreover, Life’s network covers 94.8 % Ukraine’s population who live in different province. Besides subscription quantity-marketing strategy, innovative service, wireless intelligence, and dynamic network have performed efficiently. Rather than mother country, Life has demonstrated its dynamism in Belarus market by collaborating with the government.
- Innovation: Life always favours customers’ view, when other operators provide only single package Life offers customers’ own contents potentiality. More than 150 value added services represent Life’s strong innovative market leader image. Some of them are- voice SMS, mobile TV, Bluetooth or Infrared port, Mellowing, five times high speed data transfer infrastructure EDGE, Push-To-Talk, wireless telephone connection, GPRS roaming for Internet connectivity in anywhere, mobile chat, a lot of mobile functions and so on.
- Customer certainty: Life’s customer segmentation involved in pre-paid, contract, account refill through ATMs or bank branches, corporate, and VIP clients. Within 171 countries of the world, Life has already discovered 429 mobile operators by their wide network roaming. In different campaigns, Life offers both simpler and high quality services and tariff plans. 488 exclusive shops and 34,600 non-exclusive shops are already ready to provide customer service in 178 different cities of Belarus and Ukraine. For high level customer support, Life’s 24/7 informational and consulting service operated by the Global Bilgi Company.
- Awards: In June 2006, first time the Ukraine Company Astelit won “The Oscar of business society” award in category of “Best New Company of the World”.
- Community: Besides efficient service Life also aware of global citizen, society, sate, natural and environmental resources preserve from any hazard. During 2007, they joined with the UN Global Compact, and after that, they took all necessary initiatives to encourage CSR-practices. Life’s CSR involved in- labour standards, 10 fundamental human rights, corruption fights etc.
- Weaknesses: On the other side of enormous success, Life has faced a few of limitation and these are:
- Considerable skill is absent in a small part of their operation.
- Within a few territory their branding programme is not enough strong.
- Though Life is a market leader in terms of subscription, distribution accessibility is not satisfactory in all operating areas.
- Contract with outsourcing companies sometimes make poor their supply chain management.
- Opportunities: Life has huge opportunities in home as well as in abroad. Some of these are quoted in bellow (Life, 2010, p. 4-16)
- Jump to Life program: For student welfare 2009, Life launched a new program “Jump to Life” with 20 ambitious program participants. This program provides both theoretical and practical experiences to start career in the best companies of Ukraine. Develop real business environment skill and move forward professional steps there have a lot of opportunity in this program. In addition, other than local companies international connection is also available for the job hunter.
- Special project opportunity: Special project opportunity is a mode to promote new product and services, projects of mobile subscribers. In this case, Life’s vision supports to take care of business proposal throughout technical support, monitor, and development.
- Partner ecosystem: Partner ecosystem is a circular flow of life where all of their current organism and partners are bound to provide best value added services (VAS). Since big opportunities come from big ecosystem is Life’s another philosophy.
- Advance technology: nursing advanced technology would open new milestone for Life.
- New distribution channel: by expanding distribution channel Life would be widen their business edge both in foreign and in local.
- Threats: due to large competition, every day threats from competitors and other related factors left barriers for Life. Major portion of those are – (Life, 2010, p. 4-6)
- Transformation customer base: transformation of customer choice is one of key threats to decrease subscribers.
- Tax increases: increase tax by government is a constraint to move forward and skilled service.
- Geographic markets termination: both in domestic and international geographic market are a symbol of prospect. Different issues are played behind to terminate geographic market such as- natural adversity, war, flu etc.
- Advance technology: it’s an era of nano technology. Fail to acquire most recent is also a threat to retain existing consumers.
- Government policy change: inflexible government policy would be barren the business field.
Ansoff’s matrix for MTS& Life
Ansoff’s matrix of MTS
It is a strategic vision of corporate growth for starting or acquiring businesses outside the MTS’s existing products and markets. It is helpful for understanding the growth of cell phone services regarding market penetration development along with product development and diversification (Kotler and Armstrong, 2006). So, the Ansoff’s model of MTS can be shown as-
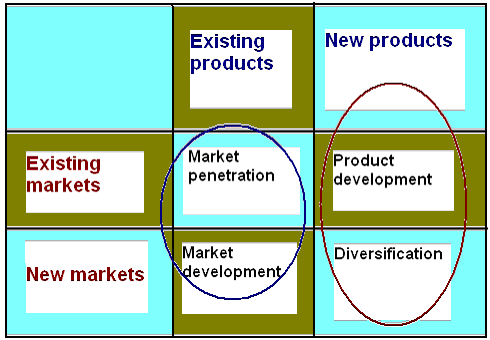
- Market penetration: Here, MTS provides its existing mobile servicing to the existing local and global markets in terms of generating profits by promoting their seams, networks, and extra benefits without any types of change.
- Market development: Here, the company markets their existing offerings in a new market boundary. For example, now MTS is planning to enter into Indian market for delivering services under same brand name.
- Product development: Here, MTS develops and offers new offerings for replacing the present ones. Using of 2G, 3G, and CDMA are examples of such criteria (ADB, 2006).
- Diversification: At this point, this operator delivers exclusively new forms of cell phone services for new segment. Such as, for Indian market penetration, MTS would offer a new mobile internet package for attracting young generation who are the major subscribers of both handset and internet.
Ansoff’s Matrix of Life
Description of Life’s products and services with required market growth strategy has taken into Ansoff’s matrix. Approaches of Ansoff’s matrix suggests prerequisite of business growth, existing products and services and for new product development. Directions of this approach have designed through four sequential stages as shown ion the following figure.
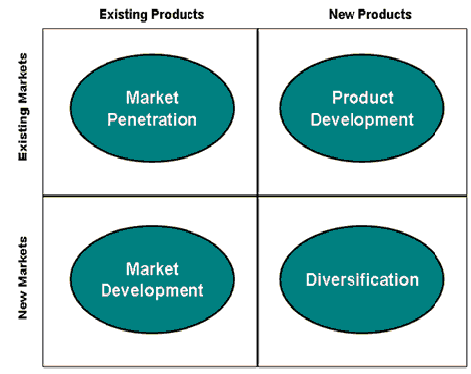
- Market penetration: At first phase, Life has concentrated on existing market or subscribers to serve their goods and services.
- Market development: Life has expanded the subscribers’ quantity through their existing products and service is the job of market development stage.
- Product development: in third stage, Life provides value added services to their existing subscribers.
- Diversification: Both subscribers and products are new in life’s diversification stage. In this stage, they like to present simpler and valued products to their customers than before.
BCG growth share matrix of MTS & Life
BCG matrix: of MTS
It is a portfolio planning procedure, which can be used to evaluate MTS’s strategic business units regarding its market growth rate and relative market share diversification (Kotler and Armstrong, 2006). It poses four (4) different considerations among which MTS occupies the distinct place below-

- Cash Cow: It is the low- growth, high- share business, or product for producing lots of cash for the company.
- Question mark: It is a low- share business unit in a high- growth market requiring huge cash for carrying on the business.
- Dog: It is a low- growth, low- share business, or product.
- Star: It is a high- growth, high- share business, or product in need of heavy investment to finance its rapid growth. As the matrix shows that MTS falls in this category since the company is a heavily financed service entity having high growth rate along with largest market share within the internal and external operating zones. The present market analysis reveals this fact of increasing market penetration regarding total market share, as:
- Russia- 135% to 140%.
- Ukraine- 119% to 120%.
- Turkmenistan- 29% to 35%.
- Uzbekistan- 52% to 56%.
BCG Matrix of Life
Under the BCG Growth Share Matrix, product portfolio of the Life is categorized into four major areas as following figure. BCG matrix assists to develop trade-off between investment and outcomes as well as shape the strategies to arrange different product line. Key strategic concept of Life’s BGC matrix walks through-develop, hold, harvest and divest. A concise introduction of Life’s BCG Matrix is conspired after consequence of following figure (Spencer, 2008).
- Stars: high market share and Utilisation lot money, within four year after voyage now Life has more than 150 value added services for 11.5 million subscribers.
- Cash cows: cash cows arranged high profitable investments that developed the star’s level for the Life.
- Questions: rapid growth of subscribers and dominant market position describes through question mark and it makes accessibility into cash cows and thereafter stars.
- Dogs: Dogs presents low market share and growth of the Life at their earlier stage and it was the time to increase profitability.
However, huge premises could easily grasp by the BCG matrix but still now, there have several limitations to annex two prime profitability indicator- industry attractiveness and competitive advantages. Following is the strategic sequence to utilise the BCG Growth Matrix of Life.
Why MTS is the Market Leader of Belarus
A number of factors have already been revealed from the previous findings of the selected companies, which can be helpful for going with further discussion, such as-
Strategic evaluation of the company: Basic competition of CIS telecommunication industry is being influenced by some integral factors. Among those some most prevalent are domestic tariff charges, quality of networking, optimum brand value, international roaming, and tariffs, supply of value- generated services and degree of customer service. In recent years, the alternative competitive scenario of MTS along with environmental essences can be presented as:
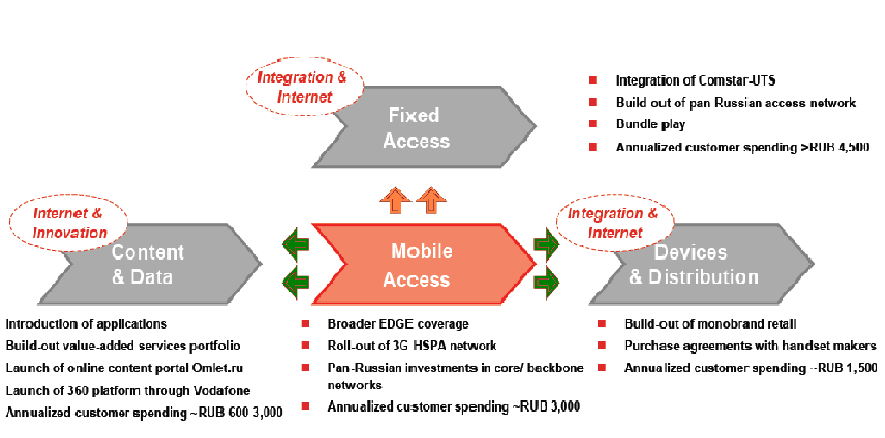
Evaluation of corporate strategies
As noted before, the company’s strategic direction is focused upon three criteria regarding integration, internet, and innovation. Accordingly, distinctively tactics are being applied at each phase, which draws some specific leverage (MTS, 2009). Thus, the 1st phase motivates upon new pipelines through touchy issues of subscribers. This offers the projected seamless subscriber for all divisions, exclusive broadband infrastructure, and interrelated sales networks. On the other hand, internet are the smarter pipelines for obtaining standard value for increasing connectivity, convincing online subscriber knowledge and better servicing. Finally, through innovation, MTS runs its corporate differentiation approach regarding the intended service mix. Such efforts are helping the company in providing exclusive services than other telecommunications, specialization of offerings for each customer division and increasing satisfactory experiences of the customers from home to movement. At a combination, all of those strategies are adding CLV (King, 2009) and producing shareholder’s long- run return for the company (Shamolin & Kornya, 2009)
Introduction of 3G network in Belarus
In terms of creating core corporate value, MTS has recently initiated the UMTS/ HSPA 3G network at Belarus with an additional extension plan. Adoption of such strategy has been enabled Life for delivering some extra services regarding video calling and usage development. Therefore, by doing so, the company is contributing greatly in developing the macro telecommunication infrastructure of that Country along with enhancing customer-telecommunication preference options. On the other hand, creation of UMTS network is similar technological strategy of MTS, which is largely encompassing the mobile broadband system with CIS with lower penetration ratio. Therefore, such networking is viewed to be progressive towards the company for meeting increased demand of the new generation. Furthermore, in Russia, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan, the company is offering CDMA-450 network as a speedy data accessing and transformational service.
Orientation of business strategy
MTS is strongly committed with sustaining their market position through network capitalization, better technologies, and new product development along with continuous servicing. According to “3+2” strategy, MTS generates comparatively better customer feelings for gaining huge retention and adequate demand rate. Promotional stimulation for increased data usage and content service are continuously delivered for easing 3G infrastructural background. Thereafter, along with capturing the internal and external market share, MTS is widely focusing upon cost efficiency and group development by implementation of various strategic mottos (Annual report, 2008), as:
- Expansion of operational criteria through revenue orientation via network development;
- Delivery of diversified tariff plans with value- added offerings covering intended customer segments by enhancing brand value and loyalty status.
- Adoption of various successful taking over, merging, and licensing plants for strengthening international market position;
- Exploration of distinguished market scopes beyond CIS, especially in Africa.
- Incorporation of cost efficiency program through functional synergies and economies of scale vision. These tasks involve centralized roaming and wholesale contact, huge traffic orientation on proprietary channels, optimized channel advantages by developing central planning and setting of equipment. Apart from that, other factors involve lowering marketing and advertisement expenditures along with other relevant overhead costs.
- Development of distribution networks in terms of establishing mono- brand channel regarding corporate retail passages, involving members for enhancing total franchises and possible taking over of present retail channels;
- Sustaining in the top position regarding management quality, personnel, and corporate culture;
- Adoption of integrated CSR activities.
Additionally, the company has been concentrating its expansion plan over specific CIS and other mentioned zones by a unique marketing strategy as well as centralized channels and operations management (Annual report, 2008).
Corporate service mix through value addition and global roaming
As a part of service mixing strategy, MTS generally offers a larger number of service options. At the same time, Life divided its product line into three categories to offer diversified products. Among those, the most notable is automatic roaming under which it offers both permanent and temporary customers an enlarged option for receiving and making global, long- distance and external calls by using personal network. However, value- added services of MTS involves a number of options regarding Blackberry, call divert and forwarding, displaying caller ID, WiFi, LBS, conference calling, SMS and mobile office and banking. Some others are WAP service, MMS, missed call alert, directory and information service and categorizing monthly bills etc.
Conclusion
Recommendations
Within a short period, Life acquired a lot of success but besides their achievement, they have a few limitations. Recommendation part of this paper presents different modes to overcome these constrains. Following are ways to recover their limitations.
- Because of the global financial crisis, many customers would like to use the product of Life as it provides services with competitive price. In addition, the existing market leader MTS offers high price for its products in Belarus market. Therefore, Life should increase budget promotional activities to highlight their pricing strategy to customers and its promotional area has to amend immediately to retain their potential growth. However, celebrity engagement for promotional movements will help to develop brand image like MTS;
- From the beginning, Life emphasizes more on increasing subscription quantity with high quality and it has already earned numerous international awards, so it has a prospect to become market leader in Belarus market. However, it should equally consider the growth strategy for both domestic and international market, because, Life leads the market of Ukraine in terms of subscription whereas in Belarus, Life is in third position. In addition, entrance into new area like Belarus would help the company to assemble and develop their all operational departments.
- Continuous research on Belarus market is an effective way to develop it position, so it should increase the budget for R&D to concentrate on this issue;
- It should consider market risks, such as high regulatory costs and fall of foreign exchanges;
- Life should strongly control the issues of interpersonal conflict and politics to minimise the risk of low profitability for managerial disappointment.
- Life should concentrate on investment policy and operating costs.
Although the overall comparative strategic vision of MTS has been focused on several stronger and potential issues sustained by the company, some integrated risk factors are needed to be altered, as:
- MTS should consider more external pressures and uncontrollable factors in its acquisition policy since it is associated with several vulnerable issues associated with economy, politics, and taxation of the pointed countries.
- Since, along with newer market entrance, the company is not adequately building further distribution channels, such option would hamper its long- run profitability and customer relationship. For this, it should take an immediate consideration in building new distribution outlets.
- The company should hold high sense for technological obsolesce since the telecommunication industry is highly innovative regarding technical and non- technical superiority.
- Then, MTS should also revise its geographic segmentation strategy because a slight mistake of proper planning and judgment would change the profitability scenario. This task involves engagement of industry experts and other specialized force for an identification of segment structural attractiveness and sustainable growth potential.
- Since inter- government complications of Ukraine would the operational smoothness regarding intended rating, the company should adopt an essential contingency plan to overcome that risk.
- It should keep a sound supplier relationship through the transactional period. As the present scenario is showing some sort of conflicting stage, MTS should strongly handle that in order to increase the profitability of the overall value chain.
Conclusion
At the end, it has become very clear to understand that as having the position of market leader within the served market of Belarus, MTS Company is a subject of maintaining and implementing several technical and functional issues. All such aspects are related with corporate macro level mission, vision, goal, and objectives, which can be identified in terms of different operational, managerial, marketing, and technological criteria. Additionally, the critical evaluations and marketing analysis have revealed some core internal and external strategies of the company that are not only paving its global but also international market expansion strategies. Based on a wider number of service options, the company is now fulfilling the telecommunication demand of its million of subscribers along with creating newer technological demand among them. Although the company is facing some integral pressure and challenging issues, alternative market- oriented operational drives as noted in the recommendation section would help itself to be competitive enough than others.
Life’s marketing strategies have overviewed all of the major marketing areas. The paper has examined that mobile operator Life is famous as much as necessary but in Belarus their market condition is ranked at lower position rather than becoming market leader. They have evaluated and supplied any of the customer demand properly. On the other hand, in Ukraine Life’s journey is constructed by customer view. This inverse scenario points towards an underprivileged international continuation as well as market brand image. Additionally, integrated marketing is also absent in Belarus. Life would progress if they exercised efficiencies and experiences of the Ukrainian market in Belarus.
Reference List
Belch, G. E. & Belch, M. A. (2004). Advertising and promotion. 6th ed. New York: McGraw Hill.
Cohen, L. Manion, L. & Morrison, K., (2007) Research Methods in Education. 6th ed. London: Routledge.
Colne, W. (2009) Marketing Effectiveness Overview. Web.
Doroshevich, M. (2005) State owned GSM-operator BeST plans to begin construction of the cellular network in the near future. Web.
Doroshevich, M. (2008) Belarus. Web.
Drummonda, M., Cookeb, J., and Walleyc, T. (1998) Economic evaluation under managed competition: Evidence from the U.K. Web.
Fisher, R. A. (1990) Statistical Methods, Experimental Design, and Scientific Inference, 1st ed. J. H. Bennett Editor, NY: Oxford University Press.
Hirschhausen, C. V. (1996) Deregulation and Enterprization in Central and Eastern Telecommunication – A Benchmark for the West? Web.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001) Strategic Management. 4th ed. South-Western Thomson Learning.
Johnson, G., Scholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2008) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. 5th ed. Prentice Hall.
King, M. (2009) Belarus Telecommunications Report 2009. Web.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2006) Principles of Marketing. 11th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2006) Marketing Management. 11th ed. Prentice Hall.
Krause, R. (2009) Russia’s Mobile TeleSystems Plans To Be A Leader In Rollout Of 4G. Web.
Kwoka, J. E. (1977) Large Firm Dominance and Price-Cost Margins in Manufacturing Industries. Southern Economic Journal, Vol. 44,. Issue- 5. Web.
Life. (2009) Individual Life. Web.
Life. (2009) Individual life Tariffs. Web.
Life. (2009) Life Platinum. Web.
Life. (2009) Life Platinum Tariffs. Web.
Life. (2009) Promotions. [Online]. Web.
Lisitsyn, N. Sutyrin, S. F. Trofimenko, O. Y. & Vorobieva, I. V. (2005) Russian Telecommunication Company MTS Goes to the CIS. Web.
Malhotra, N. K., (2009) Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. 5th edition. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Massey, G. R. & Dawes, P. L. (2004) Functional and dysfunctional conflict in the context of marketing and sales. Web.
Menon, A. Bharadwaj, S. G. & Howell, R (1996), The quality and effectiveness of marketing strategy: Effects of functional and dysfunctional conflict in intra-organisational relationships. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, Vol. 24, issue 4.
Millard, B. (2006) Sequence of Strategy Utilising the BCG Growth / Market Share Portfolio Matrix. Web.
MTS (2008) Annual report 2008 of MTS. Web.
MTS. (2009). Corporate strategy. Web.
MTS. (2009). How to become a subscriber. Web.
MTS (2009) Mobile TeleSystems Announces Financial Results for the Third Quarter Ended. Web.
MTS. (2009). Products and Services. Web.
MTS (2010) Corporate governance: Mobile Telesystems OJSC Comparison of Corporate Governance Practices. Web.
MTS (2010) Corporate Social Responsibility. Web.
MTS (2010) Dividend policy. Web.
MTS (2010) History of MTS.Web.
MTS (2010) Our markets. Web.
Nikita, E. et al (2005) Outward Internationalisation of Russian Leading Telecom Companies. Web.
Nissan, E. (2003) Relative Market Power versus Concentration as Measure of Market Dominance. Journal of Insurance, Vol. 26, Issues 2. Web.
NTT DoCoMo (2004) NTT DoCoMo and MTS Form Strategic Partnership for i-mode in Russia and Other CIS Countries. Web.
Perry, C. (1998) A Structured Approach to Presenting Theses. Web.
Pickford, M., & Haslett, S. (1999) A Statistical Test of Single Firm Market Power. New Zealand Economic Journal, Vol. 33, 1999. Web.
Porter, M. E. (2004) Competitive Strategy. Export Edition. New York: The Free Press.
Rajagopalan, N., Rasheed, M. A. & Datta, D. K. (1993) Strategic decision processes: critical review and future directions. Journal of Management, Vol. 19, issue 2. Web.
RBFSC (2010) Fieldwork Methodology, Reserved Barcelona Field Studies Centre S.L. Web.
Rhoades, S. A. (1985) Market Share as a Source of Market Power: Implications and Some Evidence. Journal of Economics and Business. Web.
Ruekert, R. W. & Walker, O. C. (1987) Marketing’s interaction with other functional units: a conceptual framework and empirical evidence. Journal of Marketing, Vol. 51, Issue-1. Web.
Sanchez, R., Heene, A. & Thomas, H. (1996) Dynamics of Competence-Based Competition. 2nd ed. London: Thomson Learning.
Saunders, M. Thornhill, A., & Lewis, P., (2003) Research Methods for Business Students. 4th ed. London: FT Prentice Hall.
Schiffman, L. G. & Kanuk, L. L. (2007) Consumer Behavior. 9th ed. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice-hall.
Sekaran, U., (2006) Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach. 4th ed. John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Shamolin, M. & Kornya, A. (2009) Group financial results for the third quarter year 2009. Web.
Sladew, M. E. (2004) Market Power and Joint Dominance in UK. Journal of Industrial Economics, Vol. LII, Issue No. 1. Web.
Smirchich, L. & Stubbart, C. (1985) Strategic Management in an Enacted World. Academy of Management Review , Vol. 10, pp. 724-736.
Spencer, T. (2008) BCG growth matrix. Web.
Stewart, M. (2009) Marketing Budgets 2010: Effectiveness, Measurement & Allocation. Web.
Teece, D.J., Pisano, G. & Shuen, A. (1990) Firm Capabilities, Resources, and the Concept of Strategy: Four Paradigms of Strategic Management. 2nd ed. London: Thomson Learning.
Teece, D. J. & Pisano, G. (1994) The dynamic capabilities of firms: An introduction. Industrial and Corporate Change, Vol. 3, pp. 537–556.
TeliaSonera. (2008). Strong positions in mobile growth markets. Web.
Thompson, A. et al (2007) Strategic Management. 13th ed. Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited.
Trebing, H. M. (1998) Concentration and the Sustainability of Market Power in Public Utility Industries. Web.
Tutor2u (2010) Ansoff’s product / market matrix. Web.
Ward, J. L. & Stasch, S. F. (1986) When Are Market Leaders Most Likely To Be Attacked? Journal of Consumer Marketing, Vol. 3 Issue: 4, 42- 48.
Wilson, R. M. S. & Gillian, C. (2005). Strategic Marketing Management. 3rd ed. Oxford: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
Zeithaml, V. A. & Bitner, M. J. (2006).Services Marketing. 4th ed. New York: McGraw Hill.
Zikmund, W. G. (2003) Business Research Methods. 8th ed. Ohio: Thomson South-western.
Appendix
Questionnaire
The present literature does not make it available to assess the impact of Mobile provider on the functional model of the Mobile market with a suitable instrument. Thus, a suitable appliance has been developed to enumerate this assessment. The questionnaire has been developed in an attitude that has conserved its internal cohesiveness; special care has been provided to ensure that each question focuses on one exact issue.
On a scale from 1 to 5 ( 1 – low level, 5 – excellent/high level ) please assess the issues asked in the questionnaire marking a necessary column with a sign of X.
Footnotes
- Mobile TeleSystems
- Return on Investment
- Unique Value Proposition
- Belorusskaya Telekomunikatsionnaya
- Local Area Network
- Commonwealth of Independent States
- Value Added Services