McDonald’s is one of the most famous brands in the USA, symbolizing the American way of life. The company is now facing serious challenges due to economic constraints and COVID-19 pandemic. People’s consumption patterns are transforming, so hospitality companies need to adapt to the new environment. One of the strategies to utilize is the focus on CSR practices. The service delivery department of McDonald’s should place emphasis on this concept, which will enable the company to maintain its competitive advantage. The corporation will need to allocate additional funds to engage in CSR projects. However, this effort will have a positive impact on the company’s image and performance. This paper includes a brief SWOT analysis of McDonald’s, as well as a description of the CSR approach as the most appropriate strategy to choose to address the most urgent issues. The choice is supported by the analysis of the current research on the strengths and weaknesses of CSR.
McDonald’s is one of the most famous brands globally that has been one of the leaders in the fast-food market. First restaurants opened in 1940, and as far back as 1948 the company developed its major strategy, its central menu components, that largely persists into these days (McDonald’s, 2019a). The iconic menu includes hamburgers, potato, soft drinks, coffee, milk, and a pie. The company’s services are also associated with several basic concepts, including self-service, drive-in, quality, cleanliness, and service (McDonald’s, 2019a). However, the company has to operate in a highly competitive market with several major and a myriad of smaller competitors. Marketing efforts have been effective for decades, but McDonald’s is facing certain challenges, mainly associated with external factors that require certain changes in terms of the strategies to be employed. This report includes a brief analysis of the efficiency of the service delivery department and a description of the strategies that should be utilized to maintain the company’s leading role in the U.S. market.
SWOT Analysis
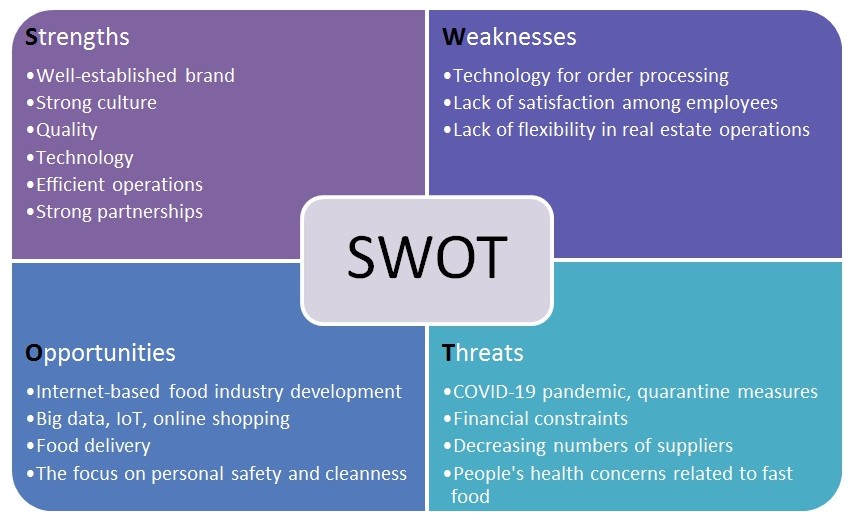
In order to analyze the most appropriate strategy to be adopted, it is essential to consider internal and external factors that have an impact on the organization. The SWOT analysis has proved to be an effective tool to identify the most influential factors (Harvard Business Review, 2005). The tool involves the focus on four larger areas, including strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. In order to examine the internal aspects (strengths and weaknesses), the VRIO tool can be used, while PESTEL analysis can be effective in determining external influences (opportunities and threats). PESTEL has been a widely utilized instrument that enables managers to consider the most influential domains, such as political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal (see Table 1).
As far as the external factors are concerned, the vast majority of the forces affecting the development of the company in question are linked to the COVID-19 pandemic that has had a tremendous impact on the global scale. Political aspects affecting McDonald’s development this year are associated with the presidential elections that will take place this year in the USA. For instance, the rumors regarding the donations of McDonald’s and other fast-food restaurant chains to Trump avert some people from visiting their favorite dining places (Taylor, 2020). It is noteworthy that only occasional cases of some franchisers or partners of McDonald’s have donated to presidential elections of both candidates.
Table 1: PESTEL Analysis
Economic issues have a more substantial effect on the prospects of the hospitality industry. The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in diverse restrictions related to people’s way of life, including but not confined to attended the places they used to visit on a regular basis (Haddon, 2020). For weeks and, in some regions, for months, restaurants were closed or worked to their minimal capacity. The drive-in services became vital for McDonald’s at that period although they still were not sufficient for covering all operational costs.
As for the social aspect, even after the end of quarantine measures, many people are less willing to visit fast-food restaurants due to their fears regarding the infection, which has a negative effect on the financial performance of the company. The fast-food chain in question is still associated with unhealthy lifestyles. Technological aspects provide a wide range of opportunities for many companies, including McDonald’s. The development of software and mobile applications enable organizations to satisfy customer needs and develop new products and services. New services related to food delivery are becoming popular, and companies can benefit from these technologies (Nicola et al., 2020). Environmental factors also have an impact on the company’s development as the issues related to waste management and the use of resources persist although the organization has undertaken numerous steps to be a responsible corporate citizen (Langert, 2019). Finally, legal issues associated with the company’s environmental or social input regularly arise and have a negative influence on the image of the organization (Astor, 2019). For instance, Astor (2019) reports that U.S. employees are demanding higher wages.
In order to examine the internal factors that influence the development of the company, it is possible to use the VRIO tool. This instrument can help in identifying an organization’s competitive advantage, its application, and possible ways to improve it (Barney and Clifford, 2010). The analysis of the resources the organization in question has suggests that the company utilizes the available opportunities and resources effectively although some improvements are needed (see Table 2).
Table 2: VRIO Model for McDonald’s
It is clear that the company manages to utilize the opportunities and capabilities rather effectively. For instance, such resources as brand image and the development of relationships with partners is a considerable competitive advantage of McDonald’s. The brand is properly established in the USA, and its competitors can hardly reach a similar level of recognition and appraisal. However, the company can lose its competitive advantage in other areas due to other fast-food chains and hospitality companies are managing certain capabilities efficiently. Technology is one of the areas to pay attention to as some organizations are enhancing their popularity and increasing the market share. Online sales have increased during the pandemic, and people’s buying habits are changing, so new entrants may win a competitive advantage (Haddon, 2020; Settembre, 2020). Such aspects as quality, recipes, franchise operations, and HR management and culture need specific attention.
Recommended Strategy
McDonald’s has to operate in a highly competitive market and has managed to maintain a competitive advantage. However, the company is facing certain internal and external challenges that need to be addressed rapidly in order to secure its leading position in the USA. At that, the most pressing issues are related to the changing consumer behaviors due to the pandemic. In such turbulent times, companies may exploit diverse strategies to remain competitive, but the development or keeping a positive image should be one of the major priorities.
Restaurant-Based Strategies for Service Delivery Department
It is necessary to pay more attention to health-related issues, pandemic-related aspects, and economic problems, or rather the methods the corporation utilizes to address them. It has been acknowledged that the ability of a company to align its values with the values and needs of the society (or target population) tends to determine the effectiveness of CSR activities (Porter and Kramer, 2006). McDonald’s has the necessary capabilities as the organizations’ highest priorities are cleanness, quality, and speed of service (McDonald’s, 2019a). These properties are now most valued in the society where sanitation requirements and social distancing are highly needed and appreciated (Rizou et al., 2020; Settembre, 2020). Hence, the fast-food chain should build on these values drawing people’s attention to safe food production, high-paced and high-quality service that minimizes social contacts and assists in obtaining affordable and comparatively healthy meals.
People will still attend public places and dine out as it is a part of modern people’s needs associated with basic needs and socialization. People do not only consume food in restaurants but spend time with their close ones. Hence, the service delivery unit should make sure that McDonald’s restaurants are safe and comfort places for such pastimes. The department should provide direct guidelines to franchisees who should pay even more attention to cleanness and safety. The use of advanced sanitation measures, development of safe zones (with the utilization of plastic shields between rows), improved ventilation systems are all possible ways to improve service delivery.
McDonald’s can become one of the leaders in the post-lockdown period and offer the value customers will appreciate. The dining habits of Americans have been transforming steadily, which requires certain changes in fast-food chains’ strategies (Haddon, 2020; Nicola et al., 2020). A certain portion of customers acknowledged the benefits of food delivery and is likely to resort to such services, even in their post-pandemic lives (Lucas, 2020; Settembre, 2020). Some people will minimize their visits to restaurants (even fast food chains) due to health concerns and financial issues (Haddon, 2020; Nicola et al., 2020). On the one hand, visiting public places will still be associated with a higher risk of being infected, which will divert customers. On the other hand, the most vulnerable groups will have to reduce their budgets, which will make them increase the consumption of home-cooked food.
McDonald’s drive-in options can become the basics of the new service delivery policy. The convenience of this service delivery has been acknowledged as people can eat their favorite food in their working places or even cars. Customers concerned with the need to visit a public place will feel safe and will be able to follow their daily routines (Haddon, 2020). The increase in drive-in points and improvement of order processing can be needed to address this customer need.
Online-Based Service Delivery
At the same time, food delivery based on online shopping has gained momentum, so McDonald’s should seize this opportunity using its online platforms. This strategy will be associated with considerable investment in big data management. Another option to consider can be the Internet of Things, which can start a new era of service delivery for McDonald’s. An increasing number of people start working from home, so they pay more attention to food delivery (Settembre, 2020). The company should offer its customers diverse options related to the use of their smart tools (smartphones and smart technologies in the homes). Regular deliveries to people’s doorsteps may become popular, so the development of the online platform as well as the staff to deliver food will be needed.
The changes in packaging will be beneficial as well and will address social and environmental spheres. Food delivery orders, as well as drive-in orders, are increasing as people often take food for several people (the entire family, or even office employees). Therefore, the company will reduce some packaging while still paying attention to individual packages. Large lunch boxes and beverage bottles may be used to deliver better service to customers. Clearly, these novelties should be accompanied by a campaign explaining these transformations with the focus on sanitation norms and environmental benefits as large boxes and new individual packaging will translate in the decreased use of materials.
The pandemic drew people’s attention to the role healthcare professionals play and can play in the development or even survival of communities. The hard work of healthcare practitioners became acknowledged and praised. A considerable number of people (including the franchisees of McDonald’s and the company itself) launched some campaigns to support those who were in the frontline during the most difficult stages of the pandemic (Weisholtz, 2020). Free meals to medical staff and donations to health-related organizations were rather common. These programs should be implemented even after the end of quarantine measures and the most intense period of the pandemic. McDonald’s should contribute to the development of communities through its assistance to the country’s healthcare system. Free delivery to healthcare organizations or significant discounts can be offered. The company can also offer special food delivery offers to cater for medical staff needs. The lockdown of the American economy was specifically painful for the hospitality industry, so the company’s involvement in addressing the associated health issue can be positively viewed by the public.
Food Quality and Menu
As mentioned above, McDonald’s has quite an inconsistent image characterized by their efforts to improve their menu making it healthier, but the organization remains a symbol of unhealthy eating (Blake, 2018). At the same time, the company articulates its commitment to making their meals healthier and making the world a better place for people (McDonald’s, 2019b). People’s growing concerns linked to the pandemic, as well as the persistent attention to environmental issues, as well as enhancing activism, make it clear that the development of an appropriate corporate image is essential for an organization.
Obviously, McDonald’s should continue working on the improvement of its food and making it healthier to contribute to addressing one of the most urgent public health issues, including but not confined to the prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. The company pays substantial attention to the nutritional attributes of its products. Nevertheless, the implemented efforts still seem insufficient, and McDonald’s meals are still seen as affordable but unhealthy (Blake, 2018). In order to become a true corporate citizen, the company should address this negative image.
The development of healthier recipes, the collaboration of nutritionists, the involvement of nutritional campaigns can help the corporation solve the problem. It is possible to improve the nutritional value of McDonald’s food by adding more vegetables and reducing the use of sugar and fat. The use of products that enhance people’s resistance to respiratory infections can make menus more diverse and more attractive to people concerned about their health and the situation related to COVID-19. The delivery of healthy products to vulnerable groups can be one of the possible projects to carry out. The company will be able to display its commitment to the development of American communities and the improvement of Americans’ wellbeing.
Helping Communities
Helping communities is one of the aspects of CSR efforts. McDonald’s highlights its projects aimed at helping communities grow, but these are mainly associated with the areas where components are produced (McDonald’s, 2019a). The company launches various projects to assist farmers and people involved in growing coffee. However, deeper involvement in the life of American communities should become one of the CSR priorities of the corporation. As mentioned above, Americans are facing considerable financial constraints, so the organization has to pay more attention to this area. When serving food to customers, it is possible to mention exact farmers or organizations delivering their products. The company’s staff can display some information about community-based producers in restaurants and at drive-in points, which will not require significant investment. These additions to the service delivery process may contribute to the development of a better attitude towards the fast-food chain.
McDonald’s claims that it provides valuable opportunities to the American youth providing employment, but these efforts receive certain negative characteristics. Dilday (2018) notes that the residents of inner cities are becoming less financially secure, and low wages offered by the fast food chain in question contribute to the growing dissatisfaction and marginalization of certain groups. People in many states are becoming more concerned with this trend and start articulating their dissatisfaction. For example, people in several states took part in several strikes demanding a higher wage for McDonald’s workers (Astor, 2019). Notably, political parties exploited that opportunity and contributed to the intensification (and publicizing) of the events. Therefore, the company’s CSR campaigns should be linked to these sentiments as well. The company should reconsider its rewarding systems and let people know about the improvements as well as their involvement in making Americans’ lives better. Dilday (2018) mentions that the corporation’s effort related to educational and employment opportunities were effective. The company should continue implementing such projects and making them well-known to the public.
CSR Analysis
Background
In order to define the major areas to focus on when using CSR strategies, it is necessary to consider the strengths and weaknesses of the concept. Corporate social responsibility has become an influential concept comparatively recently. The pioneer of the CSR research was Bowen (1953), who stressed that corporations had a substantial impact on societies, which made them responsible for shaping their decisions and operations to produce a positive effect in the social sphere. Almost a decade later, Davis (1960) introduced an important idea that companies’ social responsibility was a moral responsibility as well as an economically favorable approach for organizations.
In the 1990s, when such companies as Nike and Shell Oil found themselves involved in serious scandals, many organizations and the public started paying more attention to corporate’s impact on the social and environmental spheres (Porter and Kramer, 2006). Nike had to address the issues related to the allegations related to inappropriate working conditions of its employees, while Shell Oil had to develop effective solutions for their Brent Spar they had planned to sink in the Northern Sea (Porter and Kramer, 2006). After the 1990s, companies acknowledged the potential economic benefit related to CSR and started adopting this strategy, which led to further investigation and operationalization of the concept (Carroll, 2015). McDonald’s, as well as many other fast food chains, has also faced numerous attacks of activists accusing the businesses of the increasing pandemic of obesity and inappropriate waste management. Customers started being more attentive to the area of corporations’ input, which made organizations develop CSR plans and follow them in order to develop proper relationships with existing and potential customers.
CSR Strengths
It has been acknowledged that corporate social responsibility has a positive effect on companies’ performance. One of the most obvious and most mentioned benefits of CSR practices is the improvement of customer relations (Kumar, Boesso and Michelon, 2016; Wang and Sarkis, 2017). People have become more conscious regarding the origins of the products they consume and more willing to buy from corporate citizens rather than companies involved in scandals. The Nike scandal mentioned above led to a boycott that, in its turn, resulted in substantial losses for the company (Porter and Kramer, 2006). On the other hand, people are supportive of organizations that reveal their commitment to social and environmental responsibility, which is specifically meaningful during financial crises (Lins, Servaes and Tamayo, 2017). During turbulent economic times, companies high on CSR manage to increase sales, improve performance, and enhance their relations with investors. Hence, companies should pay sufficient attention to their CSR practices to ensure their proper performance and high levels of sales.
Another positive effect characterizing organizations’ CSR is related to cost reduction and efficiency. Companies concerned with their environmental footprint tend to use efficient energy resources and recycle waste, which translates into the reduction of costs in the medium- and long-term perspectives (Wang and Sarkis, 2017). In addition to the decrease in operational costs, companies adopting CSR practices manage to avoid environment-related issues (contamination, disasters) that are associated with considerable financial and reputational losses. The development of a positive image of a company in the modern world is impossible without being ecofriendly.
Businesses’ commitment to CSR also enhances organizations’ accountability and transparency with existing and potential investors, shareholders, and the media (Nofsinger, Sulaeman and Varma, 2019). Apart from the favorable image of a responsible actor, companies manage to access larger funds as investors are willing to invest in transparent enterprises that are associated with lower risks (Lins, Servaes and Tamayo, 2017). The media play an important role in the creation of a positive or negative image of a company, so transparency contributes to the development of a favorable public attitude (Albuquerque, Koskinen and Zhang, 2019). Companies also try to develop partnerships with businesses that use CSR practices in order to minimize risks. Therefore, it is clear that organizations’ commitment to CSR can improve companies’ performance and help in the creation and maintenance of a favorable image that translates into increased sales and appropriate investment.
CSR Weaknesses
At the same time, it has been acknowledged that researchers tend to concentrate on the positive aspects of CSR and corporate social performance, ignoring some weaknesses (Farrington et al., 2017). The challenges linked to the use of CSR strategies can have a serious negative impact on organizations and their development. Therefore, it is critical to take them into account when applying the principles of corporate social responsibility.
First, businesses have to invest considerable funds to remain committed to the CSR approach. Although this aspect is specifically critical for small and medium-sized companies, large multinationals should also consider this point (Kumar, Boesso and Michelon, 2016). When developing or participating in CSR projects, companies need to estimate the associated costs and outcomes to decide whether this involvement can be beneficial for the organization. This precision is crucial for many corporations in the period of financial constraints. In the post-pandemic world, these factors should be analyzed with special attention. It is noteworthy that this kind of analysis can be difficult to implement due to the lack of sound methodology that can be utilized to measure potential outcomes of CSR incentives (Kim, Kim and Kim, 2017). Companies’ top management has to decide whether to implement this or that project based on their knowledge, experience, and assumptions.
The role of the leader in organizations’ focus on CSR practices is closely linked to the negative aspects of the concept. As far as companies’ commitment to CSR, top managers are put in a difficult position as they are responsible for increasing profits (Maas, 2018). Shareholders expect executives to be effective and ensure a certain level of profit on a regular basis (Ali, Frynas and Mahmood, 2017). As mentioned above, the implementation of CSR projects tends to require significant investment, which results in the reduction of shareholders’ gains. Hence, leaders may be unwilling to participate in certain programs and remain committed to the CSR approach due to their fear of losing their job (Nofsinger, Sulaeman and Varma, 2019; Silvestri and Veltri, 2020). Leaders’ personal traits and experiences have an influence on their decisions as well.
Another weakness of CSR practice is associated with the concept of greenwashing. Some companies proclaim their commitment to environmental and social responsibility but do not engage in meaningful CSR projects (Wang and Sarkis, 2017). Such organizational behavior undermines the development of the CSR movement as people become less trustful and receptive regarding companies’ CSR efforts. Customers may lose their trust and change their attitudes to a company, which will lead to decreased sales and overall deterioration of performance. Greenwashing can also lead to lower performance due to the inconsistency of the corporate culture with the actual conduct of an organization. Employees committed to CSR practice may underperform when they learn about their companies’ greenwashing. Associated scandals also lead to reputational and financial losses.
Steps to Undertake
Based on the analysis of the internal and external factors affecting McDonald’s as well as the potential outcome of the use of CSR, it is possible to identify a number of areas to consider. First, the involvement of the fast food chain’s franchisees in charitable projects that encompassed the provision of free meals to first responders to COVID-19 can be seen as a beneficial initiative (Weisholtz, 2020). This kind of social engagement should be publicized, and the corporation can encourage others to follow and expand the boundaries of the incentive. It is possible to provide free meals to some vulnerable populations.
Such CSR projects will not require considerable investment but will be favorably accepted in the American society. The company will display its true commitment to CSR practices and will diminish the negative effects of the existing sentiments concerning the organization’s CSR projects in the inner city setting (Dilday, 2018). At present, people are becoming more concerned with the economic situation in the country due to major losses linked to quarantine measures. Hence, such CSR initiatives are likely to contribute to the development of a more favorable image of a true corporate citizen.
The fast food chain should also build on its core values and create projects associated with their commitment to quality, speed, and cleanness. During the pandemic that became a shock to many countries, being responsible in terms of certain sanitation and hygiene norms is a part of the CSR approach. Hospitality companies are facing serious challenges due to people’s health concerns (Haddon, 2020). McDonald’s can pay more attention to its delivery services and stress their safety and convenience. Keeping customers and employees safe is an illustration of the corporation’s commitment to CSR. The company’s service delivery department should also develop a new concept of customer experience. Making visits to restaurants safe and affordable, as well as meaningful, is another priority.
Finally, although environmental responsibility is associated with the allocation of larger funds, this area cannot be ignored even in the post-pandemic society. Americans reveal their deep concerns about climate change and people’s negative environmental input. McDonald’s publicizes its packaging policies, but it is also necessary to pay more attention to diverse innovations related to the use of resources. The maintenance of facilities, orders processing, and service delivery should be facilitated by innovative technology and strategies. The company should shed light on the utilized innovative methods to improve the environment.
Conclusion
On balance, it is necessary to note that McDonald’s has to address serious challenges related to the COVID-19 crisis. The hospitality industry is likely to undergo considerable changes, and the corporation under analysis should also transform accordingly. The major concept the service delivery department of the company can employ is corporate social responsibility. The focus on CSR approach and the organization’s involvement in the corresponding incentives that will be properly publicized can help McDonald’s to maintain its competitive advantage. Although CSR is associated with certain weaknesses such as substantial investment and inconsistent decision-making of top management, CSR is the most viable option for McDonald’s. The company should concentrate on social issues and the support of local communities. It is important to pay specific attention to healthcare professionals (as recognition and appraisal) and some of the most vulnerable groups of the American society (as acknowledgement and support). Environmental incentives also require appropriate coverage to make people aware of the efforts made and outcomes received. McDonald’s has had to react to negative publicity throughout its history, so it is time to ensure the development of a positive image of a corporate citizen who is committed to American values.
Reference List
Albuquerque, R., Koskinen, Y. and Zhang, C. (2019) ‘Corporate social responsibility and firm risk: theory and empirical evidence’, Management Science, 65(10), pp. 4451-4469.
Ali, W., Frynas, J. G. and Mahmood, Z. (2017) ‘Determinants of corporate social responsibility (CSR) disclosure in developed and developing countries: a literature review’, Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 24(4), pp. 273-294.
Astor, M. (2019) ‘2020 democrats join McDonald’s workers striking over wages and harassment’, The New York Times, Web.
Barney, J. and Clifford, P. G. (2010) What I didn’t learn in business school: how strategy works in the real world. Brighton, MA: Harvard Business Publishing.
Blake, I. (2018) ‘Burgers and fries at McDonald’s are now WORSE for your health than they were in 1989 – despite chain’s efforts to offer more healthy options’, Daily Mail, Web.
Bowen, H. R. (1953) Social responsibilities of the businessman. Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa Press.
Carroll, A. B. (2015) ‘Corporate social responsibility: The centerpiece of competing and complementary frameworks’, Organizational Dynamics, 44(2), pp. 87–96.
Davis, K. (1960) ‘Can business afford to ignore social responsibilities?’, California Management Review, 2(3), pp. 70–76.
Dilday, A. (2018) ‘“Your own McDonald’s!”: race, McDonald’s, and the inner cities’, The American Papers, (2017-2018), pp. 74-77.
Farrington, T., Curran, R., Gori, K., O’Gorman, K. D. and Queenan, C. J. (2017) ‘Corporate social responsibility: reviewed, rated, revised’, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 29(1), pp. 30-47.
Haddon, H. (2020) ‘McDonald’s sales fall as coronavirus pandemic changes dining habits’, The Wall Street Journal, Web.
Harvard Business Review. (2005) Strategy: create and implement the best strategy for your business. Brighton, MA: Harvard Business Publishing.
Kim, Y. S., Kim, Y. and Kim, H. D. (2017) ‘Corporate social responsibility and internal control effectiveness’, Asia-Pacific Journal of Financial Studies, 46(2), pp. 341-372.
Kumar, K., Boesso, G. and Michelon, G. (2016) ‘How do strengths and weaknesses in corporate social performance across different stakeholder domains affect company performance?’, Business Strategy and the Environment, 25(4), pp. 277-292.
Langert, B. (2019) The battle to do good: inside McDonald’s sustainability journey. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing.
Lins, K. V., Servaes, H. and Tamayo, A. (2017) ‘Social capital, trust, and firm performance: the value of corporate social responsibility during the financial crisis’, The Journal of Finance, 72(4), pp. 1785-1824.
Lucas, A. (2020) ‘DoorDash scores valuation of $16 billion as coronavirus pushes it to top of food-delivery chain’, CNBC, Web.
Maas, K. (2018) ‘Do corporate social performance targets in executive compensation contribute to corporate social performance?’, Journal of Business Ethics, 148(3), pp. 573-585.
McDonald’s. (2019a) History. Web.
McDonald’s. (2019b) Scale for good. Web.
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C., Agha, M. and Agha, R. (2020) ‘The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review’, International Journal of Surgery, 78, pp. 185-193.
Nofsinger, J. R., Sulaeman, J. and Varma, A. (2019) ‘Institutional investors and corporate social responsibility’, Journal of Corporate Finance, 58, pp. 700-725.
Porter, M. E. and Kramer, M. R. (2006) ‘Strategy & society: the link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility’, Harvard Business Review, (December), p. 1-16.
Rizou, M., Galanakis, I. M., Aldawoud, T. M. S. and Galanakis, C. M. (2020) ‘Safety of foods, food supply chain and environment within the COVID-19 pandemic’, Trends in Food Science & Technology, 102, pp. 293-299.
Settembre, J. (2020) ‘Fast food chains compete for coronavirus delivery spike’, FOX Business, Web.
Silvestri, A. and Veltri, S. (2020) ‘Exploring the relationships between corporate social responsibility, leadership, and sustainable entrepreneurship theories: A conceptual framework’, Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 27(2), pp. 585-594.
Taylor, K. (2020) ‘People are accusing fast-food giants like Wendy’s and McDonald’s of funding Trump’s reelection. Here’s what is really happening’, Business Insider, Web.
Wang, Z. and Sarkis, J. (2017) ‘Corporate social responsibility governance, outcomes, and financial performance’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 162, pp. 1607-1616.
Weisholtz, D. (2020) ‘McDonald’s giving out free meals to health care workers and first responders’, Today, Web.