Change encompasses one of the inevitable experiences for any organization that operates in the current dynamic globalized business environment. Thus, it is not a new phenomenon or even a simple fact. Indeed, organizations operate under the constant force of change, failure to which they may be rendered obsolete. This claim is true, especially for organizations that operate in a technological industry such as telecommunications, the internet, and the electronics industry such as the Apple and Google companies. While some organizations embrace change, others vehemently resist it. In this context, Mullins (2010) suggests that acceptance or resistance to change depends on the personality of individuals, but the management department can do nothing about resistance to change. This section debates against this point using the case of Apple Company to verify that managers have a responsibility of mitigating any resistance to change.
Although people can either resist or embrace change, it is possible to manage or lead them to ensure that they create organizational change. It is also achievable to influence and motivate people who oppose to embrace it. WIPRO video addresses the OCM (Organisational Change Management) concept as an effort by heads to ensure the achievement of the anticipated performance heights after the introduction of any change in the organizational operations. A possible way of achieving this goal encompasses encouraging employees to become innovative and creative. In this process, people embrace and initiate change without their knowledge that their contributions in the development of new products and services amount to organizational change. However, external agents may fail to embrace it as Mullins (2010) confirms, and hence the reason why the change curve in figure 3 captures a state of denial by the change agents.
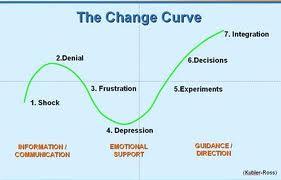
This observation suggests that the creation of an organizational culture that encourages creativity and innovation may help managers to implement change successfully. Apple and Google are good examples of companies, which have managed to build their competitive advantage around change that has been implemented through fostering employee innovation and creativity. Another example of an organization that has embarked on organizational change is the multinational company Wal-Mart. The company’s evident series of organizational changes have improved its performance in the section in which it operates.
Competitive advantage is gained when solutions are provided for operations challenges that are encountered by organizations. Such solutions often capture new opportunities for placing products and/or creating new ones with the chief aim of increasing both productivity and efficiency (Blanton 2009). While enacting and implementing strategies that produce various solutions, creativity and innovation are vital. The Apple Company is one of the businesses whose competitive advantage depends on the capacity to ensure that employees come up with new products as one of the ways of driving organizational change. The company appreciates the value of innovation and creativity in its future success. In this line of argument, Dalal (2011) reckons that Apple has come up with an inventive industrial unit that is capable of harnessing the company’s employee unbridled creativity. The unit provides room for a generation of new ideas while at the same time stimulating and/or making it possible to launch successful strategic decisions and profitable innovations.
Apple Company operates in the technological industry. This means there are lots of technological changes and influxes that result in the obsolescence of products. To counter this challenge, it focuses on creating new products that meet the new technological demands. For Apple to realize these concerns, it ‘leverages its diverse ecosystem of employees, customers, suppliers, partners, and global networks, proven innovation process, and a winning culture that does not accept second place – to seize the new opportunities in the marketplace and grow its business exponentially’ (Dalal 2011, Para. 4). Seizing new opportunities in the market demands an organization to keep at par with innovative and creative strategies that characterize the industry within which an organization operates.
When a technology change occurs, the Apple Company must also respond accordingly. It offers this response through effective leadership approaches during change. For instance, company management engages in ardent communication about the significance of adopting new production methodologies to enhance its survival. Even though employees may be resisting change akin to their personality traits as discussed by Mullins (2010), integrated communication ensures that they embrace it in a bid to protect their source of livelihood. Although the resistance to change is undesirable, the Apple Company also benefits from it as it leads to constructive organizational conflicts in the form of different ideas on how to handle the emerging challenges. Such conflicts lead to the establishment of optimal decisions and strategies for countering competitive forces.
Future leaders and managers may embrace organizational change as a factor to improve productivity and performance. Constant rebranding may be associated with improved performance due to upgrading in sales. My future role as a leader will also involve engaging in organizational change for better results at the stations that I plan to work in.
References
Blanton, G 2009, Creativity, Innovation and Quality, McGraw Hill, New York, NY.
Dalal, S 2011, Apple’s Innovation Strategy – Learn How Apple Innovates, Web.
Mullins, J 2010, Management and Organisational Behaviour, Pearson Higher Education, Harlow.
WIPRO 2012, Organisational Change Management, video recording, Video Education Australasia, Bendigo, VIC, Web.