Introduction
The main objective of this dissertation is to discuss the impact of global financial crisis on the strategy and HRM of multinational companies.
Background of the problem
According to the report of Krolicki & Bailey (2008), largest automaker GM’s quarterly loss was $4.2 billion and shares tumbled 13% whereas Ford posted more than $2.98 billion quarterly operating loss. In this article, Reuters (2011) reported that GM experienced unexpected losses in recession and this company required rescue package from the US government, but this company failed to recover its financial position. Somerville (2011) pointed out that GM faced huge losses in the North American market though according to the annual report 2010, GM’s present market situation in this zone is outstanding in terms of market share and volume of sales. Here, it is important to mention that most of the automakers like Toyota and Honda changed their strategies and gained their market position in the recession, but GM failed to overcome due to having problem in internal management and strategic decision-making process. For instance, from 1990 to 2008, the US market share of GM fell by 35.5% to 18.8% while Toyota and Honda’s market share climbed by 18.3% to 26.2% in this zone and this market trend was one of the most important external factors to face the worst position in global financial crisis. In this context, this dissertation will identify the effect of recession on the company and other severe strategic dilemmas of GM to recommend the company to save their position.
Justification of the research
Many professional writers and academic researchers have suggested different type of strategy formulation, design, and implementation process for the multinational companies to regain their market position in adverse economic condition, but these strategies need a long-time and financial involvement to observe success or failure; therefore, these companies need to take immediate actions. At the same time, they pointed out that different companies have faced different types of problems and required different solutions, but most of the management professionals were puzzled regarding the questions how reproduction strategy or a particular plan can resolve any business crisis while the companies seemed bailout or loan can solve their recessionary problem. In order to mitigate this research gap, this paper will analyze the case of GM along with other multinationals to find out some common factors of success.
Research question and objectives
Many large companies have redesigned their strategies to save the company from adverse effect of economic downturn; for instance, BA signed an agreement with two companies to buy sustainable jet fuel and establish a plant to produce 16.0 million gallons green jet fuel by processing and converting 500,000.0 tonnes of waste. At the same time, Tyco International adopted divestiture strategy, Ford Motor changed leadership strategy, Apple developed new product line, and Ryanair reduced operating costs, and so on.
In 2009, GM’s sales revenue reduced 30% than the previous year’s revenue. This company had fired international white- collar payroll from 73000 to 63000 with downsizing of 3400 US employees. It would not sustain for long without a bailout from the US government. Therefore, this paper would analyze the case of GM to analyze the topic. In order to reach the research objectives the researcher has designed following research questions
- What are the roots and origins of the global economic downturn;
- What is the microeconomic and macroeconomic impact of global recession on the multinationals companies?
- How do multinationals response in the crisis to save the company from this economic disaster;
- How General Motors has responded to the effects of the US recession and gain desired economic growth?
Scope of the study
This dissertation mainly observes the position of multinationals in adverse business environment and investigates whether the simulation of strategy could contribute to overcome recession or not. However, this dissertation topic has many potential issues to curry out research such as –
- The researcher of this dissertation has the opportunity to use available secondary data sources for resourceful information like internet resources, news, journal articles, and books;
- This dissertation has scope to research on the overall business structure, strategies and human resource plan of the multinational companies;
- However, this study has also scope to give the theoretical framework in relation with practical condition;
- It has scope to provide an effective strategic and human resource plan to overcome from global economic downturn.
Literature Review
Roots of Global financial crisis
Lapavitsas (2009) identified the roots of global financial crisis that has instigated from the US macroeconomic failure and spread out all over the world, which gradually grounded from the stock market and housing bubble, unpredictable involvement of the commercial bank in the property market that generated credit crash for which unfastened monetary policy of the US central bank is liable. The household dynamics of the US society has failed to generate individual savings out of their disposable income, which were around ten percent in eighties, but gradually decreased at 0.4% in 2006 and it tends to zero. During the credit crash in September 2008, personal savings explored in negative figure and demonstrated the unpredictable crisis of capitalist economy.

Under the US market economy, the monetary policy has failed to respond in right direction during the stock market bubble in the fiscal year 1999-2000, the central bank antagonistically to cut the interest rates with the aim to pump up the housing bubble during 2001 to 2006 and generated domestic macroeconomic imbalances linking with global unevenness. The housing bubble escorted mass people to jump over there and imposed extra burden of housing liabilities, and due to lack of personal savings, people failed to encounter with the crisis and drove to recession. In September 2008, the collapse of Lehman Brothers has noticed rest of the world to what extent the US economy is imbalanced and how the global financial system is an unavoidable part of the US economy (Mohan 2009).
Mohan (2009) pointed out that the spread out of global financial crisis and it escalating nature has denoted the emergence for both academia scholars and policymakers to rethinking about the role of central banks as well as financial regulatory systems by identifying the roots and causes of the crisis. Following the bankrupt of Lehman Brothers, huge number of European and US Banks come in to light their credit crush by proving the failure of the prevailing monetary policy along with financial regulatory mechanisms, the substantially of free market economy has no longer prospect to resolute the crisis.
Krugman (2011) pointed out that the Keynesian prescription worked well to overcome the great depression in thirties, but has failed to address concurrent global financial crisis through the government bail out, pumping money through increasing governmental spending is just a temporary solution to gear up purchase power and market demand. It is the most prevalent weakness of the Keynesian economists and capitalist overview that output may be demand-constrained, spending obliged to be equal to the income, supply would generate its own demand, where necessary savings would be auto generated and robotically invested. The malpractice of monetary and fiscal tools by the Federal Reserve Bank is thus another cause of global financial crisis and the concurrent “Occupy Wall Street” movement has spread out from US to all-overs the world demanding redistribution of wealth and complaining against the governments that the State is busy to safeguard 1% corporate owners rather than 99% hunger people. All the governmental initiatives to encounter the crisis with bail out have failed to keep any contribution to create any job opportunities and the activists of Occupy Wall Street” movement indicates to the political solution for the crisis.
Recessionary Impact on HRM of MNCs
Vösa (2010) addressed that four crucial areas of human resource management (HRM)1 of multinational companies (MNCs) are highly affected through global economic downturn. Furthermore, clearly global recession has severe impact on domestic or international labour market of a country along with on HRM functions. A widespread threat for global nations as well as respective MNCs is elevating unemployment number where common circumstances involved with gradual slender of major HRM functions. Dramatic change in labour market is now require to adjust with rather competitive labour and business market though if an individual enrich of stronger professional skills2. Alternatively, Viljanen & Lähteenmäkia (2009) addressed that, entire atmosphere of an organisation experienced poor performance and loss of greater volume of financial resources, but best measure of recessionary impact is significant reduction of human capital where widespread practice of company’s economic functions and human consequences are extensively absent. Additionally, common phenomenon of transparent cost saving tendency of crisis stricken organisations downsize through reducing number of employees as a result, proper employment of employee talent and skills has faced rather tough circumstance than ever. Conversely, transparent cost saving approach is required persistence of employee benefits ahead of termination in order to craft competitive advantages in time of recession. Regarding this view it can also reveal that social contracts is another crucial facts of HRM that required extra concern in assessing recessionary impact on HRM of MNCs. After effects is another cause of recessionary impacts on HRM that transmit stern distress as well as resentment in the middle of the survivors and conversely increase workload with wider responsibilities among job holders. Thus, recessionary impact on HRM generate survivor syndrome closely relate with stress and illness that drastically affect on employees productivity as well as workplace manner3. For more clarification, following is the comparison table of HRM practice before recessionary period and during recessionary period.
Table 2: Comparison Table of HRM Practice of MNCs before Recession and during recession (Source: Self Generated)
Response of the MNCs
In defining response of MNCs during recessionary period, Bakar et al. (2011) stated that, successful business firms during financial crisis required responding towards significant environmental changes by adjusting entire organizational outlook as well as fundamentals. Key objective of recessionary responses is principally termed as the SSVs4 where motto of the environmental changes obligatorily needed to deal with little to do more. This part of the paper, hypothetically illustrate survival strategies of automobile companies during recessionary period where SSVs outlined through Porter’s generic strategies as an expert of dealing with environmental uncertainties. Alternatively, Michell (2010) pointed out that, strategically, MNCs response during recessionary period should to emphasis on three forces namely, financial risk, business risk, and management risk as following figure.
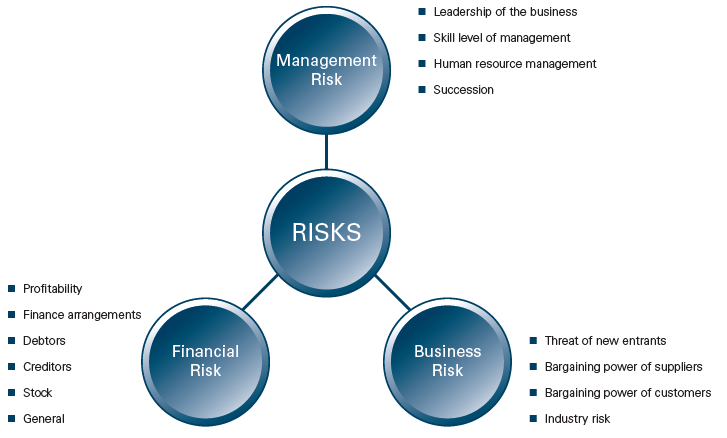
In brief, SSVs of automobile industries attached with managerial functions, market penetration, product and service quality improvement as well as product and service development. Regarding these States, companies in emergent to keep attach with faster innovation that would proficient to tackle strongest rivals along with external environmental forces. Concerning these attributes, porter’s generic strategies assembled through three dynamics namely, i) cost leadership, ii) product differentiation and iii) focus as plotted in following figure.
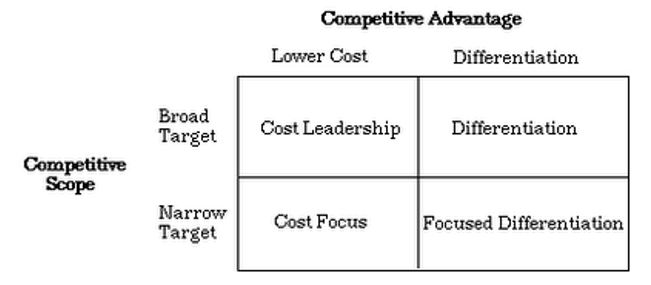
In execution of aforesaid strategic phases, MNCs should be kept in mind that every strategy has involved with respective risk factors. Moreover, SSVs have an essential attachment with market share, internal dynamics like strengthens and weaknesses, financial position like liquidation, scope of investment and lifecycle stage. Conversely, limitations of porter’s SSVs criticized through two ways namely, a) key achievement from the SSVs and b) key facts of the entire process. Furthermore, these two criticisms have developed through considering four keys generic perspective specifically – i) classical, ii) evolutionary, iii) procedural, and iv) systematic. Ignoring all of limitations following is the table of key strategic dynamics of recessionary responses of MNCS in brief.
Table 3: Keys Strategic Dynamics of MNCS during Recession. Source: Self Generated
Restructuring Strategy of different companies
Nanto (2009) pointed out that the global financial crisis has thrown the world economy to the bottom line global recession that has been causing extensive business reduction, unexpectedly increasing job cut, reducing spending for corporate social responsibilities, and decreasing government revenues. Governmental initiatives to pumping money in the market with bailout bill have failed due to non-cooperation of the corporations and extremely higher pay for the executives rather than employees job protection. The corporations have gained bailout package, but up-to-date data recognise that the large companies may have touched the bottom line and are eager to restructuring strategy to recover with conservative manner without taking any further risk and for the most parts job cuts are still ongoing process. Most of the corporations are still facing enormous troubles to initiate their restructuring strategy though the recovery and reinvestment plan of all affected counties have supported to back them browning from the IMF5 by the national governments and announced different economic incentive packages.
Nanto (2009) also added as the global financial crisis has not kept its impact limited to the US mortgage market, but explored serious impact all over the world, proves the fundamental lacking of international financial systems and established the burden sharing interconnection and interdependency of the modern economies due to troublesome policy features. The restructuring strategy to deal with the crisis by the big corporations throughout the world has been evident in few basic phases, where at the top they are straggling to bring back confidence upon the system with amazing measures both in pubic and private sector by analysing risk and scopes reach. Moreover, the corporations are looking forward to the emerging countries where social safety net has enough addressed to encounter with the recessionary and shift capital to those prospective markets. At the same time, they are emphasising to strengthen international financial system that would be enough capable to cope with the socio political impact of the crisis by changing regulatory measures.
Restructuring Strategy of GM
ICIS news (2009) reported that the US automobile giant GM has filed for bankruptcy protection under Companies Act 2006, Chapter 11 as an integral part of restructuring plan backed by the government while the restricting plan aimed to providing another opportunity to sustain the company from the sock of global financial crisis. The bankruptcy filing of GM Motors has pointed as the third largest bankruptcy after Lehman Brothers and WorldCom and urged for immediate recovery with restructuring strategy. To implement the restricting plan, at first, the government has provided US$ 20 billion and the pumped another US$ 30 billion on condition that 60% stake of the reengineered GM would be owned by the state. It was also mentioned that UAWU6 would purchase 17.5% in shares, while Canadian government would provide lend US$ 9.5 billion in exchange for 12% stake and kept US$ 1.5 billion for debt return, infect such rescue plan for General Motors evidenced the continuous governmental support automobile industry. Under the restructuring strategy, GM has taken rigorous action plan to shut down six production units and three service centres in 2009, further additional seven in 2010 and all other unprofitable units in 2011, while each of the closing caused huge job cut.
Reuters (2009) reported that the restructuring strategy placed by GM to the U.S. Treasury Department, has argued that the automobile giant GM is eager get US$ 30 billion of taxpayer endowment to ensure sustainable recovery together with US$ 7.5 billion general credit line from the government simultaneously, while the company’s sales revenue gravely drooped due to recessionary economy. General Motors (2009) presented its large volume of restructuring strategy to the government for, here the key factors of the plan has pointed as follows
- Brands and Manufacturing Plants Restructuring Strategy: GM has aimed to emphasis only on few of its famous and renowned brands globally rather than pointing to huge number of brands, for instance Chevrolet, Cadillac, and Buick, while the company also urged to sale out few brands like Saturn and cut out number of manufacturing plant at 33 by 2012;
- Cost Reduction and Job Cut Strategy: GM has set up its target to reduce its costs by cutting jobs in the US market and evidenced to cut 47,000 jobs in 2009 which would be 92,000 by 2012;
- Dealers Reduction Strategy: For better outcomes, GM would restructure its dealership network by reducing number of dealers in the small markets and it would be at least 25% lower than the normal by 2012;
- Labour Costs Restructuring Strategy: The most dilemmas that GM encounters with the US market is higher labour cost, next to global financial crisis GM urged to the United Auto Workers Union to finding the right way to make the labour cost competitive and still GM is keeping its continuous efforts to come in an agreement with the Labour organisations;
- Bonds United Restructuring Strategy: The restructuring strategy of GM has aimed to put away of US $1 billion per annum cost of capital measured as interest and would like to covert seventy-five percent of its huge and risky public debt to equity from US$ 28 billion to US $9 billion with triumphant bond exchange, while the filing of bankruptcy would protect the company from immediate liquidation;
- Technological Lending Strategy: GM keeps its effort to get a sophisticated technological loan for US$ 7.7 billion from the U.S. Energy Department that would enhance the company to improve energy efficiency for further production and GM would produce fuel efficient cars from 2009 to 2012;
- GM has large plants and properties globally, and it has planned to sell out to emphasis on the economically viable projects; for instance, AC Delco in France has liquidated for US$ 1.5 billion in 2009,
- Overseas Governmental Aid: GM stated its negotiation with foreign governments and hopeful to raise fund of US $6 billion as assistance and all these efforts aimed to raise GM’s net present value from US$ 5 billion to US$ 14 billion by 2014;
- Risk Mitigation Strategy: The cost of GM of bankruptcy would cost US$ 100 billion, which is so risky, costly, and time-consuming, thus the restructuring is the only way for high- risk mitigation, government already contributed US$ 13.4 billions of taxpayer’s money to GM, and it is not requesting further US$ 16.6 billion in 2011.
Research Methodology
Research Approach
The researcher of this dissertation would follow case study approach of Robert Yin in order to organise the paper because this method is perfect while in-depth assessment is essential about a precise issue. However, Yin’s approach gives the opportunity to the researcher to apply own discretion to formulate the paper. As secondary sources are more authentic, resourceful and easy to collect within shot period, this paper would be based on secondary data sources such as books, journal articles, and so on.
Justification for Case Study Approach
- Robert Yin’s case study approach would help the researcher co-ordinate the understanding with strategic theories while findings and results chapter focuses on the position of GM in view of both hypothetical and realistic perception (Yin, 2003);
- Case study of GM and the multinational companies of different industry would support the researcher to progress future investigations in this topic;
- Additionally, case study approach is useful here because this study about the impact of strategic decision-making process of Multinationals and GM would consider many factors including external and internal environment
Secondary data sources
According to the view of Cohen, Manion & Morrison (2007), books and journals are always useful source materials for research as these sources contain the accumulated wisdom along with latest progressive ideas. On the other hand, Sekaran (2006, p.59-60) and Malhotra (2009, p.108) pointed out that secondary data has already existed and organized data while Zikmund (2006, p.73) argued that secondary data sources are more reliable because publishers, academia, and famous scholars have already acknowledged these papers and supported the view of the previous researchers in most of the cases. However, the researcher of present management project would consider scholarly journals, management books, annual report 2010 of General Motors, annual report 2010 of British Airways, annual report 2010 of Tesco, Financial statement 2008 of GM, and so on. In order to upgrade the quality of the paper, this study would also use reports of Reuters, statistical bulletin, case studies on global financial crisis, e-journals, e-books, and conference papers etc.
Primary research
Renowned research-methodology book writer Saunders, et al (2006), and Cohen, et al (2007) pointed out that primary data focuses on the specific research problems though it is time-consuming and costly process. However, this dissertation would not use this type of data because it needs to cover strategic responses of the multinational companies due to save the company from recession and it is not possible to collect data from the management of different companies to know their strategic viewpoint.
Data Collection Process
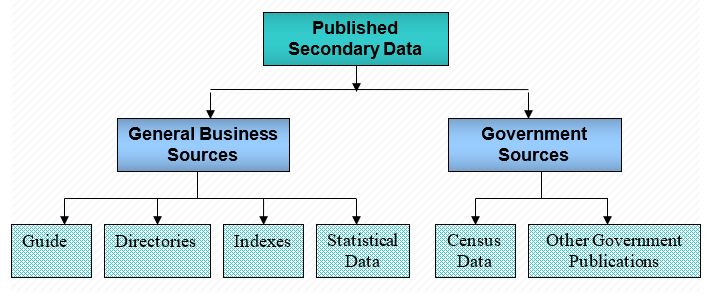
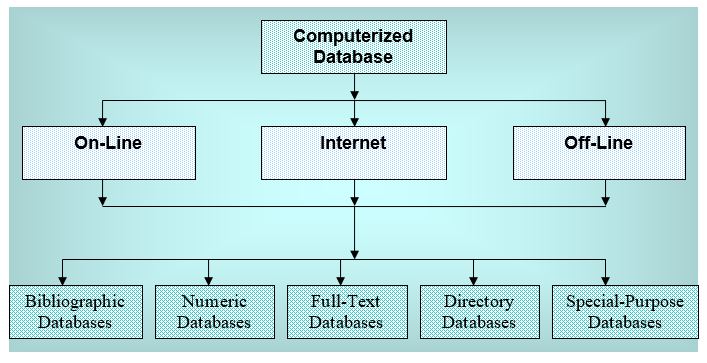
In addition, the researcher would concentrate on the internet databases besides published data as this is a simple and less expensive method of data collection; however, the following figures show classification of published secondary sources and categorization of computerized databases
Limitation of Data Collection
As the dissertation based on Robert Yin’s case study approach, the researcher has faced few challenges to organise the paper with proper information. However, these problems are
- The word limit of this dissertation is limited to cover all aspects related with topic and it was not possible to consider primary data due to word boundary;
- In addition, the topic demands case study approach, which influences the researcher to consider only secondary data sources;
- On the other hand, this project needs to focus more on the descriptive research approach instead of quantitative or qualitative research approach. As a result, the researcher of this dissertation depends on the previous research paper, which is also a difficult task as there are many available secondary resources on global financial crisis and strategic responds of the multinationals, but not all journal articles or books were relevant. Thus, find out appropriate secondary data is one of the most important factors;
- Finally, short deadline for the completion of the dissertation was another problem to the researcher.
Findings and Results
Recessionary Impact and Financial Analysis of GM
In the light of General Motors (2010), financial position of domestic and international subsidiaries of General Motors affected drastically due to high credit score and poor liquidity position. In brief, at then of 2009, aggregate sales and revenue fall down by 30.60% or valued USD $10.60 billion where wholesale volumes of international market specifically in the UK declined by 26.70% or amounted 99,000, in Russia by 70.20 %, Italy 16.80 % and in domestic market by 94.40% but surprisingly in Germany increased by 23.40% or 65,000 automobiles. Here, point should quote that, all of wholesales program operated through Federal Government’s subsidiary. Alternatively, due to bankruptcy filing poor financial position reflects through severe unemployment rate, unfavourable foreign currency conversion and increase of price of raw materials reduce productivity. For this reason, automobile pricing affected by USD $1.30 billion and aggregate revenue declined by USD $0.80 billion.
Table 4: Financial Overview 2008 to 2010 of GM Corporation. Source: Self generated from Yahoo Finance (2011)
Major Challenges of GM
According to GM) (2010), at early of recessionary period GM’s market position was declining in North America in terms of reducing volume of market share by decreasing net sales value of 34.30 % or in terms of amount USD $29.60 billion. Secondly, reduction of revenue by USD $36.70 billion, significant reduction of wholesale volumes by USD $4.80 billion and considering high credit score, GM opened a bankruptcy file in November 2008. Thus, most challenging issue for GM was to restructuring their business operation by reducing cost as well as additional capacity. Moreover, inheritance labour costs along with official obligations of deanship networking make rather poor GM’s competitiveness than newly entrance into a market due to high credit score. On another hand, cost reduction initiatives of GM through transaction of capital markets along with selling assets incurred greater amount of loss that results high liquidity crisis. Considering these issues GM challenges during recessionary period experienced deplorable turmoil in the mortgage markets that harshly affected operating performances, financial factors, and liquidity position. In brief, following are the challenging issues of GM during recession.
Reduction of Credit Score: according to UST Loan Agreement7, settlement of credit score by repaying entire loans, interests as well as expenses and in addition, refund of all Federal Government financial support.
Acceptance of Federal Fuel Efficiency Deed: for the segment of advance technology vehicles like hybrid cars, GM was under pressure to compliance with the deed of US Federal Government fuel efficiency as well as emission requirements for domestic market operations.
Reposition of Financial Status: improvement of financial positions by achieving positive net present value (NPV) as well as assessing activity based costs of entire projects to ease of calculation future projected costs.
Rationalise Costs, Capital and Operating Capacity: in order to restructure factory workforce, respective suppliers as well as dealers for a competitive product mix along with cost strategies.
Reduction of Debt: reducing two third of unsecured public debts into equity through conversion.
Modifications of Human Resources: modifications of available human resources by satisfactory compensation where termination, laid off would available with a competitive manner.
Modifications of VEBA8: another modes of employee benefits that obligatorily consistent with UAW9 Settlement Deed of 2008 to satisfy retiree healthcare obligations and source of GM payment should from of their common stock.
Environmental Analysis of GM
To illustrating environmental analysis of General Motors during recessionary period, this part of the paper assembled SWOT analysis and PEST analysis to discover internal, external and macro environmental position of the company.
SWOT Analysis
Bergh et al. (2009) pointed out that, significance of SWOT analysis learn both internal and external environmental circumstances where strengths and weaknesses exhibit companies internal atmosphere and conversely, opportunities and threats involved with external atmosphere. For more details following is brief outlook of General Motor’s SWOT analysis.
Strengths
GM dealerships have strong demand in both domestic market and international regions that quantifies more than 21,000. In the Asia Pacific as well as in Latin America’s business growth has evolved gradually. Since pre recessionary period, cost and quality improvements have held 25.0 % through outsourcing. Strong value pricing policy elimination execute by means of regular incentive programs. Spent almost USD $8.10 billion for research and development program in are of radial product engineering and manufacturing engineering. Recently, GM accomplished highest annual productivity among close industry rivals and in addition, electronic stability control, fresh leadership, fresh strategic atmosphere, and fresh financial opportunities. Get involved in new joint venture with China. For international sourcing process, GM decision-making group operated through nuclear budget. In order to lead educated global entrances continue strategic alliance with fellow rivals10. GM seizes highest market shares in terms of volume of US market and high concern on environmental policy.
Weaknesses
Word of mouth spread by print and electronic media, down sales of existing market share though GM has highest volume of US market, high pension debt, and high resale value due to public and private usage. Moreover, depressing perceived value due to high incentive program, elevated healthcare costs reduce benefits for retirees, ageing workforce, gradually poor financial performances, down quality of overseas production, price concession results supply chain bankruptcy, poor pricing strategies, and bureaucratic culture.
Threats
Elevated raw material and transportation costs, gradually decline of light vehicles demand, declining support of UAW11 and devaluation of currency influence high export cost. Conversely, high-perceived values of close rivals of GM are generating better product quality that would foster domestic and international competition, customer lawsuits, lack of official intellectual property rights in Chinese market, fleets elimination because of global warming and risks of joint ventures in domestic market.
Opportunities
Due to elevated demand for renewable energy resources GM has string prospect to produce additional 4.50 million unites vehicles by 2013 and in addition, accomplishment of amazing technological success. Secondly, expertise on GMNA12 chain would deliver utilisation of one design globally thus; fresh engineering would be able to convey low cost, high quality and shorter life cycle products and services. Third, global expansion keeps strong potentiality of entering into emerging markets. Finally, more strategic alliances by integrating new technologies13 and would craft almost USD $2.90 billion by translating foreign currency.
PEST Analysis
According to the Hong Kong Times (2011) following is the details of GM’s PEST analysis.
Political: politically, emerging markets are more interest in hybrid technology and being a successful hybrid car manufacturer, GM is another strong threat for international rivals in the international automobile industry.
Economical: from early of global recession like other economic ingredients, oil market is also turmoil due to high price and gradually deplete of oil sources. Regarding this issue, in the international market GM has greater prospect of producing hybrids technology cars rather than petrol cars and increase market share as well.
Socio–Cultural: compare to petrol cars, hybrid and electric automobiles have not yet satisfy consumer demands in terms of mileage and performance. For this reason, in order to satisfy retain and potential consumers, GM has obligatorily required to pay more attention on product features and branding and thus GM would transmit probable flow of urbanisation globally.
Technology: due to dwindle of sources natural energy resources, currently global automobile industry move towards renewable energy sources like, hybrid technology, electricity, nuclear technology. In this global financial crisis, technologically GM is in crisis of low demand for petrol cars and high demand for hybrid technology cars.
Human Resource Management of GM
UNCTAD (2009) and Trumbull (2009) reported that, human resource management of GM is a means of enjoying competitive advantages as a leading automobile maker in the USA. The grant of bailout during 2008 by the US Government to provide rescue opportunity from recessionary damages, GM was in emergent to restructure itself under bankruptcy code of Chapter 11 s.363. Concerning this fact, GM restructuring involved to cut cost as well as capital spending and conversely, bulk funds by selling assets. As a result, significant changes took place in the areas of GM HRM as well as HR strategies. For more details, GM announced to close temporarily one of its subsidiaries Daewoo in Korea during December 2008. Moreover, in same time, another announcement of GM revealed that their newly started production factory in Argentina cut jobs though experienced record production since September 2008. Conversely, from December 2008–January 2009 factories in Thailand close down their production plant along with vast job cut in the Gliwice plant of Poland. Opel another subsidiary in Germany was in severe crisis that results significant job cut in Europe and additionally, large amount of public support to recover. In an aggregate form, after filing bankruptcy, GM experienced approximately 20,000-job cuts and thus not only GM HRM, but also US national automobile jobs anguish by one million jobs. Conversely, Trax (2008) illustrated that other than job cuts GM has also suffered from managing employee benefits like medical benefits, health insurance, retire allowances. For instance, according to 401 (k), GM failed to cover health insurances as well as tuition reimbursement. More specifically, employer contribution of GM decreased by 63.30% where as it was only 20.0% in prior five years and employee remuneration package devalued by 5.50% with 50.0–74.9 % low employee contribution and 25.0% low health insurance coverage.
Key initiatives for sustainable development
For attaining sustainable development, GM has planned to reconstruct its business model as shown in the figure below:
Kahl (2009) pointed out that by filing bankruptcy under chapter -11, the US operation of General Motors rescued from liquidation and identified as New GM and the leadership of New GM has expected to come out from the ruins of old GM and operates both in home and abroad except Europe, while the corporate structure has restructured as follows –
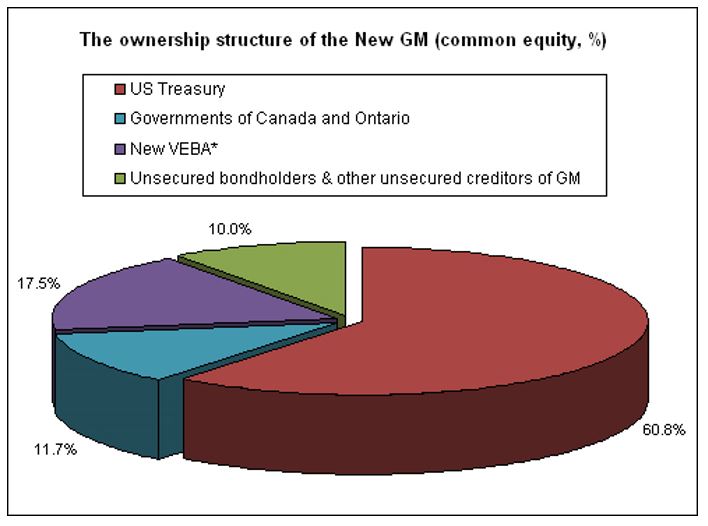
In the figure, it has demonstrated that the Old GM would only possess 10% of the common stocks while as the major contributor the US Department of Treasury has independently gained 60.8 %, new ‘Voluntary Employee Beneficiary Association’ (VEBA) possesses 17.5 % for medical benefits, and the governments of Canada and Ontario: 11.7 % as reported by the new management. It has also directed that the new GM would not go for pubic trade until it would demonstrate accountability, profitability, transparency in the practice of reporting system to bring back public confidence, although there is target to pay back governmental loans by 2015 and going for public trade is the tool to finance the loans.
Conclusion
Recommendations
- GM should hit the market by restructuring their pricing strategy as Japanese car manufacturing companies developed their brand image in global market by using effective pricing strategy;
- At the same time, global automobile industry is becoming more competitive within short time in terms of features of the product line, innovative and technological adoption, dependability, safety, price structure, fuel expenditure, environmental friendly products, investment, CRM projects, and so on. In this circumstance, the management of GM needs to be more responsive in meeting above requirements in order to regain its market leading position in the US market and capture large share of and international market;
- As competition among automobile industry is too high, GM should focus on its fundamental service delivery to restore its competitive advantage;
- As GM’s sales have been lowered by 30% in 2009 than previous year, the company should reduce annual operating costs; however, top-level management of GM decided to fire 3800 employees in order to overcome the recessionary impact by decreasing operating costs. This dissertation recommends the management of GM that job-cut is the process of cost reduction, but it should not follow this strategy because this strategy could reduce the confidence of the employees and adversely affect the production system and entire supply- chain management system. As a result, GM should restructure its human resource management plan, for instance, it should recruit efficient employees from Asian market as they are more skilled, but they satisfied with low pay and they become more efficient after getting short training;
- To increase sales profit in this recessionary period, GM should introduce few low cost model that means it should emphasis on the new product development in new market or existing market to attract the customer of both develop and developing countries, for instance, Tata Nano is a popular brand to the middle class people in the recessionary period;
- The management of GM and other companies need to be more alert to avoid internal conflicts and ethical dilemmas by developing and maintaining appropriate co-ordination within its global distribution channel as lack of proper monitoring and controlling system the operating costs and other non- monetary costs of the companies can increase significantly.
- Development of CRM system is an effective strategy to increase loyal customer base, therefore, GM should take technological advantages and check the CRM strategies of the competitors as Volkswagen and Ford have already integrated CRM tools to increase sales revenue and provide prompt reply to the customers regarding after sales service.
- The company should decrease annual budget for promotional activities and use multimedia marketing strategies to increase brand image to the customers;
- At the same time, the marketer of Gm should increase the annual budget for research works in order to identify potential risks and give suggestion to minimise these risks;
- However, the company should follow divestiture strategy and focus more on core business, for instance, it can reduce the production of few luxurious brands and can focus more on profitable segments;
- It should introduce low cost eco-friendly products to sustain as a market leader in the US market since Toyota generates huge profits from eco-friendly Toyota Prius brand;
- GM should offer safe and comfortable products to customers;
- It must follow the recommendation of directors and independent non-executive directors to avoid further loss;
- GM should adopt joint venture strategy in order to enter new market because it should minimal start-up costs in enter in this way whereas in case of acquisition, it requires a large financial investment for the initial purchase along with infrastructure development costs.
Conclusion
The Global financial crisis has explored the underlying catastrophe of the king of global automaker GM, after more than a century’s muscular operation it has turned into bankrupt in 2009, which is the third largest corporate failure or scandal in the USA after WorldCom and Lehman Brothers. Through governmental interference, bailout, and other financing it has get a chance for fresh start a new GM and have started operation in the USA and overseas excluding Europe, the new GM would be more caring to minimise the risk of any further failure. This paper has analyzed and identified some issues and factors those would be helpful for new GM to sustain in the concurrent recessionary economy and in the emerging market.
References
Bakar, A. H. A. et al. (2011) Survival Strategies of Construction Companies in Malaysia during Two Periods of Recession. International Journal of Academic Research, 3(4). Web.
Bergh, K. et al. (2009) General Motors Corporation Case One – Internal Analysis. Web.
Cohen, L., Manion, L. & Morrison, K. (2007) Research Methods in Education. 6th ed. New York: Routledge.
General Motors (2009) Restructuring Plan 2009 – 2014. Web.
General Motors (2010) General Motors Company 2010 Annual Report. Web.
ICIS news (2009) GM files for bankruptcy, details restructuring. Web.
Kahl, M. (2009) The New GM – A First Look. Web.
Krolicki, K. & Bailey, D. (2008) (Reuters) – GM, Ford losses worse than expected, burning cash. Web.
Krugman, P. (2011) Mr. Keynes, and the Moderns. Web.
Lapavitsas, C. (2009) The Roots of the Global Financial Crisis. Web.
Malhotra, N. K. (2009) Marketing Research- An Applied Orientation. 5th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Michell, S. et al. (2010) Managing your firm through the global financial crisis”, Volume 1. Web.
Mohan, R. (2009) Global financial crisis – causes, impact, policy responses and lessons. Web.
Nanto, D. K. (2009) The Global Financial Crisis: Analysis and Policy Implications. Web.
Reuters (2009) FACTBOX: Highlights of GM’s restructuring plan. Web.
Reuters (2011) Treasury to be “patient” with GM stake. Web.
Saunders, M., Thornhill, A. & Lewis., P. (2006) Research Methods for Business Students. 4th ed. London: FT Prentice Hall.
Sekaran, U. (2006) Research Method for Business. 4th ed. London: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Somerville, G. (2011) Treasury to be “patient” with GM stake. Web.
The Hong Kong Times (2011) PEST Analysis. Web.
Trax (2008) Cuts at General Motors Bring Benefit Trends to the Forefront. Web.
Trumbull, M. (2009) GM bankruptcy: How will it impact the US? The automaker got key concessions from bondholders this weekend to help smooth bankruptcy proceedings, which are expected to begin Monday. Web.
UNCTAD (2009) Assessing the impact of the current financial and economic crisis on global FDI flows. Web.
Viljanen, M. & Lähteenmäkia, S. (2009) Good HRM Aims – Tough Consequences: Finnish Mncs’ Reactions To The Global Financial Crisis. Web.
Vösa, H. (2010) The Impact of Economic Crisis on HRM Practices in Estonia. Web.
Yin, R. K. (2003) Case Study Research: Design and Methods. 3rd ed. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Zikmund, W. M. (2006) Business Research Methods. 7th ed. Orlando: Harcourt Publishers.
Footnotes
- Recruitment and Selection Process, ii) Rewarding and Motivation, iii) Training and Development and iv) Performance Appraisal
- English Language Competence, Foreign Education Degrees, Competitive Computer Literacy Skills & Competent Work Experience
- Trust, Commitment, Performance Level & Job Satisfaction
- Survival Strategy Variables
- International Monetary Fund
- United Auto Workers Union
- United States Department of the Treasury Loan
- Voluntary Employees’ Beneficiary Association
- United Auto Workers
- Fiat, Daewoo, SAIC, Suzuki, Isuzu, Saab & AvtoVaz
- United Automobile Workers of America
- Government National Mortgage Association
- Apple or Google