Introduction
Research Problem
As a result of globalization e-commerce has really grown in the past few years. Many business organizations have started offering their products and services through technological (internet) platforms and banks have not been left behind. Banks have started offering internet banking services to their clients. However everything employed in this planet has advantages and disadvantages. As a result though internet banking has quickened banking operations, it has also exposed banks to several risks for instance banking security.
In Vietnam, the director of Vietnam Computer Emergency Response Team notes that vietinbank’s security network is among the networks that are at high risk of being attacked by hackers if there will be no proper management of the system. The bank has been a favourite target for hi-tech criminal. The bank holds the view that internet banking has been increasing its risk of being attacked by hackers. A study carried out by Bach Khoa Inter-network Security Centre showed that even vietinbank which was under the survey is not secure. It was found that there were certain vulnerabilities particularly when transferring money. Similarly, password recovery function to users account could be used to change the customer’s password (Guerrero, Egea & González, 2005).
Though vietinbank adopted the new technology of internet banking with the aim of gaining competitive advantage in the banking sector, the bank has not carried out enough studies to come up with ways of minimizing transaction risks in its internet banking transactions. In the fast place, it is important to establish whether the management are aware of the various internet banking risks. Statistics show that in 2010 alone, over one thousand websites were attacked by hackers; this figure is double of the 2008 figures and slightly above 3 times the 2007 figures. Over 80.0% of banks in the country have fully established or have plans underway to provide their customers with internet banking services and associated solutions (Nguyen, 2011). Consequently, it is generally agreed by those in the banking industry that adopting the concept of internet banking increases the risk of the institutions being invaded by network criminals (Clayton & Waldron, 2003). As a result risk management policies pertaining internet banking in vietinbank has not yet grown at the same rate as internet banking technology, and this has posed a great problem in VietinBank to adopt internet banking. As an effect there is need for research to be carried out to come up with strategies through which transaction risks encountered by vietinbank in internet banking operations can be minimized, hence increasing knowledge in internet banking risk management. Additionally, it has been observed that majority of Vietamese are reluctant when it comes to adopting online banking, major reason being insecurity. Knowledge from the research will be used by vietinbank as well as other banks in Vietnam to prevent internet banking transaction risks which have been found to soil banks’ reputations. Consequently more customers will therefore stop perceiving vietinbank as being unsafe, hence will start joining resulting to good businesses.
Research questions
- Are the management aware of the internet banking risk in VietinBank?
- How effective are the current transaction risk management strategies?
- Why does the current risk management fail to improve the transaction risk of VietinBank?
- What internal and external provisions can be formulated to curb transactional risks in VietinBank?
Research objectives
The main aim of this dissertation is to come up with ways through which transaction risks in internet banking can be minimized, taking VietinBank in Vietnam as a case study. However in achieving this broad objective, the following specific objectives will be used to guide the study;
- To establish whether the management of VietinBank are aware of the internet banking risk in the bank.
- To examine how effective the current transaction risk management are in curbing identified transaction risks in VietinBank.
- To analyse the reasons why the current risk management failled to improve the transaction risk of VietinBank.
- To propose the internal and external provisions to help curb transaction risk in VietinBank.
Implications of the Study
This dissertation is useful for banks intending to use internet banking platform as it highlight major strategies which can be employed in dealing with internet banking insecurity. This paper’s findings are also of great help for customers intending to use internet banking platform for future transactions. This is because; internet banking users are educated on the importance to ensure secured financial information by acquainting them on safety precautions they can take individually.
Due to the fact that internet banking platform has not been implemented by many banks in developing countries, the recommendations made in this dissertation will be used by such banks as a guide when adopting internet banking services. The results under this dissertation are of great help for policy makers when developing regulations meant to govern internet banking. Additionally knowledge and ideas that will be created herein will be of help to scholars interested in carrying out future studiers relating to this topic.
Research Subject
The structure of VietinBank is characterized by an amalgamation of several entities to form the giant financial institution. VietinBank is 80% owned by the government of Vietnam and 10% owned by an affiliate of World Bank which is known as IFC (Vietnam Today, 2010). The rest of the shares are owned by other entities. In the coming years VietinBank intends to merge with other entities in the banking sector. More prominently Nova Scotia Bank, which is based in America, stands to gain from this plan because in 2012 the company intends to merge with the global giant (Vietnam Today, 2010). This merger is expected to add more global banking experience to Vietinbank’s body of knowledge especially in internet banking.
VietinBank is deemed a pioneer of internet banking in Vietnam because most banks in the country have not adopted the technology yet. VietinBank has been using the SSL certificate with extended validation since the year 2007 (this certification is deemed the safest in internet banking) (VietinBank Group, 2011). Vietinbank adopted internet banking in 2005 and since then it has been able to attract many customers. In two months the bank has witnessed the rise in customer numbers (those who want to use internet banking) from 11,000 in January, 2007 to about 117,000 in February 2007. In December 2007 the bank had already witnessed a surge of internet banking consumers to about 150,000. These numbers have been sustained in the year 2008 and the bank’s internet banking customers still grow by the day. However it is also crucial to note that the bank has witnessed an increase in the volume of internet banking transactions by more than 50% during the same period (VietinBank Group 2011).
Outline of the Report
To achieve these specific objectives outlined in this study, this paper constitutes a literature review of existing academic materials (concerning overview of VietinBank, regarding how to reduce transaction risks in internet banking); a research design (to explain how the intended study is to be done), a results and discussion section that aims in analyzing the findings from the study and a conclusion as well as recommendation section.
Literature Review
Internet Banking
Online banking sometimes known as internet banking has been defined as the process of conducting business on the internet by employing a combination of tools and establishing a server presence for users. This technology can be used in different business environments such as business to business, business to customers, business to government and even government to constituents (Khalfan et al., 2006). Advancement in technology coupled with ever changing customer needs and globalization has led to many financial institutions to offer online financial services to their clients. According to review of a research ‘Role of information technology in banking industry’ it was established that majority of the customers believed that information Technology in Banking Industry positively impact on rendering of services to customers, for this reason more banks are trying to embrace the technology to deliver a cost effective services (Chang, 2004).
As suggested by Khalfan et al 2006, internet banking has been adopted by most of the banking industry with the believe that it’s inevitable in ensuring that they survive in the future, improve their operations, reach out to their customers, gain competitive advantage, efficient provision of service, improve customer’s loyalty, providing better services while reducing cost and generate more revenue. The concept involves the stipulation of banking services including account access, funds transfer between various accounts as well as offering other online financial services to clients.
It is worth to note that profitable transaction in Vietnam over the internet commenced in 1995. The most promising application of the Internet banking is in the bank, i.e., financial transactions that could actually take place online. The arrival of Internet-based electronic finance provides substantial opportunities for financial institutions to expand their client base as well as rationalizing their business venture.
The internet has been the number one resources for enabling the ecommerce to be effective; e-banking has been enabled by these factors. The bank has the major fact of being in control on the provision of electronic banking. This is to complement the fact that one can transact through their local bank when abroad. There are various distribution electronic channels that are very essential due to the development of the internet technology that the bank can adapt (Guerrero, Egea & González, 2005).
Chang (2004) articulates that most of the Vietnam banks are still reluctant to deploy online banking due to the system management and most of their clients are shifting for more flexible online bankers that offer online banking services. It’s worth noting that the most notable driving force that make customers yearn for online banking facilities include but not limited to; convenience, cost effectiveness, efficiency, reliability, privacy, quickness, accessibility as well as no fear of fraud. The quest to adopt online banking and other financial services is faced by a number of problems such as security, competition and the cost of installing the new technology among others (Petrus & Ndubisi, 2006).
In Vietnam, internet banking has become a common trend. Majority of banks such as Citibank, HSBC and ANZ which are foreign banks are leading the way in providing customers with online banking. Among the local banks that have adopted internet banking include VietinBank, Techcombank, Agribank as well as Bank for Investment and Development of Viet Nam. In all these banks, there is no more falling in line while in banks, no more waiting for hours before being served as all major transactions such as paying bills, salaries can be done using one card. It is worth noting that for one to use internet banking customers need to be in a possession of a computer and access internet. The banking industry should always adapt to the new technology today and basically make the necessary adjustments to gain competitive advantage with other competing banks which VietinBank has done (Petrus & Ndubisi, 2006).
Statistics show that in 2010 alone, over one thousand websites were attacked by hackers; this figure is double of the 2008 figures and slightly above 3 times the 2007 figures. As mentioned previously, a study of 40 banks by Bach Khoa Inter-network Security Centre (BKIS) found that 20 of them were not fully secured. The same study established that there were vulnerabilities particularly in money transfer and that password recovery function to user accounts could also be used to change the customer’s password. Additionally customer question and complaint forms could be used to install dangerous codes into the server and control the internet banking system. In Vietnam, the banking security networks are always at risk of being invaded if there is no proper management of the systems said the director of the Ministry of Information and Communication Viet Nam Computer Emergency Response Team. On the same note, it has been brought forth that the banking industry in the country is a favourite target for criminal who have techno savvy. Additionally, existing vulnerabilities in network securities at Vietnamese banks was attributed to the lack of an independent security assessment process of internet banking systems as well as a lack of standards on information security (Guerrero, Egea & González, 2005).
As suggested by Nguyen, 2011 over 80.0% of banks in the country have fully established or have plans underway to provide their customers with internet banking services and associated solutions. Consequently, it is generally agreed by those in the banking industry that adopting the concept of internet banking increases the risk of the institutions being invaded by network criminals (Clayton & Waldron, 2003). To help curb the problem associated with internet banking risk, banks have resorted to heavily invest in security enhancement. According to Dang Manh Pho, who is the boss on information technology department at the Bank for Investment and Development of Viet Nam revealed that they secured a banking system worth over VND1.6 trillion in 2009 to boost security of internet banking and about VND1 trillion in 2010 to do the same. Bach Khoa Inter-network Security Centre officials have tried their level best to provide banks to successfully deal with risks to their internet banking systems for instance using independent assessment to establish the pitfalls in their systems, adopting and implementing ISO 27001 standards on information security, using computer antivirus as well as adopting digital signature certification aimed at securing online transactions (Petrus & Ndubisi, 2006).
Ideally, although internet banking is associated with a number of advantages, there are serious risks and for that matter it is usually vital to be informed of these risks. The major types of risks in internet banking have been categorized into transactional or operational risks, security risks, reputational risks, legal risks, systematic risks strategic risks and money laundering. The former is of interest in this study (Petrus & Ndubisi, 2006).
Internet banking in Vietnam
In Vietnam, banking rate is only 10 percent of the Vietnam population, implying that, informal might be the underlying factor that is contributing to satisfaction of banking needs in the Vietnamese population, which according to Nguyen (2011), indicates a very high level of risk as well as instability. As a result, there is very high competition both in financial institutions like banks as well as informal financial markets. Due to this competition, it is logic that profits in banking sector has been reducing year after year; as a result, banks have been looking for means and ways of reducing operation costs a long with portfolio diversification in the process of sustaining their productivity levels.
One of the means of portfolio diversification and cost reduction has been through internet banking services. This sector of internet banking in Vietnam is still at abby stage of development. This sector also depends much on computerization of all banking services that were being offered traditionally. In most Vietnamese banks, there are websites used for communication between banks and their clients, as well as presentation of banks’ information. However, most banks have been much reluctatnt in adopting internet banking as a major tool for growth.
In dealing with internet banking security systems, in 2005, the government introduced bank identifier code (SWIFT), however, by 2007, only few banks like Vietinbank, Incombank and others had started providing home banking. This services was being offered inform of telephone banking, mobile-banking. In the current times, ATM banking has become a daily experience for a large population of Vietnamese. The awareness of ATM cards, credit cards, along with debit cards has been increasing in Vitnam. Moreover, Visa payments are coming in at a very high speed.
According to Nguyen (2011), ATM banking services is growing at a higher rate as compared to other internet banking services due to inadeguate means of internet banking security security systems in the country. In the process of overcoming high rates of fraudulence in the country, the state bank of Vietnam introduced new online banking system having high protection technology. This came after the loss had lost about $37 million dollars as a result of fraud in the year 2008.
In Vietnam, the thorny issue in banking sector is internet banking transaction risks. Studies have indicated that, security has remained being the biggest issue preventing internet banking in Vietnam. It was found out by Nguyen, (2011) that 100 percent of banks offering internet banking services in Vietnam internet security problems. These problems are including “personnel, process, ICT network, transmission, central management platform and environment, and E-banking technology applications” (Nguyen 2011). These problems have been posing a great threat in the smoth running of internet banking operations in Vietnam.
Due to the fact that Vietnam is among the countries whose financial markets are growing rapidly, there is need for quick circulation of cash to meet the increasing capacity of capital requirements. As a result, internet banking along with mobile banking is very essential in this country.
Types of internet banking in Vietnam
There are different types of internet banking in Vietnam; one of them is web-based banking. In this type of banking, clients usually access their accounts through the internet. The second type entails the usage of modem in dialing up to the bank’s sarver with the aim of accessing bank accounts. The second type of internet banking is called ‘dial up banking’. One of the most specialform of dial up banking is extranet, which is a private network between banks and their corporate clients.
In vietname market place, there are three levels of online banking. Such levels include communicative, informational and transactional. At informational level, which is identified as being the first level of online banking, banks have marketing information concerning the bank’s products or/and services on a server that is standlone. The fraud risk at this level is very low as the level does not allow pathway banks’ internal network and the server. In communicative, also refered to as simple transactional, there exist interactions between the banks’ systems and clients. However, the interaction is only limited to e-mails, inquiry of accounts, application of loans, as well as static file updates. This level does not allow any form of money transfer. Last but not least is the transactional level of online banking, which allows some transactions to take place between clients and their respective banks. These transactions are usually through electronic money transfer from clients’ accounts to paying bills or even conducting other transactions online.
Attitudes of clients towards internet banking
In general, technological innovations have great improvements in people’s livelihoods. “Research on consumer attitude and adoption of internet banking showed there are several factors predetermining the consumer’s attitude towards online banking such as person’s demography, motivation and behavior towards different banking technologies and individual acceptance of new technology” (Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce 2010). Some of the factors attitudes are based on prior experience towards new technologies and computers. Adoption of internet banking has forced cients look at issues like integrity of passwords, privacy and confidentiality of personal information, encryption of data, and hacking. It has been found that, clients undertaking internet transctions are using it on an ongoing basis, and always desire to get some comforts with it, so that they can continue using it.
For most financial institutions, client adoption remains the greatest dilemma particularly in undertaking strategic plans. Researchers have conducted several studies with the aim of identifying the reasons that make clients to preffer ceratin banks as compared to others, and results have shown that, “convenience, service facilities, reputation and interest rates” (Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce (2010), are the major reasons. In ost cases, potential clients have very little time to visit their banks physically; as a result, they will always look for convenient and accessible banks. On the issue of quality services, banks offering internet banking transactions have to induce clients to start undertaking online banking and keep on using them based. This can be achieved through explanation of its importance, easy to use, reliable, security measures, responsiveness, along with improvements that are continous. Moreover, accuracy, speed, user-friendly as well as involvement and convenience are perceived as being the most significant attributes that makes clients to start and keep on undertaking internet banking transactions
Some of the crucial issues affecting adoption of online banking operations include the client’s age, technology usability, fear of changes in banking sector as a result of technology development, and inadeguate information concerning the services and products provided through internet operations. Issues like transaction speed as well as transaction costs are not of significant consideration according to Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce (2010). Amongst the electronic service quality dimensions, the following are very important “provision of convenient/accurate electronic banking operations; the accessibility and reliability of service provision; good queue management; service personalization; the provision of friendly and responsive customer service; and the provision of targeted customer service, usefulness, security and privacy” (Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce 2010).
Transaction risks in Internet Banking
It is worth to first understand what risk are, in the jounal titled “The Adoption of Electronic Banking in Tunisia: An Exploratory Study” written by Azouzi, 2009 risks have been defined as “a combination of of uncertainty plus seriousness of outcome involved”. Ideally risk is potential for loss in pursuit of a desired outcome of using an-eservice. This later definition will be adopted in this paper. Having in mind that uncertainty is inherent in innovation, they indeed contain at least some degree of perceived risk Operational or transactional risk is a category of risk as a result of activities, processes, infrastructure, technology or other influences that practice functional effect as well as fraudulent acts. Ideally, this kind of risk is a risk off occurring damage due to insufficient, inadequate internal processes as well as systems or from human factors or other external reasons. The difference of this kind of risk and others is that it does not stem from the desire of financial institutions to make profits but an innate feature of banking activities. This type of risk is mainly associated with bad operation of information system as well as processes of reports. Transactional risks are inherent in all products and services as well as the entire relevant department. Ideally, the risk usually arises from negligence damage and can lead to bank going bankrupt (Guerrero, Egea & González, 2005). It is apparent that banks have not succeeded in effectively managing this situation in an organized and systematic way. Human beings are the major causes of this issue. Although employees have been blamed for knowingly or unknowingly enhance transactional risk in the traditional banking, the development of computers and internet offers a platform where the same risks are transformed into the system thereby having far much devastating effects.
It has been shown that transaction risks are linked to how safe the transactions are done usually dependent on handling as well as the structure of electronic system of providing the financial services, integrity as well as correct record management and involvement of a third party. The later has been deemed to constitute a serious problem when it comes to transactional risks. The rate at which financial institution have experienced as a result of offenses of information systems is alarming. The whole problem has worsened due to lack of insufficient controls on certification as well as authenticity of contracted third party. This has resulted to hacker being successful in accessing vital information pertaining customers and the respective banks. It is worth noting that the severity depends on those who are carrying out these attacks. More often then not, hackers heavily rely on technical weaknesses of the banks systems. It has been established that although hackers are outsiders, they usually get assistance from employees of the targeted bank. In planning to obtain vital information, software is used to record periodical or permanent malfunction of the banks system. Financial institutions have resorted in contracting a third party to supply it with the relevant systems. In one side, this is advantageous to banks as it cuts down costs but the big problem is that the banks do not have control over such systems. There has been serious issues particularly when the contracted third party do not have enough experience or it is a new firm and do not take in the risks the bank may face (Dyk, 2011).
Transaction risks in internet banking are as a result of several issues surrounding fraud and errors. Such risks have been present in almost all products offered through internet banking; however its origin is process development, poor planning and implementation of mechanisms aimed at mitigating such risks. The risks associated with internet banking fall into two broad categories. The first risk is centered on the banks, which provide the basic products and services through internet banking. Here, customers may experience the risk of enrolling for financial services which their banks may fail to offer through their internet banking platform (even though they are enlisted). Moreover, this risk comes with the fact that, most customers who use internet banking are normally very impatient and would not tolerate any instances of error (on the part of the bank) (Carmichael, 2011). Furthermore, such customers normally expect internet banking to be extremely prompt and “error free” because they are not subject to human incompetence. This is not true.
The second type of risk centers on forces which are external to the banks. Usually, they are mastered by third parties who intend to launch an attack on the bank’s internet banking platform to steal information or funds from unsuspecting customers (or even from the bank itself) (Carmichael, 2011). Unfortunately, this type of risk is the most common. Incidentally, it is very difficult to overcome or even avoid this risk. Usually, such types of attacks can be launched from various quarters. However, they are mostly done online. Experts note that, these online attacks can happen in two ways. The attackers may exploit the software weaknesses of the bank’s internet banking platform, or they may devise ways to gain unauthorized access to the internet banking platform. These online attacks can occur in several ways, including sniffing, guessing passwords, brute forcing, random dealing, social engineering, and hijacking. Online attacks can also occur through the launch of viruses, spyware, Trojan horses and the likes (Carmichael, 2011). These elements are usually launched in one server and spread to several other sub-servers through a local area network (LAN) or similar medium.
Categories of perceived risk in internet banking
For simplicity there are five major categories as proposed by Azouzi, 2009 and they include financial risk which is the continuous fear of transaction errors that may lead to a possible loss in money meaning that online banking lak the assurance usually enjoyed through traditional banking. Performance risk is the fear brought about by thoughts of losing money when the system malfunctions. Disconnection from the internet has been shown to to lead to huge and unexpected losses. Social risk is as a result of the fear of being seen or perceived negatively by those close to one. Privacy risk is one of the serious issues of contention in internet banking. It refers to the possibily of loss as a result of fraud or hackers who compromise the security of an online bank user. The risk is real and growing due to existence of phisers who try to lure customers in a fraudulent manner to provide their personal information. Lastly there is the issue of time risk where individual are worried of lateness in payment as well as challenges when navigating through the website of a bank especially if it is not well organized.
It is upon banks to convince their customers that the website they are using are safe and sufficiently safeguarded for secure transactions. Additionaly according to Rahmath, 2010 safegurding the privacy of customers’ financial information as well as profile is an imperative task for the bank if it wishes to have more online banking customers. Generally the procedures used to examine banking activities include customer privacy, threat of intrusion from hackers as well as issues regarding interlink of customer anonymity on the internet and bank’s responsibility to monitor suspicious activities. Other security measures that have been proposed in western countries include agreement with third party vendors, strategic planning as well as auditing procedures for the enire system.
Internal Measures of Minimizing Transaction Risks in Internet Banking
Information security is among the most important issues of concern in internet banking. Banks are often advised to assess the level of security accorded to the information they possess because certain information may be sensitive or classified (Koch 2009). The security of such information is often a ‘hot’ issue in internet banking. Internet banking normally offers an easy access to such information (sensitive and classified information) for online attackers who may want to gain unauthorized access to them. It is therefore the duty of the banks to provide controls and safeguards through reliable security mechanisms and structures. For a long time the internet firewall has been used to protect sensitive information from online attackers especially through the local area networks. However it is proven that the internet firewall by itself cannot adequately prevent the occurrence of transaction risks in internet banking (Koch, 2009). In this regard, internet security experts suggest that different types of firewalls need to be designed for specific control measures in the internet banking platform. Moreover such a system upgrade requires competent technicians who will develop and monitor the system regularly. These requirements led to the development of several strategies to further prevent transaction risks in internet banking. One such method was authentication.
Authentication is the verification of a user’s identity to minimize the risk of fraudulent persons accessing a bank’s internet platform. This is done through the issuance of personal identification numbers (PINs), encoding data and biometrics data (Carmichael, 2011). The use of PIN is the most traditional form of authentication but it is also subject to several weaknesses, including forgetting a person’s PIN or the theft of PIN numbers. It is from these weaknesses that more sophisticated authentication tools such as data encoding and use of biometrics arose. The use of biometrics is the most sophisticated form of authentication because it is based on the typical behaviours of humans. It includes tools such as scanning a person’s retina, fingerprint verification, facial imagery recognition and the likes (Koch, 2009). The most sophisticated form of verification is the observance of a person’s vein. Here the level of sophistication is extremely high and it is almost difficult to impersonate someone. The biometrics method works by determining a person’s haemoglobin and blood vein patterns which is very difficult to steal (Dyk 2011).
Somewhat these measures helped to curb the rampant cases of internet fraud when they were invented. This experience is shared in many countries across the globe. For instance the United States (US) was able to launch its internet banking platform in the 90s through moderate internet security features necessitated by the various authentication features described above (Koch, 2009). Singapore also falls in the same category; but collectively in an interesting twist these two countries exposed the importance of including the input of the central bank in reducing the transaction risk of internet banking. However as opposed to internet banking in Singapore and the USA there is very little public awareness among most Vietnamese about the transaction risks of internet banking. As a result there are minimal efforts designed to curb this problem because without the awareness needed to fight transaction risks, there is very little that can be done to prevent its occurrence (Mermod, 2011.).
External Measures of Minimizing Transaction Risks in Internet Banking
The Monetary Authority of Singapore is of the view that, a robust framework for reducing transaction risks in internet banking depends on the management framework developed by a company’s board. The agency reports that this responsibility calls for banks to perform risk analysis by identifying information systems assets, vulnerabilities and determining safe threats, estimating the likelihood of attacks or exploitation, evaluation potential losses that it is associated with these risk events and taking suited security measures and controls for property protection (Carmichael, 2011).
In India similar measures have been suggested by the country’s reserve bank because mobile commerce has quickly gained prominence in the region and many banks offer internet banking. To safeguard against the risk of internet banking the country’s reserve bank provided several guidelines for banks to follow. These guidelines centred on; supervisory and regulatory issues, registration of bank customers, technology and security standards, interoperability, clearing and settling of interbank transactions, addressing customer complains, transaction limits, board approvals and approvals from the reserve Bank of India (Koch, 2009).
In line with the above regulations the Federal Reserve Bank only authorizes banks which have a physical presence in India to undertake internet banking services, based on mobile banking (Mermod, 2011). Only customers who hold a debit or credit accounts are allowed to use internet banking services (subject to the reserve bank of India guidelines). Internet banking transactions are also only limited to local transactions (in rupee). Any international banking transactions are not allowed. Furthermore Indian banks are only allowed to use third party correspondents who have been approved by the country’s reserve bank to undertake internet banking transactions. Any other third party is not allowed to operate in this capacity. Existing guidelines formulated by the reserve bank of India relating to ‘money laundering’, ‘know your customer’ and ‘combating the financing of terrorism’ also apply to internet banking. Furthermore not all banks are allowed to provide internet banking services; only banks which have provided core banking solutions are allowed to do so. Similarly all banks that provide internet banking services are bound to provide suspected transaction reports to the relevant authorities for an evaluation of the transaction procedures (Dyk, 2011).
The bank of Mauritius aims at limiting the occurrence of transaction risk to improve the country’s financial market sector and improve the confidence that people have on internet banking. The same guidelines have also been set up to encourage more banks to teach their clients about the importance of upholding internet security standards for their own privacy and security of their money (Koch, 2009). Finally the bank has also formulated stringent guidelines to facilitate the development of cheaper and convenient online payment methods. However the bank of Mauritius does not prevent any financial institution from adopting more stringent internet banking guidelines than it already provides (Nath, Schrick & Parzinger, 2001).
In the US banks which provide internet banking services are required to abide by the country’s internet banking guidelines, providing legal documents that outline the bank’s internet banking plan, internet security policy, risk management plan, client charter on internet banking, terms and conditions for the use of internet banking and any plans to outsource some of the internet banking services from a third party. These measures are formulated to reduce the transaction risk of internet banking in the country.
Similarly banks are required to report periodically to the Federal Reserve and explain the progress they have made in implementing the stipulated internet banking guidelines (Koch, 2009). However there are some transactions risks experienced by major banks that may be unique to their circumstances and therefore they are to adopt of a local (bank) policies to curb these risks. This task has been given to the board of directors for any bank that provides internet banking services should oversee several responsibilities (Petrus & Ndubisi, 2006).
Top among the list of responsibility is the assurance that every board ensures that the bank’s internet banking strategy complements the overall vision of the bank (Koch, 2009). Respective boards should also approve the strategic internet banking plan and any risk management plan before they are adopted. The board is also required to monitor any internet banking project that may have a significant impact on the transaction risk experienced or posed to the bank. Also the board of directors is required to ensure there are adequate internal controls that safeguard against transaction risk plus an assurance that there is a strong team of competent employees that know how to circumnavigate issues regarding transaction risks in internet banking (Petrus & Ndubisi, 2006).
The bank also outlines that management boards need to ensure their internal controls are functional and well-monitored to ensure no transaction risk occurs. The management is also required to ensure adequate resources are available to curb transaction risks in terms of policy formulation, adoption and implementation (Nath, Schrick & Parzinger, 2001). There are also several security guidelines that need to be observed by banks which provide internet banking services. These guidelines are centred on upholding data privacy and confidentiality, data integrity, business continuity, authentication of users, non-repudiation of internet banking products and access control system design to ensure unauthorized personnel do not access the internet banking platform (Carmichael, 2011). There is also need to ensure network access data control structures are functional to restrict unauthorized control of the internet banking platform (from unauthorized personnel).
Similarly all financial institutions are to provide a strong user identification method which is tested and authenticated. The authentication procedures also need to be periodically reviewed through various testing procedures, such as penetration testing to ensure they are effective. A combination of several authentication techniques is however recommended because it improves the level of security clearance for internet banking transactions. These authentication techniques include firewalls, passwords, and encryptions (Carmichael, 2011). Adopting periodic audits has also been deemed helpful when dealing with transaction risks. There is also need to lays a lot of emphasis on virus attacks; to attain this banks opt to implement a detection and prevention program against this attack. This program is expected to contain a lot of elements, including virus awareness, user training programs and end-user policies. Additionally having a real-time monitoring program that detects any instances of intrusion is vital (Carmichael, 2011). Based on these policy guidelines the role of the central bank is pivotal in minimizing financial risks in internet banking. Therefore from a comprehensive point of view it is easy to establish that a combination of the external and internal control systems will go a long way towards ensuring transaction risks are effectively minimized. This analysis explains the need for strengthening traditional banking controls in a virtual manner.
Methodology
Research design
This study employed a mixed research design. On top of secondary data sources, qualitative study is also used with the aim of conceptualizing this study by immersing the researcher into a scenario. Due to the fact that this study aimed at coming up with strategies of limiting internet banking transaction risks, qualitative approach was more effective in answering certain questions efficiently and effectively as compared to what quantitative approach could have done. In particular, this deals with getting reasons and facts how and why internet banking transactions are not safe.
Population and Sampling Technique
The population of interest for the study is employees of VietinBank and the VietinBank clients using internet banking services. This is because they were in a better position to provide the necessary and relevant information regarding this study. Among the question these group of individual answered pertains to existence and types of internet banking risks, the effectiveness of the existing transaction risk management strategies, reasons why the present strategies has failed to improve the efforts aimed at curbing internet banking risks and finally the possible external as well as internal provisions that can be used to curb risks associated with online banking by VietinBank. Since the study cannot take the entire population, a representative sample of 70 participants was selected. In sample selection, probabilistic technique was employed. Probabilistic method was selected as it has the ability to ensure that every member in the population has a non-zero probability of being selected. Probabilistic method was also selected because it has higher chances of calculating sampling error. As an effect, the result will be reported with either a plus or minus the sampling.
Under this technique, every person in the population had an equal probability of being selected. The population was not divided into groups or partitioned; they were just selected depending on luck. As a result, this ended up minimizing baseness, hence simplifying the process of analyzing results. Particularly, the variance between individuals’ results within the sample was a good indicator of variance in the entire population, which at the end of the paper makes it relatively result estimation much accurate, (Adèr, et al 2008).
On the other hand, the researcher tried as much as possible to reduce the sampling error that would have been as a result of random selection. This is because, a times, the selected sample might not reflect the makeup of the population under study. Though it was not possible to avoid some mistakes, for instance, when carrying out simple random sampling of ten people from a given area will on average produce five bank employees and five bank clients; but there are times when one might over represent one side. In addition, the process of carrying out simple random sampling might be very cumbersome particularly when the population is large enough.
Other possible sampling techniques that could be used include snowball sampling and careful biased sampling (Creswell, 2003). The reason being that these approaches coulkd help the researcher reach respondent whom he does not know or are hidden and specific group of participant is identified to provide certain information that can not be provided by the other groups such as the top management. Random sampling ensured that each member of the entire population has an equal chance of being selected to represent it in the research being done.
Careful biased sampling was also employed to ensure that specific individuals especially Vietinbank clients using internet banking were reached. Moreover snowball sampling a technique which entails developing a research sample where current study subjects recruit future subjects from among their acquaintances was used. Thus the sample group appears to grow like a rolling snowball. As the sample built up enough data were collected. This sampling technique is often used in hidden populations which are difficult for researchers to access.
According to Salganik & Heckathorn (2004), this kind of sampling allows the researcher to include individuals he/she might not be knowing in the study, similarly the technique allowed location of individuals having vital information that are otherwise difficult to locate. The main down fall of the sampling technique is that it’s prone to creating biasness.
Due to the fact that the population size under study was infinite, the sample size that was chosen for the study was 70 respondents, all aged 17 years and above, and were either VietinBank employees or VietinBank clients. Though the sample size looks big for interviews, the subject under study is crucial, hence needs a large sample size to come up with the ideas. This study needs to generate ideas for new security strategies or improvement of available strategies, hence the need for a large sample size to generate more authentic and general conclusion (Bradburn & Seymour, 1988). This large sample size also helps in increasing precision and accuracy to ensure that results are reliable. As a result the obtained data projected the thoughts of the whole population under study. This sample size reduced sampling error. However this large sample size will consume more time and lots of resources just for minimal benefits. In addition according to the law of diminishing returns the larger the sample size usually beyond a certain limit little benefits will be attained.
Data collection and Analysis
For this study to collect required data to address all the objectives and research questions, perusal of secondary as well as primary data sources were used. Primary data collection has been defined as being the original source of material that is very closer to individual, information or even period and ideas. The reason for utilizing primary sources of data is that it helps provide upto date information which is aunthetic with no or very minimal levels of biasness. Additionally it provided the researcher with a firtst hand information vital for developing a good thesis. On the other hand, a secondary data is such data that was collected by someone else other than the researcher him/herself. It is important to state that before data collection, I requested permission from the relevant authorities from the VietinBank institution as it was the main target. This was done to eliminate plagiarism and make the report comprehensive and conclusive.
Primary method of data collection was chosen because it allows the researcher to control the research process. As a result, the researcher was allowed to determine the method to use in the process of collecting and time duration that the data collection process will take. Hence, the researcher had opportunities of only focusing on specific aspects of his/her study. In addition, primary data collection method allowed the researcher to dig for more information that concerns specific aspects. In addition, primary data collection method provides one with original and unbiased data, as compared to secondary data; the researcher also had to interact with information sources to get original data that had not been analyzed with the aim of suiting a particular premise, (Keman, 2008).
However primary data collection method consumes lots of time, as the researcher will have to make lots of preparations with the aim of meeting different process demands and manage time effectively (Breakwell, Hammond & Chris, 1995). Apart from time consumption, the sources entail collection of large volumes of primary data. This is based on the fact that, since it entails interacting with different people, will also prove much tedious when going through them when analyzing and evaluating their findings.
Having such like advantages and disadvantages, primary data collection method was chosen as it is much reliable and concentrates only on specific areas of interest, hence much easy for the researcher to control the type of data that is being collected (Breakwell, Hammond & Chris, 1995).
Interviews were used to collect primary data. In this method, the researcher interviewed the sample population through face to face technique as well as through telephones for those who were not available for face-to-face interviews. I took the leading role to guide interviewees. The interview was divided into two sections, Part A and Part B. In the part A, the guide will contain clients’ interview questions, among the question included whether they carry out internet banking. This will help in establishing how customers use internet banking. The same will also help us establish the duration in section b of the same question. Other question customers are asked is whether they are allowed to carry internet banking transaction overseas, this will be used to gauge how strong the security of the same is. Similarly, if the response is no, the reasons behind are brought to light. Additionally, the motivation behind adopting internet banking transaction is also asked. This will help us understand the advantages of this kind of transaction. What risks a customer has experience while engaging in internet banking is also asked. This ill give me the green light on the issue at hand. Lastly, based on customers knowledge, am interested to establish the measures the banks has put in place to help curb the occurrence of internet banking risks. Part B will contain interview questions for employees of the bank. The guide was separated into two sections to ensure that every group is asked relevant questions according to their capability. Among the question in this part include whether banks allow overseas internet banking transactions, if they have a third party whom they conduct internet banking with, what motivated the bank to adopt internet banking transaction, whether the bank has experience internet banking transaction risks, the measures the bank has taken to curb the mentioned risks and the kind of regulations set by the government to deal with the problem in Vietnam.
This technique was employed because it had the ability to provide the researcher with the opportunity to have direct contacts with the respondents and obtain first hand information. The interviewer and the interviewee would be able to clarify on issues of the research done hence being able to obtain information which is well elaborated and authentic (Yu & Cooper, 1983). The main questions to be asked will be revolving around the research questions where the interviewee will be asked to briefly expound on issues with regard to internet banking transaction risks. In addition this technique is very flexible when collecting data, as when questions are not well grasped by the interviewee the interviewer had an opportunity to rephrase and elaborate them. Interview also allows the researcher to learn about things and facts that cannot be observed directly and finally it adds internal viewpoints to outward behaviours.
Though interview technique has lots of advantages as mentioned above according to Beiske, (2002) the method is slow as the process needs the interviewer to interview one person at a time. Another disadvantage is that interview method cannot fully trace events and trends that occurred in the past due to forgetfulness and the desire to burry bitter memories. Additionally interview is an expensive tool to use; it is also subject to respondent and interviewer bias. This was eliminated through a tight time and structural frame work that ensured that everything is done on time and appropriately.
For secondary data, materials from the library, internet and related research reports were used to provide the required data and information concerning internet banking, as well as strategies to minimize it. VietinBank Internal sources regarding internet banking transaction risks, as well as strategies to minimise them were also sought after. On the other hand, external data sources included information from the government sources, previous research studies and academic institution (colleges and universities material related to internet banking transaction risks). According to Creswell, 2003 the secondary sources were very essential in supporting what has been collected in the primary data session i.e. from the interviews. In addition, this method is not expensive, provides opportunities for studying trends over a certain period of time. Collecting data through secondary sources also ensured that time and other resources are saved especially when one has at his disposal access to relevant documents. On the other hand, the method might provide incomplete information, and might not be accurate, location of relevant documents might prove challenging. Moreover, secondary data will be of great help in showing how the Vietinbank has grown from the time it launched internet banking transactions. The desire to obtain data through secondary sources is to help augment the finding of what primary data sources will bring forth. There is always need to link once finding and those of previous scholars. The kind of information sought after pertains to the major types of transaction risks and how the same can be addressed.
The most common method of qualitative data analysis was employed and this was just through observation impression. This is where the observer examines the collected data and then interprets it by the use of personal impression formation and ends up reporting his/her impression in structured forms. Interpretation is usually done by the use of different means and techniques. The presentation of the results will be done by using tables, graphs and charts which will present the required information of the population and what they have said about internet banking transaction risks.
Research ethics
Since this study entailed human subjects, ethical considerations were upheld to the highest level. At first the population under study was provided with relevant information concerning the study in advance. For instance the reasons for carrying out the survey as well as how they stand to gain from the study were brought out clearly. In addition it was made clear from the onset that participation is voluntarily. There were no influences be it monetary or otherwise for instance giving of incentives, rewards or gifts. It is important to note here that the rights and welfare of the participants involved in the study were protected and guaranteed. To do this, their identities were kept confidential. Nevertheless, data collected were kept confidential and was not to be used for any other purpose apart from what was initially intended for. Interviewees or respondents were ethical and provided accurate information to the best of their knowledge.
The researcher opted to be ethical in providing the participant especially the respondent’s guidelines and necessary information that are correct. Similarly I was not judgmental on the information I was provided with during the interview and was just neutral as possible during the entire process. Lastly there is no personal biasness that arose; this was done at the end of the study. This is with the knowledge that such bias can negatively impact on the statistical analysis.
Research limitation
The research has a regional scope highlighting the various Strategies of Limiting Internet Banking Transaction Risks using a case study of VietinBank. As a result, the research faced the following limitations:
- Time limitation; there was very limited time for the researcher to carry extensive data collection through interviews and secondary sources. As a result, the presented data is just a drop in the ocean.
- Financial constrains; this made the researcher to only use one method of primary data collection on a few people. Due to the fact that this study was conducted in a single bank in one country, the results might be limited; hence conclusions might not generalize the whole banks and other financial institutions.
Results and Discussion
Participants Age Group
According to the interview results obtained after interviewing VietinBank clients, it is clear that most of their customers using internet banking transaction are in the age groups of 46-55 as shown in figure 1 below.
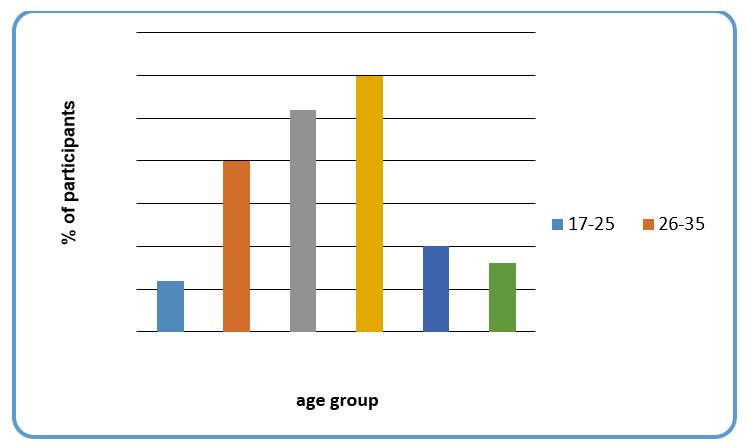
From figure 1 above, it is clear that 30% of participants are in the age bracket of between 46-55 followed by 36-45, 26-35, 56-65, 66-75 and then 17-25 respectively. 46-55 age brackets recorded the highest number of participant (30%) because it is this age group that undertakes lots of bank transactions in Vietnam. This is because, under this group, people have lots of responsibilities ranging from family issues to business matters. According to Vietnam Today (2010), most business owners in Vietnam are in the age bracket of between 40 years to 60 years. Due to business transactions, this group sends and receives money through online.
Moreover, 36-45 registered the second percentage of 26% because part of this population is involved in business while the other group has more family issues like paying school fees for their children and other family members. According to Nguyen, (2011), a large percentage of this age group do not receive money through the internet, but most of their transactions deal majorly with sending money through the internet banking. 56-65 and 66-75 age brackets produced a percentage which does not differ much from each other, though 56-55 age bracket had a higher percentage. Most individuals under this two age brackets in Vietnam do not involve themselves in much transactions because some of them have already retired from work, others have no family issues because their children are already old and can now take care for themselves. Those who used to own business have passed over business responsibilities to their children. As a result, most of them use internet banking just in receiving money, not sending.
The age bracket of between 17-25 years had the lowest percentage because most of them are still in schools and collage. However, there are those who do not even own bank accounts because they are considered as being young. According to VietinBank Group (2011), most young people aged between up to the age of 23 in Vietnam are still in school. As a result, they are taken care of by their parents and elder family members.
Concerning the question of how many years the participant has carried out internet banking transaction, the results are as indicated in Figure 2 bellow.
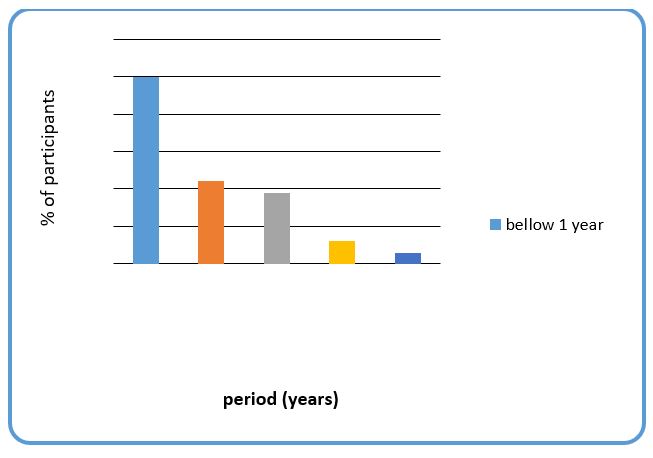
This question was asked with the aim of gauging experience of participants on matters concerning internet banking transactions. However, it was found that, 50 percent of VietinBank clients undertaking internet banking transactions have used it just for less than a year. This is based on the fact that, it is just in the recent past that internet banking transaction serves were launched by most banks in Vietnam. According to the secondary literature from Vietnam, though most banks launched internet banking transactions in early 1990s, but intensive marketing started in early 2000. As a result, only 2 percent of participants had used for more than 16 years. John adds that, Vietnamese who have used internet banking transaction for more than 10 years have not spend most of their time Vietnam, they might have been working or living in other countries like US and England, where internet banking transactions were intensified long time ago.
In addition, there are some security measures that have been put in place by VietinBank not long ago. These measures have encouraged many people to join internet banking transactions. However, before 2007, there were many internet transaction risks especially fraud, hence many Vietnamese were keeping a way from internet banking. This also explains why many people have used internet banking for less than a year.
Motivating Factors
When asked about the motivating factors that made them start engaging in internet banking transactions, the following factors were given:
- Internet banking is very fast and efficient.
- The costs involved in internet banking transactions are less as compared to traditional banking transactions.
- Internet banking transactions are very easy.
- There are no bouncing checks.
According to t Nguyen (2011), internet banking is very fast and effective as there are long queues as those found in counter transactions. Moreover, opening accounts through internet banking is very easy and simple as there is no much paper works involved. As compared to traditional banking system which has been very slow hence consuming a lot of time, internet banking is 100% faster. This is because; transaction time has reduced drastically in internet banking. Moreover, individuals using internet banking have an opportunity of making transactions anywhere at any time; it is not a must that one has to avail himher-self at the bank office to obtain any information concerning one’s account.
Nguyen (2011) adds that, of late, individuals in Vietnam are going for internet banking because the service allows them to make inter account transfers very fast. It is much efficient as compared to phone services and has the ability of saving people from making regular trips to banks.
On the other hand, VietinBank also had its own motivating factors that led to the adoption of internet banking transactions risks. One of the major reasons was to have a competitive advantage over its competitors. According to VietinBank Group, (2011), since the bank started offering internet banking transactions, it has really improved. VietinBank’s capacity to pay its debts has significantly improved in recent times because in 2009, it registered a bad debt ratio of 1.41%, but in 2010, it registered the same measure at 1.02%. Currently, the bank is attached to a VND 900 trillion loan with Vietnam National shipping industry, but since the company is registering a good financial performance, there are no fears that VietinBank will suffer any losses arising from a loss of the principal amount or any interests accrued (Charlton Media Group, 2011). The bank’s provisional fund is also said to be very stable and it can offset the total debts owed by the bank.
The bank’s capital adequacy ratio also increased to about 9.82% (as per the bank’s mid annual results) and this shows an increased growth of about 1.8% if the same figures were compared to the same time in the year 2010 (Charlton Media Group, 2011). As a result, we can establish that, VietinBank currently enjoys a healthy financial growth.
VietinBank has a very broad network for offering its financial services partly as a result of internet banking services. This is because the bank spans across 56 provinces across Vietnam. Compared to other banks, VietinBank’s capacity to offer banking products and services, greatly outweigh its competitors. VietinBank Groupd explains that, Vietinbank has 03 Transaction Offices, 01 Head Office, 140 branches, 258 transaction points, 188 transaction departments; 742 automated teller machines (ATM); 02 representing offices, 191 saving funds; and 03 belonging companies include VietinBank Stock Ltd Company (VietinBankSC), Debt Management and Asset Exploitation Company and Financial Leasing Company; 03 enterprise units include Human Resource Training and Development School, Card Center and Information Technology Centre, (VietinBank Groupd, 2011).
Apart from these facilities, VietinBank stands above the rest of the competition in terms of its technical capacities. This is the reason VietinBank has been a pioneer in internet banking (within its region).
Internet banking transaction risks in VietinBank
According to the interview response, figure 1 indicates common internet banking transaction risks identified by both VietinBank employees and VietinBank clients engaged in internet banking transactions. The results were combined because they all gave similar answers.
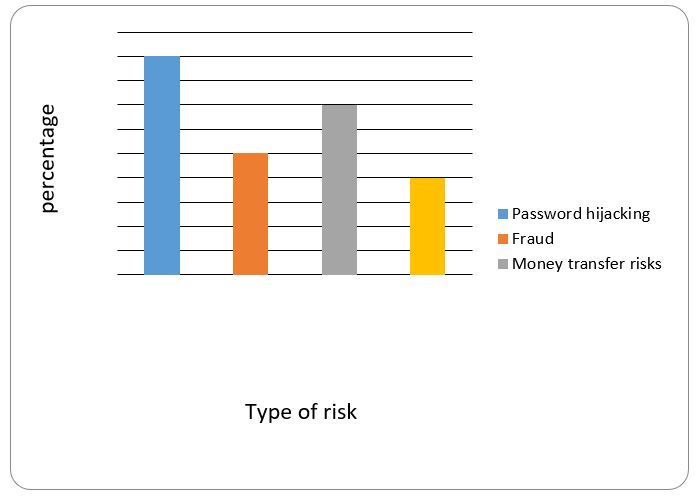
According to the interview results from VietinBank employees and clients, internet banking transaction risks include password hijacking, fraud, money transfer risks and human errors. However not all risks are known to all people hence there were some risks which are widely known, while others are just known by a few people. According to the interview results, 90% of respondents have knowledge about password hijacking, 70% know about money transfer risks, 40% about human error and 50% identity fraud as being a risk. This implies that the most frequent or most common risk in VietinBank is password hijacking, followed by money transfer risk, then human error during money transfer and lastly identity fraud.
According to secondary literature from Vietnam, similar internet banking transaction risks are outlined. Meaning that literature data indicate similar internet banking transaction risks as these found in the interview. For instance, Vietnambusiness.asia (2011) and vietnamsociety.dztimes.net (2011) identified vulnerabilities of network securities in VietinBank internet banking. It is argued that “vulnerabilities in the money transfer function may make the fall victim to fraudulent money transfers” (Vietnambusiness.asia, 2011). On the other hand, vietnamsociety.dztimes.net (2011) adds password cracking and network criminology as being other internet banking transaction risks. Moreover network securities installed by most Vietnam banks VietinBank being among them are much vulnerable to network criminals. Going with these results password cracking is the major internet banking transaction risk.
These risks are not far from what has been experienced from the other parts of the world. Other parts have experienced fraud and error in their internet banking transactions. According to Carmichael (2011) human error is the major internet banking transactions. This issue of errors has been mostly resulted from the bank itself, as some of bank employees are incompetent.
On the other hand, Carmichael (2011) supports the notion found in the interview that password hijacking leading to fraud most common internet transaction risks. He argues further that, this risk has been as a result of various quarters, though they are mostly done online. In supporting this point, Koch (2009) states that, Transaction risks in internet banking are as a result of several issues surrounding fraud and errors. Such risks have been present in almost all products offered through internet banking; however its origin is process development, poor planning and implementation of mechanisms aimed at mitigating such risks. This implies that interview result, literature from Vietnam concur that internet banking transaction risks like hijacking, fraud, and human error are real, and has been occurring in different parts of the world. This risk of fraud usually happen in two ways, first, attackers may exploit the software weaknesses of the bank’s internet banking platform, and secondly, attackers may devise ways to gain unauthorized access to the internet banking platform. To use the two ways, hijackers usually sniff, guess passwords, brute force, random deals, social engineering, and hijacking. Fraud has also been as a result of launched viruses, spyware, Trojan horses among others malwares. To use these elements, hijackers implant just one server at the beginning, but after some time, these elements start spreading to other sub-servers through networks like local area network. According to the theoretical model of building trust, the identity theft as well as cyber crimes are the major factors affecting internet banking worldwide.
According to vietnambusiness.asia (2011), most of these risks are mainly as a result of two major reasons, namely: inadequate security assessment of online banking systems, and application of security information systems that are of low standards. However, Nguyen, Et al. (2011) states that these risks originate from process development, poor planning and implementation of mechanisms aimed at mitigating such risks. Moreover, existing vulnerabilities in network securities at Vietnamese commercial banks was attributed to the deficiency of an independent security evaluation process of internet banking systems as well as a deficiency of standards on information security (vietnamsociety.dztimes, 2011).
Literature has divided internet banking risks into two categories. The first category comprises of all risks whose causes originate from the banks operations. According to Carmichael (2011), bank clients in other parts of the world have been experiencing the risk of enrolling for financial services which their banks ends failing to offer through their internet banking transaction services. In addition, risks in this category arise due to the fact that most clients using internet banking transactions are usually impatient when it comes to matters of tolerating error instances on the bank’s side. Such clients expect that since internet banking does not involve human subjects like incompetence, it should be error free and prompt. However, this error does not only occur on the banks’ side, there are errors which occur as a result of client mistakes as experienced in the interview.
Other parts have experienced error in their internet banking transactions. According to Carmichael (2011) human error is the major internet banking transactions. This issue of errors mostly results from the bank itself as some of bank employees are incompetent.
The second category of internet banking transaction risk comprises of all those risks that are due to external forces, usually mastermind by third parties who intend to attack on the bank’s internet banking platform to steal vital information or funds from unsuspecting customers (or even from the bank itself) (Carmichael, 2011). This category comprises of risks like fraud, and hijacking among others. On the other hand, Carmichael (2011) supports the notion found in the interview that password hijacking is the leading risk commonly experienced by banks that offer internet banking transaction services. He argues further that, this risk has been as a result of various quarters though they are mostly done online.
Internal provisions that can be formulated to curb transactional risks in VietinBank
Just like risks, client’s response and employees’ response in this section were also combined. This was because the responds from the two parties were similar. Table 1 indicates what VietinBank has done to minimize internet banking transaction risks and the percentage of those who proposed the strategy.
Table 1: Proposed strategies which can be used by VietinBank in minimizing internet banking risks
Going with the results shown in table 1 above, 60% of VietinBank employees and clients proposed that, the bank should start using password recovery systems, 40% proposed that the bank should apply information security systems which have ISO standards, 95% proposed the use of computer anti-virus, 70% proposed the use of digital signature certification, 60% proposed that the bank should start installing dangerous codes into their server, and 90 percent of respondents proposed that VietinBank should start assessing its network security systems independently with the aim of determining its weaknesses.
Nonetheless, when reporting about Vietnamese internet banking insecurity, vietnambusiness.asia (2011) and vietnamsociety.dztimes.net (2011) support some of the strategies proposed during the interview. It argues that, if Vietnam’s banks want to reduce or minimize money transfer risks, they should start utilizing password recovery systems in their process of changing the password of account users. It is clear that the internet banking transaction risks have been increasing since 2009 in VietinBank because the bank has not been caring about its client’s passwords. As a result, it is high time for banks like VietinBank to start applying questions as well as consumer response complaint forms when installing dangerous keys into their servers with the aim of controlling internet banking transactions. In addition, the site highlights that, banks should start carrying out independent assessments on their network security systems to determine their weaknesses. It is also recommended that banks should perform ISO 27001 standard on information security management, all computer anti-virus solutions and application of digital signature certification to curb transaction risks in the bank (vietnambusiness.asia, 2011). In implementing this strategy, VietinBank Group (2011) states that equipments used in data security will be of higher quality, hence minimizing equipment weaknesses which have been utilized by hijackers in getting into the system.
Koch (2009) agrees with the findings highlighted in Vietnam literature as well as in the interview results. He argued that banks should be assessing the level of their security systems regularly to ensure that some of sensitive and classified information is not be accessed by attackers. As a result, banks should be providing reliable security mechanisms to secure such like information. Some of these mechanisms include using standardized information security systems. Though internet firewall can provide such safeguards, by they are not adequate for internet banking transaction risks. Contrary to other places where banks are using sophisticated firewall with the aim of controlling specific internet banking transaction risks, VietinBank is yet to implement this strategy. By borrowing what Koch (2009) suggested about authentication, VietinBank has tried to use Authentication measures in the process of accessing internet banking systems. The bank has tried to achieve this through assurance of personal identification numbers (PINs), but encoding data and biometrics data has not been implemented in this bank. Though PINs are being used by VietinBank, but some and bank employees claim that they also have their own weaknesses, hence, clients have been exposed to lots of dangers as their accounts can be accessed by unauthorized individuals.
However, results found during the interview as well as from literature can be used to explain building trust in e-banking theoretical framework. For instance, the model talks of privacy and security as being the major factors affecting the user interface. This implies that, when banks implement these proposed strategies of minimizing internet banking transactions, they will be providing security and privacy of user information. In case these objectives are achieved, more and more customers will be attracted to internet banking transactions.
External provisions that can be formulated to curb transactional risks in VietinBank
Table 2 bellow indicates what Vietnam government should do to minimise internet banking transaction risks, and the percentage of those who proposed the strategy.
Table 2: Proposed strategies which Vietnam government employ to minimise internet banking risks
Interview result shown in table 2 above indicate that 60% of respondents proposed that the government should ensure that banks update their internet network security on a regular basis, 80% proposed that the government should ensure that only standardised network security technologies are applied in internet banking transaction risk management, 90% believe that, if only reputable banks are licensed to conduct online banking activities, then online banking transaction risks will reduce, 70% believed that the government should limit the geographical area of internet banking operations, 90% proposed that the government should call upon banks to start educating their clients on matters concerning internet banking security systems and measurement, 60% made it clear that the Vietnam government should make it compulsory for banks to be providing internet transaction audit reports to the them (government) regularly, and 40% called upon the government should ensure that banks offering internet banking transactions are providing legal documents concerning their plans.
Vietnam literature has also confirmed this results, for instance, Clayton & Waldron (2003) stated that, Vietnam government through the State Bank of Vietnam has been ensuring that all banks providing internet banking transaction have advanced technologies for security protection. In addition, the government also introduced a standardised design of bank identifier code, SWIFT, though most banks have not complied with this regulation. So it is the responsibility of the government to ensure that this is followed to the later. Nguyen, Et al (2011) adds that, the number of banks which the government has permitted to operate internet banking service are very few. The criterion of permitting such banks is based on banks reputations and capacity to implement security measures on their services.
When discussing internet banking transaction risk solutions in different countries, Petrus & Ndubisi (2006), stated that most countries are suffering from internet transaction insecurities public awareness in such countries is very low. Most people in such countries do not understand risks encountered during internet banking transactions. This can be proved by interview results which indicate that some internet banking transaction risks are unknown to some clients and bank employees. As a result, government should start forcing banking institutions offering internet banking transactions to start educating their clients about the risks involved in their services. Banks should also educate their clients on different security strategies that have been put in place by banks to minimise such transaction risks.
When looking at internet banking in India, Petrus & Ndubisi (2006) identified that banks have been called upon by the government to implement risk analysis by recognizing information systems assets, vulnerabilities and determining security threats, estimating the likelihood of attacks or exploitation, evaluating potential losses combined with these risk events and taking suitable security measures and controls for asset protection. In line with these regulations, India’s reserve bank only allows banks having physical presence in India to undertake these services. This is in line with what clients proposed. This policy is very effective in ensuring that in case of fraud from a certain bank, it is very easy for the complaint to access the bank physically. In addition, in India, online banking operations are only allowed to take place within a limited local area, hence international al online banking are not allowed to take place in India. This is similar to what was proposed during the interview. In addition, Indian banks are also not allowed to use third party correspondents who are not approved by the reserve bank; as unauthorized third parties are not allowed to undertake any activity in this capacity. This is very important because unregistered third parties have proved to being headache especially when a risk occurs. Such parties might not appear in case they have engaged in fraud cases.
In addition, Petrus & Ndubisi (2006) concurred with the interview results by confirming that, in Vietnam not all banks are allowed to provide internet banking services; only banks which have provided core banking solutions are allowed to do so. Similarly, all banks providing internet banking services are called upon by the central bank of Vietnam to provide suspected transaction reports to the relevant authorities for an evaluation of the transaction procedures.
In addition, though the Vietnam Central bank is has regulated internet banking transactions, but it’s level is still low as compared to what has happened in Mauritius and India; the Bank of Mauritius has set guidelines that aim at reducing internet banking transaction risks. These guidelines have been of great help particularly in financial sector, creating confidence in online banking, as well as encouraging banks to educate their clients about the significance of upholding online security standards for privacy and secure money transfer. However, the difference between Mauritius and India is that, in Mauritius, every bank is permitted to carry out online banking operations, as opposed to India’s case where the operations are limited to only a few banks.
In Mauritius, apart from providing periodical reports explaining how they have been performing as well as implementing internet banking guidelines, Banks are also required to abide to online banking guidelines. For instance every board ensures that, the bank’s internet banking strategy complements the overall vision of the bank (Koch 2009).
Most of these guidelines provided by the Bank of Mauritius, aims at providing data privacy and confidentiality, integrity as well as authentication to ensure that unauthorized individuals do not get access to internet banking platforms. The bank has recommended the use of various identification methods as is a way of improving security levels. In line with interview results concerning internal measures VietinBank can implement to minimise internet banking transaction risks, banks are called upon to review their authentication measures regularly. According to Koch, (2009), Mauritius banks are required by the government through the Bank of Mauritius to always provide audit trails. They are also called upon to implement detection and prevention programs against any form of attack.
On the other hand, building trust in E-banking theoretical framework also supports these guidelines. The framework assumes that reputable and big banks have the capacity of providing security measures with the aim of providing privacy and confidentiality of user information. This implies that, states should only allow banks having good name as well as capacity to implement security measures to operate internet banking transactions.
Conclusions and Recommendations
This dissertation was investigating strategies, through which transaction risks in internet banking can be minimised, a case study of VietinBank in Vietnam. The results from interview as well as Vietnam literature have indicated that, most people using internet banking in Vietnam are in the age bracket of 46 to 55, and the least population using the transaction are in the age bracket of 17 to 25. However, most people are motivated to engage in internet banking because of its speed, convenience, and low costs. However, VietinBank launched internet banking transaction services with the aim of gaining competitive advantage.
Moreover, the study finds that internet banking really exist in VietinBank, some of these risks are unknown to some clients and even employees. Amongst the risks facing the operation of internet banking in VietinBank include password hijacking, Fraud, money transfer risks and human error. However, the most common risk on this list, password hijacking. This is because, 90 percent of respondents are aware of it. Password hijacking is considered as being the more risky because the bank has failed to put in place security measures to deal with it. The bank is not using sophisticated firewall to deal with the problem. On the other hand, the least known risk is human error; this is because only 40 percent of the people interviewed mentioned it. This is attributed to the fact that most people assume that making an error in internet banking is not a risk, but in real sense, it can make one expose his/her sensitive data.
Though the Vietnam government has tried to come up with rules and regulations governing internet banking transactions, but these rules are still not enough to curb this problems, there is still more for the Vietnam government to do as this report will recommend.
According to the survey carried out on a sample of 100 people (50 VietinBank employees and 50 VietinBank clients), confirmed with the available literature on matters concerning internet banking transaction risks. According to studies which have been carried out in other parts of the world like in India and Mauritius, similar risks were identified. This implies that, these results can be generalized to represent the kinds of risks encountered by banks offering and clients using internet banking transactions. So, to minimise these risks, this dissertation recommends that VietinBank should:
- Be assessing its security systems on a daily basis to determine its weaknesses to ensure that classified and sensitive information does not get into the hands of internet criminals. In doing this, the bank should use sophisticated intrusion detection programs like anti-virus. This will also help in controlling network traffic in real time. However, these programs should be in a position of withstanding third party attacks.
- Come up with new firewall designs which have the ability to control specific internet banking systems. In developing and monitoring of this firewall designs, competent technicians should be involved.
- Should also develop authentication measures for user identification to minimise fraudulent people who might attack internet banking transactions. It should not just relay on the use of personal identification numbers, as they also have their own weaknesses, instead, it should develop more sophisticated methods of authentication like biometrics and data encoding.
- Should also start educating its clients on the types of risks available in internet transaction, and the significance of maintaining and keeping security measures in place. However, this training should also involve acquainting them on ways of using them.
However, apart from banks, policy makers also have a role to play in minimising internet banking transaction risks, as a result, this dissertation recommends that, policy making agents like governments and states should: Come up with a regulations and policies that aim at reducing internet banking transaction risks. For instance, the state should not just authorise any bank to involve in internet banking transactions without attaining a certain level. In additional, governments should restrict geographical areas under which online banking is allowed, for instance, governments should not allow international transactions. In doing this, governments will be following what Indian government has already done.
In conclusion, in case banks offering internet banking transactions and their governments can be in a position to implement the above stated recommendations, internet banking transactions risks will be highly minimised.
References
Text book
Adèr, J., Mellenbergh, G. & Hand, D. 2008, Advising on research methods: A consultant’s companion, Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing.
Balasubramanian, S., Konana, P. & Menon, N., 2003, Consumer Satisfaction in Virtual Environments: A Study of Online Investing, Management Science.
Beiske, B., 2002, Research Methods: Uses and Limitations of Questionnaires, Interviews, and Case Studies, Manchester: University of Manchester.
Bradburn, M. & Seymour, S., 1988, Polls and Surveys: Understanding What They Tell Us, San Francisco, California: Jossey-Bass.
Breakwell, G., Hammond, S. & Chris, F., 1995, Research Methods in Psychology, London: Sage.
Carmichael, D., (2011), Accountants’ Handbook, London, John Wiley and Sons.
Casalo, L., Carlos, F. & Miguel, G., 2007, The role of security, privacy, usability and reputation in the development of online banking, Online Information Review.
Clayton, L. & Waldron, B., 2003, E-commerce adoption and business Clayton and Waldron, E-commerce adoption and business impact: A progress report. Economic Trends.
Creswell, A., 1994, Research design. Qualitative and quantitative approaches. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage.
Jarvenpaa, L., Naom, T. & Vitale, M., 2000, Consumer trust in an Internet store: Information Technology and Management, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Keman, H. 2008, ‘Comparative research methods’, in: D. Caramani (ed.), Comparative politics, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kotler, P., and Gary, A., 2010, Principles of Marketing, 13th edition, Pearson Education, USA.
Kotler, P., et al. 2009, Marketing Management: An Asian Perspective, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall, Singapore
Koch, T., 2009, Bank Management, London, Cengage Learning.
McNabb D. E., 2004, Research Method for Political Science, USA: M.E.Sharpe, Inc.
Miles, M.B. & Huberman, M.A. 1994, Qualitative Data Analysis: An Expanded Sourcebook. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications, Inc.
Zikmund, W. 2000, Business Research Methods 6th Edition, Dryden Press: Ontorio.
Graziano, AM and Raulin, ML, 1997, Research Methods-A Process of Inquiry, 3rd Ed., New York: Addison-Wesley Educational Publisher Inc
Kotler, P. & Gary, A. 2007, Principles of Marketing , 12th Edition, Prentice Hall; Person Education South Asia Pre Ltd.
Yin R.K. 1994, Case Study Research, Design and Methods 2nd edition, Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications
R. Copoper, D and S. Schindler, (2008), Business Research Methods (Tenth edition) The McGraw – Hill International Edition, New York, USA
Sekaran, U. 2003, Research Methods for Business – A skill building approach, Fourth edition, John Wiley and Sons, Inc, USA.
Sekaran, U. 2002, Researcher Methods for business, 3th edition, John Wiley and Sons, Inc, USA.
W.Lawrence, N. 2000, Social Research Method: qualitative and quantitative approach (Fourth edition) A Pearson Education Company, USA.
Taylor, S. & Bogdan, R., 1998, Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods, New York: Wiley, 1998
Saunders M, Lewis P. & Thornhill A 2000, Research Methods for Business Students 2nd edition, Essex. Pearson Education Limited.
Saunders, M; Lewis, P and Thornhill, A, 2009, Research methods for business students, fifth edition, Pearson Education Limited, UK.
Journal
Azouzi, D. 2009. The Adoption of Electronic Banking in Tunisia: An Exploratory Study. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, vol. 14, no.3, pp. 1-11.
Doney, P. & Cannon, P., 1997, An examination of the nature of trust in buyer-seller relationships, Journal of Marketing, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 221-236.
Gerrard, P., Cunningham, B. & Devlin, J., 2006, Why Consumers Are Not Using Internet Banking: A Qualitative Study, Journal of Services Marketing, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 77-96.
Gronroos, C, (1984) A service quality model and its market implications, European Journal of Marketing, vol.18, no.4, pp. 1221-1236.
Mermod A.2011. Customer’s Perspectives and Risk Issues on E-Banking in Turkey; Should We Still be Online? Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, vol. 16, no.1, p. 1-15.
Mukherjee, A. & Nath, P., 2003, A model of trust in online relationship banking. International Journal of Bank Marketing, pp. 302-326.
Nath, R., Schrick, P.& Parzinger M., 2001. Bankers’ Perspectives on Internet Banking. e-Service Journal, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 21-36.
Petrus, G. & Ndubisi, N., 2006, Borneo online banking: evaluating customer perceptions and behavioural intention, Management Research News, 29 (1).
Rahmath, S. 2010. Customer Perspectives on E-business Value: Case Study on Internet Banking. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, vol. 15, no.1, pp. 1-13.
Yu, J., & Cooper, H., 1983, A quantitative review of research design effects on response rates to questionnaires, Journal of Marketing Research, vol. 15, no.1, pp. 11-23.
Website (Online resources)
Charlton Media Group, (2011), “VietinBank Gains VND4.4T Profit Before Tax”. Web.
Chang, T., 2004, “Dynamics of Banking Technology Adoption: An Application to Internet Banking”. Coventry: University of Warwick Press. Web.
Chun, W and Zheng W, (2006), “The impact of Internet on Service Quality in the Banking Sector”. Web.
Dyk, D, 2011, “Internet Banking Fraud Risks”. Web.
Khan, M.S., Mahapatra, S.S. and Sreekumar (2009) “Service quality evaluation in internet banking: an empirical study in India”. Web.
Hanh, BT (2003) “E-banking in Vietnam: Real situation and solutions”. Web.
Guerrero, M., Egea, J., &González, V., 2005, “Profiling the adoption of online banking services in the European Union”, Journal of Internet Business. Web.
P. Munhurrun, P. Naidoo, (2006), “The Impact of Internet Banking Service Quality on Satisfaction and Behavioral Intentions”. Web.
Panan, L; Prasong P. and Natsapun, P. “A Quality Study of Internet Banking in Thailand”. Web.
Sang, L.H, Seung B, “Antecedents and Consequences of Service Quality in Online Banking: An Application of the SERVQUAL Instrument”. Web.
Nguyen, TPT (2008) “Service quality of E-banking – Comparision between Servqual and Gronroos”. Web.
Nguyen, VH (2008) “Promoting the staff quality in the Bank for Investment and Development of Vietnam”. Web.
Nguyen, T. 2011, “Assessing E-commerce in the Commercial Banks in Nam Dinh, Viet Nam” – Adopting TAM Model. Web.
Journal of Public Transportation, (2010) “Determinants of Customer Satisfaction on Service Quality: A Study of Railway Platforms in India”. Web.
VietinBank Groupd, (2011), “Press Release of Initial Public Offering by Vietnam Bank for Trade and Industry – VietinBank”. Web.
Vietnam Today, (2010), “Nova Scotia Bank buys into VietinBank”. Web.
Vietnambusiness.asia, 2011, “Vietnamese Internet Banking Proven Unsecured”. Web.
Vietnamociety.dztimes.net, (2011), “Hackers pose growing threat to internet banking system”. Web.
VietinBank (2008) “Annual Report 2008”. Web.
VietinBank (2009) “Annual Report 2009”. Web.
Thao, LT (2008) “The service development in Asia Commercial Bank (ACB)”. Web.