Abstract
Team learning is essential to enabling for an active Business lives. ‘Has team learning increased productivity of the staff of Royal Mail’ depends on the causal motivation of the transaction learning method. The management theories demonstrate that the risk of both public companies and their stockholders are well diversified and become more competitive and complex. To get recompense in this competitive world organisations are enchanting different tools and theories. Team Learning is one of the wide rapping cultured practices in modern business. Team learning indicates to gathering the skill to resolve diverse nature of problems arisen in business by a group of inhabitants.
The present dissertation “Has team learning increased productivity of the staff of Royal Mail” aimed to investigate the implication of implement team learning and draw conclusions, which will support the development of a business plan and the proposal for the implementation of team learning. With this exposure, this study has undertaken a review of the literatures regarding team learning and identified the clear areas of consideration in this regards. A crystal clean justification has been provided for implementing Team learning and devises a logical business case.
The aim of this dissertation is to explore the implications of Team learning within the Royal Mail’s setting and develop a business case for service improvement. As part of Author’s role as a lead in Management Team/ Advanced Practitioner in team learning, is responsible for exploring and developing new ways of working to ensure service remains management focused and in doing so addresses the requirements of the managers and stakeholders.
The author has essentially assessed knowledge alteration making use of relevant change theory of team learning. It has emulated on author’s role in service development, orientation to leadership as well as collaborative working. The decision making of team learning evaluating appropriate factors those has implemented in Royal mail and need to expand existing service.
Problem Statement
Introduction
This dissertation critically illustrates the perceptions and attitudes of team learning factors touching their motivation and exploration within the organisation. The dissertation has been contained the six major episodes described below
Problem Statement
This episode introduces the dissertation’s organisation with a study in wide-ranging, endow with the underlying principle and hypothetical agendas for the research; asks the research questions and affirms the limitations and scope of the study; delineates and specifies the terms used within this present dissertation.
Literature Review
This installment launches with a chronological indication of team learning and its motivation theory; then, recites too more up to date literature integrating modern theories and expression on accomplishment of success factors including productivity and project motivation; illuminates what the research would add to the configuration of knowledge in the field of learning.
Research Methodology
This episode furnishes the explanation on how the research has been conducted, describes position and population selection, data assembly, analysis and treatment, give explanation of the process and states limitations.
Result/ Findings
This segment of the dissertation specifies the collected data and enlightens the results in reflecting to the research questions; denotes unexpected results by concreting on the findings as well as hypothetical uses for the information delivered from this learning and proposes idea generation for the research.
Discussion
This section analysis the methodological hypothetic and summaries the process with business proposal; provides key recommendations and advises sensible outcomes.
Conclusions
This final episode constructs the findings; develops a qualitative analysis of the data and promotes conclusions as well as implications of this study.
Background of Problem
The Independent (2008) reported that the Dutch postal service company TNT has expressed its interest to buy 33% of Royal Mail where the investment should go for materialisation of Royal mail. The Business Secretary John Hutton supported that the part privatisation of Royal Mail would bring benefits for all stakeholders mentioning that it would defend the collective service for consumers and provides Royal Mail Group to new opportunities of modernise, service development and amplifying profit. Consequently, Royal Mail would turn into the market leader of resourceful postal operators in UK and its staffs would gain a further safe and sound pension arrangement. Lord Mandelson the business secretary added that by this venture the Royal Mail would get fresh investment to reengineering organisation and the new prospects to nurture the European mail market as well as to offer new services internationally.
BBC News (2009) that the postal workers of Royal Mail have been protested in Westminster against the partial privatisation of Royal Mail. They stand against the raising capital for materialisation of the organisation by selling out its 30% shares of Royal mail. More than 120 Members of Parliament (MPs) of Labour Party has been stand against the government decision and urged to hold a voting to keeping Royal Mail Group in public sector due to apprehension of major job cut. The business secretary Hutton, J. responded that the organisational service would stay behind publicly owned. However, in an interview with BBC he argued that new investment has very much looked-for the Royal Mail, as it has been suffering scarcity of finance and in danger of collapse for money. Lord Mandelson also concentrated his views on pension deficit and added that the taxpayer may perhaps not be anticipated to financing the potential liabilities of £8 billon devoid of considering an enhancement of the performance of Royal Mail.
The Communication Workers’ Union argued that the government is trying to welcome a foreign company to sprint the Royal Mail, which is unreasonable. The Union is capable to protest any condition discernments such as when the Royal Bank of Scotland has been nationalised why the Royal Mail should be privatised. Under this protest, Prime Minister Gordon Brown possibly would face a major backbench revolt for his favour on the bill and going to be face the most horrible threat of reelected. Too many former ministers and acting Members of Parliament have supported to the protest of the union. The Unions also argued that the Royal Mail produced a vigorous profit in 2008 and capable to overcome the needs of its materialisation costs from its own profit. They are worried about possible job losses and the impact of the private sector involvement on the universal service. BBC (2008) also added that not only the union even mass people are also eager to see the Royal Mail has been kept in the public sector without any question of privatisation.
Under such dilemma as an experienced postal operator of UK Royal Mail would like to warm up with its team to carry out highly required investment for modernisation as well as augmented efficiency including its management expertise to facilitate the organisation to be converted into a strong and practicable postal player of the future. The current financial downturn has also added a new dimension of the dilemma. Team learning is a development tools that Royal mail is use to practice. Thus, under the recessionary economy the question ‘has team learning increased the productivity of the staffs of Royal Mail?’ is a most shocking question for Royal Mail
Rationale for the Research
Kiedrowski (2006) states the improvement and changes in organisations are always unpredictable, uncertain, and turbulent business conditions with comparing the source of competitive advantages. The absence of organisational learning can create lacking of capability and disposition in measurement of progress in learning organisation and organisational performances. Senge’s learning organisation interventions in an organisation that developed for lack of quantitative assessment, also match with qualitative case of LO interventions, including quantitative measurement. Therefore, employees with truly desired results can create the purpose of Senge in organisational changes.
Loo and Thorpe (2002) stated that reflective learning, where teamwork is difficult for conflicts between members and leader of the team. It can be managed partially by training, communicating between team and leader’s skills and first stage is creation of awareness. This means consciousness about the positive attitude towards different learning situation. The next stage is critical thinking. Here individuals analyse the present condition and make clear perceptions about it. They evaluate and examine the situation and correlated it with their growing self-awareness. The final stage is the outcomes of the two stages, which is the Learning.
Loo and Thorpe (2002) also added that awareness is a present situation and critical thinking connects this present with the past and the upcoming future. Learning is the future aspects. Different journals help to establish these theories. Safe environment is another issue, which certifies the supportiveness of the teams. Communication within the teams, leadership and initiative, management skills and personal improvement, conflict between individual and tem work and stresses in teamwork are the key influencer of learning according to this theory. Royal mail can increase their effectiveness by diminishing the stresses in work place. Royal mail can achieve the learning by create awareness of the individual and analysis of the situation.
Yeo, R., (2002) illustrated with evidence to mail operator companies that the situation is particularly annoying because the learning perhaps the most essential indicator of their internal staff development. When team learning and team building moderate the risk of low productivity and consequently the value of firms should increased as the predictable operating cost should be reduced. Thus, team learning can help to safeguard the financially distressed service organisations of the mail market. When the buyers with more than enough capital or with free cash flow settle on their potential targets cautiously, the value would rise since the transactions may possibly have the potentials to strengthen their core business. This would also convey them diverse business by enhancing their market influence, and give them service benefits.
Sun, Y. T. P., & Scott L. J., (2005) provided an explanation for why team learning may create value. It anticipates that when contracts of two firms are imperfect, firms may desire to purchase the assets of the other firm to get hold of a greater fraction of surplus from the investments including major nonhuman assets. It also predicts that extremely balancing assets must be kept under common rights. The pre-existing interactions are quite familiar among firms that practice team learning. For instance, the Royal Mail may have already owned some of the equity of the target and the integration of team learning may create more value than usual.
The Daily Telegraph (2006) stated that the strategic vision and objectives of Royal Mail is to gear up forward motion of the process to finding, interview, selection and hiring 40,000 personnel with in a year. Royal Mail is also eager to considerably trim down the cost of staffing, get better the quality of workforce hired as well as condense employee’s turnover. Royal Mail also looked for to shift from the traditional human resource recruitment strategy to a direct online strategy with effective learning integration. To achieving this strategic goals, Royal Mail has to face the challenge of keeping it as a quite public organisation with essential mineshaft to the technique Royal Mail has to engage the highest use of its all primary resource at the same time. It also needed to look for to invest in new technology in order to compete when it rational to investigate the team learning outcomes on the staffs of Royal Mail.
Research Question and Objectives
This study has designed to respond the subsequent research questions. What factors most influence to establish team learning within the organisation its effectiveness, effective solution, acceptable to the stakeholders and to understand the potential barriers of implementing team learning. The answer to this question would enable managers to organise the workplace environment toward greater motivation and increased productivity of the organisation. Four research objectives are listed as below-
- To determine what factors most influence firms to make Team learning and Team learning effective.
- To determine whether those factors are consistent over time cost effectively
- To identify what actions considered most appropriate to increase productivity and acceptability of Team learning at Royal Mail.
- To ascertain whether Team learning creates value to explore a speedy drive for Royal mail
Scope and Limitations of the Study
Kolb, D. A. (1983) argued that the Reflective Observation would be based on solid experience gathered through four stages of learning that has been presented with his theory of learning cycle. The reflective observations would lead to an abstract impression and then vigorously tested with trials. The primary objective of this study is to explore the implications of implementing Team learning and within the departments of Royal Mail and develop a business case for its service development. As part of author’s role as a Management professional, the author is responsible for exploring and developing new conducts of working to ensure team learning and team effectiveness that remains value adding focus to the organisation and by doing so addresses the needs of the managers and stakeholders as well.
The quality of these studies has varied considerably. Cohen, L. et al (2007) stated that some qualitative studies posses a small figure of participants and selection was not random. For illustration, one cross sectional research interviewed only five managers. With reference to poor number of managers, for the logistical constraints, just a sampling interviewer has been used to determine the follow a line of investigation data. Sekaran, U. (2006) mentioned that the data gathered from the wide-ranging survey has collected over the time from an inadequate sample of respondents. The scope of research questions deal with the present study possibly sometimes limited.
On the other hand, in spite of the variability of all studies have comparable findings. It is outstanding that the findings would support each other strappingly irrespective of whether the studies have been conducted by using qualitative or quantitative approaches. The unstructured temperament of the open-ended survey questions as well as resulting free-form responses initiates opportunity for misinterpretation of the responds and creates the possibility of excessively broad grouping of the responses keen on factor categories. The results have been aggregated within the standard factors as reported in the Findings section of this paper.
Time is also a limitation for this present study. A larger response rate from the supervisory survey has been pleasing, as a more methodical random sampling plan for the workforce surveys. Nevertheless, from the consistent nature of the results, this researcher doubts that a more sophisticated sampling plan or more wide-ranging research design would show the way to extensively different conclusions.
Interestingly, the managers from various geographical region and ethnic background have been shared similar views. These are the significant considerations for planning Team learning and staff’s productivity.
The review advocates that the managers would be in favour of Team learning and increasing productivity of the staffs when they think it in common can happen to any organisation could be asymptomatic as well as has long-term effects.
Today team learning underpins the success of leading companies in the UK like no team learning, no growth. The landscape team learning has shifted considerably over the last few years. The fast growth of private equity and increasingly positive interest taken by overseas investors in the performance of public companies and growth of globalisation are coming collectively to remodel the dynamics of mail marketplace. This is pretentiousness of enormous challenges for the management of the Royal Mail. This paper would go for discussing some of these challenges and how to succeed in the new environment is specialising in Royal mail. What are the main areas of weakness of Royal mail? It may not be accurate to pronounce that there are just general weaknesses diagonally the patched. The realities for all businesses function in changing period and shifting environments. The mail market scenarios are moving very dramatically.
Definition of Terms
Although Team Learning and Group training are frequently expressed in the same breath and used as they are synonymous but in legal sense the terms team learning denote somewhat different things. All the way through this report, with respect to the survey results, the words: “Team learning,” Revans, R. W. (1991) defines Team learning is an edition of action learning on condition that the solutions to business dilemmas by raising an open approach to questioning and arrive to the solution. The course of action of Team Learning identifies the key questions to be addressed. They then seek to use their resources to find the answers by knowledge sharing among the team members.
Summary
This episode describes the perceptions and opinions of Team learning concerning value addition to the organisational factors touching their motivation and exploration. It also provides the Background of the Research including Research Question and Objectives including the scope and limitation of the Study.
Relevant Literature Review
Overview of the Topic
This literature review has been incorporated the writings, research and scholarly opinion concerning the description, dimension and evaluation of team learning and team learning management. The design and motivations are associated to creating value of the organisation and the overall success of team learning. It provides the background desirable for evaluation of what team learning and team learning factors are most significantly persuade the organisational success.
The scrutiny and illumination of contemporary researchers concerning team learning and its motivation, programme strategies and acceptance and effectiveness are also discussed simultaneously. The chronological theories as well as modern approaches form an unyielding foundation from which it is deliver a research study. It has further distinct a business proposal and the implications of changes in practice.
Scope and Limitations of this Review
The research works replicate the authors and researchers paying attention in the description, dimension, evaluation of team learning as well as team learning management within the organisation and its resultant effects in the organisation. The report highlights on studies those converses on the implications of change in practice, to the organisation’s service development, knowledge utilisation, and skills in change management. The extraordinary emphasis has been laid upon the fruitful reception and the management excellence. The both remarkable and contemporary writings are reviewed with added concentration provided to those authors’ theories. These theories have accomplished massive acceptance otherwise have been mostly simulated. The special attention also has been given to generate a Business Proposal as well as Service Development Plan.
With massive width of literature concerning team learning, this evaluation has been limited to the mainly sustained theories as well as established principles. It has just a prototype of the mass of team learning literature. Similarly, the extensive assortment of beneficial writings related to organisational success where management are effectively necessitated. This review has been taken out from principally mainstream works of time-honoured authors. The underlying assumptions for building these limiting selections are that the management professionals are implicated in unique, singular thoughts on team learning and managers motivations.
Organisation of the Literature Review
Hong, J. (1999), and Clutterbuck D., (2003) argued that Team learning is a way to learn something in a group of small numbers of people. Bang, T. Y. (2008) expressed that it is a multiple process of conjunctive and mutually dependent activities, which are done through experiment, insightful communication and knowledge codification. Bang, T. Y. (2008) also suggested that in these processes of tem learning, the members of the team get and share extraordinary knowledge and information and test what is useful and what is harmful for the collective performance. Teams are now being given autonomous power and authority. Chan C. A.C. Pearson, C., and Entrekin, L., (2003), said that the reason is that, team learning gives the ability to cultivate numerous numbers of knowledge, innovative ideas, experiences and communication media, as because competitive advantage is a key outcome of team learning, it is getting more importance day by day.
The employees of the Royal mail always discuss how to prevent the ongoing problems and they also learn from previous mistakes. Chan, C. A & Lim, L., (2003) argued that a team should take time in order to find the processes to develop their work procedures and after that it should communicate with all team members and should take their opinions with high aspiration. Loewen, P., & a Loo, R., (2004) argued that there should have a unity among the teams of any organisation in order to meet the organisational goal and in this stage, they should contact with people who are the beneficiary of the organisation. Chan C. A.C. Pearson, C., and Entrekin L., (2003), argued that there are many differences among the concept of the team learning, organizational learning and individual learning. Jennet, B., (2001) and Chan, C A., & Lim, L., (2003) argued that organizational learning possess the ethical issues, shared vision and corporate social responsibility. Jennet, B., (2001) also stated that in case of team learning all the response should come publicly but most of the time it comes privately.
Senge, M. P., (2009) was first introduced the term ‘learning organisation’ in his book The fifth discipline where he mentioned that the procedure of team learning is the way of aligning and increasing the capability to make the truly desired outcomes. It means equality will be ensured considering the skills and the efforts of all the employees. Senge M. P., (2009) also argued that different employees have different talents and skills but shared vision for a common goal. Yazici, H. J., (2005), provides another important notion of this theory, that is teams create smooth path for getting competitive advantages and team learning brings higher productivity than individual learning.
Based on these two theories, a new notion can be introduced. The key point is that, Team learning is able to give greater opportunities in the competitive marketplace by sharing experiences and visions among the members of the group. However, the team learning will not be attaining without individual learning. Honold, L., (2006) and Senge M. P., (2009) explained that individual learning confirms a member of the team to work properly within a team and through team learning, teams confirm the competitive advantages to the organisation.
Honold, L., (2006), and Senge M. P., (2009) stated that explained that in an organisation has to take some decision mainly depending on the members involved in the decision making process and the knowledge and capabilities of the team members. Hong, J. (1999) and Briner W., (2001) Organisational learning is the way to imply the knowledge of the members in decision-making process. Learning Organisation stands for the Organisation, which continuously is increasing its capability to build its strong promises to do better in future.
The literature review of this dissertation will discuss different theory of team learning, comparison of different theories and the effectiveness of these theories for Royal Mail. Srikantia, P., and Pasmore, W., (1996) stated that the doubt and conviction are two stages of team learning, where the doubt concerned with the effectiveness of the course of action of the organisation is the primary step of learning. The subsequently stage is conviction. Ortenblad, A., (2001), argued that confusion and doubt embark on the learning process where conviction carries on the process by accommodating active carrying out tests. Both of the two are psychological states of interior effort. The magnitude of doubt is illustrates that the identifier of the correspondence among the individual learning and group conviction.
Yeo, R. (2002) explained that the organisational learning as a three dimensional sword. These three-dimensional are as flexible systems, shared vision and team dynamics. The role of leadership here is as a significant enabler. Their observation is that the learning carries system development with strategic goals designs. The learning and conversation with expression is the results of an assortment of facets of learning.
Yeo, R. (2002) presented the above the above graph aimed to interactions of shared views inside the teams including open and easier operating systems as well as quality and ability of the teams provide the learning that brings restitution and alteration in the behaviour, environment, quality and productivity of the organisation.
Ortenblad, A. (2001) argued that the organisational learning and learning organisation as two different things. He states organisational learning as an implemented systems and learning organisation as a type of organisation. Existing three distinctions are:
- In organisational learning processes and structures is “Character of the content”, where in a learning organisation it is the form of the organisation.
- In organisational learning “Amount of normatively” can be of descriptive but in a learning organisation it is normative.
- “Group of target” is academics in case of organisational learning but it is the practitioners and consultants in a learning organisation.
Chan, C. C. A., Pearson, C., and Entrekin, L. (2003) examined the effect of team learning on team performance with evidence of Australian hospital and concluded that both external and internal team learning enhanced performance within the groups. Barker, M. and Neailey, K., (1999) shaped a 4 stage team learning style. This theory entails that the failure of context of providing the lack of weightiness to plan to take into care of team learning and restrictedness of the procedure of learning appraisal the hold back team of learning. It also taken into account a few numbers of total innovations are the key characteristic to measuring the success. There are some significant contributors for the success. First of all, it makes the process out of the predisposition to be fashionable but not to making inclusive. It point toward the convivial propensity of anyone who wishes to contribute.
Barker, M. and Neailey, K., (1999) has presented the comparison among team and individual learning. They argued that the team learning is dependent relative to a position of individual learning to underneath the individual with key issue. It involves the oppressiveness of innovative thinking encouraging diverse categories ideas.
Sun, Y. T. P., & Scott L. J., (2005) mentioned the rising of blockades of knowledge relocation at various levels of the organisation with Delphi technique designed. The course of action of knowledge formation has anticipated through the illumination and move of the supported theory. Various questions on the subject of the organisational culture may create blockade to knowledge transfer. There are four stages of organisational knowledge transformation method where each of these levels with own variety.
Hong, J. (1999) states that the academies and various practices of organisational learning, formation of knowledge and management became buzzing words since 1991, which is extremely a great deal of significant for knowing competitive advantages of the organisation. For better sympathetic concerning organisational learning, the awareness regarding information-processing capacity has gathered.
Hong, J. (1999) added that the organisational learning also could be gathered by change of insight, modern structure of organisation, and current actions of the experiences of problematic situation of individuals in an organisation. The outcome of organisational learning can be benefited the organisation by:
- Well- built concept of Economic disciplines
- Measurement of manufacturing cost reductions
- Increasing production volume
- Gaining efficiency in work and external environment
Kiedrowski (2006), the improvement and changes in organisations are always unpredictable, uncertain, and turbulent business conditions with comparing the source of competitive advantages. The absence of organisational learning can create absent capability and disposition in measurement of progress in learning organisation and organisational performances.
Loo R., and Thorpe K., (2002) has developed a study of reflective learning, where teamwork is difficult for conflicts between members and leader of the team. It can be managed partially by training, communicating between team and leader’s skills.
According to this theory, the first stage is creation of awareness. This means consciousness about the positive attitude towards different learning situation. The next stage is critical thinking. Here individuals analyse the present condition and make clear perceptions about it. They evaluate and examine the situation and correlated it with their growing self-awareness. The final stage is the outcomes of the two stages, which is the Learning.
Loewen and Loo developed a study with some disciplines, where they talked about main supporter in learning organisations. Another restrain, they also talked about are personal mastery and third one is ability to recover internal view of world by mental model, fourth discipline is developed as team learning, last and fifth one is acquisition of learning in individual and group levels. This process is done by sharing, generating, evaluating, and combining members’ knowledge. There are mainly nine types of learning in any organisation:
The individual and team learning tools are used in critical process of learning, for understand and improve their learning. There are some actions taken for teams to determine meaning, reflect actions in determination of reflect and future actions based upon those actions.
However, many of the UK companies have broadly adopted this team role theory in both training department and team expansion and the evidence shows that it influenced the team performance. Chong, E., (2007), argued that the Belbin’s team role theory has maintained that high performing teams require to have all nine roles which have balanced naturally. The following diagram of the inspection of Belbin’s theory is describes both positive and negative side of high performing teams and from here it will be possible to identify, how the team members were managed their time efficiently functioning within their own remit. These types of team can successfully continue their activities under high pressure because before taking any decision they discuss the problem, and then fix their planning. From the above discussion, it can be said that the Belbin’s team role theory is effective for organisation.
Methodology
Research Methodology
Perry, C. (1998) argued that the research methodology would be carried out to make it clear the appropriate research problem has been identified as well as justified cautiously. Perry, C. (1998) also added that thought research methodology is a tertiary episode of the study but would sketch by researcher earlier then problem identification. The central intention of this chapter is to discover how the preferred research methodology would go with the main objective of the dissertation inquiry and how it would be accomplished. For all intents and purposes, there are two types of research methodology and these are qualitative and quantitative research. The quantitative researches are accepted during get hold of primary data through questionnaires. The qualitative researches are the research those are accomplished by interviews and observations. Consequently, the method facilitates the researcher to investigate the niceties of entity perceptions on particular happening.
Overview
Fisher, R. A. (1990) emphasised on regression as well as t-tests to analyse and remove the data inconsistency and randomisation to gaining the altitude of trustworthiness within the research. The topic of the present dissertation is ‘has team learning increased productivity of the staff of Royal Mail?’ This paper would go conduct qualitative research through interview of Royal Mail’s senior manager. This method would be capable to investigate bona fide information of Royal Mail.
Research Approach
Saunders, et al. (2003) addressed that the evocative research method utilises observation and surveys to make the study easier and time worthy suggesting unforeseen assumption regarding the research approach. The research approach with the purpose of developing the methodology has explicated underneath predestined upon evocative research theory as well as inductive interpretation. This is essential to enlarge the underpinning next to which the research would be deliberated, conducted, and accordingly analysed.
Saunders, et al. (2003) also supported to use Likert scale up to fifth level to scoring respondents views to enhancing the levels of trust within the research. Firstly of all it is essential to set up the research approach in order to generate a momentous qualitative methodology. The research approach embarks on an explicit design through selected strategy to get hold of the necessary information for responding to the research questions. The research approach also would evaluate the category of research design as well as data collection methods. Thus, research approach has to assemble on rational relationships without any confusion.
The expressive research has to be applied when the research questions are implicit. In this present research approach, the data dimensions are reliant on gathering of necessary information as well as the quality of the information. The effects of the research are dependent on the dimension of the events applied to collecting data as well as the variety of collected data.
It is a significant perception of qualitative research anywhere the explanation is both inductive and deductive. The inductive research embarks on with a query and look for illustrate it whereas deductive research embarks on with the dilemma by operational rearward to the answers. Hence, this research applies the inductive approach to erect the theory from the Royal Mail’s gathered data to explore possible conclusions towards team learning.
Primary research – Research Strategy
Here the engaged research methodology is a descriptive interview with one or more manager at Royal Mail in London. The author accepts as true that the interviewer would attain the entire mandatory information essential to erect an entire image of the impact of introduction to team learning service. This would be a well thought-out interview, which kept central of attention on team learning and its modifications on SCM1 of the Royal Mail and its overall productivity. Secondary research is to appraisal of published articles, previously researches and journals, which would be analysed to achieving a wider point of views on the issue.
Saunders, M. Thornhill, A., & Lewis, P. (2003) addressed that the query of research strategy uniting the moves toward as an inductive, qualitative explanation with an entrenched research strategy would permit for an enhanced data analysis. In next of kin to research strategy, the ground of strategic management has build on more than a few different schools together with perspective as well as emergent approaches. The balanced setting up of school defines the intention in advance by shaping the existing strategic position and then applying a dogmatic approach that embodies the strategic analysis expansion as well as implementation. Saunders, M. et al (2003) also argued that a strong foundation of the research as the standpoint approach is an efficient method that follows in progression. On the other hand, the evolving strategy would shape the strategy from trial, error, conducting tests as well as dialogue. This has been applied like a cyclical approach of a sequence of rationales as an alternative of being sequential and is most frequently observed in continuously analysed organisational environment and strategy. The strategy of this present research is the coherent point of view where the data analysis as well as the final recommendations follows the chronological congregation of information.
Reliability, Validity of Interviews
Firstly, why an interview with a member of staff of the Royal Mail has been given a priority surrounded by other means of data collection? The most important cause of an interview with frontline managers has been preferred amongst the other probable methods are that the author’s believe is that a dialogue would take place with one of the representatives of the organisation. In this case Royal Mail plc, would be further rewarding than any other feasible means ever since these employees would be at the peak awareness of comparative of research issues like what are the internal complexities that the organisation had to triumph over and how do they take preparation to face upcoming complications.
The Interviews
Saunders, M. Thornhill, A., & Lewis, P. (2003) identified the interview as ‘a purposeful discussion’ among two or more people, and gathering of data, which are both trustworthy and valid. Saunders et al (2003) illustrates a prearranged interview by applying questionnaires based on predestined and customary or indistinguishable sets of questions. A semi-structured interview would have a list of subject matters and questions to be covered. The unstructured interview is an informal but used to scrutinise in depth a broad-spectrum area of interest. In this present research, a semi-structured interview has been used. This semi-structured interview has been chosen for the reason that it set aside for specific data to be exposed based on the manager’s sensitivity. The semi-structured interview would be applicable in the state of affairs where the respondents’ assortment of replies possibly would be estimated and there are needs for spell out details, opinions, as well as ideas.
The interview would be formed supported by the following influential criteria
- What data would be wanted to draw out from the interviewees,
- Who are available to be interviewed and why;
- How to elucidate the aims of the interview;
- Where the interview would take place;
- Whether to pilot the interviewees;
- How to evaluate and follow up 20 the interviews;
Cohen, L. Manion, L. Morrison, K. (2007) pointed out that in an interview the questions should be unambiguous and non-threatening; the interviewee be supposed to speak more than the interviewer does. The interview should avoid complicated, double barreled, and dichotomous as well as most important questions. Zikmund, W. M. (2006) mentioned that a number of ethical implications could take place when gathering data for the duration of interviews. If it has required the interview possibly, would not interrupt into the sales staff’s private life and reassure that the analysis keeps up privacy and inscrutability. Royal Mail managers were chosen as participants for the reason that preliminary meetings with Royal Mail representatives has recognised that organisational stakeholders would accept a advantageous description of internal complicatedness and happenings those have arisen for the reason that the management strategies have been applied in the field of Team learning and Supply Chain Management of the Royal Mail Group. This would show the way of recommendations as well as possible modeling to planning for prevail over potential complications. The contributors have selected are the two managers of Royal Mail Group of London. One of the managers has been authorised for interview and the second interview is waiting for authorisation for middle to late June. The interview data would be collected all the way through scheduled deliberations with the selected managers. The managers were preferred pedestal on their schedule as well as enthusiasm to participate.
The foremost issues those are going to be move up during the interviews are as following
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): The author has taken into account that the discussion of SCM in view of the fact that the alteration or engagements of team learning in Royal Mails like the evidence of SCM implementation. In this argument the author has taken more than a few sources including trade magazines, CPA Journal as well as official website of Royal Mails as a base to a creation of relevant questions which are to be concentrated on to the interviewer.
- Information on team learning implementation in Royal: In this dialogue, the author would take the opportunity to use primary resources from the official website of Royal Mail. Another source has been taken from one of Royal Mail’s vendor of service regulatory system, Postcomm. Postcomm is the Postal Services Commission formed under Postal Services Act-2000 as an independent regulator of the postal service market as well as a non-ministerial public department. Postcomm has been offered authentication system for the Royal Mail’s team learning. Postcomm is well-known producer of authentication products for the British mail market, e-business and e-commerce integration for the all player of mail market. Consequently, apposite enquiries would be forwarded to the interviewer to expand an internal point of view of how to the best knowledge of the interviewer, the company put into operation the systems and what were the short term as well as long term alterations to which both the employees and the customers of the Royal Mail had to become accustomed.
- Productivity Issues of Team learning. In this section the author would take a consideration of all the arguments from the point of views that the built concept of economic disciplines are measured by manufacturing cost reductions, increasing production volume and gaining efficiency in work and external environment from government legislations sources. The general public opinion in other words, all potential users of the service, that have great concerns on the online service up-gradation. All the material would be incorporated in order to put up a consistent argument, which would be onward to the interviewer.
Data Analysis
Within the course of interview the entire data would be gathered from the process and prior to any actual analysis would take place the data should be pre-accepted by the interviewer as well as a senior manager of the same Royal Mail branch. Just once the approval would be gained; all the irrelevant data that has been composed during the itinerary of the interviews would be abolished in order not to generate any bias.
Reynolds, T. J., and Gutman, J. (1988) argued that the historical document research and the interview as well as the data analysis turns to ways in which qualitative information could be analysed. Reynolds, T. J., and Gutman, J. (1988) addressed this analysis methodology tenured as “laddering” for exposure means-end hierarchies distinct by these solution elements as well as connective relationships. The laddering incorporates a customised interviewing layout using first and foremost a series of bound for probes with the articulated goal of formative sets of linkages between the key insights diagonally from the range of attributes such as- (i) values (ii) consequences and (iii). The theory of linkages is the groundwork for the interview enlargement. Consequently, the classification of the interviews would follow at the same time as previously noted, where each of them has a phenomenology loom of unfolding the circumstances and responses and are categorised by features, consequences as well as value. The attributes are the explanation of the environment and episodes those would be explored by using the inductive approach along with a goal for a chronologic explanation of the renovation in management strategy. The values are the pragmatic evidence of why these alterations take place, likewise what organisational goals shaped the changes in management strategy are also interconnected to the subject matter. The consequences are treated as the domino effect. This gives a depiction of what happens subsequent to the environment and occurrences altered for the reason that the organisational goals and values are changed. By connecting these three grouping together this research would be capable to give a holistic view of Team learning modifications in Supply Chain Management of the Royal Mail and production issues.
Contingency Plans
For any unforeseeable grounds if the composed data from the interview wouldn’t work sufficient enough for analysis and to draw a conclusion, the research method would be reshaped and as beforehand mentioned a qualitative method of a data collection for the analysis would be engaged.
The qualitative research methodology more than ever non-participant surveillance methods such as questionnaire and published materials would be tailored. The foremost explanation for that alternative is the fact that this method would consent to the author to execute the research within a shorter time span. In accumulation, the motivation of employing close watch in this research for the reason that it enables researchers with an indulgent about the sensitivity of the things or inhabitants who has been observed. In order to put a stop to bias, this sovereign of a research would incorporate an assortment of acceptable resources essentially such as questionnaire and in adding up magazines, journals as well as books; those have been written by illustrious authors and researchers of all time.
Secondary Research
Sekaran, U. (2006) added that the selection of secondary sources are the published materials such as magazines, books, journals and previously execute researches would be utilised to put on the perspective at the internal and external impenetrability that Royal Mail had to overcome with the introduction of the team learning service. At the same time, it would try to answer a question what were the sort-term and the long-term compensation and shortcoming of the choices they made when integrate team-learning service.
Primary Research
A questionnaire would be assembled and sent out to the customers of Royal Mail. This would generate a broader approaching as to a feedback from the general public; the illustration would take account of the younger layer of society, age bracket stuck between the ages of 18-24. The rationale of this questionnaire is to expand an approaching to customer feedback and contribution in the online Royal Mailing activities, which would settle on their level of trust and in the safety measures provision of their Royal Mail. The most important issues that would be move up are:
- Modification in service issues, necessary or not
- The level of trust in the Royal Mailing systems,
- Future trends and potentials,
- Advantages and disadvantages of the services provided by Royal mail.
Data Analysis
Just once the data has been composed once more all the inappropriate information and data would be expelled for not to encounter any bias. The outstanding data would be checked up, weighed against and distinguished with previous research in order to finding out on the level of time how the Royal Mail customer’s point of view concerning team-learning activities has been shaped and what is the future trend of Royal Mail for team learning as well as organisational productivity?
Limitation of Data Collection
The selected data collection methods within the course of this study, the author would evaluate the strengths and limitations for apiece method and would make a decision if that method would work by means of the questions surroundings the present study. This researcher would decide on the most excellent amalgamation of methods where the limitations could be rewarded with the strengths of a balancing one.
Results & Findings
Historical background of Royal Mail
Royal mail Holdings plc is the UK government owned public limited company. In the field of mail, post office and parcels business, Royal mail has uniqueness. It has four operating units. These are:
- Royal mail
- General Logistic system (GLS)
- Parcel force Worldwide
- Post office
For 370 years, it is stretching its service and it becomes a tradition for Royal mail. It has gone through various changes for these 3 centuries. In 26 March 2001, it started its journey as a Public Limited Company. In 2004, the mail market was liberalized. After that, along with the effect of broad technological development, the volume of mail and the strength of the competition declined in January 2006. The legal structure for Royal mail has been demonstrated in Figure-1.
Present scenario of Royal mail
The mail market faces a lot of problems and threats according to the technological development of the world. In the last year, Royal mail continues its success, development, and diversification throughout the actions of the group. By the year-end, it’s delivery of mail exceeds its target for the year. From Annual Report 2008 of Royal Mail Holdings plc, the financial and non-financial overview of Royal mail can be found. The amplification of financial and Non-financial assets of Royal mail due to effectiveness of team learning has been shown in Table-1.
From the above two list, it can be noticed that, the profit after the tax was 135 million pounds in 2008, which was 286 million pound in 2007. Therefore, here is the decline of Royal Mail’s profit is very significant to asses the recessionary situation. But the external revenue was increased from £ 9179 million to £ 9388 million; however, in 2007-08, revenues come from the four sources has been demonstrated in Figure-2.
From the non-financial analysis, the most noticeable things are the numbers of complaints, which was increased in 2008, but the customer satisfaction index was increased and reached almost 100%. The most important deals for the year were the second phase modernization through automation of the letter sector, the reformation of new pension plan, new products and services introduced, first step in rollout in new technology and ongoing improvement in post-office, parcelforce and GLS sector. It is clear that Royal Mail letter business and post office faced loss in 2008. The Chairman-Alan Leighton and CEO-Adam Crozier mentioned three reasons for the losing situation in the Royal Mail
- Fall in mail volumes,
- Customers down trading to low priced and low quality products,
- Impact of high range and increasing amount of competition in the market place
In different business sector’s external revenue and operating profit/loss, comparison between 2007 and 2008 has demonstrated in Table- 1 & 2. From the above Table it is clear that, the group revenue has increased up to 209 million pounds. However, 71 million pounds decrease the Group profit. The Royal Mail was decreased the numbers of its employees in 2008. Productivity of each of the four disciplines is the key way to measure the actual success of Royal mail. According to the Royal Mail Holdings plc Annual Report 2008, the capability of handling and delivering items are shown bellow:
The effective team learning has produced efficiency in handling and delivering items during the period, no of complaints received, resolved and remain unresolved at the end of the period. Organisational learning is a continuous process to develop by information search and process of individual responses. It produces the increasing ability of searching, encoding, distributing and interpreting external information. There are four important factors should be developed in organisational learning process.
Effectiveness of Team Learning at Royal Mail
Rushmer (1997) argued that, team management Index (TMI) is helpful enough to build or make teams for organisational development (OD). It can be used as an instrument and the effectiveness of this tool can make wide procedural and epistemological initiatives to get data regarding the effectiveness of the Organisational development and its efficiency. The measurement techniques are rounded. The changes in the organisation, which are brought by organisational development and it is not represent that there is a casual relation between these. Team’s effectiveness and the effective development of teams depend on the resulting changes and organisation should be able to foster, sustain and assist the procedures of these changes.
The Royal mail’s team has with lot of practices in consultancy in the field of industries and commercialisation, by surveying on 6,000 managers over the world. In their study, they developed an analysis of key work functions with the help of psychological and learning activities. There are mainly eight key work functions used by them:
Different people perceive teamwork in different context in these functions. From these functions, they can measure their work preferences with different team roles, which have defined as Team Management Wheel. Figure-5 demonstrates that the wheel helps people to make mental map of their job preferences according with key roles in high performance. By this logo, they can view their position, where they can give their effort at best level. With the definition of researchers, every individual has a major and two minor roles in team management. These roles are described briefly in below:
- Reporter-Advisers: In team management, the correct and effective report must need to take proper actions, for that, reporter is playing important roles. On the other hand, advisors are giving their valuable knowledge and idea about any critical or decision-making situation of the team.
- Creator-Innovators: The term creator means the person who gives his/ her creativity any functions of team managing and maintaining criteria, whereas, innovators are defined as the value finder of the correct situation and criteria.
- Explorer-Promoters: The person, who can explore his / her skills to other people of the team properly, is explorer, and the person who can find out and maintain the skills of others in team in the proper situation is promoter.
- Assessor-Developers: In the team, one who evaluates the performance and results of others in team is assessor, where, developer maintains and re- evaluates the skills of people by proper training and motivation.
- Thruster-Organisers: The person, who can make and find the best opportunities in any problem, is thruster, on the other side, the person, who maintains and organise the team properly is organiser.
- Concluder-Producers: The person, who helps to reach the end product or services to direct consumers are concluder, and one who finish and give a shape to any goods properly is producers.
- Controller-Inspectors: In team management, the controller evaluates the results with the previously making standards and judges it, and inspector is analysing the results, whether there are any fraud or errors.
- Upholder-Maintainers: The person, who supports the whole team with correct way, is upholder and maintainer is keeping the team stable with motivation and best performances.
- Linker: Linker is the vital role, played as leaders in the team management.
All of these roles are important in team performances, to build up an effective team with the preferences of work in their opinion of their job area. These roles can be balanced with the team management by using strengths and compensate weakness of their works in the team.
These areas are depending on workload, power status, relevant information, frequent interaction, expected consequences and cost of distribution. The last part of processing, organisational memory changes over time, events’ success, new behaviour, and organisational capability. Levels of organisational learning can be the point of view from individual, group, and organisation, showing by the table -8
Organisational structure learning is depending on valuable and useful information in levels of organisations. The importance of structure is creating knowledge capability, determined by group dynamics and accommodation in changing process. The information processing capabilities is the fundamental way of favourable organisational design. Hierarchical structure is applicable with predictability of consistent behaviour over time. The new form organisations’, first one, N-form organisation, which defines new and novelty, with the features of:
- To put things together
- To make temporary group of people
- To give importance of personnel at lower levels
- To make creative communication and dialogue
- To focus on rich potentials in combination of knowledge elements
Another one is J-type organization
From this study, it can be concluded that, organisations are the single entities with cognitive capacity and analysis of different levels. The problem states in this study are oversimplification, which can be melted by process of interaction between different members of the organisations.
Hypothesis is built up for testing research questions, to determine employees’ acceptances of LO concepts and job satisfaction of them in Senge LO intervention. First hypothesis focuses on the improvement of employees’ attitudes and job satisfaction after accepting Senge LO interventions. Another hypothesis is concerning about the improvement of intervention organisation after accepting Senge LO in it. The measures of variables in this research are Senge LO interventions, acceptance of the concept, employees’ job satisfaction. This research is defined itself reliable by working on it 56 months. The experimental purpose of this research is valid with its instruments.
Discussion
Overview
The outcomes of the team learning service evaluation are to be used to influence practices or processes outside the instantaneous setting and the work has not managed within the Research Governance Framework of this study. There would carry a risk of the public being exposed is to changes without a sound evidence based on Royal Mail. The evaluation of Royal Mail would be generalised to other settings or populations should consequently be managed within the Research Governance Framework.
The Chartered Institute of Marketing (2008) argued that most valuable assets are the well-trained, experienced human resources that understand the business are beyond price. So that numerous companies are, structuring comprehensive competency frameworks of team learning, which would deliberate effective L&D2 programmes those, would ultimately keep hold of excellent staffs as well as impact on the corporate frontline. The CIM3 has progressively more encouraged to working with organisations to develop solutions those would meet the L&D requirements and the Royal Mail is an instance of gaining this opportunity.
The key objective of the decision makers of Royal Mail for L&D is to mark out the development needs. The senior managers of HR, Marketing and Sales of Royal Mail; provide more emphasis to recognise the value of improving inhabitants. Here the development takes place all the way through internal expertise whether the managers fit into place with an external specialist to generate a tailored L&D resolution for Royal Mail. Royal Mail has developed a competency support for its managers may previously have requirements of the sales and marketing expertise to take it ahead and rotate team learning into a precious development tools.
The developing and keep hold of Royal Mail’s HR to create an exclusive skill set for the organisation, which would ultimately produce an impenetrable and very useful competitive advantage. The new employees of Royal Mail could convey qualifications and exterior experience when the existing employees comprehend with the organisational culture, processes, measures and the fine distinction Royal Mail’s business. Coordinating the both old and new employees in team learning, they would paramount to accomplishment in modern aggressive business environment of mail market.
The Chartered Institute of Marketing (2008) addressed that the bespoke solution to acquire the results of team learning Royal Mail needs to exertion with understanding its business. Royal Mail can shape its existing training to match the needs of building a modified solution, which would fit all the members of their team learning where it would organise workshop, coaching and case study developing the team learning with the experts those can assist to discover the most cost-effective solution.
Achievement & Direction of team learning
Triad consulting (2004) mentioned that the teams are the combination or collection of people, who are directed towards a common goal. The teams organized with the mixture of small number of eligible people directed to observe, examine, apply and suggest some obvious and particular aims. Everyone of the team is responsible collectively to achieve those aims with there are different types of teams. Organisations create these types of teams to diversify different levels of skills and knowledge.
Ellis, P. J. A., et al. (2000), argued that team has differentiated people with different nature of skill, knowledge, attitudes and beliefs. The ultimate goal to develop a team is to gather these different kinds of skill and knowledge and use them to different types of situations. To do so, learning or giving and sharing lessons within a team is done. Team learning means to increase the capability of the team members to determine, accumulate and regain work related information from time to time through bringing a relative and permanent change in intensity of the skill and knowledge available in the team members. Team learning offers a simple method to learn lessons, which has many ways of conjunctive and dependant works. These works can be done through research, perceptive contact and codification of knowledge and skill.
Chan C.A.C., Pearson, C., and Entrekin L., (2003), argued that the outcome of team learning is a performance and abstract of some actions like- investigation or asking relevant questions, feedback, inspect information, discussion regarding mistakes and measuring the results. The team learning follows a critical process. The first step is to Innovate idea. In this step, various types of ideas are generated which deserves discussion and sharing of views and knowledge of the team members. Then, planning and sharing of the knowledge is come. Here, the planning of the learning process is designed and sharing of this plan with the team members is happened. The next stage is to implement actions according to this plan. Finally, the decision is being made and team-learning process completes
Strength of team learning
Edmondson et al., (2006) mentioned that the methods of learning approaches from different people used in learning process and the collection of skills and relevant knowledge are the key base where the strength of team learning relies on. These approaches differs time to time and situation to situations. It can be easily assumed that, strength of the individual of the team is the strength of the team as a whole. There are different factors, which can be drawn as the strength of the team learning. These are:
- Combination of different skills and knowledge
- Possible increase of production
- Increase of creativity of team members
- Reducing response time of the members
- Prudent decision making
- Task mastery
Edmondson et al., (2006) argued that combination of different skills and knowledge is the major advantage because a team can earn through team learning. In a team, different types of people of different discipline are gathered together. They have some unique skills and knowledge, which are not being found in other member. Therefore, by team learning these individually held skills and knowledge are being shared and thus in the workplace or in any type of problems if raised, team can use these combination of knowledge to overcome it. Thus, it is strength of team learning.
Hartenian S. L. (2003) argued that Most of the team learning is practiced in the firms and most of the firms are production based. These firms organise team learning to increase their production and supplement their operations and increases their revenues. Through team, learning there creates a possibility of increasing the productivity of the team members and increase in the productivity of the team members resulted in the increase of the productivity of the organisation. He also added that when the team members communicate their different views within the team and get proper feedback and appreciation, their creativity in those fields of expertise would increase. They tried to act as an expert as because they are sharing their knowledge with others. This increase in creativity is strength for team learning in a sense that it will facilitate future sharing of increased knowledge.
Hartenian S. L. (2003) stated that time is a key factor in a production and operation management of a firm. When a firm establishes a team, one of the main objectives is to reduce the time associated with production. When a team is being formed, the members gather relevant knowledge by sharing and become swift to response in a certain situation. Therefore, this is strength for a team learning also. The decision made by more than one person is much dependable and safe compared with the decision made by one. The reason is, one person has certain limitations in his attitudes, beliefs and knowledge but if there are many persons, these limitations are overcome and there is little or almost no chance that the decision will be a wrong one.
Edmondson et al., (2006) argued that task mastery refers to the ability to complete an assigned task as an expert. That is having extraordinary control to do a task. Teams has the way to point out shared understanding of who has what knowledge, who has the ability to do a specific task and effective and efficient interaction towards a assigned task. Task mastery remains to ensure the use of all unique knowledge by individuals, to allow specialization, to decrease disused information and to develop accountability in a structured way.
Limitations of team learning
Robbins, S. P, (2005) argued that teams have some negative sides as learning in a team is an issue of communicating, controlling and discussion within people of different types of people. So, this distinguish features of people brings some limitations to the team learning (Fig-12).
Team members are of different type of personalities, beliefs traits and self image. These differences pose some negative conflicting situations which not only hamper the working conditions but also deteriorate the production of the firm. Robbins, S. P, (2005) mentioned that these conflicts may arise between the members of the team, or with the supervisor or instructor. The decision regarding any situations may be accepted by one member and rejects some others. These also imply conflicting conditions.
Hartenian S. L. (2003) added that the team members may start to treat one another as competitor and thus irrelevant completion may arise. In a team learning process it is important to share the skill and knowledge with others. But because of competition, team members may deny sharing this knowledge and thus the total team learning process will be hampered. This unnecessary competition may arises conflicts also and sometimes hamper the ultimate goal of forming a team.
Robbins, S. P, (2005) argued that time is a crucial factor in terms of production and operation of a firm. One of the key objective to establish a team is to minimise the time needed to do certain operation. But, team learning is a time consuming process also. Establish a team, finding proper members of the team, creation of suitable environment for the team, run the learning process by hiring perfect instructors and measurement of the effect of learning are the key steps of team learning which needs time. Not only the learning stage of the team learning is time consuming but also the implementation or use the leanings of the team also requires time.
Run the team learning process is much more difficult than to establish a team. The main problem is, the team demands money to operate properly. One example may be the hiring of the instructor or creating the suitable environment for learning needs money. Team members may demand more money or monetary benefits for sharing their unique knowledge. For these, use the team effectively cut offs a good number of profits of the firm.
Present problems of Royal Mail Group
Royal mail group is a partially privatized government owned postal service which is in a leading position of mails, postal service and parcel business. It has about 181,000 employees, who are the main strength to reach almost everyone in United Kingdom. About 80 million pieces of items are delivered in about 28 million addresses everyday by Royal mail. It has 13, 852 post office branches through which about 24 million customers can be served in a week. From the annual report, 2008 of Royal Mail Holdings plc, it can be found that it has four distinctive service options available for their customers. These are:
- Royal mail
- General logistic systems
- Parcel force world wide
- Post office
The Annual report- 2008 of Royal mail provides that Royal mail group is now facing some problems regarding its customers, service and the technological support system and these problems are:
- Repeated failure in quality of service targets
- Threats from technological advancement
- Competitive ascent in Account Handling and pension payment system
- Barriers to modernise
- Competition in online shopping
- Cost for new technologies
The royal mail group set service quality standards every year. But in recent years, it fails repeatedly to achieve the target. This alarming situation deteriorating the fame of the group and customers are starting to refuse royal mail.
Royal mail (2008) mentioned that the technological advancement in communication sector keeps increasing pressure to the group. Phone, cellular mobile phone, fax, e-mail, online chatting etc become threat for the progress of the group. People now prefer to communicate through e-mail, rather the traditional mailing system. People prefer this because these are less time consuming. An e-mail can reach to its destination within a minute or less.
Royal mail (2008) added that there are many other private organisations which are giving the mail or post office facilities like Royal mail. The system of handling account and designing the pension schemes of these firms engage the royal mail group to restructure its traditional systems. For the technological advancement the mail volumes are decreasing. Thus the profit associated with the services is reducing. For this reason, royal mail can not put enough funds to modernise its service delivery and operation system. Online shopping facilities create opportunities but at the same time it increases the competition. Customers are now can easily verify many service offerings within a short time and without almost any cost. To increase the service quality, new technological instruments are necessary. Royal mail needs funds to set up these technologies. This is a key problem that is related with arrangement of funds.
Possible contribution of team learning to these problems
Royal mail practicing team based operation system and team learning for few years. Team learning can help to overcome these problems. Team members can help to avoid the challenges of technological advancement through creating innovative ideas. In a team learning process the team members’ share their views about these advancements and thus some ideas will generate which may be say how to divert the effects of the changes or to get enough profit beside the changes.
Team learning can be effective in increasing the service quality. When the team members learn trough team learning, they can communicate the problems or key reasons behind the poor service quality. These identifications will served as a research base which recommends some possible solution. Team members can lern the proper technique to serve the customers. The service quality related problem can be diminished in this way.
Team learning procedures facilitate the account handling system in a way that, effective and efficient learning about the handling process will increase the efficiency in handling accounts. Team members can find the proper pension scheme through team learning which can be effective to compete with the private firms. The team members can instigate the feedback getting system from the employees and design the pension scheme.
The team members can learn from the team learning process why the quantity of mail is decreasing in numbers. There may be other crucial factors associated with these beside the technological advancement. Team members can do it by sharing information in the team learning process.
Online competition can be checked in different ways. Team learning can help to design the online shopping offerings and the competitive preferences. The team members may share investigate the offers of the competitors. Different team members can assign to assess different competitors. In team learning process, every team member shares his/her findings and thus takes collective decision regarding what to do.
SAP Integration at Royal Mail Group
SAP AG (2003) reported that the Royal Mail Group is a gigantic organisation with yearly sales of over £8 billion and with its 220,000 employees has implemented SAP successfully. In 2001, Royal Mail has moved by efficient and competitive team learning the foremost SAP accomplishment among eighteen business units with 10000 users. Within this team learning its internal processes and stimulated all inheritance coordination in a particular dependable platform where the subsequent segment of growth has in progress with augmentation of decision-making support capabilities to facilitate Royal Mail’s business more successfully. The Strategic and Decision Support 4 by using SAP, Royal Mail Group has before now conveying major reimbursements to their business and team edification has been an essential success factor.
The Royal Mail team worked with SAP UK Education Team by means of very close corporation to expand and carry out a tailored learning programme and resulted highly outstanding. The teams from IT department of Royal Mail employees and most surprising thing is that 50% of the team members have turned into Certified SAP Consultants. The reimbursement has been instantaneous and gone beyond the expectations of management. SAP AG (2003) has quoted Steve Swindail one of the Certified SAP Consultants from the Royal Mail team member mentioning that the underlying principle of the successful outcomes was basically that the project has followed team learning and the SAP team just has helped to shape their future direction. Consequently, the team members acquired enormous benefits in terms of benevolence from the attendees as well as ideas invention of business specialists and most of team members are now become software specialist as well.
SAP UK Education Team has been admired the Royal Mail’s team learning stating that the learning environment worked predominantly well with the loom that they took in affiliation with Royal Mail was really a balanced, well organised team learning process with joined-up education. Within this four-stage programme, the technical and business proficiency with team spirit of the Royal mail team has helped specifically to short up and prickly knowledge-transfer sittings intended to fit into the entire team members. Their team learning approach spread over a period and encouraged communication among the strands on condition that enough time to discussing among the groups would make advancement for the organisation. The senior managers of Royal mail were always absent from this workshop but they not only advocates the learners also strongly supported to achieve the objectives of the SAP implementation.
Lockheed Martin’s Training at Royal Mail Group
Drake, Michael (2009) stated that in 1999, the Lockheed Martin has been reward the contract of Royal Mail’s A-1 project for 5 years which was valued £130 million to Interpretation its group learning. The project has been increased capabilities of Royal Mail to be acquainted both with the both written and machine printed addresses by this means escalating the use of automation for packaging and handling letters and parcels. As a keystone project A-1 uphold the vision of Royal Mail in context of nationally mail processing scheme which would make available the more effectual and resourceful service with enhanced customer satisfaction.
The A-1 scheme has been pedestal on a the very much modular open architecture organism which would robotically make out the addresses of mail materials which has been redundant by legacy equipment and make out an accurate location of delivery. A-1 has been designed to develop the team learning by provide supplementary information concerning mail stamp and delivery categorisations to get better the Royal Mail’s production performance. It has also integrated system-wide competence for data storage and salvages the review exposure within the pipeline performance capacity.
Drake, M. (2009) also quoted Dr. Schoultz the president of Lockheed Martin mentioning that venture with Royal Mail was their first significant contract to implementing such training for the organisational development by integrating the employees with digital technology and their team learning amplified the way of learning in greater extend. The scheme of Royal mail was a milestone for Lockheed Martin as the major systems integration that leads the Royal Mail’s staffs as an excellent team that become familiar with most up-to-date technology from Bell & Howell, IBM UK Ltd and Siemens as a pioneer of postal market.
Adoption of DNA at Royal Mail Group
Development Needs Analysis5 is an analytic tool introduced by CIM6 that make out the skills cracks and advocate for appropriate training solutions for the teams and folks assisting them to integrating the maximum potential from the team members. Royal Mail is the pioneer of implementing the DNA tools to walk around their major challenges and to pick up internal processes to identify and diminishing the skills gaps of the Royal Mail workforce. (Figure: -9)
CIM (2008) has presented the case study of DNA implementation of Royal Mail in 2001. With a recorded, loose of £1 million with in a day Royal Mail turns out to be as a public limited company completely holds by the Government. This transformation carried an operational profit of £537 million in 2004-05. Within this period, Royal Mail worked with 12000 post offices all over the country with 193,000 employees.
Outcomes of team learning at Royal Mail
Hartenian L. S. (2003) mentioned that the benefits of team learning are extensive in both the terms of Royal Mail’s competitive advantage and the personal gaining of members. For Royal Mail team learning has become more useful in many ways such as
- Improvement of the productivity of the firm
- Increasing the creativity of the members
- Decrease the time to response of the members
- Development in decision making
At Royal Mail the decision-making of the team mainly depends on the members of the decision making process and the capability of the members to give their knowledge and work. Organisational learning is the way to imply the knowledge of the members in decision-making process. Hence, the term learning at Royal Mail stands for the organisation, which continuously is growing its competence to build itself strong promises to do better in future. Learning at Royal Mail has been emphasised as
- The continuous growth of true desired result oriented capability of the members are happened,
- Culturing off innovative and extensive methods of thinking are being done,
- Make the collective ambition free,
- The teaching of how to learn collectively is done continuously.
The criterion of Royal Mail’s effective learning is as
- Increase the adaptability of the Royal Mail to take the changes positively.
- Strengthening management to enhance strategic planning, describes the suitability of team learning.
- Decrease in paradigm blindness plaguing of the Royal Mail.
As a modern learning organisation, Royal Mail becoming follows avoiding strategy of threats and vulnerabilities. It has been certified by different studies and researches that, Organisational learning or integrating learning at Royal Mail is completely dependable on the collective learning of the employees. Another postulation is to compete as it should be in the current competitive market, is more or less dependence in the internal relationship connecting the learning process of the individual, teams and Royal Mail management level. An important view towards the organisational learning is that, the success of organisational learning is not the individuals who learn during the team learning process but the effectiveness and advantages of the process of learning. Thus, team learning at Royal Mail has linked with organisational learning.
It has been identified that, capture, retention, recall, and application these four issues are associated with the learning at Royal Mail. Inter linked behavioural activities are build the organisational learning process. Idea contraption, communicative aptitude, decision making and act as per the decision are the key activities.
In this way, the members of the Royal Mail teams would be able to identify the mistakes and can get the opportunity to correct them. When a group of people identifies and corrects their mistakes endlessly, at one time, it results almost zero mistake and consequently, the improvement of efficiency and the betterment of the product quality occurs. Team learning gives the collective expertise of attaining a goal, which will help the members in future.
Team Learning & Productivity of Royal Mail
Royal Mail (2008) in its Annual Report stated that Royal mail is not only an old organisation; nevertheless, it is also a big one. A massive numbers of employees are working in this organisation. To maintain these gigantic numbers of employees, Royal mail took different types of diversifications continuously. Recently it has changed its pension scheme and started to modernise its mail service including other organisational changes. These are the paradigms of these diversifications. There are so many departments within Royal Mail. For long-term uniformity, Royal Mail must have to maintain an affirmative and influential operational conditions and linkage between these departments. These acts are more or less dependent on the working behaviour, productivity, and working excellence of the employees. The external and internal environment of the Royal Mail is also more significant issue of the betterment of the organisation. Employees of Royal Mail are directly involved with external and internal environment of the organisation, for this reason a grand study of the employees effectiveness is essential for the consistency of these environments. The incensement of the productivity of employee would result increase in company’s output and predict good profit. Correspondingly, when the productivity of the company is increased, it states that the productivity of the employee is also increased.
The large number of employee and the extremely large size of the company have some problems with the staffs as well. The internal conflict among the union members and non-member staffs sometimes cause ambiguity and problems in co-ordination among front line staffs (Thomas, 2005). Through team learning, Royal mail is trying to prevail over these situations. Prevention of duplication of service and make the delivery practice quicker, appreciating innovative ideas and declining the amount of error are the key outcomes has enjoyed by the Royal Mail through team learning. Now a day, the customer satisfaction is becoming more rapidly to 100%, which indicates the betterment of the service improvement by the employees.
The productivity of Royal mail becomes could be assessed from the annual report of the previous financial year 2008. Because of the advancement of the technologies and various communication apparatus, traditional mailing system is in front of threats. However, the delivery of the parcels and many other post office based services are still done by traditional ways. Besides, though communication becomes easier (for illustration- e-mail, fax, online chat and many more), the traditional importance of letters has been changed to the people. Nevertheless, the numbers of these types of acts are decreasing in an alarming way day by day. The volume of the item decreased, which results decline in profit for Royal Mail. Royal Mail (2008) reported the decreasing situation of the profit does not imply that, the productivity has decreased. To comment about the Royal Mail’s productivity and the productivity of the employees needs a close inspection and observation of unlike figures mentioned in the Royal Mail’s Annual Report where it has supported that the Return on sales (ROS) increased 1.7% accordingly.
An additionally significant finding from the Royal Mail annual report on the first quarter of the 2009 is the number of complaints. Within the period, the number of complaints received was 307,449. Nevertheless, the resolve of these huge amounts of complaints is much more than complains arrived, which amounted 314,470. This fact supports that the efficiency of the employees also increased. The result of these observations is that the Royal Mail’s productivity of the employees turned greater than before.
Besides, in almost every section, the external revenue has been increased. Though the volume handled in the process becomes lees than the last year, Increase in revenue implies a good indication of the production of the Royal Mail and productivity of the employees.
In 2007, about 27 millions addresses were accessed in the database of Royal Mail. This number has been increased by 1 million in the financial year of 2008. In parcel force worldwide, the number of parcels delivered every day increased by 37,000 in 2008. The numbers of satisfied customers were increased up to 99.8% from 95%. In the general logistic system section, the total numbers of parcel handled in a day remain constant as the previous year at 1 million. The most significant information is that, Royal Mail had 188,000 employees in 2007 when the number was decreased 181,000 in 2008.
From the above scenario, it is clear that in all section of the royal mail, there is a significant increase in the total employee related activities. Though the number of the employees were cut down, the productivity did not hampered rather increase. That is, Royal Mail Holdings plc is doing better with its fewer work forces.
Now, the key question arises, why and how Royal Mail’s condition becomes better? It is facing threats from declining volume of items, technological advancement, down trading tendency of the customers, increase in the cost of the mail related products, and the ongoing increase in the competition in the market. Nevertheless, these threats do not keep any pressure to its productivity; rather it is declaring a higher amount of pension for its employees.
The reason after the impressive business of Royal mail is the effect of team learning. The royal mail Holdings plc, has a laboratory where different teams are frequently generates brainstorming ideas, sketch different ways and discuss different issues regarding their operations. Thus, the flexibility among the work of the employees and the total delivery process has done. The champions group is another innovative unit composed in the organisation. Champion is being used as a role model for the rest of the teams. The other teams find the champion as a symbol of diversity and work accordingly to get diversified. Thus, the teams are learning and supporting the management. When a new recruit comes to the organisation, the groups ‘team of experts help him to learn through a team. The productivity of the employees is increasing day by day for the effect of the team learning, which results the increase in the productivity of the organisation. Therefore, it is clear that team learning has increased the productivity of the Royal Mail.
Essential Appraisal
Team learning is essential for Royal Mail not only in the sense of attaining competitive advantages but also for the betterment of the employees. There are nine key competencies of tem learning. These are
- Advising: A team can advise the Royal Mail by attaining and submitting various types of information.
- Innovating: By generating new ideas, a team can be helpful for the organisation.
- Promoting: the teams do Identification and reporting of potential opportunities.
- Developing: After designing new ideas, assessing and testing of these processes are also done by the teams.
- Organizing: Cultivating the ways to work with individual is also a key duty for the team members
- Producing: Production of a Royal Mail has also done by the teams. Different teams also do delivery of the products.
- Inspecting: Teams do the work of monitoring and auditing of the systems.
- Maintaining matching the standards of the product with previously established standards is a key work of the team. Teams help the Royal Mail by safeguarding of these standards and procedure of production.
- Linking: the organisation’s teams also do communicating and coordinating between the external and internal people.
It has been evidenced that team learning has a positive impact not only to the organisation, but also to the members of the Teams. Team learning is the abridgment of all the processes to learn through a collective nature and share the Knowledge, experience, by which members of the teams can realize their mistakes and take initiatives to resolve that mistakes. By resolving these mistakes, it has directed towards the achievement of the goals of the Royal Mail.
Critical Analysis and reflection
Kolb, D. A. (1983) anticipated that learning behaviour take place as an uninterrupted learning cycle that demonstrated in figure-10. It unconditionally delineates a behavioural agenda that is obscured surrounded by a set of segments and point toward a set of hierarchy that the learners would pass in the course of a formal use of an institutional reflective observation. The Royal Mail group featured a fresh challenge in 2006 by introduction of perfect competition rather than its monopoly in the British mail market. The vision of Royal Mail has been set up to be obviously the excellent and most dependable postal services company within the globe. To congregate a long phrase vision of first-rate performer of the global mail market, the organisation has to compete with new threats of new entrants in the market. The management of Royal Mail recognised that they need to streamline and spending for their workforce. There were no proper systems available to review the marketing efforts, detailed skills, potentials and learning requirements of the marketers of Royal Mail.
CIM7 has extended it hands to overcome the challenge of downturn of Royal mail by introducing DNA tools. As an analytical tools DNA was discovered by long research of CIM to identify the potential solutions based on US team analytics system due to the primarily reason is that the employees of Royal Mail are more flexible team configuration and most professional industry standards. Royal Mail has applied DNA at all level of its marketing team incorporated with individual and team benefits. Within this drive, amalgamation of web-based solution for measuring the performance has facilitated the HR department to look after overall scenarios from a single platform at once.
Formerly Royal Mail preserved only the yielding comprehension of skills and expansion requirements and after DNA practice, the Human Resources of Royal Mail gained the capabilities to report on hard information and facts from the database. The team development themes has been acknowledged with illustrated outputs like different charts and graphs and provided to the line managers to starting the exchange of ideas and arguments for training requirements of the teams.
The Royal Mail employed the DNA tool fashioned for team learning requirements with four improvement themes, which would be meeting up in the course of tailored learning for groups of folks to ensuring the particular needs of Royal Mail. DNA has been assisted to identify the areas of strength and weakness of the teams within the existing market conditions as well as learning needs. The Internal coaches of Royal Mail and managers were identified to sharing knowledge as well as mentoring the backward team members. Thus by using DNA the team learning was fully successful in context of return on investment8 measures.
Key Recommendation
In the light of above discussion, this paper would go to draw key recommendation for Royal mail is as
- The Royal Mail should make unprecedented investment in UK in order to improve Mail provider service on need of customers and dramatically reduce the time that customers wait for mail delivery. The cost effective and time saving solution for these needs could be meeting up by outsourcing. It should arrange by setting up delivery outlets, which could be run by private operators and Royal Mail only pay of the outsourced services, not for set up. One experimental mail delivery centre in London could be setup by private operators that should be consider the national procurement of mail delivery centre run and managed by the independent sector.
- Every entrepreneur should provide scope to participate in bidding with the objective of floating Independent sector mail delivery centres. If the bidders fulfill the mail market standard fixed by Royal Mail, the contracts would subsequently renew. It would be easier to receive high standard of customers care, offered additional staffing capacity and provided good value for money to Royal Mail.
- The Postal Services Commission Postcomm should launch an extensive forward planning exercise. All Strategic mail operators would be asked to identify, in conjunction with their respective primary care expectation of the self-governing sector mail delivery centres. It should emphasise on any anticipated gaps in their capacity needed to meet within specific time targets.
- The Royal Mail should prioritise independent operation and capacity building by effective team learning. The programme has been expected to provide an average of standard for Mail provider over five years and represents an investment suitable for team learning.
- It should be required substantial procurement of additional capacity from the independent sector of mail operators. It also helps the Royal Mail to meet the Royal Mail’s target that by 2010 all Royal Mail customers should be treated for mail providing within shortest possible time.
- It has to lay emphasis on innovation in every department of Royal Mail. It is essential to finding the means by which it could be shared. The sacks of innovation survive both in service delivery and in facility design within the Royal Mail as they implement it in the independent sector as well as mail market economies. The ail market outsourcing service providers would be able to build on the best practice in the Royal Mail. Leading international independent sector for Mail provider is running them, which have extensive record of accomplishment of running monopoly in the mail market.
- Chartered Institute of Marketing carried on mail market analysis and showed that the introduction of private operators are already exerting a downward pressure for their high charges and forcing for reform of private sector provision.
- Royal Mail also suggested to arranging authentic post-delivery follow-up by receiving customer’s feedback and supervision for complications are essential to delivering high quality and prompt mail delivery for its customers. In the first wave of outsourcing procurement, each contract should specify the approach of Royal mails cost reducing and partial privatisation alternative solution. The quality of post-delivery customers follow-up should ensure that the mail delivery of complications must be resolved very soon.
- The Royal Mail’s guiding principle in launching Mail provider is to ensure that the customer’s welfare and safety of parcel is paramount and all the other considerations accounted as secondary mater.
- Group learning would be offered for Mail providing staffs, where there is shifting activity and subsequent local training committees have to be established with a view to increasing training contracts as per the requirement of any particular department of Royal Mail. When fully time-honored the contracts would include prerequisite for supervisors and allied training professional who are efficient for group coaching. They possibly would cover up operative techniques that are appropriate to the general norms of mail market including customer care as a priority case. These dynamics would offer the trainees a predictable preparatory environment for learning in where the learners could concentrate on appropriate issues in a time conscious manner. The training specialists are contractually dedicated to the stipulation of enduring professional expansion and working out for the Royal Mail staff. The training would consist of beginning to operate and delivery of mails with safely continuing professional development.
- It should lay emphasis on strict inspection planning. Post offices should made registration under the Postal Services Act-2000 and subject to a mandatory inspection by the regulatory arm of Postcomm the Postal Services Commission. The inspections would hold a minimum of twice a year visit and may be announced or unannounced supervision to the delivery staffs.
Conclusion
Has team learning increased the productivity of Royal Mail – to conclude this research has enabled the author to organise the workplace environment toward greater motivation and increased productivity of the Royal Mail. It has determined the factors most influence the organisation to coordinate Team learning and to implement those factors is consistent over time cost effectively. It has been ascertained that the Team learning already created value to explore a speedy drive for Royal mail and to doing so actions that considered most appropriate to increase productivity and acceptability of Team learning at Royal Mail.
In view of the fact that team, learning at Royal Mail is a key component of postal players in UK mail market. Among the myriad approaches of team, learning has a broader perspective both for the public sector as well as for private investors. The team learning implies the uncertain staff development could be accomplished with rehabilitated into sureness of their productivity and at the same time, team-learning reverse the risk of employee’s turnover rate. At first step, the supported starting points along with the effects of team learning on top of priority could be valuated as the value of a business or asset. With the robust growth of assets of Royal Mail after team learning introduction, the regulatory authorities could emphasis to develop their areas of investments in Royal Mail where the growth rate scenario, under the present recessionary macroeconomic environment would sustain well, which are better than the crisis of global financial system and bailout. The study has provided established record of proper team learning and value addition to the organisation. Finally, it can be suggested in short that, the Royal Mail should monitor mail and request the legislation for government investment rather than partial privatisation and integrating team learning, it could be a way out for Royal Mail to overcome the present crisis both in locally and globally.
In regulating to meet up the most challenges of amplified competitions, increasing needs of investment and protecting the threat of partial privatisation, the management of Royal Mail has been trying to face the major changes by the attempts to improve efficiency through team learning and technological development as well as outsourcing services. As an organisation Royal mail has both strength and weaknesses when its large network of mail collection and delivery has been accounted as the major strength, the huge requirement of investment has been identified as it major weakness.
The global system of mail market is the act of regulations on international level of business for mail communication. The regulatory framework for mail operators should be matched financial markets of mail operators today. Every department of Royal Mail, not even in UK only, but also global mail should maintain the above themes or logistic sectors in all countries.
In recent time, the financial crisis of well-established market mail or Logistic market like UK is going through the global recession in all area of investment and also in property market. For this reason, investors are facing uncertainty in the borrowed amount by the mail operators of UK. This crisis is in full swing and warning to high cost of capital and lower rate of return in UK operators by economic meltdown. By having strong economy, UK mail market also facing recession. The high level of team learning can contribute the organisation to overcome the present crisis and argue to greater enhancement
As it is seen Royal Mail has emerging mail market with the shock of other European players, thus it could be concluded, the studies have to be developed by assessing mail market performances, distinguish undesired behaviour and monitoring continuously. The mail market of UK should develop their area of market efficiency, customer’s dependency, and also the value of the service by proper research and development, which should ensure the most competitive pricing with best service.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- ABI: Association of British Insurers
- CIM : The Chartered Institute of Marketing
- DNA : Development Needs Analysis
- Lab : Accredited Laboratory
- L&D : Learning & Development
- LDP : Local Delivery Plan
- RMG : Royal Mail Group
- ROI : Return on Investment
- SDS : Strategic and Decision Support
- TMI : Team Management Index
- OD : Organisational Development
Appendix-1
List of Figures
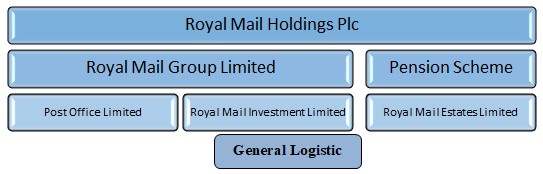
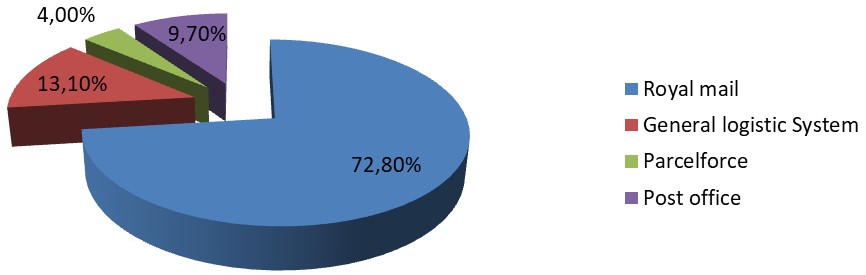
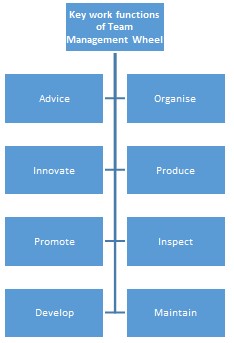
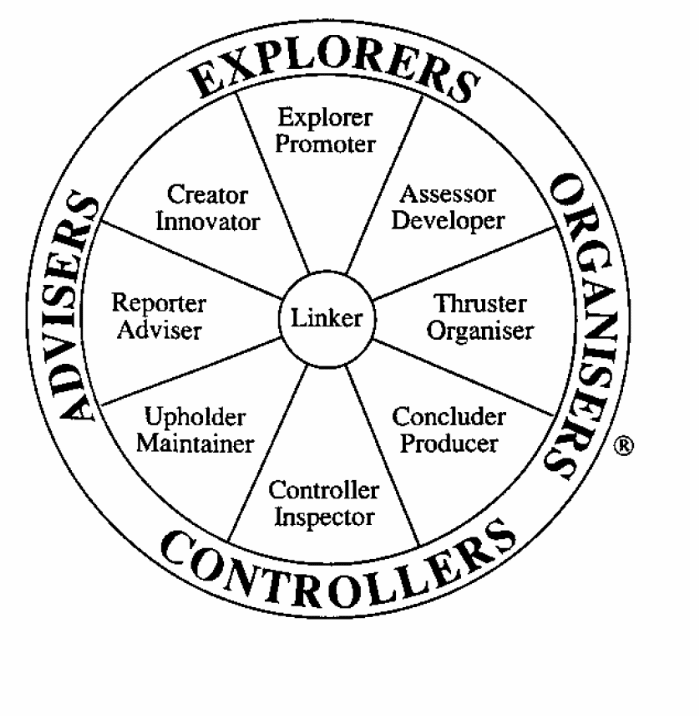
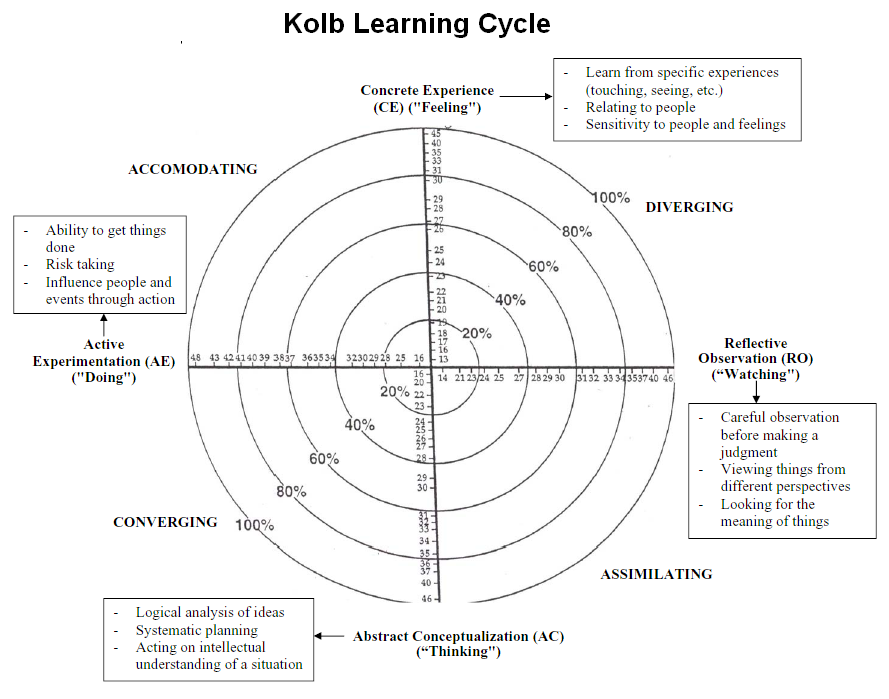
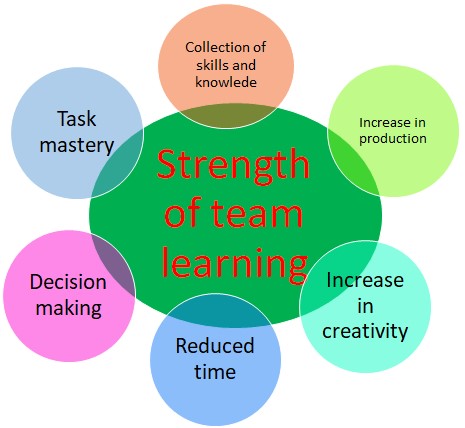
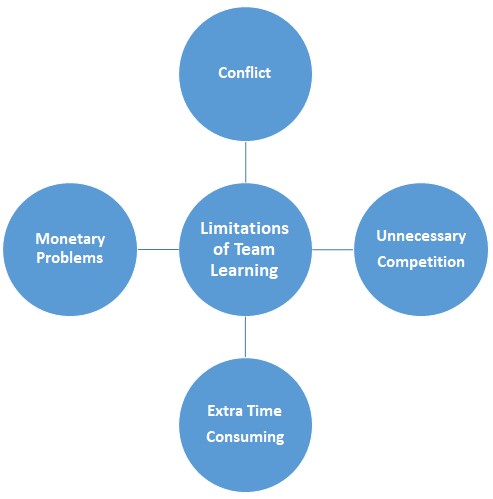
List of Tables
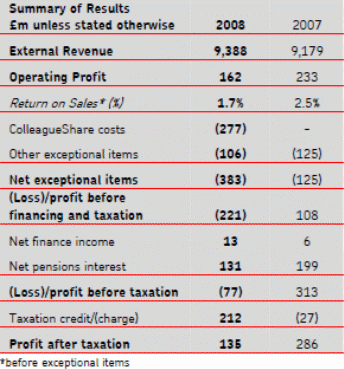
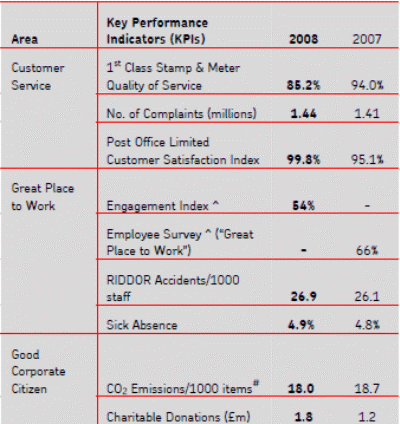
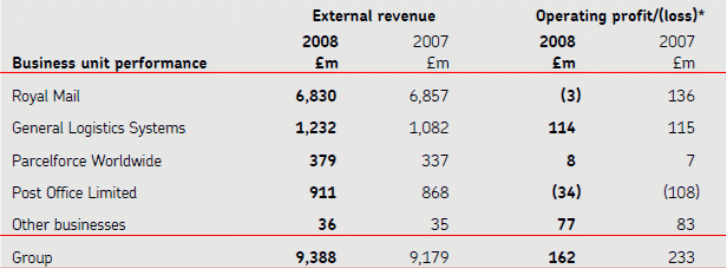
Table-4: Numbers of employees. Source: Royal Mail Holdings plc Annual Report, 2008
Table-5: Capability of handling and delivering items. Source: Royal Mail Group Plc, 2008, Regulatory Financial Statements 2007-08
Table-6: Efficiency in handling and delivering items-2008. Source: Royal Mail Holdings plc Annual Report, 2008
Table-7: Efficiency in handling and delivering items. Royal Mail Group Plc, 2008, Regulatory Financial Statements 2007-08.
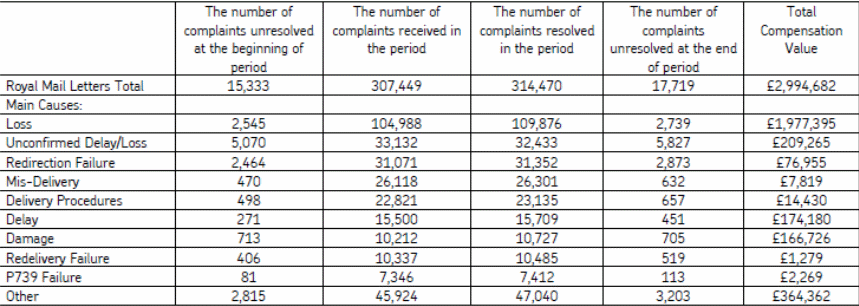
No of complaints received, resolved and remain unresolved.
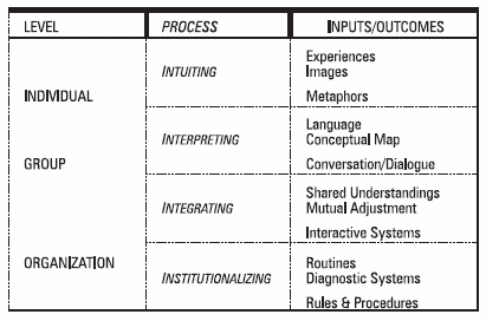
Table 10: Drummond List
Appendix-2
Reflection Notes
King, K. M. & Kitchener, K. S. (1994) pointed out that the Reflective verdict would refer to the explicit sphere of influence of cognitive expansion that illustrate how individuals argue their judgments regarding complex topics. The personality that makes a reflective notes to carry out the disclosure of tentative situations, would demonstrate his critical reflection skills that has been obtained robotically during the study. Throughout this research the author has the appraisal of reflective opinion by arguing a supple estimation process that would be applied for learning and research adjustable to any level of concerning open-ended dilemma on how team learning improved the productivity of staffs of Royal mail. The author’s reflective philosophy encompasses huge levels of action including a core of reflection on the outset of consciousness of self knowledge, hypothesis as well as previous experiences and critically investigation. The author also has centered his thinking appropriate to the behavior features regardless to his prospective intensity of intellectual performance as behavior features prejudice the author to exceedingly focal point on the element such as uncertainty, originality and alteration.
Performance Measures
The present literature does not make available with a suitable instrument to asses the impact of Mail provider on the functional model of the Mail market. Thus, a suitable appliance has been developed to enumerate this assessment. The questionnaire has been developed in an attitude that has conserved its internal cohesiveness; special care has been provided to ensure that each question focuses on one exacting issue. Likert Scales (1-7) affords the evaluation method for the various aspects
Table-11: Questionnaire
Feature that would be quantified through this questionnaire, scale quantifies the importance of the various issues, which has been raised by this questionnaire, when 1 being the least important and 7 would be the most important. The Likert’s scale has been widely used to quantifying the opinions of the respondents.
All answers have been given on a scale of 1 to 7 with 1 being the least important and 7 being the most important.
Table: 12
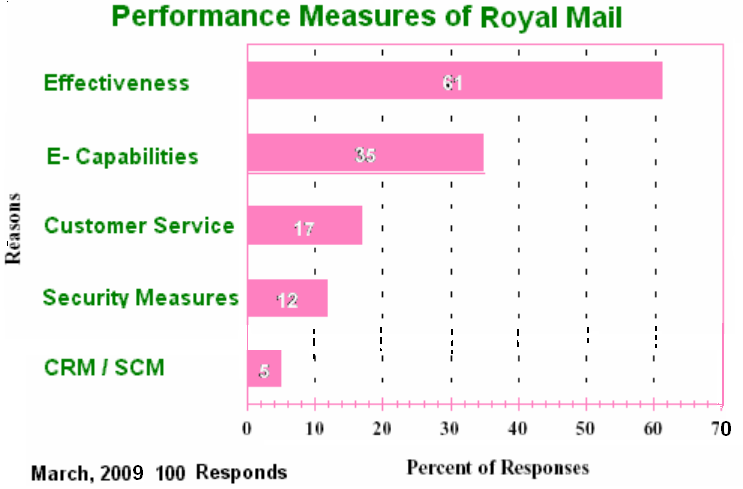
Bibliography
Bang, T. Y., 2008, An Exploratory Study of the Team Learning Typology Based on Environmental Fit. Contemporary Management Research.
Barker, M. and Neailey, K., 1999, From Individual Learning to Project Team Learning and Innovation: A Structured Approach. Web.
BBC News, 2009, Row Grows over Royal Mail Plans, 2009, 22:31 GMT.
Briner W., 2001, Team and Organisational learning in a cross-functional community of practice: the importance of privileging voices. Web.
Comment, R., and Jarrell, G., 1995, Corporate Focus and Stock Returns, Journal of Financial Economics 37, 67-87.
Cohen, L. Manion, L. Morrison, K., 2007, Research Methods in Education, 6th edition, London: Routledge, ISBN: 978-0-415-36878-0.
Clutterbuck D., 2003, Teams and learning: the agenda has changed: Does an over-concentration on task drive out learning? Web.
Chan C. A.C., Pearson, C., and Entrekin L., 2003, Examining the effects of internal and external team learning on team performance. Web.
Dodd, P., and Ruback, R., 1977, Tender Offers and Stock Returns: An Empirical Analysis, Journal of Financial Economics 5, 351-374.
Drake, Michael, 2009, Lockheed Martin Awarded £130 Million Royal Mail Contract, Lockheed Martin Corporation. Web.
Ellis, P. J. A., et al. 2000, Capacity, Collaboration, and Commonality: A Framework for Understanding Team Learning.
Edmondson A. C., et al., 2001, Disrupted routines: Team Learning and New Technology implementation in hospitals.
Fisher, R. A. 1990, Statistical Methods, Experimental Design, and Scientific Inference, 1st ed. J. H. Bennett Editor, NY: Oxford University Press, ISBN-10: 0198522290.
Hartenian S. L. 2003, Team member acquisition of team knowledge, skills, and abilities, Emaraldinsight. Web.
Hong, J., 1999, Structuring for organisational learning, The Learning Organisation, Volume-6, Number-4 pp. 173-185. Web.
Hoffman J R., and Rogelberg, S.G., 1996, A guide to team incentive systems. Web.
Hollensen, S., Saunders, M., Thornhill, A., and Lewis, P., 2006, Global Marketing: and Research Methods for Business Students: A Decision-oriented Approach, 4th edition, Financial Times Prentice Hall, London, ISBN-10: 1405853832.
Honold, L., 2006, Reflective Notes: a tool for individual and team learning. Web.
Hartenian L. S., 2003, Team member acquisition of team knowledge, skills, and abilities.
Jackson, C. J., (2001), Predicting team performance from a learning process model. Web.
Jennet, B., 2001, The relationship between team and organisational learning.
King, K. M. & Kitchener, K. S. 1994, Developing Reflective Judgment: Understanding and Promoting Intellectual Growth and Critical Thinking in Adolescents and Adults, San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Inc.
Kolb, D. A. 1983, Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development, 1st edition, London: Prentice Hall, ISBN-10: 0132952610.
Lang, L., Stulz, R., and Walking, R., 1989, Managerial Performance, Tobin’s Q, and the Gains from Successful Tender Offers, Journal of Financial Economics 24, 137-154.
Loo R., and Thorpe K., 2002, Using reflective learning journals to improve individual and team performance. Web.
Loewen, P., & a Loo, R., 2004, Assessing team climate by qualitative and quantitative approaches Building the learning organisation. Web.
Margerison, C., 2001, Team Competencies. Web.
McCann, D 2006, Team Learning.
Ortenblad, A., 2001, On differences between organisational learning and learning organisation. Web.
Perry, C. 1998, A Structured Approach to Presenting Theses. Web.
Phillips, J. J. and Phillips, P. P., 2003, Required Course: Manager’s Role in Learning and Performance, ROI Institute, Inc. Web.
Reynolds, T. J., and Gutman, J., 1988, Laddering theory, method, analysis, and interpretation, Journal of Advertising Research, 1988, World Advertising Research Center Ltd.
Reynolds, T. J. and Whitlark, D. B., 1995, Applying Laddering Data to Communications Strategy and Advertising Practice, Vol. 35, No. 4, 1995, Journal of Advertising Research.
Robbins, S. P., 2005. Organizational Behavior, 11th edition, Pearson Prentice Hall, ISBN: 978-0131642249.
Ross T. M., Jones E c., & Adams S. G., 2008, Can team effectiveness be predicted? Web.
Royal Mail Group Plc, 2008, Regulatory Financial Statements 2007, Part 1: Audited financial information. Web.
Rushmer, K. R., 1997, How do we measure the effectiveness of team building? Is it good enough? Team Management Systems –a case study. Web.
Revans, R. W., 1991, Action Learning In Practice, ed. Pedler, M., 2nd edition, Gower, Aldershot.
Saunders, M. Thornhill, A., & Lewis, P., 2003, Research Methods for Business Students, 4th edition, London: FT Prentice Hall. ISBN: 0273701487.
SAP AG 2003, Royal Mail Group Success Story: SAP implementation. Web.
Sekaran, U., 2006, Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach, 4th edition, John Wiley & Sons Inc, Singapore, ISBN: 9814126748.
Senge, P. 1990, Review of the fifth discipline: The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organisation. Web.
Senge M. P., 2009, Mental Models. Web.
Senge, P., 1994, Review of The Fifth Discipline, The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organisation. Web.
Smith, P. A. C., 1997, Performance Learning, Management Decision Journal, Vol. 35, No. 10, 1997.
Srikantia, P., and Pasmore, W., 1996, Conviction and doubt in organisational learning, Volume: 9, Pp. 42-53, ISSN: 0953-4814. Web.
Sun, Y. T. P., & Scott L. J., 2005, An investigation of barriers to knowledge Transfer. Web.
The Chartered Institute of Marketing 2008, Maximise your people potential: Tailored and Customised Learning. Web.
The Chartered Institute of Marketing, 2008, DNA case study: Royal Mail Group plc, Tailored and Customised Learning. Web.
The Independent, 2008, ‘Part-privatisation’ unveiled for Royal Mail, Independent News and Media Limited. 2008.
The Daily Telegraph, 2006, Global Recruitment: Royal Mail case Study, 2006. Web.
Triad consulting, 2004, Introduction to team learning. Web.
Yazici H. J., 2005, A study of collaborative learning style and team learning performance.
Yeo, R., 2002, From Individual to Team Learning: Practical Perspectives on The Learning Organisation. Web.
Zikmund, W. M., 2006, Business Research Methods, 7th edition, Orlando: Harcourt Publishers, ISBN: 0030184320.
Footnotes
- Supply Chain Management.
- Learning & Development.
- Chartered Institute of Marketing.
- SDS.
- DNA.
- The Chartered Institute of Marketing.
- The Chartered Institute of Marketing.
- ROI.