Introduction
Samsung is a conglomerate industry that primarily focuses on creating and marketing electrical products. The company focuses on manufacturing and developing a wide range of electrical products, including semiconductors, digital media devices, integrated systems, electronics, and memory chips (Gadalla, 2020). For Samsung Company to achieve its goal, develop a sustainable environment and generate a profit, the organization must ensure the efficiency and dependability of its employees by improving their competencies and defining their duties. An efficient framework may benefit the organization by removing communication obstacles, creating a good business climate, enhancing productivity and performance, encouraging employees, and inciting creative ideas (Heizer et al., 2014). Proper organization structure and marketing strategies are excellent for Samsung Company to commit its technology and talent to develop plentiful commodities that help make the world better.
Organization Structure
The members, including the Samsung organizational structure employees, are disciplined and have a strong propensity for formalization. The company then prioritized processes, and every department remains distinct, with a solid aversion to outsourcing, a strong preference for internal procurement, and a possessive sense of its capital and technology (Jones et al., 2005). Samsung Electronics has a hierarchical administrative architecture; the corporation’s board of Directors (BOD) comprises five independent directors and four executives (Haizar et al., 2020). Samsung’s structure aims to increase the board’s autonomy and independence and the openness of the decision-making process.
Moreover, there exist six committees beneath the BOD: the Audit Committee, the Related Party Transactions Committee, the Management Committee, the Compensation Committee, the committee of Independent Director Recommendation, and the newly formed committee of Corporate Social Responsibility, all of which collaborate with the staff to gain knowledge and experience (Samsung company, 2022). Nevertheless, because the management of Samsung is centralized, focused on a single team, the application arrangement and policies must be evaluated and approved by the BOD.
Samsung Electronics organizes its companies in technology, marketing, and consumers as Device Solutions (DS), reinforcing their separate operational structure. DMC is divided into two divisions, namely: IT & Mobile Communications (IM) and Consumer Electronics (CE) (Haizar et al., 2020). The CE division oversaw the department of home appliances and the department of visual display business. The IT & Mobile Communications division covers wireless companies, media solutions, digital imaging displays, network business, and IT Solutions.
This restructure incorporates workforce developments such as the employment of soft power experts, which has become more crucial than ever in the ‘Smart’ age. Samsung has already proclaimed its desire to become a soft-driven corporation and has developed a Software center to improve its software capacity until it is on top par with renowned global manufacturers (Samsung company, 2022). Changes were also made in the Device Solutions (DS) division, such as the growth of the entities in charge of controller, solution, and software, controller development to assure special teams for each.
The software-related groups were expanded to accomplish Samsung Electronics’ ambition of generating new experiences and values by combining Samsung’s current hardware design prowess with efficient software and an emotionally attractive user interface (UI). Samsung Electronics further extended the group in charge of the medical and biological device sectors (Haizar et al., 2020). Then Bio Lab at the Samsung Technology Research Center was renamed the research center of Bio. They also employed biomaterial specialists to improve their fields of study and increase biosimilar and biomedical research funding.
Structure of the Supply Chain
Samsung Suppliers
Samsung’s global supplier network includes mostly first-tier suppliers; these companies offer components of their products that are useful, raw materials, and equipment. A substantial portion of Samsung’s supplier network is based in the United States, Vietnam, Korea, Japan, China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and the United Kingdom (Bondarenko, 2021). China is the dominant supplier nation for many notable brands, including Samsung’s main competitors, Apple and Huawei, and numerous other technological companies.
Through strategic supply chain management, Samsung aims to ensure that there is the existence of operational efficiency and cost competitiveness while also focusing on sustainability. Samsung’s strategic supply chain management is built around five fundamental requirements: price competitiveness, response to risks, delivery of goods on time, the competitiveness of the supplier, and human resource capacity (Bondarenko, 2021). The company focuses on its supply chain activities’ social, environmental, and economic elements to control its influence in all three key aspects.
Social Aspect
Corporate accountability and social responsibility among suppliers are significant focal points of Samsung’s strategic supply chain management. Additionally, Samsung guarantees that its suppliers follow international regulations and standards in human rights, ethics, work environment, and conflict minerals to create a transparent system that engages all stakeholders throughout the supply chain (Bondarenko, 2021). While dealing with its suppliers, the company always ensures that it complies with the ethical standards and laws to protect its environment.
Economic Aspects
Concerning the economic aspect, Samsung’s strategic supply chain management is to maintain a comprehensive competitive advantage. The act can be accomplished in terms of delivery, applied technology, cost, quality delivered, and human resources to enhance the efficiency and speed of its suppliers and create a business ecosystem that allows long-term growth (Bondarenko, 2021). The company’s primary concern areas are product quality, technology, and efficiency cost applied in supply chain management.
Environmental Factors
Samsung only works with Eco-Partner authorized distributors to provide an environmentally sustainable supply chain. This guarantees that the effects of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and other production effluents on the environment are managed and assessed simultaneously (Bondarenko, 2021). Samsung developed best practices for manufacturing sustainability (Bondarenko, 2021). Its manufacturing strategy aims to make products financially viable through eco-friendly design from the planning stage forward. To maintain a pollution-free environment, the company invests in environmentally friendly means of production, and to some extent, it recycles its products.
Marketing Strategies at Samsung
The strategies of marketing at Samsung Company are centered on producing novel advanced, user-friendly devices backed by robust promotional and branding procedures. The company’s unique competitive strategy is manufacturing and promoting special interests while simultaneously positioning Samsung as a high-quality brand, fashionable, and worthy of a premium price (Bondarenko, 2021). The objective was to carve out a particular position through technical innovation while appealing to a younger generation and affluent clients worldwide.
Design and Development of Products
Acknowledging that cutting-edge technology often does not guarantee success, Samsung also focused on product development and design. Their goal was to create goods that deliver benefits that specific buyers consider valuable (Bondarenko, 2021). Because the help of several commodities is subjective, the development of the new electronic devices at Samsung Company often involved various designers who mutually collaborate with the marketers, production teams, and engineers.
Research and Development (R&D) into the Innovative Technology
According to Samsung Sustainability Report (2020), for a decade now, the Samsung industry has been investing 1.5 trillion dollars in its major R&D projects, a strategy that has kept it at the top. The tech company chooses to invest in research and innovation to gain a competitive advantage by pioneering its competitors on the novel technologies immensely. In the 1990s, Sony Electronics had consumer dominance, but it was built on analog technology (Bondarenko, 2021). As the digitalization needed new devices, Samsung invested heavily in developing large-area chipsets, cellphones, Liquid Crystal Displays.
Campaign to Build Brand
The marketing strategy of Samsung is centered on developing a publicity strategy to enhance the brand image of Samsung. Samsung streamlined its roster of advertising companies from 55 to one worldwide advertising company like Wire and Plastic Products plc, which conducted the organization’s first brand-building campaign, to guarantee adequate marketing communications globally (Samsung company, 2022). Additionally, to guarantee Samsung’s distribution route is consistent with good quality, several of Samsung’s items were taken from shops that offer low discounts and transferred through big-box electronics retailers (Samsung company, 2022). Restructuring their marketing activities was just as crucial to the success of a new strategic plan since even the most technically complex and well-designed items are prone to failures unless buyers learn of their existence.
Financial Strength
One of the most noticeable assets of Samsung Electronics is its intense financial situation. On a cumulative basis, Samsung has upheld a 35 percent debt ratio, a stable financial structure, a 73.9 percent equity ratio, and an 11 percent return on equity ratio (Bondarenko, 2021). According to Gadalla (2020), seven years back, the international electronics firm generated South Korean won (KRW) 200.7 trillion in revenue and consolidation profits of over South Korean won 25 trillion (Bondarenko, 2021). Proper management of its financial affairs has also been one of its survival strategies over the years.
Samsung Inc. vs. Apple Inc. and Huawei
Samsung is a South Korean company that consists of multiple affiliated businesses. As of 2020, it had the eighth highest international brand value. It was founded in 1898 by Lee Byung-Chul as a trading company (Kang, 2018). Three decades after founding, the group diversified into other areas, including insurance, food processing, textiles, securities as well as retail. It entered the electronics sector in the late 1960s, plus the construction as well as shipbuilding industries in the middle of the 70s (Kang, 2018). These are the areas that have led to the immense growth the company boasts of currently. Following the founder’s death, the company separated into five groups, that is, Shinsegae Group, Samsung Group, Joongang Group, CJ Group, and Hansol Group (Kang, 2018). In the electronics sector, the Samsung Group has faced stiff competition from companies such as Apple and Huawei. This section focuses on comparing the three companies in regard to vision, goals, strategy, and investment philosophy.
Vision
Samsung Inc.’s vision is to inspire with innovative technologies, products as well as designs that enrich individuals’ lives plus contribute to social prosperity by creating a different future. This statement forces someone to pay attention to its leadership position as well as how it directs the market plus upgrades life with its products as well as services (Kang, 2018). The vision statement’s characteristics include inspiring the world, focusing on innovations, and contributing to social prosperity (Chang et al., 2019). It is obvious that the company does not develop products without precision as it aims to inspire (Omer, 2019). It accomplishes this by understanding the diversity of people in the world (Yun et al., 2019). This way, it can design every product to cater to the needs of everyone regardless of their location.
The standard for designing its products is very high, possibly the highest in the industry. The company has developed an image of showcasing highly innovative products with the most advanced technologies, for instance, smartphones as well as personal computers (Kang, 2018). Samsung also considers its presence in the market as a great chance to modify how individuals live as well as relate for the better (Kang, 2018). The care plus individualized needs that it considers while producing products says a lot about how it recognizes the ease of utilization as a critical factor in all things it develops. This betters how individuals work, interact as well as carry out other social duties.
Goals and Strategy
Samsung has devoted all its human resources as well as technology to enable them to create superior products plus services, thus contributing to a better global society. According to its business operations, as well as current global industry positioning, the company has focused on human and technological resources, the superiority of products plus services, and the betterment of society (Zhou, 2020). To achieve its goals, the company has to remain competitive in the market against others such as Apple and Huawei (Omer, 2019). It thus applies a broad differentiation generic competitive strategy (Browne et al., 2021). The strategic aim of this approach is to maintain a competitive edge by offering peculiar products that target a wide market.
To attain the company’s strategic plans for growth as well as expansion in the international market, this approach needs the application of product development as a key intensive growth strategy to rival others mentioned earlier. Its investments in product development are an approach implication of the generic approach (Almeida et al., 2021). For instance, Samsung invests in technological innovation to support the competitiveness of its products in the market (Haizar et al., 2020). The second implication of this approach is the company’s marketing mix as well as approaches that promote products as different options to most competitors.
The marketing approach, as well as technological innovation, sustains Samsung’s competitive advantage plus value chain effectiveness in satisfying consumer needs. Other strategies applied in the company operations include differentiation focus, cost leadership as well as cost focus, which enables the company to be the best cost provider (Zhou, 2020). Lastly, regarding investment philosophy, the company believes in devoting its talent plus technology to creating products as well as services that lead to a better society.
Comparison with Apple and Huawei
Apple Inc.
Vision
Apple Inc.’s vision is to create the best products on the planet and leave the world a better place. The Vice President of the company for Environment, Policy, as well as Social Initiatives, stated that they aim to create not only the best products on earth but also the best products for the world (Almeida et al., 2021). Therefore, the vision statement is in line with the company’s corporate social responsibility approach as well as stresses sustainability, the overall betterment of ecological influence of the business, and environmental conservation.
Goals and Strategy
Apple Inc.’s goal is to bring the best personal computers and support students, designers, educators, engineers, scientists, business people, as well as consumers worldwide. This shows that the company considers the changing landscape that impacts the probabilities of what it can do (Podolny & Hansen, 2020). For example, it recognizes changes and trends in the market as well as the industry environment. As mentioned earlier, Samsung Inc. uses a generic strategy and intensive growth. Apple, too, utilizes this approach as it relates to the firm’s approaches in marketing, pricing, plus other business areas (Amron, 2018). This approach is designed to help the firm maintain competitiveness in the consumer electronics as well as information technology plus service market.
Investment Philosophy
Investment decisions at Apple Inc. are based on value factors as well as financial criteria. Value investing is a critical technique in-stock selection (Tien, 2019). It is important to effectively choose the value stock while considering basic analysis as well as assessing fiscal ratios. The idea of value investment was first suggested by David Dodd and Benjamin Graham (Kang, 2018). Later, Warren Buffet made it popular among investors due to his research and practice. The study on value investment has been conducted to explore its effectiveness in the market as well as asset return.
Huawei
Vision
Huawei has the vision to bring digitalization to all people, at home as well as in the organization for a completely connected and intelligent world. The company has stated that it will offer ubiquitous connectivity to provide every individual with equal access to connections (Dmitrijevs, 2020). It will also offer pervasive intelligence to steer businesses in the forward direction (Wu et al., 2021). Thirdly, the company has stated that it will build digital platforms to aid all the sectors and firms to become more efficient, agile as well as vibrant (Shuhua, 2018). Lastly, it will deliver an individualized experience to everyone, respecting the peculiar characteristics of people and allowing the full potential of all to be realized.
Goals
Huawei aims to connect all the people, firms, and homes that are still not online. It also aims to continue driving broadband as well as ultra-fast broadband adoption. Additionally, the company is infusing artificial intelligence connectivity so that its networks can adapt to the ever-changing needs of consumers (Dmitrijevs, 2020). Going forward, the intelligent networks will require to adapt to bandwidth plus latency in real-time so that the company can offer consumers a user-oriented experience.
Strategy
The core of Huawei’s pricing approach has been to guarantee lower prices than its competitors, such as Apple Inc. and Samsung Inc. It does with care so that it does not go too low on the prices to bring to question the quality of its products. Companies that have offered exceptionally low prices have appeared to the public as low-cost and low-quality (Benatallah, 2019). Thus, the company prices itself only five to fifteen percent lower than its major rivals in the industry (Alkhawajah, 2019). For customers in mature markets such as Europe and the United States, the company may have to consider another pricing approach.
Consumers use pricing as a reliability and quality indicator, whether consciously or unconsciously. In the market, premium pricing shows a premium or high-quality product. Additionally, pricing is important for the company to avoid the adverse perception of low-cost low-quality (Alkhawajah, 2019). Regarding investment philosophy, Huawei’s strategy is to keep a considerable profit margin, invest more later plus share more value with consumers, suppliers as well as partners (Benatallah, 2019). Competition, openness as well as collaboration are the fundamental principles the company adopts to improve its core competencies plus build a good business ecosystem.
Samsung Financial Analysis
Financial analysis of an organization is the investigation of the company’s economic performance. Its result leads to supplement management, effectivity, utilization of the production capacity, and efficiency. It is significant in identifying the organization’s strengths and weaknesses through its diagnostic tools leading to the generation of essential information to the owners or the management. The key purpose of financial analysis is to present its financial position in the market and its assets for critical decision-making. An organization’s financial review is acknowledged by arranging financial indicators that have to be organized and designed to portray all the crucial features of a financial situation. For that reason, ratio indicators are preferred for the description of the analysis.
Using ratio indicators is significant as it enables the company to compare its performance with other institutions or previous periods. In analyzing the Samsung financial performance, the paper will use indicators such as return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), net income growth, operating cash flow, quick ratio, and cash ratio (Alexander, 2018). Other significant measures utilized for the analysis include current ratio, total debt to total equity, price to cash flow ratio, receivable turnover, price to sales ratio, and return on invested capital (ROIC).
Return on Assets (ROA)
The return on asset is a type of investment return that assesses the organization’s profitability according to its overall assets. It compares the company’s net income to the capital it has invested. An organization having a higher return shows that it is productive in the market, and its management effectively utilizes economic resources (Alexander, 2018). Samsung Company has a high ROA of 9.75, higher than its previous financial period. The company has a large volume of assets indicating showing its high ROA. Also, the company performance in 2021 is higher than that of 2020, which may be attributed to the external environment. The eternal environment was influenced by the high rates of COVID-19, which impacted its performance during that period. However, the ROA of its major competitors, such as Apple, is higher when compared to Samsung’s performance as it has a ROA of 28.06.
Return on Equity (ROE)
The return on equity ratio is an indicator that measures the company’s ability to make a profit from the investments of the shareholders. This portrays the profit generated by every dollar of the shareholders’ equity (Alexander, 2018). It is an essential measure used by investors when identifying its efficiency in using the money towards profit realization (Alexander, 2018). Furthermore, the measure shows how the management can use equity financing in growing the company and funding its operations. Return on equity relies strongly on the ROA and the interest rate of the capital borrowed. Samsung has an ROE of 13.92 during the 2021 financial period, and their competitor Apple has an ROE of 147.44. Samsung ROE portrays that the company can fund its business activity and expansion despite its top competitor being much ahead. The increased ROE of Samsung is because of the loosened regulations set during the pandemic.
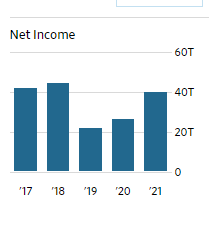
Net Income Growth
Net income growth portrays the ability of the organization to boost its business growth. Many investors prefer investing in organizations with a high net income growth because of the high returns generated (Alexander, 2018). It shows how the company is growing from the previous subsequent years (Alexander, 2018). The growth rate is calculated depending on the period, such as the one-year growth rate and the three-year growth rate. By comparing the two types of growth rates, one can identify whether the company’s net income is growing or slowing down. Samsung has a three-year net income growth of 65.13%, which shows that the company net incoming has been increasing for the last three years. This is significant as it enables potential investors to invest in Samsung Company. Samsung’s net income growth is higher than its competitor Apple which has a net income growth of 64.92%.
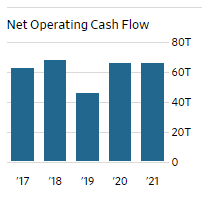
Operating Cash Flow
The operating cash flow measures its cash generation from its normal business operations. This measure is significant in showing how the organization is able to generate adequate cash flow for business maintenance and growth of the organization, or it requires external funding sources for its capital expansion (Alexander, 2018). This measure is significant as it is free from accounting anomalies and provides a clear picture of the business operations. Samsung’s cash flow has been increasing for the last three years, and this shows that the company can finance its core business operations without the need for external funding sources. This makes Samsung’s business sustainable in the long run hence providing a suitable environment for investors to invest.
Quick Ratio
The quick ratio measures the organization’s short-term liquidity, and it asses the organization’s ability to fulfill its short-term obligations using liquid assets. This focuses on the organization using liquid assets that can be converted quickly into cash to cater to the current liabilities (Alexander, 2018). It is noted that a significant quick ratio is greater than 1.0 as it shows that the company is able to handle its liabilities (Alexander, 2018). Samsung has a quick ratio of 2.04, which shows that its performance is healthy and can cater to its liabilities. Samsung is financially secure to handle its short-term future, plus portraying that it has a significant growth in the sales and business as it collects the accounts receivable efficiently.
Cash Ratio
The cash ratio is a liquidity measure that shows that an organization can pay off its short-term obligations using cash and its equivalents. This liquidity indicator is compared to other measures such as the current and quick ratios (Alexander, 2018). This is because it only involves cash and its equivalents (liquid assets). It is a measurement of the organization’s liquidity involving ratio comparison on the total cash, its equivalents, and the current liabilities (Alexander, 2018). This figure is significant when the organization is in need of a loan. Samsung has a quick ratio of 1.41, which is greater than 1indicating that the organization is in a good position when converting the value of the current assets into cash. The organization is able to cover its short-term debts and remain with cash to fund business operations. However, a high cash ratio may also mean that the organization is focused on future profitability, thereby accumulating capital to protect it from sudden market changes such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Current Ratio
The current ratio is also a liquidity measure that shows the organization’s ability to fulfill its short-term debt obligations within a year. This shows how the company can maximize its current assets on the balance sheet and meet the current debts and other requirements (Alexander, 2018). This is evaluated by the organization’s average and is considered significant when above average. Samsung has a current ratio of 2.51, indicating that it is stable in the market. This makes the company suitable for investors to invest in as it shows that it is not struggling to solve its current debt requirements.
Total Debt to Total Equity
The total debt to total equity is significant in evaluating the organization’s financial leverage. It helps show how the organization uses debts to finance its operation compared to its funds. This helps in portraying whether an organization has substantial shareholders’ equity that will enable it to pay off the debts whenever it has experienced a decrement in the profits (Alexander, 2018). This ratio may also be used in identifying a company’s short-term leverage, which is a crucial factor that the investors usually consider (Alexander, 2018). Samsung has a total debt to equity ratio of 6.21, portraying that the organization uses debts to finance most of its operations and projects. The ratio is significant for Samsung Company as it enables understanding the shareholders’ earnings and comparing itself with other competitors in the market. In the case of Apple Company, the organization has a total debt to total equity ratio of 216.39, portraying that Samsung is well off when the profits decrease in case of market shifts.
Price to Cash Flow Ratio
The price to cash flow ratio is a measure of stock valuation that assesses the organization’s stocks price in relation to the operating cash flow per share. It also asses the organization’s earnings in relation to the prices of the stock (Alexander, 2018). This measure is a significant investment indicator because it cannot be easily manipulated as earnings because of factors such as depreciation and non-cash charges (Alexander, 2018). Samsung has a price to cash flow ratio of 8.17, indicating that its stock is valued in the market hence a possible venture for potential investors.
Receivable Turnover
The receivable turnover ratio is a measure that assesses the organization’s effectiveness in collecting the amount owed by the clients. This measure shows how the company manages and uses the credit that it has extended to the clients (Alexander, 2018). It also shows the efficiency of collecting debt within the organization as a firm with a good record of collecting payments has a high receivable turnover ratio (Alexander, 2018). Samsung has a receivable turnover ratio of 7.01, indicating that its debt collection is efficient and has an incredibly significant number of quality customers who quickly pay the debts owed.
Price to Sales Ratio
The price to sales ratio is a significant measure that asses the company’s stocks value. It uses revenue and the organization’s market capitalization in identifying whether the stock is valued properly (Alexander, 2018). This measure is also significant for investors as it enables them to decide whether to invest in the company or not (Alexander, 2018). An organization having a low price to sales ratio is a significant venture portraying its stock’s valuation in the market. Samsung has a price to sales ratio of 1.90, indicating that the organization is profitable.
Return on Invested Capital (ROIC)
The return on the invested capital is a measure that assesses the organization’s efficiency in capital allocations that manage investments that are profitable. This measure s significant in showing the company’s competitiveness in the market (Alexander, 2018). It portrays whether the company is earning higher profits when compared to its competitors in the market. This is significant as an organization is competitive when its production cost is lower compared to its competitors (Alexander, 2018). This enables the organization to attain a competitive advantage in the market. The ROIC measure is significant as it portrays how its competitive advantage will be durable. Samsung has an ROIC of 13.76, indicating that the organization has a competitive advantage making it profitable.
Financial Risk Management
The Samsung organization focuses on handling financial risks such as liquidity, credit, and market risks emanating from the business. The organization has implemented several measures that mitigate the risk through fiscal policy and other programs. Furthermore, the company uses derivatives to handle certain financial risks (Samsung Electronics, 2021). It also monitors the foreign exchange rate in most major business zones to manage the foreign exchange risk. In monitoring the liquidity risks, the organization uses an integrated finance structure (Samsung Electronics, 2021). Financial risk management comprises financial assets such as trade receivables, cash and cash equivalents, financial assets at amortized cost, and short-term financial instruments.
Market Risk
Foreign Exchange Risk
Samsung Company is vulnerable to risks resulting from the foreign exchange because it operates in a global environment. The main currency affected by foreign exchange risk is Indian Rupee, Euro, and US dollar (Samsung Electronics, 2021). The organization tackles the foreign exchange risk by having an equal volume of assets and liabilities in the country it is operating. Furthermore, the organization management uses normal transactions in exports and imports and financing borrowing and depositing (Samsung Electronics, 2021). This is significant as it aids in matching the cash-in currency and the cash-out currency. Additionally, the organization monitors foreign exchange rates valuation and devaluation to prevent speculations.
Interest Rate Risk
The interest rate risk is generated by the fluctuation of the market interest rates. Samsung Company is vulnerable to interest rate risk because of its exposure to interest-bearing deposits and debt obligations (Samsung Electronics, 2021). It has employed various policies that are significant in curbing the uncertainty arising from this risk.
Price Risk
The company is vulnerable to price risk because of the direct and indirect investments of the company’s equity instruments. The price fluctuation impact is a significant factor as between 2020 and 2021, the organization’s marketable equity securities were affected by 1%, resulting in income changes.
Credit Risk
The credit risk usually arises due to investing and transaction activities as clients cannot fulfill their obligation. The organization monitors the client’s credit limit following their financial conditions, history, and other significant factors (Samsung Electronics, 2021). For clients in high-risk countries, the organization uses insurance coverage to secure them from the credit risk that may emanate. This risk can also arise from the transactions between the company and the financial institutions involving deposits, cash, and equivalents (Samsung Electronics, 2021). To minimize this problem, the company makes transactions with institutions with high credit ratings in the market. Furthermore, the company monitors all the contracts of its clients, thereby reducing the losses.
Liquidity Risk
The company has numerous investments in various regions, making it critical to maintain an adequate level of liquidity risk. The organization strives to maintain this by periodically predicting the capital balance, approximating the required cash levels, and carefully managing its expenses and income (Samsung Electronics, 2021). The liquidity risk is maintained by forecasting the cash flow and identifying the anomalies associated with the cash flow. The organization later uses the integrated finance structure to solve the problem through activities such as cash pooling (Samsung Electronics, 2021). Furthermore, the organization uses financial support catered for by the company and local financial institutions.
Organization Considerations
For Samsung to achieve its goals, it must critically consider its organizational structure, supply chain, marketing strategy, and financial status. To outdoor other competitors, the company has to properly coordinate its activities in hierarchical leadership and production sectors, with these high-quality products being produced constantly in large quantities. The production of the products is done as per the socioeconomic and environmental requirements. In addition to that, maintaining good supplier relations is also a key concern for the company. This ensures a constant flow of raw materials and other production requirements. Samsung also does consider strategic marketing strategies centered on the novel, innovative skills backed by powerful promotional, branding activities, and proper financial management.
Conclusion
Ever since its founding, Samsung Inc. has been focused on providing consumers with the best products in the industry while also maintaining uniqueness. The company has devoted much of its resources, both human and technological, to enable them to produce products that contribute to a better society. To achieve organizational goals, the company utilizes a generic competitive strategy which is the same as Apple Inc. This approach helps the two companies to remain competitive and top their rivals by giving out new and unique products. Companies, especially the ones in the same industry, have been known to apply different strategies in their operations so that they appear different in the eyes of the consumers. However, businesses can also use a similar approach if it helps them achieve their goals.
This paper has shown the organization structure, supply chain, and marketing strategies. Also, the paper has portrayed the financial analysis of Samsung Company. For instance, Samsung Inc.’s vision is to inspire with its innovative technologies, products, and designs that improve people’s lives as well as contribute to social prosperity. On the other hand, Apple Inc. aims to create the best products and leave the planet a better place. Lastly, Huawei has the vision to avail digitalization to every individual in both homes and firms to ensure complete connectedness. These vision statements guide how the companies approach their operations. Employees recruited are taught and trained to understand what they are expected to achieve.
The paper has also shown that pricing is an important aspect of marketing. Consumers want products that are of high quality but at reasonable prices. For instance, they want to be able to afford the items. Therefore, many companies aim to offer electronic devices that are of lower prices than others. However, they cannot go too low with their prices as this might be a bad indicator. Consumers perceive very low-priced items as low quality, which means that they tend to avoid them. It is thus important when setting prices that a company sets a limit on how low they could get.
References
Alexander, J. (2018). Financial Planning & Analysis and Performance Management (1st ed.). Wiley.
Alkhawajah, W. (2019). Huawei: An information and communications technology company. Journal of Information Technology and Economic Development, 10(1), 1-10. Web.
Almeida, M., Sousa, E., Rodrigues, C., Candeias, M. B., & Au-Yong-Oliveira, M. (2021). Samsung vs. Apple: How different communication strategies affect consumers in Portugal. Administrative Sciences, 11(1), 19. Web.
Amron, A. (2018). The Influence of Brand Image, Design, Feature, and Price on Purchasing Decision of Apple iOS Smartphone in Surakarta, Indonesia. The International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Invention, 5(12), 5187-5191. Web.
Benatallah, A. (2019). Analysis of Huawei Company’s International Marketing Strategy. MO’assira Economic Research, 2(2), 137-156. Web.
Bondarenko, P. (2021). Samsung. Encyclopedia Britannica. Web.
Browne, S. H., Bernstein, M., & Bickler, P. E. (2021). Accuracy of Samsung smartphone integrated pulse oximetry meets full FDA clearance standards for clinical use. medRxiv. Web.
Chang, V., Zhang, W., & Xiong, C. (2019). The strategic view and development of corporate social responsibility: the case study of Samsung. International Journal of Strategic Decision Sciences (IJSDS), 10(1), 105-130. Web.
Dmitrijevs, R. (2020). Research on marketing strategy of Huawei mobile phone in European market. Open Journal of Business and Management, 8(03), 1138. Web.
Gadalla, A. (2020). Samsung Management. Web.
Haizar, N. F. B. M., Kee, D. M. H., Chong, L. M., & Chong, J. H. (2020). The impact of innovation strategy on organizational success: A study of Samsung. Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Education (APJME), 3(2), 93-104. Web.
Heizer, J., Render, B., & Griffin, P. (2014). Operations management (Canadian Edition). Don Mills, Canada: Pearson Canada Inc. Chapter 12.
Jones, G. R., Mills, A. J., Weatherbee, T. G., & Mills, J. H. (2005). Organizational theory, design, and change (Canadian ed.). North York, Canada: Pearson Canada Inc. Chapter 4.
Kang, T. (2018). Samsung v. Apple. Berkeley Technology Law Journal, 33, 889-916. Web.
Omer, S. K. (2019). SWOT analysis implementation’s significance on strategy planning Samsung mobile company as an example. Journal of Process Management. New Technologies, 7(1), 56-62. Web.
Podolny, J. M., & Hansen, M. T. (2020). How Apple is organized for innovation. Harvard Business Review, 98(6), 86-95. Web.
Samsung company. (2022). About us. Web.
Samsung Electronics. (2021). Consolidated financial statements of Samsung electronics co., ltd. And its subsidiaries index to financial statements. Web.
Samsung Sustainability Report (2020) Samsung Electronics. Web.
Shuhua, C. (2018). A study of marketing strategy of Huawei Company in Thailand (Doctoral dissertation, Siam University). Web.
Tien, N. H. (2019). International distribution policy comparative analysis between Samsung and Apple. International Journal of Research in Marketing Management and Sales, 2020(1), 2. Web.
Wu, Z., Wu, J., Hou, Q., Jiang, H., & Chen, F. (2021). The strategy of international brand expansion of its enterprises: A case study based on Huawei. Procedia Computer Science, 183, 733-744. Web.
Yun, B. S., Lee, S. G., & Aoshima, Y. (2019). An analysis of the trilemma phenomenon for Apple iPhone and Samsung Galaxy. Service Business, 13(4), 779-812. Web.
Zhou, Y. (2020). The Samsung story. Web.