Introduction
Organizations face numerous risks in their everyday activities. In most cases, the majority of businesses fail to achieve their set goals and objectives due to the lack of appropriate strategies for the management of any potential risks (Zsidisin, Panelli, & Upton, 2000; Power, 2009). In the human situation, risk has become quite unavoidable in the lives of people in the private, and public sector (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002). In spite of this, various contexts of risks determine its definition (Tohidi, 2011). For example, risk can be defined differently based on technical causes, stakeholders, or even in the insurance context. In spite of the difference in the contextual meaning of risks, there is a common element of uncertainty in outcomes (Hallikas, Karvonen, Pulkkinen, Virolainen, & Tuominen, 2004). For this reason, it is evident that all organizations experience risks in their operations. Most often, risk management in various organizations is only applicable to elements that are predetermined to occur (Haimes, 2015). Still, empirical evidence shows that few organizations prioritize their approaches to the management of risks.
With the advent of technology, Tohidi (2011) asserted that there is more concern than ever about the occurrence of various uncertainties. Such a scenario comes at a time when the majority of organizations rely on technology to develop safer systems (Haimes, 2015). As such, the occurrence of risks amidst advanced technology calls for the adoption of significant models that are focused on risks causation based on the dynamism of the current business environment (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002). Often, the socio-technical system that is used in the management of organizational risks takes into consideration a number of levels such as system operators, work planners, managers, and legislators. However, considering a change in technology experienced nowadays, the public pressure, different regulatory practices, competitive environment, as well as increasing aggressiveness, it is more likely that the system is under stress.
Based on the traditional approach to risk management, each level of the system is examined independently followed by a general model that outlines various requirements for risk management across all systems (Power, 2009). For this reason, effective risk management requires cross-modeling with a lot of emphasis on aspects of controlling any problems and categorizing them accordingly (Haimes, 2015). As such, the effective management of risk in the current business environment requires the adoption of a system-oriented strategy with the focus on functional abstraction as opposed to structural decomposition. The implication of this assertion is that a model of behavior shaping mechanisms ought to be adopted to replace the action sequences as well as the occasional deviation that lead to human errors (Tohidi, 2011). Such an approach would ensure the analysis of the work system challenges, any boundaries related to the performance acceptance, as well as the acceptance of organizational change based on various risks (Haimes, 2015).
According to Haimes (2015), there is a need for all organizations to adopt risk management programs that focus on the compliance, operational, financial, strategic, as well as knowledge risks for all the organizational functions and departments. Nevertheless, the majority of organizations are still reluctant and ignorant of the significance of effective risk management. On the other hand, a significant number of organizations face numerous challenges in the management of organizational risks due to the fact that the inventory of risks is ever-evolving. For this reason, the subject of technology risk management in organizations is worth exploring to establish challenges, benefits, and the opportunities that are available.
Problem Statement
Many operations fail due to numerous uncertainties (Power, 2009). In the event that organizations do not adopt the right measures towards risk management, the achievement of set organizational goals becomes impossible (Hallikas et al., 2004). The implication is that risk management is a crucial element of organizational success and ought to be given high priority.
Objectives of the Study
Primarily, this study seeks to provide an insight into the subject of technology risk management in organizations. Also, the study has specific objectives as listed below:
- To find out the impacts of the process of identifying risks on the performance of organizations;
- To establish some of the significant sources of organizational risks;
- To learn about some of the challenges that organizations face in their attempt to manage risks;
- To determine whether or not there is a relationship between risks and organizational performance;
- To establish several practices that can be adopted to manage risks.
Research Questions
Concerning the above-mentioned research objectives, the study will seek to answer the following research questions:
- Are there any impacts in the process of identifying risks on the performance of organizations?
- What are some of the significant sources of organizational risks?
- What are some of the challenges that organizations face in their attempt to manage risks?
- Is there a significant relationship between risks and organizational performance?
- What practices can be adopted to manage risks?
Hypothesis
- HO: It is more likely that technology risks do not have adverse impacts on the performance of any organization.
- H1: Technology risks have adverse impacts the performance of any organization
Structure of the Thesis
The thesis is divided into five chapters: introduction, literature review, methodology, data analysis and findings, and discussion and conclusion. The literature review chapter provides an in-depth review of the past studies that are closely related to the study phenomenon. It provides essential information on the role of effective risk management in organizational success, the challenges, and opportunities associated with risk management. The methodology chapter covers the research design and methods adopted in the collection and analysis of the required data. It involves the sampling frame, sample size, as well as the sampling technology. The findings and data analysis chapter provides a significant synthesis of the collected data in line with the research objectives. The last chapter, discussion and conclusion, covers a detailed overview of the study findings concerning the highlighted research questions. In addition, this chapter includes a summary and conclusion of the entire study.
Concept of Risk Management
This section of the paper provides a review of the concept of risk management in organizations with a lot of emphasis on the past studies. As such, the review of related literature focuses on the previous conducted studies addressing the subject of technology risk management and the necessary approaches that are required to ensure that organizations are prepared for future uncertainties.
There are two safety management principles that are related to organizational management of uncertainties that include risk-based safety management and consequence-based safety management (Miller & Waller, 2003). According to the consequence-based safety management principle, organizations should not suffer any consequences that are outside particular limits (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002). On the other hand, the risk-based safety management principle highlights the need to analyze residual risk based on the nature of the impact as well as on the probabilistic nature. The implication of this principle is that even though unlikely events can occur, organizations ought to have the necessary measures in place to deal with such events.
The concept of risk management has been around for ages. It plays a significant role in the decision-making process and general management of any organization. Often, different organizations’ departments are faced with numerous risks (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002; Power, 2009). Nowadays, the occurrence of risks has become so common that most organizations are considering the adoption of various standards to systematically describe a functional group based on a given hierarchy (Haimes, 2015). In spite of this, it is evident that such an approach can only be effective for a given industry, and thus, cannot be used in any other organization (Mikes, 2011). For this reason, risk management can be considered as a systematic approach that takes notice of the best course of action in preparedness for any future uncertainties. Such an approach involves identification, assessment, understanding, action, as well as communication of risky issues.
According to Tohidi (2011), the application of effective risk management in any organization requires the development of a suitable culture. This is attributable to the fact that the availability of such a culture makes it possible for any organization to support its mission, vision, as well as objectives (Miller & Waller, 2003). In addition, the development of the risk management culture is important in that it draws the boundaries and limits in the process of addressing uncertainties in an organization (Haimes, 2015). Therefore, the primary objective of having effective risk management approaches is to ensure that the decision-making process of any organization is based on the organizational objectives (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002).
Technology Risk Management
The introduction and development of information technology have revolutionized many aspects of business (Haimes, 2015). Advanced technology plays a major role in the operations of financial institutions, which is evident in the development and use of online card payments, contactless payments, as well as in the use of mobile technology for making and receiving payments. Furthermore, financial institutions and companies have become common users of IT outsourcing that can be attributed to the fact that IT labor is readily available nowadays (Tohidi, 2011). Evidently, technology has greatly changed approaches used by organizations as far as their way of operation is concerned (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002; Miller & Waller, 2003). Such growth in technology has been instrumental in the overreliance of technology among companies for every process.
Considering the increased use of technology in organizations nowadays, there is a need to put technology risk management measures in place (Haimes, 2015). It arises from the fact that even though technological advancement has brought in significant benefits to organizations, there are numerous risks associated with it (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002). For example, cases of cybercrimes as well as breach of private data are high nowadays. As such, this is the time for all organizations to consider the inclusion of technology in their list of risk management strategies (Mikes, 2011).
Risk Management Process
To enhance effective risk management, organizations ought to mind various considerations (Power, 2009). For instance, Alberts and Dorofee (2002) pointed out that there should be a process that is followed in the identification of all risk causes as well as how they can be handled to have positive impacts on an organization. The first step in risk management is the establishment of the context. It comes before the actual risk can be identified because it is essential for organizations to know what the risk is, especially the objectives, aims, and scope of managing it as related to the operations of organizations. This phase helps organizations to determine what resources can be used for the management of risks. The second step is the identification of the risk. The major activities in this step include determining and revealing the main risks the company is facing. It is known as the most important step in the process since it gives a basis for the right work in future in terms of the establishment and execution of new programs to use during the control of risks. This step is very much dependent on the organizational culture and the practices within the organization.
Risk analysis is the third step used in the management of risks. It focuses on determining risk characteristics and if they can be analyzed further. Each identified risk is allocated a certain rating depending on its possible effects on the organization. Therefore, the major purpose of this step is to help in the provision of information to the management about decisions regarding how they can set priorities as well as how to treat each risk (Giunipero & Aly Eltantawy, 2004). Once such information is available, the risk management team can proceed to the fourth stage which is risk evaluation. It mostly focuses on the decision as to action plans can work better if they are implemented as well as whether the risk requires acceptance or treatment. In most cases, this stage depends on the number of risks that companies face. If they are complicated situations, the evaluation process may be hard. On the other hand, fewer risks make the process simpler for a company (McNeil, Frey, & Embrechts, 2015). An organization then invests its resources in risk treatment which is the fifth stage. Some risks may be recommended for further investigation to get more information about them if they have higher chances of re-occurring in the future. Moreover, in such cases, the company can implement risk mitigation plans. The approach may either be reactive, when actions are taken as a result of the risk, or proactive, where actions are taken before the occurrence of the risk. Proactive activities help in the transfer and avoidance of risk, reducing the consequences as well as the likelihood of risk occurrence.
When every activity to manage risk has been implemented, the company has to engage people in measuring the outcomes (Beasley, Clune, & Hermanson, 2005). As a result, the sixth stage is the monitoring and review of how effective the plan of risk treatment was. The management also needs to ensure that the circumstances of risk that occur do not bring negative changes to the priorities of risk (Miller & Waller, 2003). The last stage is then communication and consultation. The entire process requires consultation with employees from all departments, as well as the organizational stakeholders. These are the most important assets of organizations as they make the biggest contribution towards the successful attainment of the organizational goals and objectives. Therefore, it is credible to assert that organizations ought to have proper strategies of communication that provide effective consultation and communication.
Risk Management and Organizational Performance
Every organization works towards ensuring that there is a positive relationship between its strategies and objectives. Risk management is among the essential components of every organization (Miller & Waller, 2003). Organizations need to invest their resources in managing risks so that their operations are not faced by some unmanageable risks. As a result, there is a need to make it an ongoing process through the utilization of various methods and tools (Power, 2009). These tools and methods play a key role in the identification of possible risks, determination of the most critical ones to be solved first, as well as the execution of companies’ strategies to handle risks (Miller & Waller, 2003). Since the desire by organizations to keep up with advanced technology pushes them to acquire new technology, there is a need to ensure the adopted technology does not negatively interfere with the operations of the company (Tohidi, 2011). Organizations can do this by ensuring they have strategies and rules of risk management.
The effective management of risks is essential for all companies that have various projects contributing towards their overall objectives (Alberts & Dorofee, 2002). For instance, it ensures that projects are completed on time, customers are satisfied, and the financial performance of an organization improves. Risk management plays a key role in improving communication across the organization (Miller & Waller, 2003). For instance, it helps to assure that communication with customers is clear and their needs and preferences are sorted in the best way possible. In addition, risk management provides senior management with information on the major threats which the organization is likely to face, thus assisting in decision-making.
Confronting the Challenges
The evolution of information technology has become a significant part of every business nowadays. Nevertheless, it comes with an increased vulnerability of businesses to risks. This is attributable to the fact that it has become extremely difficult for organizations to contain IT events without it having adverse impacts on the productivity of businesses. For example, presently, corruption and inaccessibility, the loss of data, and failures in infrastructure and system have enormous impacts on the operations and success of any organization. For this reason, they need to gain the necessary knowledge as far as wide-scale effects associated with IT risk are concerned.
Therefore, to confront the challenges associated with the adoption and use of IT, organizations are required to become highly committed to the management of technology risks. Presently, the majority of organizations’ approaches to the management of technology risk are either poor or average. The implication is that there is a need for seriousness when it comes to technology risk management in organizations. Even though it might be quite impossible to completely eliminate technology risks, it is important to strike a balance as far as the risk management selection is concerned, focusing on the value associated with such commitment.
There is high interdependence between a technology and business process because these are the major elements of comprehensive solution of risk management. The lack of such knowledge puts organizations in a vulnerable risky position. There are numerous potential consequences associated with the failure to enhance the interdependence of technology and business processes alongside the absence of effective risk management approaches. These include overlooking significant risks, failing to meet fiduciary obligations, the vulnerability of business processes, reduction in profits, as well as the creation of negative publicity. For this reason, effective management of technology risk requires the following: the evaluation of the impacts and threats associated with the corruption or disruption of technology services, effective identification, and the measure of the influence of technology risks on the business operations. Moreover, organizations are required to define effective approaches towards management of technology risks judiciously, implement ongoing technology risk management, as well as a governance program. Additionally, effective risk management should involve continuous monitoring of technology risks as well as taking a suitable and timely approach towards the mitigation of any identified risks.
Methodology
Creswell (2009) defined a study design as the plan of action that involves a systematic application of various approaches for the purpose of collecting and analyze data to provide answers to given research questions in proof of various hypotheses. As such, the choice of the research design used in any study is determined by the type of data needed as well as the scope of the concerned study. Such assertion is based on the fact that there are several study designs ranging from the descriptive, explorative, and cross-sectional to experimental designs. The choice of the research design should also be influenced by the research methodology that is used. Kothari (2005) describes the research methodology as the processes and procedures that a researcher uses to collect information needed to address a given societal problem. Therefore, the methodology chapter covers the research methodology used to examine the concept of risk management in organizations as well as the research design adopted.
Study Designs
The primary focus of this study is on the examination of the concept of technology risk management in organization. As such, the research emphasizes on what has been achieved as far as the management of risks in organizations is concerned. Additionally, it uses quantitative data in relation to risk management practices and organizational performance. The quality of the quantitative data will be supplemented through the use of interviews to collect additional information from selected organizations’ managers on their opinions regarding the impacts of risk and risk management practices on the performance of organizations.
Deductive approach
Deductive approach was used in this study. The choice this approach was based on the fact that there was a need to gain understanding of the concept of technology risks and their impacts on organizational performance from the empirical perspective, and then testing the hypothesis based on study participants’
Descriptive research design
To ensure that comprehensive data is required, the research applied the descriptive research design, where survey approach was used in the collection of the data. The rationale for using the descriptive research design is based on the fact that the study focuses on the provision of answers to a number of research questions. In the views of Mitchell and Jolly (2010), the descriptive research design is often used to help researchers provide answers to any research questions with regard to the impact of a given study phenomenon on the societal well-being. In the case of the current study, descriptive research design will be very useful in gauging the importance of effective risk management practices in an organization. This is attributable to the fact that the investigation of the impacts of risk and risk management practices will require the description of tangible evidence as far as organizational performance is concerned. Furthermore, the descriptive study design will be suitable for this study especially in relating various research variables.
According to Mitchell and Jolly (2010), descriptive research design is appropriate for any study because it can give indexes to study variables that are under examination. Therefore, the use of the descriptive research design in this case will ensure that quality and reliable data is collected for the purpose of drawing the necessary inferences regarding technology risk management in organizations. Occasionally, the descriptive research design is used as a predecessor for quantitative research.
Target Population
The study’s target population is defined as the entire units or people. The research plans to obtain the required data for the purpose of drawing a meaningful conclusion. In this study, the focus is on the impacts that risk and risk management practices have on the performance of organizations. Therefore, it aims to obtain the necessary information from selected organizational managers. As such, the targeted managers will be identified from the sampled organizations. The research targets organizations within the private and public sectors in the US. Further, several individuals tasked with the responsibility of managing risks in the selected organizations will be interviewed.
Sampling Design
According to Denzin and Lincoln (2008), a sample in any study refers to a section of the entire study’s target population. Kothari (2005) pointed out that in order to obtain the right sample size for any study, there is a need for the adoption of appropriate sampling techniques. On the other hand, Creswell (2009) asserted that the appropriate sample size should be representative of the target population. The sampling frame for this research is the private and public organizations. Such categories of organizations are the immediate beneficiaries of effective risk management practices. Kothari (2005) pointed out that while a sample is obtained from a study’s target population, the sample frame refers to the working population used in any given study. In this study, only organizations that have implemented risk management practices will be considered.
Sampling Techniques
Sampling techniques can be described as approaches used in obtaining the appropriate sample size to use in any study. While there are various sampling techniques that can be used in obtaining the sample size, this study used a simple random sampling procedure. According to Mitchell and Jolly (2010), the simple random sampling technique is highly effective especially when used to obtain a sample that is representative of the target population. As such, it was useful in this study since it gave all the organizations within the sample frame equal chances of inclusion to the sample size. In addition, the simple random sampling technique has high efficiency due to the fact that it does not classify errors and it is free of human bias. For this reason, the correct application of this technique will ensure that a highly representative sample is obtained.
Moreover, the study used the purposive sampling methods to identify the people to be interviewed. The rationale for the use of this approach is that it is based on a researcher’s judgment to select the individuals to be included in any given study. On the other hand, Creswell (2009) noted that the purposive sampling technique is advantageous because it puts emphasis on specific units or population of a study whenever collecting information about a given research phenomenon. Therefore, this approach ensured that certain information on risk management, such as the challenges and impacts of risks on organizational performance, will be easily obtained from the specific individuals within the target population. As such, combining the two sampling methods will ensure that the research uses comprehensive data.
Sample Size
The sample size to be used in any study depends on the required data, the purpose of the study, the available resources, and the number of replications applicable to making the necessary inferences about the study phenomenon (Neumann, 2007). The size of study sample plays a significant role in the determination of the precision and accuracy of a research. With the help of the simple random sampling technique, this study used a sample size of 20 organizations. However, the number of the study participants was 150, although the required information dictated this.
Methods of Data Collection
As outlined earlier, the primary objective of this study was to examine the subject of technology risk management in organizations. For this reason, several research questions were adopted to help in the determination of the impact of risk on organizational performance as well as the role of risk management practices in the success of organizational operations. Based on the assertions of Denzin and Lincoln (2008), the person carrying out a research, research strategies, as well as the point of data collection influence the choice of data collection methods. This study will rely on both primary and secondary sources of data to examine the aspect of technology risk management in organizations.
For example, secondary sources of data that contained past data about the research phenomenon were reviewed. In this study, journals and books were used to provide insights into the subject of technology risk management in organizations. On the other hand, primary data was obtained from the selected study participants through the use of the questionnaire method. Therefore, to obtain the required data on risk management in the specific organizations, several managers from the sampled organizations were required to fill out a questionnaire.
The choice to use this data collection tool was influenced by the assertions of Denzin and Lincoln (2008) that the use of the questionnaire method allows a researcher to collect in-depth information about a given research phenomenon based on the perceptions and attitudes of research participants. Moreover, the questionnaire approach is suitable especially in studies that focus on the exploration of personal outcomes, experiences, and differences with regard to a given study phenomenon. The questionnaire was guided and contained simple and clear questions to ensure that the required data was gathered.
Data Analysis
Data analysis according to Neumann (2007) refers to the synthesis of any collected data from a study for the purpose of adding meaning to it to enable the drawing of significant inferences with respect to the study objectives. A number of statistical approaches are employed in the analysis of data. For example, the statistical package for social sciences, regression analysis, t-test, and alpha test can be used in the analysis of any collected data (Foster & Yarvosky, 2006). In this research, the responses from the survey were analyzed and compared to examine the percentage contribution of each participant regarding a given aspect of the subject under investigation.
Findings and Analysis of Data
The objective of this study was to examine the concept of technology risk management in organizations. Such examination was informed by the fact that there is an influx in the adoption and implementation of technology in the operations of many organizations all over the world. Nevertheless, only a small fraction of organizations have adopted significant technology risk management approaches. This section of the dissertation provides a description of the sample used to collect data, an analysis of the collected data as well as survey results.
Sample Description
The target sample is comprised of 150 organizations’ managers and other staff. As such, 150 questionnaires were distributed among the target population. In cases where there were logistic challenges, the survey was conducted either on the phone or via the email. In spite of the fact that 150 questionnaires were distributed, only 134 were collected back for analysis. In addition, nine out of the collected questionnaires were missing data, since some sections were not answered as expected, while others were left blank. As such, only 125 questionnaires were suitable for the analysis on the subject of technology risk management in organizations.
Age of Respondents
The majority of the respondents (60%) were between 31 and 40 years old, while only a small percentage of the total study participants (8%) were above 50 years of age as evident in the table below.
Table 1: Study participants’ ages
The 31-40 age section is comprised of young individuals who are technology-knowledgeable, and hence, tend to use technology in organizations more than the older generation. This category was significant for the study as the individuals are exposed to the daily risks of technology in business operations.
Gender of Respondents
The majority of the study participants were males, accounting for 60% of the total sample size, while the females accounted for 40% of the total participants in the study as shown in the table below.
Table 2: Gender of the respondents
Results
The study participants were required to point out the methods of risk identification that they preferred the most. The table below provides a summary of the results from the study.
Table 3: Results
The majority of the study participants (60%) reported that they used a risk register more often. Only a small percentage of the entire sample size (8%) cited that they relied on surveys to identify risks in their organization. The remaining 20% and 12% reported that they relied on previous risks assessments and brainstorming respectively. The figure below shows a graph on the methods of identifying risks, effects of identifying risks, as well as the types of risks that organizations face nowadays.
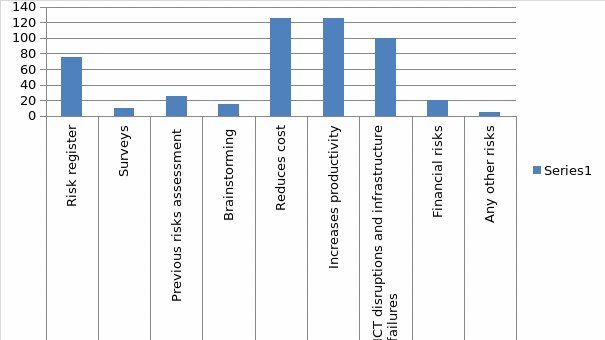
Besides, the study participants were required to provide their responses regarding the effects of identifying risks on the performance of organizations. All of the respondents agreed that identification of risks within an organization is an important process. This statement aligned to empirical evidence stating that the process of identifying potential risks gives organizations the chance to adopt suitable approaches towards their solution as well as ensuring that the organization’s goals are achieved.
Further, the study focused on establishing some of the significant organizational risks. It was evident that there were several categories of risks in organizations which included technological, environmental, political, market, as well as financial risks. Even though the emphasis of the study was on technology risk management, it was important to examine each category of risk.
The majority of the study participants (80%) pointed out that ICT disruptions and infrastructure failures were the major risks that affected organizational performance. Secondly, 16% of the respondents claimed that financial risks affected the operations of their organizations greatly. On the other hand, only a small percentage of them indicated that the performance of organizations was affected by any other risk. Evidently, the analysis indicated that technological risks had the greatest impact on organizational performance. Such a response could be attributed to the fact that the majority of the organizations have become over-reliant on information and technology for all organization’s operations.
However, when asked for their response about the sources of the risks that they encounter in their organizations, the majority of the study participants (96%) pointed out that most of the risks come from external and internal sources. As such, 60% of them strongly agreed that organizations have control over risks that come from within organizations because their personnel causes them, while 16%, 14.4%, and 9.6% agreed, disagreed, and strongly disagreed with this opinion respectively.
The table below provides a summary of the responses on the challenges that organizations face when managing risks.
Table 4: Challenges
As for the challenges that organizations face in the process of managing risks, 48% of the study participants emphasized the lack of the necessary risk preparedness within their organizations. On the other hand, 32% pointed out that technological risk management is a challenge due to the complexity of tasks required in its management, stressing that the lack of IT knowledge is a major challenge. On the other hand, 12% of the study participants noted that organizations’ attempts to manage risks were affected by the lack of the necessary resources. The rest of the respondents (8%) reported that the lack of understanding of various sources of risks affected the attempts of organizations to manage risks as shown in the graph below.
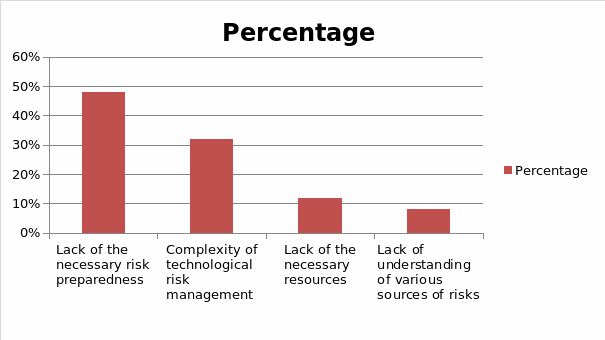
Table 5: The descriptive statistics
Based on the responses, the study participants were required to offer their suggestions regarding practices that can be adopted to manage risks. The majority of the respondents (60%) cited the need for the adoption of a risk management culture, while 20% reported that organizations need to understand the role of technology in business processes. In addition, 20% of the respondents stated the need for organizations to create awareness about risk management among employees.
Сonclusion
The primary objective of this study was to analyze the concept of technology risk management in organizations. Therefore, the study used a survey method to examine the impacts of the process of identifying risks on the performance of organizations, the significant sources of organizational risks, some of the challenges that organizations face in their attempt to manage risks, as well as establish several practices that can be adopted to manage risks. Generally, the study sought to find out whether or not there is a significant relationship between risks and organizational performance.
According to the survey responses, it was evident that organizations suffer from a number of risks ranging from technological to financial risks. In spite of this, the study established that different categories of risks have diverse impacts on the performance of any organization. For example, most of the respondents reported that technological risks had the greatest impact on the operations of any organizations, which aligns with empirical evidence on the role of technology in organizational performance. In addition, the fact that many organizations are in danger of technological risks is attributable to the high use of technology in major organizations’ operations. The implication is that risks have adverse effects on the performance of any organization. The rationale behind this is that the occurrence of risks negatively affects the ability of organizations to achieve the set goals within the schedule time.
Despite the impact of technology risks on organizations’ performance, few of them have what it takes to curb such risks. This is attributable to the lack of resources, complex requirements, and the lack of awareness of the various sources of risks.
With regard to the impact of risks on the operations of any organization, it is important for organizations to adopt effective practices that can help in risk management. Some of the suggestions include the adoption of a risk management culture and the provision of an understanding of the role of technology in business processes. On the other hand, all employees in different organizations are required to be aware of the impact of risk management on organizational performance. Such an approach not only gives employees the necessary knowledge but also sets a platform for effective risk management.
As such, there is a need for organizations to have necessary measures in place to assess, identify, as well as mitigate any risks. Therefore, they ought to understand the role of effective management of risk in the current business environment. Based on the ongoing technological changes, it is important for an organization to adopt a system-oriented strategy that focuses on functional abstraction rather than structural decomposition. Such an approach would be very instrumental in ensuring that organizational practices are shaped for the purposes of enhancing the efficiency of operations within an organization to reduce internal risks. On the other hand, the development of a risk management culture creates a platform for all stakeholders in an organization to help in managing risks by ensuring the effective analysis of the work system challenges, any boundaries related to performance acceptance, as well as the acceptance of organizational change based on various risks. For this reason, organizations are required to adopt and implement risk management strategies with a lot of emphasis on the compliance, operational, financial, strategic, and the knowledge management risk with regard to all organizational functions and departments.
References
Alberts, C. J., & Dorofee, A. (2002). Managing information security risks: the OCTAVE approach. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc..
Beasley, M. S., Clune, R., & Hermanson, D. R. (2005). Enterprise risk management: An empirical analysis of factors associated with the extent of implementation. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy, 24(6), 521-531.
Creswell, J. (2009). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches. Thousand oaks, CA: Sage.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln, Y.S. (2008). Colllecting and interpreting qualitative materials. Malden, MA: Blackwell.
Foster, J., &Yavorsky, C. (2006). Understanding and using advanced statistics. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Giunipero, L. C., & Aly Eltantawy, R. (2004). Securing the upstream supply chain: a risk management approach. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 34(9), 698-713.
Haimes, Y. Y. (2015). Risk modeling, assessment, and management. John Wiley & Sons.
Hallikas, J., Karvonen, I., Pulkkinen, U., Virolainen, V. M., & Tuominen, M. (2004). Risk management processes in supplier networks. International Journal of Production Economics, 90(1), 47-58.
Kothari, C.R. (2005). Research methodology- methods and techniques. New Delhi: Wiley Eastern Limited.
McNeil, A. J., Frey, R., & Embrechts, P. (2015). Quantitative risk management: Concepts, techniques and tools. Princeton university press.
Mikes, A. (2011). From counting risk to making risk count: Boundary-work in risk management. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 36(4-5), 226-245.
Miller, K. D., & Waller, H. G. (2003). Scenarios, real options and integrated risk management. Long range planning, 36(1), 93-107.
Mitchell, M., & Jolly, J. (2010). Research design explained. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Neumann, W. L. (2007). Social research methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches. London: Allyn & Bacon.
Power, M. (2009). The risk management of nothing. Accounting, organizations and society, 34(6), 849-855.
Tohidi, H. (2011). The Role of Risk Management in IT systems of organizations. Procedia Computer Science, 3(1), 881-887.
Zsidisin, G. A., Panelli, A., & Upton, R. (2000). Purchasing organization involvement in risk assessments, contingency plans, and risk management: an exploratory study. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 5(4), 187-198.