Human resource (HR) is defined as individual contribution to an organization in terms of efforts, skills and capabilities. On the other hand, human resource management (HRM) is the division of the organization that deals with the management of human resource (Dessler 4). Human resource management can be viewed in two perspectives. First, human resource management is the personnel or support functions in an organization. Secondly, HRM is a top management function. Whether in the formal or informal sector, the management of employees is always a function of the top management (Rafat, Shams and Javadi 11943).
Initially, human resource management (personnel management) was regarded as an administrative subject. In addition, HR measurements were based on the turnover rate, non-attendance and parallel measurements (Dessler 4). At the moment, Human resource management in its most basic form emphasizes on building competitive advantage through the strategic use of contemporary HRM techniques to develop competent personnel. This characterization aims to sum up the view of the present companies subscribing to the idea of employees being the most significant asset (Rafat, Shams and Javadi 11944).
The management and staffing in numerous organizations are done by individuals and without them organizations cannot exist. As a matter of fact, the prospects and challenges of developing and managing an organization are normally led by individual-related problems. On the other hand, individual-related problems often emerge from the misconception that all people are equal and deserve equal treatment in organizations. However, this is far from the truth. Each and every individual is unique both physically and psychologically and should be treated differently (Dessler 5).
To ensure that organizations acquire the right personnel at the right time, Human resources systems, for instance, human resource planning, recruitment and selection have to be engaged. Human resource planning is a process of developing strategies to organize the elements and skills of the personnel as per the needs of the organization. On the other hand, recruitment refers to the process of identifying potential candidates and persuading them to apply for the current or foreseeable position (Dessler 7).
Selection is the process of picking qualified and competent candidates from a pool of new applicants (York 12). According to York, organizations can consciously and practically determine the composition of the personnel needed to realize strategic goals by ensuring that the recruitment and selection practices match with the existing policies and programs (14). This essay will focus on the application of Ulrich’s model on the HR systems. The paper will be based on vacancies in HR related jobs in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), for example, human resource specialist, human resource manager, compensation expert, and employee relations manager. The paper will analyse the requirements of these jobs using Ulrich’s model and discuss their implications to potential candidates and organizations.
David Ulrich’s Model
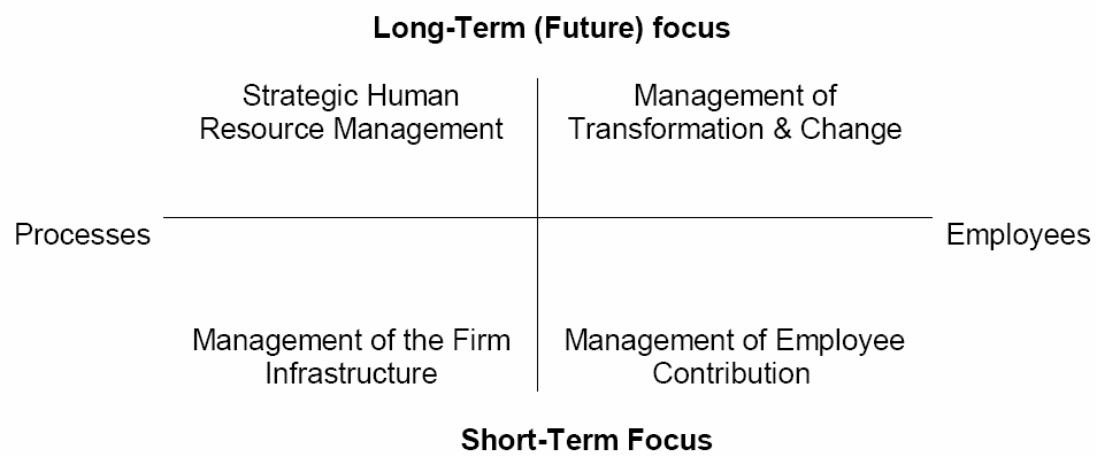
Ulrich’s (1997) model is one of the most expressed and acknowledged model for the contemporary HR. The model is well illustrated in the figure below. The model presents a simple model, in which the vertical axis emphasizes on the long-term and short focus and the perpendicular axis emphasizes on the processes and employees. The first quadrant (long-term focus and processes) emphasizes on strategic HRM, while the second quadrant (long-term focus and employees) emphasizes on management of transformation and change. The third quadrant (processes and short-term focus) focuses on management of the company’s infrastructure. Lastly, the fourth quadrant (employees and short-term focus) emphasizes on the management of employee contribution.
Strategic HRM emphasizes on the role of HR as a strategic partner. The conversion of organizational strategies to HR trends assist businesses in a number of ways. First, it enables businesses to adapt to changes. Second, it helps businesses to meet consumer demands since consumer strategies are transformed into special trends. Last but not least, it enhances business performance through efficient strategy execution. The HR trends assist in the achievement of business goals (Rafat, Shams and Javadi 11945).
The management of business infrastructure (quadrant 3) is the conventional function of the HR. This role involves effective implementation of the employment process, that is, compensation, benefits and compliance with business policies. Successful implementation of this role creates administrative efficiency. This role is also known as the role of an “administrative expert” or “shared services”. Administrative expert role divides the administrative services of the firm’s divisions, while safeguarding the quality of services. The term shared services refer to the basic provision of HR services (Rafat, Shams and Javadi 11945).
The management of employee contribution (quadrant 4) emphasizes on employee relations and labour relations. It focuses on the role of employee relations expert. The HR professionals should support the employees by linking their contribution to business success. This will enhance their capability and commitment to work. The metaphor for employee relations expert is “employee champion”. An “employee champion” understands employees’ needs and enhance their contribution (Rafat, Shams and Javadi 11946).
The fourth role of an HR expert is the management of transformation and change (quadrant 2). As culture protects and changes factors, the HR manages the transformation process. Change is a common feature in organizations. The capacity to handle such changes is the core competence of success in organizations. HR professional is very important in enforcing change. This is partly due to the fact that they are the custodian of organizational values, which is one of the principal strategic elements determining business potential. In addition, the HR professional understands the key change processes and can commit to them (Ulrich, 1997, p. 35).
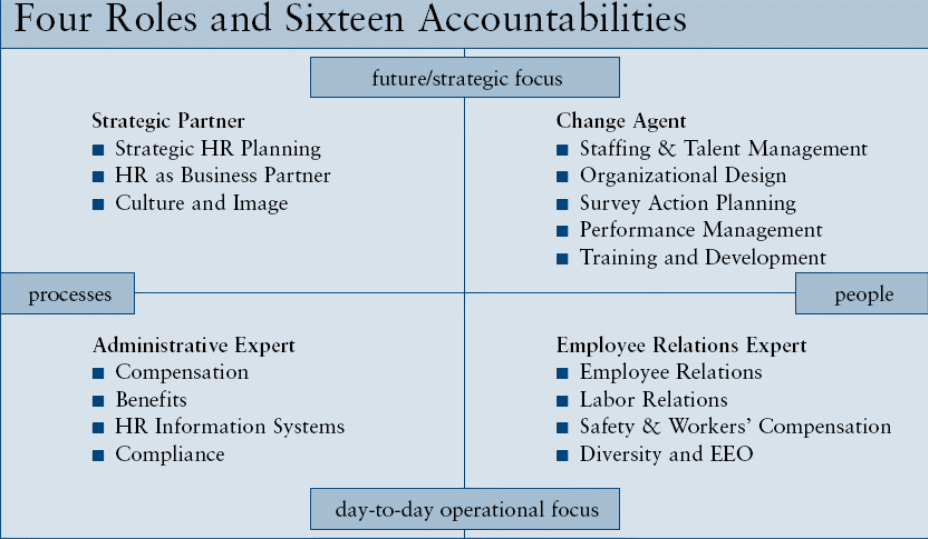
The extended Ulrich model (see figure 2 below) also presents a simple model, in which the horizontal axis emphasizes on processes and people and the perpendicular axis emphasizes on routine operations or strategic focus. The first quadrant (process and strategic focus) highlights the role of the strategic partner, whereas the second quadrant (strategic focus and people) highlights the role of the change agent. The third quadrant (process and routine operations) accentuates the role of the administrative expert. Last but not least, the fourth quadrant (people and routine operations) emphasizes on the role of the employee relations expert (Vosburgh and Mirage 14).
The accountabilities represent the expectations of each HR role.
Case Study: Analysis of the requirements of the four HR Related Jobs in the UAE
This section explores and analyses the requirements for HR related jobs in the UAE using Ulrich’s model. The requirements are based on a sample of online job vacancy adverts. The requirements and descriptions of the HR roles are examined, evaluated, and put in the four quadrants of Ulrich’s model.
The requirements for the HR roles are analysed and categorized according to the proposed four roles of Strategic Partner, Administrative Expert, Employee Relations Expert, and Change Agent. From the analysis of different job vacancies, it is clear that the level of requirements varies according to HR positions. For instance, senior HR managers are associated with the role of strategic partner and change agent. The roles of a strategic partner cutting across all the senior HR positions include development and evaluation of HR strategies and improvement of HR policies. On the other hand, the leading role of a change agent is sourcing and hiring (headhunting). However, the requirement level for the two roles depends on the general HR policy of a given company. For example, HR executives in VFS Global play all the three significant roles except the role of an employee relations expert. Nevertheless, the focus is on the conventional role of a strategic partner.
The situation is different in AMZ Group where the HR managers perform nearly all the four roles, but focuses on the role of employee relations expert and strategic partner. The HR manager in Charterhouse is expected to perform all roles according to Ulrich’s Model. The adverts provide clear distinction between roles. Landmark Gulf Group emphasizes on strategic HR doctrines and, therefore, the requirements are skewed towards the role of a strategic partner and change agent. The role of the HR assistant is limited to the role of change agents and administrative experts for nearly all the companies. However, HR assistants focus on the role of a change agent and administrative expert.
The implication of the Analysis
The results of the analysis are important for both potential candidates and organizations. The potential applicants should be aware that most companies in the UAE are looking for candidates with knowledge and experience in strategic management and programme implementation. The role of a change agent and administrative expert are also emphasized. Therefore, an individual applying for senior HR management positions must be able to align organizational strategies to HR strategies and trends. This enables businesses to adapt to change, meet consumer demand, and enhance business performance through efficient strategy execution. The candidates should also be aware that HR jobs in the UAE are very competitive. For this reason, they must possess extensive knowledge and experience in HR practices. Specialization is a disadvantage because companies expect a lot from the HR managers. The analysis establishes that HR managers carry nearly all the responsibilities stated in the Ulrich’s model. In other words, companies have increased their requirements.
Lessons for Applicants
There is a clear distinction between the senior HR related jobs and low-ranking HR jobs. The requirements for senior HR positions are so many, hence candidates looking for such jobs must possess far-reaching knowledge and experience in HR practices. However, their main focus should be on strategic HR management. On the other hand, the junior positions do not have a lot of requirements. The role of a junior manager is restricted to a change agent and administrative expert.
Lessons for Organizations
From the analysis, companies in the UAE pay a lot of attention to the role of a strategic partner. The emphasis on strategic HRM supports the idea that current organizations cannot attain competitive advantage without exploring HR strategies and trends. These strategies create a foundation for further growth and development. They also encourage companies to be more proactive that reactive in shaping their destiny. In addition, the role of a change agent is very important. HR managers are very important in enforcing change in the organization. This is due to the fact that they are the principal custodians of organizational values and culture, which are the main strategic elements determining companies’ potential.
Recommendations
- It is important for companies to base their HR strategies and trends on Ulrich’s model.
- When advertising job vacancies, organizations should be more specific. They should avoid generalization of HR roles through excess requirements.
- The roles of HR executives should be limited. Currently, HR managers are performing nearly all the roles stated in the Ulrich’s model.
- Candidates looking for senior HR related jobs in the UAE should try as much as possible to gain more knowledge and experience in HR practices. This is because the labour market in UAE is very competitive.
- Since UAE has a very competitive business environment, companies must pay a lot of attention to the role of a strategic partner and change agent in order to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage.
Conclusion
In the current business environment, success cannot be realized without strategic thinking. As a result, strategic management dominates the business world today. Numerous strategic management theories have been provided. Most of these theories and models focus on organizational objectives and the logic of achieving those objectives. Ulrich’s (1997) model is one of the most expressed and acknowledged model for the contemporary HR. The model defines different HR roles and their requirements (accountabilities). The analysis of the requirements of different HR related jobs in the UAE opens a Pandora’s Box. Most organizations in the UAE do not conform to the modern HR practices. The role of the HR manager is not well defined. Even though these companies emphasizes on the role of a strategic partner, the responsibility of HR managers extend to other roles defined in the Ulrich’s model.
Works Cited
Dessler, Gary. Human resource management, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 2008. Print.
Rafat, MohebbiFar, Shams Mahboobeh and Javadi Amir. “Analysis of the human resource management role in hospitals using Ulrich model”. African Journal of Business Management 6.50 (2012): 11943-11952. Print.
Ulrich, David. Human Resource Champions, Boston, MA: Harvard Business School
Press, 1997. Print.
Vosburgh, Richard and Mirage Resorts. “Developing HR as an Internal Consulting Organization”. Human Resource Planning 30.3 (2010): 11-23.
York, Kenneth. Applied Resource Management: Strategic Issues and Experiential Exercise, New York: Sage Publications, Inc., 2009.Print.
Appendix 1: HR Vacancies’ Advertisements


