Abstract
E-commerce has been hailed as the next formidable communication medium after telephones and cordless mobile technology and has made deep and impressionable forays into the technological progress of a business. E-Commerce has been a major innovation of the 20th Century as has transformed the way business is being done in modern times. It has revolutionized corporate thinking and has paved the way for innovative, dynamic business and greater knowledge processing in the conduct of internet and allied business processes. By annihilating distances, shrinking geographical barriers, and reinforcing trade cultures, it has set the benchmark of scorching pace for trade and commerce in the manufacturing, trading, and utility areas. E-business has made large contributions to the largesse of developed economies, so much so that today, many web-enabled businesses cannot conceive of business other than e-commerce aided business settings. In this study, it is proposed to take up the study of its impact on supply chain management and how each has underpinned the other in modern business. The methodology that has been used is through personal interviews and questionnaires (Annexure I in Appendix) which reinforced the hypothesis that e-commerce serves the greater interests of supply chain management behaviors.
In a rapidly changing world economic order where corporate is exposed to the vagaries and threats of global competition, the deployment of e-commerce aided technology for competitive advantages and judicious decision-making, and thus acquires strategic importance and critical implications. Given the kind of competitive advantages the Internet could provide to business endeavors and business promotion and growth avenues, it is only time and technology that could appraise e-commerce on its fullest extended scope In the distant future.
Tables and Figures

Introduction
E-commerce has been one of the most useful communication inventions since the advent of the telephone and mobile phones and is now considered a lifestyle rather than a means of communication.
The usefulness of eCommerce is sought to be explained through this example.
A homemaker in South London switches on her PC and logs on to the website of a popular supermarket. She browses through the grocery section of its online marketing page and selects her requirements. As soon as each item is selected, she clicks on ‘add to cart. After her ‘shopping’ is over, she selects make payment and is directed to make the payment using her credit card. The next day by noon, her order is delivered to her home. “Over the last two years, the UK has become something of a showcase for online retailing: plaudits for having the world’s largest online grocer in the form of Tesco.com:” (Understanding the growth of online retailing in the UK, Muriel Wilson-Jeanselme and Jonathan Reynolds, Page 7, Grocery ECommerce: Consumer Behaviour and Business Strategies, Edgar Elgar Publishing).
All this has happened with the shopper sitting in front of her computer. Imagine detailing this to a store owner or shopper living in the 1970s. He would be flooded with doubts as to how the payment can reach the store, the logistics, the storage, and transportation requirements, and a whole myriad of issues that most of us take for granted today regarding eCommerce and its usage.
Hypothesis: The role of e-commerce in supply chain management business
Objectives of this study
This paper deals with e-commerce and the supply chain in e-commerce transactions. It studies in detail how e-commerce deals with connectivity or establishing relationships and communicative abilities along the supply chain. It is an essential study because of the growing popularity of e-commerce. This study can be a valuable aid in introducing businessmen who wish to go online for the first time and to any person who may be interested in the working pattern of different types of e-commerce businesses worldwide.
The primary objective is to delve into eCommerce and how it underpins supply chain management. It offers illustrations of examples of companies like Dell computers and Contrary to popular belief, e-commerce transactions have taken place even before the internet came into existence. The humble telegraph and facsimile systems were the precursors of instruments of e-commerce. However, they were not interchangeable in the sense that only facsimile machines could receive such messages. The real use of electronics for commerce started during the 1960s when large corporations began the electronic transfer of information by direct linking of computers. However, the existence of different systems and incompatibility between them did not enable inter-company communication. The American National Standards Institute developed the ASC X12 for setting a common standard for EDI. “ASC X12 is the ANSI Accredited Standards Committee charged with developing EDI standards for use in the United States.” (Accredited Standards Committee (ASC X12), Electronic Data Interchange: An Overview of EDI Standards for Libraries (1993), IFLANET, UDT Series on Data communication Technologies and Standards for Libraries).
This was followed by the standard known as the UN/EDIFACT (United Nations Directories for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport) standard. EDI systems were also called VAN or value-added networks and were very popular especially in the United States as a medium of electronic data exchange. “Before the Internet even left the educational space, value-added networks (VANs)—operated by providers such as IBM, GEIS, and AT&T—have been connecting the Global 2000 companies, reliably carrying EDI messages, optimizing collaboration, and reducing costs in international business.” (Electronic Data Interchange, A Brief History of Electronic Data Interchange, Chapter 1).
Another system that became very popular was the Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT). The telegraph was one of the earliest facilities used for EFT, which, basically means, transferring money from an account in one bank to another account in the same bank or a different bank. “Since the 19th century, and with the help of telegraphs, funds transfers were a usual thing in commercial transactions.” (From where did it come? What is EFT or Electronic Funds Transfer and how does it work? Transactmoney.com). Swiping the credit card after purchase at a point of sale is a typical example of early-day fund transfer. The ATMs and the cash card are other examples that were in existence even before the internet was used for e-commerce. Both EDI and EFT were primarily used for communication, to reduce or obviate paperwork and speed up transactions. For example, the maximum that could be done in these cases was to use the telephone in ordering goods from a nearby store. It was more helpful in the transfer of money and using fewer currencies. These two instances were stated because they were the forerunners of e-commerce that is in vogue today.
It was only after the advent of the internet that the concept of e-commerce began to take off. It is interesting to note that the internet or the ARPANET was pressed in for military communication. The concept started way back in 1962 when one of the pioneers called J C R Licklider first mooted an idea of global connectivity of computers for scientific and military use. He worked with the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency and started work on it. Other developments like packet switching, TCP/IP protocols developed over time. Until 1991, the internet was not used for commercial purposes. Commercial use of the internet was through fees charged for sending emails. However, in 1991, the National Science Foundation stopped the sponsorship of the internet and privately-owned companies began to take charge. “The net’s dramatic growth continues with NSF lifting any restrictions on commercial use”. (1991, Exhibits, Computer History Museum).
Even during this period, eCommerce retained the same old system of money transactions only. The development of security protocols like HTTP and DSL during the late 1990s ultimately changed the nature of eCommerce. Companies began to offer online purchases of goods through the internet and people reluctantly began to respond. Companies like Amazon, eBay, and Dell were the pioneers of online retailing and selling. Businessmen found that doing business through the net had certain advantages and by 2000, a large number of companies soon started having their presence on the World Wide Web. “Online vendors, in their turn, also get distinct advantages. The web and its search engines provide a way to be found by customers without an expensive advertising campaign. Even small online shops can reach global markets. Web technology also allows to track customer preferences and to deliver individually-tailored marketing”. (History of Ecommerce, Commerce Land).
Ecommerce has grown to such an extent that almost every single transaction done traditionally is now being done electronically. The list would be too voluminous to be listed here, but repetitive illustrations would be relevant. Purchase and sale of goods, funds transfer, booking tickets, gambling, auctions, books and publications, trading in shares and stocks, e-ticketing, and online teleconferencing are some of the models that have successfully adapted to the eCommerce model today. New business models like business, knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) has evolved, and new ones will continue to emerge in the future also. For example, the BPO concept would not have been possible without the availability of dedicated and high-speed bandwidth. In the days before the internet, outsourcing would have to be done locally or within a region, whereas now geographical boundaries are no longer a barrier or functional constraint.
E-Commerce and Supply Chain Management: The advent of e-commerce has had a great impact on the supply chain management of companies engaged in this type of business. In most cases, it has helped to simplify the supply chain. In some cases, it has helped to almost eliminate the supply chain systems of a company. To give an example, a software company can deliver goods through the internet by making the customer download it to his computer from the company website. In this case, there is no need to physically deliver the product to the customer thereby eliminating the company’s delivery system. In any case, e-commerce has seen an impact on the delivery chain by varying degrees depending on the type of goods and services. The supply chain in e-commerce is taking the shape of a pull model, whereby the customers can pull the product from the manufacturer or supplier by placing an online order.
Traditional systems of supply chain management were more of a linear model whereby the suppliers of raw materials were at one end of the chain and the end-users were at the other. This linear system has also changed with each participant in the supply chain now being able to have direct contact with the users and end-user. In other words, whereas it was the retailer that had contact with the customer, now even wholesalers or manufacturers can have a direct link to the customer. “The old “push” model involves a linear flow of commerce that keeps many members of the supply chain relatively isolated from end-users. With the new customer-driven pull model, it is no longer a linear process. The new supply chain has each participant scrambling to establish direct electronic connections to the end customer” (E-Commerce Supply Chain Pull Model, Supply Chain Basics, Alberta future entre).
Literature review
Although eCommerce has been a major factor in business for the last four decades or so, the current literature does little to justify the importance that is now being attached to this aspect of global business and its ramifications.
Coming specifically to the case of Supply chain management use in e-commerce, it could be said that the first feature could be in terms of selecting and qualifying the desired supplier and the careful break-up of the sub-activities. Next, it is necessary to identify the population of the candidates, the next stage would be the stratifying of the population, using preset criteria, next is the collecting of preliminary secondary data which has many candidates, the next step would be the collection of primary data from selected candidates and the next would be in terms of collecting the basic data, the next step would be in terms of developing choice criteria to assess the true worth of the candidates and collecting primary data from selected candidates in the developing of choice criteria to assess candidates
In the next stage, it would be necessary to collect supplementary data that survive the first assessment and assess the candidates accordingly.
The final aspect in this stage would be the interaction among the parties and the interest of processes.
There are chains of sub-processes, which are regularly linked to one another, and in the composing of tasks, the focus of which are the smooth interacting between one sub-process and the next, it is necessary to learn directly to the inherent tasks, the smooth integration of one sub-process into the next, the next stage is about establishing and managing inbound logistics and the designing and managing international logistics.
The use of sub-processes has been illustrated by the use of illustration regarding the arrival of trucks in the manufacturing plant carrying raw materials, components, and supplies. The sub-processes must be well-coordinated, and it is needed that the arrival of trucks carrying supplies of raw materials, components, and stores materials must be co-coordinated with the plant’s input and inventory acquisitions and storage facilities. In addition, e-commerce would ensure that, upon arrival of the goods, the stock inward records, the purchases records, and creditors records are updated simultaneously. Therefore, the sub-processes ensure that the direct connectivity between the external agencies, suppliers, customers, customers, etc. is maintained.
This clarity has been established regarding the importance of business processing.
E-commerce throws up large scope for reassessing each core operation process.
It is believed that e-commerce is the annihilator of distances and measure of progressiveness of the industry.
It is widely believed that the rule of law is important and the interpretations of the results are speculative. Electronic commerce means buying and selling through the internet, and a web page could be as simple as just a catalog page with just a contact phone number or it could be a full-fledged site with numerous links and sub links.
Several factors impinge upon the functionality of e-commerce and they are:
- Privacy of operability
- Valuation
- Security
- Trust and authenticity
- User acceptance
- Pricing
- Legacy system
- Situation changes
- Inter-operability bandwidth limitations
- Information overlook knowledge management
- User interface measurements
- Payment procedure.
Ecommerce management in the context of SCM involves the designing, receipting, and flow of goods, services industrial items, and finance and the coordination with the respective responsibility heads for supplies of raw materials, goods, and services consumer items, etc.
“This process includes product design, order generation, order taking, information feedback, and the efficient and timely delivery of goods and services, and typically involves many or more of the business functions in firms that are linked to specific supply chains. Efficient and effective supply chain management assists an organization in getting the right goods and services to the place needed at the right time, in the proper quantity and at an acceptable cost.” [All conferences.com: Third Annual Supply Chain Management Symposium (2000- 2008)]
The objectives of the SCM in terms of improvement of the comprehension on how to transform the supply chain and associated activities, increasing the competitiveness aspects of business, government, and non-profit making organizations. The effective and efficient use of SCM invokes the getting of suitable goods and services to the requisite place at the right time, in the right quantity, at the right price, and following the right quality demanded.
We shall now consider the difficulties presented in e-commerce transactions: it could be seen that the lack of the physical infrastructural environment for nurturing and establishing e-commerce is a major hurdle to be overcome including the high costs of Personal Computers and the need to operate at a cost-efficient telecommunication system that facilitates e-commerce transactions. There are also aspects of transactional integrity and due to competitive and other reasons, comprehensive reports of firms’ e-commerce may not be very easily forthcoming- there are also aspects of “originating as they do in fundamental information asymmetries exacerbated by low entry and exit costs.” (Questia: Oxley E Joanne & Yeung Bernard (2008): Journal of International Business Studies: Vol 32, 2001: E-commerce Readiness: Institutional environment and international Competitiveness: Transactional integrity in e-commerce: The Hazards of Online Markets)
Since there are no direct linkages between buyers and sellers, a party may exit the market, and reenter it in another name, and nobody would be able to detect the fraud committed on the majority of web surfers. Moreover, there are also other aspects like tracking of offenders and absconders that would be difficult to identify and initiate legal proceedings against.
The Government, however, has thought of ways and means to reduce the incidence of internet frauds and it is possible now to have software installed, that could identify and penalize internet offenders. Therefore, it becomes necessary to seek the overall integrity of the national transactional system related to the degree to which the economy is severed by rule of law. The authenticity of payments changes available to E-Commerce participants, relating to the degree to which the economy is served by the rule of law. The second aspect relates to the authenticity of the channels of payments available to the e-commerce participants which is the function of the country‘s Financial institutions administration. Questia: Oxley E Joanne & Yeung Bernard (2008): Journal of International Business Studies: Vol 32, 2001: E-commerce Readiness: Institutional environment and international Competitiveness: Transactional integrity in e-commerce: The Hazards of Online Markets).
The efficacy of the rule of law concerns itself with transactional integrity and it affects the efficacy of transactions in three ways, namely, 1. To determine the limits of acceptable behaviors and ensure that this is maintained at all times 2. Effective punishment of wrongdoing would have a salutary effect on honest and genuine businessmen 3. The general attitude of the trade is important since it determines the manner and implications of internet trading and its wider impact on general trade.
Payment through internet channels is mainly executed through credit card systems and such credit card companies play a pivotal role in providing assurances to both buyers and sellers.
However, without access to personal computers and internet connections, consumers would find it extremely difficult to move from traditional to e-commerce guided markets. Even if enterprises have the necessary infrastructure to enforce an e-commerce regime, they may not be very keen on the idea unless they have confidence in the integrity of the transactions over the internet. Thus, the presence of reasonable interest in the internet, although a necessity, is not a Pre-requisite for development of e-commerce in today’s world.
The business of electronic commerce (e-commerce) and electronic business (e-business) are synonymous and could be used interchangeably. While e-business makes use of electronic platforms, such as intranets, extranets, and the internet to conduct a company’s business, at a macro-level, e-commerce deals with the buying and selling of products, services, and utilities reinforced by electronic means, in most cases, the use of Internet technology. (Philip Kotler & Gary Armstrong (2005): Glossary: G3: Principles of Management (New Delhi) Prentice Hall of India Private Limited.
The various aspects of e-commerce about SCM could be seen as follows:
- B2B (Business to Business): This is intended as an online vehicle to use B2B trading networks, auction sites, spot exchanges, online products, catalogs, barter sites, and other online resources to service new and existing clients and customers more effectively and achieve buying efficiencies and better prices. (Philip Kotler & Gary Armstrong (2005): Glossary: Principles of Management (New Delhi) Prentice Hall of India Private Limited.
- B2C (Business to Consumers): The online selling of goods, services, and utilities to final consumers- (Philip Kotler & Gary Armstrong (2005): Glossary: Principles of Management (New Delhi) Prentice Hall of India Private Limited. It is to be noted that in B2C, there is a direct transfer of goods, services, and utilities to the consumer without the need for any intermediaries or intermediaries.
- C2B (Consumer to Business): Online exchanges in which consumers search out for sellers of products, services, and utilities, learn about their terms of offers, and begin initiation of purchases, often, even negotiating the terms of transactions. Philip Kotler & Gary Armstrong (2005): Glossary: Principles of Management (New Delhi) Prentice Hall of India Private Limited.
- C2C (consumers to consumers) online exchanges of information regarding goods, services, and utilities for finding out final consumers Philip Kotler & Gary Armstrong (2005): Glossary: Principles of Management (New Delhi) Prentice Hall of India Private Limited
The level of competition requires that since the customers are limited, without them, the Company ceases to exist and plans must be laid to acquire and keep customers. The level of competition to acquire and retain customers assumes center stage in both the domestic and international business and it demands that the enterprise be quick, agile, and flexible to compete with effectiveness and sagacity.
“Electronic commerce, commonly known as e-commerce or eCommerce, consists of the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. The amount of trade conducted electronically has grown extraordinarily since the spread of the Internet. A wide variety of commerce is conducted in this way, spurring and drawing on innovations in electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. “(Frat file: 2008: e-commerce)
Supply chain management not only envisages internet business transactions but also encompasses all round efficiencies at all levels. Supply Chain means all inter-linked resources and activities needed to create and deliver products and services to customers. In the truest sense, the supply-chain spans from the point where natural resources are removed from the earth to the point where they are replaced in the earth: “from dirt to dirt.” (The role of SCM in e-commerce: Shaojun Xiao)
The literature review of this article finds that in the 21st century, the competition would not be between companies but between different supply chains. There are a series of questions to be answered, which are as follows:
- Is your product design attuned to supply chain considerations?
- Are your suppliers and outsourcers strategies co-coordinated?
- Do you and your partners have performance measures in place to measure true supply chain effectiveness?
- Is your organizational structure inhibiting successful supply chain management?
- What will be the effect of the Internet on your supply chain?
With a good SCM in place, it is possible to answer positively to all the above questions.
We shall now take up some illustrations and find out how the integration of SCM has benefited them:
Only Bookstores
Her customers span from Shanghai only to over 30 cities in China and overseas as well. The sales revenue has increased by 20%, and the sales cost has reduced 10%. In the meantime, inventory has reduced 30%, and the stock-in period has reduced to 1~2 days from 7~15 days.
Jincheng group
The waiting time for parts has been reduced by 10% per month, which contributes to total revenue of 6 million RMB annually. The total inventory level has been reduced by 20~30%. The finished product stock period has been reduced 10~15% while the stock period of parts and products-in-process has been reduced about 10%. It at least saved a storage cost of 20 million RMB in procurement.
Sondrio Group
Sondrio Group has increased the interchanging capabilities of her motorcycles parts by 50%, which has saved at least 6 million RMB costs The product series the development process has been shortened by 50%, which is about from 8 months to 3 months. The Group also accomplished a new product development with a reduction of design errors by 70%, which reduced approximately 7 million RMB losses The whole new product development cycle has been shortened from 15 months to 9 months, which brought a profit of 18 million RMB out of the added sales revenue of 120 million RMB within a year.
Case study: Dell Computers
Dell Computers is a glowing example of how effective use of the supply chain could make a good company an excellent one. Dell Computers established itself as an assembler of Personal Computers and servers over some years. It had boldly initiated its direct channel model when its customers were using indirect models. By the use of a make-to-order and postponement approach, supplier-held inventories, and other innovative technologies, it was able to gain a vital market hold and retain it over the period. (John Gattorna, Robert Olivlin, Mark W. Reynolds: Gower Handbook of Supply Chain Management : P 449: Which company has succeeded in building best-of-breed status)
Through the deployment of e-commerce aided supply chain management, it has been able to perform well regarding printers, PDA, and scanners. Despite several critical situations throughout its eventful history, Dell has always managed to come on top. It has realized that personal computers are not the only devices that users can use and therefore, the test of Dell’s Supply chain working would be its ability to adapt and adapt to the new world and gain multiple internet access. Nowadays miniaturization of PC is an accepted fad and Dell also needs to think seriously about it. Dell has always made it a policy to remain focused on delivery and made it their target for enhanced performance and excellence through management support. John Gattorna, Robert Olivlin, Mark W. Reynolds: Gower Handbook of Supply Chain Management: P 449: Which company has succeeded in building best-of-breed status:
Traits of SCM:
The most important characteristic of a supply chain management system is its agility to any new cooperation structure. The global economy makes the heterogeneous complexity of a virtual organization becomes unpredictable.
The current literature reviews seem to suggest that e-commerce has an all-pervasive effect on the entire business perspective of modern-day business and a lot of significant changes are occurring all over the globe due to the impact of e-commerce and SCM. Whereas in earlier times there were only selected options available for buyers and sellers for transacting in goods, services, and utilities, now thanks to e-commerce it is possible for suppliers to have a greater choice over the selection of their markets in terms of volume outputs, pricing and terms, and conditions governing the sale. Similarly, buyers could also exert greater discretionary powers regarding where, whom, and when to buy and also at the prices which were most favorable to them. In this process, the markets enlarged considerably, and also, greater choices and preferences became available.
As a direct impact of e-commerce and effects of SCM, quality received a major boost since now the buyers could switch over to new suppliers in case the existing supplier was not in a position to maintain quality and other exacting standards that were needed. Similarly, high-quality products and services were also needed to become wary of market trends and movements since now buyers had greater autonomy and were willing to exercise it. However, the other side of greater market choices was that persuasions and the impact value of the web became decisive factors. Servicing of orders became crucial since now the dimensions of speed; efficiency in servicing orders also became crucial factors. The sellers had to become more agile, market-responsive, attuned to the needs of the buyers, and ever responsive to changing market trends, conditions, and product preferences.
Whereas in the earlier times, the rapport of business connections served well, nowadays, it was a question of professionalism in attending orders and servicing it, which gained more priorities.
Since SCM invoked the entire gamut of the movement of products since it left the premises of the seller, until it reached the destination of the buyer, including channels of distribution, logistics, warehousing, after-sales servicing, and a host of other aspects, it now became important that all aspects along the Supply Chain Management system became efficient and responsive to market demands and client servicing. Moreover, another important aspect regarding SCM e-commerce is that, at any particular point in time, the buyers should be able to locate the exact position of the products or the stage of service provision, and this has been made possible with e-commerce. The tracking of in-transit goods and services was made more transparent and visible through the use of e-commerce, and the various service orientation it offered.
The various aspects of e-commerce with SCM could be seen as follows:
Privacy: It is important that the privacy of transactions needs to be maintained at the highest levels so that the transactions are held confidential from both the buyer’s and seller’s perspectives. These gains more significance, especially in a highly competitive market where rivals and business competitors may cause undermining of business value through unethical and highly competitive moves, which could affect the business of another player
High level of security and safety: E-Commerce-enabled transactions must be secure, especially the payment aspects. One of the main reasons why e-commerce still needs to be more developed is because of the notions of people who may not be willing to give out their credit cards and PINs to others for security and confidentiality reasons. Therefore, a higher degree of security and confidentiality must be imposed upon e-commerce-enabled transactions so that the buyers have the highest degree of trust and confidence in making eCommerce transactions. In addition, the level of trust and confidence, e-commerce has is directly linked with the volume of trade that could be generated in this environment.
Valuation: This is also an important aspect of the e-commerce-linked business since high-value transactions need to be serviced efficiently and effectively and also, the valuation needs to be consistent over a period to bring about the benefits of e-commerce transactions to the business community. It is also necessary that e-commerce is alive to the needs of the community to provide the best possible products, services, and utilities to them, and thereby enhance the prospects of trade in the future.
Trust and authenticity: It is necessary that considering the fact, that e-commerce is facilitating business among virtual strangers, trust and authenticity become hallmarks of the transactions. Both the sellers and buyers need to be in a position to trust and believe each other in totality and the transactions need to be authentic ones. This is because it would be difficult to distinguish a genuine site from a bogus one until a detailed examination and analysis are done, and by this time, it may be too late for the buyer not to be cheated by unscrupulous and bogus swindlers. Therefore, it becomes necessary those only aesthetic sites are surfed and business transacted after careful study, analysis, and confirmation of business sites. It is sad but true that often-genuine sites are made to become victims of wrong dongs by bogus operators since they would be imitating the design and contents of the original genuine websites, and the impact of bogus operators would also cause detriment to the genuine players.
User acceptance: This is an important aspect in e-commerce since the users must be fully convinced and aware of the fact that user acceptance of e-commerce is an important constituent of business dealing in today’s world and therefore, it becomes important that the total user acceptance be received in such transactions.
Pricing: By far this constitutes the most important yet undermined aspect of e-commerce transactions and forms the core of any business relationship. In the e-commerce area, the pricing is determined by mutual negotiation between the buyers and sellers and this is maintained over transaction negotiating and finalizing.
Legacy system: Under this, it is seen that legacy forms a retarding constituent since over some time e-commerce with SCM goes over numerous changes to remain on course, and e-commerce must remain competitive and useful over a long period through the efficiency of its deployment and results. Ignoring legacy systems by which no new improvements in the supply chain can be enforced due to traditional brick and mortar systems.
Situation changes: It is seen that technological changes are quick, rapid, and often radical, and E-commerce is aware of the devastating form that structural changes in any organization could result. Moreover, it is also seen that over some time, the sustenance of e-commerce would depend upon how much it could contribute to the efficacy and overall corporate growth of the enterprise, and also keep systems in place that could improve the bottom lines of the company Inter-operability bandwidth limitations: There are often cases when different forms of bandwidth are operated by different computer systems. Under such circumstances, inconsistency in bandwidth could result in inter-operability limitations. Therefore, it becomes necessary that necessary consistency be adopted for such limitations and action taken accordingly.
Information overlooks knowledge management:
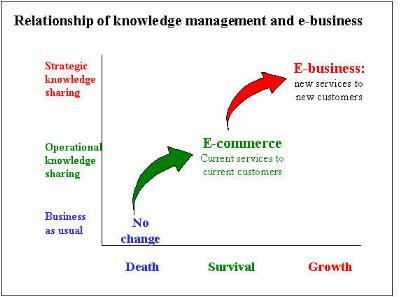
A minimal response to enable survival in this fast-paced world is to offer e-commerce, in which sharing of existing services and products electronically through the Web. For this purpose, the rapid sharing of expertise among employees is already a necessity. Without it, the company finds itself unable to respond to the requirements of the marketplace, whether it be Business to Business (B2B), Business to Consumer (B2C ), B2E, or 2E (Knowledge management and e-business: (2004).
Payment procedure. This is usually done through the use of credit cards but sufficient care has to be ensured that the payment channels are clear. Since the internet offers wide scope for fraud and misrepresentation, effective protection needs to be given through double encryption and other security precaution measures.
Benefits of e-commerce
The benefits of e-commerce can be seen from the fact that a customer sitting in Australia could order something through the Internet from a seller in England at any time of the day (or night) and could have the order processed almost immediately. One of the major efforts of eCommerce has been the use of the term “disintermediation” to mean the elimination of intermediate steps or organizations in the supply chain management systems or e-commerce.
Therefore in the present scenario, travelers purchase air tickets directly from the airlines and they thus eliminate the need for travel agents or intermediates. Again, in the case of trading stocks/ bonds, with the advent of the internet, the need for agents or brokers has been greatly obviated. Thus, due to the coming of the internet, most manufacturers are now selling products directly to their final customers, therefore obviating the need for a chain of intermediaries all along with the supply chain management system.
The interaction with the customers is important and the service teams recognize that technology is always subject to changes and the methods of doing business and its strategies help the firms to invest in strategies for increasing market share and revenue generations. If a company is not able to do so, it may result in a loss of customers.
Performance needs to be constantly upgraded and improved, and some managers need to recognize that decisions to adapt and adapt themselves to newer situations and conditions and need to be driven by the need not only to improve productivity but also improve the perfection of operations and result in better operational services.
Salient features of e-commerce
Along with the performance, it is also necessary to improve knowledge about customers. It is seen that in many cases, the management of organizations are fully aware of the customers’ purchasing behaviors and preferences and the past conduct of business with such customers,
The proper use of technology can provide a service company with a competitive advantage through its ability to be better understood with its behavioral patterns and past experiences with each of its customers.
One another main aspect of e-commerce with SCM has been the aspect of customization. In the past, technology offered service managers to provide for their customers a wide range of options. However, with the advent of technology, the services aspects have increased and the broad framework has reduced to customized order generation and servicing.
In the case of many corporates, whereas in the past, the Annual Reports of certain financial groups have been heavily bound and voluminous reports containing detailed reports of all the firms’ activities. Presently, each fund holder gets a much thinner but customized and easier–to–read booklet with summary information about all the mutual funds and detailed information only on the holdings of the individual fundholder.
Fundamentals of Operations Management
Mark M. Davis, Nicholas J Aquilano, Richard B. Chase, Jaydeep Balakrishnan (2005): McGraw-Hill Ryerson (P. 88).
One of the main effects of e-commerce has been the usage of e-commerce for effecting reduced operational costs. Just as, in the case of a manufacturing company, assets are acquired to realize cost savings, similarly, in a Service Company, technology can be applied in economies of scale and reducing of costs.
Economies of scale are often affected due to the processes of centralization and consolidation. In a given instance, while the number of operators remains the same, the level of traffic doubles, which results in additional savings. Again, the ability of the firm to relocate from high costs to low-cost areas, thus rendering high savings through the use of low-cost- of- living areas.
How e-commerce helps the retail sector in Europe
It is now proposed to take up a case study involving the retail sector in Europe, which caters to the selling and reselling of new and refurbished products to the public for personal or household consumption. In the European context, the retail business is a formidable one since it provided direct employment to more than 15 million people. (Enterprise and industry: Forthcoming study: Retail rationale.
The main areas that need to be focused on could be seen as:
- How e-business could address SCM challenges that retailers face.
- The impact that ICT and e-business have in the industry
- What is the kind of role that e-commerce plays in the retail industry.
It is common knowledge that e-business and e-commerce have conspicuously changed the business process of both retailers and consumers.
Retailers who are functioning in the “internet target segment” have been under constant pressure from competitors to adapt to internet sales studies. The rapid spread of e-commerce has indeed affected retailers’ conception of SCM and its significant role in present-day business transactions.
It is a dynamic field of study with rapid changes in technology and processes taking place regularly. A detailed study on e-commerce and its relationship and effect on the supply chain is covered along with this study with areas of strengths, weaknesses, and threat zones.
This is achieved as follows. “It allows an organization to execute electronic transactions with any individual entity along the value chain—suppliers, logistics providers, wholesalers, distributors, service providers, and end customers.” (L. Fahey et.al: IBM: System Journal: Volume 40: No. 4, 2001: Knowledge Management: Linking e-business and operating Processes: The role of knowledge management)
In the context of e-commerce, it needs to be seen that knowledge is not just about the assimilation of factual data but needs to concern itself also with its logical sequentialising and patterning of the thinking process, which also forms a significant part of e-commerce activities. How e-commerce could contribute to useful and positive harnessing to technological changes is also a matter of conjecture and thought process and needs to be contextualized for improving the quality and scope of e-commerce in the matters of modern technology and commerce.
It is also seen that, in simple terms, e-commerce deals with connectivity or establishing relationships and communicative abilities along the supply chain. This electronic connectivity may be used for different purposes to suit the requirements of the organization. The main aspects of connectivity over e-commerce could be seen as:
- Finding solutions to customers’ preferences and making candid attempts to achieve them. What are the kinds of customers and the problems that beset them and how e-commerce could possible take care of future customer solutions? The next aspect is in terms of rivals; how is it that in the case of business rivals, only certain customers are responsive to their marketing overtures while the rest are not? What are the criteria that determine the movements of the marketplace and whether the induction of e-commerce could bring about innovative models for strategic planning and execution that could vastly improve the future business prospects of the company? The use of e-commerce strategic models is also necessary to overcome the threats posed by competitive rivals and there is also a need for progressive firms to be able to integrate their business to suit the new e-commerce models, to reap the benefits of long-term benefits. In this case, it has been seen that certain firms are more successful in adapting to e-commerce when compared to others, and the strategic reasons for this need to be known understood, and utilized in its correct perspective. This is because they are favorably inclined to bring about new strategic models for the use of e-commerce in the firm, or institution, which has benefited from its usage over its continuance.
- The second aspect of e-commerce is concerning overcoming the activities and scope of rival firms. It is seen that a rival firm that could successfully integrate e-commerce into its working environment would stand in a more advantageous competitive position than one, who which is less successful in inculcating e-commerce. Since most of the competitive and viable manufacturers, distributors, or dealers are now enjoying the benefits of e-commerce through intranet and internet access, the firms that do not use e-commerce would be significantly disadvantaged, in terms of supply chain management servicing and meeting the challenges posed by competitive and rival firms. “Moreover, in today’s markets, where demand for a product can suddenly shift, a manufacturer needs to be able to configure and reconfigure a supply-chain network quickly, to meet changing demand.” (M.Shaw, R.Blanning, T. Stradell, A.Whinston Enterprise Channel Integration, and Mass Customization: Chapter 1: P. 17: Electronic Commerce: State of the Art: Handbook on Electronic Commerce)
- It is also necessary to perform an internal cost vis-à-vis benefit analysis to know whether the deployment of e-commerce has resulted in overall gains for the organization. It is necessary to know which assets have gone up and which assets have fallen in value, or in other words, the appreciation, and depreciation in the asset.
It is necessary to evaluate the performance of real assets in the e-commerce business and whether it has yielded desired results. “The business environment is rapidly changing, and intellectual capital has become a key asset of the enterprise. By managing its knowledge assets, an enterprise can improve its competitiveness and adaptability and increase its chances of success.” (Birman, Alex Ritsko, John J., IBM: Systems Journal 2001: Entrepreneur.com: Preface)
Nowadays, it is seen that a large number of transactions are being handled through the e-commerce gateway which has resulted in faster, efficient, and prompt servicing of clients.
It has been possible to link up different locations of a firm or company in diversely spread locations using WAN networks and brings about better business servicing and better customer servicing.
“The characteristics of the transmission facilities lead to an emphasis on efficiency of communications techniques in the design of WANs. Controlling the volume of traffic and avoiding excessive delays is important.” [Wide Area Networks (WANs)]
It has also been possible for the outsourcing of materials or supply chain management to be aligned into the e-commerce for excellent corporate results. Such acquisition, dissemination, and utilization of vital business information help corporates to function in a more streamlined and efficacious manner and being about all-around benefits in their operations. The challenges offered by internet and intranet transactions have redefined the scope and operational abilities of e-commerce and have redefined the contours of this business facility.
It is also necessary to review the disadvantages and negative aspects of e-commerce in the present context. One of the most vital dangers of e-commerce and internet-related business is that it could be subjected to identity thefts and fraudulent impersonation for illegitimate gains. Technology, though extremely beneficial to any field, also suffers from some disadvantages if used without care and discretion. Similar is the case of the application of the use of e-commerce.
The main concerns in this sector are as follows:
- Online thefts: Unauthorised persons can gain passwords, access codes, and useable personal details and then have them illegally used by impersonators and fraudsters.
- Systems breakdowns: There may be a total systems failure due to malfunctioning of critical components. If alternatives are not presented, this could lead to massive losses.
- Viruses such as worms, Trojan horses, etc could attack the systems and cause severe damage to them. This is possible since unknown hackers could cause viruses or other forms of attacks to invade the systems. Cyber-attacks have become a major cause of concern in modern-day internet settings.”In computers, a Trojan horse is a program in which malicious or harmful code is contained inside apparently harmless programming or data in such a way that it can get control and do its chosen form of damage” (TechTarget: SearchSecurity.com (2003).
Security systems work efficiently but a crisis could test its limits.
Therefore, it becomes necessary that security aspects be prioritized according to a level of risk, tried and tested, during the installation of the system itself. This can ensure the prevention of future breakdowns. Also, regular ‘mock’ exercises need to be conducted to make the employees acquaint with such crises and remain operationally competent and fighting fit.
4. ‘Phishing’ is a cause of major worry in today’s internet world. Under this system, fraudsters, posing as authentic websites, require sensitive personal details like Access Codes, Credit Card and Bank Account Numbers, etc. Having gained knowledge about these details, they systematically use it for illegally siphoning off funds from accounts, or for other fraudulent purposes. “The messages may look quite authentic, featuring corporate logos and formats similar to the ones used for legitimate messages. Typically, they ask for verification of certain information, such as account numbers and passwords, allegedly for auditing purposes.” (Russell Kay: Quick study: Phishing)
The very merits of the e-commerce system, in terms of speed, transparency, and ease in operations could prove its undoing. Therefore, it is necessary to inculcate several layers of security to thwart nefarious plans of hackers, invaders, or infiltrators globally, and it could be sterilized to prevent viruses or other forms of attacks from dubious sources. The best way to overcome these threats would be to take steps for doubly reinforcing security and protection aspects on a constant and regular basis and to protect the internet from possible acts of violation of internal privacy and the subversive actions of criminals and fraudsters. This needs to be coordinated with a team of IT specialists and professionals in the field who have hands-on experience in dealing with such kinds, of internet piracy and invasions. The implementation of the robust system along with the backup of suitably strong and deterrent legislation is necessary to ensure that the over +1 billion-strong internet users in the world are being provided the best services in terms of e-commerce utility value and usage and the phenomenal growth of the internet shall remain undeterred in the future.
In this context, it also needs to be mentioned that e-commerce methods offer multiple means to develop the human connections that must not only surround the electronic interconnectivity but that in turn, enable insights and intelligence to emanate that are fundamental to the unavoidably tough decisions that characterize moving (and many times moving rapidly) to e-business-driven operating processes.” (L. Fahey et.al: IBM: System Journal: Volume 40:No. 4, 2001: Knowledge Management: Linking e-business and operating Processes: The role of knowledge management)
E-commerce constitutes the capacity of the organization to connect, via electronic media, in a variety of ways, many organizations, both internally and externally for a large number of commercial purposes. It provides for one organization to execute electronic transactions with another individual or entity along the value chain –suppliers, logistic providers, wholesalers, distributors, service providers, and final customers. It facilitates real-time connectivity simultaneously along with entities for specific purposes.
Thus, the benefits that could be derived from e-commerce could be seen in terms of:
- New customer solutions
- How changes affect future customer services.
- Differentiations in the level of utility value for consumers.
- How rivals are leveraging e-business to provide new varieties of customer values.
- The methods by which e-commerce is giving rise to new types of competitors and business rivals.
- The techniques by which emerging markets will reshape traditional industrial boundaries, by the active use of e-commerce platforms.
- It could also be seen in terms of what new strategic models business is giving rise to, and the deployment of strategies by which firms may be able to surpass rivals by the use of e-commerce.
The reason why some firms are in a better position to integrate and derive more benefits from the use of e-commerce is that they are better positioned to integrate it into the currency of marketplace strategies. There are also factors like the increase or decrease in the use of assets due to e-business.
According to the previous research on the subject, business processes also plays an important part in the use of specific assets. Business processes are used to redesign and integrate solutions into the clients’ requirements.
Methodology
The following sources need to be used for e-supply, e-operation, and e-sales. It is proposed to use both primary and secondary data for this study.
Primary data
- Case studies that would result from data collected from several organizations.
- Semi-structured interviews and organizational documents form the main data resources
- Retail and logistic surveys would be gleaned through personal interviews conducted with the decision-makers of several retail enterprises in other countries
- In-depth interviews with retail industry experts to foster understanding of key issues in these cases.
Other aspects that need to be considered at the methodology stage are the following:
- Upstream Supply Chain Management in terms of the benefits and challenges of the integrated supply chain: While wide and diverse ranges of supply chain solutions are available to organizations, it is not cogent how popular and widespread these systems are with European retail enterprises. By taking up the study of the supply chain solutions not only as e-procurement and e-storage applications but also within the retail sector in Europe.
- Identification of the level of its penetration and suppliers in the retail industry. This would allow the location of the specialty pattern of a retail supply network. The focus must be on medium-sized and large retailers.
Supply Chain Interfacing: One of the main challenges confronting organizations today is in terms of the blending of in-house technology with new and existing ones. The main challenges would be in terms of data duplication due to the absence of data integrity and other inherent deficits in the organization. Aspects such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Business Process Management (BPM), and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) are needed to be integrated into retail systems but it is observed that retailers may not be fully aware of, or feel the need for these advanced systems to be integrated into the present sphere of retail activities.
Again, while considering the downstream e-commerce systems. It is seen that over the years these aspects of e-commerce have been gaining popularity and usage, so much so that in 2007,
6% of the total retail off takes has been with e-commerce. Thus, modern retailers are more inclined to invest in retail e-commerce enabled electronic systems, which are proving a business threat to the brick-and-mortar retail outlets. ( Enterprise and industry: Forthcoming study: Retail rationale)
Forward Supply Chain Management: This needs to be integrated into the business enterprises and it is now common knowledge that large companies are trying to gain a larger share of business profits by cutting costs to customers by employing effective supply chains. Modern business enterprises use outsourcing, but effective outsourcing predominately needs supply chains to be beneficial to business organizations.
The business needs to think about how to improve the level of service to customers by SCM-enabled e-commerce. The question of sending goods to the customers is called supply chain, but what about the return of goods back to the company, which is termed as reverse supply chain. (Third Eyesight: 2008: How efficient is your reverse supply chain)
The aspects of risks in the supply chain are always present. This is especially so in the case of businesses that has a limited buyer and selling options. In the case of limited buying options, or single-source purchasing, this has both benefits and threats. The benefits would be in terms of increased revenue generation and profitability and the other side would be in case of disruptions in volume and regularity of service. What would be the results in such cases?
Such enterprises must have built-in systems, which could monitor and review activities regularly.
The following aspects need to be pursued to ensure that the business runs smoothly and without hindrances:
Comprehensive & overall Model of supply chain taking into consideration, the totality of business activities and crucial supply chain management operations.
Using this model to localize risks that could be reduced or managed through process variations.
Implementation of IT solutions, wherever possible, which could provide clarity for planned activities and could also deal effectively with unexpected circumstances.
Enforcing a contingency plan that allows for processes, proceedings, and procedures that could effectively deal with potential risk situations.
Plugging of loopholes in the supply chain systems and the methods by which it could be effectively dealt with on a long-term basis.
(Understanding and managing Supply Chain Risks: Business process Innovation: SAP Insight P 9: narrowing the gap)
Both upstream and downstream supply chains need to be reviewed in light of possible lowering of performances relevant to such areas and its impact on future business prospects.
Reiteration of goals and objectives of the study:
The objective of this research has been to conduct a qualitative survey of how e-commerce affects the Supply chain management business and what is derived therefrom.
This could be seen in the context of the following aspects of e-commerce in business settings:
Since they affect the mode and outcome of this research:
- Speed of operations
- Connectivity
- Information visibility
- Market structure
- Uncertainty
For many years the aspects of physical technological advancement along with upgrading communication infrastructure have been high on the agendas of commercial enterprises. The reinforcement of supply chain conveniences along the freight and transportation business has also been acutely felt. The results have been both astounding and rapid. Conspicuous development in logistics has extended beyond traditional lines and has opened the vistas of a ‘new economy’, which has remodeled old thinking in the field of e-commerce and enhanced performance.
It could be very well reasoned that one of the greatest threats to the success of any organization in the industry is the desire and potential of enterprises to adapt to new situations and challenges. The one aspect that many services or utility areas may not fully utilize would be in terms of supply chain management for enhanced profits and cost savings.
The supply chain is an effective marketing tool and all members of the supply chain would need to integrate their efforts to suit the requirements of customers and their need satiation.
“Computer technology has made even greater supply chain improvements possible by providing greater information availability, increased savings opportunities, and the potential to increase internal customer service levels. Armed with more resources and better decision-making tools, supply chain managers can tackle many e-commerce initiatives that can make a significant and immediate positive impact on supply chain performance. (Enporion (2002) Dynamic commerce & your supply chain: Gaining a strategic competitive advantage: The supply chain evolution)

(Enporion (2002) Dynamic commerce & your supply chain: Gaining a strategic competitive advantage)

(Enporion (2002) Dynamic commerce & your supply chain: Gaining a strategic competitive advantage)

(Enporion (2002) Dynamic commerce & your supply chain: Gaining a strategic competitive advantage)
Integration of e-commerce into supply chain business:
It is seen that the integration of e-commerce is the most significant aspect of SCM and could be achieved in a variety of ways:
- Integrating internal procurement systems into marketplaces, and services such as financial settlement, logistics, and fulfillment, will give many companies the impetus to conduct more of their commerce through marketplaces
- Integrating internal procurement systems into marketplaces, and services such as financial settlement, logistics, and fulfillment, will give many companies the impetus to conduct more of their commerce through marketplaces.
- Finally, internal processes must be upgraded to reflect the changes introduced by the e-SCM systems. (Ian S. Hayes: Clarity Consulting: Optimizing the e-Supply Chain: The Final Frontier?)
The goal of supply chain management is to apply a systems approach to taking care of the entire gamut of information, materials services, and utilities from the stage of raw materials through the manufacturing processes to the final customers. Supply chains can be used by both producing units and service or utilities. The myriad aspects that are concerned with the delivery of products to the firm from suppliers are referred to as inbound logistics. After the firm has added value by changing the structure from raw stage to fully processed product, the finished products are then passed on to the customer through the firm’s distributors or local service providers before delivery to the end customers and this is termed as outbound logistics. The localization aspects may be just the delivery of the product or service to the customers or it may involve further processing or changing to suit the requirements of the product or service to the local markets.
From a macro angle, it could be seen that the supply chain can be defined as a group of organizations that would be performing the various tasks that are required to make the final product. If one were to take the process backward, it would be found that where the final product was a piece of furniture, then the supply chain, going backward would be (a) the retail operation where the furniture was acquired (b) the shipping company that delivered it (c) the producer of the furniture (d) the maker of the furniture (e) the hardware manufacturer and finally the timber company that harvested the wood from the forests.
Supply chain management could therefore be said to be the ability of the firm to work along with its suppliers to provide a working relationship with suppliers to provide the highest quality materials and components that are competitively priced. It is believed that the choice of the words supply chain management reflects the importance of suppliers in the ultimate goal realization of the business.
Supply chain management is a relatively new concept in business. Previously management theory suggested that the overall efficiency of the technical core or production function could be significantly improved by detaching the core functions from the uncertain outside environment.
In the past, the companies had to keep large quantities of raw materials and finished goods stocks for trading and other purposes. However, over the years, with the advent of supply chain management and other scientific systems, it became possible for companies to work more closely with their suppliers so that they are more responsive to cater to the variety of customers and their myriad demands and changing needs of the customers over time. While doing so, largely it was also possible to reduce, or in some cases, even eliminate, the buffer inventories carried previously. With modern techniques like JIT (Just in Time), it was possible for companies, like Toyota, etc to carry just the barest minimum stocks that were required to complete the programmed production, before the need for the next batch of orders would be requiring new stocks of raw materials, etc. After JIT, the next step in the SCM evolution concerned itself with the use of a single logistic supplier that could address all the transportation and distribution. The modern concept of innovation in SCM is the incorporation of the suppliers and their workers within the same manufacturing facility.
How a valid supply chain is designed and maintained:
A supply chain needs to address the following design aspects:
- Use of technology
- Logistics
- Procurement
- Performance metrics
- Inventory and stores control
- Location of facility
- Vertical integration
Vertical integration: It refers to the portion of a supply chain that the company owns or can use for itself. It is often seen that the greater the degree of control or influence that a company can exercise for its product lines, the higher is the vertical integration of the company. However, the current trend is that the lesser the vertical integration, the better off it is since they could concentrate on scarce resources to reinforce their core competencies, while suppliers could focus on their core competencies, and this way, both the companies would be more productive and useful to each other.
For certain product lines, it is better to have higher vertical integration as compared to others. For instance, clothing manufactures who own factories, would like to exercise stronger control over the supply chain and therefore would prefer a higher vertical integration, as compared to a make-or-buy decision. In a make or buy decision, the concerned decision-maker has to make up its mind whether to purchase the component or part from outside or to manufacture it by oneself. The profit aspects of the make or buy decisions has to be taken, and if competitive advantage is realized through designing and making the component or part may not be outsourced.
In the case of the enterprises, the total number of manufacturing units, retail outlets? and warehouses is a crucial decision since it involves financial decision making and needs to be made after careful analysis and thought.
Procurement: Over the years, procurement policies have refined themselves to establishing long-term business rapports with few highly reliable and quality vendors than having a plethora of sources for each type of purchasing the item. However, it needs to be exercised with care, since the total costs are needed to be considered for making business decisions. Purchase costs may entail not only the cost of materials but may also include transportation, insurance, warehousing, packing and forwarding, octroi and road duties, training of labor to use the products and operational and maintenance costs, etc.
However, certain other aspects also need to be addressed in terms of the fact that with product life cycles becoming shorter and development costs becoming costlier, the risks associated with these new product lines are also increasing. Companies are beginning to realize the importance of corporate responsibility in their management of supply chain facilities and there is added need for supplier companies to be conscious, profess good employee relationships? and obey the law of the land in letter and spirit.
Inventory management: This is by far an important aspect of supply chain management and involves the conversion of raw materials into finished goods, which is concerned with the storage, and movement of different varieties of inventories. The aspects regarding inventory would be in terms of the quantity to be available in stocks, the reordering quantity, the danger levels for stocks? and the relevant carrying costs of inventories. Aspects of reordering and carrying costs need to be weighed with the actual quantities needed for production and the decision of keeping excess stocks has to be weighed against budgetary considerations and carrying costs and risks involved. Moreover, investments in slow-moving stocks could be diverted to more productive avenues in the Company.
Logistics: This term has taken up added significance in the context of globalization and e-commerce aided business, where activities in one part of the world could affect life in another part, due to commercial interdependence and business interrelationships.
The continued focus on globalization with relation to both suppliers and customers has been the chief reason for the supply chain to become longer in terms of time and distance. Further, the logistics associated with the delivery of raw materials, components, and spare parts has assumed importance, due to competitive elements and price factors.
However, it also needs to be said that the lengthening of the supply chain runs contrary to the need of the enterprise to be able to serve the customers with speed and efficiency in all circumstances. This may be compromised during periods of material shortages, etc, due to unexpected or unforeseen circumstances when the supplier is not able to meet order commitments.
Mode of transportation: Different modes of transportation have their benefits and challenges and it would depend upon the characteristics of the firm and their business priorities to decide as to which line of transportation, or blending of modes, would be necessary for the enterprise.
The table below would depict the relative pros and cons of the different methods of transports available. As has been mentioned, the priorities have to be determined by the firm itself and the decisions taken on that basis. It is often the case that the firm may be using traditional methods, which may not be economical in the present juncture and needs to be reviewed and reassessed to suit present requirements. The Table shows the relative features of different modes of modern transportation methods and their comparative demerits and merits.
Table showing relative modes of transportational facilities.
Vendor-managed inventories (VMI ): in certain companies which have strong record-keeping costs and scheduling, it becomes necessary for inventor4is in the firm’s facility to be the responsibility of the supplier and the supplier has to maintain the same as and when necessary. This is referred to as VMI or vendor-managed inventories. It obviates the need for the manufacturer to maintain inventory records and tracking of transactions since all are maintained and records are kept by the vendor company.
Third-party logistics: This is an integral part of e-commerce aided supply chain management. In addition, is done through the establishment of strategic partnerships with logistic partners or allies. The approach entails using storage and warehousing facilities or distribution centers, which could conspicuously alleviate the delivery lead-time for critical item customers.
The process of disintermediation is important since it is at the core of e-commerce aided supply chain management in today’s world. In most cases of disintermediation, the intermediaries are eliminated or reduced significantly from the supply chain, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing costs. Many labors and time-saving devices and ideas, especially about port services and transportation conveniences form the core of the disintermediation process.
Also in the case of airlines that are, now directly interacting with customers to avoid commission fees to travel agents. This is done through airlines websites, which are equipped to provide online ticketing instructions and electronic ticketing.
Inventory positioning: This decided when and in what form to stock inventory in the supply chain. When a company has just one warehouse, the question of distribution to far-off locations would be severely compromised since it would take more time and costs to reach there. This has to be compared with the relative costs of setting up a warehouse near the customers’ place. There could also be situations when the company directly delivers to the customers, bypassing the warehouse or stores available in the location.
Inventory controls
A common method in inventory control deals with postponement, in which the aspects of mass customization are seen. It is seen that in the case of major computer companies, stocks of major components and not the final product are kept, and therefore the final assembly of customized product is made, only after the order is received from the customer. Similarly, in certain restaurants, the foods are procured only after the order is received which thus obviates the need for carrying wasteful inventory stocks. Thus, this method called postponement is a method by which companies carry out inventories without having to fret about its usage.
Performance Metrics: Companies often evaluate the performance of their supply chains with such measures as stock turns, lead-time for delivery of orders, and overall costs. This allows the company to benchmark its performance against that of its competitors and rivals.
A balanced scorecard method was adopted in certain cases, which evaluates benchmarks regarding financial, customers business, learning process, etc. There are several risks involved, which included the need to balance a variety of objectives during operations.
Use of technology
Technology and its use have a significant bearing on the supply chain e-commerce system. This provides a direct linkage between the manufacturers’ database and that of suppliers. In interest, the segment of Business 2 business has made rapid strides and the main reasons for this are that markets have evolved or developed for specific purposes.
Electronic commerce provides for a plethora of auction sites, etc. Sometimes, an auction site may become counterproductive since the main aspect is the determination of the highest bid and its eventual set off to such a bidder. Another aspect that is fast gaining currency is that of QR or quick response.
Another aspect is that of the freedom given to the suppliers to access the firm’s data, which could reduce the possibility of non- informant being made available.
Several aspects impinge on the successful implementation of a robust supply chain management program.
They are:
Trust, is an essential item between the vendor and the client and is the bedrock upon which participation and contribution of the new product development cycle are made.
Long-term relationships: With suppliers assuming strategic roles in the company, the need to establish a long-term rapport that allows the sharing of strategic foresight for the company.
Thus, it is possible that vendor and client can benefit each other through joint efforts and mutual assistance
Information sharing is a vital area, which delineates that all successful companies require the sharing of information between vendors and customers.
Individual strengths of organizations: The entering of joint relationships with the vendor is to enforce the best interests of the business or along time. A good customer would see to it that the business is profitable and strong. The selection of the vendor is very important.
Choosing the right type of supply chain: There are two aspects of supply chain functions, (a) the first being physical- the transformation of raw materials into finished goods (b) Market mediation, that is, the constant endeavors to ensure that the right type of products has entered the vicinity. However, in such cases, a lot would depend upon product characteristics and the typicality of products under review. Innovative products, it is believed to need a robust and responsive supply chain where customer preference and market demands are not easy to predict; however in the case of utility products, like foodstuff, the physical aspects of the business are more important.
It is to be seen that the main objective is not just to minimize costs but also to assume market mediation since the product must reach the customer on time.
Thus, it is seen that circumstances and market trends play an important role indeterminate of the type of supply chains and the nature of the product, service, or utility.
Thus, it is seen that the importune of supply chain management continues as long as companies become dependent on their suppliers. The reasons include (a) the increased emphasis on core competencies (b) the urgent need for flexibility in operations. (c) the need to share risks connecting with new ventures.
Due to the preponderance of these factors, it has become necessary for business firms to scour for talent to meet requirements from the various parts of the globe. The impact of globalization and the e-commerce revolution has transformed the way of doing business in the 21st century, especially since the length of the supply chain having been made longer, there are movements towards disintermediation, or, as explained earlier, the elimination of several middlemen and intermediary positions in the supply chain. The firms have felt the necessity to design and implement a robust supply chain management system, and abide by it for the long run.
Modern technology, especially in the movement of goods and services is moving rapidly, and the effects of competitive business are all-pervading issues in today’s corporate world.
It has become necessary to set up a strong and useful supply chain system that could address the issues at hand and contribute to enhancing working performance and profitability in future years for the enterprise.
It is also necessary to initiate changes in the SCM management procedures whenever it is needed to be addressed, and the marketing environment changes are poised for the future growth and prosperity of the enterprise.
Results with discussions
The results indicated that infrastructural and external factors have contributed immensely to the change in supply chain management strategies. The respondents were of the considered opinion that as companies strive to promote customer-based loyalty, the challenge to supply chain systems is also getting increasingly complex and intricate. (John R. Kennedy Jr.: Modus link: Meeting the challenge of supply chain management)
In the survey nearly 55 % of the respondents felt that the contribution of e-commerce to SCM has been immense, especially considering the role of the internet, intranet, and virtual reality (VR) in SCM business.
This has been reemphasized in certain services like shipping and air services where constant tracking of goods at any point of time, is necessary to serve the customers professionally.
Again, nearly 78% of the respondents believed that e-commerce has progressively built supply chains in many industries and has made SCM a strong force. The main advantages, according to most lay in creating efficiencies and reducing costs and creating avenues for faster SCM growth. The main grouse against e-commerce aided SCM laid in that competitive pressures that would belie high growth ventures and the concomitant results thereof.
According to the results of the survey, nearly 76% of the respondents the wider role and responsibility that could be taken up by eCommerce would be in terms of competitive advantages, market penetration and consolidation, brand building, and customer servicing including reverse supply chain functions. Nearly 73% of the respondents felt that strategic planning would be necessary to build and expand markets, especially, in non-urban areas.
According to the results of the survey, nearly 67% of the respondents felt that many areas needed to be strengthened in the context of supply chain management. This would be in terms of client servicing, meeting marketing and production deadlines, and improving employee morale and productivity, besides better training and induction facilities for staff.
As a result of the survey, nearly 64% of the interviewed respondents believed that there are perceived threats and challenges to e-commerce that needs to be ironed out, especially in the areas of logistics and business building. Since e-commerce is subject to modifications over time and technological changes, it is necessary to forecast and effect changes that could benefit the future investments in SCM business, which deals, mainly with client servicing and product distribution. In addition, the threats need to be seen in the context of competitive forces and rival activities, which may be directed towards destabilizing and demeaning the growth of this enterprise.
According to the majority, the role of e-commerce in the context of the supply chain could be enhanced in the future by first analyzing the present systems, their pros and cons, and the likely benefits, or challenges that enhancement would bring, in its wake. It should not occur that improvements prove harmful in the long run and thus, nearly 87% of the respondents believed that improvements need to be tested and certified, before becoming operationalized.
In the conducted survey, nearly 78% of the interviewees believed that the results seemed to reemphasize the fact that virtual improvements in the supply chain were overdue and this could be in terms of creating better and more productive avenues for deployment of internet, and e-business facilities in newer outlets and expanding the vistas of present business opportunities. It could also be gleaned in terms of better use of present technology for business gains and better corporate profits.
The integration of e-commerce- enabled business through supply chain management business could be further enhanced by adopting state-of-the-art functions and greater deployment of service provision with e-commerce routed SCM. These measures would not only ensure compliance with financial regulatory norms but would also incur totality business performance efficiencies, not only in key areas but also streamline business segments like production planning, inventory controls, strategic vendor relationships, and the control logistics relating to the movement of goods, services, and utilities to all parts of the globe. It is seen that e-working capabilities have a significant impact on the nerve center of supply chain functionings, especially in the context of growing world economies, which have to interact to bring about socio-economic development of developing and underdeveloped economies of the world.
The role of e-commerce could be increased in the future through direct and indirect procurements policies, fulfillment of e-business commitments both by the buyer and the seller, creating favorable balances between demand and supply of products, services, and utilities.
The main factors that would deter e-commerce aided SCM in the future would be in terms of the following:
“Traditionalism in the sensors market is expected to breed reluctance to adopt this modern sales channel and as a result, this market is not expected to fulfill its potential for some time. Concerns over security issues and a lack of familiarity towards purchasing via the internet will also deter new customers.”(Engineer live) E-commerce is a major challenge to sensor makers and distributors)
During the interaction with the respondents, nearly 76% of them thought that the major threats would be in terms of changing technology and entry of modern methods of eCommerce in preference to current ones in use.
With growing technological advancement, the number of options available for the industry would increase and there would be more “commercial websites, intranets, extranets, e-marketplaces, and trade exchanges.” (Engineer life) E-commerce is a major challenge to sensor makers and distributors:
It is seen that the major challenges to e-commerce would be in terms of the following:
- Reduction of transaction costs would be a major problem
- Shorter lead times would create outbound logistic pressures on suppliers.
- With increased globalization it is possible that competition level also increased dramatically, thus offsetting advantages over rivals
- The question would arise whether to go about e-commerce along with the firm or in tandem with others. Both have attendant risks and challenges while benefiting in terms of exposure to sharing costs, information, and markets.
- Criticality of operational system, especially in an emergency.
- The use of logistics is critical since any weakness would reflect and undermine a global strategy. (Enarsson Laif (2006): Future logistics challenges: P 66: Global logistics)
According to the majority of the respondents, the following challenges also continue to haunt the e-commerce industry:
- lack of merchandise selection on the sites for fear of cannibalizing sales or for reducing sales margins. (Ravi Kalakota and Marcia Robinson P 86: e-business 2.0 roadmap for success)
- Difficulties in integrating web chain into existing supply chains
- Having second-tier staff to man websites
- In e-commerce it is necessary to invest heavily without possible immediate returns. Therefore, companies need to take the plunge and work for the rewards, which may take time depending upon the market conditions and other factors.
Therefore, in terms of future challenges, the e-commerce functions in enterprises would need to take stock of existing market conditions, keep an eye for the future and adapt themselves to changing conditions over a short period.
In the context of e-commerce in supply chain management, it could be said that the benefits far outweigh the risks. This was expressed by around 85% of the respondents who believed that challenges are disguised opportunities in the e-commerce realms of business and need to be nurtured carefully and nourished with high doses of investments and infrastructure to provide lasting profits and benefits.
The questions that were asked to respondents were in terms of whether the benefits of e-commerce would be permanent. To this question, most of the respondents in this study research were of divided opinions. While around 59% believed that accrued benefits would be lasting, having been invested outside, nearly 69% felt that if the profits and gains need to be invested in Bonds gilt securities, and other high yielding return instruments to be truly effective and of a permanent nature. They quoted examples of large companies like World.com, Enron energy, and other giants whose dot com diversions provide their undoing in the end. While all such companies have amassed wealth during the boom years but they squandered it away during lean years and ultimately caused the untimely demise of such companies. Therefore, investments in high risks and critical areas need to be avoided as much as possible, and moderate and no-frills investments outside the company would be safe options that could satisfactorily answer their question on the risks posed by and needed to be addressed in the present context of permanency of e-commerce benefits.
Since the main risks relate to organizations, uncertain business environments, and trading with unknown entities, or individuals, the level of caution and circumspection that needs to be taken needs to be of the highest levels and commensurate with the level of activities and anticipated financial performance of the company in the years to come.
Nearly 76% of the respondents believed that permanency in the context of eCommerce would be more of a non-entity giving the environmental vagaries of operations and fluctuating fortunes of the e-commerce-induced business. Therefore, it is necessary to hedge risks with caution and in anticipation of business profits, and not make hasty and impassioned investments or acquisitions, that could prove fatal in the end. It is also necessary that proper research needs to be done on developing necessary strategies in one’s organizations by which the effects of change agents could be minimized and risks assuaged. A continuing policy guideline combined with executive action was what most 65% of the respondents felt was necessary for tiding over permanency or no permanency of operations. To gain permanency, was to conduct business as though it need to operate over the long term, and therefore investments in men, materials machines, and methods need to be established.
The final question that was posed to the respondents was concerning aspects of the reverse supply chain, that is materials moving from the customers back to the production units, and interaction with the management. The foremost reason behind companies giving importance to the reverse supply chain is that it reduces operating costs by reusing products or components. Though companies have been successful in fine-tuning their traditional supply chains, they need to make a change in their existing supply chain management systems to implement reverse supply chain management systems. This could be done by making plans, policies, processes, procedures, and protocols that could effectively deal with the reverse supply chain and help build a strong reverse supply chain network that deals with such issues. The reverse supply chain is the last bastion of the supply chain, which remains to be set into place for the organization, and most respondents believed that this was a necessary part of the success story of the enterprise.
Reverse supply chain compliments the existing forward supply chains systems and, according to the respondents needs to be further integrated into the system through a stronger and reinforced system backup so that the benefits of customer interaction could be further enjoyed and enhanced.
It is seen that for establishments to survive in a competitive business environment it is necessary that it is matched and fully integrated into the systems so that product customers are given the first and foremost priority and their needs and complaints are taken care of. In the final analysis, it would d be the customers who would determine the success or failure of organizations and this aspect of business needs to be fully understood and implemented in the future. Most of the research respondents believed that the reverse supply chain should be integrated well into the existing systems so that its benefits could be fully utilized and customer interaction further strengthened and reinforced by having a strong and viable reverse supply chain. Most of them were of the considered opinion that at the present juncture of business activities, this aspect of reverse supply was not given due importance and this may spell disaster since it would be akin to lowered standards of customer satisfaction and service.
Therefore, 69% of the respondents believed that this area of customer servicing needs to be further strengthened and reinforced in all organizations. In the manufacturing industries, the reverse supply chain would be in terms of accounting and dealing with returns, rejections, and defectives. However, in the case of services and utility industries, it would constitute feedback from the customers in terms of product acceptance, dealing with quality and service complaints, suggestions for improvements, and other feedback, especially for an enhanced level of customer servicing and interfacing in the supply chain management business processes.
Conclusions
From the above, it is seen that although e-commerce is a recent phenomenon, it has captured the essence of the 21st-century business and is seen as the forerunner of futuristic supply chain business. The main objectives of web-enabled e-commerce are to reduce business complexities and increase all-around efficiencies in all major areas of corporate accountability.
Ecommerce lends a sense of urgency and commitment to web-related transactions in the functioning of goods, services, and utilities, and co-ordination with SCM provides managerial impetus and efficiency to business enterprises.
Because of the studies made, the main benefits of e-commerce could be seen in terms of benefits in the following areas:
It is seen that in the modern world, business is becoming increasingly complex with more and more statutory and non-statutory requirements governing business in countries. The business of business is to do business is an oft-repeated quote and is very relevant in the context of internet business. Although since internet business transcends geographical and regional barriers in its quest for increased business growth, it is necessary to respect laws and regulations governing internet business in transacting countries. A lot of laxities are allowed for web-enabled commercial transactions but they need to be within the ambit of laws relating to contract formation, interaction, and payment regulations. Thus, internet laws could be said to be of significant considerations in business dealings, especially in a multi-national business setting.
The second aspect governing the internet is that it is a global phenomenon and is growing rapidly. “Internet-based technology provides the fuel and the spark for many changes to today’s industry supply chains.” (Graham Sharman e-supply chain management –venturing beyond e-commerce: P. 24: Issues and challenges for management)
The supply chain management is concerned about the logistics of marketing and e-commerce provides internet and intranet support to its activities. “The supply chain management concerns organizational aspects of integrating legally separated forms, as well as co-coordinating materials and information, flows within production-distribution networks.” ( Hartmut Stadtler, Christoph Kirger :2008: it world Canada:
Supply chain management and planning.
The other advantages of eCommerce would be in terms of redefining the frontiers of electronic technology and making newer use of existing e-commerce techniques for advancement. It is important that a complete study of existing systems needs to be evaluated before decisions are taken regarding its ultimate implementation and execution in the organization, especially in financial and other crucial areas. The purpose of e-commerce is to simplify and streamline existing models while saving costs and achieving efficiency. In a large organization with diverse business interests and locations, the internet and intranet serve to gain optimum usage of communication channels and build a better business. However, there are also security factors to be considered.
“The vast array of opportunities to be found through the deployment of intranet and Internet solutions underscores the absolute need for using a Web server with solid security completely integrated with the operating system.” (MSDN (1999): Microsoft: Internet Information server security overview: conclusion.
Other aspects in e-commerce may cause it to be at risk and this is about security risks and virus attacks. Although internet sites are protected sites, they could be subject to the virus, or attacks from hackers who could infiltrate the system and cause untold harm to the computer systems. The need for firewalls, double encryption, and reinforced PINs is needed to offer maximum security to the users. In addition, users need not disclose classified and confidential information to anybody other than authorized personnel after proper identification of their status. These could ensure that maximum security is provided to internet users.
Although e-commerce has merits and high utility value in the present business settings, it comes with a price. Efficient systems need installation costs, and more significantly, maintenance and operating costs over their useful life. Therefore, economic and financial reviews must be conducted before investment proposals are committed. It is also necessary to conduct tests for Return on Investments (ROI),
Payback period analysis, Present value analysis (PVA), etc. to gauges the risks involved and the quantum of investments required. It is also necessary to ascertain cost-benefit analysis (CBA) before investments are made.
It is seen that B2B (Business to Business) has evolved more rapidly than B2C or E2. This is because the need for high volume business to business information transfer is more in demand than to consumers. But it is also necessary that consumer needs through the internet need to be encouraged, and more and more people, especially in 3rd ( Third ) World and emerging economies in the Indian sub-continent, Far East, and developing regions in African countries are exposed to the internet and computer technology. The concentration of greater use of e-commerce in the developed countries of Europe, the Middle and the Far East, especially China, has created regional imbalances and has not given the importance that it needed to receive in these areas.
Finally, it could be said that the concept of globalization need not be an enrichment of developed countries at the expense of poorer economies, especially in Africa and certain parts of Asia, etc. E-commerce with SCM needs to develop a holistic approach to electronic communication and its positive impact in not only the fields of business but also critical areas like education, healthcare, agriculture and industry, environmental studies, defense, and other equally important areas.
Ecommerce needs to widen the vistas of its deployment to cover major areas that have hitherto been neglected either due to poor infrastructural facilities or lack of authentic information.
It is also equally important that respective governments be enlightened about the widening scope of e-commerce and business for use in government departments to aid good governance and exercise greater control over the activities of the State.
E-commerce has taken the world to great heights due to its sound deployment for human benefits, but it also needs to be realized that retrograde steps could spell disaster for the world economy. This could be possible if e-commerce is used for unethical uses, which in the end would be self-destructive.
In the final analysis, it could be said that the benefits and positive aspects of e-commerce-aided SCM far outweigh its challenges. It is necessary that in the years to come, greater utility value needs to be assigned to e-commerce aided supply chain management for the overall growth and development of the world economy. It is also necessary that with greater resource building and value creation in e-commerce, it could be successfully applied either more widely in existing uses, or newer areas could be explored that could immensely benefit existing businesses that are bereft of e-commerce benefits.
It is only thus that greater gains could ensure to the world community that has been using e-commerce for corporate growth and wider applicability.
Appendix 1
Questionnaire
- How do you view the contribution of e-commerce in the supply chain management business?
- What, according to you, are the main advantages of e-commerce in the supply chain business?
- Given the present role of e-commerce in SCM, what wider role and responsibilities, on a macro level, do you envisage for e-commerce in the context of SCM?
- Which areas, in your opinion, need to be improved on e-commerce’s role in SCM?
- What are the perceived threats and challenges of e-commerce in SCM?
- What are the possible interventions by which these threats and challenges could be met by enhancing the utility of e-commerce?
- Do you feel that role of e-commerce in the context of SCM be increased in the future? How?
- Could present e-commerce in the present environment of globalization and changing facets of the business environment be sustainable in the future? How?
- What, in your opinion, are the major challenges to e-commerce in the future?
- Do you feel that that e-commerce benefits in supply chain management are a permanent feature of modern business? If yes, Why? If not, why not?
- Do you think that the process of ‘reverse supply chain’ could become a regular feature of e-commerce in SCM business?
Cited Works
Modus Link: Meeting the challenges of Supply Chain Management: Models Success: determining the right model: Meet specific demand needs. Web.
Graham Sharman : e-supply chain management –venturing beyond e-commerce: P 20 Internet- Based information accelerates key supply: Supply Chain Trend. Web.
Understanding the growth of online retailing in the UK, Muriel Wilson-Jeanselme and Jonathan Reynolds, Page 7, Grocery ECommerce: Consumer Behaviour and Business Strategies, Edgar Elgar Publishing. Web.
Accredited Standards Committee (ASC X12), Electronic Data Interchange: An Overview of EDI Standards for Libraries (1993), IFLANET, UDT Series on Data communication Technologies and Standards for Libraries. Web.
E Commerce Supply Chain Pull Model, Supply Chain Basics, Alberta efuturecentre. Web.
Electronic Data Interchange, A Brief History of Electronic Data Interchange, Chapter 1. Web.
From where did it come? What is EFT or Electronic Funds Transfer and how does it work? Transactmoney.com. Web.
1991, Exhibits, Computer History Museum. Web.
History of Ecommerce, Commerce Land. Web.
E Commerce Supply Chain Pull Model, Supply Chain Basics, Alberta efuturecentre.
All conferences.com: Third Annual Supply Chain Management Symposium (2000- 2008).
E Commerce Supply Chain Pull Model, Supply Chain Basics, Alberta efuturecentre. Web.
Questia: Oxley E Joanne & Yeung Bernard (2008): Journal of International Business Studies: Vol 32, 2001: E-commerce Readiness: Institutional environment and international Competitiveness: Transactional integrity in e-commerce: The Hazards of Online Markets.
Philip Kotler & Gary Armstrong (2005): Glossary: Principles of Management (New Delhi) Prentice Hall of India Private Limited.
The role of SCM in e-commerce : Shaojun Xiao. Web.
John Gattorna, Robert Olivlin, Mark W. Reynolds : Gower Handbook of Supply Chain Management : P 449 : Which company has succeeded in building best-of-breed status : Web.
Knowledge management and e-business : (2004). Web.
Fundamentals of Operations Management: Mark M. Davis, Nicholas J Aquilano, Richard B. Chase, Jaydeep Balakrishnan (2005): McGraw-Hill Ryerson (P. 88).
Birman, Alex Ritsko, John J., IBM: Systems Journal December 2001: Entrepreneur.com: Preface: Web.
Wide Are Networks (WANS). Web.
Techtarget :SearchSecurity.com (2003). Web.
Russell Kay : Quick study :Phishing : Web.
L. Fahey et.al: IBM: System Journal: Volume 40:No. 4, 2001: Knowledge Management: Linking e-business and operating Processes: The role of knowledge management: Web.
Enterprise and industry: Forthcoming study: Retail rationale: Web.
Third Eyesight: 2008: How efficient is your reverse supply chain : Web.
Understanding and managing Supply Chain Risks: Business process Innovation: SAP Insight P 9 : narrowing the gap : Web.
Enporion (2002) Dynamic commerce & your supply chain: Gaining a strategic competitive advantage: Web.
Ian S. Hayes: Clarity Consulting: Optimizing the e-Supply Chain: The Final Frontier? Web.
John R. Kennedy Jr.: Modus link: Meeting the challenge of supply chain management: Web.
Engineer live : E-commerce is major challenge to sensor makers and distributors: Web.
Enarsson Laif (2006): Future logistics challenges: P 66: Global logistics: Web.
Ravi Kalakota and Marcia Robinson P 86: ebusiness 2.0 roadmap for success: Web.
Graham Sharman e-supply chain management –venturing beyond e-commerce : P.
24: Issues and challenges for management : Web.
Hartmut Stadtler, Christoph Kirger :2008: it world Canada: Supply chain management and advance planning : Web.
msdn (1999): Microsoft:Internet Information server security overview: conclusion. Web.