Introduction
A market-oriented company is characterized by having a set of behaviors and also activities which have been implemented in order to reflect the degree to which a marketing concept has been adopted as a philosophy in an organization. This is because of the competitive landscape and the firm’s ability in maintaining and acquiring a market orientation that is effective has further gained strong attention in the current literature strategy.
Review of the literature on the organizational and managerial characteristics of a market-oriented company and the antecedents of this orientation
In order for a business to improve its performance then it must rely on the market orientation that is based on doctrine of the classic marketing. According to this doctrine the satisfaction of the customers’ needs and requirements is the major path to the improvement of the business performance market orientation refers to the implementation of the marketing concept.
Even though the concept was introduced in 1960s its impact on business performance was not a subject of study until in the early 1990s. Since that time there has been a very new perspective of viewing the marketing concept since its implementation within the marketing literature has already occurred. However there are five different perspectives that have been advanced which visualize the market orientation as the implementation of the marketing concept and they include;
- The decision making perspective.
- The market intelligence perspective.
- The culturally based behavioural perspective.
- The strategic perspective.
- The customer orientation perspective.
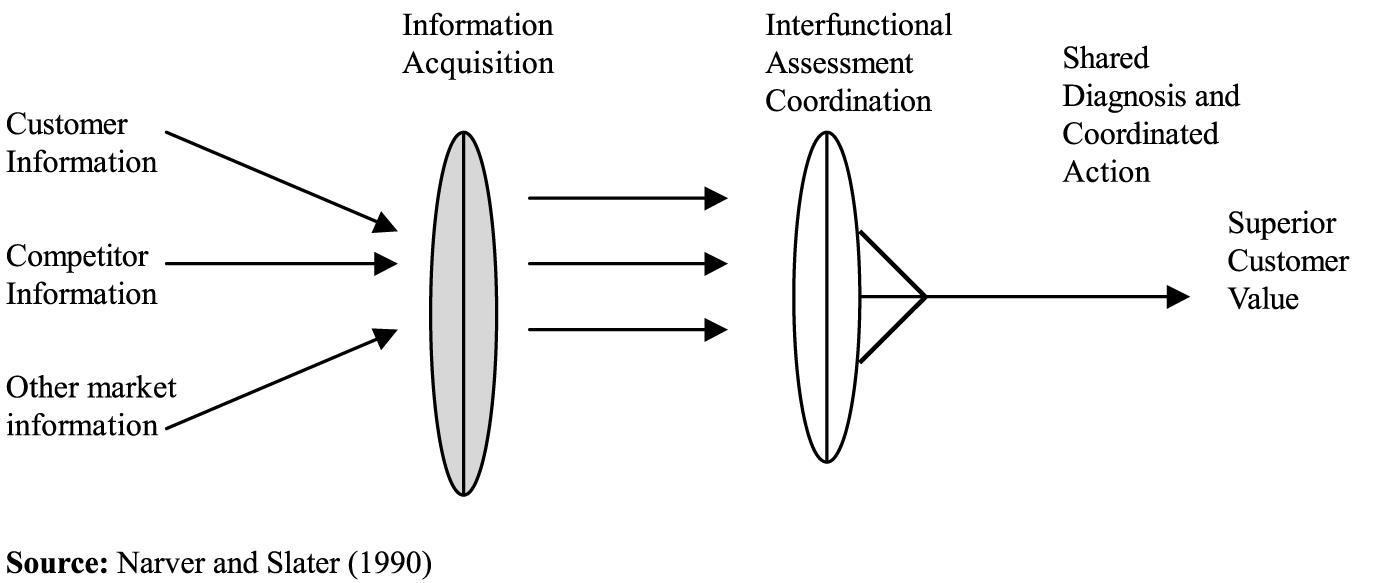
Out of the above mentioned perspectives the culturally based and the market intelligence perspective have reached the scholars and the practitioner’s attention. The culturally based behavioral perspective has defined the market orientation as a business culture that commits a particular organization to creating a super value for the customers and it is further supported by the work of Slater and Narver (1990).
This model includes the behavioural components of the market orientation all of which are incorporated to the intelligence dissemination and generation. Market orientation similarly includes a long term focus as well as the organizations profitability as criteria in decision making. The market intelligence perspective of the market orientation refers to specified behaviors that lead the improvement of a company’s performance.
Some researchers viewed the market orientation as implementing a market concept in other words a firm that is market oriented has actions that are consistent with the concept of marketing. There was a proposal by Kohli and Jawarski (1990) on the three core themes in the marketing concepts;
- customer focus
- profitability
- customer focus
Market intelligence perspective refers to the collection and assessment of the customers both present and the future needs including the impact of the government regulation, technology environmental forces and also competition. However market intelligence should be disseminated and communicated in an entire organization in both informal and the formal ways.
The effective dissemination of the market orientation is very vital since it makes a provision for a shared basis of the collaborative efforts by the various departments in an organization.
While the marketing concept has always been accepted as an article of faith then the market orientation concepts remains highly ill-defined some researchers such as Shapiro (1988) equates the market driven with the customer oriented. On the other hand Slater and Narver (1990) include the competitor as well as the customer orientation in their definitions of the market orientation.
Other researchers looked at the thirty five years of the marketing literature and the work n the related disciplines and concluded that it further revealed lack of a clear definition. A market orientation includes the monitoring of factors such as the governments regulations and the competition which further influences the consumer’s needs and also preferences..
An example of the specific factors which relate to the concept of the market oriented product development that is taken from the literature includes;
- the extent of contact with the customers and the market during the product development
- the extent of the upfront marketing
- the marketing process representation in the development process
- knowledge of the competitors and the markets
- the presence of a marketing competence
- use of the market research advanced techniques
- the extent of the product superiority
There has been a very close link in the literature to the culture of a particular firm and since an orientation of a market is highly embedded in a firm’s culture thus this leads to the exploitation of the core competencies which are inherent within the firm. On the other hand this may be the most dynamic and also predictable source of a sustainable competitive advantage in the new and also changing environment. (Webster (1994)
A market orientation similarly has the following behavioral components which include; the customer orientation, the competitor orientation and also the inter-functional co-ordination. For the reason that there is a changing competitive environment there is a stream of research which has been developed to focus on studying the orientation of the markets. Most of the research studies further examine the behavioral aspects of the market orientation.
For a firm to be a competitor oriented it should face on the short term as well as the long term strength’s and weaknesses of the competition. On the other hand if a firm has to be consumer oriented then it must understand its target buyers and the firm should also be able to create a super value for the target buyers (Lilien 1989).
Similarly if a firm needs to achieve an inter-functional coordination then it must actively co-ordinate the usage of the company resources in order to create a superior value for the target customers. Slater and Narver (1990) however from their literature review stated that the three behavioral components are all of equal importance.
In this era of increasing turbulence in the market place and the intensifying of the competition there is a strategic necessity of a robust market orientation. The market oriented firms perform better than the firms which are not market oriented. The market oriented firms have superior skills of understanding, keeping and also attracting their customers so that they can further a superior customer value as well as keep their strategies in alignment with the changing market requirements.
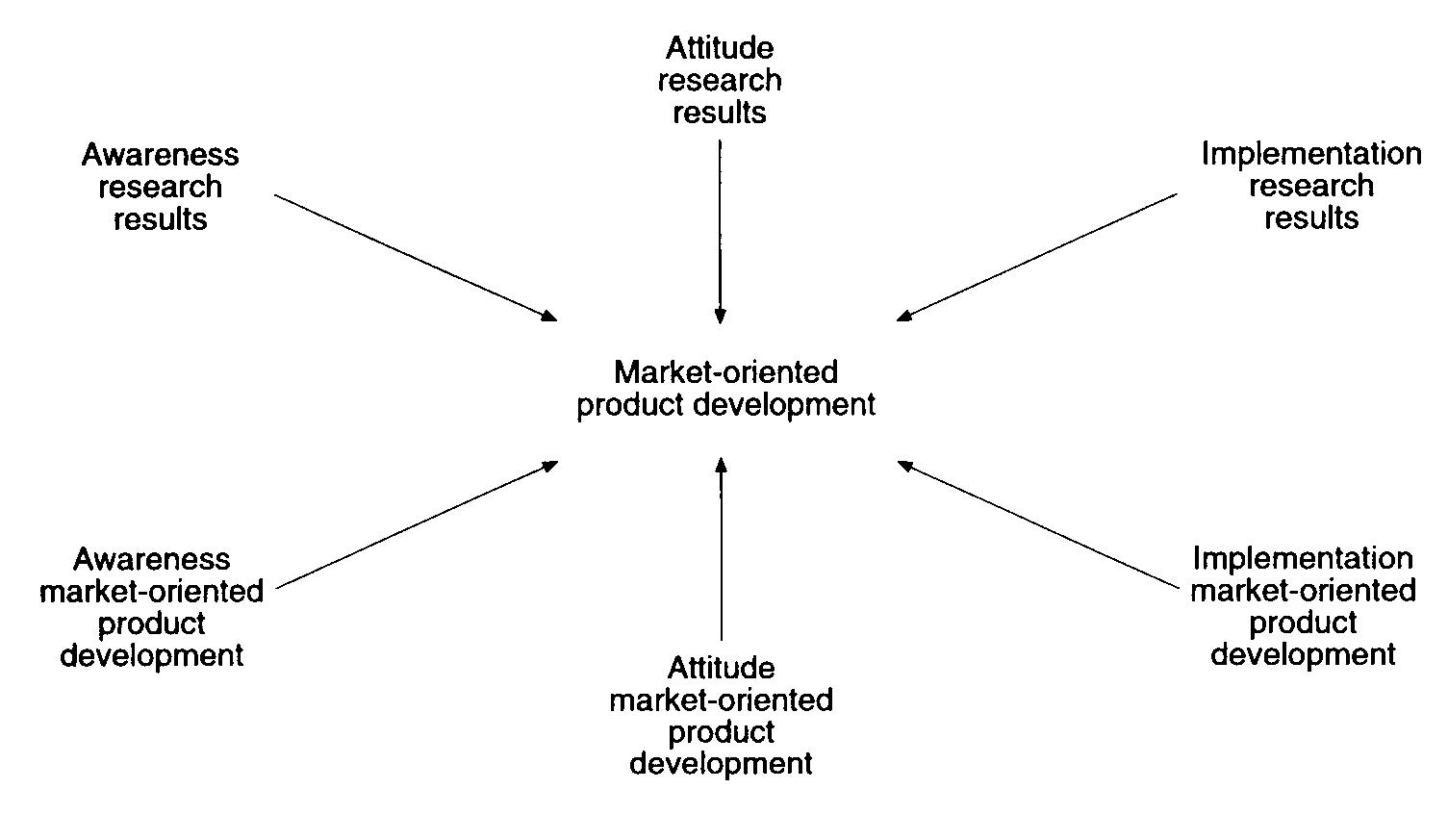
When a firm becomes market oriented then it has the internal strengths which are very hard to imitate and which are also not transparent or even transferable. Research has shown that the capabilities of the market driven organizations which include; market relating, market sensing and also market relating are clearly and directly linked to the underlying company values and also its culture.
These issues can be considered to be stemming from the cultural openness of the company such as its external orientation to the market, the company’s clarity in its strategy structure and also vision, the leaders role model relevance, the immaterial and material rewarding of the employees and also the quality of the information systems.
A market oriented company is also characterized by the production of goods under its own brand name with a Database of various consumers who purchase the company’s goods and the company also has a regular system of communicating with its customers. Similarly a marketing oriented company further gets past its first customers be it the manufacturers or even the distributors and the company also knows how its components and its products benefit the end users. (Malik 1994)
On the other hand a market oriented company is aware of what the consumer market wants even before the distributors and the retailers know about it. The manufacturers can get the market knowledge through their sales representative or even through the systematic marketing research that is conducted on the consumer wants and needs
In the marketing literature there is a preposition that any firm which has the ability to raise its market orientation level will further improve its performance in the market place. The market oriented firms are further defined by their superior understanding 0f their customers and also the future and current needs and the ability for the firm to offer solutions that need to be related to the consumers’ superior needs and the rival’s offerings. (Johne 1995)
The degree of market orientation in any given organization highly depends on the presence or even the absence of some external and internal factors. Such factors are then labeled as the market orientation antecedents. Organizations senior management characteristics, the departmental dynamics and the organizational characteristics are the internal antecedents or the internal factors.
Similarly the technological and the market turbulence together with the five competitive forces intensity are the external antecedents or the external forces.
Application of this literature to The Body Shop and comment on the market orientation of this organization
Body shop is a chain store that has more than 200 stores in more than fifty countries and its headquarters is in England. It further deals with a very wide range of products for the body, hair, face and also home. The body shop is said to be market oriented since its culture is systematically and also entirely commuted to the continuous creation of a superior value for its customers.
The organization clearly understands its market and it is also committed to leadership in the markets in which it serves. The body company also delivers a total quality so as to guarantee that its customers are well satisfied. The company has however been using the three management characteristics which include the customer focus, the competitor’s orientation and also the teams approach. (Hayes 1980)
This has made the organization to have a very strong orientation as it works towards creating communicating and also delivering the customers solutions. This has also further led the company translating into high levels of consumer satisfaction and also profitability. When the customers are satisfied by a company’s products and also services then the business profits greatly increase and the organization then retains its customers.
The organizations target market selection and also its product positioning involves two key aspects which are the process of market segmentation and the customization programs and their offer. The body shop chain stores have a trading charter that defines the trading relationships of the organization to the suppliers, franchisers and also the suppliers.
This has made the company to maintain commercially viable and mutually beneficial relationships that are based o trust. The company has also applied the concept of the market orientation in the development of its new products. In the recent past the company was confronted with the changing market conditions and this led to its restructuring which highly emphasizes on the market orientation. (Eccles 1992)
The company has however shown a great deal of interest in the market orientation concept and this has made it the very core issue of the organizations marketing concept.
Retailing in body shop demands a more complex and a multifaceted approach than it is already being offered in the existing frameworks of the market orientation. Based on the previous literature the body shop products are offered as a mix of the physical goods that have been put together as product ranges and both the services and facilities.
Body shop stores environments includes components which range from the methods used in exposing their products to the long queues at the cashiers. At the same time the offering includes the location of the stores while stressing the need to be physically present and to further understand the local markets that the body shop organization intends to serve its customers.
The company’s products are the main part of the retail offering and the brand image of body shop together with the quality of the supplier’s products directly influences the company’s shopping experiences of the retail customers. Consequently the organizations functions of body group which includes buying and management of the many suppliers relationship is directly part of the market orientation (Cooper 1979).
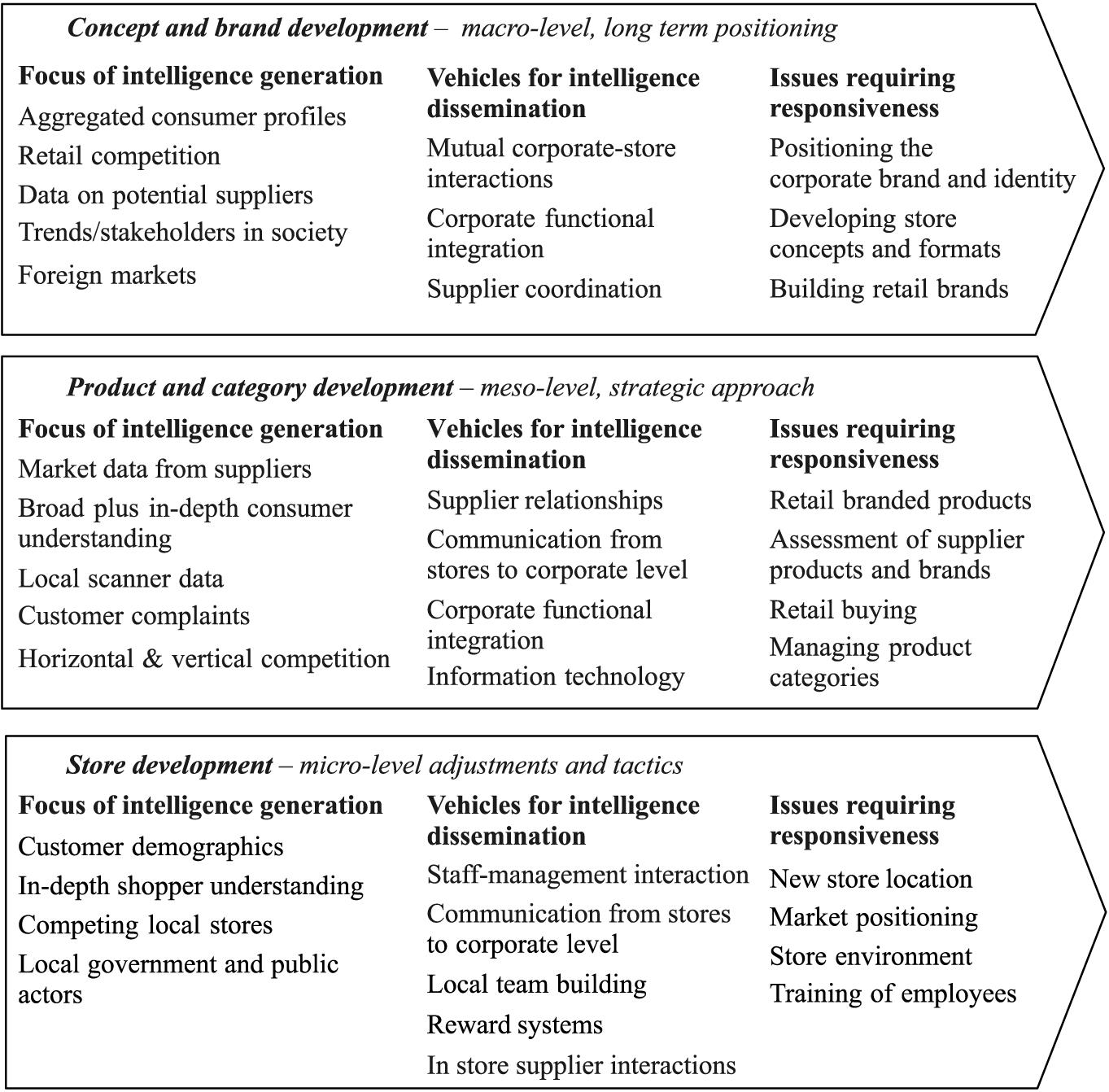
The company depends on its suppliers for its market orientation. The company on the other hand deals with three distinct market oriented processes which concerns the different organizations levels. First and foremost the store development process places much emphasis on the single retail units and their adaptations to the company’s local conditions.
On the other hand the product and the category development processes are concerned with the interactions between the corporate strategies and the local units that concerns body groups’ products and categories. Thirdly the store concept and also the brand development processes highly emphasize on the on the strategic positioning of the whole retail firm that is on the long term and which also involves the corporate level management. In the body group company the market orientation processes in have stressed different factors but to a certain degree (Barclay 1992).
The market orientation in the store development process
The body group company has been developing its existing and also its new store units. It has succeeded in the store development process by the use of the local data decision making and also interactions. The company’s managers have had more freedom in making the local adaptations but the body group new stores locations and the positioning of the existing local units required their responsiveness of the local market.
The organization has developed specific competencies on the management of its contacts with the officials from the local governments who handle the permits to establish new stores.
The market orientation in the category and product development process
The body group company has a very effective co-operation with the manufacturers and the other retailers. Even though the company has been very reluctant in initiating the joint activities which involve the supplier presence in its stores. The company’s managers develop the specifications of their new products internally and this is also inclusive of a range of issues such as the packaging aspects and the prices levels. They then present their offers to their suppliers for an evaluation based on the economic criteria.
The market orientation in the brand and store concept development process
The managers from the body group company have co-operated with the external agencies which have access to the information systems and this has helped the company make an analysis on its performance in the different categories and the retail labels. The company has further invested in the IT systems at their store levels and the company’s database has been developed to systematically register the reported complaints from its various stores on its retail brand products (Ames 1989).
Conclusion
The performance of a business is highly determined by its market orientation and thus there is a subtle relationship which exists between a company’s profitability and its market orientation and this is dependent on the nature of the company’s products. An increase in the market orientation will result into an improved inter-functional coordination and a higher percentage of the successful introductions of the new products
Reference
Ames, B. (1989): Market Driven Management, Prescriptions for Survival in a Turbulent World, Business One Irwin, Homewood, IL.
Barclay, I. (1992): The new product development process, past evidence and future practical application, part 1, R&D Management, Vol. 22 No.3,
Cooper, R. (1979): Identifying industrial new product success: project New Prod, Industrial Marketing Management, Vol. 8
Eccles, R. (1992): Beyond the Hype, Rediscovering the Essence of Management, Harvard Business School Press. Boston, MA.
Hayes, R. (1980): Managing our way to economic decline, Harvard Business Review, Vol. 58 No.
Kohli, A and Jaworski, B (1993): Market orientation, antecedents and consequences Journal of Marketing, Vol. 57
Johne, F. (1995): Evaluating product development success within a business development context. John Wiley & Sons publishers, Chichester, New York, NY
Kohli, A and Jaworski, B (1990): Market orientation, the construct, research propositions, and managerial implications. Journal of Marketing, Vol. 54.
Lilien, G. (1989): Determinants of new product performance, a strategic re-examination of the empirical literature. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, Vol. 36 No.1
Malik, M. (1994): Marketing myth, philosophy and business practice. University of Groningen, Proceedings of the 10th IMP Annual Conference, Vol. II
Narver, J. and Slater, S. (1990): The effect of a market orientation on business profitability. Journal of Marketing, Vol. 54 No.
Webster, F. (1994): Market-driven Management, Using the New Marketing Concept to Create a Customer-oriented Company. John Wiley & Sons publishers, New York, NY,.