Executive Summary
This paper entails an analysis of the challenges, drivers, and opportunities encountered in organizations’ efforts to promote sustainable development. Projects are identified as one of the practices that organizations can integrate into their quest to attain sustainable development. However, projects are high-risk and complex activities. Furthermore, different stakeholders execute projects, and thus effective project management is paramount. For a project to be implemented effectively, a firm’s management team should take into account the element of innovation. This paper emphasizes the importance of ensuring that innovation is managed efficaciously. The core innovation drivers that organizations must take into account include investing in effective talent management, mentoring employees, implementation of an effective leadership strategy, and nurturing a high level of collaboration amongst the project participants. The paper also evaluates the main challenges that might hinder effective innovation. Some of the main challenges that are identified include lack of an optimized organizational design, lack of clarity, and adoption of poor innovation strategies. The paper argues that these challenges limit effective management of innovation by limiting the development of synergy amongst the various project stakeholders. The author cites motivation as a critical element in promoting effective management of innovation, and hence the attainment of the desired sustainable development. This is achieved by reviewing two main conceptual models, which include the goal-setting model and the expectancy model. The model emphasizes the significance of motivation in developing a high level of commitment amongst the project participants. In a bid to illustrate the application of management of innovation in the real business environment, two case studies of projects in Exley, which is a governmental entity in the UAE, are evaluated in this paper.
Introduction
Businesses and individuals have numerous and wonderful prospects for the 21st century. Guo-Jie (2001, p.1) suggests that the ‘21st century is a boi-scientific era, an economic globalization age, a spatial exploration time, a scientific and technological globalization, and information epoch’. These prospects and forecasts present a bright future for organizations. Furthermore, the 21st century can be defined as a period when individuals are required to synchronize with the environment. Adopting sustainable development is one of the strategies that organizations can integrate with their strategic management in the pursuit to achieve sustainability. Sustainable development is a fundamental component in the modern business environment. Its significance can be explained by the competing economic, social, and environmental needs of society.
A study conducted by the United Nations (UN) on how to augment sustainable development in organizations affirms that sustainable development is incomplete in the absence of technology and innovation (Emelo 2013). Innovation is no longer a privilege for developed economies. Subsequently, the less developed economies must consider how they can improve their innovative capacity (Joby 2005). Businesses in different sectors are facing diverse environmental, economic, and social pressures. Management consultants and scholars think that such pressures present an excellent opportunity for businesses to attain sustainable development. However, this goal is attainable if the element of innovation is integrated effectively (Hall & Vredenburg 2003). The objective of this study is to identify the challenges, drivers, and opportunities associated with the implementation of innovation in organizations’ efforts to achieve sustainable development.
Literature review
Sustainable development; objectives and components
Sustainable development aims at increasing individuals’ level of contentment and quality of life. Kates, Thomas, and Leiserowitz (2004) assert that sustainable development is comprised of two main concepts, which include the idea of limitations and the concept of needs. Kates, Thomas, and Leiserowitz (2004) identify environmental, social, and economic aspects as the core facets in achieving sustainable development. The economic facet assumes that a sustainable system must have the capability to engage in a continuous production process. Furthermore, the system must have the capability to maintain minimal debts. The environmental component holds that the system must have a stable resource base without over-exploit the available natural resources. On the other hand, the social facet argues that a sustainable system should be fair about the distribution and provision of services.
Innovation and change
Change is a fundamental component in an organization’s effort to achieve a competitive advantage. Schwartz (2009) defines change as the alteration in an organization’s structure, technology, and people. Schwartz (2009, p.13) further opines that change ‘is occurring at an ever-increasing and accelerated pace’. Therefore, change is unpredictable and uncertain. In a bid to survive in such an environment, it is imperative for organizations to consider the most effective way to adjust to such changes.
Innovation requires change for successful implementation. Windrum and Koch (2008) argue that innovation is a fundamental element in businesses’ efforts to achieve long-term survival. An organization’s ability to implement change continuously influences its competitive advantage. Furthermore, implementing change determines the effectiveness with which an organization attains sustainable value creation.
Innovation is a critical factor in promoting equality, economic growth, poverty alleviation, and social cohesion. Businesses are increasingly adopting innovation as a new organizational method. The lack of an effective innovation system is one of the major challenges in organizations’ efforts to facilitate technological innovation. Developing an effective innovation system is complex. Subsequently, different participants such as learning institutions, governments, and businesses are involved in the innovation process (Bokova 2009).
Role of projects in attaining sustainable development
The current business environment is undergoing a high rate of evolution. Subsequently, the degree of complexity in the business environment has increased remarkably. Subsequently, businesses have to pay attention to the prevailing competitive threats. Schwartz (2009) argues that projects are effective and appropriate mechanisms that businesses can integrate into their quest to cope with turbulent times. Organizations mainly depend on projects that are backed by their corporate strategy in order to attain a competitive advantage. Bokova (2009, p.92) asserts that understanding ‘how strategic business objectives are aligned at the project level is critical for competitive positioning and high-performing organizations’.
It is imperative for organizations’ management teams to ensure that their operational activities and resources are coordinated and aligned effectively in order to enhance optimal organizational performance. Most organizations have formulated operational strategies, which may be formal or structural. The formulated strategies aid in determining the most effective scheme to adopt in the resource allocation process, and hence the projects that are selected. Newton (2012, p.121) argues that projects ‘are one of the key ways of achieving strategic and they should be aligned with it’. One of the ways through which organizations can ensure that projects align with strategy is by adopting a disciplined and joined-up approach to managing change. Furthermore, organizations have to ensure that the set projects are strongly connected with the set organizational strategy. Aligning projects to an organization’s corporate strategy is fundamental in achieving sustainable development. First, effective project alignment creates an opportunity for firms to ensure that organizational resources are utilized optimally (Turner 2012).
Drivers of innovation
Talent fostering
People are a fundamental component in organizations’ pursuit of innovation. Most firms, which are focused on attaining sustainable development, have integrated various measures aimed at transforming themselves into employee-centric entities. Examples of such firms include Silicon Valley firms. Their success can be attributed to an extremely talented workforce (Sullivan 2013). Nidumolu, Prahalad, and Rangaswami (2009) contend that innovation is dependent on the presence of people who can generate and utilize ideas and knowledge in the workplace. Some of the most important skills that human resource managers should consider in their employee selection process include problem-solving, collaborative, technical, and communication skills.
Chun and Evans (2014) identify talent as one of the key drivers of innovation. Subsequently, it is imperative for organizations to develop a strong workforce. Diversity is one of the core aspects that organizations should take into account in their pursuit to nurture a strong human capital. Human resource managers should take into account several aspects to enhance a diverse workforce. First, human resource managers should not discriminate against employees based on disability, race, gender, sexual orientation, or age. Krieger (2010) argues that it is essential for organizations to select, hire, and develop talent in order to nurture an organizational culture that fosters innovation. Hiring the right talent by considering the candidates’ feelings, behavior, and thoughts about an organization increase the likelihood of attaining top performance.
Organizations should also appreciate the importance of integrating an effective employee-training program. The program should be designed effectively to address the employees and organizational needs. This move will contribute towards the development of a high degree of organizational identification. Integrating a high level of employee engagement is one of the strategies through which an organization can enhance the development of talent. Brandon and Lu (2008) assert that engaged employees are more creative. The chart below illustrates the results of a study conducted by Gallup Business Journal on the relationship between innovation and creativity at the workplace.
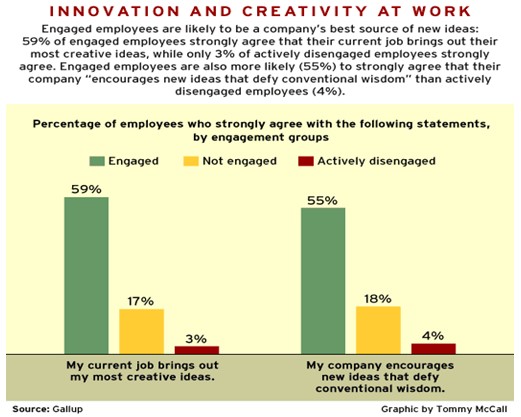
Furthermore, the study also revealed that nurturing a high level of collaboration by encouraging friendship amongst employees stimulates creativity.
Employee engagement further stimulates employees to generate new ideas. Engaged employees feel relaxed and are hence innovative. To stimulate the level of creativity amongst its workforce, Toyota usually takes its employees from the ordinary work environment in an area that is free from work pressure. This aspect provides them with an opportunity to brainstorm. Furthermore, the firm also inspires its employees by providing them with diverse and numerous reading materials (Mika 2007). The graph below illustrates the study’s findings on the relationship between employee engagement and level of creativity.
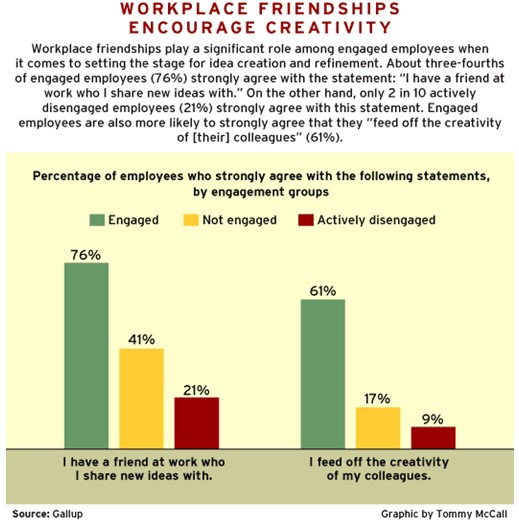
Mentoring, leadership, and collaboration
In a bid to enhance innovation successfully, it is imperative for organizations to ensure that the workforce is guided and mentored effectively. Subsequently, organizations should have super mentors. Mentoring is essential in a firm’s efforts to transfer knowledge to its workforce. Mentors are usually professionals in their respective fields. Lowenstein (2004) asserts that the process of mentoring may be comprised of a number of issues some of which include imparting new skills to protégés, hence stimulating their intellectual development. Furthermore, mentoring enables the protégés to understand the customs and values associated with a particular profession.
Effective leadership also plays a fundamental role in an organization’s efforts to promote the level of creativity amongst its workforce. The management should guide its workforce on how to be innovative in executing their duties. According to Green, Stankosky, and Vandergriff (2010), optimal leadership is essential in transferring knowledge from leaders to employees.
Organizational managers should focus on nurturing an environment that fosters a high level of collaboration. Soosy and Sloan (2005) contend that such collaboration is fundamental in promoting innovation. This assertion emanates from the view that collaboration enhances knowledge sharing amongst employees from diverse departments. Prahalad and Krishnan (2008) assert that employees possess diverse knowledge and experiences. Subsequently, their perception of different issues varies remarkably. Such variations on how to deal with situations can lead to the uncovering of innovative solutions. The role of diversity in stimulating innovation shows that the probability of driving innovation in an organization comprised of a diverse workforce is high. Emelo (2013, par. 12) asserts that the ‘spirit of the mentoring program provides a platform for diverse knowledge sharing across the organization.
Challenges experienced in innovation
Innovators face numerous problems and challenges in their quest to stimulate organizational performance. Some of these challenges are illustrated herein.
Lack of an optimized organizational design
The success with which an organization promotes innovation is subject to the extent to which it can utilize its capabilities. However, most organizations in different economic sectors are characterized by the underutilization of capabilities. Failure to nurture and capitalize on their core competencies is a major factor that hinders innovation. Furthermore, some organizations are characterized by a high degree of conservatism. Subsequently, they are not proactive in implementing change occurring in the business environment. Strange and Bayley (2008) opine that the existence of ‘not-invented-here syndrome’ [NIH] is a major limitation in organizations’ effort to promote innovation. Hussinger and Wastyn (2011, p.1) define NIH as the ‘internal resistance in a company against externally developed knowledge’.
Lack of clarity
Previous studies show that innovation requires change for successful implementation. However, the innovation process is hindered by the existence of uncertainty and lack of clarity. Some organizations have adhered to the notion that innovation is everyone’s job. Such a notion limits accountability in the innovation process. A high level of coordination is critical in an organization’s efforts to stimulate innovation. This aspect can only occur if effective communication is integrated.
Poor innovation strategy
Howard (2003, p.262) posits that innovation strategy ‘serves as an effective tool for pursuing a firm’s corporate strategy. Subsequently, an optimal strategy is critical in a firm’s effort to develop a culture of innovation. The strategy formulation process aids in establishing a link between ideas and opportunities. Therefore, it is essential for an organization to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the environment in order to generate ideas, which will form the basis of innovation. This aspect forms the foundation of formulating the innovation strategy. The second phase entails implementing the selected innovation strategy. Poor formulation of innovation strategy is a major challenge in an organization’s effort to implement and manage innovation. Lack of a well-defined innovation strategy leads to confusion and wastage of resources in pursuing innovation.
Impact of motivation in delivering sustainable solutions/projects; review of conceptual models
Motivation underscores the extent to which an individual is focused and persistent towards the attainment of a certain goal. Kreitner and Mohapatra (2008) argue that the degree of motivation amongst employees is influenced by different factors. Researchers have formulated different conceptual models in an effort to explain motivation amongst employees. An example of such a model is the expectancy model. The model is based on the expectancy theory. The theory argues that employees are motivated to a level at which they believe that their actions will lead to the attainment of acceptable performance. Secondly, employees think that their efforts will be rewarded. The flow chart below illustrates the main components of the expectancy model.

The expectancy model hinges on chance, which ranges between 0 and 1. The model argues that if an employee perceives that the likelihood of his or her effort in attaining the desired outcome is minimal, then the expectancy is zero. On the other hand, if the probability of completing a task high, then the expectancy is rated one. The model postulates that the relationship between effort, performance, and reward influences the level of motivation amongst employees in undertaking a particular task. However, it is possible for organizational leaders to influence the employees’ expectations by integrating and nurturing optimal organisational experiences and managerial strategies.
One of the managerial strategies that organizational leaders can integrate entails formulating and implementing a comprehensive employee-training program. Managers should ensure that employees are trained adequately to undertake certain tasks. Furthermore, organisational leaders should focus on ensuring that employees develop the perception that it is possible to complete the assigned tasks if they are committed coupled with putting in the necessary efforts. The model further asserts that it is imperative for organisational leaders to develop a comprehensive understanding of the employees’ expectations and rewards. Subsequently, managers should have the necessary listening skills.
Kreitner and Mohapatra (2008) assert that employees are inclined to work hard if they believe that they will achieve personal and meaningful rewards. Taking into account the aforementioned elements increases the motivational strength amongst employees. Subsequently, the likelihood of completing a particular project, hence achieving the desired level of sustainable development is high.
The second conceptual model formulated by researchers in an effort to explain motivation is the goal-setting model. Kreitner and Mohapatra (2008) assert that the model has received tremendous research support as an optimal tool that enhances employee performance. The goal-setting model is strongly entrenched in the management-by-objective system. The model further asserts that goals have a remarkable influence on employees’ behavior.
The model postulates that an individual’s behavior is determined by his or her values and intentions [goals]. Individuals’ value influences their motivation to undertake tasks that align with their goals. Furthermore, goals influence the level of job performance amongst individuals. Subsequently, goals have an impact on the employees’ attention and action. Setting challenging goals stimulates the employees’ effort, energy, and commitment. Furthermore, goals motivate individuals to formulate strategies that increase their input, hence improving the likelihood of attaining the desired outcome. Achieving the set goal leads to improvement in the employees’ level of satisfaction motivation (Lunenburg 2011).

The goal-setting model illustrates the impact of goals and desires on the employees’ behavior, and hence their commitment towards executing the assigned tasks. Subsequently, the model highlights a strong correlation between the employees’ level of motivation and the likelihood of achieving sustainable solutions.
Case studies
Exley Limited is one of the agencies established by the UAE government. The agency was established in 1993 and it has provided information services to clients successfully. Exey has integrated sustainable development as one of its goals. This decision has been motivated by a number of factors such as the need to provide optimal services to its clients. The UAE government has over the past few years advocated for a high level of competitiveness amongst its departments. Furthermore, the government’s motivation towards sustainable development is promoted by the need to attain competitiveness by ensuring effective and efficient service delivery.
Case study 1: implementation of ERM system in Exey
In a bid to achieve its goal, the firm has adopted projects as one of the avenues through which it can achieve sustainable development. One of the projects that the firm has undertaken relates to the implementation of the Enterprise Risk Management system. The system was implemented to enhance the firm’s risk management capabilities. The ERM system will improve Exey’s ability to manage and coordinate risks. Subsequently, the firm will be in a position to attain economic sustainability. For example, the firm will manage risks, hence minimizing the likelihood of the associated losses.
Before the implementation of the ERM project, the firm’s management team formulated an ERM plan. The plan formulation process entailed ensuring that the project aligned with the set organizational strategy. In a bid to achieve this goal, the organization’s management team conducted a workshop in which all the senior and lower-level managers identified the challenges that might hinder the successful implementation of the project. During the brainstorming process, the managers were required to identify the various internal and external challenges that might limit the implementation of the project. Some of the challenges that were identified related to technological, economic, and social factors. Lack of well-experienced human capital concerning the operation of the ERM system and employee resistance was cited as one of the major hindrances.
In a bid to deal with these challenges, the firm’s management team decided to integrate several measures. The first measure entailed outsourcing the services of ERM professionals from within the UAE. The professional was charged with the responsibility of training and mentoring the firm’s employees on how the new technology can be utilized. Through outsourcing, the firm was in a position to nurture and improve its workforces’ talent. Subsequently, most employees felt that the firm was addressing their personal and career development goals due to the new knowledge gained. For example, the employee-training program emphasized the importance of being innovative in the process of executing diverse duties to attain the desired goals. Furthermore, the employee training contributed towards the development of ERM culture. Lam (2009, p. 81) argues that there ‘is a strong correlation between taking culture into account and successful implementation of a project’.
Lam (2009) further argues that employees are usually resistant to change due to the high degree of uncertainty associated with change. To eliminate such resistance, Exley integrated a number of measures. First, the firm ensured that all employees were informed adequately about the intended change in the firm’s operation. This goal was achieved via establishing an effective communication system between the management team and the lower-level employees. The communication process mainly focused on ensuring that employees understood the benefits that the firm would gain by implementing the new system. Subsequently, the firm eliminated the perception that the project would be a threat to the employees’ jobs.
The second aspect that the firm considered entailed teamwork. The project manager designed a project team by selecting team members from different departments. This move was necessitated by the need to develop strong collaboration between employees from different departments. Furthermore, adopting this move was motivated by the need to develop effective communication between the various stakeholders. Subsequently, the firm nurtured a high level of knowledge sharing. The training and the mentorship program played a critical role in nurturing a sense of innovativeness, collaboration, and the need to adopt performance-oriented activities.
Project 2: Implementing a customer service training program
Exey is cognisant of the importance of providing its clients with optimal customer services. The firm associates customer service with the development of a high level of customer loyalty. Subsequently, the firm’s effectiveness in serving its clients will improve remarkably. As a result, the firm will be in a position to attain economic sustainability by increasing its sales revenue, and hence the level of profitability. In a bid to achieve this goal, the firm’s management team decided to integrate a customer service training program. The project aimed at equipping employees with effective skills that would improve their ability to deliver services to customers. Subsequently, the organization would be transformed into a customer-centric entity. The firm ensured that employees understood the benefits that would be derived from the customer-service training.
The participation process played a critical role in enabling the firm to develop a holistic view of the issues that employees focus on in the process of delivering services. As a result, the firm was identified possible gaps. Furthermore, the customer service-training project also entailed training employees on how to utilize the online information center that the firm had previously developed in serving customers. For example, the firm ensured effective communication between the firm’s management team and the lower-level employees. This move played a critical role in nurturing a high level of collaboration between employees from diverse departments.
Conclusion
Businesses and organizations operate in an increasingly complex environment. Therefore, firms’ management teams must consider the most effective way to cope with the adverse effects of change. One of the most effective strategies that firms should consider entails achieving sustainable development. The study shows that achieving sustainable development can contribute towards the achievement of competitive advantage. The study shows that innovation is a critical element in driving change, and hence attainment of sustainable development in organizations. However, optimal management of innovation is critical to implement change successfully.
Recommendations
In a bid to manage innovation successfully, it is fundamental for organizations to take into consideration the following.
- Integration of core drivers of innovation; some of the most important drivers that organizations should consider in the process of managing innovation include ensuring effective talent fostering, mentoring employees, implementing effective leadership, and ensuring a high level of collaboration between internal and external project participants.
- Implementation of an optimized organizational design; will ensure that all the internal stakeholders participate in the project implementation process.
- Effective communication; an effective internal and external communication system should be implemented to enhance a high level of clarity on the project being implemented.
- Innovation strategy; organizational managers should ensure that an effective innovation strategy is implemented.
- Nurturing a high level of motivation– project managers should ensure that the parties charged with the responsibility of implementing the project are motivated adequately by designing a comprehensive reward system.
Reference List
Bokova, I 2009, An integrated policy approach in science, technology and innovation for sustainable development, UNESCO, New York.
Brandon, P & Lu, S 2008, Clients driving innovation, Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester.
Chun, E & Evans, A 2014, The new talent acquisition frontier; integrating HR and diversity strategy in the private and public sectors and higher education, Stylus Publishing, Sterling.
Guo-jie, C 2001, ‘Sustainable development facing challenges in 21st century ’, Chinese Geographical Science, vol. 11 no. 4, pp. 289-293.
Green, A, Stankosky, M & Vandergriff, L 2010, In search of knowledge management; pursuing primary principles, Emerald, Bingley, UK.
Emelo, R 2013, Connect to collaborate.
Hall, J & Vredenburg, H 2003, The challenges of innovating for sustainable development.
Howard, P 2003, ‘Gaining competitive advantage through customer service training’, Industrial and Commercial Training, vol. 35 no. 7, pp. 259-262.
Hussinger, K & Wastyn, A 2011, In search for the not-invented-here syndrome; the role of knowledge sources and firm success, Centre for European Economic Research, Luxembourg.
Joby, J 2005, Fundamentals of customer service focused management: Competing through service, Greenwood Publishing, New Jersey.
Kates, R, Thomas, P & Leiserowitz, A 2004, What is sustainable development; goals, indicators, values, and practice, Corbis, New York.
Kreitner, R & Mohapatra, M 2008, Management, Dreamtech Press, New York.
Krieger, J 2010, Creating a culture of innovation, Gallup Inc., New York.
Lam, J 2009, Enterprise Risk Management: From Incentives to Controls, Wiley, Hoboken.
Lowenstein, A 2004, Fuszard’s innovative teaching strategies in nursing, Jones and Bartlett, Sudsbury, MA.
Lunenburg, F 2011, ‘Goal-setting theory of motivation’, International Journal of Management, Business and Administration, vol. 15 no. 1, pp. 1-6.
Mika, S 2007, The four drivers of innovation.
Newton, R 2012, Brilliant checklists for project managers; your shortcut to success, Pearson Education, London, UK.
Nidumolu, R, Prahalad, C & Rangaswami, M 2009, Why sustainability is now the key driver of innovation, Harvard Business Review, New York.
Prahalad, C & Krishnan, M 2008, The new age of innovation; driving co-created value through global networks, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Schwartz, A 2009, Change, challenge, and innovation, Schwartz Copyright, Boston.
Soosy, C & Sloan, T 2005, ‘Driving change; innovative management in distribution centres’, Journal of Asia Entrepreneurship and Sustainability, vol. 3 no. 5, pp. 1-21.
Strange, T & Bayley, A 2008, Sustainable development; linking economy, society and environment, OECD, New York.
Sullivan, J 2013, Innovation drivers; key talent management lessons from Silicon Valley.
Turner, J 2012, Gower handbook of project management, Gower Publishing, New York.
Windrum, P & Koch, P 2008, Innovation in public sector services; entrepreneurship, creativity and management, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, UK.