Introduction
Quality has been defined as fitness for use or conformance to the set standards (Garvin, 1988). The present day business management has increased an emphasis on quality of the products that are supplied to the market. This is because quality has become an area of key concern among many consumers and regulating authorities.
Consumers are keen to purchase goods and services that are regarded as top quality (Ishikawa, 1985). This is because it is generally held that high quality goods and services usually ensure that the consumers derive higher utility from the high quality goods than they from other goods and services.
The quality control bodies and authorities ensure that the products supplied to the market are fit for the use by the public and usually conform to the set standards. Companies that place high emphasis on quality usually have a competitive edge over the other players in the market (Garvin, 1988). This has resulted to organizations refocusing from productivity to quality management. Once a firm conforms to the set quality, it becomes automatic that the productivity will eventually will be enhanced.
Some firms have suffered huge losses due to the quality compromise and subsequent discovery by the consumers. Such firms have experienced significant loss of reputation and this has resulted to decreased revenues and subsequent loss of goodwill. Firms that compromise on product quality usually face an uphill task of restoring the customer confidence and loyalty (Naylor, 1996).
This is because competitors make take the advantage of the poor quality products to win on the customers who were loyal to the particular products. This paper discusses the points in the Coca-Cola Company global supply chain that are mainly susceptible to quality problems. It also looks at available ways and means of addressing these problems to ensure that the company continues to offer the high quality, top brand products to its consumers.
Coca-Cola company analysis
Coca-Cola Company is the global leading manufacturer, distributor and marketer of non-alcoholic beverages. With brand presence in virtually all the countries of the world, the company has enjoyed undisputed leadership for several decades. Its core competencies that ensure that it produces high quality products has steered it to the top of the best brands in the world and this has gone a long way in ensuring that it maintains a high reputation that ensures preference among many consumers.
The company has however had its share of quality problems with cases of product defects leading to criticisms by various quality control boards and consumer watch dogs.
The company’s products have been frequently subjected to quality criticisms by various watchdogs and governments across the globe. This is has majorly been caused by the company’s raw materials usage and the ingredients mix that come up with the final product for the consumers.
It has been widely claimed that the company uses contaminated water and cheaper sources of sugar for the manufacturing of the concentrate that is supplied to the various bottling centers. Claims of the use of toxins that can cause cancer and a breakdown of the immune system have caused the company to be banned in major markets in the world.
Its secret mixture has also been a major cause of concern among various watchdogs and consumers. This has made the company to lose a significant reputation in several markets such as India and Europe.
The areas in the company supply chains that have been exposed to quality problems are the suitability of the products bearing in mind quality concerns that have been raised. The company’s products have therefore faced a major quality concern all over the world. Various means of addressing such concerns have been put forward by many quality management gurus.
Juran’s Trilogy concept
One of the quality management gurus is Joseph M. Juran. According to Juran, quality is defined by as fitness for use. This is a definition that ought to be congruent with the Coca-Cola Company’s quality management. This is because of the various criticisms that have been raised against the Coca-Cola products pointing on the health concerns with regards to the products. The Company management should ensure that the products that are made available to the consumers are fit for consumption and that they pass the set targets (Shingo, 1985).
Juran’s concept of trilogy will ensure that the management states that management for quality consists of three processes that are quality related. These processes include planning, quality control and quality improvement. By planning the management ought to put prior step and measures that ensure that the products delivered to the market pass the quality test. This would necessitate the management to put internal quality controls that ensure that the products are appraised to ascertain whether they are compliant or not (Garvin, 1988).
The importance of planning in Coca-Cola Company cannot be over emphasized. This is because the management ought to put proper measures that ensure that the numerous bottling plants across the world comply with the set quality standards. This will cushion the Company against the various quality concerns because the company will be able to deliver high quality products. Quality control measures will ensure that the company continues to grow confidence among various consumers and watchdogs (Barhami, 1992).
The cases of quality compromise that have been raised over the past years have made the company’s reputation to go down. The management should therefore carry out regular quality control measures such as inspection of the production processes and regular testing of the products. This will help the management to uncover any possible defects and therefore control the release of the product to the market.
The quality control should also extend to the final products to ascertain their suitability and conformity to the set standards (Kenneth, 2002). By carrying out the quality control, Coca-Cola Company will ensure that the products are always on top of the quality check list. It will also ensure that the brand continues to grow to become a common household favorite among the competitors.
Quality improvement is another important aspect of Juran’s trilogy. It is a management technique that ensures that all stakeholders in an organization’s internal environment are included in the quality management. All the member of an organization are involved so as to ensure that the quality management is a holistic approach that seeks to identify all the quality hazards, properly analyze these problems and designing processes that ensure that the product quality is in constant improvement process.
The management of Coca-Cola Company should employ the process of quality improvement to ensure that the changing consumer preferences are aptly addressed by the innovated products offered to the market.
This entail the management to continue to invest in research and development as well as market research to ensure that the products maintain their high quality standard among the various consumers. This will eliminate possible flaws in the products since a constant research exposes the existing defects and also addresses the future expectations of the consumers.
Crosby’s Zero defect concept
According to Crosby, the products ought to have no defects whatsoever. This means that the products specifications must meet all the specifications to the latter. This quality standard requires great deal of diligence in all the functional areas of an organization. This would ensure that the final products are of the highest quality standards possible (Hall, 1983). The management of Coca-Cola Company therefore ought to employ tight measures that ensure that the all functional areas of the organization including the various distribution plants across the world comply with.
To do this the company needs to ensure all quality parameters are communicated and comprehended by all the employees and the various distributors of the products (Ishikawa, 1985). The company should also ensure that all internal participants to the value chain are committed to achieving these quality measures.
This will ensure a holistic approach to quality and subsequent high quality products. Finally the company should enforce a system of sustainable quality adherence so as to ensure that the quality procedures are a way of life and not just a one off process.
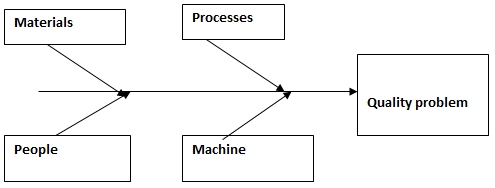
A basic illustration of the Ishikawa’s fishbone diagram helps identify the various combinations of the company’s internal environment factors that can be used to identify the root cause of quality problems at Coca-Cola Company including its various bottling plant across the world. According to Ishikawa, these various attribute of a company’s operational environment are useful in establishing the source of the problems (Ishikawa, 1985). These sources can be classified into materials, processes, People, and Machine.
Material defects originate from the various shortcoming attributes that the raw materials possess. A look at this factor would provide insightful information on such problems as the use of toxic substances and substandard raw materials. This would therefore offer management with guidelines that would ensure they take corrective measures to address the issue of substandard raw materials.
The same diagram would also be helpful in establishing processes that are faulty. This is because every internal parameter is exhaustively analyzed to ascertain its compliance to the set quality procedures. These sources are therefore ranked in order of compliance and the necessary actions are taken.
The bottling plants can therefore use this information to diagnose the root cause of the quality problem. Machines being operated in the plants are regularly checked for compliance thus ensuring that they operate at their optimal levels. People are also regularly evaluated to ascertain their skills and competencies which ensure that they are updated with the most advanced production methods (Ishikawa, 1985).
People are a source of Human capital. Human capital is an important resource in any organization. They can therefore be a source of success to the organization as well as a source of failure through non compliance
Ishikawa’s fish bone diagram is therefore an important tool in assessing the root cause of the quality problems. Once a management establishes the root cause using this tool, corrective measures are easily identified and pursued to restore a situation of quality compliance. The company can therefore rest assured that the various internal organization attributes are considered to ensure that compliance is kept on all functional areas.
Shingo’s Poka-yoke devices
Poka-yoke was a concept that was formulated to aid an equipment operator from making mistakes in the production processes. This concept is based on behavior-shaping and aims to provide measures that result in production of products that conform to the set qualities.
In Coca-Cola Company this concept can be applied to ensure that the various production processes are free from defect. This concept can be employed in any manufacturing step to ensure that the products match the set standards. To achieve this, the Company may set the procedures that must be strictly followed to ensure that the final product is compliant.
Using the Poka-Yoke devices the Company may also install various alert points that are aimed at raising the alarm in time to ensure that the manufacturing process does not continue without addressing the problem so detected. In Coca-Cola these measures may be installed in the operations that include the chemical raw materials mixing. If any particular mixture is not in its rightful proportions, the process is stopped to ensure that corrective measures are taken.
Conclusion
The key to successful implementation of quality measures rests with the management. A company that has a good management will certainly have systems and procedures which ensure that the quality measures are strictly considered. The customers are the final recipients of the finished products, whether they are of good quality or not.
Therefore the company should pay close attention to the quality specifications to ensure products with zero defects and which are fit for use while conforming to the set standards. A keen look at these quality procedures and control measures as presented will ensure that Coca-Cola Company continues to enjoy its global leadership in the production of quality products.
References
Barhami, H. (1992). The emerging Flexible organisation: perspectives from silicon valley. California Management Review , 33-52.
Garvin, D. A. (1988). Managing Quality: The Strategic and Competitive Edge,. New York: The Free Press.
Hall, R. W. (1983). Zero Inventories. Illinois: Dow-Jones Irwins Publishers.
Ishikawa, K. (1985). What is Quality Control ? The Japanese Way. New York: Prentice Hall.
Kenneth, S. S. (2002). International Academy for Quality: Best of Quality. ASQ Quality Press.
Naylor, J. (1996). Operations Management. London: Pitman Publishers.
Shingo, S. (1985). A Revolution in Manufacturing: The SMED System. Cambridge: Productivity Press.